User login
SAN DIEGO –
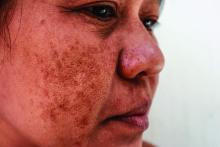
“They need to understand that melasma is going to require long-term maintenance,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
Hydroquinone is a mainstay of melasma therapy, but instead of the commonly used 4% formulation, she prefers to use 12% hydroquinone with 6% kojic acid in VersaBase cream. “It’s a high concentration but the VersaBase makes it more tolerable,” she said. “I have patients take a pea-sized amount and mix it in a regular moisturizer. It’s too strong to spot treat, so it goes on the whole face.”
Mindful that chronic hydroquinone use can cause ochronosis (permanent darkening), she has patients alternate with a nonhydroquinone bleaching agent such as lignin peroxidase, oligopeptide, Lytera, Melaplex, 4-n-butylresorcinol, Cysteamine cream, tranexamic acid, or oral antioxidants. In a study sponsored by SkinMedica, investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, half-face study in females with moderate to severe facial hyperpigmentation to assess the efficacy and tolerability of three new skin brightener formulations containing SMA-432, a prostaglandin E2 inhibitor, compared with 4% hydroquinone. They found that the nonhydroquinone skin formulations were better tolerated and were just as effective as 4% hydroquinone.
Chemical peels and laser treatments
Chemical peels are another treatment option for melasma, but Dr. Ortiz prefers glycolic peels over salicylic and other peels, “because there is no downtime,” she said.
As for laser-based approaches, melasma patients respond best to low energy devices such as the 1,927-nm fractional diode laser at a 3.75% density. “This also can increase the skin permeability of topicals, so when you’re combining it with hydroquinone it can be more effective,” she said.
In an observational study of 27 women with refractory melasma, with phototypes II-V, New York City–based dermatologist Arielle Kauvar, MD, combined microdermabrasion with the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. “The settings she used were very low fluence, so there was no clinical endpoint or no whitening,” said Dr. Ortiz, vice president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS). Specifically, Dr. Kauvar used the laser at 1.6-2 J/cm2 with a 5- or 6-mm spot size immediately following microdermabrasion every 4 weeks; Patients received an average of 2.6 treatments, and were assessed 3-12 months after the last treatment. Study participants were on a standard skin care regimen of a broad spectrum sunscreen, hydroquinone, and tretinoin or vitamin C.
Most of the patients showed at least 50% clearance of melasma 1 month after the first treatment, and 81% showed more than 75% clearance of melasma; remission lasted at least 6 months.
“I personally prefer to use picosecond over Q-switched lasers, because they deliver the energy faster, and you can use a 1,064-nm picosecond laser that is safe in all skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said. “There is minimal downtime, and it doesn’t require anesthesia. You have to consider these things when you’re treating melasma, because this usually requires monthly treatments. If you do something that requires a week of downtime every month, it’s not practical for patients.”
In a study published in 2021, Dr. Ortiz and Tanya Greywal, MD, used three passes of the 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser to treat melasma in 10 patients with skin types II-V. The device had a 650-microsecond pulse duration, a 6-mm spot size, and an energy mode of 11-14 J/cm2. The researchers observed a mean melasma improvement of 26%-50% as early as 3 weeks. “There was no downtime, and no anesthesia was required,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Researchers have discovered a vascular component to melasma, which may have treatment implications. Houston-based dermatologist Paul M. Friedman, MD, and his colleagues used spectrocolorimetry to detect an underlying prominent vascular component in a retrospective review of 11 patients with melasma, with skin types II-IV. They determined that melasma lesions exhibiting subtle or subclinical telangiectatic erythema may be improved by combining vascular-targeted laser therapy with fractional low-powered diode laser therapy.
“So, combining a vascular laser with a 1,927-nm fractional diode laser showed more improvement than with just the diode laser alone,” said Dr. Ortiz, who was not involved with the analysis.
To optimize results following the laser treatment of melasma, she uses one application of clobetasol immediately after the procedure. “This can help reduce swelling and inflammation to decrease the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation,” she said. “You can also use a skin cooling system like Cryomodulation for controlled cooling.”
Tranexamic acid and PLE
Another strategy for melasma patients involves oral treatment with extract of Polypodium leucotomos (PLE), a fern from the Polypodiaceae family with antioxidant properties that has been shown to be photoprotective against UVA and UVB radiation. “I explain to my patients that it’s like an internal sunscreen,” Dr. Ortiz said. “It does not replace your external sunscreen, but it adds extra protection.”
