User login
Management, Evaluation of Chronic Itch in Older Adults
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
‘Doesn’t Fit Anything I Trained for’: Committee Examines Treatment for Chronic Illness After Lyme Disease
WASHINGTON — Advancing treatment for what has been variably called chronic Lyme and posttreatment Lyme disease (PTLD) is under the eyes of a National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) committee of experts for the first time — a year after the NASEM shone a spotlight on the need to accelerate research on chronic illnesses that follow known or suspected infections.
The committee will not make recommendations on specific approaches to diagnosis and treatment when it issues a report in early 2025 but will instead present “consensus findings” on treatment for chronic illness associated with Lyme disease, including recommendations for advancing treatment.
It’s an area void of the US Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies, void of any consensus on the off-label use of medications, and without any current standard of care or proven mechanisms and pathophysiology, said John Aucott, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Medicine Lyme Disease Clinical Research Center, Baltimore, one of the invited speakers at a public meeting held by the NASEM in Washington, DC.
“The best way to look at this illness is not from the silos of infectious disease or the silos of rheumatology; you have to look across disciplines,” Dr. Aucott, also associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, told the committee. “The story doesn’t fit anything I trained for in my infectious disease fellowship. Even today, I’d posit that PTLD is like an island — it’s still not connected to a lot of the mainstream of medicine.”
Rhisa Parera, who wrote and directed a 2021 documentary, Your Labs Are Normal, was one of several invited speakers who amplified the patient voice. Starting around age 7, she had pain in her knees, spine, and hips and vivid nightmares. In high school, she developed gastrointestinal issues, and in college, she developed debilitating neurologic symptoms.
Depression was her eventual diagnosis after having seen “every specialist in the book,” she said. At age 29, she received a positive western blot test and a Lyme disease diagnosis, at which point “I was prescribed 4 weeks of doxycycline and left in the dark,” the 34-year-old Black patient told the committee. Her health improved only after she began working with an “LLMD,” or Lyme-literate medical doctor (a term used in the patient community), while she lived with her mother and did not work, she said.
“I don’t share my Lyme disease history with other doctors. It’s pointless when you have those who will laugh at you, say you’re fine if you were treated, or just deny the disease completely,” Ms. Parera said. “We need this to be taught in medical school. It’s a literal emergency.”
Incidence and Potential Mechanisms
Limited research has suggested that 10%-20% of patients with Lyme disease develop persistent symptoms after standard antibiotic treatment advised by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Dr. Aucott said. (On its web page on chronic symptoms, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention presents a more conservative range of 5%-10%.)
His own prospective cohort study at Johns Hopkins, published in 2022, found that 13.7% of 234 patients with prior Lyme disease met symptom and functional impact criteria for PTLD, compared with 4.1% of 49 participants without a history of Lyme disease — a statistically significant difference that he said should “put to rest” the question of “is it real?”
PTLD is the research case definition proposed by the IDSA in 2006; it requires that patients have prior documented Lyme disease, no other specific comorbidities, and specific symptoms (fatigue, widespread musculoskeletal pain, and/or cognitive difficulties) causing significant functional impact at least 6 months from their initial diagnosis and treatment.
In the real world, however, where diagnostics for acute Lyme disease are often inaccurate, erythema migrans is often absent, and the symptomatology of Lyme IACI is variable (and where there is no approved laboratory test or objective biomarker for diagnosing Lyme IACI), PTLD represents only a subset of a broader, heterogeneous population with persistent symptoms.
The term “Lyme IACI,” pronounced “Lyme eye-ACK-ee” at the meeting, builds on conversations at the 2023 NASEM workshop on infection-associated chronic illnesses and “encompasses a variety of terms that are used,” including PTLD, PTLD syndrome, persistent Lyme disease, and chronic Lyme disease, according to committee documents. Symptoms are distinct from the known complications of Lyme disease, such as arthritis or carditis.
The findings from Dr. Aucott’s SLICE cohort likely represent “the best outcome,” he said. They’re “probably not generalizable to a community setting where we see lots of missed diagnoses and delayed diagnoses,” as well as other tick-borne coinfections.
One of the challenges in designing future trials, in fact, relates to enrollment criteria and whether to use strict inclusion and exclusion criteria associated with the IDSA definition or take a broader approach to trial enrollment, he and others said. “You want to enroll patients for whom there’s no controversy that they’ve had Lyme infection ... for a study people believe in,” Dr. Aucott said during a discussion period, noting that it’s typical to screen over 100 patients to find one enrollee. “But it’s a tension we’re having.”
Timothy Sellati, PhD, chief scientific officer of the Global Lyme Alliance, urged change. “It’s really important to try to figure out how to alter our thinking on identifying and diagnosing chronic Lyme patients because they need to be recruited into clinical trials,” he said during his presentation.
“We think the best way to do this is to [develop and] employ composite diagnostic testing” that looks at unique Borrelia signatures (eg, protein, DNA, RNA, or metabolites), genetic and/or epigenetic signatures, inflammation signatures, T-cell-independent antibody signatures, and other elements, Dr. Sellati said.
Researchers designing treatment trials also face unknowns, Dr. Aucott and others said, about the role of potential mechanisms of Lyme IACI, from persistent Borrelia burgdorferi (or Borrelia mayonii) infection or the persistence of bacterial remnants (eg, nucleic acids or peptidoglycans) to infection-triggered pathology such as persistent immune dysregulation, chronic inflammation, autoimmunity, microbiome alterations, and dysautonomia and other neural network alterations.
The NASEM’s spotlight on Lyme IACI follows its long COVID-driven push last year to advance a common research agenda in infection-associated chronic illnesses. Investigators see common symptoms and potential shared mechanisms between long COVID, Lyme IACI, myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), and other complex chronic illnesses following infections.
At the Lyme IACI meeting, invited speakers described parts of the research landscape. Avindra Nath, MD, of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, for instance, described a recently published deep phenotyping study of 17 patients with ME/CFS that found decreased central catecholamine synthesis, circuit dysfunction of integrative brain regions, and immune profiling differences (eg, defects in B-cell maturation or T-cell exhaustion), compared with matched controls, that suggest the persistence of microbial antigens.
And John Leong, MD, PhD, of Tufts University, Boston, described his lab’s focus on understanding the microbe-host interactions that enable bloodstream dissemination and tissue invasion of B burgdorferi to take hold, increasing the risk for persistent symptoms. Other research at Tufts, he noted during a discussion period, has demonstrated the persistence of B burgdorferi to antibiotics in microtiter dishes. “Those organisms that survive are really difficult to eradicate in vitro,” Dr. Leong said.
Other physician investigators described research on nociplastic pain — a category of pain that can be triggered by infections, causing both amplified sensory processing and augmented central nervous system pain — and on whether reactivation of the Epstein-Barr virus could potentiate autoimmunity in the context of Borrelia infection.
Researchers are ready to test therapies while pathophysiology is unraveled — provided there is funding, Dr. Aucott said. The Clinical Trials Network for Lyme and Other Tick-Borne Diseases, coordinated by Brian Fallon, MD, of Columbia University, New York City, and funded several years ago by the Steven & Alexandra Cohen Foundation, has a slate of small pilot studies underway or being planned that address potential mechanisms (eg, studies of pulse intravenous ceftriaxone, tetracycline, transauricular vagus nerve stimulation, and mast cell modulation). And should full multisite trials be designed and funded, the network is ready with an infrastructure.
Need for Patient-Centered Outcomes
Persistent symptomatology is on the NIH’s radar screen. Efforts to understand causes were part of a strategic tick-borne disease research plan developed by the NIH in 2019. And in 2023, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) funded seven projects addressing persistent symptoms that will run through 2028, C. Benjamin Beard, PhD, deputy division director of the CDC’s Division of Vector-Borne Disease, said at the NASEM committee meeting.
Patient advocates maintained that too much emphasis is placed on tick biology and pathophysiology. When Wendy Adams, research grant director and advisory board member of the Bay Area Lyme Foundation, and a colleague analyzed NIAID tick-borne disease funding from 2013 to 2021, they found that 75% of the funding went toward basic research, 15% to translational research, and “only 3% went to clinical research,” Ms. Adams told the committee.
Only 3% of the basic research budget was spent on coinfections, she said, and only 1% was spent on neurologic disease associated with tick-borne infections, both of which are survey-defined patient priorities. Moreover, “12% of the overall NIAID [tick-borne diseases] budget was spent on tick biology,” she said.
Research needs to involve community physicians who are utilizing the guidelines and approaches of the International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society to treat most patients with Lyme IACI, Ms. Adams said. “They have data to be mined,” she said, as does LymeDisease.org, which maintains a patient registry, MyLymeData, with over 18,000 patients. The organization has published two treatment studies, including one on antibiotic treatment response.
Lorraine Johnson, JD, MBA, CEO of LymeDisease.org and principal investigator of MyLymeData, stressed the importance of using patient-centered outcomes that incorporate minimal clinically important differences (MCIDs). “A change in the SF-36 score [without consideration of MCIDs] is not inherently important or meaningful to patients,” she said, referring to the SF-36 survey of health-related quality of life.
“This may seem like an esoteric issue, but two of the four clinical trials done [on retreatment of] persistent Lyme disease used the SF-36 as their outcome measure, and those studies, led by [Mark] Klempner, concluded that retreatment was not effective,” Ms. Johnson said. “Patients have been and continue to be harmed by [this research] because they’re told by physicians that antibiotics don’t work.”
A 2012 biostatistical review of these four RCTs — trials that helped inform the 2006 IDSA treatment guidelines — concluded that the Klempner studies “set the bar for treatment success too high,” Ms. Johnson said. Three of the four trials were likely underpowered to detect clinically meaningful treatment effects, the review also found.
The NASEM committee will hold additional public meetings and review a wide range of literature through this year. The formation of the committee was recommended by the US Department of Health and Human Services Tick-Borne Disease Working Group that was established by Congress in 2016 and concluded its work in 2022. The committee’s work is funded by the Cohen Foundation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Advancing treatment for what has been variably called chronic Lyme and posttreatment Lyme disease (PTLD) is under the eyes of a National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) committee of experts for the first time — a year after the NASEM shone a spotlight on the need to accelerate research on chronic illnesses that follow known or suspected infections.
The committee will not make recommendations on specific approaches to diagnosis and treatment when it issues a report in early 2025 but will instead present “consensus findings” on treatment for chronic illness associated with Lyme disease, including recommendations for advancing treatment.
It’s an area void of the US Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies, void of any consensus on the off-label use of medications, and without any current standard of care or proven mechanisms and pathophysiology, said John Aucott, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Medicine Lyme Disease Clinical Research Center, Baltimore, one of the invited speakers at a public meeting held by the NASEM in Washington, DC.
“The best way to look at this illness is not from the silos of infectious disease or the silos of rheumatology; you have to look across disciplines,” Dr. Aucott, also associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, told the committee. “The story doesn’t fit anything I trained for in my infectious disease fellowship. Even today, I’d posit that PTLD is like an island — it’s still not connected to a lot of the mainstream of medicine.”
Rhisa Parera, who wrote and directed a 2021 documentary, Your Labs Are Normal, was one of several invited speakers who amplified the patient voice. Starting around age 7, she had pain in her knees, spine, and hips and vivid nightmares. In high school, she developed gastrointestinal issues, and in college, she developed debilitating neurologic symptoms.
Depression was her eventual diagnosis after having seen “every specialist in the book,” she said. At age 29, she received a positive western blot test and a Lyme disease diagnosis, at which point “I was prescribed 4 weeks of doxycycline and left in the dark,” the 34-year-old Black patient told the committee. Her health improved only after she began working with an “LLMD,” or Lyme-literate medical doctor (a term used in the patient community), while she lived with her mother and did not work, she said.
“I don’t share my Lyme disease history with other doctors. It’s pointless when you have those who will laugh at you, say you’re fine if you were treated, or just deny the disease completely,” Ms. Parera said. “We need this to be taught in medical school. It’s a literal emergency.”
Incidence and Potential Mechanisms
Limited research has suggested that 10%-20% of patients with Lyme disease develop persistent symptoms after standard antibiotic treatment advised by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Dr. Aucott said. (On its web page on chronic symptoms, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention presents a more conservative range of 5%-10%.)
His own prospective cohort study at Johns Hopkins, published in 2022, found that 13.7% of 234 patients with prior Lyme disease met symptom and functional impact criteria for PTLD, compared with 4.1% of 49 participants without a history of Lyme disease — a statistically significant difference that he said should “put to rest” the question of “is it real?”
PTLD is the research case definition proposed by the IDSA in 2006; it requires that patients have prior documented Lyme disease, no other specific comorbidities, and specific symptoms (fatigue, widespread musculoskeletal pain, and/or cognitive difficulties) causing significant functional impact at least 6 months from their initial diagnosis and treatment.
In the real world, however, where diagnostics for acute Lyme disease are often inaccurate, erythema migrans is often absent, and the symptomatology of Lyme IACI is variable (and where there is no approved laboratory test or objective biomarker for diagnosing Lyme IACI), PTLD represents only a subset of a broader, heterogeneous population with persistent symptoms.
The term “Lyme IACI,” pronounced “Lyme eye-ACK-ee” at the meeting, builds on conversations at the 2023 NASEM workshop on infection-associated chronic illnesses and “encompasses a variety of terms that are used,” including PTLD, PTLD syndrome, persistent Lyme disease, and chronic Lyme disease, according to committee documents. Symptoms are distinct from the known complications of Lyme disease, such as arthritis or carditis.
The findings from Dr. Aucott’s SLICE cohort likely represent “the best outcome,” he said. They’re “probably not generalizable to a community setting where we see lots of missed diagnoses and delayed diagnoses,” as well as other tick-borne coinfections.
One of the challenges in designing future trials, in fact, relates to enrollment criteria and whether to use strict inclusion and exclusion criteria associated with the IDSA definition or take a broader approach to trial enrollment, he and others said. “You want to enroll patients for whom there’s no controversy that they’ve had Lyme infection ... for a study people believe in,” Dr. Aucott said during a discussion period, noting that it’s typical to screen over 100 patients to find one enrollee. “But it’s a tension we’re having.”
Timothy Sellati, PhD, chief scientific officer of the Global Lyme Alliance, urged change. “It’s really important to try to figure out how to alter our thinking on identifying and diagnosing chronic Lyme patients because they need to be recruited into clinical trials,” he said during his presentation.
“We think the best way to do this is to [develop and] employ composite diagnostic testing” that looks at unique Borrelia signatures (eg, protein, DNA, RNA, or metabolites), genetic and/or epigenetic signatures, inflammation signatures, T-cell-independent antibody signatures, and other elements, Dr. Sellati said.
Researchers designing treatment trials also face unknowns, Dr. Aucott and others said, about the role of potential mechanisms of Lyme IACI, from persistent Borrelia burgdorferi (or Borrelia mayonii) infection or the persistence of bacterial remnants (eg, nucleic acids or peptidoglycans) to infection-triggered pathology such as persistent immune dysregulation, chronic inflammation, autoimmunity, microbiome alterations, and dysautonomia and other neural network alterations.
The NASEM’s spotlight on Lyme IACI follows its long COVID-driven push last year to advance a common research agenda in infection-associated chronic illnesses. Investigators see common symptoms and potential shared mechanisms between long COVID, Lyme IACI, myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), and other complex chronic illnesses following infections.
At the Lyme IACI meeting, invited speakers described parts of the research landscape. Avindra Nath, MD, of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, for instance, described a recently published deep phenotyping study of 17 patients with ME/CFS that found decreased central catecholamine synthesis, circuit dysfunction of integrative brain regions, and immune profiling differences (eg, defects in B-cell maturation or T-cell exhaustion), compared with matched controls, that suggest the persistence of microbial antigens.
And John Leong, MD, PhD, of Tufts University, Boston, described his lab’s focus on understanding the microbe-host interactions that enable bloodstream dissemination and tissue invasion of B burgdorferi to take hold, increasing the risk for persistent symptoms. Other research at Tufts, he noted during a discussion period, has demonstrated the persistence of B burgdorferi to antibiotics in microtiter dishes. “Those organisms that survive are really difficult to eradicate in vitro,” Dr. Leong said.
Other physician investigators described research on nociplastic pain — a category of pain that can be triggered by infections, causing both amplified sensory processing and augmented central nervous system pain — and on whether reactivation of the Epstein-Barr virus could potentiate autoimmunity in the context of Borrelia infection.
Researchers are ready to test therapies while pathophysiology is unraveled — provided there is funding, Dr. Aucott said. The Clinical Trials Network for Lyme and Other Tick-Borne Diseases, coordinated by Brian Fallon, MD, of Columbia University, New York City, and funded several years ago by the Steven & Alexandra Cohen Foundation, has a slate of small pilot studies underway or being planned that address potential mechanisms (eg, studies of pulse intravenous ceftriaxone, tetracycline, transauricular vagus nerve stimulation, and mast cell modulation). And should full multisite trials be designed and funded, the network is ready with an infrastructure.
Need for Patient-Centered Outcomes
Persistent symptomatology is on the NIH’s radar screen. Efforts to understand causes were part of a strategic tick-borne disease research plan developed by the NIH in 2019. And in 2023, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) funded seven projects addressing persistent symptoms that will run through 2028, C. Benjamin Beard, PhD, deputy division director of the CDC’s Division of Vector-Borne Disease, said at the NASEM committee meeting.
Patient advocates maintained that too much emphasis is placed on tick biology and pathophysiology. When Wendy Adams, research grant director and advisory board member of the Bay Area Lyme Foundation, and a colleague analyzed NIAID tick-borne disease funding from 2013 to 2021, they found that 75% of the funding went toward basic research, 15% to translational research, and “only 3% went to clinical research,” Ms. Adams told the committee.
Only 3% of the basic research budget was spent on coinfections, she said, and only 1% was spent on neurologic disease associated with tick-borne infections, both of which are survey-defined patient priorities. Moreover, “12% of the overall NIAID [tick-borne diseases] budget was spent on tick biology,” she said.
Research needs to involve community physicians who are utilizing the guidelines and approaches of the International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society to treat most patients with Lyme IACI, Ms. Adams said. “They have data to be mined,” she said, as does LymeDisease.org, which maintains a patient registry, MyLymeData, with over 18,000 patients. The organization has published two treatment studies, including one on antibiotic treatment response.
Lorraine Johnson, JD, MBA, CEO of LymeDisease.org and principal investigator of MyLymeData, stressed the importance of using patient-centered outcomes that incorporate minimal clinically important differences (MCIDs). “A change in the SF-36 score [without consideration of MCIDs] is not inherently important or meaningful to patients,” she said, referring to the SF-36 survey of health-related quality of life.
“This may seem like an esoteric issue, but two of the four clinical trials done [on retreatment of] persistent Lyme disease used the SF-36 as their outcome measure, and those studies, led by [Mark] Klempner, concluded that retreatment was not effective,” Ms. Johnson said. “Patients have been and continue to be harmed by [this research] because they’re told by physicians that antibiotics don’t work.”
A 2012 biostatistical review of these four RCTs — trials that helped inform the 2006 IDSA treatment guidelines — concluded that the Klempner studies “set the bar for treatment success too high,” Ms. Johnson said. Three of the four trials were likely underpowered to detect clinically meaningful treatment effects, the review also found.
The NASEM committee will hold additional public meetings and review a wide range of literature through this year. The formation of the committee was recommended by the US Department of Health and Human Services Tick-Borne Disease Working Group that was established by Congress in 2016 and concluded its work in 2022. The committee’s work is funded by the Cohen Foundation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Advancing treatment for what has been variably called chronic Lyme and posttreatment Lyme disease (PTLD) is under the eyes of a National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) committee of experts for the first time — a year after the NASEM shone a spotlight on the need to accelerate research on chronic illnesses that follow known or suspected infections.
The committee will not make recommendations on specific approaches to diagnosis and treatment when it issues a report in early 2025 but will instead present “consensus findings” on treatment for chronic illness associated with Lyme disease, including recommendations for advancing treatment.
