User login
VA Choice Bill Defeated in the House
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
A U.S. House of Representatives appropriation to fund the Veterans Choice Program surprisingly went down to defeat on Monday. The VA Choice Program is set to run out of money in September, and VA officials have been calling for Congress to provide additional funding for the program. Republican leaders, hoping to expedite the bill’s passage and thinking that it was not controversial, submitted the bill in a process that required the votes of two-thirds of the representatives. The 219-186 vote fell well short of the necessary two-thirds, and voting fell largely along party lines.
Many veterans service organizations (VSOs) were critical of the bill and called on the House to make substantial changes to it. Seven VSOs signed a joint statement calling for the bill’s defeat. “As organizations who represent and support the interests of America’s 21 million veterans, and in fulfillment of our mandate to ensure that the men and women who served are able to receive the health care and benefits they need and deserve, we are calling on Members of Congress to defeat the House vote on unacceptable choice funding legislation (S. 114, with amendments),” the statement read.
AMVETS, Disabled American Veterans , Military Officers Association of America, Military Order of the Purple Heart, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Vietnam Veterans of America, and Wounded Warrior Project all signed on to the statement. The chief complaint was that the legislation “includes funding only for the ‘choice’ program which provides additional community care options, but makes no investment in VA and uses ‘savings’ from other veterans benefits or services to ‘pay’ for the ‘choice’ program.”
The bill would have allocated $2 billion for the Veterans Choice Program, taken funding for veteran housing loan fees, and would reduce the pensions for some veterans living in nursing facilities that also could be paid for under the Medicaid program.
The fate of the bill and funding for the Veterans Choice Program remains unclear. Senate and House veterans committees seem to be far apart on how to fund the program and for efforts to make more substantive changes to the program. Although House Republicans eventually may be able to pass a bill without Democrats, in the Senate, they will need the support of at least a handful of Democrats to move the bill to the President’s desk.
These Four Factors Account for 18 Years of Life Expectancy
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Two individuals in the United States are celebrating their 30th birthdays. It’s a good day. They are entering the prime of their lives. One is a married White woman with a university degree. The other is a never-married White man with a high school diploma.
How many more years of life can these two individuals look forward to?
There’s a fairly dramatic difference. The man can expect 37.1 more years of life on average, living to be about 67. The woman can expect to live to age 85. That’s a life-expectancy discrepancy of 18 years based solely on gender, education, and marital status.
I’m using these cases to illustrate the extremes of life expectancy across four key social determinants of health: sex, race, marital status, and education. We all have some sense of how these factors play out in terms of health, but a new study suggests that it’s actually quite a bit more complicated than we thought.
Let me start by acknowledging my own bias here. As a clinical researcher, I sometimes find it hard to appreciate the value of actuarial-type studies that look at life expectancy (or any metric, really) between groups defined by marital status, for example. I’m never quite sure what to do with the conclusion. Married people live longer, the headline says. Okay, but as a doctor, what am I supposed to do about that? Encourage my patients to settle down and commit? Studies showing that women live longer than men or that White people live longer than Black people are also hard for me to incorporate into my practice. These are not easily changeable states.
But studies examining these groups are a reasonable starting point to ask more relevant questions. Why do women live longer than men? Is it behavioral (men take more risks and are less likely to see doctors)? Or is it hormonal (estrogen has a lot of protective effects that testosterone does not)? Or is it something else?
Integrating these social determinants of health into a cohesive story is a bit harder than it might seem, as this study, appearing in BMJ Open, illustrates.
In the context of this study, every person in America can be placed into one of 54 mutually exclusive groups. You can be male or female. You can be Black, White, or Hispanic. You can have a high school diploma or less, an associate degree, or a college degree; and you can be married, previously married, or never married.

