User login
Katie Lennon is editor of MDedge's Family Practice News and Internal Medicine News. She has also served as editor of CHEST Physician; a staff writer for Financial Times publications; and a reporter for the Princeton Packet, Ocean County Observer, and South Bend Tribune. She is a graduate of the University of Notre Dame, South Bend, Ind. Follow her on Twitter @KatieWLennon.
Hair straighteners’ risk too small for docs to advise against their use
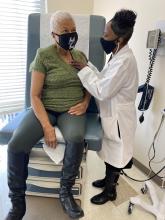
Clarissa Ghazi gets lye relaxers, which contain the chemical sodium hydroxide, applied to her hair two to three times a year.
A recent study that made headlines over a potential link between hair straighteners and uterine cancer is not going to make her stop.
“This study is not enough to cause me to say I’ll stay away from this because [the researchers] don’t prove that using relaxers causes cancer,” Ms. Ghazi said.
Indeed, primary care doctors are unlikely to address the increased risk of uterine cancer in women who frequently use hair straighteners that the study reported.
In the recently published paper on this research, the authors said that they found an 80% higher adjusted risk of uterine cancer among women who had ever “straightened,” “relaxed,” or used “hair pressing products” in the 12 months before enrolling in their study.
This finding is “real, but small,” says internist Douglas S. Paauw, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Dr. Paauw is among several primary care doctors interviewed for this story who expressed little concern about the implications of this research for their patients.
“Since we have hundreds of things we are supposed to discuss at our 20-minute clinic visits, this would not make the cut,” Dr. Paauw said.
While it’s good to be able to answer questions a patient might ask about this new research, the study does not prove anything, he said.
Alan Nelson, MD, an internist-endocrinologist and former special adviser to the CEO of the American College of Physicians, said while the study is well done, the number of actual cases of uterine cancer found was small.
One of the reasons he would not recommend discussing the study with patients is that the brands of hair products used to straighten hair in the study were not identified.
Alexandra White, PhD, lead author of the study, said participants were simply asked, “In the past 12 months, how frequently have you or someone else straightened or relaxed your hair, or used hair pressing products?”
The terms “straightened,” “relaxed,” and “hair pressing products” were not defined, and “some women may have interpreted the term ‘pressing products’ to mean nonchemical products” such as flat irons, Dr. White, head of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences’ Environment and Cancer Epidemiology group, said in an email.
Dermatologist Crystal Aguh, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, tweeted the following advice in light of the new findings: “The overall risk of uterine cancer is quite low so it’s important to remember that. For now, if you want to change your routine, there’s no downside to decreasing your frequency of hair straightening to every 12 weeks or more, as that may lessen your risk.”
She also noted that “styles like relaxer, silk pressing, and keratin treatments should only be done by a professional, as this will decrease the likelihood of hair damage and scalp irritation.
“I also encourage women to look for hair products free of parabens and phthalates (which are generically listed as “fragrance”) on products to minimize exposure to hormone disrupting chemicals.”
Not ready to go curly
Ms. Ghazi said she decided to stop using keratin straighteners years ago after she learned they are made with several added ingredients. That includes the chemical formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, according to the American Cancer Society.
“People have been relaxing their hair for a very long time, and I feel more comfortable using [a relaxer] to straighten my hair than any of the others out there,” Ms. Ghazi said.
Janaki Ram, who has had her hair chemically straightened several times, said the findings have not made her worried that straightening will cause her to get uterine cancer specifically, but that they are a reminder that the chemicals in these products could harm her in some other way.
She said the new study findings, her knowledge of the damage straightening causes to hair, and the lengthy amount of time receiving a keratin treatment takes will lead her to reduce the frequency with which she gets her hair straightened.
“Going forward, I will have this done once a year instead of twice a year,” she said.
Dr. White, the author of the paper, said in an interview that the takeaway for consumers is that women who reported frequent use of hair straighteners/relaxers and pressing products were more than twice as likely to go on to develop uterine cancer compared to women who reported no use of these products in the previous year.
“However, uterine cancer is relatively rare, so these increases in risks are small,” she said. “Less frequent use of these products was not as strongly associated with risk, suggesting that decreasing use may be an option to reduce harmful exposure. Black women were the most frequent users of these products and therefore these findings are more relevant for Black women.”
In a statement, Dr. White noted, “We estimated that 1.64% of women who never used hair straighteners would go on to develop uterine cancer by the age of 70; but for frequent users, that risk goes up to 4.05%.”
The findings were based on the Sister Study, which enrolled women living in the United States, including Puerto Rico, between 2003 and 2009. Participants needed to have at least one sister who had been diagnosed with breast cancer, been breast cancer-free themselves, and aged 35-74 years. Women who reported a diagnosis of uterine cancer before enrollment, had an uncertain uterine cancer history, or had a hysterectomy were excluded from the study.
The researchers examined hair product usage and uterine cancer incidence during an 11-year period among 33 ,947 women. The analysis controlled for variables such as age, race, and risk factors. At baseline, participants were asked to complete a questionnaire on hair products use in the previous 12 months.
“One of the original aims of the study was to better understand the environmental and genetic causes of breast cancer, but we are also interested in studying ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, and many other cancers and chronic diseases,” Dr. White said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Clarissa Ghazi gets lye relaxers, which contain the chemical sodium hydroxide, applied to her hair two to three times a year.
A recent study that made headlines over a potential link between hair straighteners and uterine cancer is not going to make her stop.
“This study is not enough to cause me to say I’ll stay away from this because [the researchers] don’t prove that using relaxers causes cancer,” Ms. Ghazi said.
Indeed, primary care doctors are unlikely to address the increased risk of uterine cancer in women who frequently use hair straighteners that the study reported.
In the recently published paper on this research, the authors said that they found an 80% higher adjusted risk of uterine cancer among women who had ever “straightened,” “relaxed,” or used “hair pressing products” in the 12 months before enrolling in their study.
This finding is “real, but small,” says internist Douglas S. Paauw, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Dr. Paauw is among several primary care doctors interviewed for this story who expressed little concern about the implications of this research for their patients.
“Since we have hundreds of things we are supposed to discuss at our 20-minute clinic visits, this would not make the cut,” Dr. Paauw said.
While it’s good to be able to answer questions a patient might ask about this new research, the study does not prove anything, he said.
Alan Nelson, MD, an internist-endocrinologist and former special adviser to the CEO of the American College of Physicians, said while the study is well done, the number of actual cases of uterine cancer found was small.
One of the reasons he would not recommend discussing the study with patients is that the brands of hair products used to straighten hair in the study were not identified.
Alexandra White, PhD, lead author of the study, said participants were simply asked, “In the past 12 months, how frequently have you or someone else straightened or relaxed your hair, or used hair pressing products?”
The terms “straightened,” “relaxed,” and “hair pressing products” were not defined, and “some women may have interpreted the term ‘pressing products’ to mean nonchemical products” such as flat irons, Dr. White, head of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences’ Environment and Cancer Epidemiology group, said in an email.
Dermatologist Crystal Aguh, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, tweeted the following advice in light of the new findings: “The overall risk of uterine cancer is quite low so it’s important to remember that. For now, if you want to change your routine, there’s no downside to decreasing your frequency of hair straightening to every 12 weeks or more, as that may lessen your risk.”
She also noted that “styles like relaxer, silk pressing, and keratin treatments should only be done by a professional, as this will decrease the likelihood of hair damage and scalp irritation.
“I also encourage women to look for hair products free of parabens and phthalates (which are generically listed as “fragrance”) on products to minimize exposure to hormone disrupting chemicals.”
Not ready to go curly
Ms. Ghazi said she decided to stop using keratin straighteners years ago after she learned they are made with several added ingredients. That includes the chemical formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, according to the American Cancer Society.
“People have been relaxing their hair for a very long time, and I feel more comfortable using [a relaxer] to straighten my hair than any of the others out there,” Ms. Ghazi said.
Janaki Ram, who has had her hair chemically straightened several times, said the findings have not made her worried that straightening will cause her to get uterine cancer specifically, but that they are a reminder that the chemicals in these products could harm her in some other way.
She said the new study findings, her knowledge of the damage straightening causes to hair, and the lengthy amount of time receiving a keratin treatment takes will lead her to reduce the frequency with which she gets her hair straightened.
“Going forward, I will have this done once a year instead of twice a year,” she said.
Dr. White, the author of the paper, said in an interview that the takeaway for consumers is that women who reported frequent use of hair straighteners/relaxers and pressing products were more than twice as likely to go on to develop uterine cancer compared to women who reported no use of these products in the previous year.
“However, uterine cancer is relatively rare, so these increases in risks are small,” she said. “Less frequent use of these products was not as strongly associated with risk, suggesting that decreasing use may be an option to reduce harmful exposure. Black women were the most frequent users of these products and therefore these findings are more relevant for Black women.”
In a statement, Dr. White noted, “We estimated that 1.64% of women who never used hair straighteners would go on to develop uterine cancer by the age of 70; but for frequent users, that risk goes up to 4.05%.”
The findings were based on the Sister Study, which enrolled women living in the United States, including Puerto Rico, between 2003 and 2009. Participants needed to have at least one sister who had been diagnosed with breast cancer, been breast cancer-free themselves, and aged 35-74 years. Women who reported a diagnosis of uterine cancer before enrollment, had an uncertain uterine cancer history, or had a hysterectomy were excluded from the study.
The researchers examined hair product usage and uterine cancer incidence during an 11-year period among 33 ,947 women. The analysis controlled for variables such as age, race, and risk factors. At baseline, participants were asked to complete a questionnaire on hair products use in the previous 12 months.
“One of the original aims of the study was to better understand the environmental and genetic causes of breast cancer, but we are also interested in studying ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, and many other cancers and chronic diseases,” Dr. White said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Clarissa Ghazi gets lye relaxers, which contain the chemical sodium hydroxide, applied to her hair two to three times a year.
A recent study that made headlines over a potential link between hair straighteners and uterine cancer is not going to make her stop.
“This study is not enough to cause me to say I’ll stay away from this because [the researchers] don’t prove that using relaxers causes cancer,” Ms. Ghazi said.
Indeed, primary care doctors are unlikely to address the increased risk of uterine cancer in women who frequently use hair straighteners that the study reported.
In the recently published paper on this research, the authors said that they found an 80% higher adjusted risk of uterine cancer among women who had ever “straightened,” “relaxed,” or used “hair pressing products” in the 12 months before enrolling in their study.
This finding is “real, but small,” says internist Douglas S. Paauw, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Washington in Seattle.
Dr. Paauw is among several primary care doctors interviewed for this story who expressed little concern about the implications of this research for their patients.
“Since we have hundreds of things we are supposed to discuss at our 20-minute clinic visits, this would not make the cut,” Dr. Paauw said.
While it’s good to be able to answer questions a patient might ask about this new research, the study does not prove anything, he said.
Alan Nelson, MD, an internist-endocrinologist and former special adviser to the CEO of the American College of Physicians, said while the study is well done, the number of actual cases of uterine cancer found was small.
One of the reasons he would not recommend discussing the study with patients is that the brands of hair products used to straighten hair in the study were not identified.
Alexandra White, PhD, lead author of the study, said participants were simply asked, “In the past 12 months, how frequently have you or someone else straightened or relaxed your hair, or used hair pressing products?”
The terms “straightened,” “relaxed,” and “hair pressing products” were not defined, and “some women may have interpreted the term ‘pressing products’ to mean nonchemical products” such as flat irons, Dr. White, head of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences’ Environment and Cancer Epidemiology group, said in an email.
Dermatologist Crystal Aguh, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, tweeted the following advice in light of the new findings: “The overall risk of uterine cancer is quite low so it’s important to remember that. For now, if you want to change your routine, there’s no downside to decreasing your frequency of hair straightening to every 12 weeks or more, as that may lessen your risk.”
She also noted that “styles like relaxer, silk pressing, and keratin treatments should only be done by a professional, as this will decrease the likelihood of hair damage and scalp irritation.
“I also encourage women to look for hair products free of parabens and phthalates (which are generically listed as “fragrance”) on products to minimize exposure to hormone disrupting chemicals.”
Not ready to go curly
Ms. Ghazi said she decided to stop using keratin straighteners years ago after she learned they are made with several added ingredients. That includes the chemical formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, according to the American Cancer Society.
“People have been relaxing their hair for a very long time, and I feel more comfortable using [a relaxer] to straighten my hair than any of the others out there,” Ms. Ghazi said.
Janaki Ram, who has had her hair chemically straightened several times, said the findings have not made her worried that straightening will cause her to get uterine cancer specifically, but that they are a reminder that the chemicals in these products could harm her in some other way.
She said the new study findings, her knowledge of the damage straightening causes to hair, and the lengthy amount of time receiving a keratin treatment takes will lead her to reduce the frequency with which she gets her hair straightened.
“Going forward, I will have this done once a year instead of twice a year,” she said.
Dr. White, the author of the paper, said in an interview that the takeaway for consumers is that women who reported frequent use of hair straighteners/relaxers and pressing products were more than twice as likely to go on to develop uterine cancer compared to women who reported no use of these products in the previous year.
“However, uterine cancer is relatively rare, so these increases in risks are small,” she said. “Less frequent use of these products was not as strongly associated with risk, suggesting that decreasing use may be an option to reduce harmful exposure. Black women were the most frequent users of these products and therefore these findings are more relevant for Black women.”
In a statement, Dr. White noted, “We estimated that 1.64% of women who never used hair straighteners would go on to develop uterine cancer by the age of 70; but for frequent users, that risk goes up to 4.05%.”
The findings were based on the Sister Study, which enrolled women living in the United States, including Puerto Rico, between 2003 and 2009. Participants needed to have at least one sister who had been diagnosed with breast cancer, been breast cancer-free themselves, and aged 35-74 years. Women who reported a diagnosis of uterine cancer before enrollment, had an uncertain uterine cancer history, or had a hysterectomy were excluded from the study.