It’s an area void of the US Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies, void of any consensus on the off-label use of medications, and without any current standard of care or proven mechanisms and pathophysiology, said John Aucott, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Medicine Lyme Disease Clinical Research Center, Baltimore, one of the invited speakers at a public meeting held by the NASEM in Washington, DC.
“The best way to look at this illness is not from the silos of infectious disease or the silos of rheumatology; you have to look across disciplines,” Dr. Aucott, also associate professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, told the committee. “The story doesn’t fit anything I trained for in my infectious disease fellowship. Even today, I’d posit that PTLD is like an island — it’s still not connected to a lot of the mainstream of medicine.”
Rhisa Parera, who wrote and directed a 2021 documentary, Your Labs Are Normal, was one of several invited speakers who amplified the patient voice. Starting around age 7, she had pain in her knees, spine, and hips and vivid nightmares. In high school, she developed gastrointestinal issues, and in college, she developed debilitating neurologic symptoms.
Depression was her eventual diagnosis after having seen “every specialist in the book,” she said. At age 29, she received a positive western blot test and a Lyme disease diagnosis, at which point “I was prescribed 4 weeks of doxycycline and left in the dark,” the 34-year-old Black patient told the committee. Her health improved only after she began working with an “LLMD,” or Lyme-literate medical doctor (a term used in the patient community), while she lived with her mother and did not work, she said.
“I don’t share my Lyme disease history with other doctors. It’s pointless when you have those who will laugh at you, say you’re fine if you were treated, or just deny the disease completely,” Ms. Parera said. “We need this to be taught in medical school. It’s a literal emergency.”
Incidence and Potential Mechanisms
Limited research has suggested that 10%-20% of patients with Lyme disease develop persistent symptoms after standard antibiotic treatment advised by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), Dr. Aucott said. (On its web page on chronic symptoms, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention presents a more conservative range of 5%-10%.)
His own prospective cohort study at Johns Hopkins, published in 2022, found that 13.7% of 234 patients with prior Lyme disease met symptom and functional impact criteria for PTLD, compared with 4.1% of 49 participants without a history of Lyme disease — a statistically significant difference that he said should “put to rest” the question of “is it real?”
PTLD is the research case definition proposed by the IDSA in 2006; it requires that patients have prior documented Lyme disease, no other specific comorbidities, and specific symptoms (fatigue, widespread musculoskeletal pain, and/or cognitive difficulties) causing significant functional impact at least 6 months from their initial diagnosis and treatment.
In the real world, however, where diagnostics for acute Lyme disease are often inaccurate, erythema migrans is often absent, and the symptomatology of Lyme IACI is variable (and where there is no approved laboratory test or objective biomarker for diagnosing Lyme IACI), PTLD represents only a subset of a broader, heterogeneous population with persistent symptoms.
The term “Lyme IACI,” pronounced “Lyme eye-ACK-ee” at the meeting, builds on conversations at the 2023 NASEM workshop on infection-associated chronic illnesses and “encompasses a variety of terms that are used,” including PTLD, PTLD syndrome, persistent Lyme disease, and chronic Lyme disease, according to committee documents. Symptoms are distinct from the known complications of Lyme disease, such as arthritis or carditis.
The findings from Dr. Aucott’s SLICE cohort likely represent “the best outcome,” he said. They’re “probably not generalizable to a community setting where we see lots of missed diagnoses and delayed diagnoses,” as well as other tick-borne coinfections.
One of the challenges in designing future trials, in fact, relates to enrollment criteria and whether to use strict inclusion and exclusion criteria associated with the IDSA definition or take a broader approach to trial enrollment, he and others said. “You want to enroll patients for whom there’s no controversy that they’ve had Lyme infection ... for a study people believe in,” Dr. Aucott said during a discussion period, noting that it’s typical to screen over 100 patients to find one enrollee. “But it’s a tension we’re having.”
Timothy Sellati, PhD, chief scientific officer of the Global Lyme Alliance, urged change. “It’s really important to try to figure out how to alter our thinking on identifying and diagnosing chronic Lyme patients because they need to be recruited into clinical trials,” he said during his presentation.
“We think the best way to do this is to [develop and] employ composite diagnostic testing” that looks at unique Borrelia signatures (eg, protein, DNA, RNA, or metabolites), genetic and/or epigenetic signatures, inflammation signatures, T-cell-independent antibody signatures, and other elements, Dr. Sellati said.
Researchers designing treatment trials also face unknowns, Dr. Aucott and others said, about the role of potential mechanisms of Lyme IACI, from persistent Borrelia burgdorferi (or Borrelia mayonii) infection or the persistence of bacterial remnants (eg, nucleic acids or peptidoglycans) to infection-triggered pathology such as persistent immune dysregulation, chronic inflammation, autoimmunity, microbiome alterations, and dysautonomia and other neural network alterations.
The NASEM’s spotlight on Lyme IACI follows its long COVID-driven push last year to advance a common research agenda in infection-associated chronic illnesses. Investigators see common symptoms and potential shared mechanisms between long COVID, Lyme IACI, myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), and other complex chronic illnesses following infections.
At the Lyme IACI meeting, invited speakers described parts of the research landscape. Avindra Nath, MD, of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, for instance, described a recently published deep phenotyping study of 17 patients with ME/CFS that found decreased central catecholamine synthesis, circuit dysfunction of integrative brain regions, and immune profiling differences (eg, defects in B-cell maturation or T-cell exhaustion), compared with matched controls, that suggest the persistence of microbial antigens.
And John Leong, MD, PhD, of Tufts University, Boston, described his lab’s focus on understanding the microbe-host interactions that enable bloodstream dissemination and tissue invasion of B burgdorferi to take hold, increasing the risk for persistent symptoms. Other research at Tufts, he noted during a discussion period, has demonstrated the persistence of B burgdorferi to antibiotics in microtiter dishes. “Those organisms that survive are really difficult to eradicate in vitro,” Dr. Leong said.
Other physician investigators described research on nociplastic pain — a category of pain that can be triggered by infections, causing both amplified sensory processing and augmented central nervous system pain — and on whether reactivation of the Epstein-Barr virus could potentiate autoimmunity in the context of Borrelia infection.
Researchers are ready to test therapies while pathophysiology is unraveled — provided there is funding, Dr. Aucott said. The Clinical Trials Network for Lyme and Other Tick-Borne Diseases, coordinated by Brian Fallon, MD, of Columbia University, New York City, and funded several years ago by the Steven & Alexandra Cohen Foundation, has a slate of small pilot studies underway or being planned that address potential mechanisms (eg, studies of pulse intravenous ceftriaxone, tetracycline, transauricular vagus nerve stimulation, and mast cell modulation). And should full multisite trials be designed and funded, the network is ready with an infrastructure.
Need for Patient-Centered Outcomes
Persistent symptomatology is on the NIH’s radar screen. Efforts to understand causes were part of a strategic tick-borne disease research plan developed by the NIH in 2019. And in 2023, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) funded seven projects addressing persistent symptoms that will run through 2028, C. Benjamin Beard, PhD, deputy division director of the CDC’s Division of Vector-Borne Disease, said at the NASEM committee meeting.
Patient advocates maintained that too much emphasis is placed on tick biology and pathophysiology. When Wendy Adams, research grant director and advisory board member of the Bay Area Lyme Foundation, and a colleague analyzed NIAID tick-borne disease funding from 2013 to 2021, they found that 75% of the funding went toward basic research, 15% to translational research, and “only 3% went to clinical research,” Ms. Adams told the committee.
Only 3% of the basic research budget was spent on coinfections, she said, and only 1% was spent on neurologic disease associated with tick-borne infections, both of which are survey-defined patient priorities. Moreover, “12% of the overall NIAID [tick-borne diseases] budget was spent on tick biology,” she said.
Research needs to involve community physicians who are utilizing the guidelines and approaches of the International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society to treat most patients with Lyme IACI, Ms. Adams said. “They have data to be mined,” she said, as does LymeDisease.org, which maintains a patient registry, MyLymeData, with over 18,000 patients. The organization has published two treatment studies, including one on antibiotic treatment response.
Lorraine Johnson, JD, MBA, CEO of LymeDisease.org and principal investigator of MyLymeData, stressed the importance of using patient-centered outcomes that incorporate minimal clinically important differences (MCIDs). “A change in the SF-36 score [without consideration of MCIDs] is not inherently important or meaningful to patients,” she said, referring to the SF-36 survey of health-related quality of life.
“This may seem like an esoteric issue, but two of the four clinical trials done [on retreatment of] persistent Lyme disease used the SF-36 as their outcome measure, and those studies, led by [Mark] Klempner, concluded that retreatment was not effective,” Ms. Johnson said. “Patients have been and continue to be harmed by [this research] because they’re told by physicians that antibiotics don’t work.”
A 2012 biostatistical review of these four RCTs — trials that helped inform the 2006 IDSA treatment guidelines — concluded that the Klempner studies “set the bar for treatment success too high,” Ms. Johnson said. Three of the four trials were likely underpowered to detect clinically meaningful treatment effects, the review also found.
The NASEM committee will hold additional public meetings and review a wide range of literature through this year. The formation of the committee was recommended by the US Department of Health and Human Services Tick-Borne Disease Working Group that was established by Congress in 2016 and concluded its work in 2022. The committee’s work is funded by the Cohen Foundation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Dermatoporosis in Older Adults: A Condition That Requires Holistic, Creative Management
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
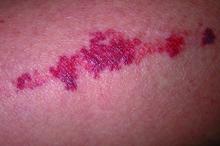
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — and conveys the skin’s vulnerability to serious medical complications, said Adam Friedman, MD, at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in the older patient.
Key features of dermatoporosis include atrophic skin, solar purpura, white pseudoscars, easily acquired skin lacerations and tears, bruises, and delayed healing. “We’re going to see more of this, and it will more and more be a chief complaint of patients,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University (GWU) in Washington, and co-chair of the meeting. GWU hosted the conference, describing it as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Dermatoporosis was described in the literature in 2007 by dermatologists at the University of Geneva in Switzerland. “It is not only a cosmetic problem,” Dr. Friedman said. “This is a medical problem ... which can absolutely lead to comorbidities [such as deep dissecting hematomas] that are a huge strain on the healthcare system.”
Dermatologists can meet the moment with holistic, creative combination treatment and counseling approaches aimed at improving the mechanical strength of skin and preventing potential complications in older patients, Dr. Friedman said at the meeting.
He described the case of a 76-year-old woman who presented with dermatoporosis on her arms involving pronounced skin atrophy, solar purpura, and a small covered laceration. “This was a patient who was both devastated by the appearance” and impacted by the pain and burden of dressing frequent wounds, said Dr. Friedman, who is also the director of the Residency Program, of Translational Research, and of Supportive Oncodermatology, all within the Department of Dermatology at GWU.
With 11 months of topical treatment that included daily application of calcipotriene 0.05% ointment and nightly application of tazarotene 0.045% lotion and oral supplementation with 1000-mg vitamin C twice daily and 1000-mg citrus bioflavonoid complex daily, as well as no changes to the medications she took for various comorbidities, the solar purpura improved significantly and “we made a huge difference in the integrity of her skin,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also described this case in a recently published article in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology titled “What’s Old Is New: An Emerging Focus on Dermatoporosis”.
Likely Pathophysiology
Advancing age and chronic ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure are the chief drivers of dermatoporosis. In addition to UVA and UVB light, other secondary drivers include genetic susceptibility, topical and systematic corticosteroid use, and anticoagulant treatment.
Its pathogenesis is not well described in the literature but is easy to envision, Dr. Friedman said. For one, both advancing age and exposure to UV light lead to a reduction in hygroscopic glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronate (HA), and the impact of this diminishment is believed to go “beyond [the loss of] buoyancy,” he noted. Researchers have “been showing these are not just water-loving molecules, they also have some biologic properties” relating to keratinocyte production and epidermal turnover that appear to be intricately linked to the pathogenesis of dermatoporosis.
HAs have been shown to interact with the cell surface receptor CD44 to stimulate keratinocyte proliferation, and low levels of CD44 have been reported in skin with dermatoporosis compared with a younger control population. (A newly characterized organelle, the hyaluronosome, serves as an HA factory and contains CD44 and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor, Dr. Friedman noted. Inadequate functioning may be involved in skin atrophy.)
Advancing age also brings an increase in matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)–1, –2, and –3, which are “the demolition workers of the skin,” and downregulation of a tissue inhibitor of MMPs, he said.
Adding insult to injury, dermis-penetrating UVA also activates MMPs, “obliterating collagen and elastin.” UVB generates DNA photoproducts, including oxidative stress and damaging skin cell DNA. “That UV light induces breakdown [of the skin] through different mechanisms and inhibits buildup is a simple concept I think our patients can understand,” Dr. Friedman said.
Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.
Skin Injury and Wound Prevention
In addition to recommending gentle skin cleansers and daily moisturizing, dermatologists should talk to their older patients with dermatoporosis about their home environments. “What is it like? Is there furniture with sharp edges?” Dr. Friedman advised. If so, could they use sleeves or protectors on their arms or legs “to protect against injury?”
In a later meeting session about lower-extremity wounds on geriatric patients, Michael Stempel, DPM, assistant professor of medicine and surgery and chief of podiatry at GWU, said that he was happy to hear the term dermatoporosis being used because like diabetes, it’s a risk factor for developing lower-extremity wounds and poor wound healing.
He shared the case of an older woman with dermatoporosis who “tripped and skinned her knee against a step and then self-treated it for over a month by pouring hydrogen peroxide over it and letting air get to it.” The wound developed into “full-thickness tissue loss,” said Dr. Stempel, also medical director of the Wound Healing and Limb Preservation Center at GWU Hospital.
Misperceptions are common among older patients about how a simple wound should be managed; for instance, the adage “just let it get air” is not uncommon. This makes anticipatory guidance about basic wound care — such as the importance of a moist and occlusive environment and the safe use of hydrogen peroxide — especially important for patients with dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman commented after the meeting.
Dermatoporosis is quantifiable, Dr. Friedman said during the meeting, with a scoring system having been developed by the researchers in Switzerland who originally coined the term. Its use in practice is unnecessary, but its existence is “nice to share with patients who feel bothered because oftentimes, patients feel it’s been dismissed by other providers,” he said. “Telling your patients there’s an actual name for their problem, and that there are ways to quantify and measure changes over time, is validating.”
Its recognition as a medical condition, Dr. Friedman added, also enables the dermatologist to bring it up and counsel appropriately — without a patient feeling shame — when it is identified in the context of a skin excision, treatment of a primary inflammatory skin disease, or management of another dermatologic problem.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a consultant/advisory board member for L’Oréal, La Roche-Posay, Galderma, and other companies; a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Incyte, BMD, and Janssen; and has grants from Pfizer, Lilly, Incyte, and other companies. Dr. Stempel reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Managing Atopic Dermatitis in Older Adults: A Common, Unique Challenge
WASHINGTON, DC — Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, said at the ElderDerm Conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“I walked out of residency under the impression that if it didn’t start in the first year or two of life, it’s not AD,” said Dr. Silverberg, professor of dermatology and director of clinical research at George Washington University. “The numbers tell us a very different story.”
The prevalence of AD in the United States fluctuates between 6% and 8% through adulthood, including age categories up to 81-85 years, according to 2012 National Health Interview Survey data. And while persistence of childhood-onset AD is common, a systematic review and meta-analysis published in 2018 concluded that one in four adults with AD report adult-onset disease.
The investigators, including Dr. Silverberg, identified 25 observational studies — studies conducted across 16 countries and published during 1956-2017 — that included an analysis of age of onset beyond 10 years of age, and other inclusion criteria. Of the 25 studies, 17 reported age of onset after 16 years of age and had sufficient data for the meta-analysis. Using random-effects weighting, the investigators found a pooled proportion of adult-onset AD of 26.1% (95% CI, 16.5%-37.2%).
The research demonstrates that “the age of onset is distributed well throughout the lifespan,” Dr. Silverberg said, with the data “indicating there are many elderly-onset cases of true AD as well.” (Thirteen of the studies analyzed an age of onset from age ≥ 65, and several looked beyond age 80).
A 2021 study of a primary care database in the United Kingdom of 3.85 million children and adults found a “fascinating” bimodal distribution of incidence across the lifespan, with peaks in both infancy and older adulthood, he said. Incidence in adulthood was relatively stable from ages 18-49 years, after which, “into the 50s, 60s and beyond, you started to see a steady climb again.”
Also intriguing, Dr. Silverberg continued, are findings from a study of outpatient healthcare utilization for AD in which he and his coinvestigator analyzed data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS). In the article, published in 2023 covering data from the 1993-2015 NAMCS, they reported that AD visits were more common among children aged 0-4 years (32.0%) and 5-9 years of age (10.6%), then decreased in adolescents aged 10-19 years (11.6%), remained fairly steady in patients aged 20-89 years (1.0%-4.7%), and increased in patients aged > 90 years (20.7%).
“The peak usage for dermatologists, primary care physicians, etc., is happening in the first few years of life, partially because that’s when the disease is more common and more severe but also partially because that’s when parents and caregivers are first learning [about] the disease and trying to understand how to gain control,” Dr. Silverberg said at the meeting, presenting data from an expanded, unpublished analysis of NAMCS data showing these same outpatient utilization patterns.
“It’s fascinating — there’s a much greater utilization in the elderly population. Why? The short answer is, we don’t know,” he said.
Risk Factors, Immune Differences
People with adult-onset AD were more likely to be women, smokers in adulthood, and have a lower childhood socioeconomic status than those whose AD started in childhood in a longitudinal study of two large birth cohorts from the United Kingdom , Dr. Silverberg pointed out.
Patients with childhood-onset AD, meanwhile, were more likely to have asthma, allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE), and known genetic polymorphisms previously associated with AD. (Each cohort — the 1958 British Cohort Study and the 1970 British Cohort Study — had more than 17,000 participants who were followed from birth through middle age.)
Data is limited, but “mechanistically,” AD in much older adults appears to have a unique serum cytokine pattern, Dr. Silverberg said. He pointed to a cross-sectional study in China of 1312 children and adults with AD in which researchers analyzed clinical features, serum samples, and skin biopsy samples.
Adults aged > 60 years showed more lesions on the trunk and extensor sites of the extremities and lower levels of serum IgE and peripheral eosinophil counts than those in younger age groups. And “interestingly,” compared with healthy controls, older patients with AD had “higher levels of serum expression of a variety of cytokines, including IL [interleukin]-4 but also high TARC levels ... and a variety of cytokines related to the Th17, TH1 axes, etc.,” he said.
“So, we’re seeing a fascinating new profile that may be a little different than younger-onset cases,” he said, noting that TARC (thymus and activation-regulated chemokine) is regarded as a “decent biomarker” for AD.
In addition to higher levels of IL-4 and TARC, the study investigators reported significantly higher levels of IL-17A, IL-6, IL-22, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in older patients, compared with healthy controls.
Research also suggests that air pollution may play a role in the onset of AD in older age, Dr. Silverberg said, referencing a 2023 study that explored the association of air pollution and genetic risk with the onset of AD after age 50. The study analyzed 337,910 participants from the UK Biobank, with a median 12-year follow-up. Genetic risks were assessed as low, intermediate, and high, based on tertiles of polygenic risk scores. Exposure to various air pollutants was assessed using weighted quantile sum and also categorized into tertiles.
The incidence of older adult-onset AD was associated with medium and high air pollution compared with low air pollution, with hazard ratios (HRs) of 1.182 (P = .003) and 1.359 (P < .001), respectively. And “to a lesser extent,” Dr. Silverberg said, incidence was associated with medium and high genetic susceptibility, with HRs of 1.065 (P = .249) and 1.153 (P = .008).
