User login
Microneedling With Bimatoprost to Treat Hypopigmented Skin Caused by Burn Scars
To the Editor:
Microneedling is a percutaneous collagen induction therapy frequently used in cosmetic dermatology to promote skin rejuvenation and hair growth and to treat scars by taking advantage of the body’s natural wound-healing cascade.1 The procedure works by generating thousands of microscopic wounds in the dermis with minimal damage to the epidermis, thus initiating the wound-healing cascade and subsequently promoting collagen production in a manner safe for all Fitzpatrick classification skin types.1-3 This therapy effectively treats scars by breaking down scarred collagen and replacing it with new healthy collagen. Microneedling also has application in drug delivery by increasing the permeability of the skin; the microwounds generated can serve as a portal for drug delivery.4
Bimatoprost is a prostaglandin analogue typically used to treat hypotrichosis and open-angle glaucoma.5-7 A known side effect of bimatoprost is hyperpigmentation of surrounding skin; the drug increases melanogenesis, melanocyte proliferation, and melanocyte dendricity, resulting in activation of the inflammatory response and subsequent prostaglandin release, which stimulates melanogenesis. This effect is similar to UV radiation–induced inflammation and hyperpigmentation.6,8
Capitalizing on this effect, a novel application of bimatoprost has been proposed—treating vitiligo, in which hypopigmentation results from destruction of melanocytes in certain areas of the skin. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% utilized as an off-label treatment for vitiligo has been shown to notably increase melanogenesis and return pigmentation to hypopigmented areas.8-10
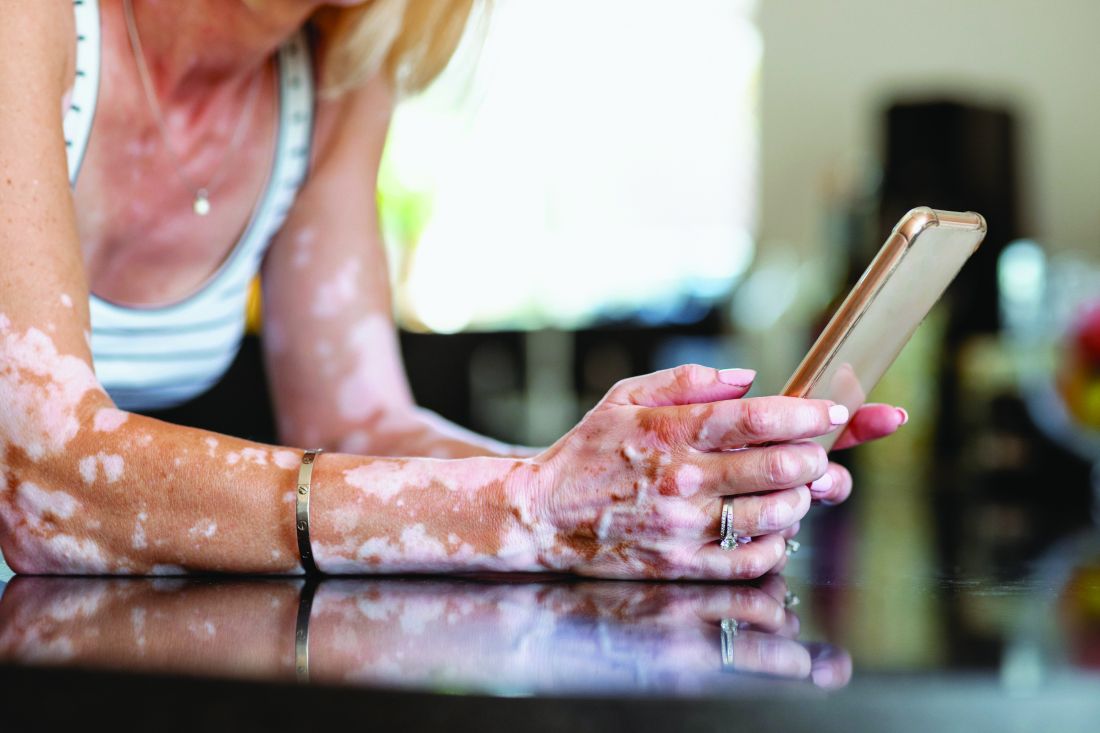
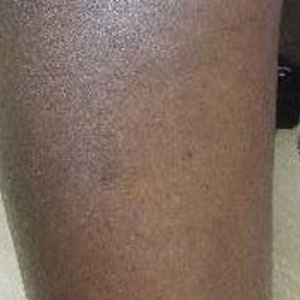
A 32-year-old Black woman presented to our clinic with a 40×15-cm scar that was marked by postinflammatory hypopigmentation from a second-degree burn on the right proximal arm. The patient had been burned 5 months prior by boiling water that was spilled on the arm while cooking. She had immediately sought treatment at an emergency department and subsequently in a burn unit, where the burn was debrided twice; medication was not prescribed to continue treatment. The patient reported that the scarring and hypopigmentation had taken a psychologic toll; her hope was to have pigmentation restored to the affected area to boost her confidence.
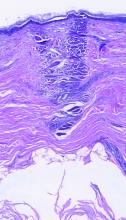
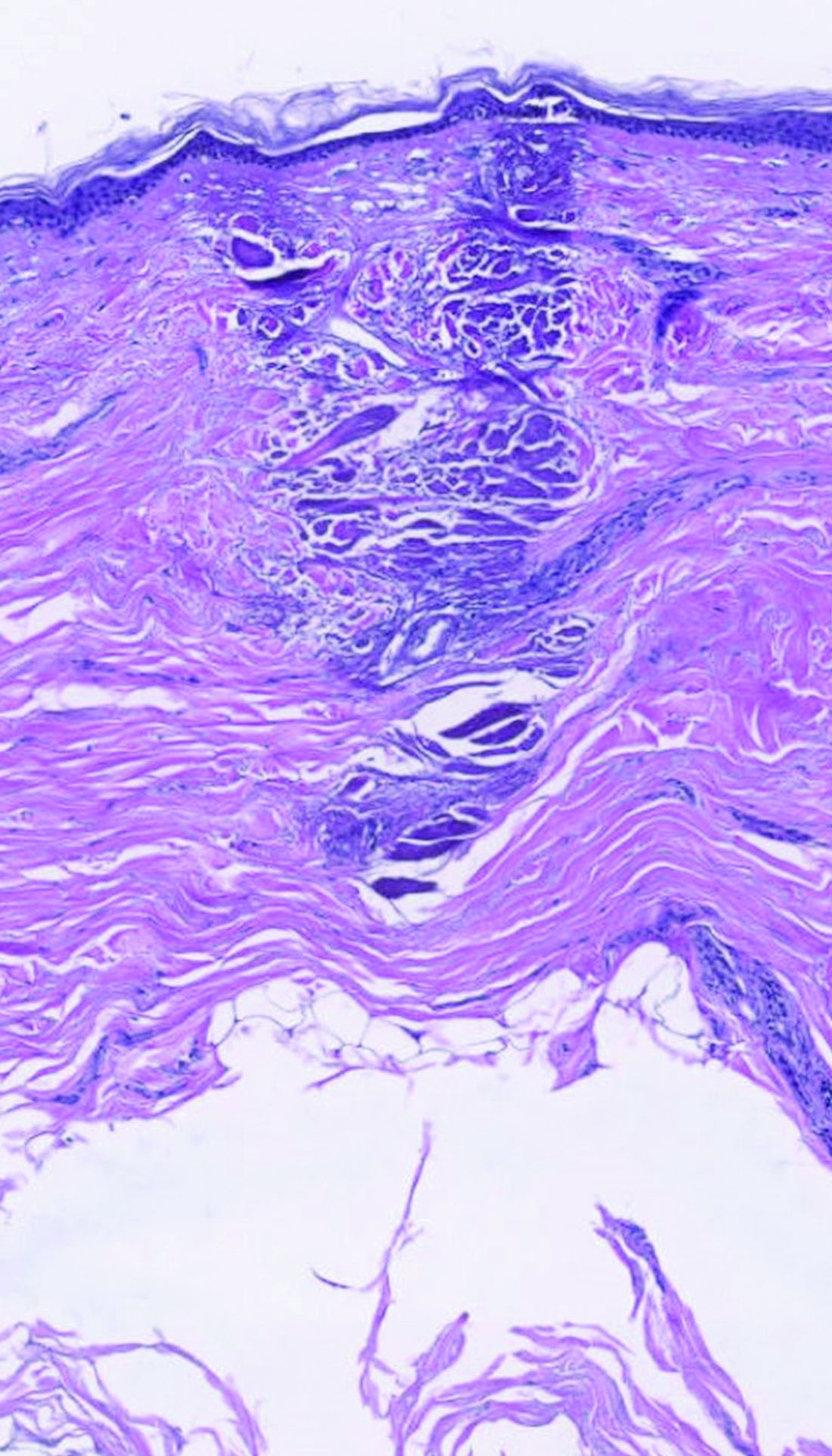
Physical examination revealed that the burn wound had healed but visible scarring and severe hypopigmentation due to destroyed melanocytes remained (Figure 1). To inhibit inflammation and stimulate repigmentation, we prescribed the calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus ointment 0.1% to be applied daily to the affected area. The patient returned to the clinic 1 month later. Perifollicular hyperpigmentation was noted at the site of the scar.
Monthly microneedling sessions with bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% were started. To avoid damaging any potentially remaining unhealed hypodermis and vasculature, the first microneedling session was performed with 9 needles set at minimal needle depth and frequency. The number of needles and their depth and frequency gradually were increased with each subsequent treatment. The patient continued tacrolimus ointment 0.1% throughout the course of treatment.
For each microneedling procedure, a handheld motorized microneedling device was applied to the skin at a depth of 0.25 mm, which was gradually increased until pinpoint petechiae were achieved. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% was then painted on the skin and allowed to absorb. Microneedling was performed again, ensuring that bimatoprost entered the skin in the area of the burn scar.
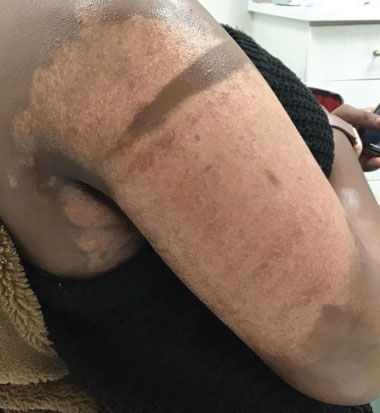
Microneedling procedures were performed monthly for 6 months, then once 3 months later, and once more 3 months later—8 treatments in total over the course of 1 year. Improvement in skin pigmentation was noted at each visit (Figure 2). Repigmentation was first noticed surrounding hair follicles; after later visits, it was observed that pigmentation began to spread from hair follicles to fill in remaining skin. The darkest areas of pigmentation were first noted around hair follicles; over time, melanocytes appeared to spontaneously regenerate and fill in surrounding areas as the scar continued to heal. The patient continued use of tacrolimus during the entire course of microneedling treatments and for the following 4 months. Sixteen months after initiation of treatment, the appearance of the skin was texturally smooth and returned to almost its original pigmentation (Figure 3).
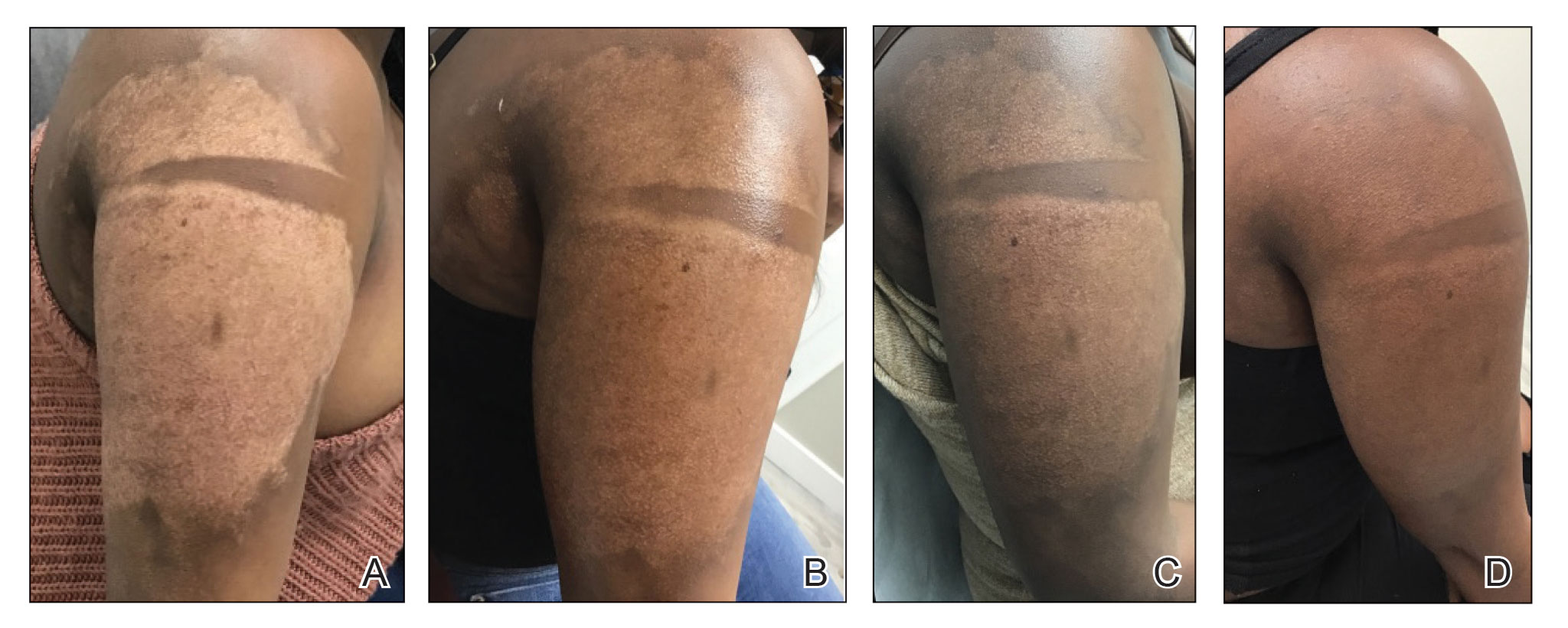
We report a successful outcome in a patient with a hypopigmented burn scar who was treated with bimatoprost administered with traditional microneedling and alongside a tacrolimus regimen. Tacrolimus ointment inhibited the inflammatory response to allow melanocytes to heal and regenerate; bimatoprost and microneedling promoted hyperpigmentation of hair follicles in the affected area, eventually restoring pigmentation to the entire area. Our patient was extremely satisfied with the results of this combination treatment. She has reported feeling more confident going out and wearing short-sleeved clothing. Percutaneous drug delivery of bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% combined with topical tacrolimus may be an effective treatment for skin repigmentation. Further investigation of this regimen is needed to develop standardized treatment protocols.