The researchers examined hair product usage and uterine cancer incidence during an 11-year period among 33 ,947 women. The analysis controlled for variables such as age, race, and risk factors. At baseline, participants were asked to complete a questionnaire on hair products use in the previous 12 months.
“One of the original aims of the study was to better understand the environmental and genetic causes of breast cancer, but we are also interested in studying ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, and many other cancers and chronic diseases,” Dr. White said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Dr. Faith Fitzgerald was dedicated to her patients, students, and friends
Dr. Fitzgerald adopted this means of transportation to allow her to examine and talk to her patients, following a hip injury and surgery, which left her unable to do the amount of walking typically required to conduct rounds at a hospital.
Her colleague, Mark C. Henderson, MD, MACP, described Dr. Fitzgerald as being “extremely dedicated to each patient,” having taken care of many of them for decades. Her will to find a way to practice with severe physical limitations exemplified this dedication, said Dr. Henderson, who worked in the hospital alongside her, including handing over patients to her.
Dr. Fitzgerald died on Dec. 3, 2021, at 78 years, after working in a career spanning 6 decades, including actively practicing internal medicine at UC Davis Medical Center for 40 years.
Her career also included working as a medical educator, influencing several people interviewed for this story in that role, and advising the staff of Internal Medicine News for more than 3 decades.
“Faith Fitzgerald was an incredible teacher and mentor for so many people,” noted Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, who practices general internal medicine and med-peds at the University of Arkansans for Medical Sciences, Little Rock and is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
‘The patient and the next generation’ were always in mind
A contributor to Dr. Fitzgerald’s success as an educator was her dogged commitment to her patients, said Dr. Henderson, who is associate dean for admissions at the University of California, Davis, and professor and vice chair for education in the department of internal medicine. The latter of these positions was previously held by Dr. Fitzgerald.
“She always arrived early for hospital rounds, often waking up her patients,” he said. “She evolved this practice to be present before all the chaos of the day ensued and honestly to spend quality of time with patients.”
“She always had two things in mind: the patient and the next generation,” Dr. Henderson continued. “A lot of times, because she had seen the patients earlier in the morning, she knew where to focus the team she was training” and “she could show her students and residents all of these interesting findings.”
“It was a very efficient way of conducting bedside teaching,” he added.
Dr. Fitzgerald taught primarily in the department of internal medicine at UC Davis Health. She joined the faculty of that school in 1980. Her 38-year-long career there included serving as residency program director for nearly 20 years, chief of general medicine, vice chair for education, and the medical school’s first associate dean for humanities and bioethics.
Several people who knew Dr. Fitzgerald well also attributed her effectiveness as a teacher and a doctor to the kindness she showed all people no matter their background or station in life.
“Every patient she saw in clinic, she booked for an hour ‘til the day she left UC Davis,” noted Carmelina Raffetto, Dr. Fitzgerald’s closest friend and former administrative assistant, during UC Davis Health’s virtual memorial ceremony for Dr. Fitzgerald.
“Her patients all had her phone number, her pager. ... She loved teaching, she loved her patients, and she loved staff.
“She treated all of us equally. Whether you were in housekeeping or in the cafeteria, or if you were just walking down the hall, she had kind words and she never wanted anyone to feel that they weren’t’ special,” added Ms. Raffetto, who is currently executive director of the Northern California American College of Physicians chapter.
Throughout her career, she received over three dozen teaching awards, according to a statement from UC Davis. In 2002, for example, Dr. Fitzgerald received the Alpha Omega Alpha medical honor society’s Robert J. Glaser Award for providing medical students with an outstanding educational experience. Additional teaching awards included the American College of Physicians Distinguished Teacher Award, the California Medical Association Golden Apple Award and the UC San Francisco Gold Headed Cane.
She also received awards from UC Davis, including the Hibbard Williams Lifetime Achievement award, the Tupper Award for Excellence in Teaching and the UC Davis School of Medicine Golden Apple Award. She was also chosen as the UC Davis Senior Class Outstanding Clinical Teacher seven times and was named the Department of Medicine Distinguished Faculty Teacher on four separate occasions, the statement said.
Her early life and family
Dr. Fitzgerald was born in Boston on Sept. 24, 1943, and “knew from early childhood that she would be a physician,” according to her biography on Changing the Face of Medicine.
She completed undergraduate studies at the University of California, Santa Barbara. She graduated from the University of California, San Francisco, in 1969 and completed her residency in internal medicine at the same institution. In addition to teaching at UC Davis, Dr. Fitzgerald served as assistant professor of medicine at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, for 2 years early in her career.
Dr. Fitzgerald is survived by her brother, Sean, and sister-in-law, Deborah Fitzgerald. Dr. Fitzgerald lived with and cared for her mother, Irene Fitzgerald – who passed away in 2005 – for more than a decade.
Dr. Fitzgerald asked for any donations in her memory to be used to establish scholarships for medical students with financial need, as she had been supported by scholarship money long ago while a student at the University of California. Donations to the Faith Fitzgerald, MD, Medical Student Scholarship Fund can be made here.
Dr. Fitzgerald adopted this means of transportation to allow her to examine and talk to her patients, following a hip injury and surgery, which left her unable to do the amount of walking typically required to conduct rounds at a hospital.
Her colleague, Mark C. Henderson, MD, MACP, described Dr. Fitzgerald as being “extremely dedicated to each patient,” having taken care of many of them for decades. Her will to find a way to practice with severe physical limitations exemplified this dedication, said Dr. Henderson, who worked in the hospital alongside her, including handing over patients to her.
Dr. Fitzgerald died on Dec. 3, 2021, at 78 years, after working in a career spanning 6 decades, including actively practicing internal medicine at UC Davis Medical Center for 40 years.
Her career also included working as a medical educator, influencing several people interviewed for this story in that role, and advising the staff of Internal Medicine News for more than 3 decades.
“Faith Fitzgerald was an incredible teacher and mentor for so many people,” noted Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, who practices general internal medicine and med-peds at the University of Arkansans for Medical Sciences, Little Rock and is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
‘The patient and the next generation’ were always in mind
A contributor to Dr. Fitzgerald’s success as an educator was her dogged commitment to her patients, said Dr. Henderson, who is associate dean for admissions at the University of California, Davis, and professor and vice chair for education in the department of internal medicine. The latter of these positions was previously held by Dr. Fitzgerald.
“She always arrived early for hospital rounds, often waking up her patients,” he said. “She evolved this practice to be present before all the chaos of the day ensued and honestly to spend quality of time with patients.”
“She always had two things in mind: the patient and the next generation,” Dr. Henderson continued. “A lot of times, because she had seen the patients earlier in the morning, she knew where to focus the team she was training” and “she could show her students and residents all of these interesting findings.”
“It was a very efficient way of conducting bedside teaching,” he added.
Dr. Fitzgerald taught primarily in the department of internal medicine at UC Davis Health. She joined the faculty of that school in 1980. Her 38-year-long career there included serving as residency program director for nearly 20 years, chief of general medicine, vice chair for education, and the medical school’s first associate dean for humanities and bioethics.
Several people who knew Dr. Fitzgerald well also attributed her effectiveness as a teacher and a doctor to the kindness she showed all people no matter their background or station in life.
“Every patient she saw in clinic, she booked for an hour ‘til the day she left UC Davis,” noted Carmelina Raffetto, Dr. Fitzgerald’s closest friend and former administrative assistant, during UC Davis Health’s virtual memorial ceremony for Dr. Fitzgerald.
“Her patients all had her phone number, her pager. ... She loved teaching, she loved her patients, and she loved staff.
“She treated all of us equally. Whether you were in housekeeping or in the cafeteria, or if you were just walking down the hall, she had kind words and she never wanted anyone to feel that they weren’t’ special,” added Ms. Raffetto, who is currently executive director of the Northern California American College of Physicians chapter.
Throughout her career, she received over three dozen teaching awards, according to a statement from UC Davis. In 2002, for example, Dr. Fitzgerald received the Alpha Omega Alpha medical honor society’s Robert J. Glaser Award for providing medical students with an outstanding educational experience. Additional teaching awards included the American College of Physicians Distinguished Teacher Award, the California Medical Association Golden Apple Award and the UC San Francisco Gold Headed Cane.
She also received awards from UC Davis, including the Hibbard Williams Lifetime Achievement award, the Tupper Award for Excellence in Teaching and the UC Davis School of Medicine Golden Apple Award. She was also chosen as the UC Davis Senior Class Outstanding Clinical Teacher seven times and was named the Department of Medicine Distinguished Faculty Teacher on four separate occasions, the statement said.
Her early life and family
Dr. Fitzgerald was born in Boston on Sept. 24, 1943, and “knew from early childhood that she would be a physician,” according to her biography on Changing the Face of Medicine.
She completed undergraduate studies at the University of California, Santa Barbara. She graduated from the University of California, San Francisco, in 1969 and completed her residency in internal medicine at the same institution. In addition to teaching at UC Davis, Dr. Fitzgerald served as assistant professor of medicine at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, for 2 years early in her career.
Dr. Fitzgerald is survived by her brother, Sean, and sister-in-law, Deborah Fitzgerald. Dr. Fitzgerald lived with and cared for her mother, Irene Fitzgerald – who passed away in 2005 – for more than a decade.
Dr. Fitzgerald asked for any donations in her memory to be used to establish scholarships for medical students with financial need, as she had been supported by scholarship money long ago while a student at the University of California. Donations to the Faith Fitzgerald, MD, Medical Student Scholarship Fund can be made here.
Dr. Fitzgerald adopted this means of transportation to allow her to examine and talk to her patients, following a hip injury and surgery, which left her unable to do the amount of walking typically required to conduct rounds at a hospital.
Her colleague, Mark C. Henderson, MD, MACP, described Dr. Fitzgerald as being “extremely dedicated to each patient,” having taken care of many of them for decades. Her will to find a way to practice with severe physical limitations exemplified this dedication, said Dr. Henderson, who worked in the hospital alongside her, including handing over patients to her.
Dr. Fitzgerald died on Dec. 3, 2021, at 78 years, after working in a career spanning 6 decades, including actively practicing internal medicine at UC Davis Medical Center for 40 years.
Her career also included working as a medical educator, influencing several people interviewed for this story in that role, and advising the staff of Internal Medicine News for more than 3 decades.
“Faith Fitzgerald was an incredible teacher and mentor for so many people,” noted Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, who practices general internal medicine and med-peds at the University of Arkansans for Medical Sciences, Little Rock and is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
‘The patient and the next generation’ were always in mind
A contributor to Dr. Fitzgerald’s success as an educator was her dogged commitment to her patients, said Dr. Henderson, who is associate dean for admissions at the University of California, Davis, and professor and vice chair for education in the department of internal medicine. The latter of these positions was previously held by Dr. Fitzgerald.
“She always arrived early for hospital rounds, often waking up her patients,” he said. “She evolved this practice to be present before all the chaos of the day ensued and honestly to spend quality of time with patients.”
“She always had two things in mind: the patient and the next generation,” Dr. Henderson continued. “A lot of times, because she had seen the patients earlier in the morning, she knew where to focus the team she was training” and “she could show her students and residents all of these interesting findings.”
“It was a very efficient way of conducting bedside teaching,” he added.
Dr. Fitzgerald taught primarily in the department of internal medicine at UC Davis Health. She joined the faculty of that school in 1980. Her 38-year-long career there included serving as residency program director for nearly 20 years, chief of general medicine, vice chair for education, and the medical school’s first associate dean for humanities and bioethics.
Several people who knew Dr. Fitzgerald well also attributed her effectiveness as a teacher and a doctor to the kindness she showed all people no matter their background or station in life.
“Every patient she saw in clinic, she booked for an hour ‘til the day she left UC Davis,” noted Carmelina Raffetto, Dr. Fitzgerald’s closest friend and former administrative assistant, during UC Davis Health’s virtual memorial ceremony for Dr. Fitzgerald.
“Her patients all had her phone number, her pager. ... She loved teaching, she loved her patients, and she loved staff.
“She treated all of us equally. Whether you were in housekeeping or in the cafeteria, or if you were just walking down the hall, she had kind words and she never wanted anyone to feel that they weren’t’ special,” added Ms. Raffetto, who is currently executive director of the Northern California American College of Physicians chapter.
Throughout her career, she received over three dozen teaching awards, according to a statement from UC Davis. In 2002, for example, Dr. Fitzgerald received the Alpha Omega Alpha medical honor society’s Robert J. Glaser Award for providing medical students with an outstanding educational experience. Additional teaching awards included the American College of Physicians Distinguished Teacher Award, the California Medical Association Golden Apple Award and the UC San Francisco Gold Headed Cane.
She also received awards from UC Davis, including the Hibbard Williams Lifetime Achievement award, the Tupper Award for Excellence in Teaching and the UC Davis School of Medicine Golden Apple Award. She was also chosen as the UC Davis Senior Class Outstanding Clinical Teacher seven times and was named the Department of Medicine Distinguished Faculty Teacher on four separate occasions, the statement said.
Her early life and family
Dr. Fitzgerald was born in Boston on Sept. 24, 1943, and “knew from early childhood that she would be a physician,” according to her biography on Changing the Face of Medicine.
She completed undergraduate studies at the University of California, Santa Barbara. She graduated from the University of California, San Francisco, in 1969 and completed her residency in internal medicine at the same institution. In addition to teaching at UC Davis, Dr. Fitzgerald served as assistant professor of medicine at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, for 2 years early in her career.
Dr. Fitzgerald is survived by her brother, Sean, and sister-in-law, Deborah Fitzgerald. Dr. Fitzgerald lived with and cared for her mother, Irene Fitzgerald – who passed away in 2005 – for more than a decade.
Dr. Fitzgerald asked for any donations in her memory to be used to establish scholarships for medical students with financial need, as she had been supported by scholarship money long ago while a student at the University of California. Donations to the Faith Fitzgerald, MD, Medical Student Scholarship Fund can be made here.