The researchers calculated a greater population-attributable fraction of air pollution (15.5%) than genetic risk (6.4%). “This means that yes, genetics can contribute even to later-onset disease ... but environment may play an even more important role,” Dr. Silverberg said.
In the Clinic
In all patients, and especially in older adults, sleep disturbance associated with AD is a consideration for care. Data collected at the eczema clinic of Northwestern University, Chicago, Illinois, between 2014 and 2019 through previsit, self-administered questionnaires show that patients ≥ 65 years of age have more profound sleep disturbance (especially trouble staying asleep) than patients aged 18-64 years, despite having similar AD severity, said Dr. Silverberg, a coinvestigator of the study.
Older age was associated with having an increased number of nights of sleep disturbance (3-7 nights in the previous week) because of eczema (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.14; 95% CI, 1.16-3.92). It was also associated with itching-attributed delays in falling asleep and nighttime awakenings in the prior 2 weeks (aOR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.05-3.39).
“The aging population has dysregulated sleep patterns and altered circadian rhythms, so some of this is just natural predisposition,” Dr. Silverberg said. “But it’s amplified [with AD and itching], and it becomes a big clinical problem when we get into treatment because it’s our natural inclination to prescribe antihistamines for their sedative properties.”
Antihistamines can cause more profound sedation, more forgetfulness, and more anticholinergic side effects, he said, noting that “there’s some evidence that high-dose antihistamines may exacerbate dementia.”
Medication side effects and medication interactions, comorbidities, and decreased renal and hepatic clearance all can complicate treatment of AD in older adults. So can mobility, the extent of social/caregiving support, and other aspects of aging. For example, “I’m a big fan of ‘soak and smears’ ... but you have to ask, can you get out of a bathtub safely?” Dr. Silverberg said. “And you have to ask, can you reach the areas you need to [in order] to apply topicals?”
With oral Janus kinase inhibitors and other systemic medications, as with other drugs, “our older population is the most vulnerable from a safety perspective,” he said. A recently published post hoc analysis of four randomized trials of dupilumab in adults ≥ 60 years of age with moderate to severe AD demonstrated efficacy comparable with that in younger patients and “a really clean safety profile,” said Dr. Silverberg, the lead author. “We really need more of these types of post hocs to have some relative contextualization” for older adults.
Dr. Silverberg reported being a speaker for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Genzyme; a consultant and/or advisory board member for Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and other companies; and an investigator for several companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, said at the ElderDerm Conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“I walked out of residency under the impression that if it didn’t start in the first year or two of life, it’s not AD,” said Dr. Silverberg, professor of dermatology and director of clinical research at George Washington University. “The numbers tell us a very different story.”
The prevalence of AD in the United States fluctuates between 6% and 8% through adulthood, including age categories up to 81-85 years, according to 2012 National Health Interview Survey data. And while persistence of childhood-onset AD is common, a systematic review and meta-analysis published in 2018 concluded that one in four adults with AD report adult-onset disease.
The investigators, including Dr. Silverberg, identified 25 observational studies — studies conducted across 16 countries and published during 1956-2017 — that included an analysis of age of onset beyond 10 years of age, and other inclusion criteria. Of the 25 studies, 17 reported age of onset after 16 years of age and had sufficient data for the meta-analysis. Using random-effects weighting, the investigators found a pooled proportion of adult-onset AD of 26.1% (95% CI, 16.5%-37.2%).
The research demonstrates that “the age of onset is distributed well throughout the lifespan,” Dr. Silverberg said, with the data “indicating there are many elderly-onset cases of true AD as well.” (Thirteen of the studies analyzed an age of onset from age ≥ 65, and several looked beyond age 80).
A 2021 study of a primary care database in the United Kingdom of 3.85 million children and adults found a “fascinating” bimodal distribution of incidence across the lifespan, with peaks in both infancy and older adulthood, he said. Incidence in adulthood was relatively stable from ages 18-49 years, after which, “into the 50s, 60s and beyond, you started to see a steady climb again.”
Also intriguing, Dr. Silverberg continued, are findings from a study of outpatient healthcare utilization for AD in which he and his coinvestigator analyzed data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS). In the article, published in 2023 covering data from the 1993-2015 NAMCS, they reported that AD visits were more common among children aged 0-4 years (32.0%) and 5-9 years of age (10.6%), then decreased in adolescents aged 10-19 years (11.6%), remained fairly steady in patients aged 20-89 years (1.0%-4.7%), and increased in patients aged > 90 years (20.7%).
“The peak usage for dermatologists, primary care physicians, etc., is happening in the first few years of life, partially because that’s when the disease is more common and more severe but also partially because that’s when parents and caregivers are first learning [about] the disease and trying to understand how to gain control,” Dr. Silverberg said at the meeting, presenting data from an expanded, unpublished analysis of NAMCS data showing these same outpatient utilization patterns.
“It’s fascinating — there’s a much greater utilization in the elderly population. Why? The short answer is, we don’t know,” he said.
Risk Factors, Immune Differences
People with adult-onset AD were more likely to be women, smokers in adulthood, and have a lower childhood socioeconomic status than those whose AD started in childhood in a longitudinal study of two large birth cohorts from the United Kingdom , Dr. Silverberg pointed out.
Patients with childhood-onset AD, meanwhile, were more likely to have asthma, allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE), and known genetic polymorphisms previously associated with AD. (Each cohort — the 1958 British Cohort Study and the 1970 British Cohort Study — had more than 17,000 participants who were followed from birth through middle age.)
Data is limited, but “mechanistically,” AD in much older adults appears to have a unique serum cytokine pattern, Dr. Silverberg said. He pointed to a cross-sectional study in China of 1312 children and adults with AD in which researchers analyzed clinical features, serum samples, and skin biopsy samples.
Adults aged > 60 years showed more lesions on the trunk and extensor sites of the extremities and lower levels of serum IgE and peripheral eosinophil counts than those in younger age groups. And “interestingly,” compared with healthy controls, older patients with AD had “higher levels of serum expression of a variety of cytokines, including IL [interleukin]-4 but also high TARC levels ... and a variety of cytokines related to the Th17, TH1 axes, etc.,” he said.
“So, we’re seeing a fascinating new profile that may be a little different than younger-onset cases,” he said, noting that TARC (thymus and activation-regulated chemokine) is regarded as a “decent biomarker” for AD.
In addition to higher levels of IL-4 and TARC, the study investigators reported significantly higher levels of IL-17A, IL-6, IL-22, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in older patients, compared with healthy controls.
Research also suggests that air pollution may play a role in the onset of AD in older age, Dr. Silverberg said, referencing a 2023 study that explored the association of air pollution and genetic risk with the onset of AD after age 50. The study analyzed 337,910 participants from the UK Biobank, with a median 12-year follow-up. Genetic risks were assessed as low, intermediate, and high, based on tertiles of polygenic risk scores. Exposure to various air pollutants was assessed using weighted quantile sum and also categorized into tertiles.
The incidence of older adult-onset AD was associated with medium and high air pollution compared with low air pollution, with hazard ratios (HRs) of 1.182 (P = .003) and 1.359 (P < .001), respectively. And “to a lesser extent,” Dr. Silverberg said, incidence was associated with medium and high genetic susceptibility, with HRs of 1.065 (P = .249) and 1.153 (P = .008).
The researchers calculated a greater population-attributable fraction of air pollution (15.5%) than genetic risk (6.4%). “This means that yes, genetics can contribute even to later-onset disease ... but environment may play an even more important role,” Dr. Silverberg said.
In the Clinic
In all patients, and especially in older adults, sleep disturbance associated with AD is a consideration for care. Data collected at the eczema clinic of Northwestern University, Chicago, Illinois, between 2014 and 2019 through previsit, self-administered questionnaires show that patients ≥ 65 years of age have more profound sleep disturbance (especially trouble staying asleep) than patients aged 18-64 years, despite having similar AD severity, said Dr. Silverberg, a coinvestigator of the study.
Older age was associated with having an increased number of nights of sleep disturbance (3-7 nights in the previous week) because of eczema (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.14; 95% CI, 1.16-3.92). It was also associated with itching-attributed delays in falling asleep and nighttime awakenings in the prior 2 weeks (aOR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.05-3.39).
“The aging population has dysregulated sleep patterns and altered circadian rhythms, so some of this is just natural predisposition,” Dr. Silverberg said. “But it’s amplified [with AD and itching], and it becomes a big clinical problem when we get into treatment because it’s our natural inclination to prescribe antihistamines for their sedative properties.”
Antihistamines can cause more profound sedation, more forgetfulness, and more anticholinergic side effects, he said, noting that “there’s some evidence that high-dose antihistamines may exacerbate dementia.”
Medication side effects and medication interactions, comorbidities, and decreased renal and hepatic clearance all can complicate treatment of AD in older adults. So can mobility, the extent of social/caregiving support, and other aspects of aging. For example, “I’m a big fan of ‘soak and smears’ ... but you have to ask, can you get out of a bathtub safely?” Dr. Silverberg said. “And you have to ask, can you reach the areas you need to [in order] to apply topicals?”
With oral Janus kinase inhibitors and other systemic medications, as with other drugs, “our older population is the most vulnerable from a safety perspective,” he said. A recently published post hoc analysis of four randomized trials of dupilumab in adults ≥ 60 years of age with moderate to severe AD demonstrated efficacy comparable with that in younger patients and “a really clean safety profile,” said Dr. Silverberg, the lead author. “We really need more of these types of post hocs to have some relative contextualization” for older adults.
Dr. Silverberg reported being a speaker for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Genzyme; a consultant and/or advisory board member for Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and other companies; and an investigator for several companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON, DC — Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, said at the ElderDerm Conference on dermatology in the older patient hosted by the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC.
“I walked out of residency under the impression that if it didn’t start in the first year or two of life, it’s not AD,” said Dr. Silverberg, professor of dermatology and director of clinical research at George Washington University. “The numbers tell us a very different story.”
The prevalence of AD in the United States fluctuates between 6% and 8% through adulthood, including age categories up to 81-85 years, according to 2012 National Health Interview Survey data. And while persistence of childhood-onset AD is common, a systematic review and meta-analysis published in 2018 concluded that one in four adults with AD report adult-onset disease.
The investigators, including Dr. Silverberg, identified 25 observational studies — studies conducted across 16 countries and published during 1956-2017 — that included an analysis of age of onset beyond 10 years of age, and other inclusion criteria. Of the 25 studies, 17 reported age of onset after 16 years of age and had sufficient data for the meta-analysis. Using random-effects weighting, the investigators found a pooled proportion of adult-onset AD of 26.1% (95% CI, 16.5%-37.2%).
The research demonstrates that “the age of onset is distributed well throughout the lifespan,” Dr. Silverberg said, with the data “indicating there are many elderly-onset cases of true AD as well.” (Thirteen of the studies analyzed an age of onset from age ≥ 65, and several looked beyond age 80).
A 2021 study of a primary care database in the United Kingdom of 3.85 million children and adults found a “fascinating” bimodal distribution of incidence across the lifespan, with peaks in both infancy and older adulthood, he said. Incidence in adulthood was relatively stable from ages 18-49 years, after which, “into the 50s, 60s and beyond, you started to see a steady climb again.”
Also intriguing, Dr. Silverberg continued, are findings from a study of outpatient healthcare utilization for AD in which he and his coinvestigator analyzed data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS). In the article, published in 2023 covering data from the 1993-2015 NAMCS, they reported that AD visits were more common among children aged 0-4 years (32.0%) and 5-9 years of age (10.6%), then decreased in adolescents aged 10-19 years (11.6%), remained fairly steady in patients aged 20-89 years (1.0%-4.7%), and increased in patients aged > 90 years (20.7%).
“The peak usage for dermatologists, primary care physicians, etc., is happening in the first few years of life, partially because that’s when the disease is more common and more severe but also partially because that’s when parents and caregivers are first learning [about] the disease and trying to understand how to gain control,” Dr. Silverberg said at the meeting, presenting data from an expanded, unpublished analysis of NAMCS data showing these same outpatient utilization patterns.
“It’s fascinating — there’s a much greater utilization in the elderly population. Why? The short answer is, we don’t know,” he said.
Risk Factors, Immune Differences
People with adult-onset AD were more likely to be women, smokers in adulthood, and have a lower childhood socioeconomic status than those whose AD started in childhood in a longitudinal study of two large birth cohorts from the United Kingdom , Dr. Silverberg pointed out.
Patients with childhood-onset AD, meanwhile, were more likely to have asthma, allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE), and known genetic polymorphisms previously associated with AD. (Each cohort — the 1958 British Cohort Study and the 1970 British Cohort Study — had more than 17,000 participants who were followed from birth through middle age.)
Data is limited, but “mechanistically,” AD in much older adults appears to have a unique serum cytokine pattern, Dr. Silverberg said. He pointed to a cross-sectional study in China of 1312 children and adults with AD in which researchers analyzed clinical features, serum samples, and skin biopsy samples.
Adults aged > 60 years showed more lesions on the trunk and extensor sites of the extremities and lower levels of serum IgE and peripheral eosinophil counts than those in younger age groups. And “interestingly,” compared with healthy controls, older patients with AD had “higher levels of serum expression of a variety of cytokines, including IL [interleukin]-4 but also high TARC levels ... and a variety of cytokines related to the Th17, TH1 axes, etc.,” he said.
“So, we’re seeing a fascinating new profile that may be a little different than younger-onset cases,” he said, noting that TARC (thymus and activation-regulated chemokine) is regarded as a “decent biomarker” for AD.
In addition to higher levels of IL-4 and TARC, the study investigators reported significantly higher levels of IL-17A, IL-6, IL-22, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in older patients, compared with healthy controls.
Research also suggests that air pollution may play a role in the onset of AD in older age, Dr. Silverberg said, referencing a 2023 study that explored the association of air pollution and genetic risk with the onset of AD after age 50. The study analyzed 337,910 participants from the UK Biobank, with a median 12-year follow-up. Genetic risks were assessed as low, intermediate, and high, based on tertiles of polygenic risk scores. Exposure to various air pollutants was assessed using weighted quantile sum and also categorized into tertiles.
The incidence of older adult-onset AD was associated with medium and high air pollution compared with low air pollution, with hazard ratios (HRs) of 1.182 (P = .003) and 1.359 (P < .001), respectively. And “to a lesser extent,” Dr. Silverberg said, incidence was associated with medium and high genetic susceptibility, with HRs of 1.065 (P = .249) and 1.153 (P = .008).
The researchers calculated a greater population-attributable fraction of air pollution (15.5%) than genetic risk (6.4%). “This means that yes, genetics can contribute even to later-onset disease ... but environment may play an even more important role,” Dr. Silverberg said.
In the Clinic
In all patients, and especially in older adults, sleep disturbance associated with AD is a consideration for care. Data collected at the eczema clinic of Northwestern University, Chicago, Illinois, between 2014 and 2019 through previsit, self-administered questionnaires show that patients ≥ 65 years of age have more profound sleep disturbance (especially trouble staying asleep) than patients aged 18-64 years, despite having similar AD severity, said Dr. Silverberg, a coinvestigator of the study.
Older age was associated with having an increased number of nights of sleep disturbance (3-7 nights in the previous week) because of eczema (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.14; 95% CI, 1.16-3.92). It was also associated with itching-attributed delays in falling asleep and nighttime awakenings in the prior 2 weeks (aOR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.05-3.39).
“The aging population has dysregulated sleep patterns and altered circadian rhythms, so some of this is just natural predisposition,” Dr. Silverberg said. “But it’s amplified [with AD and itching], and it becomes a big clinical problem when we get into treatment because it’s our natural inclination to prescribe antihistamines for their sedative properties.”
Antihistamines can cause more profound sedation, more forgetfulness, and more anticholinergic side effects, he said, noting that “there’s some evidence that high-dose antihistamines may exacerbate dementia.”
Medication side effects and medication interactions, comorbidities, and decreased renal and hepatic clearance all can complicate treatment of AD in older adults. So can mobility, the extent of social/caregiving support, and other aspects of aging. For example, “I’m a big fan of ‘soak and smears’ ... but you have to ask, can you get out of a bathtub safely?” Dr. Silverberg said. “And you have to ask, can you reach the areas you need to [in order] to apply topicals?”
With oral Janus kinase inhibitors and other systemic medications, as with other drugs, “our older population is the most vulnerable from a safety perspective,” he said. A recently published post hoc analysis of four randomized trials of dupilumab in adults ≥ 60 years of age with moderate to severe AD demonstrated efficacy comparable with that in younger patients and “a really clean safety profile,” said Dr. Silverberg, the lead author. “We really need more of these types of post hocs to have some relative contextualization” for older adults.
Dr. Silverberg reported being a speaker for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Genzyme; a consultant and/or advisory board member for Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and other companies; and an investigator for several companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Rethinking Management of Skin Cancer in Older Patients
WASHINGTON — In 2013, Vishal A. Patel, MD, was completing a fellowship in Mohs surgery and cutaneous oncology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, when a study was published showing that most nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) were treated with surgery, regardless of the patient’s life expectancy. Life expectancy “should enter into treatment decisions,” the authors concluded.
“ Dr. Patel recalled at the ElderDerm conference hosted by the Department of Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and described as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Today, however, more than a decade later, guidelines still promote surgical therapy as the gold standard across the board, and questions raised by the study are still unaddressed, Dr. Patel, associate professor of dermatology and medicine/oncology at George Washington University, said at the meeting. These questions are becoming increasingly urgent as the incidence of skin cancer, especially NMSC, rises in the older adult population, especially in patients older than 85 years. “It’s a function of our training and our treatment guidelines that we reach for the most definitive treatment, which happens to be the most aggressive, in these patients,” added Dr. Patel, who is also director of the cutaneous oncology program at the GW Cancer Center.
“Sometimes we lose track of what ... we need to do” to provide care that reflects the best interests of the older patient, he continued. “Surgery may be the gold standard for treating the majority of NMSCs ... but is it the [best option] for what our older patients and patients with limited life expectancy need?”
Learning about what truly matters to the patient is a key element of the “age-friendly, whole-person care” that dermatologists must embrace as older adults become an increasingly large subset of their patient population, Christina Prather, MD, director and associate professor of geriatrics and palliative medicine at George Washington University, said at the meeting.
By 2040, projections are that the number of adults aged 85 years and older in the United States will be nearly quadruple the number in 2000, according to one estimate.
“We know that there are less than 6000 practicing geriatricians in the country ... [so the healthcare system] needs more of you who know how to bring an age-friendly approach to care,” Dr. Prather said. Dermatology is among the specialties that need to be “geriatricized.”
NMSC Increasing in the Older Population
The incidence of skin cancer is rising faster than that of any other cancer, Dr. Patel said. One window into the epidemiology, he said, comes from recently published data showing that an average of 6.1 million adults were treated each year for skin cancer during 2016-2018 (5.2 million of them for NMSC) — an increase from an average of 5.8 million annually in the 2012-2015 period. The data come from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS), which is conducted by the US Public Health Service through the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As a frame of reference, the average number of adults treated each year for nonskin cancers during these periods rose from 10.8 to 11.9 million, according to the 2023 MEPS data. “Skin cancer is about one-third of all cancers combined,” Dr. Patel said.
Not only is the incidence of NMSC significantly higher than that of melanoma but it also shows a more prominent aging trend. This was documented recently in a long-term observational study from Japan, in which researchers looked at the change in the median age of patients with NMSC and melanoma, compared with cancers of other organs, from 1991 to 2020 and found that NMSC had by far the greatest rise in median age, to a median age of 80 years in 2021.
Even more notable, Dr. Patel said, was a particularly marked increase in the number of patients with skin cancer aged 90 years and older. In 2021, this group of older adults accounted for 17% of patients receiving treatment for skin cancer at the Japanese hospital where the data were collected.