- Juhasz MLW, Cohen JL. Micro-needling for the treatment of scars: an update for clinicians. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:997-1003. doi:10.2147/CCID.S267192
- Alster TS, Li MKY. Micro-needling of scars: a large prospective study with long-term follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145:358-364. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000006462
- Aust MC, Knobloch K, Reimers K, et al. Percutaneous collagen induction therapy: an alternative treatment for burn scars. Burns. 2010;36:836-843. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2009.11.014
- Kim Y-C, Park J-H, Prausnitz MR. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:1547-1568. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.04.005
- Doshi M, Edward DP, Osmanovic S. Clinical course of bimatoprost-induced periocular skin changes in Caucasians. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:1961-1967. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.05.041
- Kapur R, Osmanovic S, Toyran S, et al. Bimatoprost-induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation: histopathological study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:1541-1546. doi:10.1001/archopht.123.11.1541
- Priluck JC, Fu S. Latisse-induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:792-793. doi:10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.89
- Grimes PE. Bimatoprost 0.03% solution for the treatment of nonfacial vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:703-710.
- Barbulescu C, Goldstein N, Roop D, et al. Harnessing the power of regenerative therapy for vitiligo and alopecia areata. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140: 29-37. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.03.1142
- Kanokrungsee S, Pruettivorawongse D, Rajatanavin N. Clinicaloutcomes of topical bimatoprost for nonsegmental facial vitiligo: a preliminary study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:812-818. doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13648
To the Editor:
Microneedling is a percutaneous collagen induction therapy frequently used in cosmetic dermatology to promote skin rejuvenation and hair growth and to treat scars by taking advantage of the body’s natural wound-healing cascade.1 The procedure works by generating thousands of microscopic wounds in the dermis with minimal damage to the epidermis, thus initiating the wound-healing cascade and subsequently promoting collagen production in a manner safe for all Fitzpatrick classification skin types.1-3 This therapy effectively treats scars by breaking down scarred collagen and replacing it with new healthy collagen. Microneedling also has application in drug delivery by increasing the permeability of the skin; the microwounds generated can serve as a portal for drug delivery.4
Bimatoprost is a prostaglandin analogue typically used to treat hypotrichosis and open-angle glaucoma.5-7 A known side effect of bimatoprost is hyperpigmentation of surrounding skin; the drug increases melanogenesis, melanocyte proliferation, and melanocyte dendricity, resulting in activation of the inflammatory response and subsequent prostaglandin release, which stimulates melanogenesis. This effect is similar to UV radiation–induced inflammation and hyperpigmentation.6,8
Capitalizing on this effect, a novel application of bimatoprost has been proposed—treating vitiligo, in which hypopigmentation results from destruction of melanocytes in certain areas of the skin. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% utilized as an off-label treatment for vitiligo has been shown to notably increase melanogenesis and return pigmentation to hypopigmented areas.8-10
A 32-year-old Black woman presented to our clinic with a 40×15-cm scar that was marked by postinflammatory hypopigmentation from a second-degree burn on the right proximal arm. The patient had been burned 5 months prior by boiling water that was spilled on the arm while cooking. She had immediately sought treatment at an emergency department and subsequently in a burn unit, where the burn was debrided twice; medication was not prescribed to continue treatment. The patient reported that the scarring and hypopigmentation had taken a psychologic toll; her hope was to have pigmentation restored to the affected area to boost her confidence.
Physical examination revealed that the burn wound had healed but visible scarring and severe hypopigmentation due to destroyed melanocytes remained (Figure 1). To inhibit inflammation and stimulate repigmentation, we prescribed the calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus ointment 0.1% to be applied daily to the affected area. The patient returned to the clinic 1 month later. Perifollicular hyperpigmentation was noted at the site of the scar.

Monthly microneedling sessions with bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% were started. To avoid damaging any potentially remaining unhealed hypodermis and vasculature, the first microneedling session was performed with 9 needles set at minimal needle depth and frequency. The number of needles and their depth and frequency gradually were increased with each subsequent treatment. The patient continued tacrolimus ointment 0.1% throughout the course of treatment.
For each microneedling procedure, a handheld motorized microneedling device was applied to the skin at a depth of 0.25 mm, which was gradually increased until pinpoint petechiae were achieved. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% was then painted on the skin and allowed to absorb. Microneedling was performed again, ensuring that bimatoprost entered the skin in the area of the burn scar.
Microneedling procedures were performed monthly for 6 months, then once 3 months later, and once more 3 months later—8 treatments in total over the course of 1 year. Improvement in skin pigmentation was noted at each visit (Figure 2). Repigmentation was first noticed surrounding hair follicles; after later visits, it was observed that pigmentation began to spread from hair follicles to fill in remaining skin. The darkest areas of pigmentation were first noted around hair follicles; over time, melanocytes appeared to spontaneously regenerate and fill in surrounding areas as the scar continued to heal. The patient continued use of tacrolimus during the entire course of microneedling treatments and for the following 4 months. Sixteen months after initiation of treatment, the appearance of the skin was texturally smooth and returned to almost its original pigmentation (Figure 3).

We report a successful outcome in a patient with a hypopigmented burn scar who was treated with bimatoprost administered with traditional microneedling and alongside a tacrolimus regimen. Tacrolimus ointment inhibited the inflammatory response to allow melanocytes to heal and regenerate; bimatoprost and microneedling promoted hyperpigmentation of hair follicles in the affected area, eventually restoring pigmentation to the entire area. Our patient was extremely satisfied with the results of this combination treatment. She has reported feeling more confident going out and wearing short-sleeved clothing. Percutaneous drug delivery of bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% combined with topical tacrolimus may be an effective treatment for skin repigmentation. Further investigation of this regimen is needed to develop standardized treatment protocols.

To the Editor:
Microneedling is a percutaneous collagen induction therapy frequently used in cosmetic dermatology to promote skin rejuvenation and hair growth and to treat scars by taking advantage of the body’s natural wound-healing cascade.1 The procedure works by generating thousands of microscopic wounds in the dermis with minimal damage to the epidermis, thus initiating the wound-healing cascade and subsequently promoting collagen production in a manner safe for all Fitzpatrick classification skin types.1-3 This therapy effectively treats scars by breaking down scarred collagen and replacing it with new healthy collagen. Microneedling also has application in drug delivery by increasing the permeability of the skin; the microwounds generated can serve as a portal for drug delivery.4
Bimatoprost is a prostaglandin analogue typically used to treat hypotrichosis and open-angle glaucoma.5-7 A known side effect of bimatoprost is hyperpigmentation of surrounding skin; the drug increases melanogenesis, melanocyte proliferation, and melanocyte dendricity, resulting in activation of the inflammatory response and subsequent prostaglandin release, which stimulates melanogenesis. This effect is similar to UV radiation–induced inflammation and hyperpigmentation.6,8
Capitalizing on this effect, a novel application of bimatoprost has been proposed—treating vitiligo, in which hypopigmentation results from destruction of melanocytes in certain areas of the skin. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% utilized as an off-label treatment for vitiligo has been shown to notably increase melanogenesis and return pigmentation to hypopigmented areas.8-10
A 32-year-old Black woman presented to our clinic with a 40×15-cm scar that was marked by postinflammatory hypopigmentation from a second-degree burn on the right proximal arm. The patient had been burned 5 months prior by boiling water that was spilled on the arm while cooking. She had immediately sought treatment at an emergency department and subsequently in a burn unit, where the burn was debrided twice; medication was not prescribed to continue treatment. The patient reported that the scarring and hypopigmentation had taken a psychologic toll; her hope was to have pigmentation restored to the affected area to boost her confidence.
Physical examination revealed that the burn wound had healed but visible scarring and severe hypopigmentation due to destroyed melanocytes remained (Figure 1). To inhibit inflammation and stimulate repigmentation, we prescribed the calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus ointment 0.1% to be applied daily to the affected area. The patient returned to the clinic 1 month later. Perifollicular hyperpigmentation was noted at the site of the scar.

Monthly microneedling sessions with bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% were started. To avoid damaging any potentially remaining unhealed hypodermis and vasculature, the first microneedling session was performed with 9 needles set at minimal needle depth and frequency. The number of needles and their depth and frequency gradually were increased with each subsequent treatment. The patient continued tacrolimus ointment 0.1% throughout the course of treatment.
For each microneedling procedure, a handheld motorized microneedling device was applied to the skin at a depth of 0.25 mm, which was gradually increased until pinpoint petechiae were achieved. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% was then painted on the skin and allowed to absorb. Microneedling was performed again, ensuring that bimatoprost entered the skin in the area of the burn scar.
Microneedling procedures were performed monthly for 6 months, then once 3 months later, and once more 3 months later—8 treatments in total over the course of 1 year. Improvement in skin pigmentation was noted at each visit (Figure 2). Repigmentation was first noticed surrounding hair follicles; after later visits, it was observed that pigmentation began to spread from hair follicles to fill in remaining skin. The darkest areas of pigmentation were first noted around hair follicles; over time, melanocytes appeared to spontaneously regenerate and fill in surrounding areas as the scar continued to heal. The patient continued use of tacrolimus during the entire course of microneedling treatments and for the following 4 months. Sixteen months after initiation of treatment, the appearance of the skin was texturally smooth and returned to almost its original pigmentation (Figure 3).

We report a successful outcome in a patient with a hypopigmented burn scar who was treated with bimatoprost administered with traditional microneedling and alongside a tacrolimus regimen. Tacrolimus ointment inhibited the inflammatory response to allow melanocytes to heal and regenerate; bimatoprost and microneedling promoted hyperpigmentation of hair follicles in the affected area, eventually restoring pigmentation to the entire area. Our patient was extremely satisfied with the results of this combination treatment. She has reported feeling more confident going out and wearing short-sleeved clothing. Percutaneous drug delivery of bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.3% combined with topical tacrolimus may be an effective treatment for skin repigmentation. Further investigation of this regimen is needed to develop standardized treatment protocols.

- Juhasz MLW, Cohen JL. Micro-needling for the treatment of scars: an update for clinicians. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:997-1003. doi:10.2147/CCID.S267192
- Alster TS, Li MKY. Micro-needling of scars: a large prospective study with long-term follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145:358-364. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000006462
- Aust MC, Knobloch K, Reimers K, et al. Percutaneous collagen induction therapy: an alternative treatment for burn scars. Burns. 2010;36:836-843. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2009.11.014
- Kim Y-C, Park J-H, Prausnitz MR. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:1547-1568. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.04.005
- Doshi M, Edward DP, Osmanovic S. Clinical course of bimatoprost-induced periocular skin changes in Caucasians. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:1961-1967. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.05.041
- Kapur R, Osmanovic S, Toyran S, et al. Bimatoprost-induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation: histopathological study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:1541-1546. doi:10.1001/archopht.123.11.1541
- Priluck JC, Fu S. Latisse-induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:792-793. doi:10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.89
- Grimes PE. Bimatoprost 0.03% solution for the treatment of nonfacial vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:703-710.
- Barbulescu C, Goldstein N, Roop D, et al. Harnessing the power of regenerative therapy for vitiligo and alopecia areata. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140: 29-37. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.03.1142
- Kanokrungsee S, Pruettivorawongse D, Rajatanavin N. Clinicaloutcomes of topical bimatoprost for nonsegmental facial vitiligo: a preliminary study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:812-818. doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13648
- Juhasz MLW, Cohen JL. Micro-needling for the treatment of scars: an update for clinicians. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020;13:997-1003. doi:10.2147/CCID.S267192
- Alster TS, Li MKY. Micro-needling of scars: a large prospective study with long-term follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145:358-364. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000006462
- Aust MC, Knobloch K, Reimers K, et al. Percutaneous collagen induction therapy: an alternative treatment for burn scars. Burns. 2010;36:836-843. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2009.11.014
- Kim Y-C, Park J-H, Prausnitz MR. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:1547-1568. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.04.005
- Doshi M, Edward DP, Osmanovic S. Clinical course of bimatoprost-induced periocular skin changes in Caucasians. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:1961-1967. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.05.041
- Kapur R, Osmanovic S, Toyran S, et al. Bimatoprost-induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation: histopathological study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:1541-1546. doi:10.1001/archopht.123.11.1541
- Priluck JC, Fu S. Latisse-induced periocular skin hyperpigmentation. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:792-793. doi:10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.89
- Grimes PE. Bimatoprost 0.03% solution for the treatment of nonfacial vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:703-710.
- Barbulescu C, Goldstein N, Roop D, et al. Harnessing the power of regenerative therapy for vitiligo and alopecia areata. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140: 29-37. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.03.1142
- Kanokrungsee S, Pruettivorawongse D, Rajatanavin N. Clinicaloutcomes of topical bimatoprost for nonsegmental facial vitiligo: a preliminary study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:812-818. doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13648
PRACTICE POINTS
- Microneedling is a percutaneous collagen induction therapy that also may be used in drug delivery.
- Hypopigmentation can cause considerable distress for patients with skin of color.
- Percutaneous drug delivery of bimatoprost may be helpful in skin repigmentation.
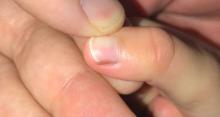
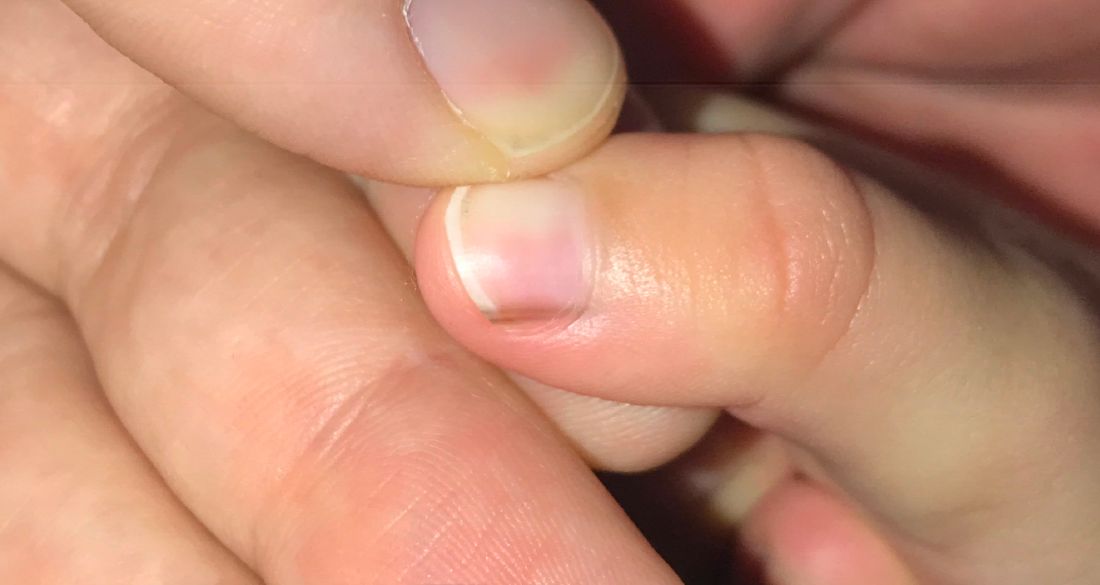
A toddler presents with a dark line on a fingernail
Given the over 1-year history of an unchanging longitudinal band of pigment without extension to the proximal or lateral nailfolds or any other nail findings, the most likely diagnosis is benign longitudinal melanonychia.
Longitudinal melanonychia, also known as melanonychia striata, describes a brown to black streak of pigment extending from the nail matrix to the free edge of the nail.1,2
This disorder can occur secondary to a wide variety of benign and pathologic causes including lentigines, nevi, melanoma, chronic trauma, inflammatory skin diseases, systemic diseases, iatrogenic causes, and genetic syndromes.3 In melanocytic causes of longitudinal melanonychia, either melanocytic activation or hyperplasia drive pigmentary development leading to the brown to black band seen in the nail.4 Benign causes of longitudinal melanonychia include benign melanocyte activation, lentigo, and benign nevus.1
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis for longitudinal melanonychia can include a wide variety of local and systemic causes. For our discussion, we will limit our differential to other locally involved disorders of the nail including subungual melanoma, subungual hematoma, onychomycosis, and glomus tumor.