In a pilot placebo-controlled study of patients with melasma on their normal regimen of hydroquinone and sunscreen, 40 Asian patients with melasma were randomized to receive either oral PLE supplementation or placebo for 12 weeks. The authors found that PLE significantly improved and accelerated the outcome reached with hydroquinone and sunscreen from about the first month of treatment, compared with placebo.
Dr. Ortiz discussed the role of oral tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic, procoagulant agent that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of menorrhagia and to prevent hemorrhage in patients with hemophilia undergoing tooth extractions. “This is a game changer for melasma treatment,” she said, but its use has been limited by the risk for thromboembolism.
In a study of 561 patients with melasma, 90% improved after a median treatment duration of 4 months, and only 7% had side effects, most commonly abdominal bloating and pain. Treatment was discontinued in one patient who developed a deep vein thrombosis, and was diagnosed with familial protein S deficiency.
The daily dosing of tranexamic acid for menorrhagia is 3,900 mg daily, while the dose for treating melasma has ranged from 500 mg to 1,500 mg per day, Dr. Ortiz said. It’s available as a 650-mg tablet in the United States. “I prescribe 325 mg twice a day, but studies have shown that 650 mg once a day is just as effective,” she said.
Prior to prescribing tranexamic acid, Dr. Ortiz does not order labs, but she performs an extensive history of current illness and does not prescribe it in patients with an increased risk of clotting, including people who smoke and those who take oral contraceptives or are on hormone supplementation. Use is also contraindicated in people with a current malignancy, those with a history of stroke or DVT, and those who have any clotting disorder.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is cochair of the Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
SAN DIEGO –
“They need to understand that melasma is going to require long-term maintenance,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
Hydroquinone is a mainstay of melasma therapy, but instead of the commonly used 4% formulation, she prefers to use 12% hydroquinone with 6% kojic acid in VersaBase cream. “It’s a high concentration but the VersaBase makes it more tolerable,” she said. “I have patients take a pea-sized amount and mix it in a regular moisturizer. It’s too strong to spot treat, so it goes on the whole face.”
Mindful that chronic hydroquinone use can cause ochronosis (permanent darkening), she has patients alternate with a nonhydroquinone bleaching agent such as lignin peroxidase, oligopeptide, Lytera, Melaplex, 4-n-butylresorcinol, Cysteamine cream, tranexamic acid, or oral antioxidants. In a study sponsored by SkinMedica, investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, half-face study in females with moderate to severe facial hyperpigmentation to assess the efficacy and tolerability of three new skin brightener formulations containing SMA-432, a prostaglandin E2 inhibitor, compared with 4% hydroquinone. They found that the nonhydroquinone skin formulations were better tolerated and were just as effective as 4% hydroquinone.
Chemical peels and laser treatments
Chemical peels are another treatment option for melasma, but Dr. Ortiz prefers glycolic peels over salicylic and other peels, “because there is no downtime,” she said.
As for laser-based approaches, melasma patients respond best to low energy devices such as the 1,927-nm fractional diode laser at a 3.75% density. “This also can increase the skin permeability of topicals, so when you’re combining it with hydroquinone it can be more effective,” she said.
In an observational study of 27 women with refractory melasma, with phototypes II-V, New York City–based dermatologist Arielle Kauvar, MD, combined microdermabrasion with the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. “The settings she used were very low fluence, so there was no clinical endpoint or no whitening,” said Dr. Ortiz, vice president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS). Specifically, Dr. Kauvar used the laser at 1.6-2 J/cm2 with a 5- or 6-mm spot size immediately following microdermabrasion every 4 weeks; Patients received an average of 2.6 treatments, and were assessed 3-12 months after the last treatment. Study participants were on a standard skin care regimen of a broad spectrum sunscreen, hydroquinone, and tretinoin or vitamin C.
Most of the patients showed at least 50% clearance of melasma 1 month after the first treatment, and 81% showed more than 75% clearance of melasma; remission lasted at least 6 months.
“I personally prefer to use picosecond over Q-switched lasers, because they deliver the energy faster, and you can use a 1,064-nm picosecond laser that is safe in all skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said. “There is minimal downtime, and it doesn’t require anesthesia. You have to consider these things when you’re treating melasma, because this usually requires monthly treatments. If you do something that requires a week of downtime every month, it’s not practical for patients.”