The 2013 study that stirred Dr. Patel as a fellow was of 1536 consecutive patients diagnosed with NMSC at two dermatology clinics (a University of California San Francisco–based private clinic and a Veterans Affairs Medical Center clinic) and followed for 6 years. “What’s interesting and worth thinking about is that, regardless of patients’ life expectancy, NMSCs were treated aggressively and surgically, and the choice of surgery was not influenced by the patient’s poor prognosis in a multivariate model” adjusted for tumor and patient characteristics, he said at the meeting.
The researchers defined limited life expectancy as either 85 years or older or having a Charleston Comorbidity Index ≥ 3. Approximately half of the patients with limited life expectancy died within 5 years, none of NMSC. Most patients with limited life expectancy were not often bothered by their tumors, and approximately one in five reported a treatment complication within 2 years. The 5-year tumor recurrence rate was 3.7%.
A more recent study looked at 1181 patients older than 85 years with NMSC referred for Mohs surgery. Almost all patients in the multicenter, prospective cohort study (91.3%) were treated with Mohs.
Treated patients were more likely to have facial tumors and higher functional status than those not treated with Mohs surgery, and the most common reasons provided by surgeons for proceeding with the surgery were a patient desire for a high cure rate (66%), higher functional status for age (57%), and high-risk tumor type (40%). Almost 42% of the referred patients were 89 years or older.
“Granted, [the reasons] are justified indications for surgery,” Dr. Patel said. Yet the study brings up the question of “whether we need to do Mohs surgery this frequently in elderly patients?” In an email after the meeting, he added, “it’s a question we may need to reconsider as the elderly population continues to increase and median age of NMSC rises.”
Underutilized Management Options for NMSC
In his practice, discussions of treatment options are preceded by a thorough discussion of the disease itself. Many lesions are low risk, and helping patients understand risks, as well as understanding what is important to the patient — especially those with limited life expectancy — will guide shared decision-making to choose the best treatment, Dr. Patel said at the meeting.
The dermatologist’s risk assessment — both staging and stratifying risk as it relates to specific outcomes such as recurrence, metastases, or death — takes on added importance in the older patient, he emphasized. “I think we underutilize the risk assessment.”
Also underutilized is the option of shave removal for low-risk squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas, Dr. Patel said, noting that, in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, “there’s an option for shave removal and nothing more if you have clear margins.”
Alternatively, disc excision with the initial biopsy can often be considered. “Having that intent to treat at the time of biopsy may be all that needs to be done” in older patients with obvious or highly suspicious lesions, he said.
Systemic immunotherapy has joined the treatment armamentarium for advanced basal cell carcinoma and advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and if early, ongoing research of intralesional programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor treatment advances, this could be another option for older adults in the future, Dr. Patel said. Targeting drug delivery directly to the tumor would lower the total dose, decrease systemic exposure, and could be used to avoid surgery for some groups of patients, such as those with limited life expectancy.
A Personal Story, a Word on Melanoma
Dr. Prather recalled when her 97-year-old grandfather had a skin lesion on his forehead removed, and a conversation he had with her mother about whether he really needed to have the procedure because he had cognitive impairment and was on oral anticoagulants.
The clinician “said it absolutely had to go. ... I can’t tell you how much his doctors’ visits and wound care consumed my family’s life for the next few years — for this thing that never quite healed,” she said.
“Was it necessary? The more I’ve learned over time is that it wasn’t,” Dr. Prather added. “We have to take time [with our older patients] and think critically. What is feasible? What makes the most sense? What is the most important thing I need to know about the patient?”
Also important, Dr. Patel noted, is the big-picture consideration of skin cancer treatment costs. The MEPS survey data showing the rising prevalence of skin cancer treatment also documented the economic burden: A nearly 30% increase in the average annual cost of treating NMSC from $5 billion in 2012-2015 to $6.5 billion in 2016-2018. (The average annual costs of treating melanoma decreased slightly.) “Skin cancer is a big drain on our limited resources,” he said.
With melanoma as well, dermatologists must think critically and holistically about the individual patient — and not have “a single view lens of the disease and how we treat the disease,” said Dr. Patel, urging the audience to read a “Sounding Board” article published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2021. The article argued that there is overdiagnosis of cutaneous melanoma stemming from increased screening, falling clinical thresholds for biopsy, and falling pathological thresholds for labeling morphologic changes as cancer.
“There’s a diagnostic disconnect and a problem of overdiagnosis ... because we’re afraid to miss or make a mistake,” he said. “It leads to the question, do all lesions denoted as skin cancers need aggressive treatment? What does it mean for the patient in front of you?”
Dr. Patel reported receiving honoraria from Regeneron, Almirall, Biofrontera, Sun Pharma, and SkylineDx and serving on the speaker bureau of Regeneron and Almirall. He is chief medical officer for Lazarus AI and is cofounder of the Skin Cancer Outcomes consortium. Dr. Prather disclosed relationships with the National Institutes of Health, AHRQ, The Washington Home Foundation, and the Alzheimer’s Association.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — In 2013, Vishal A. Patel, MD, was completing a fellowship in Mohs surgery and cutaneous oncology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, when a study was published showing that most nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) were treated with surgery, regardless of the patient’s life expectancy. Life expectancy “should enter into treatment decisions,” the authors concluded.
“ Dr. Patel recalled at the ElderDerm conference hosted by the Department of Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and described as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Today, however, more than a decade later, guidelines still promote surgical therapy as the gold standard across the board, and questions raised by the study are still unaddressed, Dr. Patel, associate professor of dermatology and medicine/oncology at George Washington University, said at the meeting. These questions are becoming increasingly urgent as the incidence of skin cancer, especially NMSC, rises in the older adult population, especially in patients older than 85 years. “It’s a function of our training and our treatment guidelines that we reach for the most definitive treatment, which happens to be the most aggressive, in these patients,” added Dr. Patel, who is also director of the cutaneous oncology program at the GW Cancer Center.
“Sometimes we lose track of what ... we need to do” to provide care that reflects the best interests of the older patient, he continued. “Surgery may be the gold standard for treating the majority of NMSCs ... but is it the [best option] for what our older patients and patients with limited life expectancy need?”
Learning about what truly matters to the patient is a key element of the “age-friendly, whole-person care” that dermatologists must embrace as older adults become an increasingly large subset of their patient population, Christina Prather, MD, director and associate professor of geriatrics and palliative medicine at George Washington University, said at the meeting.
By 2040, projections are that the number of adults aged 85 years and older in the United States will be nearly quadruple the number in 2000, according to one estimate.
“We know that there are less than 6000 practicing geriatricians in the country ... [so the healthcare system] needs more of you who know how to bring an age-friendly approach to care,” Dr. Prather said. Dermatology is among the specialties that need to be “geriatricized.”
NMSC Increasing in the Older Population
The incidence of skin cancer is rising faster than that of any other cancer, Dr. Patel said. One window into the epidemiology, he said, comes from recently published data showing that an average of 6.1 million adults were treated each year for skin cancer during 2016-2018 (5.2 million of them for NMSC) — an increase from an average of 5.8 million annually in the 2012-2015 period. The data come from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS), which is conducted by the US Public Health Service through the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As a frame of reference, the average number of adults treated each year for nonskin cancers during these periods rose from 10.8 to 11.9 million, according to the 2023 MEPS data. “Skin cancer is about one-third of all cancers combined,” Dr. Patel said.
Not only is the incidence of NMSC significantly higher than that of melanoma but it also shows a more prominent aging trend. This was documented recently in a long-term observational study from Japan, in which researchers looked at the change in the median age of patients with NMSC and melanoma, compared with cancers of other organs, from 1991 to 2020 and found that NMSC had by far the greatest rise in median age, to a median age of 80 years in 2021.
Even more notable, Dr. Patel said, was a particularly marked increase in the number of patients with skin cancer aged 90 years and older. In 2021, this group of older adults accounted for 17% of patients receiving treatment for skin cancer at the Japanese hospital where the data were collected.
The 2013 study that stirred Dr. Patel as a fellow was of 1536 consecutive patients diagnosed with NMSC at two dermatology clinics (a University of California San Francisco–based private clinic and a Veterans Affairs Medical Center clinic) and followed for 6 years. “What’s interesting and worth thinking about is that, regardless of patients’ life expectancy, NMSCs were treated aggressively and surgically, and the choice of surgery was not influenced by the patient’s poor prognosis in a multivariate model” adjusted for tumor and patient characteristics, he said at the meeting.
The researchers defined limited life expectancy as either 85 years or older or having a Charleston Comorbidity Index ≥ 3. Approximately half of the patients with limited life expectancy died within 5 years, none of NMSC. Most patients with limited life expectancy were not often bothered by their tumors, and approximately one in five reported a treatment complication within 2 years. The 5-year tumor recurrence rate was 3.7%.
A more recent study looked at 1181 patients older than 85 years with NMSC referred for Mohs surgery. Almost all patients in the multicenter, prospective cohort study (91.3%) were treated with Mohs.
Treated patients were more likely to have facial tumors and higher functional status than those not treated with Mohs surgery, and the most common reasons provided by surgeons for proceeding with the surgery were a patient desire for a high cure rate (66%), higher functional status for age (57%), and high-risk tumor type (40%). Almost 42% of the referred patients were 89 years or older.
“Granted, [the reasons] are justified indications for surgery,” Dr. Patel said. Yet the study brings up the question of “whether we need to do Mohs surgery this frequently in elderly patients?” In an email after the meeting, he added, “it’s a question we may need to reconsider as the elderly population continues to increase and median age of NMSC rises.”
Underutilized Management Options for NMSC
In his practice, discussions of treatment options are preceded by a thorough discussion of the disease itself. Many lesions are low risk, and helping patients understand risks, as well as understanding what is important to the patient — especially those with limited life expectancy — will guide shared decision-making to choose the best treatment, Dr. Patel said at the meeting.
The dermatologist’s risk assessment — both staging and stratifying risk as it relates to specific outcomes such as recurrence, metastases, or death — takes on added importance in the older patient, he emphasized. “I think we underutilize the risk assessment.”
Also underutilized is the option of shave removal for low-risk squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas, Dr. Patel said, noting that, in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, “there’s an option for shave removal and nothing more if you have clear margins.”
Alternatively, disc excision with the initial biopsy can often be considered. “Having that intent to treat at the time of biopsy may be all that needs to be done” in older patients with obvious or highly suspicious lesions, he said.
Systemic immunotherapy has joined the treatment armamentarium for advanced basal cell carcinoma and advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and if early, ongoing research of intralesional programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor treatment advances, this could be another option for older adults in the future, Dr. Patel said. Targeting drug delivery directly to the tumor would lower the total dose, decrease systemic exposure, and could be used to avoid surgery for some groups of patients, such as those with limited life expectancy.
A Personal Story, a Word on Melanoma
Dr. Prather recalled when her 97-year-old grandfather had a skin lesion on his forehead removed, and a conversation he had with her mother about whether he really needed to have the procedure because he had cognitive impairment and was on oral anticoagulants.
The clinician “said it absolutely had to go. ... I can’t tell you how much his doctors’ visits and wound care consumed my family’s life for the next few years — for this thing that never quite healed,” she said.
“Was it necessary? The more I’ve learned over time is that it wasn’t,” Dr. Prather added. “We have to take time [with our older patients] and think critically. What is feasible? What makes the most sense? What is the most important thing I need to know about the patient?”
Also important, Dr. Patel noted, is the big-picture consideration of skin cancer treatment costs. The MEPS survey data showing the rising prevalence of skin cancer treatment also documented the economic burden: A nearly 30% increase in the average annual cost of treating NMSC from $5 billion in 2012-2015 to $6.5 billion in 2016-2018. (The average annual costs of treating melanoma decreased slightly.) “Skin cancer is a big drain on our limited resources,” he said.
With melanoma as well, dermatologists must think critically and holistically about the individual patient — and not have “a single view lens of the disease and how we treat the disease,” said Dr. Patel, urging the audience to read a “Sounding Board” article published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2021. The article argued that there is overdiagnosis of cutaneous melanoma stemming from increased screening, falling clinical thresholds for biopsy, and falling pathological thresholds for labeling morphologic changes as cancer.
“There’s a diagnostic disconnect and a problem of overdiagnosis ... because we’re afraid to miss or make a mistake,” he said. “It leads to the question, do all lesions denoted as skin cancers need aggressive treatment? What does it mean for the patient in front of you?”
Dr. Patel reported receiving honoraria from Regeneron, Almirall, Biofrontera, Sun Pharma, and SkylineDx and serving on the speaker bureau of Regeneron and Almirall. He is chief medical officer for Lazarus AI and is cofounder of the Skin Cancer Outcomes consortium. Dr. Prather disclosed relationships with the National Institutes of Health, AHRQ, The Washington Home Foundation, and the Alzheimer’s Association.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — In 2013, Vishal A. Patel, MD, was completing a fellowship in Mohs surgery and cutaneous oncology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City, when a study was published showing that most nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) were treated with surgery, regardless of the patient’s life expectancy. Life expectancy “should enter into treatment decisions,” the authors concluded.
“ Dr. Patel recalled at the ElderDerm conference hosted by the Department of Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and described as a first-of-its-kind meeting dedicated to improving dermatologic care for older adults.
Today, however, more than a decade later, guidelines still promote surgical therapy as the gold standard across the board, and questions raised by the study are still unaddressed, Dr. Patel, associate professor of dermatology and medicine/oncology at George Washington University, said at the meeting. These questions are becoming increasingly urgent as the incidence of skin cancer, especially NMSC, rises in the older adult population, especially in patients older than 85 years. “It’s a function of our training and our treatment guidelines that we reach for the most definitive treatment, which happens to be the most aggressive, in these patients,” added Dr. Patel, who is also director of the cutaneous oncology program at the GW Cancer Center.
“Sometimes we lose track of what ... we need to do” to provide care that reflects the best interests of the older patient, he continued. “Surgery may be the gold standard for treating the majority of NMSCs ... but is it the [best option] for what our older patients and patients with limited life expectancy need?”
Learning about what truly matters to the patient is a key element of the “age-friendly, whole-person care” that dermatologists must embrace as older adults become an increasingly large subset of their patient population, Christina Prather, MD, director and associate professor of geriatrics and palliative medicine at George Washington University, said at the meeting.
By 2040, projections are that the number of adults aged 85 years and older in the United States will be nearly quadruple the number in 2000, according to one estimate.
“We know that there are less than 6000 practicing geriatricians in the country ... [so the healthcare system] needs more of you who know how to bring an age-friendly approach to care,” Dr. Prather said. Dermatology is among the specialties that need to be “geriatricized.”
NMSC Increasing in the Older Population
The incidence of skin cancer is rising faster than that of any other cancer, Dr. Patel said. One window into the epidemiology, he said, comes from recently published data showing that an average of 6.1 million adults were treated each year for skin cancer during 2016-2018 (5.2 million of them for NMSC) — an increase from an average of 5.8 million annually in the 2012-2015 period. The data come from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS), which is conducted by the US Public Health Service through the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As a frame of reference, the average number of adults treated each year for nonskin cancers during these periods rose from 10.8 to 11.9 million, according to the 2023 MEPS data. “Skin cancer is about one-third of all cancers combined,” Dr. Patel said.
Not only is the incidence of NMSC significantly higher than that of melanoma but it also shows a more prominent aging trend. This was documented recently in a long-term observational study from Japan, in which researchers looked at the change in the median age of patients with NMSC and melanoma, compared with cancers of other organs, from 1991 to 2020 and found that NMSC had by far the greatest rise in median age, to a median age of 80 years in 2021.
Even more notable, Dr. Patel said, was a particularly marked increase in the number of patients with skin cancer aged 90 years and older. In 2021, this group of older adults accounted for 17% of patients receiving treatment for skin cancer at the Japanese hospital where the data were collected.
The 2013 study that stirred Dr. Patel as a fellow was of 1536 consecutive patients diagnosed with NMSC at two dermatology clinics (a University of California San Francisco–based private clinic and a Veterans Affairs Medical Center clinic) and followed for 6 years. “What’s interesting and worth thinking about is that, regardless of patients’ life expectancy, NMSCs were treated aggressively and surgically, and the choice of surgery was not influenced by the patient’s poor prognosis in a multivariate model” adjusted for tumor and patient characteristics, he said at the meeting.
The researchers defined limited life expectancy as either 85 years or older or having a Charleston Comorbidity Index ≥ 3. Approximately half of the patients with limited life expectancy died within 5 years, none of NMSC. Most patients with limited life expectancy were not often bothered by their tumors, and approximately one in five reported a treatment complication within 2 years. The 5-year tumor recurrence rate was 3.7%.
A more recent study looked at 1181 patients older than 85 years with NMSC referred for Mohs surgery. Almost all patients in the multicenter, prospective cohort study (91.3%) were treated with Mohs.
Treated patients were more likely to have facial tumors and higher functional status than those not treated with Mohs surgery, and the most common reasons provided by surgeons for proceeding with the surgery were a patient desire for a high cure rate (66%), higher functional status for age (57%), and high-risk tumor type (40%). Almost 42% of the referred patients were 89 years or older.
“Granted, [the reasons] are justified indications for surgery,” Dr. Patel said. Yet the study brings up the question of “whether we need to do Mohs surgery this frequently in elderly patients?” In an email after the meeting, he added, “it’s a question we may need to reconsider as the elderly population continues to increase and median age of NMSC rises.”
Underutilized Management Options for NMSC
In his practice, discussions of treatment options are preceded by a thorough discussion of the disease itself. Many lesions are low risk, and helping patients understand risks, as well as understanding what is important to the patient — especially those with limited life expectancy — will guide shared decision-making to choose the best treatment, Dr. Patel said at the meeting.
The dermatologist’s risk assessment — both staging and stratifying risk as it relates to specific outcomes such as recurrence, metastases, or death — takes on added importance in the older patient, he emphasized. “I think we underutilize the risk assessment.”
Also underutilized is the option of shave removal for low-risk squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas, Dr. Patel said, noting that, in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, “there’s an option for shave removal and nothing more if you have clear margins.”
Alternatively, disc excision with the initial biopsy can often be considered. “Having that intent to treat at the time of biopsy may be all that needs to be done” in older patients with obvious or highly suspicious lesions, he said.
Systemic immunotherapy has joined the treatment armamentarium for advanced basal cell carcinoma and advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and if early, ongoing research of intralesional programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor treatment advances, this could be another option for older adults in the future, Dr. Patel said. Targeting drug delivery directly to the tumor would lower the total dose, decrease systemic exposure, and could be used to avoid surgery for some groups of patients, such as those with limited life expectancy.
A Personal Story, a Word on Melanoma
Dr. Prather recalled when her 97-year-old grandfather had a skin lesion on his forehead removed, and a conversation he had with her mother about whether he really needed to have the procedure because he had cognitive impairment and was on oral anticoagulants.
The clinician “said it absolutely had to go. ... I can’t tell you how much his doctors’ visits and wound care consumed my family’s life for the next few years — for this thing that never quite healed,” she said.
“Was it necessary? The more I’ve learned over time is that it wasn’t,” Dr. Prather added. “We have to take time [with our older patients] and think critically. What is feasible? What makes the most sense? What is the most important thing I need to know about the patient?”
Also important, Dr. Patel noted, is the big-picture consideration of skin cancer treatment costs. The MEPS survey data showing the rising prevalence of skin cancer treatment also documented the economic burden: A nearly 30% increase in the average annual cost of treating NMSC from $5 billion in 2012-2015 to $6.5 billion in 2016-2018. (The average annual costs of treating melanoma decreased slightly.) “Skin cancer is a big drain on our limited resources,” he said.
With melanoma as well, dermatologists must think critically and holistically about the individual patient — and not have “a single view lens of the disease and how we treat the disease,” said Dr. Patel, urging the audience to read a “Sounding Board” article published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2021. The article argued that there is overdiagnosis of cutaneous melanoma stemming from increased screening, falling clinical thresholds for biopsy, and falling pathological thresholds for labeling morphologic changes as cancer.