Honoring Dr. Paul Farmer: Dr. Serena Koenig shares her memories of working with him
Infectious disease specialist and humanitarian, Paul Edward Farmer, MD, PhD, who cofounded Partners In Health, died suddenly on Feb. 21. To celebrate his life, this news organization interviewed Serena Koenig, MD, MPH, who met Dr. Farmer when she was an internal medicine resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Koenig had worked closely with Dr. Farmer ever since they met.
Q. Can you please share one of your best memories of Dr. Farmer?
Dr. Serena Koenig: Paul and some other incredible colleagues at Partners IN Health (PIH) had started the HIV Equity Initiative, which was one of the first programs in the world to provide free, comprehensive treatment for HIV. This was at the time when millions of people in Africa were dying of HIV and many experts said it was not feasible to treat HIV in a poor country, because it was too complicated and expensive. Paul took me on some home visits with patients who had what he called the Lazarus effect, coming back from death’s door from advanced AIDS to vigorous health on antiretroviral therapy. I had just started working in Haiti with Paul and PIH, and I felt the enormous magnitude of what he was doing.
Q. What aspects of him and his work do you find most admirable?
Dr. Koenig: I most admired Paul’s humanity, his belief that every person matters and has the right to high-quality health care, and his vision of global health equity.
He said: “The idea that some lives matter less is the root of all that is wrong with the world.” Paul lived this philosophy. He has spoken extensively about harms of socialization for scarcity on behalf of those who are poor, leading policy makers to decisions regarding the feasibility of treating some diseases, but not others.
He said in an interview with the Harvard Gazette in 2018: “The most compelling thing to fight socialization for scarcity on behalf of others is health system strengthening. Health systems that integrate prevention and quality care.”
A few weeks ago, I asked him his thoughts about the high-level resources we have invested in some patients who have needed specialty care over the years, and he said: “No way that we should waste all of our emotional energy responding only to those constant, nagging critics that it’s not cost effective, not feasible, not sustainable, not even prudent. Because you know what they would have done if it was their child or family member.”
Q. When did you first meet Dr. Farmer, and what inspired you to work with him?
Dr. Koenig: When I was an internal medicine resident at the Brigham, Paul and I bonded over the care of one of my clinic patients who I followed very closely, and who was admitted to his inpatient service.
Like everyone else who has worked with Paul, I was touched by his kindness and warmth.
A couple of years later, he asked me to help him raise money to bring a young man named Wilnot from Haiti to the Brigham for an aortic valve replacement. After we raised the money, he asked me to go to Haiti to help Wilnot get his medical visa and to escort him to Boston.
That short trip to Haiti had an enormous impact on my life. I was shattered to see the poverty that the people of Haiti were enduring – and in a country a short plane flight from Miami.
Shortly after this, Paul asked me to help him find treatment for another patient, a young boy named John, who presented with neck masses that were later diagnosed as nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
It took us some time to make the diagnosis and then to arrange free care at Mass General.
When I returned to Haiti with two PIH colleagues to help John get a visa and escort him back to Boston, we found that John’s condition was much worse. We ended up medically evacuating him to Boston, because he was too sick for a commercial flight.
Tracy Kidder wrote about this heartbreaking experience in the book “Mountains Beyond Mountains.”
Throughout all of these experiences, I was deeply impressed with Paul’s commitment to do whatever it took to provide the best care for patients, as if they were members of his own family. He said “Tout Moun Se Moun” (Haitian Creole for “every person is a person”), and I could tell that he meant it.
Q. How did you collaborate with him professionally?
Dr. Koenig: I spent the first few years after residency working with Paul and Partners In Health. Initially, I served as a liaison between PIH in Haiti and the Brigham, bringing several more patients to Boston for care, and arranging specialty surgical trips to Haiti.
Later, when HIV funding became available from the Global Fund for HIV, Tuberculosis, and Malaria, I moved to rural Haiti to provide treatment for patients with HIV and/or TB at one of the first PIH expansion sites. We treated many patients with advanced stages of HIV and/or TB, and many of them recovered remarkably quickly with antiretroviral therapy.
When I returned to Boston to complete an infectious disease fellowship I switched my focus to conducting clinical research to improve HIV and TB treatment outcomes. Paul emailed his mentor and friend, Jean “Bill” Pape, the director of a Haitian NGO called GHESKIO (Haitian Group for the Study of Kaposi’s Sarcoma and Opportunistic Infections), which is an internationally celebrated center of excellence in HIV-related research and clinical care, to ask if I could collaborate with them.
Ever since that time, I have been based between the Brigham’s division of global health equity, which was led by Paul, and GHESKIO.
Paul was very supportive of our research, which aims to improve health service delivery and treatment regimens for HIV and TB.
Q. What lessons do you think other physicians can learn from him?
Dr. Koenig: As Joia Mukherjee, chief medical officer of Partners In Health, has said, Paul left us a roadmap. He wrote many books, and he was very eloquent in expressing his philosophy about equity and justice in numerous interviews. This is relevant not only for international sites, but in the United States as well, with our major disparities in health outcomes by race, geography, and socioeconomic status.
No one will be able to replace Paul, but he left us with a vision of what is achievable.
Dr. Koenig is associate physician, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, with faculty appointments in the divisions of global health equity and infectious diseases. She is also associate professor at Harvard Medical School.
Infectious disease specialist and humanitarian, Paul Edward Farmer, MD, PhD, who cofounded Partners In Health, died suddenly on Feb. 21. To celebrate his life, this news organization interviewed Serena Koenig, MD, MPH, who met Dr. Farmer when she was an internal medicine resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Koenig had worked closely with Dr. Farmer ever since they met.
Q. Can you please share one of your best memories of Dr. Farmer?
Dr. Serena Koenig: Paul and some other incredible colleagues at Partners IN Health (PIH) had started the HIV Equity Initiative, which was one of the first programs in the world to provide free, comprehensive treatment for HIV. This was at the time when millions of people in Africa were dying of HIV and many experts said it was not feasible to treat HIV in a poor country, because it was too complicated and expensive. Paul took me on some home visits with patients who had what he called the Lazarus effect, coming back from death’s door from advanced AIDS to vigorous health on antiretroviral therapy. I had just started working in Haiti with Paul and PIH, and I felt the enormous magnitude of what he was doing.
Q. What aspects of him and his work do you find most admirable?
Dr. Koenig: I most admired Paul’s humanity, his belief that every person matters and has the right to high-quality health care, and his vision of global health equity.
He said: “The idea that some lives matter less is the root of all that is wrong with the world.” Paul lived this philosophy. He has spoken extensively about harms of socialization for scarcity on behalf of those who are poor, leading policy makers to decisions regarding the feasibility of treating some diseases, but not others.
He said in an interview with the Harvard Gazette in 2018: “The most compelling thing to fight socialization for scarcity on behalf of others is health system strengthening. Health systems that integrate prevention and quality care.”
A few weeks ago, I asked him his thoughts about the high-level resources we have invested in some patients who have needed specialty care over the years, and he said: “No way that we should waste all of our emotional energy responding only to those constant, nagging critics that it’s not cost effective, not feasible, not sustainable, not even prudent. Because you know what they would have done if it was their child or family member.”
Q. When did you first meet Dr. Farmer, and what inspired you to work with him?
Dr. Koenig: When I was an internal medicine resident at the Brigham, Paul and I bonded over the care of one of my clinic patients who I followed very closely, and who was admitted to his inpatient service.
Like everyone else who has worked with Paul, I was touched by his kindness and warmth.
A couple of years later, he asked me to help him raise money to bring a young man named Wilnot from Haiti to the Brigham for an aortic valve replacement. After we raised the money, he asked me to go to Haiti to help Wilnot get his medical visa and to escort him to Boston.
That short trip to Haiti had an enormous impact on my life. I was shattered to see the poverty that the people of Haiti were enduring – and in a country a short plane flight from Miami.
Shortly after this, Paul asked me to help him find treatment for another patient, a young boy named John, who presented with neck masses that were later diagnosed as nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
It took us some time to make the diagnosis and then to arrange free care at Mass General.
When I returned to Haiti with two PIH colleagues to help John get a visa and escort him back to Boston, we found that John’s condition was much worse. We ended up medically evacuating him to Boston, because he was too sick for a commercial flight.
Tracy Kidder wrote about this heartbreaking experience in the book “Mountains Beyond Mountains.”
Throughout all of these experiences, I was deeply impressed with Paul’s commitment to do whatever it took to provide the best care for patients, as if they were members of his own family. He said “Tout Moun Se Moun” (Haitian Creole for “every person is a person”), and I could tell that he meant it.
Q. How did you collaborate with him professionally?
Dr. Koenig: I spent the first few years after residency working with Paul and Partners In Health. Initially, I served as a liaison between PIH in Haiti and the Brigham, bringing several more patients to Boston for care, and arranging specialty surgical trips to Haiti.
Later, when HIV funding became available from the Global Fund for HIV, Tuberculosis, and Malaria, I moved to rural Haiti to provide treatment for patients with HIV and/or TB at one of the first PIH expansion sites. We treated many patients with advanced stages of HIV and/or TB, and many of them recovered remarkably quickly with antiretroviral therapy.
When I returned to Boston to complete an infectious disease fellowship I switched my focus to conducting clinical research to improve HIV and TB treatment outcomes. Paul emailed his mentor and friend, Jean “Bill” Pape, the director of a Haitian NGO called GHESKIO (Haitian Group for the Study of Kaposi’s Sarcoma and Opportunistic Infections), which is an internationally celebrated center of excellence in HIV-related research and clinical care, to ask if I could collaborate with them.
Ever since that time, I have been based between the Brigham’s division of global health equity, which was led by Paul, and GHESKIO.
Paul was very supportive of our research, which aims to improve health service delivery and treatment regimens for HIV and TB.
Q. What lessons do you think other physicians can learn from him?
Dr. Koenig: As Joia Mukherjee, chief medical officer of Partners In Health, has said, Paul left us a roadmap. He wrote many books, and he was very eloquent in expressing his philosophy about equity and justice in numerous interviews. This is relevant not only for international sites, but in the United States as well, with our major disparities in health outcomes by race, geography, and socioeconomic status.
No one will be able to replace Paul, but he left us with a vision of what is achievable.
Dr. Koenig is associate physician, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, with faculty appointments in the divisions of global health equity and infectious diseases. She is also associate professor at Harvard Medical School.
Infectious disease specialist and humanitarian, Paul Edward Farmer, MD, PhD, who cofounded Partners In Health, died suddenly on Feb. 21. To celebrate his life, this news organization interviewed Serena Koenig, MD, MPH, who met Dr. Farmer when she was an internal medicine resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Koenig had worked closely with Dr. Farmer ever since they met.
Q. Can you please share one of your best memories of Dr. Farmer?
Dr. Serena Koenig: Paul and some other incredible colleagues at Partners IN Health (PIH) had started the HIV Equity Initiative, which was one of the first programs in the world to provide free, comprehensive treatment for HIV. This was at the time when millions of people in Africa were dying of HIV and many experts said it was not feasible to treat HIV in a poor country, because it was too complicated and expensive. Paul took me on some home visits with patients who had what he called the Lazarus effect, coming back from death’s door from advanced AIDS to vigorous health on antiretroviral therapy. I had just started working in Haiti with Paul and PIH, and I felt the enormous magnitude of what he was doing.
Q. What aspects of him and his work do you find most admirable?
Dr. Koenig: I most admired Paul’s humanity, his belief that every person matters and has the right to high-quality health care, and his vision of global health equity.
He said: “The idea that some lives matter less is the root of all that is wrong with the world.” Paul lived this philosophy. He has spoken extensively about harms of socialization for scarcity on behalf of those who are poor, leading policy makers to decisions regarding the feasibility of treating some diseases, but not others.
He said in an interview with the Harvard Gazette in 2018: “The most compelling thing to fight socialization for scarcity on behalf of others is health system strengthening. Health systems that integrate prevention and quality care.”
A few weeks ago, I asked him his thoughts about the high-level resources we have invested in some patients who have needed specialty care over the years, and he said: “No way that we should waste all of our emotional energy responding only to those constant, nagging critics that it’s not cost effective, not feasible, not sustainable, not even prudent. Because you know what they would have done if it was their child or family member.”
Q. When did you first meet Dr. Farmer, and what inspired you to work with him?
Dr. Koenig: When I was an internal medicine resident at the Brigham, Paul and I bonded over the care of one of my clinic patients who I followed very closely, and who was admitted to his inpatient service.
Like everyone else who has worked with Paul, I was touched by his kindness and warmth.
A couple of years later, he asked me to help him raise money to bring a young man named Wilnot from Haiti to the Brigham for an aortic valve replacement. After we raised the money, he asked me to go to Haiti to help Wilnot get his medical visa and to escort him to Boston.
That short trip to Haiti had an enormous impact on my life. I was shattered to see the poverty that the people of Haiti were enduring – and in a country a short plane flight from Miami.
Shortly after this, Paul asked me to help him find treatment for another patient, a young boy named John, who presented with neck masses that were later diagnosed as nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
It took us some time to make the diagnosis and then to arrange free care at Mass General.
When I returned to Haiti with two PIH colleagues to help John get a visa and escort him back to Boston, we found that John’s condition was much worse. We ended up medically evacuating him to Boston, because he was too sick for a commercial flight.
Tracy Kidder wrote about this heartbreaking experience in the book “Mountains Beyond Mountains.”
Throughout all of these experiences, I was deeply impressed with Paul’s commitment to do whatever it took to provide the best care for patients, as if they were members of his own family. He said “Tout Moun Se Moun” (Haitian Creole for “every person is a person”), and I could tell that he meant it.
Q. How did you collaborate with him professionally?
Dr. Koenig: I spent the first few years after residency working with Paul and Partners In Health. Initially, I served as a liaison between PIH in Haiti and the Brigham, bringing several more patients to Boston for care, and arranging specialty surgical trips to Haiti.
Later, when HIV funding became available from the Global Fund for HIV, Tuberculosis, and Malaria, I moved to rural Haiti to provide treatment for patients with HIV and/or TB at one of the first PIH expansion sites. We treated many patients with advanced stages of HIV and/or TB, and many of them recovered remarkably quickly with antiretroviral therapy.