Subungual melanoma is a rare subtype of acral lentiginous melanoma that most often presents as longitudinal melanonychia. Subungual melanoma is more common in those aged 50-70 years, individuals with personal or family history of melanoma or dysplastic nevus syndrome, and persons with African American, Native American, and Asian descent. Longitudinal melanonychia features that can be concerning for subungual melanoma include the presence of multiple colors, width greater than or equal to 3 mm, blurry borders, rapid increase in size, and extension to the proximal or lateral nailfolds (Hutchinson’s sign). Biopsy is required to make the diagnosis of subungual melanoma but is not necessary for melanonychia without atypical features.
Treatment of subungual melanoma depends on disease stage and can range from wide local excision of the nail apparatus to amputation of the affected digit and management with a medical oncologist. Given the absence of concerning neoplastic findings or personal or family history of melanoma, subungual melanoma is unlikely in this patient.
Subungual hematoma is an accumulation of blood underneath the nail plate that is typically the result of acute or chronic trauma to the distal phalanx. It can present as purple, red, pink, brown, or black discoloration under the nail plate and is most commonly found on the first toe. With acute trauma, pain is usually present upon initial injury. Subungual hematomas typically resolve on their own with normal nail growth. The absence of a history of trauma or pain, and the linear appearance of the lesion in our patient are inconsistent with a subungual hematoma.
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail caused by dermatophytes, nondermatophytes, or yeasts. It may present with longitudinal melanonychia; however, it more often presents with other nail abnormalities such as nail thickening, yellow discoloration, onycholysis, splitting, subungual hyperkeratosis, and nail plate destruction, which are not present in this patient. Furthermore, onychomycosis is more common in adults than children. Diagnosis is usually made with potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparations, histopathologic examination of nail clippings with a periodic acid-Schiff stain, fungal culture, or PCR.
Glomus tumor is a rare, benign neoplasm originating from cells of the glomus body. It is often found in the subungual region, in addition to other areas rich in glomus bodies such as the fingertips, palms, wrists, and forearms. Subungual glomus tumors present as a red, purple, or blueish lesions under the nail plate. Distal notching or an overlying longitudinal fissure may be present. Subungual glomus tumors are typically associated with pinpoint tenderness, paroxysmal pain, and cold sensitivity, features that are not present in our patient. The history and examination of our patient are much more consistent with benign longitudinal melanonychia.
It appears that melanoma associated with longitudinal melanonychia is very rare in children. According to one review published in 2020, only 12 cases of pediatric subungual melanoma have been reported.5 Recent series have observed longitudinal melanonychia in large sets of children, with findings that demonstrate that the vast majority of longitudinal melanonychia either stops progressing or regresses. These investigations therefore recommend serial observation of longitudinal melanonychia except in rare circumstances.6,7
Given the lack of troubling findings or concerning history, our patient was managed with observation. On follow-up 6 months later, he was found to have no change in his nail pigmentation.
Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; Ms. Sui is a research associate in the department of dermatology, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; and Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics, all at the University of California and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. They have no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Mannava KA et al. Hand Surg. 2013;18(1):133-9.
2. Leung AKC et al. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58(11):1239-45.
3. Andre J and Lateur N. Dermatol Clin. 2006;24(3):329-39.
4. Lee DK and Lipner SR. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):694-712.
5. Smith RJ and Rubin AI. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32(4):506-15. .
6. Matsui Y et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86(4):946-8.
7. Lee JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87(2):366-72.
Given the over 1-year history of an unchanging longitudinal band of pigment without extension to the proximal or lateral nailfolds or any other nail findings, the most likely diagnosis is benign longitudinal melanonychia.
Longitudinal melanonychia, also known as melanonychia striata, describes a brown to black streak of pigment extending from the nail matrix to the free edge of the nail.1,2
This disorder can occur secondary to a wide variety of benign and pathologic causes including lentigines, nevi, melanoma, chronic trauma, inflammatory skin diseases, systemic diseases, iatrogenic causes, and genetic syndromes.3 In melanocytic causes of longitudinal melanonychia, either melanocytic activation or hyperplasia drive pigmentary development leading to the brown to black band seen in the nail.4 Benign causes of longitudinal melanonychia include benign melanocyte activation, lentigo, and benign nevus.1
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis for longitudinal melanonychia can include a wide variety of local and systemic causes. For our discussion, we will limit our differential to other locally involved disorders of the nail including subungual melanoma, subungual hematoma, onychomycosis, and glomus tumor.
Subungual melanoma is a rare subtype of acral lentiginous melanoma that most often presents as longitudinal melanonychia. Subungual melanoma is more common in those aged 50-70 years, individuals with personal or family history of melanoma or dysplastic nevus syndrome, and persons with African American, Native American, and Asian descent. Longitudinal melanonychia features that can be concerning for subungual melanoma include the presence of multiple colors, width greater than or equal to 3 mm, blurry borders, rapid increase in size, and extension to the proximal or lateral nailfolds (Hutchinson’s sign). Biopsy is required to make the diagnosis of subungual melanoma but is not necessary for melanonychia without atypical features.
Treatment of subungual melanoma depends on disease stage and can range from wide local excision of the nail apparatus to amputation of the affected digit and management with a medical oncologist. Given the absence of concerning neoplastic findings or personal or family history of melanoma, subungual melanoma is unlikely in this patient.
Subungual hematoma is an accumulation of blood underneath the nail plate that is typically the result of acute or chronic trauma to the distal phalanx. It can present as purple, red, pink, brown, or black discoloration under the nail plate and is most commonly found on the first toe. With acute trauma, pain is usually present upon initial injury. Subungual hematomas typically resolve on their own with normal nail growth. The absence of a history of trauma or pain, and the linear appearance of the lesion in our patient are inconsistent with a subungual hematoma.
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail caused by dermatophytes, nondermatophytes, or yeasts. It may present with longitudinal melanonychia; however, it more often presents with other nail abnormalities such as nail thickening, yellow discoloration, onycholysis, splitting, subungual hyperkeratosis, and nail plate destruction, which are not present in this patient. Furthermore, onychomycosis is more common in adults than children. Diagnosis is usually made with potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparations, histopathologic examination of nail clippings with a periodic acid-Schiff stain, fungal culture, or PCR.
Glomus tumor is a rare, benign neoplasm originating from cells of the glomus body. It is often found in the subungual region, in addition to other areas rich in glomus bodies such as the fingertips, palms, wrists, and forearms. Subungual glomus tumors present as a red, purple, or blueish lesions under the nail plate. Distal notching or an overlying longitudinal fissure may be present. Subungual glomus tumors are typically associated with pinpoint tenderness, paroxysmal pain, and cold sensitivity, features that are not present in our patient. The history and examination of our patient are much more consistent with benign longitudinal melanonychia.
It appears that melanoma associated with longitudinal melanonychia is very rare in children. According to one review published in 2020, only 12 cases of pediatric subungual melanoma have been reported.5 Recent series have observed longitudinal melanonychia in large sets of children, with findings that demonstrate that the vast majority of longitudinal melanonychia either stops progressing or regresses. These investigations therefore recommend serial observation of longitudinal melanonychia except in rare circumstances.6,7
Given the lack of troubling findings or concerning history, our patient was managed with observation. On follow-up 6 months later, he was found to have no change in his nail pigmentation.
Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; Ms. Sui is a research associate in the department of dermatology, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; and Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics, all at the University of California and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. They have no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Mannava KA et al. Hand Surg. 2013;18(1):133-9.
2. Leung AKC et al. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58(11):1239-45.
3. Andre J and Lateur N. Dermatol Clin. 2006;24(3):329-39.
4. Lee DK and Lipner SR. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):694-712.
5. Smith RJ and Rubin AI. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32(4):506-15. .
6. Matsui Y et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86(4):946-8.
7. Lee JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87(2):366-72.
Given the over 1-year history of an unchanging longitudinal band of pigment without extension to the proximal or lateral nailfolds or any other nail findings, the most likely diagnosis is benign longitudinal melanonychia.
Longitudinal melanonychia, also known as melanonychia striata, describes a brown to black streak of pigment extending from the nail matrix to the free edge of the nail.1,2
This disorder can occur secondary to a wide variety of benign and pathologic causes including lentigines, nevi, melanoma, chronic trauma, inflammatory skin diseases, systemic diseases, iatrogenic causes, and genetic syndromes.3 In melanocytic causes of longitudinal melanonychia, either melanocytic activation or hyperplasia drive pigmentary development leading to the brown to black band seen in the nail.4 Benign causes of longitudinal melanonychia include benign melanocyte activation, lentigo, and benign nevus.1
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis for longitudinal melanonychia can include a wide variety of local and systemic causes. For our discussion, we will limit our differential to other locally involved disorders of the nail including subungual melanoma, subungual hematoma, onychomycosis, and glomus tumor.
Subungual melanoma is a rare subtype of acral lentiginous melanoma that most often presents as longitudinal melanonychia. Subungual melanoma is more common in those aged 50-70 years, individuals with personal or family history of melanoma or dysplastic nevus syndrome, and persons with African American, Native American, and Asian descent. Longitudinal melanonychia features that can be concerning for subungual melanoma include the presence of multiple colors, width greater than or equal to 3 mm, blurry borders, rapid increase in size, and extension to the proximal or lateral nailfolds (Hutchinson’s sign). Biopsy is required to make the diagnosis of subungual melanoma but is not necessary for melanonychia without atypical features.
Treatment of subungual melanoma depends on disease stage and can range from wide local excision of the nail apparatus to amputation of the affected digit and management with a medical oncologist. Given the absence of concerning neoplastic findings or personal or family history of melanoma, subungual melanoma is unlikely in this patient.
Subungual hematoma is an accumulation of blood underneath the nail plate that is typically the result of acute or chronic trauma to the distal phalanx. It can present as purple, red, pink, brown, or black discoloration under the nail plate and is most commonly found on the first toe. With acute trauma, pain is usually present upon initial injury. Subungual hematomas typically resolve on their own with normal nail growth. The absence of a history of trauma or pain, and the linear appearance of the lesion in our patient are inconsistent with a subungual hematoma.
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail caused by dermatophytes, nondermatophytes, or yeasts. It may present with longitudinal melanonychia; however, it more often presents with other nail abnormalities such as nail thickening, yellow discoloration, onycholysis, splitting, subungual hyperkeratosis, and nail plate destruction, which are not present in this patient. Furthermore, onychomycosis is more common in adults than children. Diagnosis is usually made with potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparations, histopathologic examination of nail clippings with a periodic acid-Schiff stain, fungal culture, or PCR.
Glomus tumor is a rare, benign neoplasm originating from cells of the glomus body. It is often found in the subungual region, in addition to other areas rich in glomus bodies such as the fingertips, palms, wrists, and forearms. Subungual glomus tumors present as a red, purple, or blueish lesions under the nail plate. Distal notching or an overlying longitudinal fissure may be present. Subungual glomus tumors are typically associated with pinpoint tenderness, paroxysmal pain, and cold sensitivity, features that are not present in our patient. The history and examination of our patient are much more consistent with benign longitudinal melanonychia.
It appears that melanoma associated with longitudinal melanonychia is very rare in children. According to one review published in 2020, only 12 cases of pediatric subungual melanoma have been reported.5 Recent series have observed longitudinal melanonychia in large sets of children, with findings that demonstrate that the vast majority of longitudinal melanonychia either stops progressing or regresses. These investigations therefore recommend serial observation of longitudinal melanonychia except in rare circumstances.6,7
Given the lack of troubling findings or concerning history, our patient was managed with observation. On follow-up 6 months later, he was found to have no change in his nail pigmentation.
Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; Ms. Sui is a research associate in the department of dermatology, division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology; and Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics, all at the University of California and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. They have no relevant disclosures.
References
1. Mannava KA et al. Hand Surg. 2013;18(1):133-9.
2. Leung AKC et al. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58(11):1239-45.
3. Andre J and Lateur N. Dermatol Clin. 2006;24(3):329-39.
4. Lee DK and Lipner SR. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):694-712.
5. Smith RJ and Rubin AI. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32(4):506-15. .
6. Matsui Y et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86(4):946-8.
7. Lee JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87(2):366-72.
Examination findings reveal a 2-mm brown longitudinal band on the radial aspect of the right thumbnail that does not extend into the proximal or lateral nailfolds. The rest of the skin and nail exam is unremarkable.
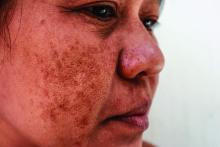
Long-term maintenance required in melasma patients
SAN DIEGO –
“They need to understand that melasma is going to require long-term maintenance,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
Hydroquinone is a mainstay of melasma therapy, but instead of the commonly used 4% formulation, she prefers to use 12% hydroquinone with 6% kojic acid in VersaBase cream. “It’s a high concentration but the VersaBase makes it more tolerable,” she said. “I have patients take a pea-sized amount and mix it in a regular moisturizer. It’s too strong to spot treat, so it goes on the whole face.”
Mindful that chronic hydroquinone use can cause ochronosis (permanent darkening), she has patients alternate with a nonhydroquinone bleaching agent such as lignin peroxidase, oligopeptide, Lytera, Melaplex, 4-n-butylresorcinol, Cysteamine cream, tranexamic acid, or oral antioxidants. In a study sponsored by SkinMedica, investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, half-face study in females with moderate to severe facial hyperpigmentation to assess the efficacy and tolerability of three new skin brightener formulations containing SMA-432, a prostaglandin E2 inhibitor, compared with 4% hydroquinone. They found that the nonhydroquinone skin formulations were better tolerated and were just as effective as 4% hydroquinone.
Chemical peels and laser treatments
Chemical peels are another treatment option for melasma, but Dr. Ortiz prefers glycolic peels over salicylic and other peels, “because there is no downtime,” she said.
As for laser-based approaches, melasma patients respond best to low energy devices such as the 1,927-nm fractional diode laser at a 3.75% density. “This also can increase the skin permeability of topicals, so when you’re combining it with hydroquinone it can be more effective,” she said.
In an observational study of 27 women with refractory melasma, with phototypes II-V, New York City–based dermatologist Arielle Kauvar, MD, combined microdermabrasion with the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. “The settings she used were very low fluence, so there was no clinical endpoint or no whitening,” said Dr. Ortiz, vice president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS). Specifically, Dr. Kauvar used the laser at 1.6-2 J/cm2 with a 5- or 6-mm spot size immediately following microdermabrasion every 4 weeks; Patients received an average of 2.6 treatments, and were assessed 3-12 months after the last treatment. Study participants were on a standard skin care regimen of a broad spectrum sunscreen, hydroquinone, and tretinoin or vitamin C.
Most of the patients showed at least 50% clearance of melasma 1 month after the first treatment, and 81% showed more than 75% clearance of melasma; remission lasted at least 6 months.
“I personally prefer to use picosecond over Q-switched lasers, because they deliver the energy faster, and you can use a 1,064-nm picosecond laser that is safe in all skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said. “There is minimal downtime, and it doesn’t require anesthesia. You have to consider these things when you’re treating melasma, because this usually requires monthly treatments. If you do something that requires a week of downtime every month, it’s not practical for patients.”