“There’s a diagnostic disconnect and a problem of overdiagnosis ... because we’re afraid to miss or make a mistake,” he said. “It leads to the question, do all lesions denoted as skin cancers need aggressive treatment? What does it mean for the patient in front of you?”
Dr. Patel reported receiving honoraria from Regeneron, Almirall, Biofrontera, Sun Pharma, and SkylineDx and serving on the speaker bureau of Regeneron and Almirall. He is chief medical officer for Lazarus AI and is cofounder of the Skin Cancer Outcomes consortium. Dr. Prather disclosed relationships with the National Institutes of Health, AHRQ, The Washington Home Foundation, and the Alzheimer’s Association.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Magnesium Sulfate’s Ability to Reduce Cerebral Palsy in Preterm Birth Reaffirmed
An updated Cochrane Systematic Review of magnesium sulfate administered before preterm birth for neuroprotection has reaffirmed that the compound significantly reduces the risk of cerebral palsy and has added the finding that it also may reduce the risk of severe neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage.
Still unknown, however, is whether the effects of magnesium sulfate vary according to patient characteristics such as gestational age, or by treatment characteristics such as timing and dose. “We need further research to determine exactly who to treat, and when and how, to ideally standardize clinical practice recommendations across the world,” said Emily S. Shepherd, PhD, lead author of the review.
Magnesium sulfate is widely used for preterm cerebral palsy prevention but variance in national and local recommendations for its use may impede its optimal uptake in some places, she and her co-investigators wrote in the review.
In the United States, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists advises institutions to develop their own guidelines regarding inclusion criteria and treatment regimens “in accordance with one of the larger trials.” (ACOG’s Committee Opinion on Magnesium Sulfate Before Anticipated Preterm Birth for Neuroprotection was originally published in 2010 and was reaffirmed in 2023.)
In a Master Class column on magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection published earlier this year in Ob.Gyn. News, Irina Burd, MD, PhD, wrote that most hospitals in the United States have chosen a higher dose of magnesium sulfate administered up to 31 weeks’ gestation (6-g bolus, followed by 2 g/hour), in keeping with the protocols used in the BEAM trial published by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). Dr. Burd is the Sylvan Frieman, MD, Endowed Professor and chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland.
The new Cochrane review included six randomized controlled trials (including the NICHD trial) covering 5917 pregnant participants and 6759 fetuses. Eligibility criteria varied, but all the RCTs included patients in preterm labor or with expected or planned imminent preterm birth at less than 34 weeks’ gestation.
Treatment regimens varied: three trials administered a 4-g loading dose only, and three included a maintenance dose (a 4-6-g loading dose and a 1-2 g/hour maintenance dose). “Although we attempted to explore variation through subgroup analyses, the ability to do this was limited,” the researchers wrote.
Up to 2 years of corrected age, magnesium sulfate reduced the risk of cerebral palsy compared with placebo (relative risk, 0.71; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.57-0.89) and death or cerebral palsy (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.98), with a high-certainty grade of evidence. The number needed to treat to prevent one case of cerebral palsy was 60 and the number needed to treat death or cerebral palsy was 56. The impact on severe intracranial hemorrhage (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.60-0.98), a secondary outcome, was backed by moderate-certainty evidence.
Compared with the 2009 Cochrane review, the new study includes two new randomized controlled trials. One of which, the MAGENTA trial, administered magnesium sulfate at 30-34 weeks gestation and included new school-age follow-up data from two previously included trials. While the available data suggest little to no difference in outcomes at school age, more follow-up data are needed to assess this with greater certainty, the reviewers wrote.
While severe adverse outcomes (death, cardiac or respiratory arrest) for pregnant individuals appear not to have increased in pregnant patients who received magnesium sulfate (low-certainty evidence), the compound “probably increased maternal adverse effects severe enough to stop treatment,” the reviewers report (average RR, 3.21; 95% CI, 1.88-5.48; moderate-certainty evidence).
Side effects that were more frequent among women receiving magnesium sulfate include hypotension, tachycardia, warmth over body/flushing, nausea or vomiting, sweating, and dizziness.
“Treatment cessation due to such side effects was in the context of trials being conducted to establish benefit,” noted Dr. Shepherd, of the University of Adelaide in Australia. “With benefit now shown, these side effects may be viewed as comparatively minor/generally tolerable considering the potential benefits for children.”
Proving the neuroprotective value of magnesium sulfate took many years, Dr. Burd explained in the Master Class, as none of the randomized controlled trials analyzed in eventual meta-analyses and systematic reviews had reached their primary endpoints. It wasn’t until researchers obtained unpublished data and conducted these analyses and reviews that a significant effect of magnesium sulfate on cerebral palsy could be seen. Dr. Burd and other researchers are now working to better understand its biologic plausibility and precise mechanisms of action.
Dr. Shepherd disclosed that she is a former editor for Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth and current sign-off editor for Cochrane Central Editorial Service but reported having no involvement in the editorial processing of the review. Other authors disclosed that they were investigators for included trials and/or have published opinions in medical journals related to magnesium sulfate to reduce cerebral palsy. Dr. Burd reported no disclosures.
An updated Cochrane Systematic Review of magnesium sulfate administered before preterm birth for neuroprotection has reaffirmed that the compound significantly reduces the risk of cerebral palsy and has added the finding that it also may reduce the risk of severe neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage.
Still unknown, however, is whether the effects of magnesium sulfate vary according to patient characteristics such as gestational age, or by treatment characteristics such as timing and dose. “We need further research to determine exactly who to treat, and when and how, to ideally standardize clinical practice recommendations across the world,” said Emily S. Shepherd, PhD, lead author of the review.
Magnesium sulfate is widely used for preterm cerebral palsy prevention but variance in national and local recommendations for its use may impede its optimal uptake in some places, she and her co-investigators wrote in the review.
In the United States, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists advises institutions to develop their own guidelines regarding inclusion criteria and treatment regimens “in accordance with one of the larger trials.” (ACOG’s Committee Opinion on Magnesium Sulfate Before Anticipated Preterm Birth for Neuroprotection was originally published in 2010 and was reaffirmed in 2023.)
In a Master Class column on magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection published earlier this year in Ob.Gyn. News, Irina Burd, MD, PhD, wrote that most hospitals in the United States have chosen a higher dose of magnesium sulfate administered up to 31 weeks’ gestation (6-g bolus, followed by 2 g/hour), in keeping with the protocols used in the BEAM trial published by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). Dr. Burd is the Sylvan Frieman, MD, Endowed Professor and chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland.
The new Cochrane review included six randomized controlled trials (including the NICHD trial) covering 5917 pregnant participants and 6759 fetuses. Eligibility criteria varied, but all the RCTs included patients in preterm labor or with expected or planned imminent preterm birth at less than 34 weeks’ gestation.
Treatment regimens varied: three trials administered a 4-g loading dose only, and three included a maintenance dose (a 4-6-g loading dose and a 1-2 g/hour maintenance dose). “Although we attempted to explore variation through subgroup analyses, the ability to do this was limited,” the researchers wrote.
Up to 2 years of corrected age, magnesium sulfate reduced the risk of cerebral palsy compared with placebo (relative risk, 0.71; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.57-0.89) and death or cerebral palsy (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.98), with a high-certainty grade of evidence. The number needed to treat to prevent one case of cerebral palsy was 60 and the number needed to treat death or cerebral palsy was 56. The impact on severe intracranial hemorrhage (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.60-0.98), a secondary outcome, was backed by moderate-certainty evidence.
Compared with the 2009 Cochrane review, the new study includes two new randomized controlled trials. One of which, the MAGENTA trial, administered magnesium sulfate at 30-34 weeks gestation and included new school-age follow-up data from two previously included trials. While the available data suggest little to no difference in outcomes at school age, more follow-up data are needed to assess this with greater certainty, the reviewers wrote.
While severe adverse outcomes (death, cardiac or respiratory arrest) for pregnant individuals appear not to have increased in pregnant patients who received magnesium sulfate (low-certainty evidence), the compound “probably increased maternal adverse effects severe enough to stop treatment,” the reviewers report (average RR, 3.21; 95% CI, 1.88-5.48; moderate-certainty evidence).
Side effects that were more frequent among women receiving magnesium sulfate include hypotension, tachycardia, warmth over body/flushing, nausea or vomiting, sweating, and dizziness.
“Treatment cessation due to such side effects was in the context of trials being conducted to establish benefit,” noted Dr. Shepherd, of the University of Adelaide in Australia. “With benefit now shown, these side effects may be viewed as comparatively minor/generally tolerable considering the potential benefits for children.”
Proving the neuroprotective value of magnesium sulfate took many years, Dr. Burd explained in the Master Class, as none of the randomized controlled trials analyzed in eventual meta-analyses and systematic reviews had reached their primary endpoints. It wasn’t until researchers obtained unpublished data and conducted these analyses and reviews that a significant effect of magnesium sulfate on cerebral palsy could be seen. Dr. Burd and other researchers are now working to better understand its biologic plausibility and precise mechanisms of action.
Dr. Shepherd disclosed that she is a former editor for Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth and current sign-off editor for Cochrane Central Editorial Service but reported having no involvement in the editorial processing of the review. Other authors disclosed that they were investigators for included trials and/or have published opinions in medical journals related to magnesium sulfate to reduce cerebral palsy. Dr. Burd reported no disclosures.
An updated Cochrane Systematic Review of magnesium sulfate administered before preterm birth for neuroprotection has reaffirmed that the compound significantly reduces the risk of cerebral palsy and has added the finding that it also may reduce the risk of severe neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage.
Still unknown, however, is whether the effects of magnesium sulfate vary according to patient characteristics such as gestational age, or by treatment characteristics such as timing and dose. “We need further research to determine exactly who to treat, and when and how, to ideally standardize clinical practice recommendations across the world,” said Emily S. Shepherd, PhD, lead author of the review.
Magnesium sulfate is widely used for preterm cerebral palsy prevention but variance in national and local recommendations for its use may impede its optimal uptake in some places, she and her co-investigators wrote in the review.
In the United States, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists advises institutions to develop their own guidelines regarding inclusion criteria and treatment regimens “in accordance with one of the larger trials.” (ACOG’s Committee Opinion on Magnesium Sulfate Before Anticipated Preterm Birth for Neuroprotection was originally published in 2010 and was reaffirmed in 2023.)
In a Master Class column on magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection published earlier this year in Ob.Gyn. News, Irina Burd, MD, PhD, wrote that most hospitals in the United States have chosen a higher dose of magnesium sulfate administered up to 31 weeks’ gestation (6-g bolus, followed by 2 g/hour), in keeping with the protocols used in the BEAM trial published by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). Dr. Burd is the Sylvan Frieman, MD, Endowed Professor and chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland.
The new Cochrane review included six randomized controlled trials (including the NICHD trial) covering 5917 pregnant participants and 6759 fetuses. Eligibility criteria varied, but all the RCTs included patients in preterm labor or with expected or planned imminent preterm birth at less than 34 weeks’ gestation.
Treatment regimens varied: three trials administered a 4-g loading dose only, and three included a maintenance dose (a 4-6-g loading dose and a 1-2 g/hour maintenance dose). “Although we attempted to explore variation through subgroup analyses, the ability to do this was limited,” the researchers wrote.
Up to 2 years of corrected age, magnesium sulfate reduced the risk of cerebral palsy compared with placebo (relative risk, 0.71; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.57-0.89) and death or cerebral palsy (RR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77-0.98), with a high-certainty grade of evidence. The number needed to treat to prevent one case of cerebral palsy was 60 and the number needed to treat death or cerebral palsy was 56. The impact on severe intracranial hemorrhage (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.60-0.98), a secondary outcome, was backed by moderate-certainty evidence.
Compared with the 2009 Cochrane review, the new study includes two new randomized controlled trials. One of which, the MAGENTA trial, administered magnesium sulfate at 30-34 weeks gestation and included new school-age follow-up data from two previously included trials. While the available data suggest little to no difference in outcomes at school age, more follow-up data are needed to assess this with greater certainty, the reviewers wrote.
While severe adverse outcomes (death, cardiac or respiratory arrest) for pregnant individuals appear not to have increased in pregnant patients who received magnesium sulfate (low-certainty evidence), the compound “probably increased maternal adverse effects severe enough to stop treatment,” the reviewers report (average RR, 3.21; 95% CI, 1.88-5.48; moderate-certainty evidence).
Side effects that were more frequent among women receiving magnesium sulfate include hypotension, tachycardia, warmth over body/flushing, nausea or vomiting, sweating, and dizziness.
“Treatment cessation due to such side effects was in the context of trials being conducted to establish benefit,” noted Dr. Shepherd, of the University of Adelaide in Australia. “With benefit now shown, these side effects may be viewed as comparatively minor/generally tolerable considering the potential benefits for children.”
Proving the neuroprotective value of magnesium sulfate took many years, Dr. Burd explained in the Master Class, as none of the randomized controlled trials analyzed in eventual meta-analyses and systematic reviews had reached their primary endpoints. It wasn’t until researchers obtained unpublished data and conducted these analyses and reviews that a significant effect of magnesium sulfate on cerebral palsy could be seen. Dr. Burd and other researchers are now working to better understand its biologic plausibility and precise mechanisms of action.
Dr. Shepherd disclosed that she is a former editor for Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth and current sign-off editor for Cochrane Central Editorial Service but reported having no involvement in the editorial processing of the review. Other authors disclosed that they were investigators for included trials and/or have published opinions in medical journals related to magnesium sulfate to reduce cerebral palsy. Dr. Burd reported no disclosures.
COCHRANE DATABASE SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Study Highlights Atopic Dermatitis Features, Treatments Among Older Patients
.
The researchers reviewed charts of patients aged 60 years and older who were seen at either a private or county dermatology clinic in Houston between 2009 and 2020 and had been diagnosed with AD by a dermatologist. The findings of their cross-sectional study further supports that AD in this age group “presents as a unique phenotype compared to AD in younger ages, which may inform dermatologists’ diagnosis of AD in these patients” they wrote.
The 791 patients in the study had an average age of 69.3 years, were predominantly women (60.1%), and were racially diverse, with almost 40% being non-Hispanic White individuals. Others were non-Hispanic Black individuals (21.8%), Hispanics (20.4%), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islanders (11.7%).
Use of topicals, mainly topical corticosteroids (92.2%), was the most frequent treatment prescribed. Oral corticosteroids and antihistamines were “frequent systemic treatments” in this population, prescribed to 10.4% and 12.1%, respectively, “likely due to management prior to a diagnosis of AD by a dermatologist,” wrote first author Hannah Y. Wang, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and her coauthors, including Soo Jung Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Baylor.
Other treatments included dupilumab in 5.4%, systemic immunosuppressants (including methotrexate, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate) in 5.4%, and UVB-phototherapy in 2.7%.
Approximately 40% of the patients had a history of allergic rhinitis, while 20% had a history of asthma. Lichenification was noted in 14.5% of patients and nummular lesions in almost 13%. Other rash characteristics — ichthyosis and hyperpigmented patches — were less frequent, seen in 9.7% and 9.1%, respectively.
AD in this older population was most commonly documented on the extensors (49.9%) and the trunk (46%) and less commonly on the hands (19.8%) and feet (9%) — a distribution that is similar to past reports, the authors wrote.
Asked to comment on the findings, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization that the data relating to clinical morphology are consistent with past reports and with his own experiences. Lichenification is a “tell-tale sign of chronic disease” and may indicate undertreatment, and the frequency of nummular plaques is unsurprising because “nummular dermatitis as an independent eczema tends to occur more so in the elderly.”
More important, he said, was the finding regarding the use of oral corticosteroid and antihistamine, “both of which are advocated against in the management of AD.”
More research is “needed to elucidate the unique features of elderly AD in pathophysiology and optimal treatments,” the authors wrote, noting that age-related factors potentially affecting AD in this population include reduced skin barrier function, immune dysregulation, and environmental exposures.
The study, Dr. Friedman said, “shines a spotlight on this demographic — they exist, they suffer, and they are at times being managed with less-than-optimal options.” Clinical trials of “the welcome additions to our historically limited armament often lack a substantial elderly study population,” he said, and Medicare makes it “painful to get these game-changing drugs for this large patient population.”
The study authors and Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The researchers reviewed charts of patients aged 60 years and older who were seen at either a private or county dermatology clinic in Houston between 2009 and 2020 and had been diagnosed with AD by a dermatologist. The findings of their cross-sectional study further supports that AD in this age group “presents as a unique phenotype compared to AD in younger ages, which may inform dermatologists’ diagnosis of AD in these patients” they wrote.
The 791 patients in the study had an average age of 69.3 years, were predominantly women (60.1%), and were racially diverse, with almost 40% being non-Hispanic White individuals. Others were non-Hispanic Black individuals (21.8%), Hispanics (20.4%), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islanders (11.7%).
Use of topicals, mainly topical corticosteroids (92.2%), was the most frequent treatment prescribed. Oral corticosteroids and antihistamines were “frequent systemic treatments” in this population, prescribed to 10.4% and 12.1%, respectively, “likely due to management prior to a diagnosis of AD by a dermatologist,” wrote first author Hannah Y. Wang, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and her coauthors, including Soo Jung Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Baylor.
Other treatments included dupilumab in 5.4%, systemic immunosuppressants (including methotrexate, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate) in 5.4%, and UVB-phototherapy in 2.7%.
Approximately 40% of the patients had a history of allergic rhinitis, while 20% had a history of asthma. Lichenification was noted in 14.5% of patients and nummular lesions in almost 13%. Other rash characteristics — ichthyosis and hyperpigmented patches — were less frequent, seen in 9.7% and 9.1%, respectively.
AD in this older population was most commonly documented on the extensors (49.9%) and the trunk (46%) and less commonly on the hands (19.8%) and feet (9%) — a distribution that is similar to past reports, the authors wrote.
Asked to comment on the findings, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization that the data relating to clinical morphology are consistent with past reports and with his own experiences. Lichenification is a “tell-tale sign of chronic disease” and may indicate undertreatment, and the frequency of nummular plaques is unsurprising because “nummular dermatitis as an independent eczema tends to occur more so in the elderly.”
More important, he said, was the finding regarding the use of oral corticosteroid and antihistamine, “both of which are advocated against in the management of AD.”
More research is “needed to elucidate the unique features of elderly AD in pathophysiology and optimal treatments,” the authors wrote, noting that age-related factors potentially affecting AD in this population include reduced skin barrier function, immune dysregulation, and environmental exposures.
The study, Dr. Friedman said, “shines a spotlight on this demographic — they exist, they suffer, and they are at times being managed with less-than-optimal options.” Clinical trials of “the welcome additions to our historically limited armament often lack a substantial elderly study population,” he said, and Medicare makes it “painful to get these game-changing drugs for this large patient population.”
The study authors and Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The researchers reviewed charts of patients aged 60 years and older who were seen at either a private or county dermatology clinic in Houston between 2009 and 2020 and had been diagnosed with AD by a dermatologist. The findings of their cross-sectional study further supports that AD in this age group “presents as a unique phenotype compared to AD in younger ages, which may inform dermatologists’ diagnosis of AD in these patients” they wrote.
The 791 patients in the study had an average age of 69.3 years, were predominantly women (60.1%), and were racially diverse, with almost 40% being non-Hispanic White individuals. Others were non-Hispanic Black individuals (21.8%), Hispanics (20.4%), and non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islanders (11.7%).
Use of topicals, mainly topical corticosteroids (92.2%), was the most frequent treatment prescribed. Oral corticosteroids and antihistamines were “frequent systemic treatments” in this population, prescribed to 10.4% and 12.1%, respectively, “likely due to management prior to a diagnosis of AD by a dermatologist,” wrote first author Hannah Y. Wang, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and her coauthors, including Soo Jung Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Baylor.
Other treatments included dupilumab in 5.4%, systemic immunosuppressants (including methotrexate, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate) in 5.4%, and UVB-phototherapy in 2.7%.