When I returned to Boston to complete an infectious disease fellowship I switched my focus to conducting clinical research to improve HIV and TB treatment outcomes. Paul emailed his mentor and friend, Jean “Bill” Pape, the director of a Haitian NGO called GHESKIO (Haitian Group for the Study of Kaposi’s Sarcoma and Opportunistic Infections), which is an internationally celebrated center of excellence in HIV-related research and clinical care, to ask if I could collaborate with them.
Ever since that time, I have been based between the Brigham’s division of global health equity, which was led by Paul, and GHESKIO.
Paul was very supportive of our research, which aims to improve health service delivery and treatment regimens for HIV and TB.
Q. What lessons do you think other physicians can learn from him?
Dr. Koenig: As Joia Mukherjee, chief medical officer of Partners In Health, has said, Paul left us a roadmap. He wrote many books, and he was very eloquent in expressing his philosophy about equity and justice in numerous interviews. This is relevant not only for international sites, but in the United States as well, with our major disparities in health outcomes by race, geography, and socioeconomic status.
No one will be able to replace Paul, but he left us with a vision of what is achievable.
Dr. Koenig is associate physician, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, with faculty appointments in the divisions of global health equity and infectious diseases. She is also associate professor at Harvard Medical School.
Editor’s note on 50th Anniversary series
While this is the last piece in a series, my intention is for it to read more like the opening of a new book on family medicine, rather than an ending to a story about the specialty.
April Lockley, DO, represents a new generation of family physicians who began their careers in the 21st century, and she is hopeful that the experiences of practicing family medicine and being the patient of a family physician will change in several ways.
Among her desires for the future, is to be able to write a prescription for a medication or physical therapy to a patient who is able “to fill the prescription without having to worry about the financial implications of paying for it,” she writes. She also hopes “patients can seek out care without the fear of discrimination or racism through an increasingly diverse work force.”
In her article, Dr. Lockley both expresses how she wants family medicine to change and what she already finds satisfying about being a family physician.
I hope you enjoyed reading about the professional journeys of Dr. Lockley and other family physicians who have written commentaries or interviewed for articles in Family Practice News’ 50th Anniversary series this year.
To revisit any of these articles, go to the 50th Anniversary bucket on mdedge.com/familymedicine.
Thank you for continuing to read Family Practice News, and I hope to celebrate more milestones with you in the future.
klennon@mdedge.com
While this is the last piece in a series, my intention is for it to read more like the opening of a new book on family medicine, rather than an ending to a story about the specialty.
April Lockley, DO, represents a new generation of family physicians who began their careers in the 21st century, and she is hopeful that the experiences of practicing family medicine and being the patient of a family physician will change in several ways.
Among her desires for the future, is to be able to write a prescription for a medication or physical therapy to a patient who is able “to fill the prescription without having to worry about the financial implications of paying for it,” she writes. She also hopes “patients can seek out care without the fear of discrimination or racism through an increasingly diverse work force.”
In her article, Dr. Lockley both expresses how she wants family medicine to change and what she already finds satisfying about being a family physician.
I hope you enjoyed reading about the professional journeys of Dr. Lockley and other family physicians who have written commentaries or interviewed for articles in Family Practice News’ 50th Anniversary series this year.
To revisit any of these articles, go to the 50th Anniversary bucket on mdedge.com/familymedicine.
Thank you for continuing to read Family Practice News, and I hope to celebrate more milestones with you in the future.
klennon@mdedge.com
While this is the last piece in a series, my intention is for it to read more like the opening of a new book on family medicine, rather than an ending to a story about the specialty.
April Lockley, DO, represents a new generation of family physicians who began their careers in the 21st century, and she is hopeful that the experiences of practicing family medicine and being the patient of a family physician will change in several ways.
Among her desires for the future, is to be able to write a prescription for a medication or physical therapy to a patient who is able “to fill the prescription without having to worry about the financial implications of paying for it,” she writes. She also hopes “patients can seek out care without the fear of discrimination or racism through an increasingly diverse work force.”
In her article, Dr. Lockley both expresses how she wants family medicine to change and what she already finds satisfying about being a family physician.
I hope you enjoyed reading about the professional journeys of Dr. Lockley and other family physicians who have written commentaries or interviewed for articles in Family Practice News’ 50th Anniversary series this year.
To revisit any of these articles, go to the 50th Anniversary bucket on mdedge.com/familymedicine.
Thank you for continuing to read Family Practice News, and I hope to celebrate more milestones with you in the future.
klennon@mdedge.com
‘Residents’ Viewpoint’ revisited
We are currently republishing an installment of this column as part of our continuing celebration of Family Practice News’s 50th anniversary.
Bruce A. Bagley, MD, wrote the first batch of these columns, when he was chief resident in family medicine at St. Joseph’s Hospital, Syracuse, N.Y. Joseph E. Scherger, MD, was the second writer for Family Practice News’s monthly “Residents’ Viewpoint.” At the time Dr. Scherger became a columnist, he was a 26-year-old, 2nd-year family practice resident at the Family Medical Center, University Hospital, University of Washington, Seattle.
Dr. Scherger’s first column was published on Feb. 5, 1977. We are republishing his “Residents’ Viewpoint” from June 15, 1977 (see below) and a new column by Victoria Persampiere, DO, who is currently a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine program at Abington Jefferson Health. (See “My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021” after Dr. Scherger’s column.).
We hope you will enjoy comparing and contrasting the experiences of a resident practicing family medicine today to those of a resident practicing family medicine nearly 4½ decades ago.To learn about Dr. Scherger’s current practice and long career, you can read his profile on the cover of the September 2021 issue of Family Practice News or on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine in our “Family Practice News 50th Anniversary” section.
Art of medicine or deception?
Originally published in Family Practice News on June 15, 1977.
In medical school I learned the science of medicine. There I diligently studied the basic sciences and gained a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology of disease. In the clinical years I learned to apply this knowledge to a wide variety of interesting patients who came to the academic center.
Yet, when I started my family practice residency, I lacked the ability to care for patients. Though I could take a thorough history, perform a complete physical examination, and diagnose and treat specific illnesses, I had little idea how to satisfy patients by meeting their needs.
The art of medicine is the nonscientific part of a successful doctor-patient interaction. For a doctor-patient interaction to be successful, not only must the illness be appropriately addressed, but both patient and physician must be satisfied.
In the university environment, the art of medicine often gets inadequate attention. Indeed, most academic physicians think that only scientific medicine exists and that patients should be satisfied with a sophisticated approach to their problems. Some patients are satisfied, but many are disgruntled. It is not unusual for a patient, after a $1,000 work-up, to go to a family physician or chiropractor for satisfaction.
I was eager to discover the art of medicine at its finest during my rotation away from the university in a rural community. During these 2 months I looked for the pearls of wisdom that allowed community physicians to be so successful. I found that a very explicit technique was used by some physicians to achieve not only satisfaction but adoration from their patients. Unfortunately, this technique is dishonest.
Early in my community experience I was impressed by how often patients told me a doctor had saved them. I heard such statements as “Dr. X saved my leg,” or “Dr. X saved my life.” I know that it does occur, but not as often as I was hearing it.
Investigating these statements I found such stories as, “One day l twisted my ankle very badly, and it became quite swollen. My doctor told me 1 could lose my leg from this but that he would take x-rays, put my leg in an Ace bandage, and give me crutches. In 3 days I was well. I am so thankful he saved my leg.”
And, “One day I had a temperature of 104. All of my muscles ached, my head hurt, and I had a terrible sore throat and cough. My doctor told me l could die from this, but he gave me a medicine and made me stay home. I was sick for about 2 weeks, but I got better. He saved my life.”
Is the art of medicine the art of deception? This horrifying thought actually came to me after hearing several such stories, but I learned that most of the physicians involved in such stories were not well respected by their colleagues.
I learned many honest techniques for successfully caring for patients. The several family physicians with whom I worked, all clinical instructors associated with my residency, were impeccably honest and taught me to combine compassion and efficiency.
Despite learning many positive techniques and having good role models, I left the community experience somewhat saddened by the lack of integrity that can exist in the profession. I was naive in believing that all the nonscientific aspects of medicine that made patients happy must be good.
By experiencing deception, I learned why quackery continues to flourish despite the widespread availability of honest medical care. Most significantly, I learned the importance of a sometimes frustrating humility; my patients with sprained ankles and influenza will not believe I saved their lives.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19 era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome, which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today; you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician. ■
Dr. Persampiere is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at victoria.persampiere@jefferson.edu or via fpnews@mdedge.com.
klennon@mdedge.com
We are currently republishing an installment of this column as part of our continuing celebration of Family Practice News’s 50th anniversary.
Bruce A. Bagley, MD, wrote the first batch of these columns, when he was chief resident in family medicine at St. Joseph’s Hospital, Syracuse, N.Y. Joseph E. Scherger, MD, was the second writer for Family Practice News’s monthly “Residents’ Viewpoint.” At the time Dr. Scherger became a columnist, he was a 26-year-old, 2nd-year family practice resident at the Family Medical Center, University Hospital, University of Washington, Seattle.
Dr. Scherger’s first column was published on Feb. 5, 1977. We are republishing his “Residents’ Viewpoint” from June 15, 1977 (see below) and a new column by Victoria Persampiere, DO, who is currently a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine program at Abington Jefferson Health. (See “My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021” after Dr. Scherger’s column.).
We hope you will enjoy comparing and contrasting the experiences of a resident practicing family medicine today to those of a resident practicing family medicine nearly 4½ decades ago.To learn about Dr. Scherger’s current practice and long career, you can read his profile on the cover of the September 2021 issue of Family Practice News or on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine in our “Family Practice News 50th Anniversary” section.
Art of medicine or deception?
Originally published in Family Practice News on June 15, 1977.
In medical school I learned the science of medicine. There I diligently studied the basic sciences and gained a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology of disease. In the clinical years I learned to apply this knowledge to a wide variety of interesting patients who came to the academic center.
Yet, when I started my family practice residency, I lacked the ability to care for patients. Though I could take a thorough history, perform a complete physical examination, and diagnose and treat specific illnesses, I had little idea how to satisfy patients by meeting their needs.
The art of medicine is the nonscientific part of a successful doctor-patient interaction. For a doctor-patient interaction to be successful, not only must the illness be appropriately addressed, but both patient and physician must be satisfied.
In the university environment, the art of medicine often gets inadequate attention. Indeed, most academic physicians think that only scientific medicine exists and that patients should be satisfied with a sophisticated approach to their problems. Some patients are satisfied, but many are disgruntled. It is not unusual for a patient, after a $1,000 work-up, to go to a family physician or chiropractor for satisfaction.
I was eager to discover the art of medicine at its finest during my rotation away from the university in a rural community. During these 2 months I looked for the pearls of wisdom that allowed community physicians to be so successful. I found that a very explicit technique was used by some physicians to achieve not only satisfaction but adoration from their patients. Unfortunately, this technique is dishonest.
Early in my community experience I was impressed by how often patients told me a doctor had saved them. I heard such statements as “Dr. X saved my leg,” or “Dr. X saved my life.” I know that it does occur, but not as often as I was hearing it.
Investigating these statements I found such stories as, “One day l twisted my ankle very badly, and it became quite swollen. My doctor told me 1 could lose my leg from this but that he would take x-rays, put my leg in an Ace bandage, and give me crutches. In 3 days I was well. I am so thankful he saved my leg.”
And, “One day I had a temperature of 104. All of my muscles ached, my head hurt, and I had a terrible sore throat and cough. My doctor told me l could die from this, but he gave me a medicine and made me stay home. I was sick for about 2 weeks, but I got better. He saved my life.”
Is the art of medicine the art of deception? This horrifying thought actually came to me after hearing several such stories, but I learned that most of the physicians involved in such stories were not well respected by their colleagues.
I learned many honest techniques for successfully caring for patients. The several family physicians with whom I worked, all clinical instructors associated with my residency, were impeccably honest and taught me to combine compassion and efficiency.
Despite learning many positive techniques and having good role models, I left the community experience somewhat saddened by the lack of integrity that can exist in the profession. I was naive in believing that all the nonscientific aspects of medicine that made patients happy must be good.
By experiencing deception, I learned why quackery continues to flourish despite the widespread availability of honest medical care. Most significantly, I learned the importance of a sometimes frustrating humility; my patients with sprained ankles and influenza will not believe I saved their lives.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19 era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome, which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today; you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician. ■
Dr. Persampiere is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at victoria.persampiere@jefferson.edu or via fpnews@mdedge.com.
klennon@mdedge.com
We are currently republishing an installment of this column as part of our continuing celebration of Family Practice News’s 50th anniversary.
Bruce A. Bagley, MD, wrote the first batch of these columns, when he was chief resident in family medicine at St. Joseph’s Hospital, Syracuse, N.Y. Joseph E. Scherger, MD, was the second writer for Family Practice News’s monthly “Residents’ Viewpoint.” At the time Dr. Scherger became a columnist, he was a 26-year-old, 2nd-year family practice resident at the Family Medical Center, University Hospital, University of Washington, Seattle.
Dr. Scherger’s first column was published on Feb. 5, 1977. We are republishing his “Residents’ Viewpoint” from June 15, 1977 (see below) and a new column by Victoria Persampiere, DO, who is currently a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine program at Abington Jefferson Health. (See “My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021” after Dr. Scherger’s column.).
We hope you will enjoy comparing and contrasting the experiences of a resident practicing family medicine today to those of a resident practicing family medicine nearly 4½ decades ago.To learn about Dr. Scherger’s current practice and long career, you can read his profile on the cover of the September 2021 issue of Family Practice News or on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine in our “Family Practice News 50th Anniversary” section.
Art of medicine or deception?
Originally published in Family Practice News on June 15, 1977.
In medical school I learned the science of medicine. There I diligently studied the basic sciences and gained a thorough understanding of the pathophysiology of disease. In the clinical years I learned to apply this knowledge to a wide variety of interesting patients who came to the academic center.
Yet, when I started my family practice residency, I lacked the ability to care for patients. Though I could take a thorough history, perform a complete physical examination, and diagnose and treat specific illnesses, I had little idea how to satisfy patients by meeting their needs.
The art of medicine is the nonscientific part of a successful doctor-patient interaction. For a doctor-patient interaction to be successful, not only must the illness be appropriately addressed, but both patient and physician must be satisfied.
In the university environment, the art of medicine often gets inadequate attention. Indeed, most academic physicians think that only scientific medicine exists and that patients should be satisfied with a sophisticated approach to their problems. Some patients are satisfied, but many are disgruntled. It is not unusual for a patient, after a $1,000 work-up, to go to a family physician or chiropractor for satisfaction.
I was eager to discover the art of medicine at its finest during my rotation away from the university in a rural community. During these 2 months I looked for the pearls of wisdom that allowed community physicians to be so successful. I found that a very explicit technique was used by some physicians to achieve not only satisfaction but adoration from their patients. Unfortunately, this technique is dishonest.
Early in my community experience I was impressed by how often patients told me a doctor had saved them. I heard such statements as “Dr. X saved my leg,” or “Dr. X saved my life.” I know that it does occur, but not as often as I was hearing it.
Investigating these statements I found such stories as, “One day l twisted my ankle very badly, and it became quite swollen. My doctor told me 1 could lose my leg from this but that he would take x-rays, put my leg in an Ace bandage, and give me crutches. In 3 days I was well. I am so thankful he saved my leg.”
And, “One day I had a temperature of 104. All of my muscles ached, my head hurt, and I had a terrible sore throat and cough. My doctor told me l could die from this, but he gave me a medicine and made me stay home. I was sick for about 2 weeks, but I got better. He saved my life.”
Is the art of medicine the art of deception? This horrifying thought actually came to me after hearing several such stories, but I learned that most of the physicians involved in such stories were not well respected by their colleagues.
I learned many honest techniques for successfully caring for patients. The several family physicians with whom I worked, all clinical instructors associated with my residency, were impeccably honest and taught me to combine compassion and efficiency.
Despite learning many positive techniques and having good role models, I left the community experience somewhat saddened by the lack of integrity that can exist in the profession. I was naive in believing that all the nonscientific aspects of medicine that made patients happy must be good.
By experiencing deception, I learned why quackery continues to flourish despite the widespread availability of honest medical care. Most significantly, I learned the importance of a sometimes frustrating humility; my patients with sprained ankles and influenza will not believe I saved their lives.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19 era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome, which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today; you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician. ■
Dr. Persampiere is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at victoria.persampiere@jefferson.edu or via fpnews@mdedge.com.
klennon@mdedge.com
Patient contact with primary care physicians declines in study
––
The reasons for this less frequent contact and the ramifications for patients and doctors practicing primary care are unclear, according to various experts. But some offered possible explanations for the changes, with patients’ increased participation in high deductible plans and shortages in primary care physicians (PCPs) being among the most often cited.
The findings, which were published online Jan. 11 in Annals of Family Medicine, were derived from researchers using a repeated cross-sectional study of the 2002-2017 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey to characterize trends in primary care use. This survey, which collected information about medical care utilization from individuals and families, included 243,919 participants who were interviewed five times over 2 years. The authors defined primary care physician contact as “in-person visit or contact with a primary care physician (primarily telephone calls) with a reported specialty of family medicine, general internal medicine, geriatrics, general pediatrics, or general practice physician.” According to the paper, “the proportion of individuals with any primary care physician contact was determined for both the population and by age group using logistic regression models,” and negative binomial regression models were used to determine the number of contacts among people with visits during 2-year periods.
The study authors, Michael E. Johansen, MD, MS, and Joshua D. Niforatos, MD, MTS, said their study suggests that previously reported decreases in primary care contact was caused by fewer contacts per patient “as opposed to an absolute decrease in the number of patients in contact with primary care.”
Harold B. Betton, MD, PhD, who practices family medicine in Little Rock, Ark., questioned this claim.
“In my reading, the authors concluded that people are seeing their primary care physicians fewer times than in the past, which suggests something is happening,” Dr. Betton said in an interview. “The fact that fewer visits are occurring may be due to multiple things, i.e., urgent care visits, visits to physician extenders – physician assistants and advanced practice nurses – or emergency room visits.”
"The paper draws observational conclusions and I fail to see the merit in the observation without knowing what the respondents were asked and not asked," he added.
Other primary care physicians suggested patients’ participation in alternative pay models and high-deductible plans have played a factor in the declines.
“Most of us have gone from fee-for-service, volume-based care to more value-based care,” Ada D. Stewart, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in an interview. The data reflect that trend, “whereas we were rewarded more for the number of people we were seeing, now we are trying to get towards more of the value that we provide,” suggested Dr. Stewart, who also practices family medicine with Cooperative Health in Columbia, S.C.
“Given the rise of high-deductible plans and copays, it is not surprising that younger patients, a generally healthier population, might well decrease their visits to a primary care physician. I would suspect that data for patients over 50 might well be different,” William E. Golden, MD, who is medical director at the Arkansas Department of Health & Human Services, noted in an interview.
Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, also cited greater participation in high-deductible plans as a possible factor that could be leading some patients to forgo visits, as well as increased financial insecurity, rendering it expensive to have the visit and also to take time from work for the visit.
“I would wonder if some of this is also due to how overloaded most primary care offices are so that instead of stopping accepting new patients or shedding patients, it is just harder for existing patients to be seen,” said Dr. Barrett, who is a general internist and associate professor in the division of hospital medicine, department of internal medicine, at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “Some of this could be from administrative burden – 2 hours per hour of clinic – and consequently reducing clinical time,” continued Dr. Barrett, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, which is affiliated with Family Practice News.
Other experts pointed to data showing an insufficient supply of PCPs as a potential explanation for the new study’s findings. The Health Resources and Services Organization, for example, reported that 83 million Americans live in primary care “health professional shortage areas,” as of Jan. 24, 2021, on their website.
New data
“The rate of any contact with a [PCP] for patients in the population over multiple 2-year periods decreased by 2.5% over the study period (adjusted odds ratio, 0.99 per panel; 95% [confidence interval], 0.98-0.99; P < .001),” wrote Dr. Johansen and Dr. Niforatos. The rate of contact for patients aged 18-39 years (aOR, 0.99 per panel; 95% CI, 0.98-0.99; P < .001) and patients aged 40-64 years (aOR, 0.99 per panel; 95% CI, 0.99-1.00; P = .002), specifically, also fell. These decreased contact rates correspond “to a predicted cumulative 5% absolute decrease for the younger group and a 2% absolute decrease for the older group,” the authors added.
“The number of contacts with a [PCP] decreased among individuals with any contact by 0.5 contacts over 2 years (P < .001). A decrease in the number of [PCP] contacts was observed across all age groups (P < .001 for all), with the largest absolute decrease among individuals with higher contact rates (aged less than 4 years and aged greater than 64 years),” according to the paper.
Outlook for PCPs
Physicians questioned about how concerning these data are for the future of PCPs and their ability to keep their practices running were hesitant to speculate, because of uncertainty about the causes of the study findings.
“A quote from the paper indicates that the respondents were interviewed five times over 2 years; however, without a copy of the questionnaire it is impossible to know what they were asked and not asked,” said Dr. Betton, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News and runs his own private practice. “In addition, it is impossible for the reader to know whether they understood what a primary care physician was to do.
“To draw a conclusion that PCP visits are falling off per patient per provider is only helpful if patients are opting out of the primary care model of practice and opting in for point-of-care [urgent] care,” Dr. Betton added.
Internist Alan Nelson, MD, said he was also undecided about whether the findings of the study are good or bad news for the physician specialty of primary care.
“Similar findings have been reported by the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. They certainly merit further investigation,” noted Dr. Nelson, who is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. “Is it because primary care physicians are too busy to see additional patients? Is it because nonphysician practitioners seem to be more caring? Should residency training be modified, and if so, how? In the meantime, I would not be surprised if the trend continues, at least in the short term.”
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Collaborative, a nonprofit organization that advocates to strengthen primary care and make it more responsive to patient needs and preferences, on the other hand, reacted with a concerned outlook for primary care.
This study and others show that “the U.S. health care system is moving away from a primary care orientation, and that is concerning,” Ms. Greiner said in an interview. “Health systems that are more oriented toward primary care have better population health outcomes, do better on measures of equity across different population groups, and are less costly.”
Authors’ take
“Future research is needed to determine whether fewer contacts per patient resulted in clinically meaningful differences in outcomes across disease processes,” wrote Dr. Johansen, who is a family medicine doctor affiliated with OhioHealth Family Medicine Grant in Columbus and with the Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine at Ohio University, Dublin, and Dr. Niforatos, who is affiliated with the department of emergency medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The study’s limitations included reliance on self-reported categorization of PCP versus specialty care physician contact, insufficient accounting for nurse practitioner and physician assistant contact, and improved contact reporting having started in 2013, they said.
How to grow patient contact
For those PCPs looking to grow their visits and patient contact, Dr. Golden suggested they strengthen their medical home model in their practice.
“Medical home models help and transform practice operations. The Arkansas model is a multipayer model – private, Medicaid and CPC+ (Medicare),” said Dr. Golden, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. It includes community-based doctors, not Federally Qualified Health Centers, and “requires 24/7 live voice access that promotes regular contact with patients and can reduce dependency on ER and urgent care center visits.”
“Greater use of patient portals and email communications facilitate access and patient engagement with their PCP,” Dr. Golden explained.
“Over the last 6 years, the Arkansas [patient-centered medical home] initiatives have altered culture and made our practice sites stronger to withstand COVID and other challenges. As our sites became more patient centered and incorporated behavioral health options, patients perceived greater value in the functionality of primary care” he said.
Dr. Barrett proposed PCPs participate in team-based care “for professional sustainability and also for patients to continue to experience high-quality, person-centered care.” She added that “telemedicine can also help practices maintain and increase patients, as it can lessen burden on patients and clinicians – if it is done right.”
“More flexible clinic hours is also key – after usual business hours and on weekends – but I would recommend in lieu of usual weekday hours and for those who can make it work with their family and other duties,” Dr. Barrett said. “Evening or Saturday morning clinic isn’t an option for everyone, but it is an option for many some of the time, and it would be great for access to care if it were available in more locations.”
Pandemic effect
The data examined by Dr. Johansen and Dr. Niforatos predates the pandemic, but PCPs interviewed by this news organization have seen declining patient contact occur in 2020 as well.
In fact, a survey of 1,485 mostly physician primary care practitioners that began after the pandemic onset found that 43% of participants have fewer in-person visits, motivated largely by patient preferences (66%) and safety concerns (74%). This ongoing survey, which was conducted by the Larry Green Center in partnership with the Primary Care Collaborative, also indicated that, while 25% of participants saw a total increase in patient volume, more than half of primary care practitioners reported that chronic and wellness visits are down, 53% and 55%, respectively.
“Sometimes we have to go looking for our patients when we have not seen them in a while,” Dr. Stewart noted. “We saw that with COVID because people were fearful of coming into our offices, and we had to have some outreach.”
The study authors had no conflicts of interest. Dr. Barrett, Dr. Betton, Dr. Golden, Dr. Nelson, and Dr. Stewart had no relevant disclosures.
Jake Remaly contributed to this article.
––
The reasons for this less frequent contact and the ramifications for patients and doctors practicing primary care are unclear, according to various experts. But some offered possible explanations for the changes, with patients’ increased participation in high deductible plans and shortages in primary care physicians (PCPs) being among the most often cited.
The findings, which were published online Jan. 11 in Annals of Family Medicine, were derived from researchers using a repeated cross-sectional study of the 2002-2017 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey to characterize trends in primary care use. This survey, which collected information about medical care utilization from individuals and families, included 243,919 participants who were interviewed five times over 2 years. The authors defined primary care physician contact as “in-person visit or contact with a primary care physician (primarily telephone calls) with a reported specialty of family medicine, general internal medicine, geriatrics, general pediatrics, or general practice physician.” According to the paper, “the proportion of individuals with any primary care physician contact was determined for both the population and by age group using logistic regression models,” and negative binomial regression models were used to determine the number of contacts among people with visits during 2-year periods.
The study authors, Michael E. Johansen, MD, MS, and Joshua D. Niforatos, MD, MTS, said their study suggests that previously reported decreases in primary care contact was caused by fewer contacts per patient “as opposed to an absolute decrease in the number of patients in contact with primary care.”
Harold B. Betton, MD, PhD, who practices family medicine in Little Rock, Ark., questioned this claim.
“In my reading, the authors concluded that people are seeing their primary care physicians fewer times than in the past, which suggests something is happening,” Dr. Betton said in an interview. “The fact that fewer visits are occurring may be due to multiple things, i.e., urgent care visits, visits to physician extenders – physician assistants and advanced practice nurses – or emergency room visits.”
"The paper draws observational conclusions and I fail to see the merit in the observation without knowing what the respondents were asked and not asked," he added.
Other primary care physicians suggested patients’ participation in alternative pay models and high-deductible plans have played a factor in the declines.
“Most of us have gone from fee-for-service, volume-based care to more value-based care,” Ada D. Stewart, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in an interview. The data reflect that trend, “whereas we were rewarded more for the number of people we were seeing, now we are trying to get towards more of the value that we provide,” suggested Dr. Stewart, who also practices family medicine with Cooperative Health in Columbia, S.C.
“Given the rise of high-deductible plans and copays, it is not surprising that younger patients, a generally healthier population, might well decrease their visits to a primary care physician. I would suspect that data for patients over 50 might well be different,” William E. Golden, MD, who is medical director at the Arkansas Department of Health & Human Services, noted in an interview.
Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, also cited greater participation in high-deductible plans as a possible factor that could be leading some patients to forgo visits, as well as increased financial insecurity, rendering it expensive to have the visit and also to take time from work for the visit.
“I would wonder if some of this is also due to how overloaded most primary care offices are so that instead of stopping accepting new patients or shedding patients, it is just harder for existing patients to be seen,” said Dr. Barrett, who is a general internist and associate professor in the division of hospital medicine, department of internal medicine, at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “Some of this could be from administrative burden – 2 hours per hour of clinic – and consequently reducing clinical time,” continued Dr. Barrett, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, which is affiliated with Family Practice News.
Other experts pointed to data showing an insufficient supply of PCPs as a potential explanation for the new study’s findings. The Health Resources and Services Organization, for example, reported that 83 million Americans live in primary care “health professional shortage areas,” as of Jan. 24, 2021, on their website.
New data
“The rate of any contact with a [PCP] for patients in the population over multiple 2-year periods decreased by 2.5% over the study period (adjusted odds ratio, 0.99 per panel; 95% [confidence interval], 0.98-0.99; P < .001),” wrote Dr. Johansen and Dr. Niforatos. The rate of contact for patients aged 18-39 years (aOR, 0.99 per panel; 95% CI, 0.98-0.99; P < .001) and patients aged 40-64 years (aOR, 0.99 per panel; 95% CI, 0.99-1.00; P = .002), specifically, also fell. These decreased contact rates correspond “to a predicted cumulative 5% absolute decrease for the younger group and a 2% absolute decrease for the older group,” the authors added.
“The number of contacts with a [PCP] decreased among individuals with any contact by 0.5 contacts over 2 years (P < .001). A decrease in the number of [PCP] contacts was observed across all age groups (P < .001 for all), with the largest absolute decrease among individuals with higher contact rates (aged less than 4 years and aged greater than 64 years),” according to the paper.
Outlook for PCPs
Physicians questioned about how concerning these data are for the future of PCPs and their ability to keep their practices running were hesitant to speculate, because of uncertainty about the causes of the study findings.
“A quote from the paper indicates that the respondents were interviewed five times over 2 years; however, without a copy of the questionnaire it is impossible to know what they were asked and not asked,” said Dr. Betton, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News and runs his own private practice. “In addition, it is impossible for the reader to know whether they understood what a primary care physician was to do.
“To draw a conclusion that PCP visits are falling off per patient per provider is only helpful if patients are opting out of the primary care model of practice and opting in for point-of-care [urgent] care,” Dr. Betton added.
Internist Alan Nelson, MD, said he was also undecided about whether the findings of the study are good or bad news for the physician specialty of primary care.
“Similar findings have been reported by the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. They certainly merit further investigation,” noted Dr. Nelson, who is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. “Is it because primary care physicians are too busy to see additional patients? Is it because nonphysician practitioners seem to be more caring? Should residency training be modified, and if so, how? In the meantime, I would not be surprised if the trend continues, at least in the short term.”
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Collaborative, a nonprofit organization that advocates to strengthen primary care and make it more responsive to patient needs and preferences, on the other hand, reacted with a concerned outlook for primary care.
This study and others show that “the U.S. health care system is moving away from a primary care orientation, and that is concerning,” Ms. Greiner said in an interview. “Health systems that are more oriented toward primary care have better population health outcomes, do better on measures of equity across different population groups, and are less costly.”
Authors’ take
“Future research is needed to determine whether fewer contacts per patient resulted in clinically meaningful differences in outcomes across disease processes,” wrote Dr. Johansen, who is a family medicine doctor affiliated with OhioHealth Family Medicine Grant in Columbus and with the Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine at Ohio University, Dublin, and Dr. Niforatos, who is affiliated with the department of emergency medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The study’s limitations included reliance on self-reported categorization of PCP versus specialty care physician contact, insufficient accounting for nurse practitioner and physician assistant contact, and improved contact reporting having started in 2013, they said.
How to grow patient contact
For those PCPs looking to grow their visits and patient contact, Dr. Golden suggested they strengthen their medical home model in their practice.
“Medical home models help and transform practice operations. The Arkansas model is a multipayer model – private, Medicaid and CPC+ (Medicare),” said Dr. Golden, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. It includes community-based doctors, not Federally Qualified Health Centers, and “requires 24/7 live voice access that promotes regular contact with patients and can reduce dependency on ER and urgent care center visits.”
“Greater use of patient portals and email communications facilitate access and patient engagement with their PCP,” Dr. Golden explained.
“Over the last 6 years, the Arkansas [patient-centered medical home] initiatives have altered culture and made our practice sites stronger to withstand COVID and other challenges. As our sites became more patient centered and incorporated behavioral health options, patients perceived greater value in the functionality of primary care” he said.
Dr. Barrett proposed PCPs participate in team-based care “for professional sustainability and also for patients to continue to experience high-quality, person-centered care.” She added that “telemedicine can also help practices maintain and increase patients, as it can lessen burden on patients and clinicians – if it is done right.”
“More flexible clinic hours is also key – after usual business hours and on weekends – but I would recommend in lieu of usual weekday hours and for those who can make it work with their family and other duties,” Dr. Barrett said. “Evening or Saturday morning clinic isn’t an option for everyone, but it is an option for many some of the time, and it would be great for access to care if it were available in more locations.”
Pandemic effect
The data examined by Dr. Johansen and Dr. Niforatos predates the pandemic, but PCPs interviewed by this news organization have seen declining patient contact occur in 2020 as well.
In fact, a survey of 1,485 mostly physician primary care practitioners that began after the pandemic onset found that 43% of participants have fewer in-person visits, motivated largely by patient preferences (66%) and safety concerns (74%). This ongoing survey, which was conducted by the Larry Green Center in partnership with the Primary Care Collaborative, also indicated that, while 25% of participants saw a total increase in patient volume, more than half of primary care practitioners reported that chronic and wellness visits are down, 53% and 55%, respectively.
“Sometimes we have to go looking for our patients when we have not seen them in a while,” Dr. Stewart noted. “We saw that with COVID because people were fearful of coming into our offices, and we had to have some outreach.”
The study authors had no conflicts of interest. Dr. Barrett, Dr. Betton, Dr. Golden, Dr. Nelson, and Dr. Stewart had no relevant disclosures.
Jake Remaly contributed to this article.
––
The reasons for this less frequent contact and the ramifications for patients and doctors practicing primary care are unclear, according to various experts. But some offered possible explanations for the changes, with patients’ increased participation in high deductible plans and shortages in primary care physicians (PCPs) being among the most often cited.
The findings, which were published online Jan. 11 in Annals of Family Medicine, were derived from researchers using a repeated cross-sectional study of the 2002-2017 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey to characterize trends in primary care use. This survey, which collected information about medical care utilization from individuals and families, included 243,919 participants who were interviewed five times over 2 years. The authors defined primary care physician contact as “in-person visit or contact with a primary care physician (primarily telephone calls) with a reported specialty of family medicine, general internal medicine, geriatrics, general pediatrics, or general practice physician.” According to the paper, “the proportion of individuals with any primary care physician contact was determined for both the population and by age group using logistic regression models,” and negative binomial regression models were used to determine the number of contacts among people with visits during 2-year periods.
The study authors, Michael E. Johansen, MD, MS, and Joshua D. Niforatos, MD, MTS, said their study suggests that previously reported decreases in primary care contact was caused by fewer contacts per patient “as opposed to an absolute decrease in the number of patients in contact with primary care.”
Harold B. Betton, MD, PhD, who practices family medicine in Little Rock, Ark., questioned this claim.
“In my reading, the authors concluded that people are seeing their primary care physicians fewer times than in the past, which suggests something is happening,” Dr. Betton said in an interview. “The fact that fewer visits are occurring may be due to multiple things, i.e., urgent care visits, visits to physician extenders – physician assistants and advanced practice nurses – or emergency room visits.”
"The paper draws observational conclusions and I fail to see the merit in the observation without knowing what the respondents were asked and not asked," he added.
Other primary care physicians suggested patients’ participation in alternative pay models and high-deductible plans have played a factor in the declines.
“Most of us have gone from fee-for-service, volume-based care to more value-based care,” Ada D. Stewart, MD, president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in an interview. The data reflect that trend, “whereas we were rewarded more for the number of people we were seeing, now we are trying to get towards more of the value that we provide,” suggested Dr. Stewart, who also practices family medicine with Cooperative Health in Columbia, S.C.
“Given the rise of high-deductible plans and copays, it is not surprising that younger patients, a generally healthier population, might well decrease their visits to a primary care physician. I would suspect that data for patients over 50 might well be different,” William E. Golden, MD, who is medical director at the Arkansas Department of Health & Human Services, noted in an interview.
Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, also cited greater participation in high-deductible plans as a possible factor that could be leading some patients to forgo visits, as well as increased financial insecurity, rendering it expensive to have the visit and also to take time from work for the visit.
“I would wonder if some of this is also due to how overloaded most primary care offices are so that instead of stopping accepting new patients or shedding patients, it is just harder for existing patients to be seen,” said Dr. Barrett, who is a general internist and associate professor in the division of hospital medicine, department of internal medicine, at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “Some of this could be from administrative burden – 2 hours per hour of clinic – and consequently reducing clinical time,” continued Dr. Barrett, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, which is affiliated with Family Practice News.
Other experts pointed to data showing an insufficient supply of PCPs as a potential explanation for the new study’s findings. The Health Resources and Services Organization, for example, reported that 83 million Americans live in primary care “health professional shortage areas,” as of Jan. 24, 2021, on their website.
New data
“The rate of any contact with a [PCP] for patients in the population over multiple 2-year periods decreased by 2.5% over the study period (adjusted odds ratio, 0.99 per panel; 95% [confidence interval], 0.98-0.99; P < .001),” wrote Dr. Johansen and Dr. Niforatos. The rate of contact for patients aged 18-39 years (aOR, 0.99 per panel; 95% CI, 0.98-0.99; P < .001) and patients aged 40-64 years (aOR, 0.99 per panel; 95% CI, 0.99-1.00; P = .002), specifically, also fell. These decreased contact rates correspond “to a predicted cumulative 5% absolute decrease for the younger group and a 2% absolute decrease for the older group,” the authors added.
“The number of contacts with a [PCP] decreased among individuals with any contact by 0.5 contacts over 2 years (P < .001). A decrease in the number of [PCP] contacts was observed across all age groups (P < .001 for all), with the largest absolute decrease among individuals with higher contact rates (aged less than 4 years and aged greater than 64 years),” according to the paper.
Outlook for PCPs
Physicians questioned about how concerning these data are for the future of PCPs and their ability to keep their practices running were hesitant to speculate, because of uncertainty about the causes of the study findings.
“A quote from the paper indicates that the respondents were interviewed five times over 2 years; however, without a copy of the questionnaire it is impossible to know what they were asked and not asked,” said Dr. Betton, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News and runs his own private practice. “In addition, it is impossible for the reader to know whether they understood what a primary care physician was to do.
“To draw a conclusion that PCP visits are falling off per patient per provider is only helpful if patients are opting out of the primary care model of practice and opting in for point-of-care [urgent] care,” Dr. Betton added.
Internist Alan Nelson, MD, said he was also undecided about whether the findings of the study are good or bad news for the physician specialty of primary care.
“Similar findings have been reported by the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. They certainly merit further investigation,” noted Dr. Nelson, who is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. “Is it because primary care physicians are too busy to see additional patients? Is it because nonphysician practitioners seem to be more caring? Should residency training be modified, and if so, how? In the meantime, I would not be surprised if the trend continues, at least in the short term.”
Ann Greiner, president and CEO of the Primary Care Collaborative, a nonprofit organization that advocates to strengthen primary care and make it more responsive to patient needs and preferences, on the other hand, reacted with a concerned outlook for primary care.
This study and others show that “the U.S. health care system is moving away from a primary care orientation, and that is concerning,” Ms. Greiner said in an interview. “Health systems that are more oriented toward primary care have better population health outcomes, do better on measures of equity across different population groups, and are less costly.”
Authors’ take
“Future research is needed to determine whether fewer contacts per patient resulted in clinically meaningful differences in outcomes across disease processes,” wrote Dr. Johansen, who is a family medicine doctor affiliated with OhioHealth Family Medicine Grant in Columbus and with the Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine at Ohio University, Dublin, and Dr. Niforatos, who is affiliated with the department of emergency medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
The study’s limitations included reliance on self-reported categorization of PCP versus specialty care physician contact, insufficient accounting for nurse practitioner and physician assistant contact, and improved contact reporting having started in 2013, they said.
How to grow patient contact
For those PCPs looking to grow their visits and patient contact, Dr. Golden suggested they strengthen their medical home model in their practice.
“Medical home models help and transform practice operations. The Arkansas model is a multipayer model – private, Medicaid and CPC+ (Medicare),” said Dr. Golden, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. It includes community-based doctors, not Federally Qualified Health Centers, and “requires 24/7 live voice access that promotes regular contact with patients and can reduce dependency on ER and urgent care center visits.”
“Greater use of patient portals and email communications facilitate access and patient engagement with their PCP,” Dr. Golden explained.
“Over the last 6 years, the Arkansas [patient-centered medical home] initiatives have altered culture and made our practice sites stronger to withstand COVID and other challenges. As our sites became more patient centered and incorporated behavioral health options, patients perceived greater value in the functionality of primary care” he said.
Dr. Barrett proposed PCPs participate in team-based care “for professional sustainability and also for patients to continue to experience high-quality, person-centered care.” She added that “telemedicine can also help practices maintain and increase patients, as it can lessen burden on patients and clinicians – if it is done right.”
“More flexible clinic hours is also key – after usual business hours and on weekends – but I would recommend in lieu of usual weekday hours and for those who can make it work with their family and other duties,” Dr. Barrett said. “Evening or Saturday morning clinic isn’t an option for everyone, but it is an option for many some of the time, and it would be great for access to care if it were available in more locations.”
Pandemic effect
The data examined by Dr. Johansen and Dr. Niforatos predates the pandemic, but PCPs interviewed by this news organization have seen declining patient contact occur in 2020 as well.
In fact, a survey of 1,485 mostly physician primary care practitioners that began after the pandemic onset found that 43% of participants have fewer in-person visits, motivated largely by patient preferences (66%) and safety concerns (74%). This ongoing survey, which was conducted by the Larry Green Center in partnership with the Primary Care Collaborative, also indicated that, while 25% of participants saw a total increase in patient volume, more than half of primary care practitioners reported that chronic and wellness visits are down, 53% and 55%, respectively.
“Sometimes we have to go looking for our patients when we have not seen them in a while,” Dr. Stewart noted. “We saw that with COVID because people were fearful of coming into our offices, and we had to have some outreach.”
The study authors had no conflicts of interest. Dr. Barrett, Dr. Betton, Dr. Golden, Dr. Nelson, and Dr. Stewart had no relevant disclosures.
Jake Remaly contributed to this article.
FROM ANNALS OF FAMILY MEDICINE
Family Practice News celebrates 50 years
This year, in each issue and on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine throughout 2021.
We plan to address the biggest breakthroughs and most influential people in family medicine over the past 50 years. The publication will also share family physicians’ expectations and hopes for the specialty in the coming years.
Are there any topics you think would be valuable to cover in light of this major milestone? The editorial staff welcomes your suggestions. Please share them by emailing us at fpnews@mdedge.com.
Happy New Year, and thank you for supporting us for so many years!
This year, in each issue and on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine throughout 2021.
We plan to address the biggest breakthroughs and most influential people in family medicine over the past 50 years. The publication will also share family physicians’ expectations and hopes for the specialty in the coming years.
Are there any topics you think would be valuable to cover in light of this major milestone? The editorial staff welcomes your suggestions. Please share them by emailing us at fpnews@mdedge.com.
Happy New Year, and thank you for supporting us for so many years!
This year, in each issue and on MDedge.com/FamilyMedicine throughout 2021.
We plan to address the biggest breakthroughs and most influential people in family medicine over the past 50 years. The publication will also share family physicians’ expectations and hopes for the specialty in the coming years.
Are there any topics you think would be valuable to cover in light of this major milestone? The editorial staff welcomes your suggestions. Please share them by emailing us at fpnews@mdedge.com.
Happy New Year, and thank you for supporting us for so many years!
WHO: Asymptomatic COVID-19 spread deemed ‘rare’
An official with the World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that it appears to be “rare” that an asymptomatic individual can pass SARS-CoV-2 to someone else.
“From the data we have, it still seems to be rare that an asymptomatic person actually transmits onward to a secondary individual,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO’s COVID-19 technical lead and an infectious disease epidemiologist, said June 8 at a news briefing from the agency’s Geneva headquarters.
This announcement came on the heels of the publication of an analysis in the Annals of Internal Medicine, which suggested that as many as 40-45% of COVID-19 cases may be asymptomatic. In this paper, the authors, Daniel P. Oran, AM, and Eric J. Topol, MD, of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif stated: “The likelihood that approximately 40%-45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic suggests that the virus might have greater potential than previously estimated to spread silently and deeply through human populations.”
"The early data that we have assembled on the prevalence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection suggest that this is a significant factor in the rapid progression of the COVID-19 pandemic," the authors concluded.
Dr. Van Kerkhove also made comments suggesting otherwise on Twitter, citing a new summary by WHO: “@WHO recently published a summary of transmission of #COVID19, incl. symptomatic, pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission.”
She also tweeted the following lines from the WHO summary: “Comprehensive studies on transmission from asymptomatic individuals are difficult to conduct, but the available evidence from contact tracing reported by Member States suggests that asymptomatically-infected individuals are much less likely to transmit the virus than those who develop symptoms.”
In an additional post, Dr. Van Kerkhove added: “In these data, it is important to breakdown truly asymptomatic vs pre-symptomatic vs mildly symptomatic... also to note that the [percentage] reported or estimated to be ‘asymptomatic’ is not the same as the [percentage] that are asymptomatic that actually transmit.”
In the paper published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Mr. Oran and Dr. Topol analyzed data of asymptomatic individuals from 16 cohorts between April 19 and May 26, 2020 – a wide-ranging group consisting of residents of cities, health care workers, individuals in homeless shelters, obstetric patients, residents of a nursing home, crew members of aircraft carriers, passengers on cruise ships, and inmates in correctional facilities. Each cohort had varying rates of asymptomatic or presymptomatic cases..
When residents of Iceland were tested, 43 of 100 individuals who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 did not show symptoms. In Vo’, Italy, 30 of 73 people (41.1%) with positive SARS-CoV-2 test results did not have symptoms in a first round of testing, and 13 of 29 (44.8%) had no symptoms in a second round of testing. Over half of residents of San Francisco’s Mission District who received testing (39 of 74; 52.7%) did not have symptoms, while slightly less than half of Indiana residents tested showed no symptoms (35 of 78; 44.8%).
A majority of 41 individuals (65.9%) who were mostly health care workers at Rutgers University reported no symptoms of COVID-19 at the time of testing. Data from homeless shelters in Boston (129 of 147; 87.7%) and Los Angeles (27 of 43; 62.7%) also showed a high rate of individuals without symptoms. Among 33 obstetric patients in New York City who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, 29 women (87.9%) were asymptomatic during a median 2-day length of stay. In a Washington state nursing facility, 12 of 23 individuals (52.1%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2 without showing symptoms in a first round of testing, with another 15 of 24 residents (62.5%) not showing symptoms in a second round of testing. Of these residents, 24 individuals (88.9%) later went on to show symptoms of COVID-19.
Most of the 783 Greek citizens who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after being evacuated from Spain, Turkey, and the United Kingdom showed no symptoms of COVID-19 (35 of 40; 87.5%). A group of 565 Japanese citizens evacuated from Wuhan, China, had a lower number of cases without initial symptoms – 13 people were positive for SARS-CoV-2, and 4 of 13 (30.8%) had no symptoms.
In closed cohorts, there appeared to also be a high rate of COVID-19 cases without initial symptoms. Of 3,277 inmates from correctional facilities in Arkansas, North Carolina, Ohio, and Virginia, 3,146 individuals (96%) had no symptoms at the time of testing. There was also a large percentage of passengers and crew of the Diamond Princess cruise ship (331 of 712; 46.5%) and an Argentine cruise ship (104 of 128; 81.3%) who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 without symptoms. On the aircraft carrier U.S.S. Theodore Roosevelt, 60% of 856 individuals, while on the French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, nearly 50% of individuals were asymptomatic.
It is difficult to tell the difference between people who are presymptomatic and will later go on to develop symptoms of COVID-19 and those who will remain asymptomatic. “The simple solution to this conundrum is longitudinal testing – that is, repeated observations of the individual over time,” but only 5 of 16 cohorts studied had longitudinal data on individuals, Mr. Oran and Dr. Topol said.
Seth Trueger, MD, an emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, said it was important to see this information all in one place, even if the data isn’t new.
“I think we’ve certainly kind of seen from the beginning there’s some level of asymptomatic and presymptomatic spread,” Dr. Trueger said. “In health care, we’ve been lucky to get those lessons early on and start to think of things like universal masking in hospitals, and unfortunate things like limiting visitors.”
A more nuanced understanding of how SARS-CoV-2 spreads has been difficult to capture, in part because of operating under a shortened time frame and handicapped testing capacity, he noted. “[Even] in the best of possible circumstances, trying to figure out epidemiology in people who don’t have symptoms is really tough,” Dr. Truegar said.
“Even the best studies are still relatively decent samples, and not totally representative,” he added.
Another limitation to capturing accurate data is method of testing. Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction using nasopharyngeal swabs can detect RNA fragments from SARS-CoV-2, which could potentially affect the results. “It’s really hard to know what is actually infected virus versus just fragments of RNA that make the test positive,” Dr. Trueger said.
If the rate of asymptomatic cases is higher than previously thought, it’s a “double-edged sword,” he noted. It may mean the infection fatality rate is lower than predicted, but “even at high levels of what we think community levels might be, we’re far from herd immunity.”
The study authors and Dr. Trueger reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Oran DP, Topol EJ. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jun 3. doi: 10.7326/M20-3012.
This article was updated 6/8/20.
An official with the World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that it appears to be “rare” that an asymptomatic individual can pass SARS-CoV-2 to someone else.
“From the data we have, it still seems to be rare that an asymptomatic person actually transmits onward to a secondary individual,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO’s COVID-19 technical lead and an infectious disease epidemiologist, said June 8 at a news briefing from the agency’s Geneva headquarters.
This announcement came on the heels of the publication of an analysis in the Annals of Internal Medicine, which suggested that as many as 40-45% of COVID-19 cases may be asymptomatic. In this paper, the authors, Daniel P. Oran, AM, and Eric J. Topol, MD, of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif stated: “The likelihood that approximately 40%-45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic suggests that the virus might have greater potential than previously estimated to spread silently and deeply through human populations.”
"The early data that we have assembled on the prevalence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection suggest that this is a significant factor in the rapid progression of the COVID-19 pandemic," the authors concluded.
Dr. Van Kerkhove also made comments suggesting otherwise on Twitter, citing a new summary by WHO: “@WHO recently published a summary of transmission of #COVID19, incl. symptomatic, pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission.”
She also tweeted the following lines from the WHO summary: “Comprehensive studies on transmission from asymptomatic individuals are difficult to conduct, but the available evidence from contact tracing reported by Member States suggests that asymptomatically-infected individuals are much less likely to transmit the virus than those who develop symptoms.”
In an additional post, Dr. Van Kerkhove added: “In these data, it is important to breakdown truly asymptomatic vs pre-symptomatic vs mildly symptomatic... also to note that the [percentage] reported or estimated to be ‘asymptomatic’ is not the same as the [percentage] that are asymptomatic that actually transmit.”
In the paper published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Mr. Oran and Dr. Topol analyzed data of asymptomatic individuals from 16 cohorts between April 19 and May 26, 2020 – a wide-ranging group consisting of residents of cities, health care workers, individuals in homeless shelters, obstetric patients, residents of a nursing home, crew members of aircraft carriers, passengers on cruise ships, and inmates in correctional facilities. Each cohort had varying rates of asymptomatic or presymptomatic cases..
When residents of Iceland were tested, 43 of 100 individuals who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 did not show symptoms. In Vo’, Italy, 30 of 73 people (41.1%) with positive SARS-CoV-2 test results did not have symptoms in a first round of testing, and 13 of 29 (44.8%) had no symptoms in a second round of testing. Over half of residents of San Francisco’s Mission District who received testing (39 of 74; 52.7%) did not have symptoms, while slightly less than half of Indiana residents tested showed no symptoms (35 of 78; 44.8%).
A majority of 41 individuals (65.9%) who were mostly health care workers at Rutgers University reported no symptoms of COVID-19 at the time of testing. Data from homeless shelters in Boston (129 of 147; 87.7%) and Los Angeles (27 of 43; 62.7%) also showed a high rate of individuals without symptoms. Among 33 obstetric patients in New York City who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, 29 women (87.9%) were asymptomatic during a median 2-day length of stay. In a Washington state nursing facility, 12 of 23 individuals (52.1%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2 without showing symptoms in a first round of testing, with another 15 of 24 residents (62.5%) not showing symptoms in a second round of testing. Of these residents, 24 individuals (88.9%) later went on to show symptoms of COVID-19.
Most of the 783 Greek citizens who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after being evacuated from Spain, Turkey, and the United Kingdom showed no symptoms of COVID-19 (35 of 40; 87.5%). A group of 565 Japanese citizens evacuated from Wuhan, China, had a lower number of cases without initial symptoms – 13 people were positive for SARS-CoV-2, and 4 of 13 (30.8%) had no symptoms.
In closed cohorts, there appeared to also be a high rate of COVID-19 cases without initial symptoms. Of 3,277 inmates from correctional facilities in Arkansas, North Carolina, Ohio, and Virginia, 3,146 individuals (96%) had no symptoms at the time of testing. There was also a large percentage of passengers and crew of the Diamond Princess cruise ship (331 of 712; 46.5%) and an Argentine cruise ship (104 of 128; 81.3%) who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 without symptoms. On the aircraft carrier U.S.S. Theodore Roosevelt, 60% of 856 individuals, while on the French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, nearly 50% of individuals were asymptomatic.
It is difficult to tell the difference between people who are presymptomatic and will later go on to develop symptoms of COVID-19 and those who will remain asymptomatic. “The simple solution to this conundrum is longitudinal testing – that is, repeated observations of the individual over time,” but only 5 of 16 cohorts studied had longitudinal data on individuals, Mr. Oran and Dr. Topol said.
Seth Trueger, MD, an emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, said it was important to see this information all in one place, even if the data isn’t new.
“I think we’ve certainly kind of seen from the beginning there’s some level of asymptomatic and presymptomatic spread,” Dr. Trueger said. “In health care, we’ve been lucky to get those lessons early on and start to think of things like universal masking in hospitals, and unfortunate things like limiting visitors.”
A more nuanced understanding of how SARS-CoV-2 spreads has been difficult to capture, in part because of operating under a shortened time frame and handicapped testing capacity, he noted. “[Even] in the best of possible circumstances, trying to figure out epidemiology in people who don’t have symptoms is really tough,” Dr. Truegar said.
“Even the best studies are still relatively decent samples, and not totally representative,” he added.
Another limitation to capturing accurate data is method of testing. Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction using nasopharyngeal swabs can detect RNA fragments from SARS-CoV-2, which could potentially affect the results. “It’s really hard to know what is actually infected virus versus just fragments of RNA that make the test positive,” Dr. Trueger said.
If the rate of asymptomatic cases is higher than previously thought, it’s a “double-edged sword,” he noted. It may mean the infection fatality rate is lower than predicted, but “even at high levels of what we think community levels might be, we’re far from herd immunity.”
The study authors and Dr. Trueger reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Oran DP, Topol EJ. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jun 3. doi: 10.7326/M20-3012.
This article was updated 6/8/20.
An official with the World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that it appears to be “rare” that an asymptomatic individual can pass SARS-CoV-2 to someone else.
“From the data we have, it still seems to be rare that an asymptomatic person actually transmits onward to a secondary individual,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, WHO’s COVID-19 technical lead and an infectious disease epidemiologist, said June 8 at a news briefing from the agency’s Geneva headquarters.
This announcement came on the heels of the publication of an analysis in the Annals of Internal Medicine, which suggested that as many as 40-45% of COVID-19 cases may be asymptomatic. In this paper, the authors, Daniel P. Oran, AM, and Eric J. Topol, MD, of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif stated: “The likelihood that approximately 40%-45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic suggests that the virus might have greater potential than previously estimated to spread silently and deeply through human populations.”
"The early data that we have assembled on the prevalence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection suggest that this is a significant factor in the rapid progression of the COVID-19 pandemic," the authors concluded.
Dr. Van Kerkhove also made comments suggesting otherwise on Twitter, citing a new summary by WHO: “@WHO recently published a summary of transmission of #COVID19, incl. symptomatic, pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic transmission.”
She also tweeted the following lines from the WHO summary: “Comprehensive studies on transmission from asymptomatic individuals are difficult to conduct, but the available evidence from contact tracing reported by Member States suggests that asymptomatically-infected individuals are much less likely to transmit the virus than those who develop symptoms.”
In an additional post, Dr. Van Kerkhove added: “In these data, it is important to breakdown truly asymptomatic vs pre-symptomatic vs mildly symptomatic... also to note that the [percentage] reported or estimated to be ‘asymptomatic’ is not the same as the [percentage] that are asymptomatic that actually transmit.”
In the paper published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Mr. Oran and Dr. Topol analyzed data of asymptomatic individuals from 16 cohorts between April 19 and May 26, 2020 – a wide-ranging group consisting of residents of cities, health care workers, individuals in homeless shelters, obstetric patients, residents of a nursing home, crew members of aircraft carriers, passengers on cruise ships, and inmates in correctional facilities. Each cohort had varying rates of asymptomatic or presymptomatic cases..
When residents of Iceland were tested, 43 of 100 individuals who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 did not show symptoms. In Vo’, Italy, 30 of 73 people (41.1%) with positive SARS-CoV-2 test results did not have symptoms in a first round of testing, and 13 of 29 (44.8%) had no symptoms in a second round of testing. Over half of residents of San Francisco’s Mission District who received testing (39 of 74; 52.7%) did not have symptoms, while slightly less than half of Indiana residents tested showed no symptoms (35 of 78; 44.8%).
A majority of 41 individuals (65.9%) who were mostly health care workers at Rutgers University reported no symptoms of COVID-19 at the time of testing. Data from homeless shelters in Boston (129 of 147; 87.7%) and Los Angeles (27 of 43; 62.7%) also showed a high rate of individuals without symptoms. Among 33 obstetric patients in New York City who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, 29 women (87.9%) were asymptomatic during a median 2-day length of stay. In a Washington state nursing facility, 12 of 23 individuals (52.1%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2 without showing symptoms in a first round of testing, with another 15 of 24 residents (62.5%) not showing symptoms in a second round of testing. Of these residents, 24 individuals (88.9%) later went on to show symptoms of COVID-19.
Most of the 783 Greek citizens who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after being evacuated from Spain, Turkey, and the United Kingdom showed no symptoms of COVID-19 (35 of 40; 87.5%). A group of 565 Japanese citizens evacuated from Wuhan, China, had a lower number of cases without initial symptoms – 13 people were positive for SARS-CoV-2, and 4 of 13 (30.8%) had no symptoms.
In closed cohorts, there appeared to also be a high rate of COVID-19 cases without initial symptoms. Of 3,277 inmates from correctional facilities in Arkansas, North Carolina, Ohio, and Virginia, 3,146 individuals (96%) had no symptoms at the time of testing. There was also a large percentage of passengers and crew of the Diamond Princess cruise ship (331 of 712; 46.5%) and an Argentine cruise ship (104 of 128; 81.3%) who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 without symptoms. On the aircraft carrier U.S.S. Theodore Roosevelt, 60% of 856 individuals, while on the French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, nearly 50% of individuals were asymptomatic.
It is difficult to tell the difference between people who are presymptomatic and will later go on to develop symptoms of COVID-19 and those who will remain asymptomatic. “The simple solution to this conundrum is longitudinal testing – that is, repeated observations of the individual over time,” but only 5 of 16 cohorts studied had longitudinal data on individuals, Mr. Oran and Dr. Topol said.
Seth Trueger, MD, an emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, said it was important to see this information all in one place, even if the data isn’t new.
“I think we’ve certainly kind of seen from the beginning there’s some level of asymptomatic and presymptomatic spread,” Dr. Trueger said. “In health care, we’ve been lucky to get those lessons early on and start to think of things like universal masking in hospitals, and unfortunate things like limiting visitors.”
A more nuanced understanding of how SARS-CoV-2 spreads has been difficult to capture, in part because of operating under a shortened time frame and handicapped testing capacity, he noted. “[Even] in the best of possible circumstances, trying to figure out epidemiology in people who don’t have symptoms is really tough,” Dr. Truegar said.
“Even the best studies are still relatively decent samples, and not totally representative,” he added.
Another limitation to capturing accurate data is method of testing. Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction using nasopharyngeal swabs can detect RNA fragments from SARS-CoV-2, which could potentially affect the results. “It’s really hard to know what is actually infected virus versus just fragments of RNA that make the test positive,” Dr. Trueger said.
If the rate of asymptomatic cases is higher than previously thought, it’s a “double-edged sword,” he noted. It may mean the infection fatality rate is lower than predicted, but “even at high levels of what we think community levels might be, we’re far from herd immunity.”
The study authors and Dr. Trueger reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Oran DP, Topol EJ. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jun 3. doi: 10.7326/M20-3012.
This article was updated 6/8/20.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
AMA offers resources for front-line physicians
.
The literature include news, advocacy, and other information to help front-line physicians provide care to patients and keep themselves safe “in a rapidly changing environment,” the organization said in a statement.
“The AMA continues to forcefully advocate for [personal protective equipment] and critical policy and regulatory changes needed to address our public health and health system needs. Because so many of the challenges of the pandemic are felt at a practice level, we are also providing new tools and information to help physicians respond,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in the statement.
The COVID-19 physician and practice resources released by the AMA include:
- A Physicians Guide to COVID-19 .
- An AMA COVID-19 online resource center and a COVID-19 FAQ.
- A Quick Guide to Telemedicine in Practice.
- Ethical guidance for physicians .
- Evidence-based resources from the The JAMA Network COVID-19 Resource Center.
- CME for physicians through the JAMA Network’s JN Learning website.
.
The literature include news, advocacy, and other information to help front-line physicians provide care to patients and keep themselves safe “in a rapidly changing environment,” the organization said in a statement.
“The AMA continues to forcefully advocate for [personal protective equipment] and critical policy and regulatory changes needed to address our public health and health system needs. Because so many of the challenges of the pandemic are felt at a practice level, we are also providing new tools and information to help physicians respond,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in the statement.
The COVID-19 physician and practice resources released by the AMA include:
- A Physicians Guide to COVID-19 .
- An AMA COVID-19 online resource center and a COVID-19 FAQ.
- A Quick Guide to Telemedicine in Practice.
- Ethical guidance for physicians .
- Evidence-based resources from the The JAMA Network COVID-19 Resource Center.
- CME for physicians through the JAMA Network’s JN Learning website.
.
The literature include news, advocacy, and other information to help front-line physicians provide care to patients and keep themselves safe “in a rapidly changing environment,” the organization said in a statement.
“The AMA continues to forcefully advocate for [personal protective equipment] and critical policy and regulatory changes needed to address our public health and health system needs. Because so many of the challenges of the pandemic are felt at a practice level, we are also providing new tools and information to help physicians respond,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in the statement.
The COVID-19 physician and practice resources released by the AMA include:
- A Physicians Guide to COVID-19 .
- An AMA COVID-19 online resource center and a COVID-19 FAQ.
- A Quick Guide to Telemedicine in Practice.
- Ethical guidance for physicians .
- Evidence-based resources from the The JAMA Network COVID-19 Resource Center.
- CME for physicians through the JAMA Network’s JN Learning website.
ACP outlines guide for COVID-19 telehealth coding, billing
and for handling clinician and staff absences due to illness or quarantine during the COVID-19 pandemic.
It strongly encourages practices to use telehealth, whenever possible, to mitigate exposure of patients who are sick or at risk because of other underlying conditions and to protect health care workers and the community from the spread of the disease.
The national organization of internists also recommends in the guidance that practices establish protocols and procedures for use by clinicians and all other staff in light of the pandemic.
The billing and coding tips are being offered to help practices deal with the rapidly changing situation surrounding the COVID-19 emergency, according to a statement from the ACP.
The coding-related guidance incorporates changes to a number of telehealth rules for Medicare beneficiaries, announced by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services on March 17.
“Now in a full state of emergency, many Medicare restrictions related to telehealth have been lifted. Patients can be at home, and non-HIPAA compliant technology is allowed. There is no cost sharing for COVID-19 testing. In addition, to encourage use by patients, Medicare is allowing practices to waive cost sharing (copays and deductibles) for all telehealth services,” the organization said in the guidance. It notes, however, that the CMS does not currently reimburse for telephone calls.
The guidance includes details of the new ICD-10 codes, and stresses the importance of using the appropriate codes, given that some service cost-sharing has been waived for COVID-19 testing and treatment.
There is detailed coding guidance for virtual check-in, online evaluation and management, remote monitoring, originating site, and allowed technology and services.
In regard to clinician and staff absence due to illness or quarantine, the ACP says “practices may need to review emergency plans related to telework and to employee and clinician absence.” Among its recommendations are that practices and employers consider temporary adjustments to compensation formulas to accommodate those clinicians who experience a loss of income because they are paid based on production.
The organization emphasizes that, given the rapidly changing availability of testing for COVID-19, practices should contact their local health departments, hospitals, reference labs, or state health authorities to determine the status of their access to testing.
The full list of the ACP’s tips are available here.
Any new guidance for physicians will be posted on the ACP’s COVID-19 resource page.
and for handling clinician and staff absences due to illness or quarantine during the COVID-19 pandemic.
It strongly encourages practices to use telehealth, whenever possible, to mitigate exposure of patients who are sick or at risk because of other underlying conditions and to protect health care workers and the community from the spread of the disease.
The national organization of internists also recommends in the guidance that practices establish protocols and procedures for use by clinicians and all other staff in light of the pandemic.
The billing and coding tips are being offered to help practices deal with the rapidly changing situation surrounding the COVID-19 emergency, according to a statement from the ACP.
The coding-related guidance incorporates changes to a number of telehealth rules for Medicare beneficiaries, announced by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services on March 17.
“Now in a full state of emergency, many Medicare restrictions related to telehealth have been lifted. Patients can be at home, and non-HIPAA compliant technology is allowed. There is no cost sharing for COVID-19 testing. In addition, to encourage use by patients, Medicare is allowing practices to waive cost sharing (copays and deductibles) for all telehealth services,” the organization said in the guidance. It notes, however, that the CMS does not currently reimburse for telephone calls.
The guidance includes details of the new ICD-10 codes, and stresses the importance of using the appropriate codes, given that some service cost-sharing has been waived for COVID-19 testing and treatment.
There is detailed coding guidance for virtual check-in, online evaluation and management, remote monitoring, originating site, and allowed technology and services.
In regard to clinician and staff absence due to illness or quarantine, the ACP says “practices may need to review emergency plans related to telework and to employee and clinician absence.” Among its recommendations are that practices and employers consider temporary adjustments to compensation formulas to accommodate those clinicians who experience a loss of income because they are paid based on production.
The organization emphasizes that, given the rapidly changing availability of testing for COVID-19, practices should contact their local health departments, hospitals, reference labs, or state health authorities to determine the status of their access to testing.
The full list of the ACP’s tips are available here.
Any new guidance for physicians will be posted on the ACP’s COVID-19 resource page.
and for handling clinician and staff absences due to illness or quarantine during the COVID-19 pandemic.
It strongly encourages practices to use telehealth, whenever possible, to mitigate exposure of patients who are sick or at risk because of other underlying conditions and to protect health care workers and the community from the spread of the disease.
The national organization of internists also recommends in the guidance that practices establish protocols and procedures for use by clinicians and all other staff in light of the pandemic.
The billing and coding tips are being offered to help practices deal with the rapidly changing situation surrounding the COVID-19 emergency, according to a statement from the ACP.
The coding-related guidance incorporates changes to a number of telehealth rules for Medicare beneficiaries, announced by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services on March 17.
“Now in a full state of emergency, many Medicare restrictions related to telehealth have been lifted. Patients can be at home, and non-HIPAA compliant technology is allowed. There is no cost sharing for COVID-19 testing. In addition, to encourage use by patients, Medicare is allowing practices to waive cost sharing (copays and deductibles) for all telehealth services,” the organization said in the guidance. It notes, however, that the CMS does not currently reimburse for telephone calls.
The guidance includes details of the new ICD-10 codes, and stresses the importance of using the appropriate codes, given that some service cost-sharing has been waived for COVID-19 testing and treatment.
There is detailed coding guidance for virtual check-in, online evaluation and management, remote monitoring, originating site, and allowed technology and services.
In regard to clinician and staff absence due to illness or quarantine, the ACP says “practices may need to review emergency plans related to telework and to employee and clinician absence.” Among its recommendations are that practices and employers consider temporary adjustments to compensation formulas to accommodate those clinicians who experience a loss of income because they are paid based on production.
The organization emphasizes that, given the rapidly changing availability of testing for COVID-19, practices should contact their local health departments, hospitals, reference labs, or state health authorities to determine the status of their access to testing.
The full list of the ACP’s tips are available here.
Any new guidance for physicians will be posted on the ACP’s COVID-19 resource page.