In a study published in 2021, Dr. Ortiz and Tanya Greywal, MD, used three passes of the 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser to treat melasma in 10 patients with skin types II-V. The device had a 650-microsecond pulse duration, a 6-mm spot size, and an energy mode of 11-14 J/cm2. The researchers observed a mean melasma improvement of 26%-50% as early as 3 weeks. “There was no downtime, and no anesthesia was required,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Researchers have discovered a vascular component to melasma, which may have treatment implications. Houston-based dermatologist Paul M. Friedman, MD, and his colleagues used spectrocolorimetry to detect an underlying prominent vascular component in a retrospective review of 11 patients with melasma, with skin types II-IV. They determined that melasma lesions exhibiting subtle or subclinical telangiectatic erythema may be improved by combining vascular-targeted laser therapy with fractional low-powered diode laser therapy.
“So, combining a vascular laser with a 1,927-nm fractional diode laser showed more improvement than with just the diode laser alone,” said Dr. Ortiz, who was not involved with the analysis.
To optimize results following the laser treatment of melasma, she uses one application of clobetasol immediately after the procedure. “This can help reduce swelling and inflammation to decrease the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation,” she said. “You can also use a skin cooling system like Cryomodulation for controlled cooling.”
Tranexamic acid and PLE
Another strategy for melasma patients involves oral treatment with extract of Polypodium leucotomos (PLE), a fern from the Polypodiaceae family with antioxidant properties that has been shown to be photoprotective against UVA and UVB radiation. “I explain to my patients that it’s like an internal sunscreen,” Dr. Ortiz said. “It does not replace your external sunscreen, but it adds extra protection.”
In a pilot placebo-controlled study of patients with melasma on their normal regimen of hydroquinone and sunscreen, 40 Asian patients with melasma were randomized to receive either oral PLE supplementation or placebo for 12 weeks. The authors found that PLE significantly improved and accelerated the outcome reached with hydroquinone and sunscreen from about the first month of treatment, compared with placebo.
Dr. Ortiz discussed the role of oral tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic, procoagulant agent that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of menorrhagia and to prevent hemorrhage in patients with hemophilia undergoing tooth extractions. “This is a game changer for melasma treatment,” she said, but its use has been limited by the risk for thromboembolism.
In a study of 561 patients with melasma, 90% improved after a median treatment duration of 4 months, and only 7% had side effects, most commonly abdominal bloating and pain. Treatment was discontinued in one patient who developed a deep vein thrombosis, and was diagnosed with familial protein S deficiency.
The daily dosing of tranexamic acid for menorrhagia is 3,900 mg daily, while the dose for treating melasma has ranged from 500 mg to 1,500 mg per day, Dr. Ortiz said. It’s available as a 650-mg tablet in the United States. “I prescribe 325 mg twice a day, but studies have shown that 650 mg once a day is just as effective,” she said.
Prior to prescribing tranexamic acid, Dr. Ortiz does not order labs, but she performs an extensive history of current illness and does not prescribe it in patients with an increased risk of clotting, including people who smoke and those who take oral contraceptives or are on hormone supplementation. Use is also contraindicated in people with a current malignancy, those with a history of stroke or DVT, and those who have any clotting disorder.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is cochair of the Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
SAN DIEGO –
“They need to understand that melasma is going to require long-term maintenance,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
Hydroquinone is a mainstay of melasma therapy, but instead of the commonly used 4% formulation, she prefers to use 12% hydroquinone with 6% kojic acid in VersaBase cream. “It’s a high concentration but the VersaBase makes it more tolerable,” she said. “I have patients take a pea-sized amount and mix it in a regular moisturizer. It’s too strong to spot treat, so it goes on the whole face.”
Mindful that chronic hydroquinone use can cause ochronosis (permanent darkening), she has patients alternate with a nonhydroquinone bleaching agent such as lignin peroxidase, oligopeptide, Lytera, Melaplex, 4-n-butylresorcinol, Cysteamine cream, tranexamic acid, or oral antioxidants. In a study sponsored by SkinMedica, investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, half-face study in females with moderate to severe facial hyperpigmentation to assess the efficacy and tolerability of three new skin brightener formulations containing SMA-432, a prostaglandin E2 inhibitor, compared with 4% hydroquinone. They found that the nonhydroquinone skin formulations were better tolerated and were just as effective as 4% hydroquinone.
Chemical peels and laser treatments
Chemical peels are another treatment option for melasma, but Dr. Ortiz prefers glycolic peels over salicylic and other peels, “because there is no downtime,” she said.
As for laser-based approaches, melasma patients respond best to low energy devices such as the 1,927-nm fractional diode laser at a 3.75% density. “This also can increase the skin permeability of topicals, so when you’re combining it with hydroquinone it can be more effective,” she said.
In an observational study of 27 women with refractory melasma, with phototypes II-V, New York City–based dermatologist Arielle Kauvar, MD, combined microdermabrasion with the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. “The settings she used were very low fluence, so there was no clinical endpoint or no whitening,” said Dr. Ortiz, vice president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS). Specifically, Dr. Kauvar used the laser at 1.6-2 J/cm2 with a 5- or 6-mm spot size immediately following microdermabrasion every 4 weeks; Patients received an average of 2.6 treatments, and were assessed 3-12 months after the last treatment. Study participants were on a standard skin care regimen of a broad spectrum sunscreen, hydroquinone, and tretinoin or vitamin C.
Most of the patients showed at least 50% clearance of melasma 1 month after the first treatment, and 81% showed more than 75% clearance of melasma; remission lasted at least 6 months.
“I personally prefer to use picosecond over Q-switched lasers, because they deliver the energy faster, and you can use a 1,064-nm picosecond laser that is safe in all skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said. “There is minimal downtime, and it doesn’t require anesthesia. You have to consider these things when you’re treating melasma, because this usually requires monthly treatments. If you do something that requires a week of downtime every month, it’s not practical for patients.”
In a study published in 2021, Dr. Ortiz and Tanya Greywal, MD, used three passes of the 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser to treat melasma in 10 patients with skin types II-V. The device had a 650-microsecond pulse duration, a 6-mm spot size, and an energy mode of 11-14 J/cm2. The researchers observed a mean melasma improvement of 26%-50% as early as 3 weeks. “There was no downtime, and no anesthesia was required,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Researchers have discovered a vascular component to melasma, which may have treatment implications. Houston-based dermatologist Paul M. Friedman, MD, and his colleagues used spectrocolorimetry to detect an underlying prominent vascular component in a retrospective review of 11 patients with melasma, with skin types II-IV. They determined that melasma lesions exhibiting subtle or subclinical telangiectatic erythema may be improved by combining vascular-targeted laser therapy with fractional low-powered diode laser therapy.
“So, combining a vascular laser with a 1,927-nm fractional diode laser showed more improvement than with just the diode laser alone,” said Dr. Ortiz, who was not involved with the analysis.
To optimize results following the laser treatment of melasma, she uses one application of clobetasol immediately after the procedure. “This can help reduce swelling and inflammation to decrease the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation,” she said. “You can also use a skin cooling system like Cryomodulation for controlled cooling.”
Tranexamic acid and PLE
Another strategy for melasma patients involves oral treatment with extract of Polypodium leucotomos (PLE), a fern from the Polypodiaceae family with antioxidant properties that has been shown to be photoprotective against UVA and UVB radiation. “I explain to my patients that it’s like an internal sunscreen,” Dr. Ortiz said. “It does not replace your external sunscreen, but it adds extra protection.”
In a pilot placebo-controlled study of patients with melasma on their normal regimen of hydroquinone and sunscreen, 40 Asian patients with melasma were randomized to receive either oral PLE supplementation or placebo for 12 weeks. The authors found that PLE significantly improved and accelerated the outcome reached with hydroquinone and sunscreen from about the first month of treatment, compared with placebo.
Dr. Ortiz discussed the role of oral tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic, procoagulant agent that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of menorrhagia and to prevent hemorrhage in patients with hemophilia undergoing tooth extractions. “This is a game changer for melasma treatment,” she said, but its use has been limited by the risk for thromboembolism.
In a study of 561 patients with melasma, 90% improved after a median treatment duration of 4 months, and only 7% had side effects, most commonly abdominal bloating and pain. Treatment was discontinued in one patient who developed a deep vein thrombosis, and was diagnosed with familial protein S deficiency.
The daily dosing of tranexamic acid for menorrhagia is 3,900 mg daily, while the dose for treating melasma has ranged from 500 mg to 1,500 mg per day, Dr. Ortiz said. It’s available as a 650-mg tablet in the United States. “I prescribe 325 mg twice a day, but studies have shown that 650 mg once a day is just as effective,” she said.
Prior to prescribing tranexamic acid, Dr. Ortiz does not order labs, but she performs an extensive history of current illness and does not prescribe it in patients with an increased risk of clotting, including people who smoke and those who take oral contraceptives or are on hormone supplementation. Use is also contraindicated in people with a current malignancy, those with a history of stroke or DVT, and those who have any clotting disorder.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is cochair of the Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
SAN DIEGO –
“They need to understand that melasma is going to require long-term maintenance,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
Hydroquinone is a mainstay of melasma therapy, but instead of the commonly used 4% formulation, she prefers to use 12% hydroquinone with 6% kojic acid in VersaBase cream. “It’s a high concentration but the VersaBase makes it more tolerable,” she said. “I have patients take a pea-sized amount and mix it in a regular moisturizer. It’s too strong to spot treat, so it goes on the whole face.”
Mindful that chronic hydroquinone use can cause ochronosis (permanent darkening), she has patients alternate with a nonhydroquinone bleaching agent such as lignin peroxidase, oligopeptide, Lytera, Melaplex, 4-n-butylresorcinol, Cysteamine cream, tranexamic acid, or oral antioxidants. In a study sponsored by SkinMedica, investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, half-face study in females with moderate to severe facial hyperpigmentation to assess the efficacy and tolerability of three new skin brightener formulations containing SMA-432, a prostaglandin E2 inhibitor, compared with 4% hydroquinone. They found that the nonhydroquinone skin formulations were better tolerated and were just as effective as 4% hydroquinone.
Chemical peels and laser treatments
Chemical peels are another treatment option for melasma, but Dr. Ortiz prefers glycolic peels over salicylic and other peels, “because there is no downtime,” she said.
As for laser-based approaches, melasma patients respond best to low energy devices such as the 1,927-nm fractional diode laser at a 3.75% density. “This also can increase the skin permeability of topicals, so when you’re combining it with hydroquinone it can be more effective,” she said.
In an observational study of 27 women with refractory melasma, with phototypes II-V, New York City–based dermatologist Arielle Kauvar, MD, combined microdermabrasion with the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. “The settings she used were very low fluence, so there was no clinical endpoint or no whitening,” said Dr. Ortiz, vice president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS). Specifically, Dr. Kauvar used the laser at 1.6-2 J/cm2 with a 5- or 6-mm spot size immediately following microdermabrasion every 4 weeks; Patients received an average of 2.6 treatments, and were assessed 3-12 months after the last treatment. Study participants were on a standard skin care regimen of a broad spectrum sunscreen, hydroquinone, and tretinoin or vitamin C.
Most of the patients showed at least 50% clearance of melasma 1 month after the first treatment, and 81% showed more than 75% clearance of melasma; remission lasted at least 6 months.
“I personally prefer to use picosecond over Q-switched lasers, because they deliver the energy faster, and you can use a 1,064-nm picosecond laser that is safe in all skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said. “There is minimal downtime, and it doesn’t require anesthesia. You have to consider these things when you’re treating melasma, because this usually requires monthly treatments. If you do something that requires a week of downtime every month, it’s not practical for patients.”
In a study published in 2021, Dr. Ortiz and Tanya Greywal, MD, used three passes of the 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser to treat melasma in 10 patients with skin types II-V. The device had a 650-microsecond pulse duration, a 6-mm spot size, and an energy mode of 11-14 J/cm2. The researchers observed a mean melasma improvement of 26%-50% as early as 3 weeks. “There was no downtime, and no anesthesia was required,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Researchers have discovered a vascular component to melasma, which may have treatment implications. Houston-based dermatologist Paul M. Friedman, MD, and his colleagues used spectrocolorimetry to detect an underlying prominent vascular component in a retrospective review of 11 patients with melasma, with skin types II-IV. They determined that melasma lesions exhibiting subtle or subclinical telangiectatic erythema may be improved by combining vascular-targeted laser therapy with fractional low-powered diode laser therapy.
“So, combining a vascular laser with a 1,927-nm fractional diode laser showed more improvement than with just the diode laser alone,” said Dr. Ortiz, who was not involved with the analysis.
To optimize results following the laser treatment of melasma, she uses one application of clobetasol immediately after the procedure. “This can help reduce swelling and inflammation to decrease the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation,” she said. “You can also use a skin cooling system like Cryomodulation for controlled cooling.”
Tranexamic acid and PLE
Another strategy for melasma patients involves oral treatment with extract of Polypodium leucotomos (PLE), a fern from the Polypodiaceae family with antioxidant properties that has been shown to be photoprotective against UVA and UVB radiation. “I explain to my patients that it’s like an internal sunscreen,” Dr. Ortiz said. “It does not replace your external sunscreen, but it adds extra protection.”
In a pilot placebo-controlled study of patients with melasma on their normal regimen of hydroquinone and sunscreen, 40 Asian patients with melasma were randomized to receive either oral PLE supplementation or placebo for 12 weeks. The authors found that PLE significantly improved and accelerated the outcome reached with hydroquinone and sunscreen from about the first month of treatment, compared with placebo.
Dr. Ortiz discussed the role of oral tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic, procoagulant agent that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of menorrhagia and to prevent hemorrhage in patients with hemophilia undergoing tooth extractions. “This is a game changer for melasma treatment,” she said, but its use has been limited by the risk for thromboembolism.
In a study of 561 patients with melasma, 90% improved after a median treatment duration of 4 months, and only 7% had side effects, most commonly abdominal bloating and pain. Treatment was discontinued in one patient who developed a deep vein thrombosis, and was diagnosed with familial protein S deficiency.
The daily dosing of tranexamic acid for menorrhagia is 3,900 mg daily, while the dose for treating melasma has ranged from 500 mg to 1,500 mg per day, Dr. Ortiz said. It’s available as a 650-mg tablet in the United States. “I prescribe 325 mg twice a day, but studies have shown that 650 mg once a day is just as effective,” she said.
Prior to prescribing tranexamic acid, Dr. Ortiz does not order labs, but she performs an extensive history of current illness and does not prescribe it in patients with an increased risk of clotting, including people who smoke and those who take oral contraceptives or are on hormone supplementation. Use is also contraindicated in people with a current malignancy, those with a history of stroke or DVT, and those who have any clotting disorder.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is cochair of the Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
AT MOAS 2022
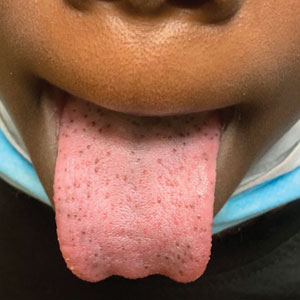
Hyperpigmented Papules on the Tongue of a Child
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
A 9-year-old Black boy presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of dark spots on the tongue. The family first noted these spots 5 months prior and reported that they remained stable during that time. The patient’s medical history was notable for autism spectrum disorder and multiple food allergies. His family history was negative for similar oral pigmentation or other pigmentary anomalies. A review of systems was positive only for selective eating and rare nosebleeds. Physical examination revealed numerous dark brown, pinpoint papules across the dorsal aspect of the tongue. No hyperpigmentation of the buccal mucosae, lips, palms, or soles was identified. Several light brown streaks were present on the fingernails and toenails, consistent with longitudinal melanonychia. A prior complete blood cell count was within reference range.