In a study published in 2021, Dr. Ortiz and Tanya Greywal, MD, used three passes of the 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser to treat melasma in 10 patients with skin types II-V. The device had a 650-microsecond pulse duration, a 6-mm spot size, and an energy mode of 11-14 J/cm2. The researchers observed a mean melasma improvement of 26%-50% as early as 3 weeks. “There was no downtime, and no anesthesia was required,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Researchers have discovered a vascular component to melasma, which may have treatment implications. Houston-based dermatologist Paul M. Friedman, MD, and his colleagues used spectrocolorimetry to detect an underlying prominent vascular component in a retrospective review of 11 patients with melasma, with skin types II-IV. They determined that melasma lesions exhibiting subtle or subclinical telangiectatic erythema may be improved by combining vascular-targeted laser therapy with fractional low-powered diode laser therapy.
“So, combining a vascular laser with a 1,927-nm fractional diode laser showed more improvement than with just the diode laser alone,” said Dr. Ortiz, who was not involved with the analysis.
To optimize results following the laser treatment of melasma, she uses one application of clobetasol immediately after the procedure. “This can help reduce swelling and inflammation to decrease the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation,” she said. “You can also use a skin cooling system like Cryomodulation for controlled cooling.”
Tranexamic acid and PLE
Another strategy for melasma patients involves oral treatment with extract of Polypodium leucotomos (PLE), a fern from the Polypodiaceae family with antioxidant properties that has been shown to be photoprotective against UVA and UVB radiation. “I explain to my patients that it’s like an internal sunscreen,” Dr. Ortiz said. “It does not replace your external sunscreen, but it adds extra protection.”
In a pilot placebo-controlled study of patients with melasma on their normal regimen of hydroquinone and sunscreen, 40 Asian patients with melasma were randomized to receive either oral PLE supplementation or placebo for 12 weeks. The authors found that PLE significantly improved and accelerated the outcome reached with hydroquinone and sunscreen from about the first month of treatment, compared with placebo.
Dr. Ortiz discussed the role of oral tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic, procoagulant agent that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of menorrhagia and to prevent hemorrhage in patients with hemophilia undergoing tooth extractions. “This is a game changer for melasma treatment,” she said, but its use has been limited by the risk for thromboembolism.
In a study of 561 patients with melasma, 90% improved after a median treatment duration of 4 months, and only 7% had side effects, most commonly abdominal bloating and pain. Treatment was discontinued in one patient who developed a deep vein thrombosis, and was diagnosed with familial protein S deficiency.
The daily dosing of tranexamic acid for menorrhagia is 3,900 mg daily, while the dose for treating melasma has ranged from 500 mg to 1,500 mg per day, Dr. Ortiz said. It’s available as a 650-mg tablet in the United States. “I prescribe 325 mg twice a day, but studies have shown that 650 mg once a day is just as effective,” she said.
Prior to prescribing tranexamic acid, Dr. Ortiz does not order labs, but she performs an extensive history of current illness and does not prescribe it in patients with an increased risk of clotting, including people who smoke and those who take oral contraceptives or are on hormone supplementation. Use is also contraindicated in people with a current malignancy, those with a history of stroke or DVT, and those who have any clotting disorder.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is cochair of the Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
SAN DIEGO –
“They need to understand that melasma is going to require long-term maintenance,” Dr. Ortiz, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
Hydroquinone is a mainstay of melasma therapy, but instead of the commonly used 4% formulation, she prefers to use 12% hydroquinone with 6% kojic acid in VersaBase cream. “It’s a high concentration but the VersaBase makes it more tolerable,” she said. “I have patients take a pea-sized amount and mix it in a regular moisturizer. It’s too strong to spot treat, so it goes on the whole face.”
Mindful that chronic hydroquinone use can cause ochronosis (permanent darkening), she has patients alternate with a nonhydroquinone bleaching agent such as lignin peroxidase, oligopeptide, Lytera, Melaplex, 4-n-butylresorcinol, Cysteamine cream, tranexamic acid, or oral antioxidants. In a study sponsored by SkinMedica, investigators conducted a randomized, double-blind, half-face study in females with moderate to severe facial hyperpigmentation to assess the efficacy and tolerability of three new skin brightener formulations containing SMA-432, a prostaglandin E2 inhibitor, compared with 4% hydroquinone. They found that the nonhydroquinone skin formulations were better tolerated and were just as effective as 4% hydroquinone.
Chemical peels and laser treatments
Chemical peels are another treatment option for melasma, but Dr. Ortiz prefers glycolic peels over salicylic and other peels, “because there is no downtime,” she said.
As for laser-based approaches, melasma patients respond best to low energy devices such as the 1,927-nm fractional diode laser at a 3.75% density. “This also can increase the skin permeability of topicals, so when you’re combining it with hydroquinone it can be more effective,” she said.