Of course, this does not capture the beautiful tapestry that is American life, but let’s give them a pass. They are working with data from the American Community Survey, which contains 8634 people — the statistics would run into trouble with more granular divisions. This survey can be population weighted, so you can scale up the results to reasonably represent the population of the United States.
The survey collected data on the four broad categories of sex, race, education, and marital status and linked those survey results to the Multiple Cause of Death dataset from the CDC. From there, it’s a pretty simple task to rank the 54 categories in order from longest to shortest life expectancy, as you can see here.
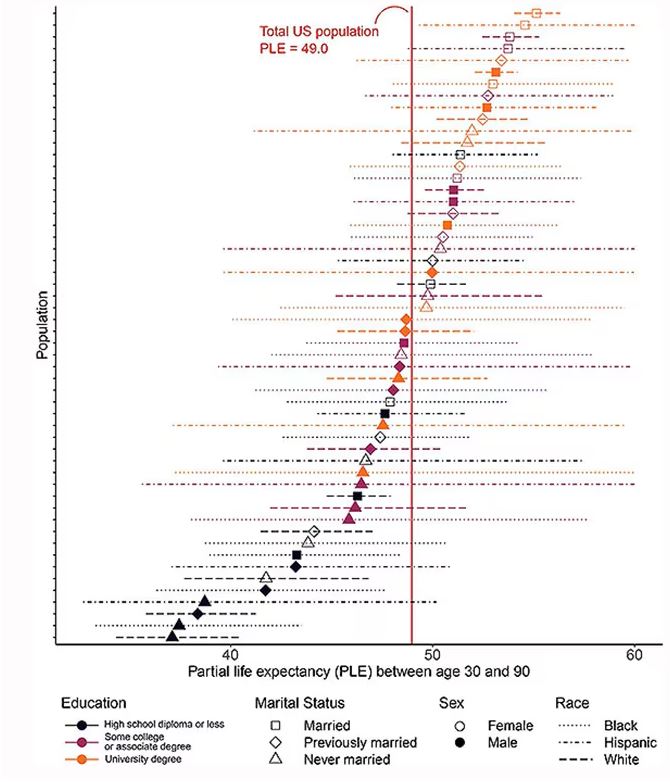
But that’s not really the interesting part of this study. Sure, there is a lot of variation; it’s interesting that these four factors explain about 18 years’ difference in life expectancy in this country. What strikes me here, actually, is the lack of an entirely consistent message across this spectrum.
Let me walk you through the second figure in this paper, because this nicely illustrates the surprising heterogeneity that exists here.
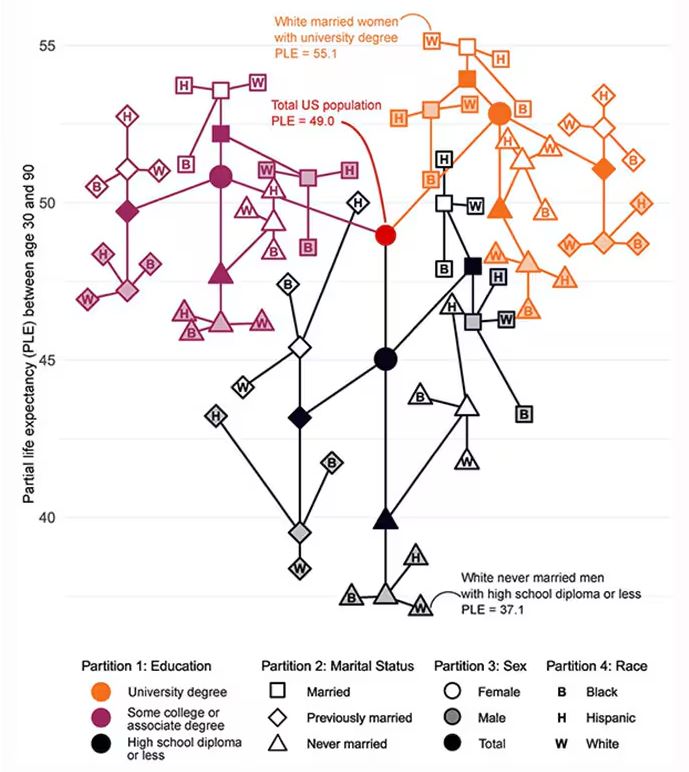
This may seem overwhelming, but basically, shapes that are higher up on the Y-axis represent the groups with longer life expectancy.
You can tell, for example, that shapes that are black in color (groups with high school educations or less) are generally lower. But not universally so. This box represents married, Hispanic females who do quite well in terms of life expectancy, even at that lower educational level.
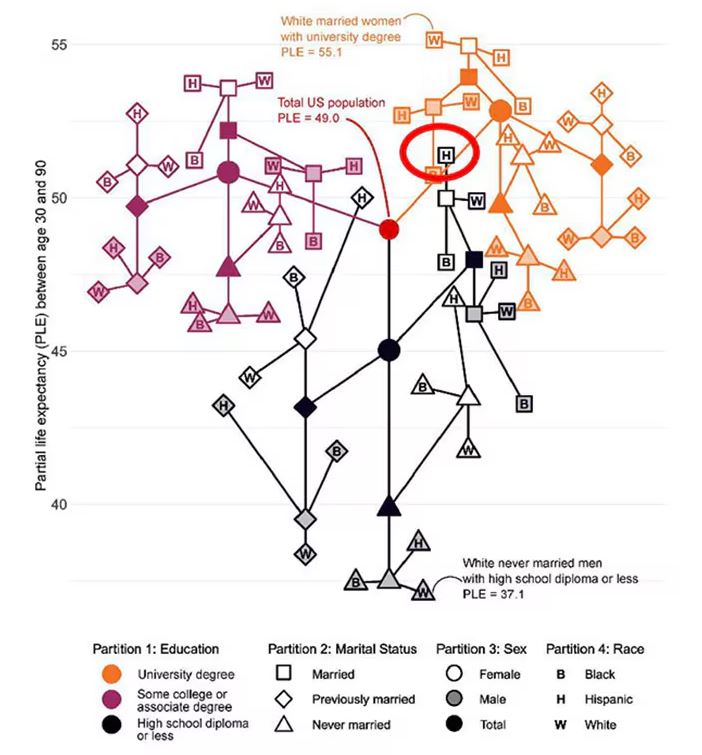
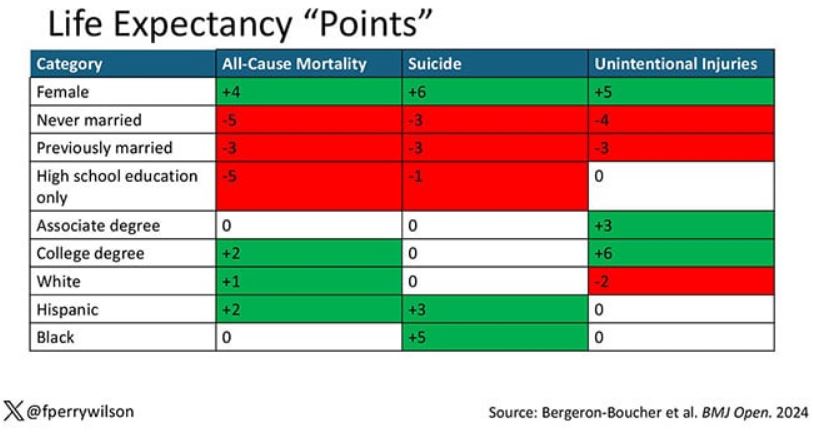
The authors quantify this phenomenon by creating a mortality risk score that integrates these findings. It looks something like this, with 0 being average morality for the United States.
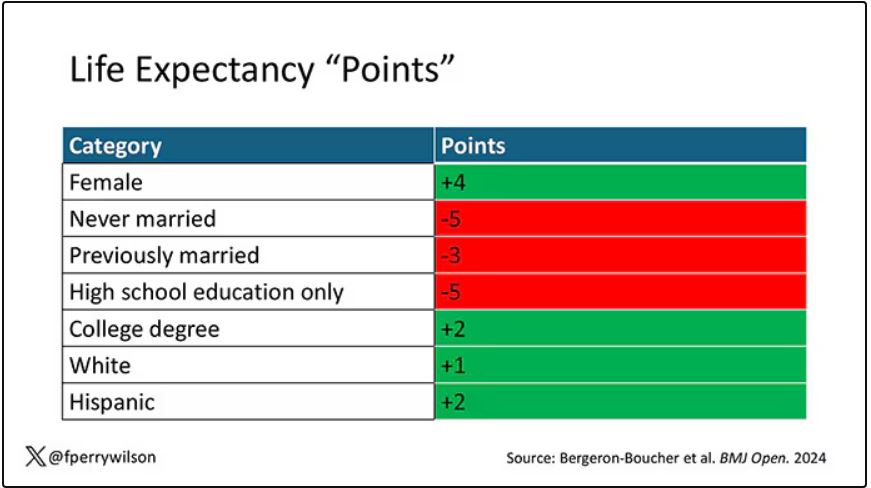
As you can see, you get a bunch of points for being female, but you lose a bunch for not being married. Education plays a large role, with a big hit for those who have a high school diploma or less, and a bonus for those with a college degree. Race plays a relatively more minor role.
This is all very interesting, but as I said at the beginning, this isn’t terribly useful to me as a physician. More important is figuring out why these differences exist. And there are some clues in the study data, particularly when we examine causes of death. This figure ranks those 54 groups again, from the married, White, college-educated females down to the never-married, White, high school–educated males. The boxes show how much more or less likely this group is to die of a given condition than the general population.
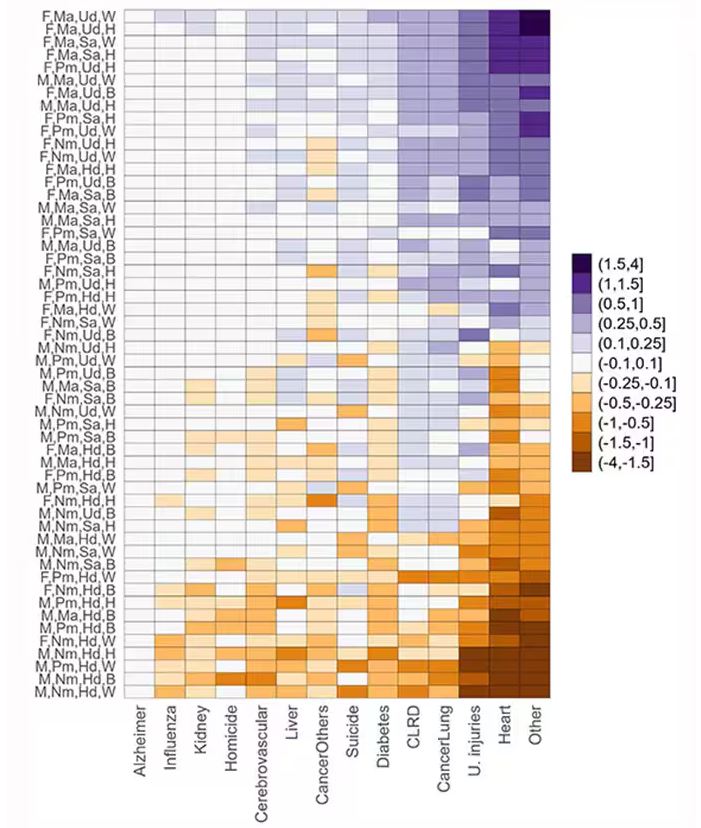
Looking at the bottom groups, you can see a dramatically increased risk for death from unintentional injuries, heart disease, and lung cancer. You see an increased risk for suicide as well. In the upper tiers, the only place where risk seems higher than expected is for the category of “other cancers,” reminding us that many types of cancer do not respect definitions of socioeconomic status.
You can even update the risk-scoring system to reflect the risk for different causes of death. You can see here how White people, for example, are at higher risk for death from unintentional injuries relative to other populations, despite having a lower mortality overall.
So maybe, through cause of death, we get a little closer to the answer of why. But this paper is really just a start. Its primary effect should be to surprise us — that in a country as wealthy as the United States, such dramatic variation exists based on factors that, with the exception of sex, I suppose, are not really biological. Which means that to find the why, we may need to turn from physiology to sociology.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Two individuals in the United States are celebrating their 30th birthdays. It’s a good day. They are entering the prime of their lives. One is a married White woman with a university degree. The other is a never-married White man with a high school diploma.
How many more years of life can these two individuals look forward to?
There’s a fairly dramatic difference. The man can expect 37.1 more years of life on average, living to be about 67. The woman can expect to live to age 85. That’s a life-expectancy discrepancy of 18 years based solely on gender, education, and marital status.
I’m using these cases to illustrate the extremes of life expectancy across four key social determinants of health: sex, race, marital status, and education. We all have some sense of how these factors play out in terms of health, but a new study suggests that it’s actually quite a bit more complicated than we thought.
Let me start by acknowledging my own bias here. As a clinical researcher, I sometimes find it hard to appreciate the value of actuarial-type studies that look at life expectancy (or any metric, really) between groups defined by marital status, for example. I’m never quite sure what to do with the conclusion. Married people live longer, the headline says. Okay, but as a doctor, what am I supposed to do about that? Encourage my patients to settle down and commit? Studies showing that women live longer than men or that White people live longer than Black people are also hard for me to incorporate into my practice. These are not easily changeable states.
But studies examining these groups are a reasonable starting point to ask more relevant questions. Why do women live longer than men? Is it behavioral (men take more risks and are less likely to see doctors)? Or is it hormonal (estrogen has a lot of protective effects that testosterone does not)? Or is it something else?
Integrating these social determinants of health into a cohesive story is a bit harder than it might seem, as this study, appearing in BMJ Open, illustrates.
In the context of this study, every person in America can be placed into one of 54 mutually exclusive groups. You can be male or female. You can be Black, White, or Hispanic. You can have a high school diploma or less, an associate degree, or a college degree; and you can be married, previously married, or never married.

Of course, this does not capture the beautiful tapestry that is American life, but let’s give them a pass. They are working with data from the American Community Survey, which contains 8634 people — the statistics would run into trouble with more granular divisions. This survey can be population weighted, so you can scale up the results to reasonably represent the population of the United States.
The survey collected data on the four broad categories of sex, race, education, and marital status and linked those survey results to the Multiple Cause of Death dataset from the CDC. From there, it’s a pretty simple task to rank the 54 categories in order from longest to shortest life expectancy, as you can see here.

But that’s not really the interesting part of this study. Sure, there is a lot of variation; it’s interesting that these four factors explain about 18 years’ difference in life expectancy in this country. What strikes me here, actually, is the lack of an entirely consistent message across this spectrum.
Let me walk you through the second figure in this paper, because this nicely illustrates the surprising heterogeneity that exists here.

This may seem overwhelming, but basically, shapes that are higher up on the Y-axis represent the groups with longer life expectancy.
You can tell, for example, that shapes that are black in color (groups with high school educations or less) are generally lower. But not universally so. This box represents married, Hispanic females who do quite well in terms of life expectancy, even at that lower educational level.

The authors quantify this phenomenon by creating a mortality risk score that integrates these findings. It looks something like this, with 0 being average morality for the United States.

As you can see, you get a bunch of points for being female, but you lose a bunch for not being married. Education plays a large role, with a big hit for those who have a high school diploma or less, and a bonus for those with a college degree. Race plays a relatively more minor role.
This is all very interesting, but as I said at the beginning, this isn’t terribly useful to me as a physician. More important is figuring out why these differences exist. And there are some clues in the study data, particularly when we examine causes of death. This figure ranks those 54 groups again, from the married, White, college-educated females down to the never-married, White, high school–educated males. The boxes show how much more or less likely this group is to die of a given condition than the general population.

Looking at the bottom groups, you can see a dramatically increased risk for death from unintentional injuries, heart disease, and lung cancer. You see an increased risk for suicide as well. In the upper tiers, the only place where risk seems higher than expected is for the category of “other cancers,” reminding us that many types of cancer do not respect definitions of socioeconomic status.
You can even update the risk-scoring system to reflect the risk for different causes of death. You can see here how White people, for example, are at higher risk for death from unintentional injuries relative to other populations, despite having a lower mortality overall.

So maybe, through cause of death, we get a little closer to the answer of why. But this paper is really just a start. Its primary effect should be to surprise us — that in a country as wealthy as the United States, such dramatic variation exists based on factors that, with the exception of sex, I suppose, are not really biological. Which means that to find the why, we may need to turn from physiology to sociology.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Two individuals in the United States are celebrating their 30th birthdays. It’s a good day. They are entering the prime of their lives. One is a married White woman with a university degree. The other is a never-married White man with a high school diploma.
How many more years of life can these two individuals look forward to?
There’s a fairly dramatic difference. The man can expect 37.1 more years of life on average, living to be about 67. The woman can expect to live to age 85. That’s a life-expectancy discrepancy of 18 years based solely on gender, education, and marital status.
I’m using these cases to illustrate the extremes of life expectancy across four key social determinants of health: sex, race, marital status, and education. We all have some sense of how these factors play out in terms of health, but a new study suggests that it’s actually quite a bit more complicated than we thought.
Let me start by acknowledging my own bias here. As a clinical researcher, I sometimes find it hard to appreciate the value of actuarial-type studies that look at life expectancy (or any metric, really) between groups defined by marital status, for example. I’m never quite sure what to do with the conclusion. Married people live longer, the headline says. Okay, but as a doctor, what am I supposed to do about that? Encourage my patients to settle down and commit? Studies showing that women live longer than men or that White people live longer than Black people are also hard for me to incorporate into my practice. These are not easily changeable states.
But studies examining these groups are a reasonable starting point to ask more relevant questions. Why do women live longer than men? Is it behavioral (men take more risks and are less likely to see doctors)? Or is it hormonal (estrogen has a lot of protective effects that testosterone does not)? Or is it something else?
Integrating these social determinants of health into a cohesive story is a bit harder than it might seem, as this study, appearing in BMJ Open, illustrates.
In the context of this study, every person in America can be placed into one of 54 mutually exclusive groups. You can be male or female. You can be Black, White, or Hispanic. You can have a high school diploma or less, an associate degree, or a college degree; and you can be married, previously married, or never married.

Of course, this does not capture the beautiful tapestry that is American life, but let’s give them a pass. They are working with data from the American Community Survey, which contains 8634 people — the statistics would run into trouble with more granular divisions. This survey can be population weighted, so you can scale up the results to reasonably represent the population of the United States.
The survey collected data on the four broad categories of sex, race, education, and marital status and linked those survey results to the Multiple Cause of Death dataset from the CDC. From there, it’s a pretty simple task to rank the 54 categories in order from longest to shortest life expectancy, as you can see here.

But that’s not really the interesting part of this study. Sure, there is a lot of variation; it’s interesting that these four factors explain about 18 years’ difference in life expectancy in this country. What strikes me here, actually, is the lack of an entirely consistent message across this spectrum.
Let me walk you through the second figure in this paper, because this nicely illustrates the surprising heterogeneity that exists here.

This may seem overwhelming, but basically, shapes that are higher up on the Y-axis represent the groups with longer life expectancy.
You can tell, for example, that shapes that are black in color (groups with high school educations or less) are generally lower. But not universally so. This box represents married, Hispanic females who do quite well in terms of life expectancy, even at that lower educational level.

The authors quantify this phenomenon by creating a mortality risk score that integrates these findings. It looks something like this, with 0 being average morality for the United States.

As you can see, you get a bunch of points for being female, but you lose a bunch for not being married. Education plays a large role, with a big hit for those who have a high school diploma or less, and a bonus for those with a college degree. Race plays a relatively more minor role.
This is all very interesting, but as I said at the beginning, this isn’t terribly useful to me as a physician. More important is figuring out why these differences exist. And there are some clues in the study data, particularly when we examine causes of death. This figure ranks those 54 groups again, from the married, White, college-educated females down to the never-married, White, high school–educated males. The boxes show how much more or less likely this group is to die of a given condition than the general population.

Looking at the bottom groups, you can see a dramatically increased risk for death from unintentional injuries, heart disease, and lung cancer. You see an increased risk for suicide as well. In the upper tiers, the only place where risk seems higher than expected is for the category of “other cancers,” reminding us that many types of cancer do not respect definitions of socioeconomic status.
You can even update the risk-scoring system to reflect the risk for different causes of death. You can see here how White people, for example, are at higher risk for death from unintentional injuries relative to other populations, despite having a lower mortality overall.

So maybe, through cause of death, we get a little closer to the answer of why. But this paper is really just a start. Its primary effect should be to surprise us — that in a country as wealthy as the United States, such dramatic variation exists based on factors that, with the exception of sex, I suppose, are not really biological. Which means that to find the why, we may need to turn from physiology to sociology.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

Cannabis Overuse Linked to Increased Risk for Head and Neck Cancer
TOPLINE:
The study analyzed data from over four million patients, highlighting the potential carcinogenic effects of the substance.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from a globally federated health research network TriNetX, which included over 90 million men and women from 64 health care organizations in the United States.
- More than 4.1 million patients were included in the analysis, including 116,076 individuals diagnosed with cannabis-related disorder and 3.9 million without the disorder. Cannabis-related disorders involve the excessive use of cannabis with associated psychosocial symptoms, such as impaired social and/or occupational functioning.
- Patients with cannabis-related disorder were matched with those without the disorder based on demographic characteristics, alcohol-related disorders, and tobacco use.
- The primary outcome was the diagnosis of head and neck cancer, including subsites such as oral, oropharyngeal, nasopharyngeal, laryngeal, hypopharyngeal, and salivary gland malignancies.
- Propensity score matching and Poisson regression analysis were used to compare the incidence of head and neck cancers between the groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the researchers, patients with a cannabis-related disorder had a higher risk for any head and neck cancer (relative risk [RR], 3.49; 95% CI, 2.78-4.39) than those without the disorder.
- The risk for specific cancers was also higher in the group with cannabis-related disorders, including oral (RR, 2.51; 95% CI, 1.81-3.47) and oropharyngeal malignancies (RR, 4.90; 95% CI, 2.99-8.02).
- The RR for laryngeal cancer was significantly higher in the patients with a cannabis-related disorder (RR, 8.39; 95% CI, 4.72-14.90).
- The findings suggest that cannabis use disorder is associated with an increased risk for head and neck cancers, highlighting the need for further research to understand the mechanisms involved.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this cohort study, cannabis disorder diagnosis was independently associated with greater risk of subsequent development of any [head or neck cancer] as well as cancers in various subsites of the head and neck among US adults. When limited to cases of [such cancers] occurring greater than 1 year after cannabis use disorder diagnosis, many of the associations increased, demonstrating additional strength in the association,” the authors of the study wrote.
“The association of cannabis and head and neck cancer in this study spanned 2 decades during a rapid growth in use. If this association is causative, the burden of [head and neck cancers] attributable to cannabis will continue to increase, and perhaps dramatically,” said the authors of an editorial accompanying the journal article. “Given that cannabis is now a $20 billion industry in the US alone with expanding availability, use, and popularity, this may be “déjà vu, all over again” without appropriate research to understand the potential carcinogenic and salutatory effects of cannabis. Or, in the words of Yogi Berra, “If you don’t know where you are going, you might wind up someplace else.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tyler J. Gallagher and Niels C. Kokot, MD, at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. It was published online in JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had limited information about cohort composition and length of follow-up, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. The lack of direct exposure duration, intensity, and dosage information limits the ability to analyze dose-response relationships. Potential inconsistency of diagnosis and reliance on medical record codes may introduce bias. Cannabis use is likely underreported, which could decrease the relative risks discovered. The study was further limited by the lack of information on dosage and frequency of cannabis use, as well as some controls, including alcohol and tobacco use.
DISCLOSURES:
Gallagher disclosed receiving grants from the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The study analyzed data from over four million patients, highlighting the potential carcinogenic effects of the substance.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from a globally federated health research network TriNetX, which included over 90 million men and women from 64 health care organizations in the United States.
- More than 4.1 million patients were included in the analysis, including 116,076 individuals diagnosed with cannabis-related disorder and 3.9 million without the disorder. Cannabis-related disorders involve the excessive use of cannabis with associated psychosocial symptoms, such as impaired social and/or occupational functioning.
- Patients with cannabis-related disorder were matched with those without the disorder based on demographic characteristics, alcohol-related disorders, and tobacco use.
- The primary outcome was the diagnosis of head and neck cancer, including subsites such as oral, oropharyngeal, nasopharyngeal, laryngeal, hypopharyngeal, and salivary gland malignancies.
- Propensity score matching and Poisson regression analysis were used to compare the incidence of head and neck cancers between the groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the researchers, patients with a cannabis-related disorder had a higher risk for any head and neck cancer (relative risk [RR], 3.49; 95% CI, 2.78-4.39) than those without the disorder.
- The risk for specific cancers was also higher in the group with cannabis-related disorders, including oral (RR, 2.51; 95% CI, 1.81-3.47) and oropharyngeal malignancies (RR, 4.90; 95% CI, 2.99-8.02).
- The RR for laryngeal cancer was significantly higher in the patients with a cannabis-related disorder (RR, 8.39; 95% CI, 4.72-14.90).
- The findings suggest that cannabis use disorder is associated with an increased risk for head and neck cancers, highlighting the need for further research to understand the mechanisms involved.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this cohort study, cannabis disorder diagnosis was independently associated with greater risk of subsequent development of any [head or neck cancer] as well as cancers in various subsites of the head and neck among US adults. When limited to cases of [such cancers] occurring greater than 1 year after cannabis use disorder diagnosis, many of the associations increased, demonstrating additional strength in the association,” the authors of the study wrote.
“The association of cannabis and head and neck cancer in this study spanned 2 decades during a rapid growth in use. If this association is causative, the burden of [head and neck cancers] attributable to cannabis will continue to increase, and perhaps dramatically,” said the authors of an editorial accompanying the journal article. “Given that cannabis is now a $20 billion industry in the US alone with expanding availability, use, and popularity, this may be “déjà vu, all over again” without appropriate research to understand the potential carcinogenic and salutatory effects of cannabis. Or, in the words of Yogi Berra, “If you don’t know where you are going, you might wind up someplace else.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tyler J. Gallagher and Niels C. Kokot, MD, at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. It was published online in JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had limited information about cohort composition and length of follow-up, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. The lack of direct exposure duration, intensity, and dosage information limits the ability to analyze dose-response relationships. Potential inconsistency of diagnosis and reliance on medical record codes may introduce bias. Cannabis use is likely underreported, which could decrease the relative risks discovered. The study was further limited by the lack of information on dosage and frequency of cannabis use, as well as some controls, including alcohol and tobacco use.
DISCLOSURES:
Gallagher disclosed receiving grants from the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The study analyzed data from over four million patients, highlighting the potential carcinogenic effects of the substance.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from a globally federated health research network TriNetX, which included over 90 million men and women from 64 health care organizations in the United States.
- More than 4.1 million patients were included in the analysis, including 116,076 individuals diagnosed with cannabis-related disorder and 3.9 million without the disorder. Cannabis-related disorders involve the excessive use of cannabis with associated psychosocial symptoms, such as impaired social and/or occupational functioning.
- Patients with cannabis-related disorder were matched with those without the disorder based on demographic characteristics, alcohol-related disorders, and tobacco use.
- The primary outcome was the diagnosis of head and neck cancer, including subsites such as oral, oropharyngeal, nasopharyngeal, laryngeal, hypopharyngeal, and salivary gland malignancies.
- Propensity score matching and Poisson regression analysis were used to compare the incidence of head and neck cancers between the groups.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the researchers, patients with a cannabis-related disorder had a higher risk for any head and neck cancer (relative risk [RR], 3.49; 95% CI, 2.78-4.39) than those without the disorder.
- The risk for specific cancers was also higher in the group with cannabis-related disorders, including oral (RR, 2.51; 95% CI, 1.81-3.47) and oropharyngeal malignancies (RR, 4.90; 95% CI, 2.99-8.02).
- The RR for laryngeal cancer was significantly higher in the patients with a cannabis-related disorder (RR, 8.39; 95% CI, 4.72-14.90).
- The findings suggest that cannabis use disorder is associated with an increased risk for head and neck cancers, highlighting the need for further research to understand the mechanisms involved.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this cohort study, cannabis disorder diagnosis was independently associated with greater risk of subsequent development of any [head or neck cancer] as well as cancers in various subsites of the head and neck among US adults. When limited to cases of [such cancers] occurring greater than 1 year after cannabis use disorder diagnosis, many of the associations increased, demonstrating additional strength in the association,” the authors of the study wrote.
“The association of cannabis and head and neck cancer in this study spanned 2 decades during a rapid growth in use. If this association is causative, the burden of [head and neck cancers] attributable to cannabis will continue to increase, and perhaps dramatically,” said the authors of an editorial accompanying the journal article. “Given that cannabis is now a $20 billion industry in the US alone with expanding availability, use, and popularity, this may be “déjà vu, all over again” without appropriate research to understand the potential carcinogenic and salutatory effects of cannabis. Or, in the words of Yogi Berra, “If you don’t know where you are going, you might wind up someplace else.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tyler J. Gallagher and Niels C. Kokot, MD, at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles. It was published online in JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The study had limited information about cohort composition and length of follow-up, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. The lack of direct exposure duration, intensity, and dosage information limits the ability to analyze dose-response relationships. Potential inconsistency of diagnosis and reliance on medical record codes may introduce bias. Cannabis use is likely underreported, which could decrease the relative risks discovered. The study was further limited by the lack of information on dosage and frequency of cannabis use, as well as some controls, including alcohol and tobacco use.
DISCLOSURES:
Gallagher disclosed receiving grants from the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Light Therapy, Phototherapy, Photobiomodulation: New Ways to Heal With Light
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Navigating Election Anxiety: How Worry Affects the Brain
Once again, America is deeply divided before a national election, with people on each side convinced of the horrors that will be visited upon us if the other side wins.