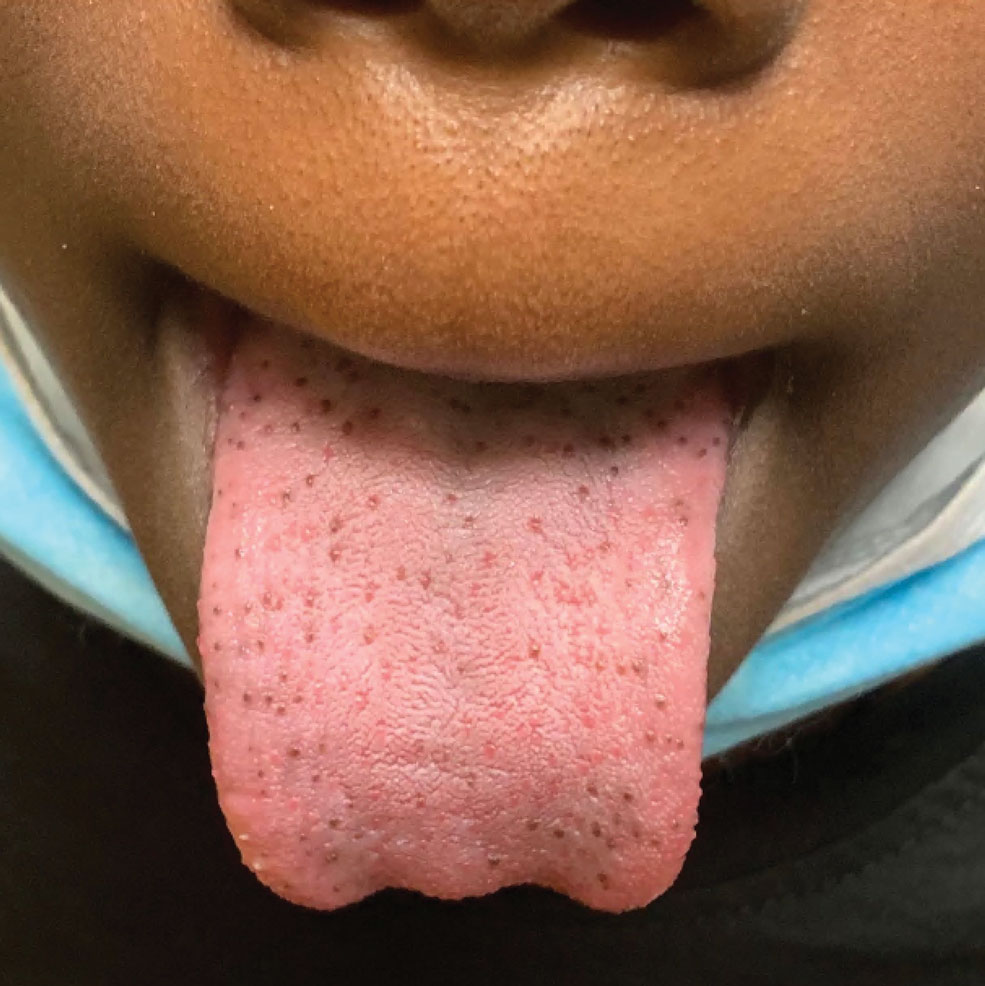
New treatments aim to tame vitiligo
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Vitiligo, an autoimmune condition that results in patches of skin depigmentation, occurs in 0.5% to 2% of the population. The average age of onset is 20 years, with 25% of cases occurring before age 10, and 70%-80% of cases by age 30 years, which means a long-term effect on quality of life, especially for younger patients, said Dr. Rosmarin, vice chair of education and research and director of the clinical trials unit at Tufts University, Boston.
Studies have shown that 95% of 15- to 17-year-olds with vitiligo are bothered by it, as are approximately 50% of children aged 6-14 years, he said. Although patients with more extensive lesions on the face, arms, legs, and hands report worse quality of life, they report that uncontrolled progression of vitiligo is more concerning than the presence of lesions in exposed areas, he noted.
The current strategy for getting vitiligo under control is a two-step process, said Dr. Rosmarin. First, improve the skin environment by suppressing the overactive immune system, then encourage repigmentation and “nudge the melanocytes to return,” he said.
Topical ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, is the latest tool for dermatologists to help give the melanocytes that nudge. In July 2022, the Food and Drug Administration approved ruxolitinib cream for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years of age and older – the first treatment approved to repigment patients with vitiligo.
Vitiligo is driven in part by interferon (IFN)-gamma signaling through JAK 1 and 2, and ruxolitinib acts as an inhibitor, Dr. Rosmarin said.
In the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies presented at the 2022 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting in Milan, adolescents and adults with vitiligo who were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream twice daily showed significant improvement over those randomized to the vehicle by 24 weeks, at which time all patients could continue with ruxolitinib through 52 weeks, he said.
Dr. Rosmarin presented 52-week data from the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies at the 2022 American Academy of Dermatology meeting in Boston. He was the lead author of the studies that were subsequently published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the two studies, 52.6% and 48% of the patients in the ruxolitinib groups achieved the primary outcome of at least 75% improvement on the Facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI75) by 52 weeks, compared with 26.8% and 29.6% of patients on the vehicle, respectively.
In addition, at 52 weeks, 53.2% and 49.2% of patients treated with ruxolitinib in the two studies achieved 50% improvement on the Total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (T-VASI50), a clinician assessment of affected body surface area and level of depigmentation, compared with 31.7% and 22.2% of those on vehicle, respectively.
Patient satisfaction was high with ruxolitinib, Dr. Rosmarin said. In the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies, 39.9% and 32.8% of patients, respectively, achieved a successful treatment response based on the patient-reported Vitiligo Noticeability Scale (VNS) by week 52, versus 19.5% and 13.6% of those on vehicle.
Ruxolitinib cream was well tolerated, with “no clinically significant application site reactions or serious treatment-related adverse events,” he noted. The most common treatment-related adverse events across the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies were acne at the application site (affecting about 6% of patients) and pruritus at the application site about (affecting 5%), said Dr. Rosmarin.
JAK inhibitors, including ruxolitinib, baricitinib, and tofacitinib, have shown effectiveness for vitiligo, which supports the potential role of the IFN-gamma-chemokine signaling axis in the pathogenesis of the disease, said Dr. Rosmarin. However, more studies are required to determine the ideal dosage of JAK inhibitors for the treatment of vitiligo, and to identify other inflammatory pathways that may be implicated in the pathogenesis of this condition.
Ruxolitinib’s success has been consistent across subgroups of age, gender, race, geographic region, and Fitzpatrick skin phototype. Notably, ruxolitinib was effective among the adolescent population, with approximately 60% achieving T-VASI50 and success based on VNS in TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2.
An oral version of ruxolitinib is in clinical trials, which “makes a lot of sense,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “Patients don’t always have localized disease,” and such patients may benefit from an oral therapy. Topicals may have the advantage in terms of safety, but questions of maintenance remain, he said. Oral treatments may be useful for patients with large body surface areas affected, and those with unstable or progressive disease, he added.
Areas for additional research include combination therapy with ruxolitinib and phototherapy, and an anti-IL 15 therapy in the pipeline has the potential to drive vitiligo into remission, Dr. Rosmarin said. In a study known as REVEAL that is still recruiting patients, researchers will test the efficacy of an IL-15 inhibitor known as AMG 714 to induce facial repigmentation in adults with vitiligo.
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed ties with AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Celgene, Concert Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo, Sanofi, Sun, UCB, and Viela Bio.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Vitiligo, an autoimmune condition that results in patches of skin depigmentation, occurs in 0.5% to 2% of the population. The average age of onset is 20 years, with 25% of cases occurring before age 10, and 70%-80% of cases by age 30 years, which means a long-term effect on quality of life, especially for younger patients, said Dr. Rosmarin, vice chair of education and research and director of the clinical trials unit at Tufts University, Boston.
Studies have shown that 95% of 15- to 17-year-olds with vitiligo are bothered by it, as are approximately 50% of children aged 6-14 years, he said. Although patients with more extensive lesions on the face, arms, legs, and hands report worse quality of life, they report that uncontrolled progression of vitiligo is more concerning than the presence of lesions in exposed areas, he noted.
The current strategy for getting vitiligo under control is a two-step process, said Dr. Rosmarin. First, improve the skin environment by suppressing the overactive immune system, then encourage repigmentation and “nudge the melanocytes to return,” he said.
Topical ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, is the latest tool for dermatologists to help give the melanocytes that nudge. In July 2022, the Food and Drug Administration approved ruxolitinib cream for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years of age and older – the first treatment approved to repigment patients with vitiligo.
Vitiligo is driven in part by interferon (IFN)-gamma signaling through JAK 1 and 2, and ruxolitinib acts as an inhibitor, Dr. Rosmarin said.
In the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies presented at the 2022 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting in Milan, adolescents and adults with vitiligo who were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream twice daily showed significant improvement over those randomized to the vehicle by 24 weeks, at which time all patients could continue with ruxolitinib through 52 weeks, he said.
Dr. Rosmarin presented 52-week data from the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies at the 2022 American Academy of Dermatology meeting in Boston. He was the lead author of the studies that were subsequently published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the two studies, 52.6% and 48% of the patients in the ruxolitinib groups achieved the primary outcome of at least 75% improvement on the Facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI75) by 52 weeks, compared with 26.8% and 29.6% of patients on the vehicle, respectively.
In addition, at 52 weeks, 53.2% and 49.2% of patients treated with ruxolitinib in the two studies achieved 50% improvement on the Total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (T-VASI50), a clinician assessment of affected body surface area and level of depigmentation, compared with 31.7% and 22.2% of those on vehicle, respectively.
Patient satisfaction was high with ruxolitinib, Dr. Rosmarin said. In the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies, 39.9% and 32.8% of patients, respectively, achieved a successful treatment response based on the patient-reported Vitiligo Noticeability Scale (VNS) by week 52, versus 19.5% and 13.6% of those on vehicle.
Ruxolitinib cream was well tolerated, with “no clinically significant application site reactions or serious treatment-related adverse events,” he noted. The most common treatment-related adverse events across the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies were acne at the application site (affecting about 6% of patients) and pruritus at the application site about (affecting 5%), said Dr. Rosmarin.
JAK inhibitors, including ruxolitinib, baricitinib, and tofacitinib, have shown effectiveness for vitiligo, which supports the potential role of the IFN-gamma-chemokine signaling axis in the pathogenesis of the disease, said Dr. Rosmarin. However, more studies are required to determine the ideal dosage of JAK inhibitors for the treatment of vitiligo, and to identify other inflammatory pathways that may be implicated in the pathogenesis of this condition.
Ruxolitinib’s success has been consistent across subgroups of age, gender, race, geographic region, and Fitzpatrick skin phototype. Notably, ruxolitinib was effective among the adolescent population, with approximately 60% achieving T-VASI50 and success based on VNS in TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2.
An oral version of ruxolitinib is in clinical trials, which “makes a lot of sense,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “Patients don’t always have localized disease,” and such patients may benefit from an oral therapy. Topicals may have the advantage in terms of safety, but questions of maintenance remain, he said. Oral treatments may be useful for patients with large body surface areas affected, and those with unstable or progressive disease, he added.
Areas for additional research include combination therapy with ruxolitinib and phototherapy, and an anti-IL 15 therapy in the pipeline has the potential to drive vitiligo into remission, Dr. Rosmarin said. In a study known as REVEAL that is still recruiting patients, researchers will test the efficacy of an IL-15 inhibitor known as AMG 714 to induce facial repigmentation in adults with vitiligo.
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed ties with AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Celgene, Concert Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo, Sanofi, Sun, UCB, and Viela Bio.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Vitiligo, an autoimmune condition that results in patches of skin depigmentation, occurs in 0.5% to 2% of the population. The average age of onset is 20 years, with 25% of cases occurring before age 10, and 70%-80% of cases by age 30 years, which means a long-term effect on quality of life, especially for younger patients, said Dr. Rosmarin, vice chair of education and research and director of the clinical trials unit at Tufts University, Boston.
Studies have shown that 95% of 15- to 17-year-olds with vitiligo are bothered by it, as are approximately 50% of children aged 6-14 years, he said. Although patients with more extensive lesions on the face, arms, legs, and hands report worse quality of life, they report that uncontrolled progression of vitiligo is more concerning than the presence of lesions in exposed areas, he noted.
The current strategy for getting vitiligo under control is a two-step process, said Dr. Rosmarin. First, improve the skin environment by suppressing the overactive immune system, then encourage repigmentation and “nudge the melanocytes to return,” he said.
Topical ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, is the latest tool for dermatologists to help give the melanocytes that nudge. In July 2022, the Food and Drug Administration approved ruxolitinib cream for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years of age and older – the first treatment approved to repigment patients with vitiligo.
Vitiligo is driven in part by interferon (IFN)-gamma signaling through JAK 1 and 2, and ruxolitinib acts as an inhibitor, Dr. Rosmarin said.
In the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies presented at the 2022 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology meeting in Milan, adolescents and adults with vitiligo who were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream twice daily showed significant improvement over those randomized to the vehicle by 24 weeks, at which time all patients could continue with ruxolitinib through 52 weeks, he said.
Dr. Rosmarin presented 52-week data from the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies at the 2022 American Academy of Dermatology meeting in Boston. He was the lead author of the studies that were subsequently published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In the two studies, 52.6% and 48% of the patients in the ruxolitinib groups achieved the primary outcome of at least 75% improvement on the Facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI75) by 52 weeks, compared with 26.8% and 29.6% of patients on the vehicle, respectively.
In addition, at 52 weeks, 53.2% and 49.2% of patients treated with ruxolitinib in the two studies achieved 50% improvement on the Total Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (T-VASI50), a clinician assessment of affected body surface area and level of depigmentation, compared with 31.7% and 22.2% of those on vehicle, respectively.
Patient satisfaction was high with ruxolitinib, Dr. Rosmarin said. In the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies, 39.9% and 32.8% of patients, respectively, achieved a successful treatment response based on the patient-reported Vitiligo Noticeability Scale (VNS) by week 52, versus 19.5% and 13.6% of those on vehicle.
Ruxolitinib cream was well tolerated, with “no clinically significant application site reactions or serious treatment-related adverse events,” he noted. The most common treatment-related adverse events across the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies were acne at the application site (affecting about 6% of patients) and pruritus at the application site about (affecting 5%), said Dr. Rosmarin.
JAK inhibitors, including ruxolitinib, baricitinib, and tofacitinib, have shown effectiveness for vitiligo, which supports the potential role of the IFN-gamma-chemokine signaling axis in the pathogenesis of the disease, said Dr. Rosmarin. However, more studies are required to determine the ideal dosage of JAK inhibitors for the treatment of vitiligo, and to identify other inflammatory pathways that may be implicated in the pathogenesis of this condition.
Ruxolitinib’s success has been consistent across subgroups of age, gender, race, geographic region, and Fitzpatrick skin phototype. Notably, ruxolitinib was effective among the adolescent population, with approximately 60% achieving T-VASI50 and success based on VNS in TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2.