In an observational study of 27 women with refractory melasma, with phototypes II-V, New York City–based dermatologist Arielle Kauvar, MD, combined microdermabrasion with the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. “The settings she used were very low fluence, so there was no clinical endpoint or no whitening,” said Dr. Ortiz, vice president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS). Specifically, Dr. Kauvar used the laser at 1.6-2 J/cm2 with a 5- or 6-mm spot size immediately following microdermabrasion every 4 weeks; Patients received an average of 2.6 treatments, and were assessed 3-12 months after the last treatment. Study participants were on a standard skin care regimen of a broad spectrum sunscreen, hydroquinone, and tretinoin or vitamin C.
Most of the patients showed at least 50% clearance of melasma 1 month after the first treatment, and 81% showed more than 75% clearance of melasma; remission lasted at least 6 months.
“I personally prefer to use picosecond over Q-switched lasers, because they deliver the energy faster, and you can use a 1,064-nm picosecond laser that is safe in all skin types,” Dr. Ortiz said. “There is minimal downtime, and it doesn’t require anesthesia. You have to consider these things when you’re treating melasma, because this usually requires monthly treatments. If you do something that requires a week of downtime every month, it’s not practical for patients.”
In a study published in 2021, Dr. Ortiz and Tanya Greywal, MD, used three passes of the 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser to treat melasma in 10 patients with skin types II-V. The device had a 650-microsecond pulse duration, a 6-mm spot size, and an energy mode of 11-14 J/cm2. The researchers observed a mean melasma improvement of 26%-50% as early as 3 weeks. “There was no downtime, and no anesthesia was required,” Dr. Ortiz said.
Researchers have discovered a vascular component to melasma, which may have treatment implications. Houston-based dermatologist Paul M. Friedman, MD, and his colleagues used spectrocolorimetry to detect an underlying prominent vascular component in a retrospective review of 11 patients with melasma, with skin types II-IV. They determined that melasma lesions exhibiting subtle or subclinical telangiectatic erythema may be improved by combining vascular-targeted laser therapy with fractional low-powered diode laser therapy.
“So, combining a vascular laser with a 1,927-nm fractional diode laser showed more improvement than with just the diode laser alone,” said Dr. Ortiz, who was not involved with the analysis.
To optimize results following the laser treatment of melasma, she uses one application of clobetasol immediately after the procedure. “This can help reduce swelling and inflammation to decrease the risk of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation,” she said. “You can also use a skin cooling system like Cryomodulation for controlled cooling.”
Tranexamic acid and PLE
Another strategy for melasma patients involves oral treatment with extract of Polypodium leucotomos (PLE), a fern from the Polypodiaceae family with antioxidant properties that has been shown to be photoprotective against UVA and UVB radiation. “I explain to my patients that it’s like an internal sunscreen,” Dr. Ortiz said. “It does not replace your external sunscreen, but it adds extra protection.”
In a pilot placebo-controlled study of patients with melasma on their normal regimen of hydroquinone and sunscreen, 40 Asian patients with melasma were randomized to receive either oral PLE supplementation or placebo for 12 weeks. The authors found that PLE significantly improved and accelerated the outcome reached with hydroquinone and sunscreen from about the first month of treatment, compared with placebo.
Dr. Ortiz discussed the role of oral tranexamic acid, an antifibrinolytic, procoagulant agent that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of menorrhagia and to prevent hemorrhage in patients with hemophilia undergoing tooth extractions. “This is a game changer for melasma treatment,” she said, but its use has been limited by the risk for thromboembolism.
In a study of 561 patients with melasma, 90% improved after a median treatment duration of 4 months, and only 7% had side effects, most commonly abdominal bloating and pain. Treatment was discontinued in one patient who developed a deep vein thrombosis, and was diagnosed with familial protein S deficiency.
The daily dosing of tranexamic acid for menorrhagia is 3,900 mg daily, while the dose for treating melasma has ranged from 500 mg to 1,500 mg per day, Dr. Ortiz said. It’s available as a 650-mg tablet in the United States. “I prescribe 325 mg twice a day, but studies have shown that 650 mg once a day is just as effective,” she said.
Prior to prescribing tranexamic acid, Dr. Ortiz does not order labs, but she performs an extensive history of current illness and does not prescribe it in patients with an increased risk of clotting, including people who smoke and those who take oral contraceptives or are on hormone supplementation. Use is also contraindicated in people with a current malignancy, those with a history of stroke or DVT, and those who have any clotting disorder.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is cochair of the Masters of Aesthetics Symposium.
AT MOAS 2022