’Tis the season — and regrettably, not to be jolly but to be worried.
As a neuroscientist, I am especially aware of the deleterious mental and physical impact of chronic worry on our citizenry. That’s because worry is not “all in your head.” We modern humans live in a world of worry which appears to be progressively growing.
Flight or Fight
Worry stems from the brain’s rather remarkable ability to foresee and reflexively respond to threat. Our “fight or flight” brain machinery probably arose in our vertebrate ancestors more than 300 million years ago. The fact that we have machinery akin to that possessed by lizards or tigers or shrews is testimony to its crucial contribution to our species’ survival.
As the phrase “fight or flight” suggests, a brain that senses trouble immediately biases certain body and brain functions. As it shifts into a higher-alert mode, it increases the energy supplies in our blood and supports other changes that facilitate faster and stronger reactions, while it shuts down less essential processes which do not contribute to hiding, fighting, or running like hell.
This hyperreactive response is initiated in the amygdala in the anterior brain, which identifies “what’s happening” as immediately or potentially threatening. The now-activated amygdala generates a response in the hypothalamus that provokes an immediate increase of adrenaline and cortisol in the body, and cortisol and noradrenaline in the brain. Both sharply speed up our physical and neurologic reactivity. In the brain, that is achieved by increasing the level of excitability of neurons across the forebrain. Depending on the perceived level of threat, an excitable brain will be just a little or a lot more “on alert,” just a little or a lot faster to respond, and just a little or a lot better at remembering the specific “warning” events that trigger this lizard-brain response.
Alas, this machinery was designed to be engaged every so often when a potentially dangerous surprise arises in life. When the worry and stress are persistent, the brain experiences a kind of neurologic “burn-out” of its fight versus flight machinery.
Dangers of Nonstop Anxiety and Stress
A consistently stressed-out brain turns down its production and release of noradrenaline, and the brain becomes less attentive, less engaged. This sets the brain on the path to an anxiety (and then a depressive) disorder, and, in the longer term, to cognitive losses in memory and executive control systems, and to emotional distortions that can lead to substance abuse or other addictions.
Our political distress is but one source of persistent worry and stress. Worry is a modern plague. The head counts of individuals seeking psychiatric or psychological health are at an all-time high in the United States. Near-universal low-level stressors, such as 2 years of COVID, insecurities about the changing demands of our professional and private lives, and a deeply divided body politic are unequivocally affecting American brain health.
The brain also collaborates in our body’s response to stress. Its regulation of hormonal responses and its autonomic nervous system’s mediated responses contribute to elevated blood sugar levels, to craving high-sugar foods, to elevated blood pressure, and to weaker immune responses. This all contributes to higher risks for cardiovascular and other dietary- and immune system–related disease. And ultimately, to shorter lifespans.
Strategies to Address Neurologic Changes Arising From Chronic Stress
There are many things you can try to bring your worry back to a manageable (and even productive) level.
- Engage in a “reset” strategy several times a day to bring your amygdala and locus coeruleus back under control. It takes a minute (or five) of calm, positive meditation to take your brain to a happy, optimistic place. Or use a mindfulness exercise to quiet down that overactive amygdala.
- Talk to people. Keeping your worries to yourself can compound them. Hashing through your concerns with a family member, friend, professional coach, or therapist can help put them in perspective and may allow you to come up with strategies to identify and neurologically respond to your sources of stress.
- Exercise, both physically and mentally. Do what works for you, whether it’s a run, a long walk, pumping iron, playing racquetball — anything that promotes physical release. Exercise your brain too. Engage in a project or activity that is mentally demanding. Personally, I like to garden and do online brain exercises. There’s nothing quite like yanking out weeds or hitting a new personal best at a cognitive exercise for me to notch a sense of accomplishment to counterbalance the unresolved issues driving my worry.
- Accept the uncertainty. Life is full of uncertainty. To paraphrase from Yale theologian Reinhold Niebuhr’s “Serenity Prayer”: Have the serenity to accept what you cannot help, the courage to change what you can, and the wisdom to recognize one from the other.
And, please, be assured that you’ll make it through this election season.
Dr. Merzenich, professor emeritus, Department of Neuroscience, University of California San Francisco, disclosed ties with Posit Science. He is often credited with discovering lifelong plasticity, with being the first to harness plasticity for human benefit (in his co-invention of the cochlear implant), and for pioneering the field of plasticity-based computerized brain exercise. He is a Kavli Laureate in Neuroscience, and he has been honored by each of the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. He may be most widely known for a series of specials on the brain on public television. His current focus is BrainHQ, a brain exercise app.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Once again, America is deeply divided before a national election, with people on each side convinced of the horrors that will be visited upon us if the other side wins.
’Tis the season — and regrettably, not to be jolly but to be worried.
As a neuroscientist, I am especially aware of the deleterious mental and physical impact of chronic worry on our citizenry. That’s because worry is not “all in your head.” We modern humans live in a world of worry which appears to be progressively growing.
Flight or Fight
Worry stems from the brain’s rather remarkable ability to foresee and reflexively respond to threat. Our “fight or flight” brain machinery probably arose in our vertebrate ancestors more than 300 million years ago. The fact that we have machinery akin to that possessed by lizards or tigers or shrews is testimony to its crucial contribution to our species’ survival.
As the phrase “fight or flight” suggests, a brain that senses trouble immediately biases certain body and brain functions. As it shifts into a higher-alert mode, it increases the energy supplies in our blood and supports other changes that facilitate faster and stronger reactions, while it shuts down less essential processes which do not contribute to hiding, fighting, or running like hell.
This hyperreactive response is initiated in the amygdala in the anterior brain, which identifies “what’s happening” as immediately or potentially threatening. The now-activated amygdala generates a response in the hypothalamus that provokes an immediate increase of adrenaline and cortisol in the body, and cortisol and noradrenaline in the brain. Both sharply speed up our physical and neurologic reactivity. In the brain, that is achieved by increasing the level of excitability of neurons across the forebrain. Depending on the perceived level of threat, an excitable brain will be just a little or a lot more “on alert,” just a little or a lot faster to respond, and just a little or a lot better at remembering the specific “warning” events that trigger this lizard-brain response.
Alas, this machinery was designed to be engaged every so often when a potentially dangerous surprise arises in life. When the worry and stress are persistent, the brain experiences a kind of neurologic “burn-out” of its fight versus flight machinery.
Dangers of Nonstop Anxiety and Stress
A consistently stressed-out brain turns down its production and release of noradrenaline, and the brain becomes less attentive, less engaged. This sets the brain on the path to an anxiety (and then a depressive) disorder, and, in the longer term, to cognitive losses in memory and executive control systems, and to emotional distortions that can lead to substance abuse or other addictions.
Our political distress is but one source of persistent worry and stress. Worry is a modern plague. The head counts of individuals seeking psychiatric or psychological health are at an all-time high in the United States. Near-universal low-level stressors, such as 2 years of COVID, insecurities about the changing demands of our professional and private lives, and a deeply divided body politic are unequivocally affecting American brain health.
The brain also collaborates in our body’s response to stress. Its regulation of hormonal responses and its autonomic nervous system’s mediated responses contribute to elevated blood sugar levels, to craving high-sugar foods, to elevated blood pressure, and to weaker immune responses. This all contributes to higher risks for cardiovascular and other dietary- and immune system–related disease. And ultimately, to shorter lifespans.
Strategies to Address Neurologic Changes Arising From Chronic Stress
There are many things you can try to bring your worry back to a manageable (and even productive) level.
- Engage in a “reset” strategy several times a day to bring your amygdala and locus coeruleus back under control. It takes a minute (or five) of calm, positive meditation to take your brain to a happy, optimistic place. Or use a mindfulness exercise to quiet down that overactive amygdala.
- Talk to people. Keeping your worries to yourself can compound them. Hashing through your concerns with a family member, friend, professional coach, or therapist can help put them in perspective and may allow you to come up with strategies to identify and neurologically respond to your sources of stress.
- Exercise, both physically and mentally. Do what works for you, whether it’s a run, a long walk, pumping iron, playing racquetball — anything that promotes physical release. Exercise your brain too. Engage in a project or activity that is mentally demanding. Personally, I like to garden and do online brain exercises. There’s nothing quite like yanking out weeds or hitting a new personal best at a cognitive exercise for me to notch a sense of accomplishment to counterbalance the unresolved issues driving my worry.
- Accept the uncertainty. Life is full of uncertainty. To paraphrase from Yale theologian Reinhold Niebuhr’s “Serenity Prayer”: Have the serenity to accept what you cannot help, the courage to change what you can, and the wisdom to recognize one from the other.
And, please, be assured that you’ll make it through this election season.
Dr. Merzenich, professor emeritus, Department of Neuroscience, University of California San Francisco, disclosed ties with Posit Science. He is often credited with discovering lifelong plasticity, with being the first to harness plasticity for human benefit (in his co-invention of the cochlear implant), and for pioneering the field of plasticity-based computerized brain exercise. He is a Kavli Laureate in Neuroscience, and he has been honored by each of the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. He may be most widely known for a series of specials on the brain on public television. His current focus is BrainHQ, a brain exercise app.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Once again, America is deeply divided before a national election, with people on each side convinced of the horrors that will be visited upon us if the other side wins.
’Tis the season — and regrettably, not to be jolly but to be worried.
As a neuroscientist, I am especially aware of the deleterious mental and physical impact of chronic worry on our citizenry. That’s because worry is not “all in your head.” We modern humans live in a world of worry which appears to be progressively growing.
Flight or Fight
Worry stems from the brain’s rather remarkable ability to foresee and reflexively respond to threat. Our “fight or flight” brain machinery probably arose in our vertebrate ancestors more than 300 million years ago. The fact that we have machinery akin to that possessed by lizards or tigers or shrews is testimony to its crucial contribution to our species’ survival.
As the phrase “fight or flight” suggests, a brain that senses trouble immediately biases certain body and brain functions. As it shifts into a higher-alert mode, it increases the energy supplies in our blood and supports other changes that facilitate faster and stronger reactions, while it shuts down less essential processes which do not contribute to hiding, fighting, or running like hell.
This hyperreactive response is initiated in the amygdala in the anterior brain, which identifies “what’s happening” as immediately or potentially threatening. The now-activated amygdala generates a response in the hypothalamus that provokes an immediate increase of adrenaline and cortisol in the body, and cortisol and noradrenaline in the brain. Both sharply speed up our physical and neurologic reactivity. In the brain, that is achieved by increasing the level of excitability of neurons across the forebrain. Depending on the perceived level of threat, an excitable brain will be just a little or a lot more “on alert,” just a little or a lot faster to respond, and just a little or a lot better at remembering the specific “warning” events that trigger this lizard-brain response.
Alas, this machinery was designed to be engaged every so often when a potentially dangerous surprise arises in life. When the worry and stress are persistent, the brain experiences a kind of neurologic “burn-out” of its fight versus flight machinery.
Dangers of Nonstop Anxiety and Stress
A consistently stressed-out brain turns down its production and release of noradrenaline, and the brain becomes less attentive, less engaged. This sets the brain on the path to an anxiety (and then a depressive) disorder, and, in the longer term, to cognitive losses in memory and executive control systems, and to emotional distortions that can lead to substance abuse or other addictions.
Our political distress is but one source of persistent worry and stress. Worry is a modern plague. The head counts of individuals seeking psychiatric or psychological health are at an all-time high in the United States. Near-universal low-level stressors, such as 2 years of COVID, insecurities about the changing demands of our professional and private lives, and a deeply divided body politic are unequivocally affecting American brain health.
The brain also collaborates in our body’s response to stress. Its regulation of hormonal responses and its autonomic nervous system’s mediated responses contribute to elevated blood sugar levels, to craving high-sugar foods, to elevated blood pressure, and to weaker immune responses. This all contributes to higher risks for cardiovascular and other dietary- and immune system–related disease. And ultimately, to shorter lifespans.
Strategies to Address Neurologic Changes Arising From Chronic Stress
There are many things you can try to bring your worry back to a manageable (and even productive) level.
- Engage in a “reset” strategy several times a day to bring your amygdala and locus coeruleus back under control. It takes a minute (or five) of calm, positive meditation to take your brain to a happy, optimistic place. Or use a mindfulness exercise to quiet down that overactive amygdala.
- Talk to people. Keeping your worries to yourself can compound them. Hashing through your concerns with a family member, friend, professional coach, or therapist can help put them in perspective and may allow you to come up with strategies to identify and neurologically respond to your sources of stress.
- Exercise, both physically and mentally. Do what works for you, whether it’s a run, a long walk, pumping iron, playing racquetball — anything that promotes physical release. Exercise your brain too. Engage in a project or activity that is mentally demanding. Personally, I like to garden and do online brain exercises. There’s nothing quite like yanking out weeds or hitting a new personal best at a cognitive exercise for me to notch a sense of accomplishment to counterbalance the unresolved issues driving my worry.
- Accept the uncertainty. Life is full of uncertainty. To paraphrase from Yale theologian Reinhold Niebuhr’s “Serenity Prayer”: Have the serenity to accept what you cannot help, the courage to change what you can, and the wisdom to recognize one from the other.
And, please, be assured that you’ll make it through this election season.
Dr. Merzenich, professor emeritus, Department of Neuroscience, University of California San Francisco, disclosed ties with Posit Science. He is often credited with discovering lifelong plasticity, with being the first to harness plasticity for human benefit (in his co-invention of the cochlear implant), and for pioneering the field of plasticity-based computerized brain exercise. He is a Kavli Laureate in Neuroscience, and he has been honored by each of the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. He may be most widely known for a series of specials on the brain on public television. His current focus is BrainHQ, a brain exercise app.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy May Be Overused in Dying Patients With Cancer
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Addressing Depression Reduce Chemo Toxicity in Older Adults?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Headache Surgery Really Work? Neurologists Remain Unconvinced
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine Doc Charged With $1.5M Fraud
In a case that spotlights the importance of comprehensive financial controls in medical offices,
Michael Lucchesi, MD, who had served as chairman of Emergency Medicine at SUNY Downstate Medical Center in New York City, was arraigned on July 9 and pleaded not guilty. Dr. Lucchesi’s attorney, Earl Ward, did not respond to messages from this news organization, but he told the New York Post that “the funds he used were not stolen funds.”
Dr. Lucchesi, who’s in his late 60s, faces nine counts of first- and second-degree grand larceny, first-degree falsifying business records, and third-degree criminal tax fraud. According to a press statement from the district attorney of Kings County, which encompasses the borough of Brooklyn, Dr. Lucchesi is accused of using his clinical practice’s business card for cash advances (about $115,000), high-end pet care ($176,000), personal travel ($348,000), gym membership and personal training ($109,000), catering ($52,000), tuition payments for his children ($46,000), and other expenses such as online shopping, flowers, liquor, and electronics.
Most of the alleged pet care spending — $120,000 — went to the Green Leaf Pet Resort, which has two locations in New Jersey, including one with “56 acres of nature and lots of tail wagging.” Some of the alleged spending on gym membership was at the New York Sports Clubs chain, where monthly membership tops out at $139.99.
The alleged spending occurred between 2016 and 2023 and was discovered by SUNY Downstate during an audit. Dr. Lucchesi reportedly left his position at the hospital, where he made $399,712 in 2022 as a professor, according to public records.
“As a high-ranking doctor at this vital healthcare institution, this defendant was entrusted with access to significant funds, which he allegedly exploited, stealing more than 1 million dollars to pay for a lavish lifestyle,” District Attorney Eric Gonzalez said in a statement.
SUNY Downstate is in a fight for its life amid efforts by New York Governor Kathy Hochul to shut it down. According to The New York Times, it is the only state-run hospital in New York City.
Dr. Lucchesi, who had previously served as the hospital’s chief medical officer and acting head, was released without bail. His next court date is September 25, 2024.
Size of Alleged Theft Is ‘Very Unusual’
David P. Weber, JD, DBA, a professor and fraud specialist at Salisbury University, Salisbury, Maryland, told this news organization that the fraudulent use of a business or purchase credit card is a form of embezzlement and “one of the most frequently seen types of frauds against organizations.”
William J. Kresse, JD, MSA, CPA/CFF, who studies fraud at Governors State University in University Park, Illinois, noted in an interview with this news organization that the high amount of alleged fraud in this case is “very unusual,” as is the period it is said to have occurred (over 6 years).
Mr. Kresse highlighted a 2024 report by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, which found that the median fraud loss in healthcare, on the basis of 117 cases, is $100,000. The most common form of fraud in the industry is corruption (47%), followed by billing (38%), noncash theft such as inventory (22%), and expense reimbursement (21%).
The details of the current case suggest that “SUNY Downstate had weak or insufficient internal controls to prevent this type of fraud,” Salisbury University’s Mr. Weber said. “However, research also makes clear that the tenure and position of the perpetrator play a significant role in the size of the fraud. Internal controls are supposed to apply to all employees, but the higher in the organization the perpetrator is, the easier it can be to engage in fraud.”
Even Small Medical Offices Can Act to Prevent Fraud
What can be done to prevent this kind of fraud? “Each employee should be required to submit actual receipts or scanned copies, and the reimbursement requests should be reviewed and inputted by a separate department or office of the organization to ensure that the expenses are legitimate,” Mr. Weber said. “In addition, all credit card statements should be available for review by the organization either simultaneously with the bill going to the employee or available for audit or review at any time without notification to the employee. Expenses that are in certain categories should be prohibited automatically and coded to the card so such a charge is rejected by the credit card bank.”
Smaller businesses — like many medical practices — may not have the manpower to handle these roles. In that case, Mr. Weber said, “The key is segregation or separation of duties. The bookkeeper cannot be the person receiving the bank statements, the payments from patients, and the invoices from vendors. There needs to be at least one other person in the loop to have some level of control.”
One strategy, he said, “is that the practice should institute a policy that only the doctor or owner of the practice can receive the mail, not the bookkeeper. Even if the practice leader does not actually review the bank statements, simply opening them before handing them off to the bookkeeper can provide a level of deterrence [since] the employee may get caught if someone else is reviewing the bank statements.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a case that spotlights the importance of comprehensive financial controls in medical offices,
Michael Lucchesi, MD, who had served as chairman of Emergency Medicine at SUNY Downstate Medical Center in New York City, was arraigned on July 9 and pleaded not guilty. Dr. Lucchesi’s attorney, Earl Ward, did not respond to messages from this news organization, but he told the New York Post that “the funds he used were not stolen funds.”
Dr. Lucchesi, who’s in his late 60s, faces nine counts of first- and second-degree grand larceny, first-degree falsifying business records, and third-degree criminal tax fraud. According to a press statement from the district attorney of Kings County, which encompasses the borough of Brooklyn, Dr. Lucchesi is accused of using his clinical practice’s business card for cash advances (about $115,000), high-end pet care ($176,000), personal travel ($348,000), gym membership and personal training ($109,000), catering ($52,000), tuition payments for his children ($46,000), and other expenses such as online shopping, flowers, liquor, and electronics.
Most of the alleged pet care spending — $120,000 — went to the Green Leaf Pet Resort, which has two locations in New Jersey, including one with “56 acres of nature and lots of tail wagging.” Some of the alleged spending on gym membership was at the New York Sports Clubs chain, where monthly membership tops out at $139.99.
The alleged spending occurred between 2016 and 2023 and was discovered by SUNY Downstate during an audit. Dr. Lucchesi reportedly left his position at the hospital, where he made $399,712 in 2022 as a professor, according to public records.
“As a high-ranking doctor at this vital healthcare institution, this defendant was entrusted with access to significant funds, which he allegedly exploited, stealing more than 1 million dollars to pay for a lavish lifestyle,” District Attorney Eric Gonzalez said in a statement.
SUNY Downstate is in a fight for its life amid efforts by New York Governor Kathy Hochul to shut it down. According to The New York Times, it is the only state-run hospital in New York City.
Dr. Lucchesi, who had previously served as the hospital’s chief medical officer and acting head, was released without bail. His next court date is September 25, 2024.
Size of Alleged Theft Is ‘Very Unusual’
David P. Weber, JD, DBA, a professor and fraud specialist at Salisbury University, Salisbury, Maryland, told this news organization that the fraudulent use of a business or purchase credit card is a form of embezzlement and “one of the most frequently seen types of frauds against organizations.”
William J. Kresse, JD, MSA, CPA/CFF, who studies fraud at Governors State University in University Park, Illinois, noted in an interview with this news organization that the high amount of alleged fraud in this case is “very unusual,” as is the period it is said to have occurred (over 6 years).
Mr. Kresse highlighted a 2024 report by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, which found that the median fraud loss in healthcare, on the basis of 117 cases, is $100,000. The most common form of fraud in the industry is corruption (47%), followed by billing (38%), noncash theft such as inventory (22%), and expense reimbursement (21%).
The details of the current case suggest that “SUNY Downstate had weak or insufficient internal controls to prevent this type of fraud,” Salisbury University’s Mr. Weber said. “However, research also makes clear that the tenure and position of the perpetrator play a significant role in the size of the fraud. Internal controls are supposed to apply to all employees, but the higher in the organization the perpetrator is, the easier it can be to engage in fraud.”
Even Small Medical Offices Can Act to Prevent Fraud
What can be done to prevent this kind of fraud? “Each employee should be required to submit actual receipts or scanned copies, and the reimbursement requests should be reviewed and inputted by a separate department or office of the organization to ensure that the expenses are legitimate,” Mr. Weber said. “In addition, all credit card statements should be available for review by the organization either simultaneously with the bill going to the employee or available for audit or review at any time without notification to the employee. Expenses that are in certain categories should be prohibited automatically and coded to the card so such a charge is rejected by the credit card bank.”
Smaller businesses — like many medical practices — may not have the manpower to handle these roles. In that case, Mr. Weber said, “The key is segregation or separation of duties. The bookkeeper cannot be the person receiving the bank statements, the payments from patients, and the invoices from vendors. There needs to be at least one other person in the loop to have some level of control.”
One strategy, he said, “is that the practice should institute a policy that only the doctor or owner of the practice can receive the mail, not the bookkeeper. Even if the practice leader does not actually review the bank statements, simply opening them before handing them off to the bookkeeper can provide a level of deterrence [since] the employee may get caught if someone else is reviewing the bank statements.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a case that spotlights the importance of comprehensive financial controls in medical offices,
Michael Lucchesi, MD, who had served as chairman of Emergency Medicine at SUNY Downstate Medical Center in New York City, was arraigned on July 9 and pleaded not guilty. Dr. Lucchesi’s attorney, Earl Ward, did not respond to messages from this news organization, but he told the New York Post that “the funds he used were not stolen funds.”
Dr. Lucchesi, who’s in his late 60s, faces nine counts of first- and second-degree grand larceny, first-degree falsifying business records, and third-degree criminal tax fraud. According to a press statement from the district attorney of Kings County, which encompasses the borough of Brooklyn, Dr. Lucchesi is accused of using his clinical practice’s business card for cash advances (about $115,000), high-end pet care ($176,000), personal travel ($348,000), gym membership and personal training ($109,000), catering ($52,000), tuition payments for his children ($46,000), and other expenses such as online shopping, flowers, liquor, and electronics.
Most of the alleged pet care spending — $120,000 — went to the Green Leaf Pet Resort, which has two locations in New Jersey, including one with “56 acres of nature and lots of tail wagging.” Some of the alleged spending on gym membership was at the New York Sports Clubs chain, where monthly membership tops out at $139.99.
The alleged spending occurred between 2016 and 2023 and was discovered by SUNY Downstate during an audit. Dr. Lucchesi reportedly left his position at the hospital, where he made $399,712 in 2022 as a professor, according to public records.
“As a high-ranking doctor at this vital healthcare institution, this defendant was entrusted with access to significant funds, which he allegedly exploited, stealing more than 1 million dollars to pay for a lavish lifestyle,” District Attorney Eric Gonzalez said in a statement.
SUNY Downstate is in a fight for its life amid efforts by New York Governor Kathy Hochul to shut it down. According to The New York Times, it is the only state-run hospital in New York City.
Dr. Lucchesi, who had previously served as the hospital’s chief medical officer and acting head, was released without bail. His next court date is September 25, 2024.
Size of Alleged Theft Is ‘Very Unusual’
David P. Weber, JD, DBA, a professor and fraud specialist at Salisbury University, Salisbury, Maryland, told this news organization that the fraudulent use of a business or purchase credit card is a form of embezzlement and “one of the most frequently seen types of frauds against organizations.”
William J. Kresse, JD, MSA, CPA/CFF, who studies fraud at Governors State University in University Park, Illinois, noted in an interview with this news organization that the high amount of alleged fraud in this case is “very unusual,” as is the period it is said to have occurred (over 6 years).
Mr. Kresse highlighted a 2024 report by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, which found that the median fraud loss in healthcare, on the basis of 117 cases, is $100,000. The most common form of fraud in the industry is corruption (47%), followed by billing (38%), noncash theft such as inventory (22%), and expense reimbursement (21%).
The details of the current case suggest that “SUNY Downstate had weak or insufficient internal controls to prevent this type of fraud,” Salisbury University’s Mr. Weber said. “However, research also makes clear that the tenure and position of the perpetrator play a significant role in the size of the fraud. Internal controls are supposed to apply to all employees, but the higher in the organization the perpetrator is, the easier it can be to engage in fraud.”
Even Small Medical Offices Can Act to Prevent Fraud
What can be done to prevent this kind of fraud? “Each employee should be required to submit actual receipts or scanned copies, and the reimbursement requests should be reviewed and inputted by a separate department or office of the organization to ensure that the expenses are legitimate,” Mr. Weber said. “In addition, all credit card statements should be available for review by the organization either simultaneously with the bill going to the employee or available for audit or review at any time without notification to the employee. Expenses that are in certain categories should be prohibited automatically and coded to the card so such a charge is rejected by the credit card bank.”
Smaller businesses — like many medical practices — may not have the manpower to handle these roles. In that case, Mr. Weber said, “The key is segregation or separation of duties. The bookkeeper cannot be the person receiving the bank statements, the payments from patients, and the invoices from vendors. There needs to be at least one other person in the loop to have some level of control.”
One strategy, he said, “is that the practice should institute a policy that only the doctor or owner of the practice can receive the mail, not the bookkeeper. Even if the practice leader does not actually review the bank statements, simply opening them before handing them off to the bookkeeper can provide a level of deterrence [since] the employee may get caught if someone else is reviewing the bank statements.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Too Much Coffee Linked to Accelerated Cognitive Decline
PHILADELPHIA – results from a large study suggest.
Investigators examined the impact of different amounts of coffee and tea on fluid intelligence — a measure of cognitive functions including abstract reasoning, pattern recognition, and logical thinking.
“It’s the old adage that too much of anything isn’t good. It’s all about balance, so moderate coffee consumption is okay but too much is probably not recommended,” said study investigator Kelsey R. Sewell, PhD, Advent Health Research Institute, Orlando, Florida.
The findings of the study were presented at the 2024 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC).
One of the World’s Most Widely Consumed Beverages
Coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages around the world. The beans contain a range of bioactive compounds, including caffeine, chlorogenic acid, and small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Consistent evidence from observational and epidemiologic studies indicates that intake of both coffee and tea has beneficial effects on stroke, heart failure, cancers, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease.
Several studies also suggest that coffee may reduce the risk for Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Sewell. However, there are limited longitudinal data on associations between coffee and tea intake and cognitive decline, particularly in distinct cognitive domains.
Dr. Sewell’s group previously published a study of cognitively unimpaired older adults that found greater coffee consumption was associated with slower cognitive decline and slower accumulation of brain beta-amyloid.
Their current study extends some of the prior findings and investigates the relationship between both coffee and tea intake and cognitive decline over time in a larger sample of older adults.
This new study included 8451 mostly female (60%) and White (97%) cognitively unimpaired adults older than 60 (mean age, 67.8 years) in the UK Biobank, a large-scale research resource containing in-depth, deidentified genetic and health information from half a million UK participants. Study subjects had a mean body mass index (BMI) of 26, and about 26% were apolipoprotein epsilon 4 (APOE e4) gene carriers.
Researchers divided coffee and tea consumption into tertiles: high, moderate, and no consumption.
For daily coffee consumption, 18% reported drinking four or more cups (high consumption), 58% reported drinking one to three cups (moderate consumption), and 25% reported that they never drink coffee. For daily tea consumption, 47% reported drinking four or more cups (high consumption), 38% reported drinking one to three cups (moderate consumption), and 15% reported that they never drink tea.
The study assessed cognitive function at baseline and at least two additional patient visits.
Researchers used linear mixed models to assess the relationships between coffee and tea intake and cognitive outcomes. The models adjusted for age, sex, Townsend deprivation index (reflecting socioeconomic status), ethnicity, APOE e4 status, and BMI.
Steeper Decline
Compared with high coffee consumption (four or more cups daily), people who never consumed coffee (beta, 0.06; standard error [SE], 0.02; P = .005) and those with moderate consumption (beta, 0.07; SE, 0.02; P = < .001) had slower decline in fluid intelligence after an average of 8.83 years of follow-up.
“We can see that those with high coffee consumption showed the steepest decline in fluid intelligence across the follow up, compared to those with moderate coffee consumption and those never consuming coffee,” said Dr. Sewell, referring to illustrative graphs.
At the same time, “our data suggest that across this time period, moderate coffee consumption can serve as some kind of protective factor against cognitive decline,” she added.
For tea, there was a somewhat different pattern. People who never drank tea had a greater decline in fluid intelligence, compared with those who had moderate consumption (beta, 0.06; SE, 0.02; P = .0090) or high consumption (beta, 0.06; SE, 0.02; P = .003).