An oral version of ruxolitinib is in clinical trials, which “makes a lot of sense,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “Patients don’t always have localized disease,” and such patients may benefit from an oral therapy. Topicals may have the advantage in terms of safety, but questions of maintenance remain, he said. Oral treatments may be useful for patients with large body surface areas affected, and those with unstable or progressive disease, he added.
Areas for additional research include combination therapy with ruxolitinib and phototherapy, and an anti-IL 15 therapy in the pipeline has the potential to drive vitiligo into remission, Dr. Rosmarin said. In a study known as REVEAL that is still recruiting patients, researchers will test the efficacy of an IL-15 inhibitor known as AMG 714 to induce facial repigmentation in adults with vitiligo.
Dr. Rosmarin disclosed ties with AbbVie, Abcuro, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Celgene, Concert Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring, Dermavant, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Revolo, Sanofi, Sun, UCB, and Viela Bio.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Skin Manifestations of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
To the Editor:
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a neurologic condition characterized by chronic pain and sensory changes, including allodynia and hyperalgesia, that usually affect the extremities.1,2 The syndrome is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as a condition that appears regionally after an injury, with a variety of symptoms that often exceed the expected clinical course both in magnitude and duration, causing impairment of motor function and variable progression.3
Although CRPS most often is described following minor peripheral trauma, other precipitating causes include surgery and vascular events.4 Additional features of the condition include autonomic dysfunction, edema, and trophic changes.1 Symptoms of CRPS traditionally present in 3 stages, with notable skin changes most often documented in stages II and III.2
Skin changes are a known manifestation of the syndrome, but reports in the dermatologic literature are scarce. Qureshi and Friedman5 identified only 23 articles in the dermatology literature since 1990 in which skin changes in CRPS were described. We present a patient with a diagnosis of CRPS who developed hyperpigmentation and sclerotic changes, including skin thickening, induration, and skin tightening.
A middle-aged Black woman presented to dermatology for evaluation of progressive hyperpigmentation, hyperhidrosis, and sclerotic changes to the skin. Approximately 3 years prior, the patient was given a diagnosis of CRPS of the hands and feet. Pain symptoms started approximately 3 years prior to the onset of symptoms. Symptoms started in the left hand and eventually spread to the right arm, left leg, and subsequently to the right leg. The first dermatologic change the patient noticed was tightening of the skin in the affected area that led to decreased mobility, which improved over time—partly on its own and partly with physical therapy.
A biopsy performed by an outside dermatologist at the initial presentation demonstrated sclerodermalike changes, which were treated with creams but without improvement. Scleroderma was later ruled out by the same dermatologist. Skin tightening improved over time, with complete resolution approximately 1 year after the onset of symptoms.
Upon presentation to our clinic, the patient reported continuing intermittent flares of CRPS; however, she said she was most concerned about diffuse hyperpigmentation, which spread to include the face, arms, abdomen, legs (Figure), and buttocks and persisted after skin tightening resolved.
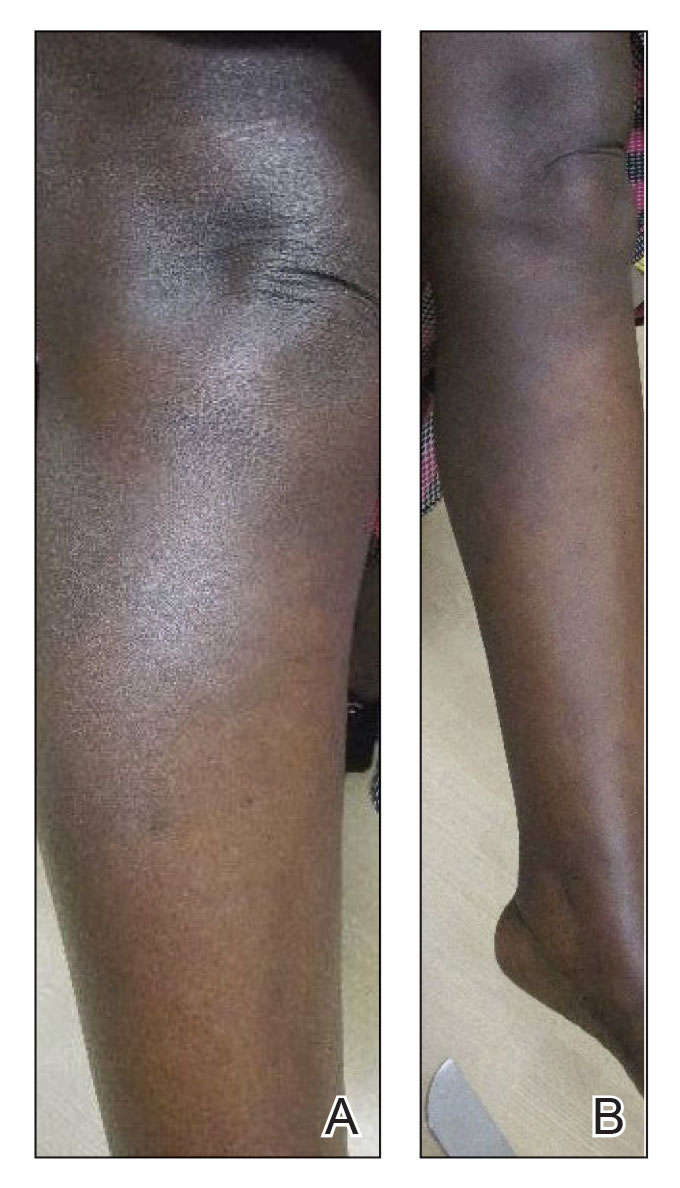
To treat the hyperpigmentation, a decision was made to first focus on a localized area. Facial hyperpigmentation was chosen because it was of greatest concern to the patient. She was instructed to use azelaic acid gel 15% in the morning, tretinoin cream 0.05% at night, and sunscreen daily. The patient had mild improvement in hyperpigmentation after a 4-month period but has been inconsistent in follow-up. She continues to have intermittent flares of CRPS, which may interfere with her response to treatment. In addition to the aforementioned regimen of azelaic acid gel and tretinoin, she has continued to work with a pain specialist to better control the neurologic symptoms and pain associated with her CRPS.
Complex regional pain syndrome, a neurological condition characterized by chronic pain, affects women 3 times more often than men. The syndrome is more common in the fourth and fifth decades of life.1,2
There are 2 subtypes of CRPS. Type I (also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy) is more common and occurs following minor trauma without peripheral nerve injury. Type II (otherwise known as causalgia) occurs following more notable trauma with injury to a peripheral nerve.1,6 Onset of symptoms most often is secondary to minor peripheral trauma. More common triggers include soft-tissue injury (40%); fractures and subsequent orthopedic surgery (25%); and visceral lesions, such as myocardial infarction and cerebral vascular accident (12%).5 Regardless of the inciting event, prolonged immobilization of a limb has been identified as an important predisposing factor. One study found that 47% of patients who received a diagnosis of CRPS previously underwent immobilization of the same limb.7
The pathogenesis of CRPS has not been fully elucidated. Possible explanations include central nervous system sensitization to thermal, mechanical, and pain stimuli; sympathetic dysfunction leading to vasomotor, pseudomotor, and trophic changes; and inflammatory cytokine release and microcirculatory dysfunction, causing tissue injury.1,2,6
The diagnosis of CRPS is a based on clinical findings. Using the Budapest Criteria established to define CRPS, a clinical diagnosis can be made when all of the following criteria are met: chronic continuing pain disproportionate to any inciting event; 1 or more reported symptoms from 3 or more of the categories of involvement including sensory, vasomotor, pseudomotor, edema, and motor or trophic; 1 or more sign at the time of evaluation in 2 or more of the categories of involvement including sensory, vasomotor, pseudomotor, edema, and motor or trophic.8 Dermatologic findings are a common presenting feature of CRPS and are included in the Budapest Criteria used for diagnosis. In a retrospective chart review (N=26), researchers found that vascular findings were the most common dermatologic manifestation of CRPS—edema in 58% of patients and erythema in 54%.9 Other common manifestations included dermatitis (35%), erythematous papules (23%), and cutaneous atrophy (23%). Hyperpigmentation, which was present in our patient, was seen in 8% of patients in the chart review.9
Complex regional pain syndrome progresses through 3 stages; dermatologic changes are present in each stage and are more severe in later stages. Stage I lasts 2 or 3 months and is characterized by onset of pain, usually burning type, accompanied by allodynia and hyperalgesia. Early vasomotor and pseudomotor changes, such as erythema and edema, may become apparent.1,2 Stage II lasts 3 to 6 months and is characterized by more severe edema and more obvious trophic changes. Functional limitations, such as limited range of motion and muscle weakness, begin to manifest. Stage III—the final and most severe stage—is characterized by obvious hair, skin, and nail changes, as well as functional limitations.1,2 The waxy thickened skin changes and hyperpigmentation observed in our patient are characteristic of stage III. Furthermore, our patient experienced decreased mobility and limited range of motion secondary to tightening of the skin, a characteristic motor change of late-stage CRPS. Although chronic pain and allodynia are the most common characteristics of CRPS, skin changes also can cause notable distress and early dermatologic manifestations can be a chief concern.
Dermatologic management is focused to address the specific skin changes of CRPS. However, traditional treatment of the common dermatologic findings of CRPS is difficult and often unsuccessful; instead, the most successful treatment of skin findings involves controlling the underlying CRPS.9 Current treatment options include removal of any nidus of tissue trauma, sympathetic neural blockade with a local anesthetic, spinal cord stimulation to interrupt dysregulated sympathetic innervation, and physiotherapy or occupational therapy to desensitize skin.1,10
Given the complexity of CRPS and the variability of its presentation, management of the syndrome and its associated dermatologic conditions often requires interdisciplinary care and coordination of multiple specialties. Dermatologists can play an important role in both identification of CRPS and co-management of affected patients. Early diagnosis of CRPS has been universally identified as a key prognostic factor. For that reason, dermatologists should be aware of CRPS and include the syndrome in the differential diagnosis when presented with severe cutaneous findings following trauma either with or without peripheral nerve damage, suggestive of CRPS.
- Sebastin SJ. Complex regional pain syndrome. Indian J Plast Surg. 2011;44:298-307. doi:10.4103/0970-0358.85351
- Kabani R, Brassard A. Dermatological findings in early detection of complex regional pain syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:640-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.7459
- Moseley L. What is complex regional pain syndrome – in plain English. International Association for the Study of Pain website. Published 2009. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.iasp-pain.org/publications/relief-news/article/what-is-complex-pain-syndrome-in-plain-english/
- Pak TJ, Martin GM, Magness JL, et al. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Review of 140 cases. Minn Med. 1970;53:507-512.
- Qureshi AA, Friedman AJ. Complex regional pain syndrome: what the dermatologist should know. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:532-536.
- Gorodkin R. Complex regional pain syndrome. Rheumatology. 2016;55(suppl 1):i12.
- Araki E, Tanioka M, Miyachi Y, et al. A case of complex regional pain syndrome: an underdiagnosed condition in dermatology. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:440-441. doi:10.2340/00015555-0281
- Pergolizzi JV, LeQuang JA, Nalamachu S, et al. The Budapest criteria for complex regional pain syndrome: the diagnostic challenge. Anaesthesiol Clin Sci Res. 2018;2:1-10. doi:10.35841/anesthesiology.2.1.1-10
- Sundaram S, Webster GF. Vascular diseases are the most common cutaneous manifestations of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:1050-1051. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114299
- Taylor RS, Van Buyten J-P, Buchser E. Spinal stimulation for complex regional pain syndrome: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effectiveness literature and assessment of prognostic factors. Eur J Pain. 2006;10:91-101. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.02.004
To the Editor:
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a neurologic condition characterized by chronic pain and sensory changes, including allodynia and hyperalgesia, that usually affect the extremities.1,2 The syndrome is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as a condition that appears regionally after an injury, with a variety of symptoms that often exceed the expected clinical course both in magnitude and duration, causing impairment of motor function and variable progression.3
Although CRPS most often is described following minor peripheral trauma, other precipitating causes include surgery and vascular events.4 Additional features of the condition include autonomic dysfunction, edema, and trophic changes.1 Symptoms of CRPS traditionally present in 3 stages, with notable skin changes most often documented in stages II and III.2
Skin changes are a known manifestation of the syndrome, but reports in the dermatologic literature are scarce. Qureshi and Friedman5 identified only 23 articles in the dermatology literature since 1990 in which skin changes in CRPS were described. We present a patient with a diagnosis of CRPS who developed hyperpigmentation and sclerotic changes, including skin thickening, induration, and skin tightening.
A middle-aged Black woman presented to dermatology for evaluation of progressive hyperpigmentation, hyperhidrosis, and sclerotic changes to the skin. Approximately 3 years prior, the patient was given a diagnosis of CRPS of the hands and feet. Pain symptoms started approximately 3 years prior to the onset of symptoms. Symptoms started in the left hand and eventually spread to the right arm, left leg, and subsequently to the right leg. The first dermatologic change the patient noticed was tightening of the skin in the affected area that led to decreased mobility, which improved over time—partly on its own and partly with physical therapy.
A biopsy performed by an outside dermatologist at the initial presentation demonstrated sclerodermalike changes, which were treated with creams but without improvement. Scleroderma was later ruled out by the same dermatologist. Skin tightening improved over time, with complete resolution approximately 1 year after the onset of symptoms.
Upon presentation to our clinic, the patient reported continuing intermittent flares of CRPS; however, she said she was most concerned about diffuse hyperpigmentation, which spread to include the face, arms, abdomen, legs (Figure), and buttocks and persisted after skin tightening resolved.

To treat the hyperpigmentation, a decision was made to first focus on a localized area. Facial hyperpigmentation was chosen because it was of greatest concern to the patient. She was instructed to use azelaic acid gel 15% in the morning, tretinoin cream 0.05% at night, and sunscreen daily. The patient had mild improvement in hyperpigmentation after a 4-month period but has been inconsistent in follow-up. She continues to have intermittent flares of CRPS, which may interfere with her response to treatment. In addition to the aforementioned regimen of azelaic acid gel and tretinoin, she has continued to work with a pain specialist to better control the neurologic symptoms and pain associated with her CRPS.