Approximately 40% of the patients had a history of allergic rhinitis, while 20% had a history of asthma. Lichenification was noted in 14.5% of patients and nummular lesions in almost 13%. Other rash characteristics — ichthyosis and hyperpigmented patches — were less frequent, seen in 9.7% and 9.1%, respectively.
AD in this older population was most commonly documented on the extensors (49.9%) and the trunk (46%) and less commonly on the hands (19.8%) and feet (9%) — a distribution that is similar to past reports, the authors wrote.
Asked to comment on the findings, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization that the data relating to clinical morphology are consistent with past reports and with his own experiences. Lichenification is a “tell-tale sign of chronic disease” and may indicate undertreatment, and the frequency of nummular plaques is unsurprising because “nummular dermatitis as an independent eczema tends to occur more so in the elderly.”
More important, he said, was the finding regarding the use of oral corticosteroid and antihistamine, “both of which are advocated against in the management of AD.”
More research is “needed to elucidate the unique features of elderly AD in pathophysiology and optimal treatments,” the authors wrote, noting that age-related factors potentially affecting AD in this population include reduced skin barrier function, immune dysregulation, and environmental exposures.
The study, Dr. Friedman said, “shines a spotlight on this demographic — they exist, they suffer, and they are at times being managed with less-than-optimal options.” Clinical trials of “the welcome additions to our historically limited armament often lack a substantial elderly study population,” he said, and Medicare makes it “painful to get these game-changing drugs for this large patient population.”
The study authors and Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAAD INTERNATIONAL
Risk of Knee OA From Weight-Bearing Exercise Seen Only With Low Muscle Mass
Weight-bearing recreational activity was associated with a 22% increased odds of developing knee osteoarthritis (OA) in a large prospective cohort study in the Netherlands, but notably, the increased risk was seen only in those with low levels of lower-limb muscle mass.
The findings point toward the value of “tailored advice” for physical activity, and suggest that “caution is needed when engaging in weight-bearing activity, especially for individuals with low levels of lower-limb muscle mass,” Yahong Wu, MD, and coinvestigators, of the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, wrote in JAMA Network Open.
Investigators used data from sequential cohorts of the longitudinal Rotterdam Study, which enrolled people aged 45 and older starting in 1990. The 5003 participants in this new analysis of physical activity and knee OA had complete records of baseline recreational physical activity, baseline knee pain, and knee radiographs from both baseline and at least one follow-up exam. Those with radiographically defined knee OA at baseline were excluded.
The incident rate of radiographically defined (x-ray) knee OA among all participants was 8.4%, with a mean follow-up time of 6.33 years. Among 3492 individuals without baseline knee pain, the researchers found no increased odds of incident radiographic OA with non–weight-bearing activity (odds ratio [OR], 1.04; 95% CI, 0.95-1.15; P = .37) but a significant association of weight-bearing activity with OA incidence (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.10-1.35; P < .001).
A stratification analysis of a subset of participants whose lower-limb mass had been measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) showed, however, that the association of weight-bearing activity with incident OA was limited to patients in the lowest third of lower-limb muscle mass index (LMI), who had a 53% increased likelihood of developing knee OA (OR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.15-2.04; P = .003).
For patients in the middle and upper tertiles, there was no significant association between weight-bearing activity and the odds of incident OA (OR, 0.93; P = .73, and OR, 1.15; P = .40, respectively).
The findings are reassuring overall, said Kelli D. Allen, PhD, research professor of medicine and exercise physiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was asked to comment on the study. “The study corroborates prior research showing that for most people, weight-bearing recreational activity does not increase the risk of knee osteoarthritis. This should be encouraging for people who want to increase their physical activity,” she said.
The study also suggests that “for people with low lower-limb muscle mass, there may be some considerations to make regarding the best type of physical activity to prevent future knee osteoarthritis,” she said in an e-mail. “The best approach may include non–weight-bearing activities, which could include biking, swimming, or other water exercises, along with strengthening exercises that help to increase muscle mass.”
Other studies, Dr. Allen said, have shown that low muscle mass itself is a risk factor for knee OA.
Physical Activity Types, Other Analyses
The researchers assessed total, weight-bearing, and non–weight-bearing physical activity using two validated questionnaires (an adapted version of the Zutphen Physical Activity Questionnaire and the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam physical activity questionnaire) that asked participants about the frequency and duration of various types of physical activity. Activity was quantified as metabolic equivalent of task (MET) hours per week, and weight-bearing activities were defined as those in which the knee joint bears the body’s weight.
Walking, gardening, golf, dancing, and ball sports were among the activities qualifying as weight-bearing activities. Non–weight-bearing activities included cycling, rowing, and swimming.
Sex, body mass index, and follow-up time were among the covariates adjusted for in the primary analysis. Similar results were found when adjustments were also made for educational level, alcohol intake, lipid levels, and diabetes.
While incident radiographic knee OA (measured using the Kellgren & Lawrence grading system) was the primary outcome, the researchers also looked at symptomatic knee OA, as defined by x-ray and a knee pain questionnaire, and found no significant association of its incidence with any of the exercise categories (total, weight-bearing, or non-weight-bearing).
Coauthor Joyce B. J. van Meurs, PhD, of the departments of internal medicine and orthopedics & sports medicine at Erasmus Medical Center, told this news organization that “pain as a subjective, recurrent symptom is more difficult to study … [and] a larger sample size or more precise measurements [of pain] in future studies would help to better understand the true association” of symptomatic knee OA and physical activity.
Similarly, analyses of the 1511 patients (out of 5003) who had knee pain at baseline found no significant association of weight-bearing or non–weight-bearing physical activity with incident radiographic knee OA. The trends were similar to those found in the population without knee pain, however, which suggests the analysis was underpowered, the researchers wrote, noting too that patients with baseline pain had lower activity levels than those without pain. (Low case numbers precluded a stratification analysis on LMI for incident symptomatic OA.)
Thigh Circumference as an Indicator of Muscle Mass
The findings build upon an international meta-analysis published in 2021 that found no association between total physical activity and knee OA and align with other studies suggesting a link between greater mechanical stress/strain and greater OA risk, the researchers wrote. (The meta-analysis couldn’t investigate different types of activity.)
“Although we cannot establish a causal relationship … we hypothesize that the mechanical loading on joints and cartilage could explain the association of weight-bearing activity with osteoarthritis in the low LMI tertile group,” they said.
It is possible that thigh muscle-specific strength or mass may temper the risk of knee OA, they wrote, but the lack of thigh strength data in the Rotterdam Study precluded such evaluation. Still, in everyday practice, the researchers noted, lower limb muscle function could be assessed using thigh circumference.
Dr. Allen agreed. “ ‘Gold standard’ assessment of muscle mass is not common in routine practice, but clinicians can evaluate muscle mass in other ways, such as thigh circumference,” she told this news organization, noting that measurement should align with procedures described by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in its anthropometry procedures manual.
“If low lower-limb muscle mass is suspected, a referral to a physical therapist can be helpful for more formally assessing muscle mass and muscle strength,” she added, “and for instructions for a safe and appropriate exercise program for building muscle and protecting joints.”
Among other limitations of the study, according to the researchers, are an ethnically nondiverse population, the unavailability of knee injury data, and the assessment of physical activity only at baseline.
Moving forward, Dr. van Meurs told this news organization, “the main question regarding physical activity and OA is still, if people already have pain or early OA complaints, what kinds of sports they can do without hurting their joints?” This “should be tested,” she said, “in a real-life, ideally trial-like intervention study.”
The study was funded by the Erasmus Medical Center and Erasmus University as well as through various government grants. Dr. Wu also had study support from the China Scholarship Council. Two of the authors reported relationships with arthritis-related organizations. Dr. Allen reported having no disclosures relevant to her comments.
Weight-bearing recreational activity was associated with a 22% increased odds of developing knee osteoarthritis (OA) in a large prospective cohort study in the Netherlands, but notably, the increased risk was seen only in those with low levels of lower-limb muscle mass.
The findings point toward the value of “tailored advice” for physical activity, and suggest that “caution is needed when engaging in weight-bearing activity, especially for individuals with low levels of lower-limb muscle mass,” Yahong Wu, MD, and coinvestigators, of the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, wrote in JAMA Network Open.
Investigators used data from sequential cohorts of the longitudinal Rotterdam Study, which enrolled people aged 45 and older starting in 1990. The 5003 participants in this new analysis of physical activity and knee OA had complete records of baseline recreational physical activity, baseline knee pain, and knee radiographs from both baseline and at least one follow-up exam. Those with radiographically defined knee OA at baseline were excluded.
The incident rate of radiographically defined (x-ray) knee OA among all participants was 8.4%, with a mean follow-up time of 6.33 years. Among 3492 individuals without baseline knee pain, the researchers found no increased odds of incident radiographic OA with non–weight-bearing activity (odds ratio [OR], 1.04; 95% CI, 0.95-1.15; P = .37) but a significant association of weight-bearing activity with OA incidence (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.10-1.35; P < .001).
A stratification analysis of a subset of participants whose lower-limb mass had been measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) showed, however, that the association of weight-bearing activity with incident OA was limited to patients in the lowest third of lower-limb muscle mass index (LMI), who had a 53% increased likelihood of developing knee OA (OR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.15-2.04; P = .003).
For patients in the middle and upper tertiles, there was no significant association between weight-bearing activity and the odds of incident OA (OR, 0.93; P = .73, and OR, 1.15; P = .40, respectively).
The findings are reassuring overall, said Kelli D. Allen, PhD, research professor of medicine and exercise physiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was asked to comment on the study. “The study corroborates prior research showing that for most people, weight-bearing recreational activity does not increase the risk of knee osteoarthritis. This should be encouraging for people who want to increase their physical activity,” she said.
The study also suggests that “for people with low lower-limb muscle mass, there may be some considerations to make regarding the best type of physical activity to prevent future knee osteoarthritis,” she said in an e-mail. “The best approach may include non–weight-bearing activities, which could include biking, swimming, or other water exercises, along with strengthening exercises that help to increase muscle mass.”
Other studies, Dr. Allen said, have shown that low muscle mass itself is a risk factor for knee OA.
Physical Activity Types, Other Analyses
The researchers assessed total, weight-bearing, and non–weight-bearing physical activity using two validated questionnaires (an adapted version of the Zutphen Physical Activity Questionnaire and the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam physical activity questionnaire) that asked participants about the frequency and duration of various types of physical activity. Activity was quantified as metabolic equivalent of task (MET) hours per week, and weight-bearing activities were defined as those in which the knee joint bears the body’s weight.
Walking, gardening, golf, dancing, and ball sports were among the activities qualifying as weight-bearing activities. Non–weight-bearing activities included cycling, rowing, and swimming.
Sex, body mass index, and follow-up time were among the covariates adjusted for in the primary analysis. Similar results were found when adjustments were also made for educational level, alcohol intake, lipid levels, and diabetes.
While incident radiographic knee OA (measured using the Kellgren & Lawrence grading system) was the primary outcome, the researchers also looked at symptomatic knee OA, as defined by x-ray and a knee pain questionnaire, and found no significant association of its incidence with any of the exercise categories (total, weight-bearing, or non-weight-bearing).
Coauthor Joyce B. J. van Meurs, PhD, of the departments of internal medicine and orthopedics & sports medicine at Erasmus Medical Center, told this news organization that “pain as a subjective, recurrent symptom is more difficult to study … [and] a larger sample size or more precise measurements [of pain] in future studies would help to better understand the true association” of symptomatic knee OA and physical activity.
Similarly, analyses of the 1511 patients (out of 5003) who had knee pain at baseline found no significant association of weight-bearing or non–weight-bearing physical activity with incident radiographic knee OA. The trends were similar to those found in the population without knee pain, however, which suggests the analysis was underpowered, the researchers wrote, noting too that patients with baseline pain had lower activity levels than those without pain. (Low case numbers precluded a stratification analysis on LMI for incident symptomatic OA.)
Thigh Circumference as an Indicator of Muscle Mass
The findings build upon an international meta-analysis published in 2021 that found no association between total physical activity and knee OA and align with other studies suggesting a link between greater mechanical stress/strain and greater OA risk, the researchers wrote. (The meta-analysis couldn’t investigate different types of activity.)
“Although we cannot establish a causal relationship … we hypothesize that the mechanical loading on joints and cartilage could explain the association of weight-bearing activity with osteoarthritis in the low LMI tertile group,” they said.
It is possible that thigh muscle-specific strength or mass may temper the risk of knee OA, they wrote, but the lack of thigh strength data in the Rotterdam Study precluded such evaluation. Still, in everyday practice, the researchers noted, lower limb muscle function could be assessed using thigh circumference.
Dr. Allen agreed. “ ‘Gold standard’ assessment of muscle mass is not common in routine practice, but clinicians can evaluate muscle mass in other ways, such as thigh circumference,” she told this news organization, noting that measurement should align with procedures described by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in its anthropometry procedures manual.
“If low lower-limb muscle mass is suspected, a referral to a physical therapist can be helpful for more formally assessing muscle mass and muscle strength,” she added, “and for instructions for a safe and appropriate exercise program for building muscle and protecting joints.”
Among other limitations of the study, according to the researchers, are an ethnically nondiverse population, the unavailability of knee injury data, and the assessment of physical activity only at baseline.
Moving forward, Dr. van Meurs told this news organization, “the main question regarding physical activity and OA is still, if people already have pain or early OA complaints, what kinds of sports they can do without hurting their joints?” This “should be tested,” she said, “in a real-life, ideally trial-like intervention study.”
The study was funded by the Erasmus Medical Center and Erasmus University as well as through various government grants. Dr. Wu also had study support from the China Scholarship Council. Two of the authors reported relationships with arthritis-related organizations. Dr. Allen reported having no disclosures relevant to her comments.
Weight-bearing recreational activity was associated with a 22% increased odds of developing knee osteoarthritis (OA) in a large prospective cohort study in the Netherlands, but notably, the increased risk was seen only in those with low levels of lower-limb muscle mass.
The findings point toward the value of “tailored advice” for physical activity, and suggest that “caution is needed when engaging in weight-bearing activity, especially for individuals with low levels of lower-limb muscle mass,” Yahong Wu, MD, and coinvestigators, of the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, wrote in JAMA Network Open.
Investigators used data from sequential cohorts of the longitudinal Rotterdam Study, which enrolled people aged 45 and older starting in 1990. The 5003 participants in this new analysis of physical activity and knee OA had complete records of baseline recreational physical activity, baseline knee pain, and knee radiographs from both baseline and at least one follow-up exam. Those with radiographically defined knee OA at baseline were excluded.
The incident rate of radiographically defined (x-ray) knee OA among all participants was 8.4%, with a mean follow-up time of 6.33 years. Among 3492 individuals without baseline knee pain, the researchers found no increased odds of incident radiographic OA with non–weight-bearing activity (odds ratio [OR], 1.04; 95% CI, 0.95-1.15; P = .37) but a significant association of weight-bearing activity with OA incidence (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.10-1.35; P < .001).
A stratification analysis of a subset of participants whose lower-limb mass had been measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) showed, however, that the association of weight-bearing activity with incident OA was limited to patients in the lowest third of lower-limb muscle mass index (LMI), who had a 53% increased likelihood of developing knee OA (OR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.15-2.04; P = .003).
For patients in the middle and upper tertiles, there was no significant association between weight-bearing activity and the odds of incident OA (OR, 0.93; P = .73, and OR, 1.15; P = .40, respectively).
The findings are reassuring overall, said Kelli D. Allen, PhD, research professor of medicine and exercise physiologist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was asked to comment on the study. “The study corroborates prior research showing that for most people, weight-bearing recreational activity does not increase the risk of knee osteoarthritis. This should be encouraging for people who want to increase their physical activity,” she said.
The study also suggests that “for people with low lower-limb muscle mass, there may be some considerations to make regarding the best type of physical activity to prevent future knee osteoarthritis,” she said in an e-mail. “The best approach may include non–weight-bearing activities, which could include biking, swimming, or other water exercises, along with strengthening exercises that help to increase muscle mass.”
Other studies, Dr. Allen said, have shown that low muscle mass itself is a risk factor for knee OA.
Physical Activity Types, Other Analyses
The researchers assessed total, weight-bearing, and non–weight-bearing physical activity using two validated questionnaires (an adapted version of the Zutphen Physical Activity Questionnaire and the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam physical activity questionnaire) that asked participants about the frequency and duration of various types of physical activity. Activity was quantified as metabolic equivalent of task (MET) hours per week, and weight-bearing activities were defined as those in which the knee joint bears the body’s weight.
Walking, gardening, golf, dancing, and ball sports were among the activities qualifying as weight-bearing activities. Non–weight-bearing activities included cycling, rowing, and swimming.
Sex, body mass index, and follow-up time were among the covariates adjusted for in the primary analysis. Similar results were found when adjustments were also made for educational level, alcohol intake, lipid levels, and diabetes.
While incident radiographic knee OA (measured using the Kellgren & Lawrence grading system) was the primary outcome, the researchers also looked at symptomatic knee OA, as defined by x-ray and a knee pain questionnaire, and found no significant association of its incidence with any of the exercise categories (total, weight-bearing, or non-weight-bearing).
Coauthor Joyce B. J. van Meurs, PhD, of the departments of internal medicine and orthopedics & sports medicine at Erasmus Medical Center, told this news organization that “pain as a subjective, recurrent symptom is more difficult to study … [and] a larger sample size or more precise measurements [of pain] in future studies would help to better understand the true association” of symptomatic knee OA and physical activity.
Similarly, analyses of the 1511 patients (out of 5003) who had knee pain at baseline found no significant association of weight-bearing or non–weight-bearing physical activity with incident radiographic knee OA. The trends were similar to those found in the population without knee pain, however, which suggests the analysis was underpowered, the researchers wrote, noting too that patients with baseline pain had lower activity levels than those without pain. (Low case numbers precluded a stratification analysis on LMI for incident symptomatic OA.)
Thigh Circumference as an Indicator of Muscle Mass
The findings build upon an international meta-analysis published in 2021 that found no association between total physical activity and knee OA and align with other studies suggesting a link between greater mechanical stress/strain and greater OA risk, the researchers wrote. (The meta-analysis couldn’t investigate different types of activity.)
“Although we cannot establish a causal relationship … we hypothesize that the mechanical loading on joints and cartilage could explain the association of weight-bearing activity with osteoarthritis in the low LMI tertile group,” they said.
It is possible that thigh muscle-specific strength or mass may temper the risk of knee OA, they wrote, but the lack of thigh strength data in the Rotterdam Study precluded such evaluation. Still, in everyday practice, the researchers noted, lower limb muscle function could be assessed using thigh circumference.
Dr. Allen agreed. “ ‘Gold standard’ assessment of muscle mass is not common in routine practice, but clinicians can evaluate muscle mass in other ways, such as thigh circumference,” she told this news organization, noting that measurement should align with procedures described by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in its anthropometry procedures manual.
“If low lower-limb muscle mass is suspected, a referral to a physical therapist can be helpful for more formally assessing muscle mass and muscle strength,” she added, “and for instructions for a safe and appropriate exercise program for building muscle and protecting joints.”
Among other limitations of the study, according to the researchers, are an ethnically nondiverse population, the unavailability of knee injury data, and the assessment of physical activity only at baseline.
Moving forward, Dr. van Meurs told this news organization, “the main question regarding physical activity and OA is still, if people already have pain or early OA complaints, what kinds of sports they can do without hurting their joints?” This “should be tested,” she said, “in a real-life, ideally trial-like intervention study.”
The study was funded by the Erasmus Medical Center and Erasmus University as well as through various government grants. Dr. Wu also had study support from the China Scholarship Council. Two of the authors reported relationships with arthritis-related organizations. Dr. Allen reported having no disclosures relevant to her comments.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Dietary Factors Linked to Development of Spondyloarthritis, Preliminary Findings Suggest
Preliminary findings from a small case-control study at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, suggest an association between diet and the development of spondyloarthritis (SpA), researchers reported in a poster at the Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
The small study involving 106 cases of incident spondyloarthritis matched 5:1 to individuals without SpA on the basis of age, sex, year, and geography found that risk was significantly higher with consumption of nondiet soda (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.76), and with use of certain supplements: folate (aOR, 2.56), B vitamins (1.98), and fish oil (1.83). Moderate alcohol use ranging from two servings per month up to five per week was associated with a significantly lower risk of SpA (aOR, 0.63).
“We have seen an association between diet and RA. There is also strong literature showing an association between the microbiome and spondyloarthritis. Putting these two together, we wanted to see if the same was true for spondyloarthritis,” Vanessa Kronzer, MD, a rheumatologist at Mayo Clinic and a coauthor of the poster, said in an email. “Our results … do suggest an association between diet and developing spondyloarthritis as we suspected, for example, with soda.”
The researchers enrolled patients through the Mayo Clinic Biobank, which aims to engage a population-based sample of primary care patients, and administered questionnaires that assessed dietary and supplement exposures. They identified incident SpA using two diagnosis codes for ankylosing spondylitis or PsA ≥ 30 days apart along with use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. To identify inflammatory bowel disease–associated SpAs, they used two diagnosis codes ≥ 30 days apart and age < 45 years. Follow-up questionnaires were administered 5 years later, Dr. Kronzer said.
Controls were matched on age, sex, year and geography. Logistic regression models adjusted for age, sex, race and ethnicity, education, and smoking, the researchers reported in their poster.
Dr. Kronzer and coauthors reported finding no significant associations with high-fat food, red meat, fish, poultry, diet soda, coffee and tea, and high alcohol use. They reported finding “trends of reduced risk with fruits and vegetables but higher risk with milk/dairy” and said these trends “should be replicated in larger studies.”
The 106 patients with incident spondyloarthritis had a mean age of 51. Three-fourths were female.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Dr. Kronzer and coauthors did not report any disclosures.
Preliminary findings from a small case-control study at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, suggest an association between diet and the development of spondyloarthritis (SpA), researchers reported in a poster at the Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
The small study involving 106 cases of incident spondyloarthritis matched 5:1 to individuals without SpA on the basis of age, sex, year, and geography found that risk was significantly higher with consumption of nondiet soda (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.76), and with use of certain supplements: folate (aOR, 2.56), B vitamins (1.98), and fish oil (1.83). Moderate alcohol use ranging from two servings per month up to five per week was associated with a significantly lower risk of SpA (aOR, 0.63).
“We have seen an association between diet and RA. There is also strong literature showing an association between the microbiome and spondyloarthritis. Putting these two together, we wanted to see if the same was true for spondyloarthritis,” Vanessa Kronzer, MD, a rheumatologist at Mayo Clinic and a coauthor of the poster, said in an email. “Our results … do suggest an association between diet and developing spondyloarthritis as we suspected, for example, with soda.”
The researchers enrolled patients through the Mayo Clinic Biobank, which aims to engage a population-based sample of primary care patients, and administered questionnaires that assessed dietary and supplement exposures. They identified incident SpA using two diagnosis codes for ankylosing spondylitis or PsA ≥ 30 days apart along with use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. To identify inflammatory bowel disease–associated SpAs, they used two diagnosis codes ≥ 30 days apart and age < 45 years. Follow-up questionnaires were administered 5 years later, Dr. Kronzer said.
Controls were matched on age, sex, year and geography. Logistic regression models adjusted for age, sex, race and ethnicity, education, and smoking, the researchers reported in their poster.
Dr. Kronzer and coauthors reported finding no significant associations with high-fat food, red meat, fish, poultry, diet soda, coffee and tea, and high alcohol use. They reported finding “trends of reduced risk with fruits and vegetables but higher risk with milk/dairy” and said these trends “should be replicated in larger studies.”
The 106 patients with incident spondyloarthritis had a mean age of 51. Three-fourths were female.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Dr. Kronzer and coauthors did not report any disclosures.
Preliminary findings from a small case-control study at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, suggest an association between diet and the development of spondyloarthritis (SpA), researchers reported in a poster at the Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
The small study involving 106 cases of incident spondyloarthritis matched 5:1 to individuals without SpA on the basis of age, sex, year, and geography found that risk was significantly higher with consumption of nondiet soda (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.76), and with use of certain supplements: folate (aOR, 2.56), B vitamins (1.98), and fish oil (1.83). Moderate alcohol use ranging from two servings per month up to five per week was associated with a significantly lower risk of SpA (aOR, 0.63).
“We have seen an association between diet and RA. There is also strong literature showing an association between the microbiome and spondyloarthritis. Putting these two together, we wanted to see if the same was true for spondyloarthritis,” Vanessa Kronzer, MD, a rheumatologist at Mayo Clinic and a coauthor of the poster, said in an email. “Our results … do suggest an association between diet and developing spondyloarthritis as we suspected, for example, with soda.”
The researchers enrolled patients through the Mayo Clinic Biobank, which aims to engage a population-based sample of primary care patients, and administered questionnaires that assessed dietary and supplement exposures. They identified incident SpA using two diagnosis codes for ankylosing spondylitis or PsA ≥ 30 days apart along with use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. To identify inflammatory bowel disease–associated SpAs, they used two diagnosis codes ≥ 30 days apart and age < 45 years. Follow-up questionnaires were administered 5 years later, Dr. Kronzer said.
Controls were matched on age, sex, year and geography. Logistic regression models adjusted for age, sex, race and ethnicity, education, and smoking, the researchers reported in their poster.
Dr. Kronzer and coauthors reported finding no significant associations with high-fat food, red meat, fish, poultry, diet soda, coffee and tea, and high alcohol use. They reported finding “trends of reduced risk with fruits and vegetables but higher risk with milk/dairy” and said these trends “should be replicated in larger studies.”
The 106 patients with incident spondyloarthritis had a mean age of 51. Three-fourths were female.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Dr. Kronzer and coauthors did not report any disclosures.
FROM RWCS 2024
New Research Dissects Transgenerational Obesity and Diabetes
FAIRFAX, VIRGINIA — Nearly 30 years ago, in a 1995 paper, the British physician-epidemiologist David Barker, MD, PhD, wrote about his fetal origins hypothesis — the idea that programs to address fetal undernutrition and low birth weight produced later coronary heart disease (BMJ 1995;311:171-4).
His hypothesis and subsequent research led to the concept of adult diseases of fetal origins, which today extends beyond low birth weight and implicates the in utero environment as a significant determinant of risk for adverse childhood and adult metabolic outcomes and for major chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that the offspring of pregnant mothers with diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes themselves.
“It’s a whole discipline [of research],” E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), said in an interview. “But what we’ve never quite understood is the ‘how’ and ‘why’? What are the mechanisms driving the fetal origins of such adverse outcomes in offspring?
At the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG), investigators described studies underway that are digging deeper into the associations between the intrauterine milieu and longer-term offspring health — and that are searching for biological and molecular processes that may be involved.
The studies are like “branches of the Barker hypothesis,” said Dr. Reece, former dean of UMSOM and current director of the UMSOM Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation, who co-organized the DPSG meeting. “They’re taking the hypothesis and dissecting it by asking, for instance, it is possible that transgenerational obesity may align with the Barker hypothesis? Is it possible that it involves epigenetics regulation? Could we find biomarkers?”
The need for a better understanding of the fetal origins framework — and its subsequent transgenerational impact — is urgent. From 2000 to 2018, the prevalence of childhood obesity increased from 14.7% to 19.2% (a 31% increase) and the prevalence of severe childhood obesity rose from 3.9% to 6.1% (a 56% increase), according to data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Obes Facts. 2022;15[4]:560-9).
Children aged 2-5 years have had an especially sharp increase in obesity (Pediatrics 2018;141[3]:e20173459), Christine Wey Hockett, PhD, of the University of South Dakota School of Medicine, said at the DPSG meeting (Figure 1). 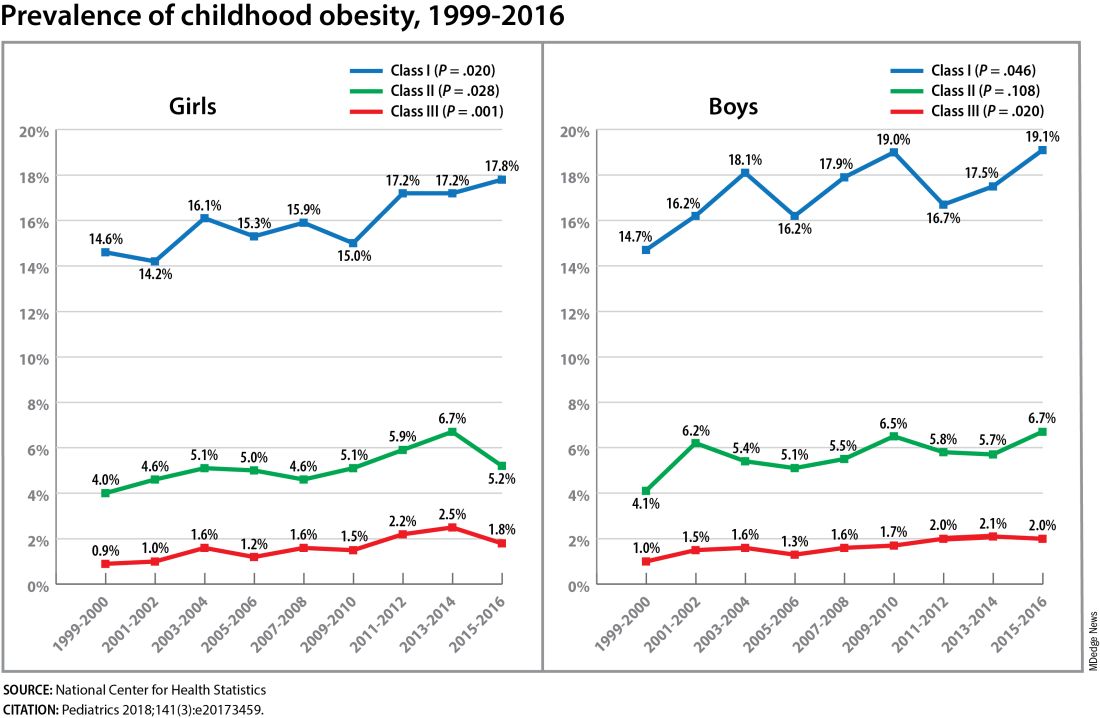
Also notable, she said, is that one-quarter of today’s pediatric diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes, which “is significant as there is a higher prevalence of early complications and comorbidities in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 diabetes.”
Moreover, recent projections estimate that 57% of today’s children will be obese at 35 years of age (N Engl J Med. 2017;377[22]:2145-53) and that 45% will have diabetes or prediabetes by 2030 (Popul Health Manag. 2017;20[1]:6-12), said Dr. Hockett, assistant professor in the university’s department of pediatrics. An investigator of the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes Among Children (EPOCH) study, which looked at gestational diabetes (GDM) and offspring cardiometabolic risks, she said more chronic disease “at increasingly younger ages [points toward] prebirth influences.”
She noted that there are critical periods postnatally — such as infancy and puberty — that can “impact or further shift the trajectory of chronic disease.” The developmental origins theory posits that life events and biological and environmental processes during the lifespan can modify the effects of intrauterine exposures.
The transgenerational implications “are clear,” she said. “As the number of reproductive-aged individuals with chronic diseases rises, the number of exposed offspring also rises ... It leads to a vicious cycle.”
Deeper Dives Into Associations, Potential Mechanisms
The EPOCH prospective cohort study with which Dr. Hockett was involved gave her a front-seat view of the transgenerational adverse effects of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia. The study recruited ethnically diverse maternal/child dyads from the Kaiser Permanente of Colorado perinatal database from 1992 to 2002 and assessed 418 offspring at two points — a mean age of 10.5 years and 16.5 years — for fasting blood glucose, adiposity, and diet and physical activity. The second visit also involved an oral glucose tolerance test.
The 77 offspring who had been exposed in utero to GDM had a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) that was 18% higher, a 19% lower Matsuda index, and a 9% greater HOMA of β-cell function (HOMA-β) than the 341 offspring whose mothers did not have diabetes. Each 5-kg/m2 increase in prepregnancy body mass index predicted increased insulin resistance, but there was no combined effect of both maternal obesity and diabetes in utero.
Exposed offspring had a higher BMI and increased adiposity, but when BMI was controlled for in the analysis of metabolic outcomes, maternal diabetes was still associated with 12% higher HOMA-IR and a 17% lower Matsuda index. “So [the metabolic outcomes] are a direct effect of maternal diabetes,” Dr. Hockett said at the DPSG meeting, noting the fetal overnutrition hypothesis in which maternal glucose, but not maternal insulin, freely passes through the placenta, promoting growth and adiposity in the fetus.
[The EPOCH results on metabolic outcomes and offspring adiposity were published in 2017 and 2019, respectively (Diabet Med. 2017;34:1392-9; Diabetologia. 2019;62:2017-24). In 2020, EPOCH researchers reported sex-specific effects on cardiovascular outcomes, with GDM exposure associated with higher total and LDL cholesterol in girls and higher systolic blood pressure in boys (Pediatr Obes. 2020;15[5]:e12611).]
Now, a new longitudinal cohort study underway in Phoenix, is taking a deeper dive, trying to pinpoint what exactly influences childhood obesity and metabolic risk by following Hispanic and American Indian maternal/child dyads from pregnancy until 18 years postpartum. Researchers are looking not only at associations between maternal risk factors (pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and diabetes in pregnancy) and offspring BMI, adiposity, and growth patterns, but also how various factors during pregnancy — clinical, genetic, lifestyle, biochemical — ”may mediate the associations,” said lead investigator Madhumita Sinha, MD.
“We need a better understanding at the molecular level of the biological processes that lead to obesity in children and that cause metabolic dysfunction,” said Dr. Sinha, who heads the Diabetes Epidemiology and Clinical Research Section of the of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) branch in Phoenix.
The populations being enrolled in the ETCHED study (for Early Tracking of Childhood Health Determinants) are at especially high risk of childhood obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Research conducted decades ago by the NIDDK in Phoenix showed that approximately 50% of Pima Indian children from diabetic pregnancies develop type 2 diabetes by age 25 (N Engl J Med. 1983;308:242-5). Years later, to tease out possible genetic factors, researchers compared siblings born before and after their mother was found to have type 2 diabetes, and found significantly higher rates of diabetes in those born after the mother’s diagnosis, affirming the role of in utero toxicity (Diabetes 2000;49:2208-11).
In the new study, the researchers will look at adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in the mothers and offspring in addition to traditional anthropometric and glycemic measures. They’ll analyze placental tissue, breast milk, and the gut microbiome longitudinally, and they’ll lean heavily on genomics/epigenomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. “There’s potential,” Dr. Sinha said, “to develop a more accurate predictive and prognostic model of childhood obesity.”
The researchers also will study the role of family, socioeconomics, and environmental factors in influencing child growth patterns and they’ll look at neurodevelopment in infancy and childhood. As of October 2023, almost 80 pregnant women, most with obesity and almost one-third with type 2 diabetes, had enrolled in the study. Over the next several years, the study aims to enroll 750 dyads.
The Timing of In Utero Exposure
Shelley Ehrlich, MD, ScD, MPH, of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, is aiming, meanwhile, to learn how the timing of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia predicts specific metabolic and cardiovascular morbidities in the adult offspring of diabetic mothers.
“While we know that exposure to maternal diabetes, regardless of type, increases the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, renal compromise, and cardiovascular disease in the offspring, there is little known about the level and timing of hyperglycemic exposure during fetal development that triggers these adverse outcomes,” said Dr. Ehrlich. A goal, she said, is to identify gestational profiles that predict phenotypes of offspring at risk for morbidity in later life.
She and other investigators with the TEAM (Transgenerational Effect on Adult Morbidity) study have recruited over 170 offspring of mothers who participated in the Diabetes in Pregnancy Program Project Grant (PPG) at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center from 1978 to 1995 — a landmark study that demonstrated the effect of strict glucose control in reducing major congenital malformations.
The women in the PPG study had frequent glucose monitoring (up to 6-8 times a day) throughout their pregnancies, and now, their recruited offspring, who are up to 43 years of age, are being assessed for obesity, diabetes/metabolic health, cardiovascular disease/cardiac and peripheral vascular structure and function, and other outcomes including those that may be amenable to secondary prevention (J Diabetes Res. Nov 1;2021:6590431).
Preliminary findings from over 170 offspring recruited between 2017 and 2022 suggest that in utero exposure to dysglycemia (as measured by standard deviations of glycohemoglobin) in the third trimester appears to increase the risk of morbid obesity in adulthood, while exposure to dysglycemia in the first trimester increases the risk of impaired glucose tolerance. The risk of B-cell dysfunction, meanwhile, appears to be linked to dysglycemia in the first and third trimesters — particularly the first — Dr. Ehrlich reported.
Cognitive outcomes in offspring have also been assessed and here it appears that dysglycemia in the third trimester is linked to worse scores on the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II), said Katherine Bowers, PhD, MPH, a TEAM study coinvestigator, also of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
“We’ve already observed [an association between] diabetes in pregnancy and cognition in early childhood and through adolescence, but [the question has been] does this association persist into adulthood?” she said.
Preliminary analyses of 104 offspring show no statistically significant associations between maternal dysglycemia in the first or second trimesters and offspring cognition, but “consistent inverse associations between maternal glycohemoglobin in the third trimester across two [WASI-II] subscales and composite measures of cognition,” Dr. Bowers said.
Their analysis adjusted for a variety of factors, including maternal age, prepregnancy and first trimester BMI, race, family history of diabetes, and diabetes severity/macrovascular complications.
Back In The Laboratory
At the other end of the research spectrum, basic research scientists are also investigating the mechanisms and sequelae of in utero hyperglycemia and other injuries, including congenital malformations, placental adaptive responses and fetal programming. Researchers are asking, for instance, what does placental metabolic reprogramming entail? What role do placental extracellular vesicles play in GDM? Can we alter the in utero environment and thus improve the short and long-term fetal/infant outcomes?
Animal research done at the UMSOM Center for Birth Defects Research, led by Dr. Reece and Peixin Yang, PhD, suggests that “a good portion of in utero injury is due to epigenetics,” Dr. Reece said in the interview. “We’ve shown that under conditions of hyperglycemia, for example, genetic regulation and genetic function can be altered.”
Through in vivo research, they have also shown that antioxidants or membrane stabilizers such as arachidonic acid or myo-inositol, or experimental inhibitors to certain pro-apoptotic intermediates, can individually or collectively result in reduced malformations. “It is highly likely that understanding the biological impact of various altered in utero environments, and then modifying or reversing those environments, will result in short and long-term outcome improvements similar to those shown with congenital malformations,” Dr. Reece said.
FAIRFAX, VIRGINIA — Nearly 30 years ago, in a 1995 paper, the British physician-epidemiologist David Barker, MD, PhD, wrote about his fetal origins hypothesis — the idea that programs to address fetal undernutrition and low birth weight produced later coronary heart disease (BMJ 1995;311:171-4).
His hypothesis and subsequent research led to the concept of adult diseases of fetal origins, which today extends beyond low birth weight and implicates the in utero environment as a significant determinant of risk for adverse childhood and adult metabolic outcomes and for major chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that the offspring of pregnant mothers with diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes themselves.
“It’s a whole discipline [of research],” E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), said in an interview. “But what we’ve never quite understood is the ‘how’ and ‘why’? What are the mechanisms driving the fetal origins of such adverse outcomes in offspring?
At the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG), investigators described studies underway that are digging deeper into the associations between the intrauterine milieu and longer-term offspring health — and that are searching for biological and molecular processes that may be involved.
The studies are like “branches of the Barker hypothesis,” said Dr. Reece, former dean of UMSOM and current director of the UMSOM Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation, who co-organized the DPSG meeting. “They’re taking the hypothesis and dissecting it by asking, for instance, it is possible that transgenerational obesity may align with the Barker hypothesis? Is it possible that it involves epigenetics regulation? Could we find biomarkers?”
The need for a better understanding of the fetal origins framework — and its subsequent transgenerational impact — is urgent. From 2000 to 2018, the prevalence of childhood obesity increased from 14.7% to 19.2% (a 31% increase) and the prevalence of severe childhood obesity rose from 3.9% to 6.1% (a 56% increase), according to data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Obes Facts. 2022;15[4]:560-9).
Children aged 2-5 years have had an especially sharp increase in obesity (Pediatrics 2018;141[3]:e20173459), Christine Wey Hockett, PhD, of the University of South Dakota School of Medicine, said at the DPSG meeting (Figure 1). 
Also notable, she said, is that one-quarter of today’s pediatric diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes, which “is significant as there is a higher prevalence of early complications and comorbidities in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 diabetes.”
Moreover, recent projections estimate that 57% of today’s children will be obese at 35 years of age (N Engl J Med. 2017;377[22]:2145-53) and that 45% will have diabetes or prediabetes by 2030 (Popul Health Manag. 2017;20[1]:6-12), said Dr. Hockett, assistant professor in the university’s department of pediatrics. An investigator of the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes Among Children (EPOCH) study, which looked at gestational diabetes (GDM) and offspring cardiometabolic risks, she said more chronic disease “at increasingly younger ages [points toward] prebirth influences.”
She noted that there are critical periods postnatally — such as infancy and puberty — that can “impact or further shift the trajectory of chronic disease.” The developmental origins theory posits that life events and biological and environmental processes during the lifespan can modify the effects of intrauterine exposures.
The transgenerational implications “are clear,” she said. “As the number of reproductive-aged individuals with chronic diseases rises, the number of exposed offspring also rises ... It leads to a vicious cycle.”
Deeper Dives Into Associations, Potential Mechanisms
The EPOCH prospective cohort study with which Dr. Hockett was involved gave her a front-seat view of the transgenerational adverse effects of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia. The study recruited ethnically diverse maternal/child dyads from the Kaiser Permanente of Colorado perinatal database from 1992 to 2002 and assessed 418 offspring at two points — a mean age of 10.5 years and 16.5 years — for fasting blood glucose, adiposity, and diet and physical activity. The second visit also involved an oral glucose tolerance test.
The 77 offspring who had been exposed in utero to GDM had a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) that was 18% higher, a 19% lower Matsuda index, and a 9% greater HOMA of β-cell function (HOMA-β) than the 341 offspring whose mothers did not have diabetes. Each 5-kg/m2 increase in prepregnancy body mass index predicted increased insulin resistance, but there was no combined effect of both maternal obesity and diabetes in utero.
Exposed offspring had a higher BMI and increased adiposity, but when BMI was controlled for in the analysis of metabolic outcomes, maternal diabetes was still associated with 12% higher HOMA-IR and a 17% lower Matsuda index. “So [the metabolic outcomes] are a direct effect of maternal diabetes,” Dr. Hockett said at the DPSG meeting, noting the fetal overnutrition hypothesis in which maternal glucose, but not maternal insulin, freely passes through the placenta, promoting growth and adiposity in the fetus.
[The EPOCH results on metabolic outcomes and offspring adiposity were published in 2017 and 2019, respectively (Diabet Med. 2017;34:1392-9; Diabetologia. 2019;62:2017-24). In 2020, EPOCH researchers reported sex-specific effects on cardiovascular outcomes, with GDM exposure associated with higher total and LDL cholesterol in girls and higher systolic blood pressure in boys (Pediatr Obes. 2020;15[5]:e12611).]
Now, a new longitudinal cohort study underway in Phoenix, is taking a deeper dive, trying to pinpoint what exactly influences childhood obesity and metabolic risk by following Hispanic and American Indian maternal/child dyads from pregnancy until 18 years postpartum. Researchers are looking not only at associations between maternal risk factors (pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and diabetes in pregnancy) and offspring BMI, adiposity, and growth patterns, but also how various factors during pregnancy — clinical, genetic, lifestyle, biochemical — ”may mediate the associations,” said lead investigator Madhumita Sinha, MD.
“We need a better understanding at the molecular level of the biological processes that lead to obesity in children and that cause metabolic dysfunction,” said Dr. Sinha, who heads the Diabetes Epidemiology and Clinical Research Section of the of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) branch in Phoenix.
The populations being enrolled in the ETCHED study (for Early Tracking of Childhood Health Determinants) are at especially high risk of childhood obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Research conducted decades ago by the NIDDK in Phoenix showed that approximately 50% of Pima Indian children from diabetic pregnancies develop type 2 diabetes by age 25 (N Engl J Med. 1983;308:242-5). Years later, to tease out possible genetic factors, researchers compared siblings born before and after their mother was found to have type 2 diabetes, and found significantly higher rates of diabetes in those born after the mother’s diagnosis, affirming the role of in utero toxicity (Diabetes 2000;49:2208-11).
In the new study, the researchers will look at adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in the mothers and offspring in addition to traditional anthropometric and glycemic measures. They’ll analyze placental tissue, breast milk, and the gut microbiome longitudinally, and they’ll lean heavily on genomics/epigenomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. “There’s potential,” Dr. Sinha said, “to develop a more accurate predictive and prognostic model of childhood obesity.”
The researchers also will study the role of family, socioeconomics, and environmental factors in influencing child growth patterns and they’ll look at neurodevelopment in infancy and childhood. As of October 2023, almost 80 pregnant women, most with obesity and almost one-third with type 2 diabetes, had enrolled in the study. Over the next several years, the study aims to enroll 750 dyads.
The Timing of In Utero Exposure
Shelley Ehrlich, MD, ScD, MPH, of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, is aiming, meanwhile, to learn how the timing of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia predicts specific metabolic and cardiovascular morbidities in the adult offspring of diabetic mothers.
“While we know that exposure to maternal diabetes, regardless of type, increases the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, renal compromise, and cardiovascular disease in the offspring, there is little known about the level and timing of hyperglycemic exposure during fetal development that triggers these adverse outcomes,” said Dr. Ehrlich. A goal, she said, is to identify gestational profiles that predict phenotypes of offspring at risk for morbidity in later life.
She and other investigators with the TEAM (Transgenerational Effect on Adult Morbidity) study have recruited over 170 offspring of mothers who participated in the Diabetes in Pregnancy Program Project Grant (PPG) at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center from 1978 to 1995 — a landmark study that demonstrated the effect of strict glucose control in reducing major congenital malformations.
The women in the PPG study had frequent glucose monitoring (up to 6-8 times a day) throughout their pregnancies, and now, their recruited offspring, who are up to 43 years of age, are being assessed for obesity, diabetes/metabolic health, cardiovascular disease/cardiac and peripheral vascular structure and function, and other outcomes including those that may be amenable to secondary prevention (J Diabetes Res. Nov 1;2021:6590431).
Preliminary findings from over 170 offspring recruited between 2017 and 2022 suggest that in utero exposure to dysglycemia (as measured by standard deviations of glycohemoglobin) in the third trimester appears to increase the risk of morbid obesity in adulthood, while exposure to dysglycemia in the first trimester increases the risk of impaired glucose tolerance. The risk of B-cell dysfunction, meanwhile, appears to be linked to dysglycemia in the first and third trimesters — particularly the first — Dr. Ehrlich reported.
Cognitive outcomes in offspring have also been assessed and here it appears that dysglycemia in the third trimester is linked to worse scores on the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II), said Katherine Bowers, PhD, MPH, a TEAM study coinvestigator, also of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
“We’ve already observed [an association between] diabetes in pregnancy and cognition in early childhood and through adolescence, but [the question has been] does this association persist into adulthood?” she said.
Preliminary analyses of 104 offspring show no statistically significant associations between maternal dysglycemia in the first or second trimesters and offspring cognition, but “consistent inverse associations between maternal glycohemoglobin in the third trimester across two [WASI-II] subscales and composite measures of cognition,” Dr. Bowers said.
Their analysis adjusted for a variety of factors, including maternal age, prepregnancy and first trimester BMI, race, family history of diabetes, and diabetes severity/macrovascular complications.
Back In The Laboratory
At the other end of the research spectrum, basic research scientists are also investigating the mechanisms and sequelae of in utero hyperglycemia and other injuries, including congenital malformations, placental adaptive responses and fetal programming. Researchers are asking, for instance, what does placental metabolic reprogramming entail? What role do placental extracellular vesicles play in GDM? Can we alter the in utero environment and thus improve the short and long-term fetal/infant outcomes?
Animal research done at the UMSOM Center for Birth Defects Research, led by Dr. Reece and Peixin Yang, PhD, suggests that “a good portion of in utero injury is due to epigenetics,” Dr. Reece said in the interview. “We’ve shown that under conditions of hyperglycemia, for example, genetic regulation and genetic function can be altered.”
Through in vivo research, they have also shown that antioxidants or membrane stabilizers such as arachidonic acid or myo-inositol, or experimental inhibitors to certain pro-apoptotic intermediates, can individually or collectively result in reduced malformations. “It is highly likely that understanding the biological impact of various altered in utero environments, and then modifying or reversing those environments, will result in short and long-term outcome improvements similar to those shown with congenital malformations,” Dr. Reece said.
FAIRFAX, VIRGINIA — Nearly 30 years ago, in a 1995 paper, the British physician-epidemiologist David Barker, MD, PhD, wrote about his fetal origins hypothesis — the idea that programs to address fetal undernutrition and low birth weight produced later coronary heart disease (BMJ 1995;311:171-4).
His hypothesis and subsequent research led to the concept of adult diseases of fetal origins, which today extends beyond low birth weight and implicates the in utero environment as a significant determinant of risk for adverse childhood and adult metabolic outcomes and for major chronic diseases, including diabetes and obesity. Studies have shown that the offspring of pregnant mothers with diabetes have a higher risk of developing obesity and diabetes themselves.
“It’s a whole discipline [of research],” E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), said in an interview. “But what we’ve never quite understood is the ‘how’ and ‘why’? What are the mechanisms driving the fetal origins of such adverse outcomes in offspring?
At the biennial meeting of the Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group of North America (DPSG), investigators described studies underway that are digging deeper into the associations between the intrauterine milieu and longer-term offspring health — and that are searching for biological and molecular processes that may be involved.
The studies are like “branches of the Barker hypothesis,” said Dr. Reece, former dean of UMSOM and current director of the UMSOM Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation, who co-organized the DPSG meeting. “They’re taking the hypothesis and dissecting it by asking, for instance, it is possible that transgenerational obesity may align with the Barker hypothesis? Is it possible that it involves epigenetics regulation? Could we find biomarkers?”
The need for a better understanding of the fetal origins framework — and its subsequent transgenerational impact — is urgent. From 2000 to 2018, the prevalence of childhood obesity increased from 14.7% to 19.2% (a 31% increase) and the prevalence of severe childhood obesity rose from 3.9% to 6.1% (a 56% increase), according to data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (Obes Facts. 2022;15[4]:560-9).
Children aged 2-5 years have had an especially sharp increase in obesity (Pediatrics 2018;141[3]:e20173459), Christine Wey Hockett, PhD, of the University of South Dakota School of Medicine, said at the DPSG meeting (Figure 1). 
Also notable, she said, is that one-quarter of today’s pediatric diabetes cases are type 2 diabetes, which “is significant as there is a higher prevalence of early complications and comorbidities in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 diabetes.”
Moreover, recent projections estimate that 57% of today’s children will be obese at 35 years of age (N Engl J Med. 2017;377[22]:2145-53) and that 45% will have diabetes or prediabetes by 2030 (Popul Health Manag. 2017;20[1]:6-12), said Dr. Hockett, assistant professor in the university’s department of pediatrics. An investigator of the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes Among Children (EPOCH) study, which looked at gestational diabetes (GDM) and offspring cardiometabolic risks, she said more chronic disease “at increasingly younger ages [points toward] prebirth influences.”
She noted that there are critical periods postnatally — such as infancy and puberty — that can “impact or further shift the trajectory of chronic disease.” The developmental origins theory posits that life events and biological and environmental processes during the lifespan can modify the effects of intrauterine exposures.
The transgenerational implications “are clear,” she said. “As the number of reproductive-aged individuals with chronic diseases rises, the number of exposed offspring also rises ... It leads to a vicious cycle.”
Deeper Dives Into Associations, Potential Mechanisms
The EPOCH prospective cohort study with which Dr. Hockett was involved gave her a front-seat view of the transgenerational adverse effects of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia. The study recruited ethnically diverse maternal/child dyads from the Kaiser Permanente of Colorado perinatal database from 1992 to 2002 and assessed 418 offspring at two points — a mean age of 10.5 years and 16.5 years — for fasting blood glucose, adiposity, and diet and physical activity. The second visit also involved an oral glucose tolerance test.
The 77 offspring who had been exposed in utero to GDM had a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) that was 18% higher, a 19% lower Matsuda index, and a 9% greater HOMA of β-cell function (HOMA-β) than the 341 offspring whose mothers did not have diabetes. Each 5-kg/m2 increase in prepregnancy body mass index predicted increased insulin resistance, but there was no combined effect of both maternal obesity and diabetes in utero.
Exposed offspring had a higher BMI and increased adiposity, but when BMI was controlled for in the analysis of metabolic outcomes, maternal diabetes was still associated with 12% higher HOMA-IR and a 17% lower Matsuda index. “So [the metabolic outcomes] are a direct effect of maternal diabetes,” Dr. Hockett said at the DPSG meeting, noting the fetal overnutrition hypothesis in which maternal glucose, but not maternal insulin, freely passes through the placenta, promoting growth and adiposity in the fetus.
[The EPOCH results on metabolic outcomes and offspring adiposity were published in 2017 and 2019, respectively (Diabet Med. 2017;34:1392-9; Diabetologia. 2019;62:2017-24). In 2020, EPOCH researchers reported sex-specific effects on cardiovascular outcomes, with GDM exposure associated with higher total and LDL cholesterol in girls and higher systolic blood pressure in boys (Pediatr Obes. 2020;15[5]:e12611).]
Now, a new longitudinal cohort study underway in Phoenix, is taking a deeper dive, trying to pinpoint what exactly influences childhood obesity and metabolic risk by following Hispanic and American Indian maternal/child dyads from pregnancy until 18 years postpartum. Researchers are looking not only at associations between maternal risk factors (pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and diabetes in pregnancy) and offspring BMI, adiposity, and growth patterns, but also how various factors during pregnancy — clinical, genetic, lifestyle, biochemical — ”may mediate the associations,” said lead investigator Madhumita Sinha, MD.
“We need a better understanding at the molecular level of the biological processes that lead to obesity in children and that cause metabolic dysfunction,” said Dr. Sinha, who heads the Diabetes Epidemiology and Clinical Research Section of the of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) branch in Phoenix.
The populations being enrolled in the ETCHED study (for Early Tracking of Childhood Health Determinants) are at especially high risk of childhood obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Research conducted decades ago by the NIDDK in Phoenix showed that approximately 50% of Pima Indian children from diabetic pregnancies develop type 2 diabetes by age 25 (N Engl J Med. 1983;308:242-5). Years later, to tease out possible genetic factors, researchers compared siblings born before and after their mother was found to have type 2 diabetes, and found significantly higher rates of diabetes in those born after the mother’s diagnosis, affirming the role of in utero toxicity (Diabetes 2000;49:2208-11).
In the new study, the researchers will look at adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in the mothers and offspring in addition to traditional anthropometric and glycemic measures. They’ll analyze placental tissue, breast milk, and the gut microbiome longitudinally, and they’ll lean heavily on genomics/epigenomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. “There’s potential,” Dr. Sinha said, “to develop a more accurate predictive and prognostic model of childhood obesity.”
The researchers also will study the role of family, socioeconomics, and environmental factors in influencing child growth patterns and they’ll look at neurodevelopment in infancy and childhood. As of October 2023, almost 80 pregnant women, most with obesity and almost one-third with type 2 diabetes, had enrolled in the study. Over the next several years, the study aims to enroll 750 dyads.
The Timing of In Utero Exposure
Shelley Ehrlich, MD, ScD, MPH, of the University of Cincinnati and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, is aiming, meanwhile, to learn how the timing of in utero exposure to hyperglycemia predicts specific metabolic and cardiovascular morbidities in the adult offspring of diabetic mothers.
“While we know that exposure to maternal diabetes, regardless of type, increases the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, renal compromise, and cardiovascular disease in the offspring, there is little known about the level and timing of hyperglycemic exposure during fetal development that triggers these adverse outcomes,” said Dr. Ehrlich. A goal, she said, is to identify gestational profiles that predict phenotypes of offspring at risk for morbidity in later life.
She and other investigators with the TEAM (Transgenerational Effect on Adult Morbidity) study have recruited over 170 offspring of mothers who participated in the Diabetes in Pregnancy Program Project Grant (PPG) at the University of Cincinnati Medical Center from 1978 to 1995 — a landmark study that demonstrated the effect of strict glucose control in reducing major congenital malformations.
The women in the PPG study had frequent glucose monitoring (up to 6-8 times a day) throughout their pregnancies, and now, their recruited offspring, who are up to 43 years of age, are being assessed for obesity, diabetes/metabolic health, cardiovascular disease/cardiac and peripheral vascular structure and function, and other outcomes including those that may be amenable to secondary prevention (J Diabetes Res. Nov 1;2021:6590431).
Preliminary findings from over 170 offspring recruited between 2017 and 2022 suggest that in utero exposure to dysglycemia (as measured by standard deviations of glycohemoglobin) in the third trimester appears to increase the risk of morbid obesity in adulthood, while exposure to dysglycemia in the first trimester increases the risk of impaired glucose tolerance. The risk of B-cell dysfunction, meanwhile, appears to be linked to dysglycemia in the first and third trimesters — particularly the first — Dr. Ehrlich reported.
Cognitive outcomes in offspring have also been assessed and here it appears that dysglycemia in the third trimester is linked to worse scores on the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI-II), said Katherine Bowers, PhD, MPH, a TEAM study coinvestigator, also of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
“We’ve already observed [an association between] diabetes in pregnancy and cognition in early childhood and through adolescence, but [the question has been] does this association persist into adulthood?” she said.
Preliminary analyses of 104 offspring show no statistically significant associations between maternal dysglycemia in the first or second trimesters and offspring cognition, but “consistent inverse associations between maternal glycohemoglobin in the third trimester across two [WASI-II] subscales and composite measures of cognition,” Dr. Bowers said.
Their analysis adjusted for a variety of factors, including maternal age, prepregnancy and first trimester BMI, race, family history of diabetes, and diabetes severity/macrovascular complications.
Back In The Laboratory
At the other end of the research spectrum, basic research scientists are also investigating the mechanisms and sequelae of in utero hyperglycemia and other injuries, including congenital malformations, placental adaptive responses and fetal programming. Researchers are asking, for instance, what does placental metabolic reprogramming entail? What role do placental extracellular vesicles play in GDM? Can we alter the in utero environment and thus improve the short and long-term fetal/infant outcomes?
Animal research done at the UMSOM Center for Birth Defects Research, led by Dr. Reece and Peixin Yang, PhD, suggests that “a good portion of in utero injury is due to epigenetics,” Dr. Reece said in the interview. “We’ve shown that under conditions of hyperglycemia, for example, genetic regulation and genetic function can be altered.”
Through in vivo research, they have also shown that antioxidants or membrane stabilizers such as arachidonic acid or myo-inositol, or experimental inhibitors to certain pro-apoptotic intermediates, can individually or collectively result in reduced malformations. “It is highly likely that understanding the biological impact of various altered in utero environments, and then modifying or reversing those environments, will result in short and long-term outcome improvements similar to those shown with congenital malformations,” Dr. Reece said.
FROM DPSG-NA 2023