Because this is an observational study, “we still need randomized controlled trials to better understand the neuroprotective mechanism of coffee and tea compounds,” said Dr. Sewell.
Responding later to a query from a meeting delegate about how moderate coffee drinking could be protective, Dr. Sewell said there are probably “different levels of mechanisms,” including at the molecular level (possibly involving amyloid toxicity) and the behavioral level (possibly involving sleep patterns).
Dr. Sewell said that she hopes this line of investigation will lead to new avenues of research in preventive strategies for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We hope that coffee and tea intake could contribute to the development of a safe and inexpensive strategy for delaying the onset and reducing the incidence for Alzheimer’s disease.”
A limitation of the study is possible recall bias, because coffee and tea consumption were self-reported. However, this may not be much of an issue because coffee and tea consumption “is usually quite a habitual behavior,” said Dr. Sewell.
The study also had no data on midlife coffee or tea consumption and did not compare the effect of different preparation methods or types of coffee and tea — for example, green tea versus black tea.
When asked if the study controlled for smoking, Dr. Sewell said it didn’t but added that it would be interesting to explore its impact on cognition.
Dr. Sewell reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – results from a large study suggest.
Investigators examined the impact of different amounts of coffee and tea on fluid intelligence — a measure of cognitive functions including abstract reasoning, pattern recognition, and logical thinking.
“It’s the old adage that too much of anything isn’t good. It’s all about balance, so moderate coffee consumption is okay but too much is probably not recommended,” said study investigator Kelsey R. Sewell, PhD, Advent Health Research Institute, Orlando, Florida.
The findings of the study were presented at the 2024 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC).
One of the World’s Most Widely Consumed Beverages
Coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages around the world. The beans contain a range of bioactive compounds, including caffeine, chlorogenic acid, and small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Consistent evidence from observational and epidemiologic studies indicates that intake of both coffee and tea has beneficial effects on stroke, heart failure, cancers, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease.
Several studies also suggest that coffee may reduce the risk for Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Sewell. However, there are limited longitudinal data on associations between coffee and tea intake and cognitive decline, particularly in distinct cognitive domains.
Dr. Sewell’s group previously published a study of cognitively unimpaired older adults that found greater coffee consumption was associated with slower cognitive decline and slower accumulation of brain beta-amyloid.
Their current study extends some of the prior findings and investigates the relationship between both coffee and tea intake and cognitive decline over time in a larger sample of older adults.
This new study included 8451 mostly female (60%) and White (97%) cognitively unimpaired adults older than 60 (mean age, 67.8 years) in the UK Biobank, a large-scale research resource containing in-depth, deidentified genetic and health information from half a million UK participants. Study subjects had a mean body mass index (BMI) of 26, and about 26% were apolipoprotein epsilon 4 (APOE e4) gene carriers.
Researchers divided coffee and tea consumption into tertiles: high, moderate, and no consumption.
For daily coffee consumption, 18% reported drinking four or more cups (high consumption), 58% reported drinking one to three cups (moderate consumption), and 25% reported that they never drink coffee. For daily tea consumption, 47% reported drinking four or more cups (high consumption), 38% reported drinking one to three cups (moderate consumption), and 15% reported that they never drink tea.
The study assessed cognitive function at baseline and at least two additional patient visits.
Researchers used linear mixed models to assess the relationships between coffee and tea intake and cognitive outcomes. The models adjusted for age, sex, Townsend deprivation index (reflecting socioeconomic status), ethnicity, APOE e4 status, and BMI.
Steeper Decline
Compared with high coffee consumption (four or more cups daily), people who never consumed coffee (beta, 0.06; standard error [SE], 0.02; P = .005) and those with moderate consumption (beta, 0.07; SE, 0.02; P = < .001) had slower decline in fluid intelligence after an average of 8.83 years of follow-up.
“We can see that those with high coffee consumption showed the steepest decline in fluid intelligence across the follow up, compared to those with moderate coffee consumption and those never consuming coffee,” said Dr. Sewell, referring to illustrative graphs.
At the same time, “our data suggest that across this time period, moderate coffee consumption can serve as some kind of protective factor against cognitive decline,” she added.
For tea, there was a somewhat different pattern. People who never drank tea had a greater decline in fluid intelligence, compared with those who had moderate consumption (beta, 0.06; SE, 0.02; P = .0090) or high consumption (beta, 0.06; SE, 0.02; P = .003).
Because this is an observational study, “we still need randomized controlled trials to better understand the neuroprotective mechanism of coffee and tea compounds,” said Dr. Sewell.
Responding later to a query from a meeting delegate about how moderate coffee drinking could be protective, Dr. Sewell said there are probably “different levels of mechanisms,” including at the molecular level (possibly involving amyloid toxicity) and the behavioral level (possibly involving sleep patterns).
Dr. Sewell said that she hopes this line of investigation will lead to new avenues of research in preventive strategies for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We hope that coffee and tea intake could contribute to the development of a safe and inexpensive strategy for delaying the onset and reducing the incidence for Alzheimer’s disease.”
A limitation of the study is possible recall bias, because coffee and tea consumption were self-reported. However, this may not be much of an issue because coffee and tea consumption “is usually quite a habitual behavior,” said Dr. Sewell.
The study also had no data on midlife coffee or tea consumption and did not compare the effect of different preparation methods or types of coffee and tea — for example, green tea versus black tea.
When asked if the study controlled for smoking, Dr. Sewell said it didn’t but added that it would be interesting to explore its impact on cognition.
Dr. Sewell reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – results from a large study suggest.
Investigators examined the impact of different amounts of coffee and tea on fluid intelligence — a measure of cognitive functions including abstract reasoning, pattern recognition, and logical thinking.
“It’s the old adage that too much of anything isn’t good. It’s all about balance, so moderate coffee consumption is okay but too much is probably not recommended,” said study investigator Kelsey R. Sewell, PhD, Advent Health Research Institute, Orlando, Florida.
The findings of the study were presented at the 2024 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference (AAIC).
One of the World’s Most Widely Consumed Beverages
Coffee is one of the most widely consumed beverages around the world. The beans contain a range of bioactive compounds, including caffeine, chlorogenic acid, and small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Consistent evidence from observational and epidemiologic studies indicates that intake of both coffee and tea has beneficial effects on stroke, heart failure, cancers, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease.
Several studies also suggest that coffee may reduce the risk for Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Sewell. However, there are limited longitudinal data on associations between coffee and tea intake and cognitive decline, particularly in distinct cognitive domains.
Dr. Sewell’s group previously published a study of cognitively unimpaired older adults that found greater coffee consumption was associated with slower cognitive decline and slower accumulation of brain beta-amyloid.
Their current study extends some of the prior findings and investigates the relationship between both coffee and tea intake and cognitive decline over time in a larger sample of older adults.
This new study included 8451 mostly female (60%) and White (97%) cognitively unimpaired adults older than 60 (mean age, 67.8 years) in the UK Biobank, a large-scale research resource containing in-depth, deidentified genetic and health information from half a million UK participants. Study subjects had a mean body mass index (BMI) of 26, and about 26% were apolipoprotein epsilon 4 (APOE e4) gene carriers.
Researchers divided coffee and tea consumption into tertiles: high, moderate, and no consumption.
For daily coffee consumption, 18% reported drinking four or more cups (high consumption), 58% reported drinking one to three cups (moderate consumption), and 25% reported that they never drink coffee. For daily tea consumption, 47% reported drinking four or more cups (high consumption), 38% reported drinking one to three cups (moderate consumption), and 15% reported that they never drink tea.
The study assessed cognitive function at baseline and at least two additional patient visits.
Researchers used linear mixed models to assess the relationships between coffee and tea intake and cognitive outcomes. The models adjusted for age, sex, Townsend deprivation index (reflecting socioeconomic status), ethnicity, APOE e4 status, and BMI.
Steeper Decline
Compared with high coffee consumption (four or more cups daily), people who never consumed coffee (beta, 0.06; standard error [SE], 0.02; P = .005) and those with moderate consumption (beta, 0.07; SE, 0.02; P = < .001) had slower decline in fluid intelligence after an average of 8.83 years of follow-up.
“We can see that those with high coffee consumption showed the steepest decline in fluid intelligence across the follow up, compared to those with moderate coffee consumption and those never consuming coffee,” said Dr. Sewell, referring to illustrative graphs.
At the same time, “our data suggest that across this time period, moderate coffee consumption can serve as some kind of protective factor against cognitive decline,” she added.
For tea, there was a somewhat different pattern. People who never drank tea had a greater decline in fluid intelligence, compared with those who had moderate consumption (beta, 0.06; SE, 0.02; P = .0090) or high consumption (beta, 0.06; SE, 0.02; P = .003).
Because this is an observational study, “we still need randomized controlled trials to better understand the neuroprotective mechanism of coffee and tea compounds,” said Dr. Sewell.
Responding later to a query from a meeting delegate about how moderate coffee drinking could be protective, Dr. Sewell said there are probably “different levels of mechanisms,” including at the molecular level (possibly involving amyloid toxicity) and the behavioral level (possibly involving sleep patterns).
Dr. Sewell said that she hopes this line of investigation will lead to new avenues of research in preventive strategies for Alzheimer’s disease.
“We hope that coffee and tea intake could contribute to the development of a safe and inexpensive strategy for delaying the onset and reducing the incidence for Alzheimer’s disease.”
A limitation of the study is possible recall bias, because coffee and tea consumption were self-reported. However, this may not be much of an issue because coffee and tea consumption “is usually quite a habitual behavior,” said Dr. Sewell.
The study also had no data on midlife coffee or tea consumption and did not compare the effect of different preparation methods or types of coffee and tea — for example, green tea versus black tea.
When asked if the study controlled for smoking, Dr. Sewell said it didn’t but added that it would be interesting to explore its impact on cognition.
Dr. Sewell reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2024