Complex regional pain syndrome, a neurological condition characterized by chronic pain, affects women 3 times more often than men. The syndrome is more common in the fourth and fifth decades of life.1,2
There are 2 subtypes of CRPS. Type I (also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy) is more common and occurs following minor trauma without peripheral nerve injury. Type II (otherwise known as causalgia) occurs following more notable trauma with injury to a peripheral nerve.1,6 Onset of symptoms most often is secondary to minor peripheral trauma. More common triggers include soft-tissue injury (40%); fractures and subsequent orthopedic surgery (25%); and visceral lesions, such as myocardial infarction and cerebral vascular accident (12%).5 Regardless of the inciting event, prolonged immobilization of a limb has been identified as an important predisposing factor. One study found that 47% of patients who received a diagnosis of CRPS previously underwent immobilization of the same limb.7
The pathogenesis of CRPS has not been fully elucidated. Possible explanations include central nervous system sensitization to thermal, mechanical, and pain stimuli; sympathetic dysfunction leading to vasomotor, pseudomotor, and trophic changes; and inflammatory cytokine release and microcirculatory dysfunction, causing tissue injury.1,2,6
The diagnosis of CRPS is a based on clinical findings. Using the Budapest Criteria established to define CRPS, a clinical diagnosis can be made when all of the following criteria are met: chronic continuing pain disproportionate to any inciting event; 1 or more reported symptoms from 3 or more of the categories of involvement including sensory, vasomotor, pseudomotor, edema, and motor or trophic; 1 or more sign at the time of evaluation in 2 or more of the categories of involvement including sensory, vasomotor, pseudomotor, edema, and motor or trophic.8 Dermatologic findings are a common presenting feature of CRPS and are included in the Budapest Criteria used for diagnosis. In a retrospective chart review (N=26), researchers found that vascular findings were the most common dermatologic manifestation of CRPS—edema in 58% of patients and erythema in 54%.9 Other common manifestations included dermatitis (35%), erythematous papules (23%), and cutaneous atrophy (23%). Hyperpigmentation, which was present in our patient, was seen in 8% of patients in the chart review.9
Complex regional pain syndrome progresses through 3 stages; dermatologic changes are present in each stage and are more severe in later stages. Stage I lasts 2 or 3 months and is characterized by onset of pain, usually burning type, accompanied by allodynia and hyperalgesia. Early vasomotor and pseudomotor changes, such as erythema and edema, may become apparent.1,2 Stage II lasts 3 to 6 months and is characterized by more severe edema and more obvious trophic changes. Functional limitations, such as limited range of motion and muscle weakness, begin to manifest. Stage III—the final and most severe stage—is characterized by obvious hair, skin, and nail changes, as well as functional limitations.1,2 The waxy thickened skin changes and hyperpigmentation observed in our patient are characteristic of stage III. Furthermore, our patient experienced decreased mobility and limited range of motion secondary to tightening of the skin, a characteristic motor change of late-stage CRPS. Although chronic pain and allodynia are the most common characteristics of CRPS, skin changes also can cause notable distress and early dermatologic manifestations can be a chief concern.
Dermatologic management is focused to address the specific skin changes of CRPS. However, traditional treatment of the common dermatologic findings of CRPS is difficult and often unsuccessful; instead, the most successful treatment of skin findings involves controlling the underlying CRPS.9 Current treatment options include removal of any nidus of tissue trauma, sympathetic neural blockade with a local anesthetic, spinal cord stimulation to interrupt dysregulated sympathetic innervation, and physiotherapy or occupational therapy to desensitize skin.1,10
Given the complexity of CRPS and the variability of its presentation, management of the syndrome and its associated dermatologic conditions often requires interdisciplinary care and coordination of multiple specialties. Dermatologists can play an important role in both identification of CRPS and co-management of affected patients. Early diagnosis of CRPS has been universally identified as a key prognostic factor. For that reason, dermatologists should be aware of CRPS and include the syndrome in the differential diagnosis when presented with severe cutaneous findings following trauma either with or without peripheral nerve damage, suggestive of CRPS.
To the Editor:
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a neurologic condition characterized by chronic pain and sensory changes, including allodynia and hyperalgesia, that usually affect the extremities.1,2 The syndrome is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as a condition that appears regionally after an injury, with a variety of symptoms that often exceed the expected clinical course both in magnitude and duration, causing impairment of motor function and variable progression.3
Although CRPS most often is described following minor peripheral trauma, other precipitating causes include surgery and vascular events.4 Additional features of the condition include autonomic dysfunction, edema, and trophic changes.1 Symptoms of CRPS traditionally present in 3 stages, with notable skin changes most often documented in stages II and III.2
Skin changes are a known manifestation of the syndrome, but reports in the dermatologic literature are scarce. Qureshi and Friedman5 identified only 23 articles in the dermatology literature since 1990 in which skin changes in CRPS were described. We present a patient with a diagnosis of CRPS who developed hyperpigmentation and sclerotic changes, including skin thickening, induration, and skin tightening.
A middle-aged Black woman presented to dermatology for evaluation of progressive hyperpigmentation, hyperhidrosis, and sclerotic changes to the skin. Approximately 3 years prior, the patient was given a diagnosis of CRPS of the hands and feet. Pain symptoms started approximately 3 years prior to the onset of symptoms. Symptoms started in the left hand and eventually spread to the right arm, left leg, and subsequently to the right leg. The first dermatologic change the patient noticed was tightening of the skin in the affected area that led to decreased mobility, which improved over time—partly on its own and partly with physical therapy.
A biopsy performed by an outside dermatologist at the initial presentation demonstrated sclerodermalike changes, which were treated with creams but without improvement. Scleroderma was later ruled out by the same dermatologist. Skin tightening improved over time, with complete resolution approximately 1 year after the onset of symptoms.
Upon presentation to our clinic, the patient reported continuing intermittent flares of CRPS; however, she said she was most concerned about diffuse hyperpigmentation, which spread to include the face, arms, abdomen, legs (Figure), and buttocks and persisted after skin tightening resolved.

To treat the hyperpigmentation, a decision was made to first focus on a localized area. Facial hyperpigmentation was chosen because it was of greatest concern to the patient. She was instructed to use azelaic acid gel 15% in the morning, tretinoin cream 0.05% at night, and sunscreen daily. The patient had mild improvement in hyperpigmentation after a 4-month period but has been inconsistent in follow-up. She continues to have intermittent flares of CRPS, which may interfere with her response to treatment. In addition to the aforementioned regimen of azelaic acid gel and tretinoin, she has continued to work with a pain specialist to better control the neurologic symptoms and pain associated with her CRPS.
Complex regional pain syndrome, a neurological condition characterized by chronic pain, affects women 3 times more often than men. The syndrome is more common in the fourth and fifth decades of life.1,2
There are 2 subtypes of CRPS. Type I (also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy) is more common and occurs following minor trauma without peripheral nerve injury. Type II (otherwise known as causalgia) occurs following more notable trauma with injury to a peripheral nerve.1,6 Onset of symptoms most often is secondary to minor peripheral trauma. More common triggers include soft-tissue injury (40%); fractures and subsequent orthopedic surgery (25%); and visceral lesions, such as myocardial infarction and cerebral vascular accident (12%).5 Regardless of the inciting event, prolonged immobilization of a limb has been identified as an important predisposing factor. One study found that 47% of patients who received a diagnosis of CRPS previously underwent immobilization of the same limb.7
The pathogenesis of CRPS has not been fully elucidated. Possible explanations include central nervous system sensitization to thermal, mechanical, and pain stimuli; sympathetic dysfunction leading to vasomotor, pseudomotor, and trophic changes; and inflammatory cytokine release and microcirculatory dysfunction, causing tissue injury.1,2,6
The diagnosis of CRPS is a based on clinical findings. Using the Budapest Criteria established to define CRPS, a clinical diagnosis can be made when all of the following criteria are met: chronic continuing pain disproportionate to any inciting event; 1 or more reported symptoms from 3 or more of the categories of involvement including sensory, vasomotor, pseudomotor, edema, and motor or trophic; 1 or more sign at the time of evaluation in 2 or more of the categories of involvement including sensory, vasomotor, pseudomotor, edema, and motor or trophic.8 Dermatologic findings are a common presenting feature of CRPS and are included in the Budapest Criteria used for diagnosis. In a retrospective chart review (N=26), researchers found that vascular findings were the most common dermatologic manifestation of CRPS—edema in 58% of patients and erythema in 54%.9 Other common manifestations included dermatitis (35%), erythematous papules (23%), and cutaneous atrophy (23%). Hyperpigmentation, which was present in our patient, was seen in 8% of patients in the chart review.9
Complex regional pain syndrome progresses through 3 stages; dermatologic changes are present in each stage and are more severe in later stages. Stage I lasts 2 or 3 months and is characterized by onset of pain, usually burning type, accompanied by allodynia and hyperalgesia. Early vasomotor and pseudomotor changes, such as erythema and edema, may become apparent.1,2 Stage II lasts 3 to 6 months and is characterized by more severe edema and more obvious trophic changes. Functional limitations, such as limited range of motion and muscle weakness, begin to manifest. Stage III—the final and most severe stage—is characterized by obvious hair, skin, and nail changes, as well as functional limitations.1,2 The waxy thickened skin changes and hyperpigmentation observed in our patient are characteristic of stage III. Furthermore, our patient experienced decreased mobility and limited range of motion secondary to tightening of the skin, a characteristic motor change of late-stage CRPS. Although chronic pain and allodynia are the most common characteristics of CRPS, skin changes also can cause notable distress and early dermatologic manifestations can be a chief concern.
Dermatologic management is focused to address the specific skin changes of CRPS. However, traditional treatment of the common dermatologic findings of CRPS is difficult and often unsuccessful; instead, the most successful treatment of skin findings involves controlling the underlying CRPS.9 Current treatment options include removal of any nidus of tissue trauma, sympathetic neural blockade with a local anesthetic, spinal cord stimulation to interrupt dysregulated sympathetic innervation, and physiotherapy or occupational therapy to desensitize skin.1,10
Given the complexity of CRPS and the variability of its presentation, management of the syndrome and its associated dermatologic conditions often requires interdisciplinary care and coordination of multiple specialties. Dermatologists can play an important role in both identification of CRPS and co-management of affected patients. Early diagnosis of CRPS has been universally identified as a key prognostic factor. For that reason, dermatologists should be aware of CRPS and include the syndrome in the differential diagnosis when presented with severe cutaneous findings following trauma either with or without peripheral nerve damage, suggestive of CRPS.
- Sebastin SJ. Complex regional pain syndrome. Indian J Plast Surg. 2011;44:298-307. doi:10.4103/0970-0358.85351
- Kabani R, Brassard A. Dermatological findings in early detection of complex regional pain syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:640-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.7459
- Moseley L. What is complex regional pain syndrome – in plain English. International Association for the Study of Pain website. Published 2009. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.iasp-pain.org/publications/relief-news/article/what-is-complex-pain-syndrome-in-plain-english/
- Pak TJ, Martin GM, Magness JL, et al. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Review of 140 cases. Minn Med. 1970;53:507-512.
- Qureshi AA, Friedman AJ. Complex regional pain syndrome: what the dermatologist should know. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:532-536.
- Gorodkin R. Complex regional pain syndrome. Rheumatology. 2016;55(suppl 1):i12.
- Araki E, Tanioka M, Miyachi Y, et al. A case of complex regional pain syndrome: an underdiagnosed condition in dermatology. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:440-441. doi:10.2340/00015555-0281
- Pergolizzi JV, LeQuang JA, Nalamachu S, et al. The Budapest criteria for complex regional pain syndrome: the diagnostic challenge. Anaesthesiol Clin Sci Res. 2018;2:1-10. doi:10.35841/anesthesiology.2.1.1-10
- Sundaram S, Webster GF. Vascular diseases are the most common cutaneous manifestations of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:1050-1051. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114299
- Taylor RS, Van Buyten J-P, Buchser E. Spinal stimulation for complex regional pain syndrome: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effectiveness literature and assessment of prognostic factors. Eur J Pain. 2006;10:91-101. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.02.004
- Sebastin SJ. Complex regional pain syndrome. Indian J Plast Surg. 2011;44:298-307. doi:10.4103/0970-0358.85351
- Kabani R, Brassard A. Dermatological findings in early detection of complex regional pain syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:640-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.7459
- Moseley L. What is complex regional pain syndrome – in plain English. International Association for the Study of Pain website. Published 2009. Accessed December 15, 2022. https://www.iasp-pain.org/publications/relief-news/article/what-is-complex-pain-syndrome-in-plain-english/
- Pak TJ, Martin GM, Magness JL, et al. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Review of 140 cases. Minn Med. 1970;53:507-512.
- Qureshi AA, Friedman AJ. Complex regional pain syndrome: what the dermatologist should know. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:532-536.
- Gorodkin R. Complex regional pain syndrome. Rheumatology. 2016;55(suppl 1):i12.
- Araki E, Tanioka M, Miyachi Y, et al. A case of complex regional pain syndrome: an underdiagnosed condition in dermatology. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87:440-441. doi:10.2340/00015555-0281
- Pergolizzi JV, LeQuang JA, Nalamachu S, et al. The Budapest criteria for complex regional pain syndrome: the diagnostic challenge. Anaesthesiol Clin Sci Res. 2018;2:1-10. doi:10.35841/anesthesiology.2.1.1-10
- Sundaram S, Webster GF. Vascular diseases are the most common cutaneous manifestations of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:1050-1051. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.114299
- Taylor RS, Van Buyten J-P, Buchser E. Spinal stimulation for complex regional pain syndrome: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effectiveness literature and assessment of prognostic factors. Eur J Pain. 2006;10:91-101. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.02.004
PRACTICE POINTS
- Common dermatologic manifestations of complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), which often are nonspecific and often the presenting symptoms of the syndrome, include allodynia, edema, erythema, hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation, and petechiae.
- Diagnosis and management of CRPS are the most important steps in treating dermatologic manifestations of the syndrome.
Researchers use AI to diagnose infantile hemangioma
a proof-of-concept study reported.
Early diagnosis of infantile hemangiomas “is essential, as there is a narrow window of opportunity to treat high-risk lesions,” April J. Zhang, MD, and coauthors noted in the study. “AI algorithms optimized for image classification through use of convolutional neural networks have been widely utilized to classify lesions in which images are readily standardized, such as skin cancers and onychomycosis.”
The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Dr. Zhang, of the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and colleagues trained a convoluted neural network to diagnose infantile hemangiomas based on clinical images from pediatric dermatology patients treated at Children’s Wisconsin between 2002 and 2019.
They used Microsoft’s ResNet-50, a publicly available network architecture, to train a binary infantile hemangioma classifier to group images as infantile hemangiomas or non–infantile hemangiomas. The team randomly split data from the model into training, validation, and test groups.
The preliminary data set contained 14,811 images, about half of which were facial lesions. The training group of images achieved an accuracy of 61.5%. Next, Dr. Zhang and colleagues limited the data set to facial-only lesions and removed poor-quality images, which left 5,834 images in the final data set: 4,110 infantile hemangiomas and 1,724 non–infantile hemangiomas. This model achieved an overall accuracy of 91.7%, with a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 90.5%.
“Our study is the first to demonstrate the applicability of AI in the pediatric dermatology population,” the authors wrote. “With current nationwide shortages in pediatric dermatologists, AI has the potential to improve patient access and outcomes through enhanced rapid diagnostic capabilities.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including a data set with greater numbers of infantile hemangiomas, compared with non–infantile hemangiomas.
“Random oversampling of the non–infantile hemangioma data set was used to combat this but may lead to model overfitting, where a model performs well on its training data but is unable to generalize to new data,” they wrote. “As infantile hemangiomas are rarely biopsied, expert clinical diagnoses were used as the gold standard without pathologic confirmation.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
a proof-of-concept study reported.
Early diagnosis of infantile hemangiomas “is essential, as there is a narrow window of opportunity to treat high-risk lesions,” April J. Zhang, MD, and coauthors noted in the study. “AI algorithms optimized for image classification through use of convolutional neural networks have been widely utilized to classify lesions in which images are readily standardized, such as skin cancers and onychomycosis.”
The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Dr. Zhang, of the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and colleagues trained a convoluted neural network to diagnose infantile hemangiomas based on clinical images from pediatric dermatology patients treated at Children’s Wisconsin between 2002 and 2019.
They used Microsoft’s ResNet-50, a publicly available network architecture, to train a binary infantile hemangioma classifier to group images as infantile hemangiomas or non–infantile hemangiomas. The team randomly split data from the model into training, validation, and test groups.
The preliminary data set contained 14,811 images, about half of which were facial lesions. The training group of images achieved an accuracy of 61.5%. Next, Dr. Zhang and colleagues limited the data set to facial-only lesions and removed poor-quality images, which left 5,834 images in the final data set: 4,110 infantile hemangiomas and 1,724 non–infantile hemangiomas. This model achieved an overall accuracy of 91.7%, with a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 90.5%.
“Our study is the first to demonstrate the applicability of AI in the pediatric dermatology population,” the authors wrote. “With current nationwide shortages in pediatric dermatologists, AI has the potential to improve patient access and outcomes through enhanced rapid diagnostic capabilities.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including a data set with greater numbers of infantile hemangiomas, compared with non–infantile hemangiomas.
“Random oversampling of the non–infantile hemangioma data set was used to combat this but may lead to model overfitting, where a model performs well on its training data but is unable to generalize to new data,” they wrote. “As infantile hemangiomas are rarely biopsied, expert clinical diagnoses were used as the gold standard without pathologic confirmation.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
a proof-of-concept study reported.
Early diagnosis of infantile hemangiomas “is essential, as there is a narrow window of opportunity to treat high-risk lesions,” April J. Zhang, MD, and coauthors noted in the study. “AI algorithms optimized for image classification through use of convolutional neural networks have been widely utilized to classify lesions in which images are readily standardized, such as skin cancers and onychomycosis.”
The results were published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Dr. Zhang, of the department of dermatology at the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and colleagues trained a convoluted neural network to diagnose infantile hemangiomas based on clinical images from pediatric dermatology patients treated at Children’s Wisconsin between 2002 and 2019.
They used Microsoft’s ResNet-50, a publicly available network architecture, to train a binary infantile hemangioma classifier to group images as infantile hemangiomas or non–infantile hemangiomas. The team randomly split data from the model into training, validation, and test groups.
The preliminary data set contained 14,811 images, about half of which were facial lesions. The training group of images achieved an accuracy of 61.5%. Next, Dr. Zhang and colleagues limited the data set to facial-only lesions and removed poor-quality images, which left 5,834 images in the final data set: 4,110 infantile hemangiomas and 1,724 non–infantile hemangiomas. This model achieved an overall accuracy of 91.7%, with a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 90.5%.
“Our study is the first to demonstrate the applicability of AI in the pediatric dermatology population,” the authors wrote. “With current nationwide shortages in pediatric dermatologists, AI has the potential to improve patient access and outcomes through enhanced rapid diagnostic capabilities.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including a data set with greater numbers of infantile hemangiomas, compared with non–infantile hemangiomas.
“Random oversampling of the non–infantile hemangioma data set was used to combat this but may lead to model overfitting, where a model performs well on its training data but is unable to generalize to new data,” they wrote. “As infantile hemangiomas are rarely biopsied, expert clinical diagnoses were used as the gold standard without pathologic confirmation.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Saururus chinensis
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Novel platform harnesses 3D laser technology for skin treatments
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Applications for laser-assisted drug delivery on the horizon, expert says
For those who view fractional ablative laser–assisted drug delivery as a pie-in-the-sky procedure that will take years to work its way into routine clinical practice, think again.
According to Merete Haedersdal, MD, PhD, DMSc, .
“The groundwork has been established over a decade with more than 100 publications available on PubMed,” Dr. Haedersdal, professor of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “There is no doubt that by drilling tiny little holes or channels with ablative fractional lasers, we enhance drug delivery to the skin, and we also empower different topical treatment regimens. Also, laser-assisted drug delivery holds the potential to bring new innovations into established medicine.”
Many studies have demonstrated that clinicians can enhance drug uptake into the skin with the fractional 10,600 nm CO2 laser, the fractional 2,940 nm erbium:YAG laser, and the 1,927 nm thulium laser, but proper tuning of the devices is key. The lower the density, the better, Dr. Haedersdal said.
“Typically, we use 5% density or 5% coverage, sometimes 10%-15%, but don’t go higher in order to avoid the risk of having a systemic uptake,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Also, the pulse energy for channel depth needs to be tailored to the specific dermatologic disease being treated,” she said, noting that for melasma, for example, “very low pulse energies” would be used, but they would be higher for treating thicker lesions, such as a hypertrophic scar.
Treatment with ablative fractional lasers enhances drug accumulation in the skin of any drug or substance applied to the skin, and clinical indications are expanding rapidly. Established indications include combining ablative fractional lasers and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for AKs and combining ablative fractional lasers and triamcinolone or 5-FU for scars. “Although we have a good body of evidence, particularly for AKs, it’s still an off-label use,” she emphasized.
Evolving indications include concomitant use of ablative fractional laser and vitamins and cosmeceuticals for rejuvenation; lidocaine for local anesthetics; tranexamic acid and hydroquinone for melasma; antifungals for onychomycosis; Botox for hyperhidrosis; minoxidil for alopecia; and betamethasone for vitiligo. A promising treatment for skin cancer “on the horizon,” she said, is the “combination of ablative fractional laser with PD1 inhibitors and chemotherapy.”
Data on AKs
Evidence supporting laser-assisted drug delivery for AKs comes from more than 10 randomized, controlled trials in the dermatology literature involving 400-plus immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. These trials have found ablative fractional laser–assisted PDT to be significantly more efficacious than PDT alone up to 12 months postoperatively and to foster lower rates of AK recurrence.
In a meta-analysis and systematic review, German researchers concluded that PDT combined with ablative laser treatment for AKs is more efficient but not more painful than either therapy alone. They recommended the combined regimen for patients with severe photodamage, field cancerization, and multiple AKs.
In 2020, an international consensus panel of experts, including Dr. Haedersdal, published recommendations regarding laser treatment of traumatic scars and contractures. The panel members determined that laser-assisted delivery of corticosteroids and antimetabolites was recommended for hypertrophic scars and cited triamcinolone acetonide suspension (TAC) as the most common corticosteroid used in combination with ablative fractional lasers. “It can be applied in concentrations of 40 mg/mL or less depending on the degree of hypertrophy,” they wrote.
In addition, they stated that 5-FU solution is “most commonly applied in a concentration of 50 mg/mL alone, or mixed with TAC in ratios of 9:1 or 3:1.”
According to the best available evidence, the clinical approach for hypertrophic scars supports combination treatment with ablative fractional laser and triamcinolone acetonide either alone or in combination with 5-FU. For atrophic scars, laser-assisted delivery of poly-L-lactic acid has been shown to be efficient. “Both of these treatments improve texture and thickness but also dyschromia and scar functionality,” said Dr. Haedersdal, who is also a visiting scientist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston.
Commenting on patient safety with laser-assisted drug delivery, “the combination of lasers and topicals can be a powerful cocktail,” she said. “You can expect intensified local skin reactions. When treating larger areas, consider the risk of systemic absorption and the risk of potential toxicity. There is also the potential for infection with pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. The take-home message here is that you should only use the type and amount of drug no higher than administered during intradermal injection.”
Dr. Haedersdal disclosed that she has received equipment from Cherry Imaging, Cynosure-Hologic, MiraDry, and PerfAction Technologies. She has also received research grants from Leo Pharma, Lutronic, Mirai Medical, Novoxel, and Venus Concept.
For those who view fractional ablative laser–assisted drug delivery as a pie-in-the-sky procedure that will take years to work its way into routine clinical practice, think again.
According to Merete Haedersdal, MD, PhD, DMSc, .
“The groundwork has been established over a decade with more than 100 publications available on PubMed,” Dr. Haedersdal, professor of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “There is no doubt that by drilling tiny little holes or channels with ablative fractional lasers, we enhance drug delivery to the skin, and we also empower different topical treatment regimens. Also, laser-assisted drug delivery holds the potential to bring new innovations into established medicine.”
Many studies have demonstrated that clinicians can enhance drug uptake into the skin with the fractional 10,600 nm CO2 laser, the fractional 2,940 nm erbium:YAG laser, and the 1,927 nm thulium laser, but proper tuning of the devices is key. The lower the density, the better, Dr. Haedersdal said.
“Typically, we use 5% density or 5% coverage, sometimes 10%-15%, but don’t go higher in order to avoid the risk of having a systemic uptake,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Also, the pulse energy for channel depth needs to be tailored to the specific dermatologic disease being treated,” she said, noting that for melasma, for example, “very low pulse energies” would be used, but they would be higher for treating thicker lesions, such as a hypertrophic scar.
Treatment with ablative fractional lasers enhances drug accumulation in the skin of any drug or substance applied to the skin, and clinical indications are expanding rapidly. Established indications include combining ablative fractional lasers and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for AKs and combining ablative fractional lasers and triamcinolone or 5-FU for scars. “Although we have a good body of evidence, particularly for AKs, it’s still an off-label use,” she emphasized.
Evolving indications include concomitant use of ablative fractional laser and vitamins and cosmeceuticals for rejuvenation; lidocaine for local anesthetics; tranexamic acid and hydroquinone for melasma; antifungals for onychomycosis; Botox for hyperhidrosis; minoxidil for alopecia; and betamethasone for vitiligo. A promising treatment for skin cancer “on the horizon,” she said, is the “combination of ablative fractional laser with PD1 inhibitors and chemotherapy.”
Data on AKs
Evidence supporting laser-assisted drug delivery for AKs comes from more than 10 randomized, controlled trials in the dermatology literature involving 400-plus immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. These trials have found ablative fractional laser–assisted PDT to be significantly more efficacious than PDT alone up to 12 months postoperatively and to foster lower rates of AK recurrence.
In a meta-analysis and systematic review, German researchers concluded that PDT combined with ablative laser treatment for AKs is more efficient but not more painful than either therapy alone. They recommended the combined regimen for patients with severe photodamage, field cancerization, and multiple AKs.
In 2020, an international consensus panel of experts, including Dr. Haedersdal, published recommendations regarding laser treatment of traumatic scars and contractures. The panel members determined that laser-assisted delivery of corticosteroids and antimetabolites was recommended for hypertrophic scars and cited triamcinolone acetonide suspension (TAC) as the most common corticosteroid used in combination with ablative fractional lasers. “It can be applied in concentrations of 40 mg/mL or less depending on the degree of hypertrophy,” they wrote.
In addition, they stated that 5-FU solution is “most commonly applied in a concentration of 50 mg/mL alone, or mixed with TAC in ratios of 9:1 or 3:1.”
According to the best available evidence, the clinical approach for hypertrophic scars supports combination treatment with ablative fractional laser and triamcinolone acetonide either alone or in combination with 5-FU. For atrophic scars, laser-assisted delivery of poly-L-lactic acid has been shown to be efficient. “Both of these treatments improve texture and thickness but also dyschromia and scar functionality,” said Dr. Haedersdal, who is also a visiting scientist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston.
Commenting on patient safety with laser-assisted drug delivery, “the combination of lasers and topicals can be a powerful cocktail,” she said. “You can expect intensified local skin reactions. When treating larger areas, consider the risk of systemic absorption and the risk of potential toxicity. There is also the potential for infection with pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. The take-home message here is that you should only use the type and amount of drug no higher than administered during intradermal injection.”
Dr. Haedersdal disclosed that she has received equipment from Cherry Imaging, Cynosure-Hologic, MiraDry, and PerfAction Technologies. She has also received research grants from Leo Pharma, Lutronic, Mirai Medical, Novoxel, and Venus Concept.
For those who view fractional ablative laser–assisted drug delivery as a pie-in-the-sky procedure that will take years to work its way into routine clinical practice, think again.
According to Merete Haedersdal, MD, PhD, DMSc, .
“The groundwork has been established over a decade with more than 100 publications available on PubMed,” Dr. Haedersdal, professor of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “There is no doubt that by drilling tiny little holes or channels with ablative fractional lasers, we enhance drug delivery to the skin, and we also empower different topical treatment regimens. Also, laser-assisted drug delivery holds the potential to bring new innovations into established medicine.”
Many studies have demonstrated that clinicians can enhance drug uptake into the skin with the fractional 10,600 nm CO2 laser, the fractional 2,940 nm erbium:YAG laser, and the 1,927 nm thulium laser, but proper tuning of the devices is key. The lower the density, the better, Dr. Haedersdal said.
“Typically, we use 5% density or 5% coverage, sometimes 10%-15%, but don’t go higher in order to avoid the risk of having a systemic uptake,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Also, the pulse energy for channel depth needs to be tailored to the specific dermatologic disease being treated,” she said, noting that for melasma, for example, “very low pulse energies” would be used, but they would be higher for treating thicker lesions, such as a hypertrophic scar.
Treatment with ablative fractional lasers enhances drug accumulation in the skin of any drug or substance applied to the skin, and clinical indications are expanding rapidly. Established indications include combining ablative fractional lasers and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for AKs and combining ablative fractional lasers and triamcinolone or 5-FU for scars. “Although we have a good body of evidence, particularly for AKs, it’s still an off-label use,” she emphasized.
Evolving indications include concomitant use of ablative fractional laser and vitamins and cosmeceuticals for rejuvenation; lidocaine for local anesthetics; tranexamic acid and hydroquinone for melasma; antifungals for onychomycosis; Botox for hyperhidrosis; minoxidil for alopecia; and betamethasone for vitiligo. A promising treatment for skin cancer “on the horizon,” she said, is the “combination of ablative fractional laser with PD1 inhibitors and chemotherapy.”
Data on AKs
Evidence supporting laser-assisted drug delivery for AKs comes from more than 10 randomized, controlled trials in the dermatology literature involving 400-plus immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. These trials have found ablative fractional laser–assisted PDT to be significantly more efficacious than PDT alone up to 12 months postoperatively and to foster lower rates of AK recurrence.
In a meta-analysis and systematic review, German researchers concluded that PDT combined with ablative laser treatment for AKs is more efficient but not more painful than either therapy alone. They recommended the combined regimen for patients with severe photodamage, field cancerization, and multiple AKs.
In 2020, an international consensus panel of experts, including Dr. Haedersdal, published recommendations regarding laser treatment of traumatic scars and contractures. The panel members determined that laser-assisted delivery of corticosteroids and antimetabolites was recommended for hypertrophic scars and cited triamcinolone acetonide suspension (TAC) as the most common corticosteroid used in combination with ablative fractional lasers. “It can be applied in concentrations of 40 mg/mL or less depending on the degree of hypertrophy,” they wrote.
In addition, they stated that 5-FU solution is “most commonly applied in a concentration of 50 mg/mL alone, or mixed with TAC in ratios of 9:1 or 3:1.”
According to the best available evidence, the clinical approach for hypertrophic scars supports combination treatment with ablative fractional laser and triamcinolone acetonide either alone or in combination with 5-FU. For atrophic scars, laser-assisted delivery of poly-L-lactic acid has been shown to be efficient. “Both of these treatments improve texture and thickness but also dyschromia and scar functionality,” said Dr. Haedersdal, who is also a visiting scientist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston.
Commenting on patient safety with laser-assisted drug delivery, “the combination of lasers and topicals can be a powerful cocktail,” she said. “You can expect intensified local skin reactions. When treating larger areas, consider the risk of systemic absorption and the risk of potential toxicity. There is also the potential for infection with pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. The take-home message here is that you should only use the type and amount of drug no higher than administered during intradermal injection.”
Dr. Haedersdal disclosed that she has received equipment from Cherry Imaging, Cynosure-Hologic, MiraDry, and PerfAction Technologies. She has also received research grants from Leo Pharma, Lutronic, Mirai Medical, Novoxel, and Venus Concept.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE