User login
Immunomodulators Do Not Affect COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy
TOPLINE:
The results of a recent study suggest that biologics and small molecule inhibitors (SMIs) do not impair the protective effect of COVID-19 vaccine against hospitalization in patients with psoriasis and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
METHODOLOGY:
- It remains unknown whether immunomodulatory therapies impair COVID-19 vaccine efficacy and increase hospitalization rates linked to COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory skin conditions such as psoriasis or HS.
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the Epic Cosmos database from January 2020 to October 2023, identifying 30,845 patients with psoriasis or HS.
- Overall, 22,293 patients with documented completion of their primary COVID-19 vaccine series were included in the analysis.
- Of the vaccinated patients, they compared 7046 patients with psoriasis on SMIs and 2033 with psoriasis or HS on biologics with 13,214 patients who did not receive biologics or SMIs.
- The primary outcome was the COVID-19 hospitalization rate.
- Treatment with biologics did not increase COVID-19-related hospitalization rates in vaccinated patients with psoriasis or HS (hospitalization rate, 6.0% for both those taking and those not taking a biologic; P > .99).
- Similarly, hospitalization rates did not significantly differ between vaccinated patients who received SMIs vs those who did not (7.1% vs 6.0%; P = .0596).
IN PRACTICE:
These findings “encourage dermatologists to continue treating [psoriasis]/HS confidently despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study led by Bella R. Lee from Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, was published online on March 13, 2024, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Multivariable adjustments could not be performed in this study due to unavailability of individual-level data, and hospital admissions that occurred outside the Epic system were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The results of a recent study suggest that biologics and small molecule inhibitors (SMIs) do not impair the protective effect of COVID-19 vaccine against hospitalization in patients with psoriasis and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
METHODOLOGY:
- It remains unknown whether immunomodulatory therapies impair COVID-19 vaccine efficacy and increase hospitalization rates linked to COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory skin conditions such as psoriasis or HS.
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the Epic Cosmos database from January 2020 to October 2023, identifying 30,845 patients with psoriasis or HS.
- Overall, 22,293 patients with documented completion of their primary COVID-19 vaccine series were included in the analysis.
- Of the vaccinated patients, they compared 7046 patients with psoriasis on SMIs and 2033 with psoriasis or HS on biologics with 13,214 patients who did not receive biologics or SMIs.
- The primary outcome was the COVID-19 hospitalization rate.
- Treatment with biologics did not increase COVID-19-related hospitalization rates in vaccinated patients with psoriasis or HS (hospitalization rate, 6.0% for both those taking and those not taking a biologic; P > .99).
- Similarly, hospitalization rates did not significantly differ between vaccinated patients who received SMIs vs those who did not (7.1% vs 6.0%; P = .0596).
IN PRACTICE:
These findings “encourage dermatologists to continue treating [psoriasis]/HS confidently despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study led by Bella R. Lee from Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, was published online on March 13, 2024, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Multivariable adjustments could not be performed in this study due to unavailability of individual-level data, and hospital admissions that occurred outside the Epic system were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The results of a recent study suggest that biologics and small molecule inhibitors (SMIs) do not impair the protective effect of COVID-19 vaccine against hospitalization in patients with psoriasis and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
METHODOLOGY:
- It remains unknown whether immunomodulatory therapies impair COVID-19 vaccine efficacy and increase hospitalization rates linked to COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory skin conditions such as psoriasis or HS.
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the Epic Cosmos database from January 2020 to October 2023, identifying 30,845 patients with psoriasis or HS.
- Overall, 22,293 patients with documented completion of their primary COVID-19 vaccine series were included in the analysis.
- Of the vaccinated patients, they compared 7046 patients with psoriasis on SMIs and 2033 with psoriasis or HS on biologics with 13,214 patients who did not receive biologics or SMIs.
- The primary outcome was the COVID-19 hospitalization rate.
- Treatment with biologics did not increase COVID-19-related hospitalization rates in vaccinated patients with psoriasis or HS (hospitalization rate, 6.0% for both those taking and those not taking a biologic; P > .99).
- Similarly, hospitalization rates did not significantly differ between vaccinated patients who received SMIs vs those who did not (7.1% vs 6.0%; P = .0596).
IN PRACTICE:
These findings “encourage dermatologists to continue treating [psoriasis]/HS confidently despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
The study led by Bella R. Lee from Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, was published online on March 13, 2024, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Multivariable adjustments could not be performed in this study due to unavailability of individual-level data, and hospital admissions that occurred outside the Epic system were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Sustained Control Reported for Anti–IL-17, Anti–IL-23 Psoriasis Treatments
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO — , but late-breaker data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology show that these types of responses are sustained for as long as patients have remained on therapy.
Of the two, the longer follow up is with the IL-17 inhibitor bimekizumab (Bimzelx). In a 4-year open-label extension study, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 rate was approximately 85% in treated patients, according to Mark Lebwohl, MD, professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City
A PASI 90 score signifies that 90% of skin surface area is cleared. The proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 100 score, signifying total clearance, approached 70% at 4 years in the group with the greatest response. PASI 90 and PASI 100 rates at this point were only modestly lower than those reported at the end of the double-blind phase 3 trial when evaluated 3 years earlier.
Follow-up with a novel oral anti-IL-23 inhibitor JNJ-2113 (JNJ-77242113) was only 52 weeks, far shorter. But again, the response for the most effective dose at the end of this period was essentially unchanged from that at 16 weeks. Among those on the highest and most effective test dose of once-daily 100 mg, the PASI 90 at 1 year was 64.3%, a rate that was essentially unchanged from week 16.
No Apparent Loss of Benefit Over Time
“We can really look at those dose-response curves and see that there is, overall, a maintenance of response,” reported Laura K. Ferris, MD, PhD, professor and director of clinical trials, Department of Dermatology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In her presentation of the data, she showed similar sustained control for the most effective doses of JNJ-2113 for multiple clinical outcomes, including an investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, also signifying clear or near clear skin.
Bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits both IL-17A and IL-17F, is already approved for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. The 52-week BE SURE trial, which provided the 478 patients who entered into the BE BRIGHT open label extension study, was published in The New England Journal of Medicine in July 2021.
In the 4-year data reported by Dr. Lebwohl, three groups were compared: Those initially randomized to an every-4-week dosing schedule of bimekizumab over the course of the 52-week BE SURE trial; those randomized to an every-4-week bimekizumab schedule who were then subsequently switched to an every-8-week schedule; and those initiated on the TNF-inhibitor adalimumab (Humira) and were then switched at week 24 to every-4-week bimekizumab.
The PASI 90 responses at 52 weeks in these three groups, respectively, were 91.2%, 89.3%, and 95.2%. At 4 years, this almost clear response was observed in 82.4%, 83.2%, and 87.6%, respectively. At 52 weeks, the PASI 100 responses in these three groups, respectively, were 75.3%, 74.2%, and 72.9%. At 4 years, 61.9%, 58.5%, and 69.5% still had complete skin clearance.
Bimekizumab was well tolerated during the randomized trial, reported Dr. Lebwohl. The rates of nasopharyngitis and oral candidiasis, which were observed in approximately 12% and 8%, respectively, of treated patients during the randomized phase remained at about the same level in the long-term follow up. There were no new safety signals, he said.
JNJ-2113 Is First Potential Oral IL-23 Inhibitor
JNJ-2113 is a first-in-class oral peptide that binds to the IL-23 receptor, blocking the IL-23 signaling pathway. If approved, it would be the first oral therapy targeting IL-23. The 16-week outcomes of the dose-finding FRONTIER 1 phase 2b trial were published in The New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year. The primary endpoint was PASI 75, achieved by 79% of those on the 100 mg twice daily dose at week 16, vs 9% on placebo, and at 52 weeks, was 76%.
“The proportion of patients achieving the FRONTIER 1 primary endpoint was maintained from week 16 to the end of week 52 in the extension study,” Dr. Ferris said, but further pointed out that rates of near or complete clearance achieved at week 16 were also essentially unchanged at week 52. This was true of PASI scores and IGA.
Clearance of psoriatic lesions on the scalp was particularly impressive. By scalp-specific IGA, rates of clear or near clear (0/1) were not just maintained but improved over the course of follow-up, reaching 75.1% at 52 weeks in the highest dose group, she said.
JNJ-2113 was well tolerated in FRONTIER 1 and remained so during long-term follow-up, in the FRONTIER 2 extension study, according to Dr. Ferris. The most common complaints with JNJ-2113, such as nasopharyngitis (18.1% vs 25.7% in placebo), did not appear to differ significantly from placebo and the treatment remained well tolerated over the course of the extended follow-up.
There are limited direct comparisons of different biologics active in the treatment of plaque psoriasis for efficacy and safety, but these data appear to show a depth and durability of benefit for psoriasis that is exceptional, Dr. Lebwohl told this news organization. “The PASI 100 scores achieved by bimekizumab exceed anything we have seen to date,” he said. “And the durability of those exceedingly high scores is remarkable.”
Dr. Lebwohl reports financial relationships with approximately 40 pharmaceutical companies, including UCB Pharma, which developed bimekizumab. Dr. Ferris reports financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Janssen, which is developing JNJ-2113.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAD 2024
Depression As a Potential Contributing Factor in Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Associated Racial Gaps
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)—a chronic, relapsing, inflammatory disorder involving terminal hair follicles in apocrine gland–rich skin—manifests as tender inflamed nodules that transform into abscesses, sinus tracts, and scarring.1,2 The etiology of HS is multifactorial, encompassing lifestyle, microbiota, hormonal status, and genetic and environmental factors. These factors activate the immune system around the terminal hair follicles and lead to hyperkeratosis of the infundibulum of the hair follicles in intertriginous regions. This progresses to follicular occlusion, stasis, and eventual rupture. Bacterial multiplication within the plugged pilosebaceous units further boosts immune activation. Resident and migrated cells of the innate and adaptive immune system then release proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor, IL-1β, and IL-17, which further enhance immune cell influx and inflammation.3,4 This aberrant immune response propagates the production of deep-seated inflammatory nodules and abscesses.3-8
The estimated prevalence of HS is 1% worldwide.9 It is more prevalent in female and Black patients (0.30%) than White patients (0.09%) and is intermediate in prevalence in the biracial population (0.22%).10 Hidradenitis suppurativa is thought to be associated with lower socioeconomic status (SES). In a retrospective analysis of HS patients (N=375), approximately one-third of patients were Black, had advanced disease, and had a notably lower SES.11 Furthermore, HS has been reported to be associated with systemic inflammation and comorbidities such as morbid obesity (38.3%) and hypertension (39.6%) as well as other metabolic syndrome–related disorders and depression (48.1%).1
Hidradenitis suppurativa may contribute to the risk for depression through its substantial impact on health-related quality of life, which culminates in social withdrawal, unemployment, and suicidal thoughts.12 The high prevalence of depression in individuals with HS1 and its association with systemic inflammation13 increases the likelihood that a common genetic predisposition also may exist between both conditions. Because depression frequently has been discovered as a concomitant diagnosis in patients with HS, we hypothesize that a shared genetic susceptibility also may exist between the 2 disorders. Our study sought to explore data on the co-occurrence of depression with HS, including its demographics and racial data.
Methods
We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Google Scholar using the terms depression and hidradenitis suppurativa to obtain all research articles published from 2000 to 2022. Articles were selected based on relevance to the topic of exploration. English-language articles that directly addressed the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, and co-occurrence of both depression and HS with numerical data were included. Articles were excluded if they did not explore the information of interest on these 2 disorders or did not contain clear statistical data of patients with the 2 concurrent medical conditions.
Results
Twenty-two cross-sectional, prospective, and retrospective studies that fit the search criteria were identified and included in the analysis (eTable).1,14-34 Sixteen (72.7%) studies were cross-sectional, 5 (22.7%) were retrospective, and only 1 (4.5%) was a prospective study. Only 6 of the studies provided racial data,1,14,17,26,28,32 and of them, 4 had predominately White patients,1,14,26,32 whereas the other 2 had predominantly Black patients.17,28
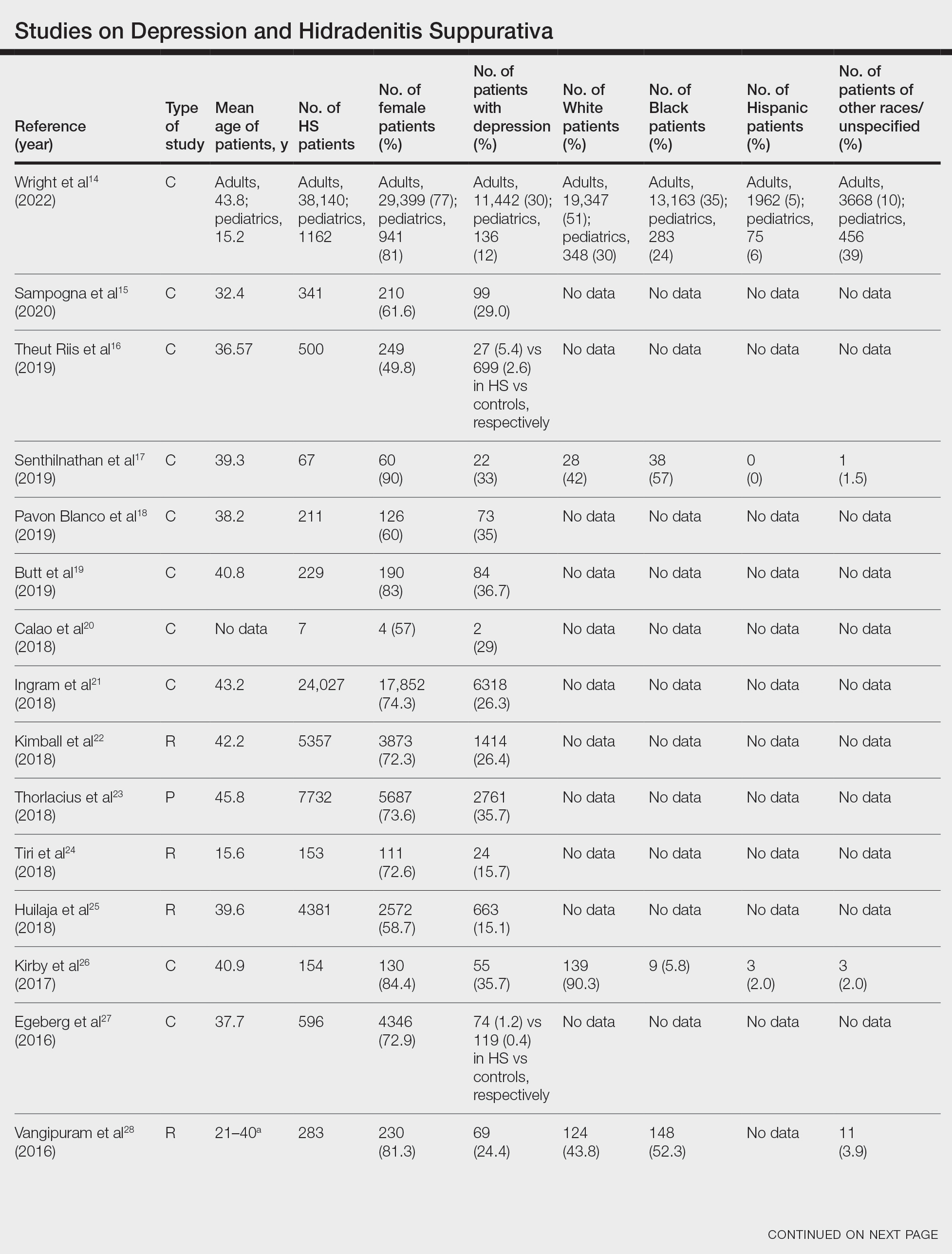
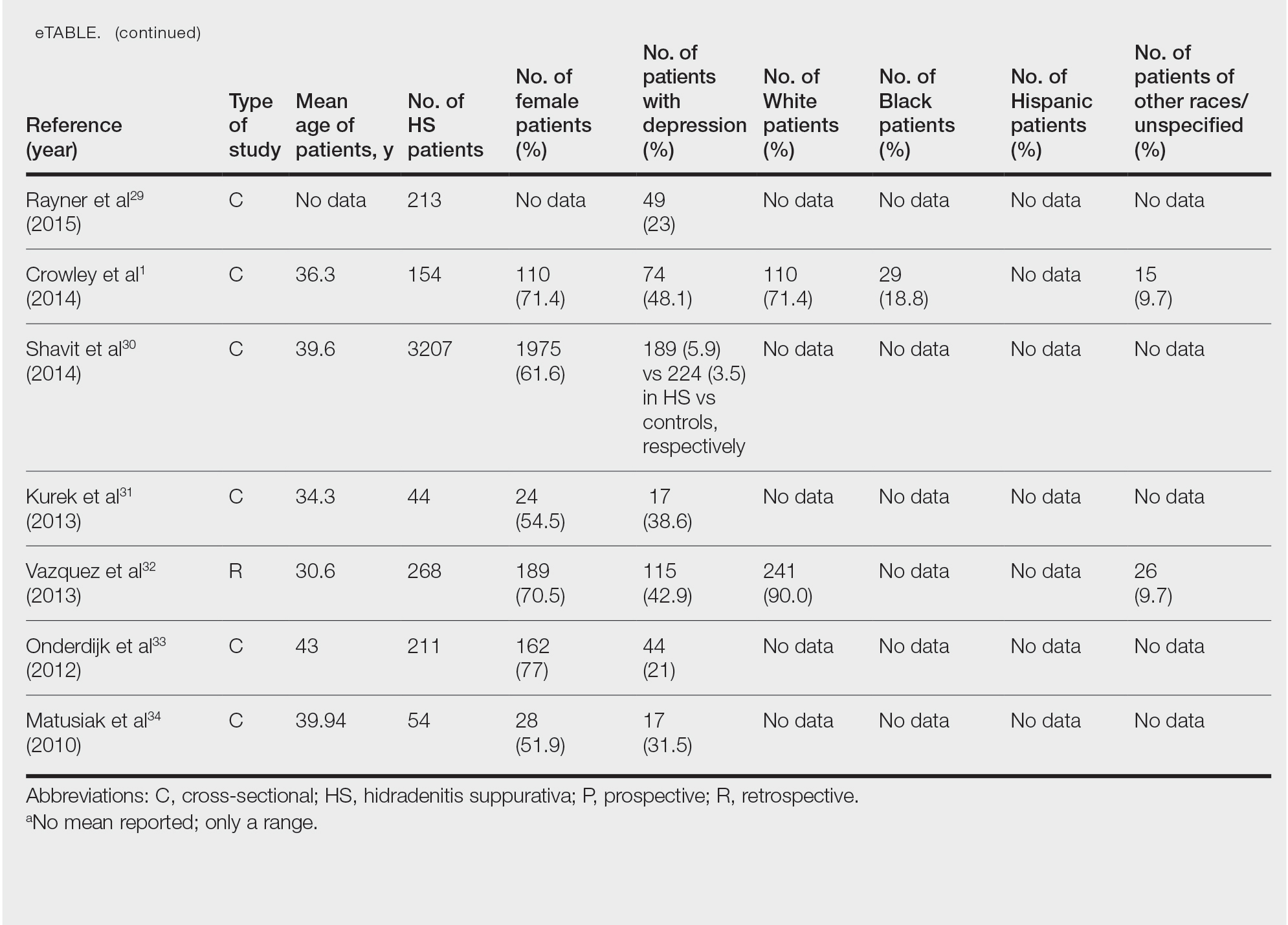
Hidradenitis suppurativa was found to coexist with depression in all the studies, with a prevalence of 1.2% to 48.1%. There also was a higher prevalence of depression in HS patients than in the control patients without HS. Furthermore, a recent study by Wright and colleagues14 stratified the depression prevalence data by age and found a higher prevalence of depression in adults vs children with HS (30% vs 12%).
Comment
Major depression—a chronic and debilitating illness—is the chief cause of disability globally and in the United States alone and has a global lifetime prevalence of 17%.35 In a study of 388 patients diagnosed with depression and 404 community-matched controls who were observed for 10 years, depressed patients had a two-thirds higher likelihood of developing a serious physical illness than controls. The depression-associated elevated risk for serious physical illness persisted after controlling for confounding variables such as alcohol abuse, smoking, and level of physical activity.36 Studies also have demonstrated that HS is more prevalent in Black individuals10 and in individuals of low SES,37 who are mostly the Black and Hispanic populations that experience the highest burden of racial microaggression38 and disparities in health access and outcomes.39,40 The severity and chronicity of major depressive disorder also is higher in Black patients compared with White patients (57% vs 39%).41 Because major depression and HS are most common among Black patients who experience the highest-burden negative financial and health disparities, there may be a shared genetic disposition to both medical conditions.
Moreover, the common detrimental lifestyle choices associated with patients with depression and HS also suggest the possibility of a collective genetic susceptibility. Patients with depression also report increased consumption of alcohol, tobacco, and illicit substances; sedentary lifestyle leading to obesity; and poor compliance with prescribed medical treatment.42 Smoking and obesity are known contributors to the pathogenesis of HS, and their modification also is known to positively impact the disease course. In a retrospective single-cohort study, 50% of obese HS patients (n=35) reported a substantial decrease in disease severity after a reduction of more than 15% in body mass index over 2 years following bariatric surgery (n=35).43 Patients with HS also have reported disease remission following extensive weight loss.44 In addition, evidence has supported smoking cessation in improving the disease course of HS.43 Because these detrimental lifestyle choices are prevalent in both patients with HS and those with depression, a co-genetic susceptibility also may exist.
Furthermore, depression is characterized by a persistent inflammatory state,13,45 similar to HS.46 Elevated levels of a variety of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-6, and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1, have been reported in patients with depression compared with healthy controls.13,45 Further analysis found a positive correlation and a strong association between depression and these inflammatory markers.47 Moreover, adipokines regulate inflammatory responses, and adipokines play a role in the pathogenesis of HS. Adipokine levels such as elevated omentin-1 (a recently identified adipokine) were found to be altered in patients with HS compared with controls.48 Results from clinical studies and meta-analyses of patients with depression also have demonstrated that adipokines are dysregulated in this population,49,50 which may be another potential genetic link between depression and HS.
In addition, genetic susceptibility to depression and HS may be shared because the inflammatory markers that have a strong association with depression also have been found to play an important role in HS treatment and disease severity prediction. In a retrospective cohort study of 404 patients, CRP or IL-6 levels were found to be reliable predictors of HS disease severity, which may explain why anti–tumor necrosis factor antibody regimens such as adalimumab and infliximab have clinically ameliorated disease activity in several cases of HS.51 In a study evaluating these drugs, high baseline levels of high-sensitivity CRP and IL-6 were predictive of patient response to infliximab.52 In a meta-analysis evaluating 20,791 participants, an association was found between concurrent depression and CRP. Furthermore, inflammation measured by high levels of CRP or IL-6 was observed to predict future depression.53 If the same inflammatory markers—CRP and IL-6—both play a major role in the disease activity of depression and HS, then a concurrent genetic predisposition may exist.
Conclusion
Understanding the comorbidities, etiologies, and risk factors for the development and progression of HS is an important step toward improved disease management. Available studies on comorbid depression in HS largely involve White patients, and more studies are needed in patients with skin of color, particularly the Black population, who have the highest prevalence of HS.10 Given the evidence for an association between depression and HS, we suggest a large-scale investigation of this patient population that includes a complete medical history, onset of HS in comparison to the onset of depression, and specific measures of disease progress and lifetime management of depression, which may help to increase knowledge about the role of depression in HS and encourage more research in this area. If shared genetic susceptibility is established, aggressive management of depression in patients at risk for HS may reduce disease incidence and severity as well as the psychological burden on patients.
- Crowley JJ, Mekkes JR, Zouboulis CC, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity with increased risk for systemic comorbidities. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:1561-1565.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Sabat R, Jemec GBE, Matusiak Ł, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2020;6:1-20.
- Wolk K, Warszawska K, Hoeflich C, et al. Deficiency of IL-22 contributes to a chronic inflammatory disease: pathogenetic mechanisms in acne inversa. J Immunol. 2011;186:1228-1239.
- von Laffert M, Helmbold P, Wohlrab J, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa): early inflammatory events at terminal follicles and at interfollicular epidermis. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:533-537.
- Van Der Zee HH, De Ruiter L, Van Den Broecke DG, et al. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: a rationale for targeting TNF-α and IL-1β. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1292-1298.
- Schlapbach C, Hänni T, Yawalkar N, et al. Expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:790-798.
- Kelly G, Hughes R, McGarry T, et al. Dysregulated cytokine expression in lesional and nonlesional skin in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1431-1439.
- Jemec GBE, Kimball AB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: epidemiology and scope of the problem. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5 Suppl 1):S4-S7.
- Garg A, Kirby JS, Lavian J, et al. Sex- and age-adjusted population analysis of prevalence estimates for hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760-764.
- Soliman YS, Hoffman LK, Guzman AK, et al. African American patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have significant health care disparities: a retrospective study. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:334-336.
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101.
- Beatriz Currier M, Nemeroff CB. Inflammation and mood disorders: proinflammatory cytokines and the pathogenesis of depression. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2012;9:212-220.
- Wright S, Strunk A, Garg A. Prevalence of depression among children, adolescents, and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:55-60.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mastroeni S, et al. Correlation between depression, quality of life and clinical severity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:1-6.
- Theut Riis P, Pedersen OB, Sigsgaard V, et al. Prevalence of patients with self-reported hidradenitis suppurativa in a cohort of Danish blood donors: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:774-781.
- Senthilnathan A, Kolli SS, Cardwell LA, et al. Depression in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:1087-1088.
- Pavon Blanco A, Turner MA, Petrof G, et al. To what extent do disease severity and illness perceptions explain depression, anxiety and quality of life in hidradenitis suppurativa? Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:338-345.
- Butt M, Sisic M, Silva C, et al. The associations of depression and coping methods on health-related quality of life for those with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1137-1139.
- Calao M, Wilson JL, Spelman L, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) prevalence, demographics and management pathways in Australia: a population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0200683.
- Ingram JR, Jenkins-Jones S, Knipe DW, et al. Population-based Clinical Practice Research Datalink study using algorithm modelling to identify the true burden of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:917-924.
- Kimball AB, Sundaram M, Gauthier G, et al. The comorbidity burden of hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States: a claims data analysis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018;8:557.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Tiri H, Jokelainen J, Timonen M, et al. Somatic and psychiatric comorbidities of hidradenitis suppurativa in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:514-519.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Kirby JS, Butt M, Esmann S, et al. Association of resilience with depression and health-related quality of life for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1263.
- Egeberg A, Gislason GH, Hansen PR. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:429-434.
- Vangipuram R, Vaidya T, Jandarov R, et al. Factors contributing to depression and chronic pain in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: results from a single-center retrospective review. Dermatology. 2016;232:692-695.
- Rayner L, Jackson K, Turner M, et al. Integrated mental health assessment in a tertiary medical dermatology service: feasibility and the prevalence of common mental disorder. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:201.
- Shavit E, Dreiher J, Freud T, et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in 3207 patients with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online June 9, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:371-376.
- Kurek A, Johanne Peters EM, Sabat R, et al. Depression is a frequent co-morbidity in patients with acne inversa. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:743-749.
- Vazquez BG, Alikhan A, Weaver AL, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa and associated factors: a population-based study of Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:97.
- Onderdijk AJ, Van Der Zee HH, Esmann S, et al. Depression in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online February 20, 2012]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:473-478.
- Matusiak Ł, Bieniek A, Szepietowski JC. Psychophysical aspects of hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:264-268.
- Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, et al. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:617-627.
- Holahan CJ, Pahl SA, Cronkite RC, et al. Depression and vulnerability to incident physical illness across 10 years. J Affect Disord. 2009;123:222-229.
- Deckers IE, Janse IC, van der Zee HH, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is associated with low socioeconomic status (SES): a cross-sectional reference study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:755-759.e1.
- Williams MT, Skinta MD, Kanter JW, et al. A qualitative study of microaggressions against African Americans on predominantly White campuses. BMC Psychol. 2020;8:1-13.
- Dunlop DD, Song J, Lyons JS, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in rates of depression among preretirement adults. Am J Public Health. 2003;93:1945-1952.
- Williams DR, Priest N, Anderson NB. Understanding associations among race, socioeconomic status, and health: patterns and prospects. Health Psychol. 2016;35:407-411.
- Williams DR, González HM, Neighbors H, et al. Prevalence and distribution of major depressive disorder in African Americans, Caribbean Blacks, and Non-Hispanic Whites: results from the National Survey of American Life. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:305-315.
- Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283:506-511.
- Kromann CB, Deckers IE, Esmann S, et al. Risk factors, clinical course and long-term prognosis in hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:819-824.
- Sivanand A, Gulliver WP, Josan CK, et al. Weight loss and dietary interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. J Cutan Med Surg . 2020;24:64-72.
- Raedler TJ. Inflammatory mechanisms in major depressive disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2011;24:519-525.
- Rocha VZ, Libby P. Obesity, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:399-409.
- Davidson KW, Schwartz JE, Kirkland SA, et al. Relation of inflammation to depression and incident coronary heart disease (from the Canadian Nova Scotia Health Survey [NSHS95] Prospective Population Study). Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:755-761.
- González-López MA, Ocejo-Viñals JG, Mata C, et al. Evaluation of serum omentin-1 and apelin concentrations in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:450-454.
- Taylor VH, Macqueen GM. The role of adipokines in understanding the associations between obesity and depression. J Obes. 2010;2010:748048.
- Setayesh L, Ebrahimi R, Pooyan S, et al. The possible mediatory role of adipokines in the association between low carbohydrate diet and depressive symptoms among overweight and obese women. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0257275 .
- Andriano TM, Benesh G, Babbush KM, et al. Serum inflammatory markers and leukocyte profiles accurately describe hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1270-1275.
- Montaudié H, Seitz-Polski B, Cornille A, et al. Interleukin 6 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein are potential predictive markers of response to infliximab in hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;6:156-158.
- Colasanto M, Madigan S, Korczak DJ. Depression and inflammation among children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2020;277:940-948.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)—a chronic, relapsing, inflammatory disorder involving terminal hair follicles in apocrine gland–rich skin—manifests as tender inflamed nodules that transform into abscesses, sinus tracts, and scarring.1,2 The etiology of HS is multifactorial, encompassing lifestyle, microbiota, hormonal status, and genetic and environmental factors. These factors activate the immune system around the terminal hair follicles and lead to hyperkeratosis of the infundibulum of the hair follicles in intertriginous regions. This progresses to follicular occlusion, stasis, and eventual rupture. Bacterial multiplication within the plugged pilosebaceous units further boosts immune activation. Resident and migrated cells of the innate and adaptive immune system then release proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor, IL-1β, and IL-17, which further enhance immune cell influx and inflammation.3,4 This aberrant immune response propagates the production of deep-seated inflammatory nodules and abscesses.3-8
The estimated prevalence of HS is 1% worldwide.9 It is more prevalent in female and Black patients (0.30%) than White patients (0.09%) and is intermediate in prevalence in the biracial population (0.22%).10 Hidradenitis suppurativa is thought to be associated with lower socioeconomic status (SES). In a retrospective analysis of HS patients (N=375), approximately one-third of patients were Black, had advanced disease, and had a notably lower SES.11 Furthermore, HS has been reported to be associated with systemic inflammation and comorbidities such as morbid obesity (38.3%) and hypertension (39.6%) as well as other metabolic syndrome–related disorders and depression (48.1%).1
Hidradenitis suppurativa may contribute to the risk for depression through its substantial impact on health-related quality of life, which culminates in social withdrawal, unemployment, and suicidal thoughts.12 The high prevalence of depression in individuals with HS1 and its association with systemic inflammation13 increases the likelihood that a common genetic predisposition also may exist between both conditions. Because depression frequently has been discovered as a concomitant diagnosis in patients with HS, we hypothesize that a shared genetic susceptibility also may exist between the 2 disorders. Our study sought to explore data on the co-occurrence of depression with HS, including its demographics and racial data.
Methods
We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Google Scholar using the terms depression and hidradenitis suppurativa to obtain all research articles published from 2000 to 2022. Articles were selected based on relevance to the topic of exploration. English-language articles that directly addressed the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, and co-occurrence of both depression and HS with numerical data were included. Articles were excluded if they did not explore the information of interest on these 2 disorders or did not contain clear statistical data of patients with the 2 concurrent medical conditions.
Results
Twenty-two cross-sectional, prospective, and retrospective studies that fit the search criteria were identified and included in the analysis (eTable).1,14-34 Sixteen (72.7%) studies were cross-sectional, 5 (22.7%) were retrospective, and only 1 (4.5%) was a prospective study. Only 6 of the studies provided racial data,1,14,17,26,28,32 and of them, 4 had predominately White patients,1,14,26,32 whereas the other 2 had predominantly Black patients.17,28


Hidradenitis suppurativa was found to coexist with depression in all the studies, with a prevalence of 1.2% to 48.1%. There also was a higher prevalence of depression in HS patients than in the control patients without HS. Furthermore, a recent study by Wright and colleagues14 stratified the depression prevalence data by age and found a higher prevalence of depression in adults vs children with HS (30% vs 12%).
Comment
Major depression—a chronic and debilitating illness—is the chief cause of disability globally and in the United States alone and has a global lifetime prevalence of 17%.35 In a study of 388 patients diagnosed with depression and 404 community-matched controls who were observed for 10 years, depressed patients had a two-thirds higher likelihood of developing a serious physical illness than controls. The depression-associated elevated risk for serious physical illness persisted after controlling for confounding variables such as alcohol abuse, smoking, and level of physical activity.36 Studies also have demonstrated that HS is more prevalent in Black individuals10 and in individuals of low SES,37 who are mostly the Black and Hispanic populations that experience the highest burden of racial microaggression38 and disparities in health access and outcomes.39,40 The severity and chronicity of major depressive disorder also is higher in Black patients compared with White patients (57% vs 39%).41 Because major depression and HS are most common among Black patients who experience the highest-burden negative financial and health disparities, there may be a shared genetic disposition to both medical conditions.
Moreover, the common detrimental lifestyle choices associated with patients with depression and HS also suggest the possibility of a collective genetic susceptibility. Patients with depression also report increased consumption of alcohol, tobacco, and illicit substances; sedentary lifestyle leading to obesity; and poor compliance with prescribed medical treatment.42 Smoking and obesity are known contributors to the pathogenesis of HS, and their modification also is known to positively impact the disease course. In a retrospective single-cohort study, 50% of obese HS patients (n=35) reported a substantial decrease in disease severity after a reduction of more than 15% in body mass index over 2 years following bariatric surgery (n=35).43 Patients with HS also have reported disease remission following extensive weight loss.44 In addition, evidence has supported smoking cessation in improving the disease course of HS.43 Because these detrimental lifestyle choices are prevalent in both patients with HS and those with depression, a co-genetic susceptibility also may exist.
Furthermore, depression is characterized by a persistent inflammatory state,13,45 similar to HS.46 Elevated levels of a variety of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-6, and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1, have been reported in patients with depression compared with healthy controls.13,45 Further analysis found a positive correlation and a strong association between depression and these inflammatory markers.47 Moreover, adipokines regulate inflammatory responses, and adipokines play a role in the pathogenesis of HS. Adipokine levels such as elevated omentin-1 (a recently identified adipokine) were found to be altered in patients with HS compared with controls.48 Results from clinical studies and meta-analyses of patients with depression also have demonstrated that adipokines are dysregulated in this population,49,50 which may be another potential genetic link between depression and HS.
In addition, genetic susceptibility to depression and HS may be shared because the inflammatory markers that have a strong association with depression also have been found to play an important role in HS treatment and disease severity prediction. In a retrospective cohort study of 404 patients, CRP or IL-6 levels were found to be reliable predictors of HS disease severity, which may explain why anti–tumor necrosis factor antibody regimens such as adalimumab and infliximab have clinically ameliorated disease activity in several cases of HS.51 In a study evaluating these drugs, high baseline levels of high-sensitivity CRP and IL-6 were predictive of patient response to infliximab.52 In a meta-analysis evaluating 20,791 participants, an association was found between concurrent depression and CRP. Furthermore, inflammation measured by high levels of CRP or IL-6 was observed to predict future depression.53 If the same inflammatory markers—CRP and IL-6—both play a major role in the disease activity of depression and HS, then a concurrent genetic predisposition may exist.
Conclusion
Understanding the comorbidities, etiologies, and risk factors for the development and progression of HS is an important step toward improved disease management. Available studies on comorbid depression in HS largely involve White patients, and more studies are needed in patients with skin of color, particularly the Black population, who have the highest prevalence of HS.10 Given the evidence for an association between depression and HS, we suggest a large-scale investigation of this patient population that includes a complete medical history, onset of HS in comparison to the onset of depression, and specific measures of disease progress and lifetime management of depression, which may help to increase knowledge about the role of depression in HS and encourage more research in this area. If shared genetic susceptibility is established, aggressive management of depression in patients at risk for HS may reduce disease incidence and severity as well as the psychological burden on patients.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)—a chronic, relapsing, inflammatory disorder involving terminal hair follicles in apocrine gland–rich skin—manifests as tender inflamed nodules that transform into abscesses, sinus tracts, and scarring.1,2 The etiology of HS is multifactorial, encompassing lifestyle, microbiota, hormonal status, and genetic and environmental factors. These factors activate the immune system around the terminal hair follicles and lead to hyperkeratosis of the infundibulum of the hair follicles in intertriginous regions. This progresses to follicular occlusion, stasis, and eventual rupture. Bacterial multiplication within the plugged pilosebaceous units further boosts immune activation. Resident and migrated cells of the innate and adaptive immune system then release proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor, IL-1β, and IL-17, which further enhance immune cell influx and inflammation.3,4 This aberrant immune response propagates the production of deep-seated inflammatory nodules and abscesses.3-8
The estimated prevalence of HS is 1% worldwide.9 It is more prevalent in female and Black patients (0.30%) than White patients (0.09%) and is intermediate in prevalence in the biracial population (0.22%).10 Hidradenitis suppurativa is thought to be associated with lower socioeconomic status (SES). In a retrospective analysis of HS patients (N=375), approximately one-third of patients were Black, had advanced disease, and had a notably lower SES.11 Furthermore, HS has been reported to be associated with systemic inflammation and comorbidities such as morbid obesity (38.3%) and hypertension (39.6%) as well as other metabolic syndrome–related disorders and depression (48.1%).1
Hidradenitis suppurativa may contribute to the risk for depression through its substantial impact on health-related quality of life, which culminates in social withdrawal, unemployment, and suicidal thoughts.12 The high prevalence of depression in individuals with HS1 and its association with systemic inflammation13 increases the likelihood that a common genetic predisposition also may exist between both conditions. Because depression frequently has been discovered as a concomitant diagnosis in patients with HS, we hypothesize that a shared genetic susceptibility also may exist between the 2 disorders. Our study sought to explore data on the co-occurrence of depression with HS, including its demographics and racial data.
Methods
We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Google Scholar using the terms depression and hidradenitis suppurativa to obtain all research articles published from 2000 to 2022. Articles were selected based on relevance to the topic of exploration. English-language articles that directly addressed the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, and co-occurrence of both depression and HS with numerical data were included. Articles were excluded if they did not explore the information of interest on these 2 disorders or did not contain clear statistical data of patients with the 2 concurrent medical conditions.
Results
Twenty-two cross-sectional, prospective, and retrospective studies that fit the search criteria were identified and included in the analysis (eTable).1,14-34 Sixteen (72.7%) studies were cross-sectional, 5 (22.7%) were retrospective, and only 1 (4.5%) was a prospective study. Only 6 of the studies provided racial data,1,14,17,26,28,32 and of them, 4 had predominately White patients,1,14,26,32 whereas the other 2 had predominantly Black patients.17,28


Hidradenitis suppurativa was found to coexist with depression in all the studies, with a prevalence of 1.2% to 48.1%. There also was a higher prevalence of depression in HS patients than in the control patients without HS. Furthermore, a recent study by Wright and colleagues14 stratified the depression prevalence data by age and found a higher prevalence of depression in adults vs children with HS (30% vs 12%).
Comment
Major depression—a chronic and debilitating illness—is the chief cause of disability globally and in the United States alone and has a global lifetime prevalence of 17%.35 In a study of 388 patients diagnosed with depression and 404 community-matched controls who were observed for 10 years, depressed patients had a two-thirds higher likelihood of developing a serious physical illness than controls. The depression-associated elevated risk for serious physical illness persisted after controlling for confounding variables such as alcohol abuse, smoking, and level of physical activity.36 Studies also have demonstrated that HS is more prevalent in Black individuals10 and in individuals of low SES,37 who are mostly the Black and Hispanic populations that experience the highest burden of racial microaggression38 and disparities in health access and outcomes.39,40 The severity and chronicity of major depressive disorder also is higher in Black patients compared with White patients (57% vs 39%).41 Because major depression and HS are most common among Black patients who experience the highest-burden negative financial and health disparities, there may be a shared genetic disposition to both medical conditions.
Moreover, the common detrimental lifestyle choices associated with patients with depression and HS also suggest the possibility of a collective genetic susceptibility. Patients with depression also report increased consumption of alcohol, tobacco, and illicit substances; sedentary lifestyle leading to obesity; and poor compliance with prescribed medical treatment.42 Smoking and obesity are known contributors to the pathogenesis of HS, and their modification also is known to positively impact the disease course. In a retrospective single-cohort study, 50% of obese HS patients (n=35) reported a substantial decrease in disease severity after a reduction of more than 15% in body mass index over 2 years following bariatric surgery (n=35).43 Patients with HS also have reported disease remission following extensive weight loss.44 In addition, evidence has supported smoking cessation in improving the disease course of HS.43 Because these detrimental lifestyle choices are prevalent in both patients with HS and those with depression, a co-genetic susceptibility also may exist.
Furthermore, depression is characterized by a persistent inflammatory state,13,45 similar to HS.46 Elevated levels of a variety of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-6, and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1, have been reported in patients with depression compared with healthy controls.13,45 Further analysis found a positive correlation and a strong association between depression and these inflammatory markers.47 Moreover, adipokines regulate inflammatory responses, and adipokines play a role in the pathogenesis of HS. Adipokine levels such as elevated omentin-1 (a recently identified adipokine) were found to be altered in patients with HS compared with controls.48 Results from clinical studies and meta-analyses of patients with depression also have demonstrated that adipokines are dysregulated in this population,49,50 which may be another potential genetic link between depression and HS.
In addition, genetic susceptibility to depression and HS may be shared because the inflammatory markers that have a strong association with depression also have been found to play an important role in HS treatment and disease severity prediction. In a retrospective cohort study of 404 patients, CRP or IL-6 levels were found to be reliable predictors of HS disease severity, which may explain why anti–tumor necrosis factor antibody regimens such as adalimumab and infliximab have clinically ameliorated disease activity in several cases of HS.51 In a study evaluating these drugs, high baseline levels of high-sensitivity CRP and IL-6 were predictive of patient response to infliximab.52 In a meta-analysis evaluating 20,791 participants, an association was found between concurrent depression and CRP. Furthermore, inflammation measured by high levels of CRP or IL-6 was observed to predict future depression.53 If the same inflammatory markers—CRP and IL-6—both play a major role in the disease activity of depression and HS, then a concurrent genetic predisposition may exist.
Conclusion
Understanding the comorbidities, etiologies, and risk factors for the development and progression of HS is an important step toward improved disease management. Available studies on comorbid depression in HS largely involve White patients, and more studies are needed in patients with skin of color, particularly the Black population, who have the highest prevalence of HS.10 Given the evidence for an association between depression and HS, we suggest a large-scale investigation of this patient population that includes a complete medical history, onset of HS in comparison to the onset of depression, and specific measures of disease progress and lifetime management of depression, which may help to increase knowledge about the role of depression in HS and encourage more research in this area. If shared genetic susceptibility is established, aggressive management of depression in patients at risk for HS may reduce disease incidence and severity as well as the psychological burden on patients.
- Crowley JJ, Mekkes JR, Zouboulis CC, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity with increased risk for systemic comorbidities. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:1561-1565.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Sabat R, Jemec GBE, Matusiak Ł, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2020;6:1-20.
- Wolk K, Warszawska K, Hoeflich C, et al. Deficiency of IL-22 contributes to a chronic inflammatory disease: pathogenetic mechanisms in acne inversa. J Immunol. 2011;186:1228-1239.
- von Laffert M, Helmbold P, Wohlrab J, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa): early inflammatory events at terminal follicles and at interfollicular epidermis. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:533-537.
- Van Der Zee HH, De Ruiter L, Van Den Broecke DG, et al. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: a rationale for targeting TNF-α and IL-1β. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1292-1298.
- Schlapbach C, Hänni T, Yawalkar N, et al. Expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:790-798.
- Kelly G, Hughes R, McGarry T, et al. Dysregulated cytokine expression in lesional and nonlesional skin in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1431-1439.
- Jemec GBE, Kimball AB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: epidemiology and scope of the problem. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5 Suppl 1):S4-S7.
- Garg A, Kirby JS, Lavian J, et al. Sex- and age-adjusted population analysis of prevalence estimates for hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760-764.
- Soliman YS, Hoffman LK, Guzman AK, et al. African American patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have significant health care disparities: a retrospective study. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:334-336.
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101.
- Beatriz Currier M, Nemeroff CB. Inflammation and mood disorders: proinflammatory cytokines and the pathogenesis of depression. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2012;9:212-220.
- Wright S, Strunk A, Garg A. Prevalence of depression among children, adolescents, and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:55-60.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mastroeni S, et al. Correlation between depression, quality of life and clinical severity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:1-6.
- Theut Riis P, Pedersen OB, Sigsgaard V, et al. Prevalence of patients with self-reported hidradenitis suppurativa in a cohort of Danish blood donors: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:774-781.
- Senthilnathan A, Kolli SS, Cardwell LA, et al. Depression in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:1087-1088.
- Pavon Blanco A, Turner MA, Petrof G, et al. To what extent do disease severity and illness perceptions explain depression, anxiety and quality of life in hidradenitis suppurativa? Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:338-345.
- Butt M, Sisic M, Silva C, et al. The associations of depression and coping methods on health-related quality of life for those with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1137-1139.
- Calao M, Wilson JL, Spelman L, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) prevalence, demographics and management pathways in Australia: a population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0200683.
- Ingram JR, Jenkins-Jones S, Knipe DW, et al. Population-based Clinical Practice Research Datalink study using algorithm modelling to identify the true burden of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:917-924.
- Kimball AB, Sundaram M, Gauthier G, et al. The comorbidity burden of hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States: a claims data analysis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018;8:557.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Tiri H, Jokelainen J, Timonen M, et al. Somatic and psychiatric comorbidities of hidradenitis suppurativa in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:514-519.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Kirby JS, Butt M, Esmann S, et al. Association of resilience with depression and health-related quality of life for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1263.
- Egeberg A, Gislason GH, Hansen PR. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:429-434.
- Vangipuram R, Vaidya T, Jandarov R, et al. Factors contributing to depression and chronic pain in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: results from a single-center retrospective review. Dermatology. 2016;232:692-695.
- Rayner L, Jackson K, Turner M, et al. Integrated mental health assessment in a tertiary medical dermatology service: feasibility and the prevalence of common mental disorder. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:201.
- Shavit E, Dreiher J, Freud T, et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in 3207 patients with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online June 9, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:371-376.
- Kurek A, Johanne Peters EM, Sabat R, et al. Depression is a frequent co-morbidity in patients with acne inversa. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:743-749.
- Vazquez BG, Alikhan A, Weaver AL, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa and associated factors: a population-based study of Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:97.
- Onderdijk AJ, Van Der Zee HH, Esmann S, et al. Depression in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online February 20, 2012]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:473-478.
- Matusiak Ł, Bieniek A, Szepietowski JC. Psychophysical aspects of hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:264-268.
- Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, et al. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:617-627.
- Holahan CJ, Pahl SA, Cronkite RC, et al. Depression and vulnerability to incident physical illness across 10 years. J Affect Disord. 2009;123:222-229.
- Deckers IE, Janse IC, van der Zee HH, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is associated with low socioeconomic status (SES): a cross-sectional reference study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:755-759.e1.
- Williams MT, Skinta MD, Kanter JW, et al. A qualitative study of microaggressions against African Americans on predominantly White campuses. BMC Psychol. 2020;8:1-13.
- Dunlop DD, Song J, Lyons JS, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in rates of depression among preretirement adults. Am J Public Health. 2003;93:1945-1952.
- Williams DR, Priest N, Anderson NB. Understanding associations among race, socioeconomic status, and health: patterns and prospects. Health Psychol. 2016;35:407-411.
- Williams DR, González HM, Neighbors H, et al. Prevalence and distribution of major depressive disorder in African Americans, Caribbean Blacks, and Non-Hispanic Whites: results from the National Survey of American Life. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:305-315.
- Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283:506-511.
- Kromann CB, Deckers IE, Esmann S, et al. Risk factors, clinical course and long-term prognosis in hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:819-824.
- Sivanand A, Gulliver WP, Josan CK, et al. Weight loss and dietary interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. J Cutan Med Surg . 2020;24:64-72.
- Raedler TJ. Inflammatory mechanisms in major depressive disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2011;24:519-525.
- Rocha VZ, Libby P. Obesity, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:399-409.
- Davidson KW, Schwartz JE, Kirkland SA, et al. Relation of inflammation to depression and incident coronary heart disease (from the Canadian Nova Scotia Health Survey [NSHS95] Prospective Population Study). Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:755-761.
- González-López MA, Ocejo-Viñals JG, Mata C, et al. Evaluation of serum omentin-1 and apelin concentrations in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:450-454.
- Taylor VH, Macqueen GM. The role of adipokines in understanding the associations between obesity and depression. J Obes. 2010;2010:748048.
- Setayesh L, Ebrahimi R, Pooyan S, et al. The possible mediatory role of adipokines in the association between low carbohydrate diet and depressive symptoms among overweight and obese women. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0257275 .
- Andriano TM, Benesh G, Babbush KM, et al. Serum inflammatory markers and leukocyte profiles accurately describe hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1270-1275.
- Montaudié H, Seitz-Polski B, Cornille A, et al. Interleukin 6 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein are potential predictive markers of response to infliximab in hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;6:156-158.
- Colasanto M, Madigan S, Korczak DJ. Depression and inflammation among children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2020;277:940-948.
- Crowley JJ, Mekkes JR, Zouboulis CC, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity with increased risk for systemic comorbidities. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:1561-1565.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Sabat R, Jemec GBE, Matusiak Ł, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2020;6:1-20.
- Wolk K, Warszawska K, Hoeflich C, et al. Deficiency of IL-22 contributes to a chronic inflammatory disease: pathogenetic mechanisms in acne inversa. J Immunol. 2011;186:1228-1239.
- von Laffert M, Helmbold P, Wohlrab J, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa): early inflammatory events at terminal follicles and at interfollicular epidermis. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:533-537.
- Van Der Zee HH, De Ruiter L, Van Den Broecke DG, et al. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: a rationale for targeting TNF-α and IL-1β. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1292-1298.
- Schlapbach C, Hänni T, Yawalkar N, et al. Expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in lesions of hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:790-798.
- Kelly G, Hughes R, McGarry T, et al. Dysregulated cytokine expression in lesional and nonlesional skin in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1431-1439.
- Jemec GBE, Kimball AB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: epidemiology and scope of the problem. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5 Suppl 1):S4-S7.
- Garg A, Kirby JS, Lavian J, et al. Sex- and age-adjusted population analysis of prevalence estimates for hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:760-764.
- Soliman YS, Hoffman LK, Guzman AK, et al. African American patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have significant health care disparities: a retrospective study. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:334-336.
- Garg A, Malviya N, Strunk A, et al. Comorbidity screening in hidradenitis suppurativa: evidence-based recommendations from the US and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1092-1101.
- Beatriz Currier M, Nemeroff CB. Inflammation and mood disorders: proinflammatory cytokines and the pathogenesis of depression. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2012;9:212-220.
- Wright S, Strunk A, Garg A. Prevalence of depression among children, adolescents, and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:55-60.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mastroeni S, et al. Correlation between depression, quality of life and clinical severity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:1-6.
- Theut Riis P, Pedersen OB, Sigsgaard V, et al. Prevalence of patients with self-reported hidradenitis suppurativa in a cohort of Danish blood donors: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:774-781.
- Senthilnathan A, Kolli SS, Cardwell LA, et al. Depression in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:1087-1088.
- Pavon Blanco A, Turner MA, Petrof G, et al. To what extent do disease severity and illness perceptions explain depression, anxiety and quality of life in hidradenitis suppurativa? Br J Dermatol. 2019;180:338-345.
- Butt M, Sisic M, Silva C, et al. The associations of depression and coping methods on health-related quality of life for those with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1137-1139.
- Calao M, Wilson JL, Spelman L, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) prevalence, demographics and management pathways in Australia: a population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0200683.
- Ingram JR, Jenkins-Jones S, Knipe DW, et al. Population-based Clinical Practice Research Datalink study using algorithm modelling to identify the true burden of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:917-924.
- Kimball AB, Sundaram M, Gauthier G, et al. The comorbidity burden of hidradenitis suppurativa in the United States: a claims data analysis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018;8:557.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Tiri H, Jokelainen J, Timonen M, et al. Somatic and psychiatric comorbidities of hidradenitis suppurativa in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:514-519.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Kirby JS, Butt M, Esmann S, et al. Association of resilience with depression and health-related quality of life for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1263.
- Egeberg A, Gislason GH, Hansen PR. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:429-434.
- Vangipuram R, Vaidya T, Jandarov R, et al. Factors contributing to depression and chronic pain in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: results from a single-center retrospective review. Dermatology. 2016;232:692-695.
- Rayner L, Jackson K, Turner M, et al. Integrated mental health assessment in a tertiary medical dermatology service: feasibility and the prevalence of common mental disorder. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:201.
- Shavit E, Dreiher J, Freud T, et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in 3207 patients with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online June 9, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:371-376.
- Kurek A, Johanne Peters EM, Sabat R, et al. Depression is a frequent co-morbidity in patients with acne inversa. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:743-749.
- Vazquez BG, Alikhan A, Weaver AL, et al. Incidence of hidradenitis suppurativa and associated factors: a population-based study of Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:97.
- Onderdijk AJ, Van Der Zee HH, Esmann S, et al. Depression in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa [published online February 20, 2012]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:473-478.
- Matusiak Ł, Bieniek A, Szepietowski JC. Psychophysical aspects of hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:264-268.
- Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, et al. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:617-627.
- Holahan CJ, Pahl SA, Cronkite RC, et al. Depression and vulnerability to incident physical illness across 10 years. J Affect Disord. 2009;123:222-229.
- Deckers IE, Janse IC, van der Zee HH, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is associated with low socioeconomic status (SES): a cross-sectional reference study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:755-759.e1.
- Williams MT, Skinta MD, Kanter JW, et al. A qualitative study of microaggressions against African Americans on predominantly White campuses. BMC Psychol. 2020;8:1-13.
- Dunlop DD, Song J, Lyons JS, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in rates of depression among preretirement adults. Am J Public Health. 2003;93:1945-1952.
- Williams DR, Priest N, Anderson NB. Understanding associations among race, socioeconomic status, and health: patterns and prospects. Health Psychol. 2016;35:407-411.
- Williams DR, González HM, Neighbors H, et al. Prevalence and distribution of major depressive disorder in African Americans, Caribbean Blacks, and Non-Hispanic Whites: results from the National Survey of American Life. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:305-315.
- Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283:506-511.
- Kromann CB, Deckers IE, Esmann S, et al. Risk factors, clinical course and long-term prognosis in hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross-sectional study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:819-824.
- Sivanand A, Gulliver WP, Josan CK, et al. Weight loss and dietary interventions for hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. J Cutan Med Surg . 2020;24:64-72.
- Raedler TJ. Inflammatory mechanisms in major depressive disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2011;24:519-525.
- Rocha VZ, Libby P. Obesity, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:399-409.
- Davidson KW, Schwartz JE, Kirkland SA, et al. Relation of inflammation to depression and incident coronary heart disease (from the Canadian Nova Scotia Health Survey [NSHS95] Prospective Population Study). Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:755-761.
- González-López MA, Ocejo-Viñals JG, Mata C, et al. Evaluation of serum omentin-1 and apelin concentrations in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021;38:450-454.
- Taylor VH, Macqueen GM. The role of adipokines in understanding the associations between obesity and depression. J Obes. 2010;2010:748048.
- Setayesh L, Ebrahimi R, Pooyan S, et al. The possible mediatory role of adipokines in the association between low carbohydrate diet and depressive symptoms among overweight and obese women. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0257275 .
- Andriano TM, Benesh G, Babbush KM, et al. Serum inflammatory markers and leukocyte profiles accurately describe hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1270-1275.
- Montaudié H, Seitz-Polski B, Cornille A, et al. Interleukin 6 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein are potential predictive markers of response to infliximab in hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;6:156-158.
- Colasanto M, Madigan S, Korczak DJ. Depression and inflammation among children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2020;277:940-948.
Practice Points
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is known to be associated with systemic inflammation and comorbidities, including depression.
- Depression may be a potential contributing factor to HS in affected patients, and studies on HS with comorbid depression in patients with skin of color are lacking.
How Good are Tools to Screen for Spondyloarthritis in Patients With Psoriasis, Uveitis, IBD?
Tools to screen for spondyloarthritis (SpA) among people with the extra-musculoskeletal conditions that commonly co-occur with SpA — psoriasis, uveitis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) — show potential for their use in target populations but have limited generalizability for patients at risk for SpA, according to findings from a scoping review of 18 tools.
Prior to the review comparing available tools, first author Vartika Kesarwani, MBBS, of the University of Connecticut, Farmington, and colleagues wrote that the performance of SpA screening tools in dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastroenterology contexts had not been evaluated.
“Given the evolving landscape of therapeutics for spondyloarthritis, recognizing the full spectrum of disease manifestations in individual patients becomes increasingly important. This knowledge can inform treatment decisions, potentially altering the course of the disease,” corresponding author Joerg Ermann, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
In the study, published on February 1 in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators identified 13 SpA screening tools for psoriasis (screening specifically for psoriatic arthritis), two for uveitis, and three for IBD. All tools with the exception of one for uveitis were patient-oriented questionnaires with an average completion time of less than 5 minutes.
Overall, the researchers found significant variability in the nature of the questions used to identify clinical features of SpA; 15 tools included at least one question on back pain or stiffness; 16 tools had at least one question on joint pain, swelling, or inflammation; 10 included questions about heel or elbow pain; and 10 included questions about swelling of digits.
All 13 of the psoriasis tools were screened for peripheral arthritis, while 10 screened for axial involvement, eight screened for enthesitis, and eight screened for dactylitis.
All three of the IBD tools were screened for axial involvement and peripheral arthritis, and two were screened for enthesitis and dactylitis.
Both of the uveitis tools were screened for axial involvement, but neither was screened for peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, or dactylitis.
Sensitivities in the primary validation groups were similar for the 16 tools for which sensitivities were reported, ranging mainly from 82% to 92% for 11 psoriasis tools, 91% to 96% for uveitis tools, and 83% to 93% for IBD tools.
Specificities for psoriasis tools ranged from 69% to 83% for all but two of the tools, which was 46% for one and 35%-89% for another across three geographical cohorts. For uveitis tools, specificities were 91%-97% for uveitis tools, and for IBD tools, 77%-90%. Most of the secondary validations involved psoriasis tools, and these were generally lower and also more variable.
The Case for a Generic Tool
The relatively few SpA tools for patients with uveitis and IBD, compared with psoriasis, may be attributable to a lack of awareness of the association between these conditions on the part of ophthalmologists and gastroenterologists, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Therefore, a generic SpA screening tool that could apply to any extra-articular manifestation might increase screening across clinical settings and streamline rheumatology referrals, they noted.
The review’s findings were limited by several factors, including the inclusion of only articles in English and the relatively few tools for uveitis and IBD patients, the researchers noted.
The findings suggested that although the performances of the tools are similar, their degree of variability supports the value of a generic tool, they concluded.
Streamlining to Increase Screening
“Compared to the large amount of research in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, relatively little has been done with regard to screening for spondyloarthritis in patients with uveitis or IBD,” Dr. Ermann told this news organization. “Despite the numerous screening tools developed for psoriatic arthritis, no ideal screening tool has emerged, and the implementation of effective screening strategies in clinical practice is challenging,” he said. In the current study, the compartmentalization of research into individual conditions like psoriasis, uveitis, and IBD was notable despite the interconnected nature of these conditions with SpA, he added.
In practice, Dr. Ermann advised clinicians to maintain a high index of suspicion for SpA in patients presenting with psoriasis, uveitis, or IBD and proactively ask patients about symptoms outside their primary specialty.
“Future research should focus on developing a universal spondyloarthritis screening tool that is comprehensive, easily understandable, and can be used across various clinical settings,” he said.
Need for Early Identification and Closer Collaboration
A delay in SpA diagnosis of as little as 6 months can lead to worse outcomes, Rebecca Haberman, MD, a rheumatologist at NYU Langone Health, New York City, said in an interview. “Patients with these conditions may first present to dermatologists, gastroenterologists, and/or ophthalmologists before rheumatologic evaluation. If we can identify these patients early at this stage, we might be able to improve outcomes, but the question remains of how we get these patients to the proper care,” she said.
The review examined the currently available screening tools for use in patients with psoriasis, IBD, and uveitis and highlights the heterogeneity of these tools in terms of use and disease characteristics, as well as the lack of tools for use in gastroenterology and ophthalmology offices, Dr. Haberman said.
The review “proposes several important ideas, such as creating a unified screening tool that can be used across diseases and fields, to reduce confusion by providers and help provide standardization of the referral process to rheumatologists,” she said.
“Even though SpA is prevalent in many patients with psoriasis, IBD, and uveitis, it remains very underdiagnosed, and often referrals to rheumatologists are not made,” Dr. Haberman told this news organization. Diagnostic challenges likely include SpA’s heterogeneous presentation, the specialists’ lack of knowledge regarding the connection between these conditions and joint disease, and time pressures in clinical settings, she said.
“Other practitioners are not always trained to ask about joint pain and often have limited time in their exams to ask additional questions. To overcome this, more collaboration is needed between dermatologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, and rheumatologists, as many of our diseases live in the same family,” Dr. Haberman said.
Improving clinician education and creating relationships can help facilitate questions and referrals, she said. Short, effective screening tools that can be filled out by the patient may also help overcome specialists’ discomfort about asking musculoskeletal-related questions and would save time in the clinical visit, she said.
More research is needed to identify the best screening tools and questions and which are the most highly sensitive and specific, Dr. Haberman said. “This will allow for rheumatologists to see patients who may have SpA earlier in their course without overwhelming the system with new referrals.” In addition, more work is needed on how and whether screening tools are being used in clinical practice, not just in research studies, she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Haberman had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tools to screen for spondyloarthritis (SpA) among people with the extra-musculoskeletal conditions that commonly co-occur with SpA — psoriasis, uveitis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) — show potential for their use in target populations but have limited generalizability for patients at risk for SpA, according to findings from a scoping review of 18 tools.
Prior to the review comparing available tools, first author Vartika Kesarwani, MBBS, of the University of Connecticut, Farmington, and colleagues wrote that the performance of SpA screening tools in dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastroenterology contexts had not been evaluated.
“Given the evolving landscape of therapeutics for spondyloarthritis, recognizing the full spectrum of disease manifestations in individual patients becomes increasingly important. This knowledge can inform treatment decisions, potentially altering the course of the disease,” corresponding author Joerg Ermann, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
In the study, published on February 1 in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators identified 13 SpA screening tools for psoriasis (screening specifically for psoriatic arthritis), two for uveitis, and three for IBD. All tools with the exception of one for uveitis were patient-oriented questionnaires with an average completion time of less than 5 minutes.
Overall, the researchers found significant variability in the nature of the questions used to identify clinical features of SpA; 15 tools included at least one question on back pain or stiffness; 16 tools had at least one question on joint pain, swelling, or inflammation; 10 included questions about heel or elbow pain; and 10 included questions about swelling of digits.
All 13 of the psoriasis tools were screened for peripheral arthritis, while 10 screened for axial involvement, eight screened for enthesitis, and eight screened for dactylitis.
All three of the IBD tools were screened for axial involvement and peripheral arthritis, and two were screened for enthesitis and dactylitis.
Both of the uveitis tools were screened for axial involvement, but neither was screened for peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, or dactylitis.
Sensitivities in the primary validation groups were similar for the 16 tools for which sensitivities were reported, ranging mainly from 82% to 92% for 11 psoriasis tools, 91% to 96% for uveitis tools, and 83% to 93% for IBD tools.
Specificities for psoriasis tools ranged from 69% to 83% for all but two of the tools, which was 46% for one and 35%-89% for another across three geographical cohorts. For uveitis tools, specificities were 91%-97% for uveitis tools, and for IBD tools, 77%-90%. Most of the secondary validations involved psoriasis tools, and these were generally lower and also more variable.
The Case for a Generic Tool
The relatively few SpA tools for patients with uveitis and IBD, compared with psoriasis, may be attributable to a lack of awareness of the association between these conditions on the part of ophthalmologists and gastroenterologists, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Therefore, a generic SpA screening tool that could apply to any extra-articular manifestation might increase screening across clinical settings and streamline rheumatology referrals, they noted.
The review’s findings were limited by several factors, including the inclusion of only articles in English and the relatively few tools for uveitis and IBD patients, the researchers noted.
The findings suggested that although the performances of the tools are similar, their degree of variability supports the value of a generic tool, they concluded.
Streamlining to Increase Screening
“Compared to the large amount of research in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, relatively little has been done with regard to screening for spondyloarthritis in patients with uveitis or IBD,” Dr. Ermann told this news organization. “Despite the numerous screening tools developed for psoriatic arthritis, no ideal screening tool has emerged, and the implementation of effective screening strategies in clinical practice is challenging,” he said. In the current study, the compartmentalization of research into individual conditions like psoriasis, uveitis, and IBD was notable despite the interconnected nature of these conditions with SpA, he added.
In practice, Dr. Ermann advised clinicians to maintain a high index of suspicion for SpA in patients presenting with psoriasis, uveitis, or IBD and proactively ask patients about symptoms outside their primary specialty.
“Future research should focus on developing a universal spondyloarthritis screening tool that is comprehensive, easily understandable, and can be used across various clinical settings,” he said.
Need for Early Identification and Closer Collaboration
A delay in SpA diagnosis of as little as 6 months can lead to worse outcomes, Rebecca Haberman, MD, a rheumatologist at NYU Langone Health, New York City, said in an interview. “Patients with these conditions may first present to dermatologists, gastroenterologists, and/or ophthalmologists before rheumatologic evaluation. If we can identify these patients early at this stage, we might be able to improve outcomes, but the question remains of how we get these patients to the proper care,” she said.
The review examined the currently available screening tools for use in patients with psoriasis, IBD, and uveitis and highlights the heterogeneity of these tools in terms of use and disease characteristics, as well as the lack of tools for use in gastroenterology and ophthalmology offices, Dr. Haberman said.
The review “proposes several important ideas, such as creating a unified screening tool that can be used across diseases and fields, to reduce confusion by providers and help provide standardization of the referral process to rheumatologists,” she said.
“Even though SpA is prevalent in many patients with psoriasis, IBD, and uveitis, it remains very underdiagnosed, and often referrals to rheumatologists are not made,” Dr. Haberman told this news organization. Diagnostic challenges likely include SpA’s heterogeneous presentation, the specialists’ lack of knowledge regarding the connection between these conditions and joint disease, and time pressures in clinical settings, she said.
“Other practitioners are not always trained to ask about joint pain and often have limited time in their exams to ask additional questions. To overcome this, more collaboration is needed between dermatologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, and rheumatologists, as many of our diseases live in the same family,” Dr. Haberman said.
Improving clinician education and creating relationships can help facilitate questions and referrals, she said. Short, effective screening tools that can be filled out by the patient may also help overcome specialists’ discomfort about asking musculoskeletal-related questions and would save time in the clinical visit, she said.
More research is needed to identify the best screening tools and questions and which are the most highly sensitive and specific, Dr. Haberman said. “This will allow for rheumatologists to see patients who may have SpA earlier in their course without overwhelming the system with new referrals.” In addition, more work is needed on how and whether screening tools are being used in clinical practice, not just in research studies, she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Haberman had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tools to screen for spondyloarthritis (SpA) among people with the extra-musculoskeletal conditions that commonly co-occur with SpA — psoriasis, uveitis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) — show potential for their use in target populations but have limited generalizability for patients at risk for SpA, according to findings from a scoping review of 18 tools.
Prior to the review comparing available tools, first author Vartika Kesarwani, MBBS, of the University of Connecticut, Farmington, and colleagues wrote that the performance of SpA screening tools in dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastroenterology contexts had not been evaluated.
“Given the evolving landscape of therapeutics for spondyloarthritis, recognizing the full spectrum of disease manifestations in individual patients becomes increasingly important. This knowledge can inform treatment decisions, potentially altering the course of the disease,” corresponding author Joerg Ermann, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
In the study, published on February 1 in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators identified 13 SpA screening tools for psoriasis (screening specifically for psoriatic arthritis), two for uveitis, and three for IBD. All tools with the exception of one for uveitis were patient-oriented questionnaires with an average completion time of less than 5 minutes.
Overall, the researchers found significant variability in the nature of the questions used to identify clinical features of SpA; 15 tools included at least one question on back pain or stiffness; 16 tools had at least one question on joint pain, swelling, or inflammation; 10 included questions about heel or elbow pain; and 10 included questions about swelling of digits.
All 13 of the psoriasis tools were screened for peripheral arthritis, while 10 screened for axial involvement, eight screened for enthesitis, and eight screened for dactylitis.
All three of the IBD tools were screened for axial involvement and peripheral arthritis, and two were screened for enthesitis and dactylitis.
Both of the uveitis tools were screened for axial involvement, but neither was screened for peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, or dactylitis.
Sensitivities in the primary validation groups were similar for the 16 tools for which sensitivities were reported, ranging mainly from 82% to 92% for 11 psoriasis tools, 91% to 96% for uveitis tools, and 83% to 93% for IBD tools.
Specificities for psoriasis tools ranged from 69% to 83% for all but two of the tools, which was 46% for one and 35%-89% for another across three geographical cohorts. For uveitis tools, specificities were 91%-97% for uveitis tools, and for IBD tools, 77%-90%. Most of the secondary validations involved psoriasis tools, and these were generally lower and also more variable.
The Case for a Generic Tool
The relatively few SpA tools for patients with uveitis and IBD, compared with psoriasis, may be attributable to a lack of awareness of the association between these conditions on the part of ophthalmologists and gastroenterologists, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Therefore, a generic SpA screening tool that could apply to any extra-articular manifestation might increase screening across clinical settings and streamline rheumatology referrals, they noted.
The review’s findings were limited by several factors, including the inclusion of only articles in English and the relatively few tools for uveitis and IBD patients, the researchers noted.
The findings suggested that although the performances of the tools are similar, their degree of variability supports the value of a generic tool, they concluded.
Streamlining to Increase Screening
“Compared to the large amount of research in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, relatively little has been done with regard to screening for spondyloarthritis in patients with uveitis or IBD,” Dr. Ermann told this news organization. “Despite the numerous screening tools developed for psoriatic arthritis, no ideal screening tool has emerged, and the implementation of effective screening strategies in clinical practice is challenging,” he said. In the current study, the compartmentalization of research into individual conditions like psoriasis, uveitis, and IBD was notable despite the interconnected nature of these conditions with SpA, he added.
In practice, Dr. Ermann advised clinicians to maintain a high index of suspicion for SpA in patients presenting with psoriasis, uveitis, or IBD and proactively ask patients about symptoms outside their primary specialty.
“Future research should focus on developing a universal spondyloarthritis screening tool that is comprehensive, easily understandable, and can be used across various clinical settings,” he said.
Need for Early Identification and Closer Collaboration
A delay in SpA diagnosis of as little as 6 months can lead to worse outcomes, Rebecca Haberman, MD, a rheumatologist at NYU Langone Health, New York City, said in an interview. “Patients with these conditions may first present to dermatologists, gastroenterologists, and/or ophthalmologists before rheumatologic evaluation. If we can identify these patients early at this stage, we might be able to improve outcomes, but the question remains of how we get these patients to the proper care,” she said.
The review examined the currently available screening tools for use in patients with psoriasis, IBD, and uveitis and highlights the heterogeneity of these tools in terms of use and disease characteristics, as well as the lack of tools for use in gastroenterology and ophthalmology offices, Dr. Haberman said.
The review “proposes several important ideas, such as creating a unified screening tool that can be used across diseases and fields, to reduce confusion by providers and help provide standardization of the referral process to rheumatologists,” she said.
“Even though SpA is prevalent in many patients with psoriasis, IBD, and uveitis, it remains very underdiagnosed, and often referrals to rheumatologists are not made,” Dr. Haberman told this news organization. Diagnostic challenges likely include SpA’s heterogeneous presentation, the specialists’ lack of knowledge regarding the connection between these conditions and joint disease, and time pressures in clinical settings, she said.
“Other practitioners are not always trained to ask about joint pain and often have limited time in their exams to ask additional questions. To overcome this, more collaboration is needed between dermatologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, and rheumatologists, as many of our diseases live in the same family,” Dr. Haberman said.
Improving clinician education and creating relationships can help facilitate questions and referrals, she said. Short, effective screening tools that can be filled out by the patient may also help overcome specialists’ discomfort about asking musculoskeletal-related questions and would save time in the clinical visit, she said.
More research is needed to identify the best screening tools and questions and which are the most highly sensitive and specific, Dr. Haberman said. “This will allow for rheumatologists to see patients who may have SpA earlier in their course without overwhelming the system with new referrals.” In addition, more work is needed on how and whether screening tools are being used in clinical practice, not just in research studies, she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Haberman had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Evaluates Factors Driving Fatigue in Patients With Psoriasis, PsA
TOPLINE:
Many factors may influence fatigue in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), researchers report.
METHODOLOGY:
- The individual components of fatigue in psoriasis and PsA have not been examined thoroughly.
- Researchers drew from the nationwide prospective Danish Skin Cohort to identify 2741 adults with dermatologist-diagnosed psoriasis (of which 593 also had PsA) and 3788 controls in the general population.
- All adults in the analysis completed the multidimensional fatigue inventory (MIF-20), a validated 20-item tool that measures five dimensions of fatigue: General fatigue, physical fatigue, reduced activity, reduced motivation, and mental fatigue. A higher score indicates more severe fatigue.
- All adults were also asked about their current intensity of joint pain over the previous 7 days, severity of pruritus and skin pain over the previous 24 hours, and sleep problems over the previous 72 hours on a numerical rating scale (NRS). The researchers applied linear regression models to continuous outcomes and adjusted for age, sex, socioeconomic status, psoriasis severity, and joint pain intensity, and beta coefficients (β) for the slopes were estimated with 95% CIs.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with the general population, higher total MFI-20 scores were observed for psoriasis and PsA, respectively. However, on the adjusted analysis, the impact on total fatigue was greatest for those with PsA (β = 5.23; 95% CI, 3.55-6.90), followed by psoriasis (β = 2.10; 95% CI, 0.96-3.25) compared with the general population (P trend < .0001).
- Increasing age was associated with a lower impact on total fatigue in psoriasis (β = −0.13; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.08) and in PsA (β = −0.10; 95% CI, −0.19 to −0.01).
- Among patients with psoriasis with or without PsA, increasing joint pain intensity was associated with overall fatigue (β = 2.23; 95% CI, 2.03-2.44) for each one-point increase in joint pain on the NRS.
- In other findings, greater intensity of itch was associated with higher fatigue scores for both psoriasis and PsA, while skin pain was significantly associated with fatigue in PsA (β = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.08-1.22) but not in psoriasis without PsA (P = .2043).
IN PRACTICE:
“The when treating psoriasis, rather than focusing on objective severity measures alone,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Alexander Egeberg, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Bispebjerg Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers were unable to assess whether the pain was inflammatory or noninflammatory or the number of affected joints. They also lacked information about the use of methotrexate, which commonly causes fatigue.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Egeberg is now an employee at LEO Pharma. He has received research funding from Pfizer, Eli Lilly, the Danish National Psoriasis Foundation, and the Royal Hofbundtmager Aage Bang Foundation, and honoraria as a consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Leo Pharma, Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd., Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Novartis, UCB, Union Therapeutics, Horizon Therapeutics, Galderma, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Three of the coauthors reported being a consultant to, an adviser for, and/or having received research support from many pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Many factors may influence fatigue in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), researchers report.
METHODOLOGY:
- The individual components of fatigue in psoriasis and PsA have not been examined thoroughly.
- Researchers drew from the nationwide prospective Danish Skin Cohort to identify 2741 adults with dermatologist-diagnosed psoriasis (of which 593 also had PsA) and 3788 controls in the general population.
- All adults in the analysis completed the multidimensional fatigue inventory (MIF-20), a validated 20-item tool that measures five dimensions of fatigue: General fatigue, physical fatigue, reduced activity, reduced motivation, and mental fatigue. A higher score indicates more severe fatigue.
- All adults were also asked about their current intensity of joint pain over the previous 7 days, severity of pruritus and skin pain over the previous 24 hours, and sleep problems over the previous 72 hours on a numerical rating scale (NRS). The researchers applied linear regression models to continuous outcomes and adjusted for age, sex, socioeconomic status, psoriasis severity, and joint pain intensity, and beta coefficients (β) for the slopes were estimated with 95% CIs.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with the general population, higher total MFI-20 scores were observed for psoriasis and PsA, respectively. However, on the adjusted analysis, the impact on total fatigue was greatest for those with PsA (β = 5.23; 95% CI, 3.55-6.90), followed by psoriasis (β = 2.10; 95% CI, 0.96-3.25) compared with the general population (P trend < .0001).
- Increasing age was associated with a lower impact on total fatigue in psoriasis (β = −0.13; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.08) and in PsA (β = −0.10; 95% CI, −0.19 to −0.01).
- Among patients with psoriasis with or without PsA, increasing joint pain intensity was associated with overall fatigue (β = 2.23; 95% CI, 2.03-2.44) for each one-point increase in joint pain on the NRS.
- In other findings, greater intensity of itch was associated with higher fatigue scores for both psoriasis and PsA, while skin pain was significantly associated with fatigue in PsA (β = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.08-1.22) but not in psoriasis without PsA (P = .2043).
IN PRACTICE:
“The when treating psoriasis, rather than focusing on objective severity measures alone,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Alexander Egeberg, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Bispebjerg Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers were unable to assess whether the pain was inflammatory or noninflammatory or the number of affected joints. They also lacked information about the use of methotrexate, which commonly causes fatigue.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Egeberg is now an employee at LEO Pharma. He has received research funding from Pfizer, Eli Lilly, the Danish National Psoriasis Foundation, and the Royal Hofbundtmager Aage Bang Foundation, and honoraria as a consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Leo Pharma, Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd., Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Novartis, UCB, Union Therapeutics, Horizon Therapeutics, Galderma, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Three of the coauthors reported being a consultant to, an adviser for, and/or having received research support from many pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Many factors may influence fatigue in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), researchers report.
METHODOLOGY:
- The individual components of fatigue in psoriasis and PsA have not been examined thoroughly.
- Researchers drew from the nationwide prospective Danish Skin Cohort to identify 2741 adults with dermatologist-diagnosed psoriasis (of which 593 also had PsA) and 3788 controls in the general population.
- All adults in the analysis completed the multidimensional fatigue inventory (MIF-20), a validated 20-item tool that measures five dimensions of fatigue: General fatigue, physical fatigue, reduced activity, reduced motivation, and mental fatigue. A higher score indicates more severe fatigue.
- All adults were also asked about their current intensity of joint pain over the previous 7 days, severity of pruritus and skin pain over the previous 24 hours, and sleep problems over the previous 72 hours on a numerical rating scale (NRS). The researchers applied linear regression models to continuous outcomes and adjusted for age, sex, socioeconomic status, psoriasis severity, and joint pain intensity, and beta coefficients (β) for the slopes were estimated with 95% CIs.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with the general population, higher total MFI-20 scores were observed for psoriasis and PsA, respectively. However, on the adjusted analysis, the impact on total fatigue was greatest for those with PsA (β = 5.23; 95% CI, 3.55-6.90), followed by psoriasis (β = 2.10; 95% CI, 0.96-3.25) compared with the general population (P trend < .0001).
- Increasing age was associated with a lower impact on total fatigue in psoriasis (β = −0.13; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.08) and in PsA (β = −0.10; 95% CI, −0.19 to −0.01).
- Among patients with psoriasis with or without PsA, increasing joint pain intensity was associated with overall fatigue (β = 2.23; 95% CI, 2.03-2.44) for each one-point increase in joint pain on the NRS.
- In other findings, greater intensity of itch was associated with higher fatigue scores for both psoriasis and PsA, while skin pain was significantly associated with fatigue in PsA (β = 0.65; 95% CI, 0.08-1.22) but not in psoriasis without PsA (P = .2043).
IN PRACTICE:
“The when treating psoriasis, rather than focusing on objective severity measures alone,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Alexander Egeberg, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Bispebjerg Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers were unable to assess whether the pain was inflammatory or noninflammatory or the number of affected joints. They also lacked information about the use of methotrexate, which commonly causes fatigue.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Egeberg is now an employee at LEO Pharma. He has received research funding from Pfizer, Eli Lilly, the Danish National Psoriasis Foundation, and the Royal Hofbundtmager Aage Bang Foundation, and honoraria as a consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Leo Pharma, Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd., Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Novartis, UCB, Union Therapeutics, Horizon Therapeutics, Galderma, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Three of the coauthors reported being a consultant to, an adviser for, and/or having received research support from many pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves 10th Humira Biosimilar, With Interchangeability
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved the first interchangeable, high-concentration, citrate-free adalimumab biosimilar, adalimumab-ryvk (Simlandi).
This is the 10th adalimumab biosimilar approved by the regulatory agency and the first biosimilar approval in the US market for the Icelandic pharmaceutical company Alvotech in partnership with Teva Pharmaceuticals.
“An interchangeable citrate-free, high-concentration biosimilar adalimumab has the potential to change the market dynamics in a rapidly evolving environment for biosimilars in the U.S.,” said Robert Wessman, chairman and CEO of Alvotech, in a company press release on February 23.
Adalimumab-ryvk was approved in the European Union in 2021 and in Australia and Canada in 2022.
Adalimumab-ryvk is indicated for adults with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis. In pediatric patients, it is indicated for polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children 2 years of age and older and Crohn’s disease in children 6 years of age and older.
Adalimumab-ryvk is the third Humira biosimilar overall granted interchangeability status, which allows pharmacists (depending on state law) to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician. Adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim, and adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), manufactured by Pfizer, were previously granted interchangeability status; however, they both are interchangeable with the low-concentration formulation of Humira, which make up only an estimated 15% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report by Goodroot.
Adalimumab-ryvk will be launched “imminently” in the United States, according to the press release, but no specific dates were provided. It is also not yet known how the biosimilar will be priced compared with Humira. Other adalimumab biosimilars have launched with discounts from 5% to 85% of Humira’s list price.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved the first interchangeable, high-concentration, citrate-free adalimumab biosimilar, adalimumab-ryvk (Simlandi).
This is the 10th adalimumab biosimilar approved by the regulatory agency and the first biosimilar approval in the US market for the Icelandic pharmaceutical company Alvotech in partnership with Teva Pharmaceuticals.
“An interchangeable citrate-free, high-concentration biosimilar adalimumab has the potential to change the market dynamics in a rapidly evolving environment for biosimilars in the U.S.,” said Robert Wessman, chairman and CEO of Alvotech, in a company press release on February 23.
Adalimumab-ryvk was approved in the European Union in 2021 and in Australia and Canada in 2022.
Adalimumab-ryvk is indicated for adults with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis. In pediatric patients, it is indicated for polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children 2 years of age and older and Crohn’s disease in children 6 years of age and older.
Adalimumab-ryvk is the third Humira biosimilar overall granted interchangeability status, which allows pharmacists (depending on state law) to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician. Adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim, and adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), manufactured by Pfizer, were previously granted interchangeability status; however, they both are interchangeable with the low-concentration formulation of Humira, which make up only an estimated 15% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report by Goodroot.
Adalimumab-ryvk will be launched “imminently” in the United States, according to the press release, but no specific dates were provided. It is also not yet known how the biosimilar will be priced compared with Humira. Other adalimumab biosimilars have launched with discounts from 5% to 85% of Humira’s list price.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved the first interchangeable, high-concentration, citrate-free adalimumab biosimilar, adalimumab-ryvk (Simlandi).
This is the 10th adalimumab biosimilar approved by the regulatory agency and the first biosimilar approval in the US market for the Icelandic pharmaceutical company Alvotech in partnership with Teva Pharmaceuticals.
“An interchangeable citrate-free, high-concentration biosimilar adalimumab has the potential to change the market dynamics in a rapidly evolving environment for biosimilars in the U.S.,” said Robert Wessman, chairman and CEO of Alvotech, in a company press release on February 23.
Adalimumab-ryvk was approved in the European Union in 2021 and in Australia and Canada in 2022.
Adalimumab-ryvk is indicated for adults with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis. In pediatric patients, it is indicated for polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children 2 years of age and older and Crohn’s disease in children 6 years of age and older.
Adalimumab-ryvk is the third Humira biosimilar overall granted interchangeability status, which allows pharmacists (depending on state law) to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician. Adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim, and adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), manufactured by Pfizer, were previously granted interchangeability status; however, they both are interchangeable with the low-concentration formulation of Humira, which make up only an estimated 15% of Humira prescriptions, according to a report by Goodroot.
Adalimumab-ryvk will be launched “imminently” in the United States, according to the press release, but no specific dates were provided. It is also not yet known how the biosimilar will be priced compared with Humira. Other adalimumab biosimilars have launched with discounts from 5% to 85% of Humira’s list price.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ixekizumab’s Final Safety Results Reported Across 25 Trials in Psoriasis, PsA, Axial SpA
TOPLINE:
Pooled data from 9225 adults with psoriasis (PsO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) showed no new safety signals with extended exposure to ixekizumab (Taltz).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers combined patient data from 25 randomized, controlled trials of the safety and effectiveness of at least one dose of ixekizumab in adults with PsO (n = 6892), PsA (n = 1401), and axSpA (n = 932).
- The study population included patients with a mean age of approximately 43-49 years; at least 49% were male and at least 74% were White across the three conditions.
- Patients’ median duration of ixekizumab exposure was 1.3 years for PsO, 1.4 years for PsA, and 2.7 years for axSpA, with data up to 6 years for PsO and up to 3 years for PsA and axSpA.
- The primary outcomes were exposure-adjusted incidence rates per 100 patient-years overall and at successive year intervals for treatment-emergent adverse events, serious adverse events, and selected adverse events of interest.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence rate per 100 person-years for any treatment-emergent adverse event was 32.5 for PsO, 50.3 for PsA, and 38.0 for axSpA; these did not increase with lengthier exposure.
- The incidence rates for serious adverse events for patients with PsO, PsA, or axSpA were 5.4, 6.0, and 4.8 per 100 person-years, respectively.
- A total of 45 deaths were reported across the studies, including 36 in patients with PsO, six with PsA, and three with axSpA.
- Infections were the most common treatment-emergent adverse events across all patient groups, reported in patients at rates of 62.5% with PsO, 52.4% with PsA, and 57.9% with axSpA; incidence of infections did not increase over time.
IN PRACTICE:
“These final, end-of-study program results surrounding the long-term use of [ixekizumab] in patients with PsO, PsA, and axSpA should serve as an important point of reference for physicians considering [ixekizumab],” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Atul Deodhar, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. The study was published online on February 12 in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the small sample sizes and short treatment durations in some studies, the primarily White study population, the inability to stratify risk, the lack of a long-term comparator, and potential survivor bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The studies in the review were supported by Eli Lilly. Lead author Dr. Deodhar disclosed an honorarium and serving on advisory boards at AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, as well as research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Pooled data from 9225 adults with psoriasis (PsO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) showed no new safety signals with extended exposure to ixekizumab (Taltz).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers combined patient data from 25 randomized, controlled trials of the safety and effectiveness of at least one dose of ixekizumab in adults with PsO (n = 6892), PsA (n = 1401), and axSpA (n = 932).
- The study population included patients with a mean age of approximately 43-49 years; at least 49% were male and at least 74% were White across the three conditions.
- Patients’ median duration of ixekizumab exposure was 1.3 years for PsO, 1.4 years for PsA, and 2.7 years for axSpA, with data up to 6 years for PsO and up to 3 years for PsA and axSpA.
- The primary outcomes were exposure-adjusted incidence rates per 100 patient-years overall and at successive year intervals for treatment-emergent adverse events, serious adverse events, and selected adverse events of interest.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence rate per 100 person-years for any treatment-emergent adverse event was 32.5 for PsO, 50.3 for PsA, and 38.0 for axSpA; these did not increase with lengthier exposure.
- The incidence rates for serious adverse events for patients with PsO, PsA, or axSpA were 5.4, 6.0, and 4.8 per 100 person-years, respectively.
- A total of 45 deaths were reported across the studies, including 36 in patients with PsO, six with PsA, and three with axSpA.
- Infections were the most common treatment-emergent adverse events across all patient groups, reported in patients at rates of 62.5% with PsO, 52.4% with PsA, and 57.9% with axSpA; incidence of infections did not increase over time.
IN PRACTICE:
“These final, end-of-study program results surrounding the long-term use of [ixekizumab] in patients with PsO, PsA, and axSpA should serve as an important point of reference for physicians considering [ixekizumab],” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Atul Deodhar, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. The study was published online on February 12 in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the small sample sizes and short treatment durations in some studies, the primarily White study population, the inability to stratify risk, the lack of a long-term comparator, and potential survivor bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The studies in the review were supported by Eli Lilly. Lead author Dr. Deodhar disclosed an honorarium and serving on advisory boards at AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, as well as research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Pooled data from 9225 adults with psoriasis (PsO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) showed no new safety signals with extended exposure to ixekizumab (Taltz).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers combined patient data from 25 randomized, controlled trials of the safety and effectiveness of at least one dose of ixekizumab in adults with PsO (n = 6892), PsA (n = 1401), and axSpA (n = 932).
- The study population included patients with a mean age of approximately 43-49 years; at least 49% were male and at least 74% were White across the three conditions.
- Patients’ median duration of ixekizumab exposure was 1.3 years for PsO, 1.4 years for PsA, and 2.7 years for axSpA, with data up to 6 years for PsO and up to 3 years for PsA and axSpA.
- The primary outcomes were exposure-adjusted incidence rates per 100 patient-years overall and at successive year intervals for treatment-emergent adverse events, serious adverse events, and selected adverse events of interest.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence rate per 100 person-years for any treatment-emergent adverse event was 32.5 for PsO, 50.3 for PsA, and 38.0 for axSpA; these did not increase with lengthier exposure.
- The incidence rates for serious adverse events for patients with PsO, PsA, or axSpA were 5.4, 6.0, and 4.8 per 100 person-years, respectively.
- A total of 45 deaths were reported across the studies, including 36 in patients with PsO, six with PsA, and three with axSpA.
- Infections were the most common treatment-emergent adverse events across all patient groups, reported in patients at rates of 62.5% with PsO, 52.4% with PsA, and 57.9% with axSpA; incidence of infections did not increase over time.
IN PRACTICE:
“These final, end-of-study program results surrounding the long-term use of [ixekizumab] in patients with PsO, PsA, and axSpA should serve as an important point of reference for physicians considering [ixekizumab],” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Atul Deodhar, MD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. The study was published online on February 12 in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the small sample sizes and short treatment durations in some studies, the primarily White study population, the inability to stratify risk, the lack of a long-term comparator, and potential survivor bias.
DISCLOSURES:
The studies in the review were supported by Eli Lilly. Lead author Dr. Deodhar disclosed an honorarium and serving on advisory boards at AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, as well as research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of Biologics for Psoriasis Found to Confer a Survival Benefit
Among patients with psoriasis, the risk of mortality was strongly associated with hepatic injury, cardiovascular disease, and psychiatric affective disorders, but was reduced among those who received systemic therapy with biologics, researchers from Canada report.
Those are key findings from a large retrospective registry study of patients with psoriasis, published in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting approximately 3% of the western populations, bears a higher risk of mortality compared to healthy individuals, possibly by inducing systemic inflammation associated with numerous comorbidities, especially cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, and others,” wrote corresponding author Robert Gniadecki, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology at the University of Alberta, Canada, and colleagues. “It has been argued that the use of systemic immunomodulatory agents quenches systemic inflammation and potentially improves patient survival. However, the evidence to support this hypothesis is limited.”
To investigate the impact of comorbidities and systemic therapies on all-cause mortality in psoriasis, the researchers used the Alberta Health Services Data Repository of Reporting database from January 1, 2012, to June 1, 2019, which represents a population base of 4.47 million individuals. They extracted data on 18,618 psoriasis cases and 55,854 controls, stratified cases according to the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), a surrogate measure for comorbidity burden, and by the type of therapy received, and conducted statistical analyses including Cox proportional hazards regression to determine absolute hazard ratios representing relative effects of specific demographic and comorbidity factors on mortality within groups.
The median age in both cohorts was 48 years, and 51% were male. The researchers observed that mortality in the psoriasis cohort was significantly higher than in the controls (5.7% vs. 3.8%, respectively; P < .05), with a median age at the time of death of 72 vs. 74.4 years.
The CCI and comorbidities strongly predicted mortality, especially drug-induced liver injury (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78), bipolar disorder and suicidal ideation (HR, 1.24-1.58), and major cardiovascular diseases, which included myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), and cerebrovascular disease (CVA) (HR, 1.2-1.4).
Among patients in the psoriasis cohort, survival of those treated with biologic agents was higher than in controls, even after matching for CCI (3.2% vs. 4.4%, respectively, P < .05). “These patients also exhibit reduced overall mortality compared to those treated with methotrexate or topical agents,” Dr. Gniadecki and colleagues wrote. “There was no difference in mortality between methotrexate patients and the topical therapy patients, but any of those treatment groups had superior survival compared to the no-treatment cohort.”
They added that despite better survival among patients treated with biologic agents, no significant improvements were detected in their comorbidity profiles. “Notably, the frequency of major cardiovascular disease (MI, CHF, CVA) was the same as in the controls, and overall, the frequency of diseases coded as cardiovascular was slightly increased,” they wrote.
The fact that some factors could not be measured, including the type and severity of psoriasis, response to treatment, smoking history, and alcohol intake, was a study limitation, they noted.
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was asked to comment on the analysis, said the study confirms prior work indicating that having psoriasis is a predictor of mortality. In addition, “there is a strong healthy user affect among patients who take and stay on biologics for psoriasis,” he told this news organization.
“The results are encouraging but are not able to establish a causal relationship between treating psoriasis with biologics and lowering mortality risk. Ultimately, randomized comparative trials will be needed to determine which approach or approaches to treating psoriasis, if any, lower the risk of psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and mortality,” said Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved with the study.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, said that “data such as these enable us to rationalize the cost of our fleet of biologics, as managing the outpatient/inpatient burden of many of these comorbidities will actually drain the healthcare system, more so than managing psoriasis in the first place. Certainly other interventions to address the well known comorbidities, such as cardiovascular and hepatic, are warranted, but what if you could prevent the problem in the first place? To be continued for that answer.”
The study was funded by Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Alberta Innovates, and by a Health Sciences TD Bank Studentship Award. Dr. Gniadecki reported conducting clinical trials for Bausch Health, AbbVie and Janssen, and he has received honoraria as consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Kyowa Kirin, Sun Pharma and Sanofi. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies. He is on the board of directors for the International Psoriasis Council and the Medical Dermatology Society. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a speaker for Janssen and Bristol Myers Squibb. He has received grants from Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Lilly, and has served as an advisor for Arcutis, Dermavant, and Janssen.
Among patients with psoriasis, the risk of mortality was strongly associated with hepatic injury, cardiovascular disease, and psychiatric affective disorders, but was reduced among those who received systemic therapy with biologics, researchers from Canada report.
Those are key findings from a large retrospective registry study of patients with psoriasis, published in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting approximately 3% of the western populations, bears a higher risk of mortality compared to healthy individuals, possibly by inducing systemic inflammation associated with numerous comorbidities, especially cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, and others,” wrote corresponding author Robert Gniadecki, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology at the University of Alberta, Canada, and colleagues. “It has been argued that the use of systemic immunomodulatory agents quenches systemic inflammation and potentially improves patient survival. However, the evidence to support this hypothesis is limited.”
To investigate the impact of comorbidities and systemic therapies on all-cause mortality in psoriasis, the researchers used the Alberta Health Services Data Repository of Reporting database from January 1, 2012, to June 1, 2019, which represents a population base of 4.47 million individuals. They extracted data on 18,618 psoriasis cases and 55,854 controls, stratified cases according to the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), a surrogate measure for comorbidity burden, and by the type of therapy received, and conducted statistical analyses including Cox proportional hazards regression to determine absolute hazard ratios representing relative effects of specific demographic and comorbidity factors on mortality within groups.
The median age in both cohorts was 48 years, and 51% were male. The researchers observed that mortality in the psoriasis cohort was significantly higher than in the controls (5.7% vs. 3.8%, respectively; P < .05), with a median age at the time of death of 72 vs. 74.4 years.
The CCI and comorbidities strongly predicted mortality, especially drug-induced liver injury (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78), bipolar disorder and suicidal ideation (HR, 1.24-1.58), and major cardiovascular diseases, which included myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), and cerebrovascular disease (CVA) (HR, 1.2-1.4).
Among patients in the psoriasis cohort, survival of those treated with biologic agents was higher than in controls, even after matching for CCI (3.2% vs. 4.4%, respectively, P < .05). “These patients also exhibit reduced overall mortality compared to those treated with methotrexate or topical agents,” Dr. Gniadecki and colleagues wrote. “There was no difference in mortality between methotrexate patients and the topical therapy patients, but any of those treatment groups had superior survival compared to the no-treatment cohort.”
They added that despite better survival among patients treated with biologic agents, no significant improvements were detected in their comorbidity profiles. “Notably, the frequency of major cardiovascular disease (MI, CHF, CVA) was the same as in the controls, and overall, the frequency of diseases coded as cardiovascular was slightly increased,” they wrote.
The fact that some factors could not be measured, including the type and severity of psoriasis, response to treatment, smoking history, and alcohol intake, was a study limitation, they noted.
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was asked to comment on the analysis, said the study confirms prior work indicating that having psoriasis is a predictor of mortality. In addition, “there is a strong healthy user affect among patients who take and stay on biologics for psoriasis,” he told this news organization.
“The results are encouraging but are not able to establish a causal relationship between treating psoriasis with biologics and lowering mortality risk. Ultimately, randomized comparative trials will be needed to determine which approach or approaches to treating psoriasis, if any, lower the risk of psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and mortality,” said Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved with the study.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, said that “data such as these enable us to rationalize the cost of our fleet of biologics, as managing the outpatient/inpatient burden of many of these comorbidities will actually drain the healthcare system, more so than managing psoriasis in the first place. Certainly other interventions to address the well known comorbidities, such as cardiovascular and hepatic, are warranted, but what if you could prevent the problem in the first place? To be continued for that answer.”
The study was funded by Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Alberta Innovates, and by a Health Sciences TD Bank Studentship Award. Dr. Gniadecki reported conducting clinical trials for Bausch Health, AbbVie and Janssen, and he has received honoraria as consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Kyowa Kirin, Sun Pharma and Sanofi. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies. He is on the board of directors for the International Psoriasis Council and the Medical Dermatology Society. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a speaker for Janssen and Bristol Myers Squibb. He has received grants from Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Lilly, and has served as an advisor for Arcutis, Dermavant, and Janssen.
Among patients with psoriasis, the risk of mortality was strongly associated with hepatic injury, cardiovascular disease, and psychiatric affective disorders, but was reduced among those who received systemic therapy with biologics, researchers from Canada report.
Those are key findings from a large retrospective registry study of patients with psoriasis, published in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting approximately 3% of the western populations, bears a higher risk of mortality compared to healthy individuals, possibly by inducing systemic inflammation associated with numerous comorbidities, especially cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, and others,” wrote corresponding author Robert Gniadecki, MD, PhD, of the division of dermatology at the University of Alberta, Canada, and colleagues. “It has been argued that the use of systemic immunomodulatory agents quenches systemic inflammation and potentially improves patient survival. However, the evidence to support this hypothesis is limited.”
To investigate the impact of comorbidities and systemic therapies on all-cause mortality in psoriasis, the researchers used the Alberta Health Services Data Repository of Reporting database from January 1, 2012, to June 1, 2019, which represents a population base of 4.47 million individuals. They extracted data on 18,618 psoriasis cases and 55,854 controls, stratified cases according to the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), a surrogate measure for comorbidity burden, and by the type of therapy received, and conducted statistical analyses including Cox proportional hazards regression to determine absolute hazard ratios representing relative effects of specific demographic and comorbidity factors on mortality within groups.
The median age in both cohorts was 48 years, and 51% were male. The researchers observed that mortality in the psoriasis cohort was significantly higher than in the controls (5.7% vs. 3.8%, respectively; P < .05), with a median age at the time of death of 72 vs. 74.4 years.
The CCI and comorbidities strongly predicted mortality, especially drug-induced liver injury (hazard ratio [HR], 1.78), bipolar disorder and suicidal ideation (HR, 1.24-1.58), and major cardiovascular diseases, which included myocardial infarction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF), and cerebrovascular disease (CVA) (HR, 1.2-1.4).
Among patients in the psoriasis cohort, survival of those treated with biologic agents was higher than in controls, even after matching for CCI (3.2% vs. 4.4%, respectively, P < .05). “These patients also exhibit reduced overall mortality compared to those treated with methotrexate or topical agents,” Dr. Gniadecki and colleagues wrote. “There was no difference in mortality between methotrexate patients and the topical therapy patients, but any of those treatment groups had superior survival compared to the no-treatment cohort.”
They added that despite better survival among patients treated with biologic agents, no significant improvements were detected in their comorbidity profiles. “Notably, the frequency of major cardiovascular disease (MI, CHF, CVA) was the same as in the controls, and overall, the frequency of diseases coded as cardiovascular was slightly increased,” they wrote.
The fact that some factors could not be measured, including the type and severity of psoriasis, response to treatment, smoking history, and alcohol intake, was a study limitation, they noted.
Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was asked to comment on the analysis, said the study confirms prior work indicating that having psoriasis is a predictor of mortality. In addition, “there is a strong healthy user affect among patients who take and stay on biologics for psoriasis,” he told this news organization.
“The results are encouraging but are not able to establish a causal relationship between treating psoriasis with biologics and lowering mortality risk. Ultimately, randomized comparative trials will be needed to determine which approach or approaches to treating psoriasis, if any, lower the risk of psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and mortality,” said Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved with the study.
Asked to comment on the results, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was not involved with the study, said that “data such as these enable us to rationalize the cost of our fleet of biologics, as managing the outpatient/inpatient burden of many of these comorbidities will actually drain the healthcare system, more so than managing psoriasis in the first place. Certainly other interventions to address the well known comorbidities, such as cardiovascular and hepatic, are warranted, but what if you could prevent the problem in the first place? To be continued for that answer.”
The study was funded by Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Alberta Innovates, and by a Health Sciences TD Bank Studentship Award. Dr. Gniadecki reported conducting clinical trials for Bausch Health, AbbVie and Janssen, and he has received honoraria as consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mallinckrodt, Novartis, Kyowa Kirin, Sun Pharma and Sanofi. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies. He is on the board of directors for the International Psoriasis Council and the Medical Dermatology Society. Dr. Friedman disclosed that he is a speaker for Janssen and Bristol Myers Squibb. He has received grants from Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Lilly, and has served as an advisor for Arcutis, Dermavant, and Janssen.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Pretreatment Lab Testing for Chronic Skin Diseases Diverges From Guidelines
in a national commercial insurance claims database.
Because of concerns for the potential reactivation of tuberculosis or hepatitis B or C, or for an increased risk for infections, myelosuppression, and hepatoxicity in the wake of immunomodulator use, some medical societies recommend screening patients for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and tuberculosis before starting these medications, wrote Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
“Conducting this study was crucial because of the increasing use of systemic immunomodulatory agents for chronic inflammatory skin diseases and the recognized need for pretreatment testing to prevent complications,” coauthor Denys Shay, a PhD candidate in population health sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, said in an interview.
“Despite recommendations from professional societies, there was a lack of clarity on how consistently these guidelines were being followed in the United States. This study aimed to fill that gap in knowledge, providing a comprehensive view of current practices and highlighting areas for improvement,” he said.
In the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology, he and his coauthors identified 122,308 adults in the United States with psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, or atopic dermatitis who started an immunomodulatory agent, including methotrexate (28,684 patients), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors (40,965), ustekinumab (12,841), interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors (6116), IL-17A inhibitors (9799), dupilumab (7787), and apremilast (16,116). The data were from a commercial insurance claims database from December 31, 2002, to December 31, 2020.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who underwent recommended screening lab tests including tuberculosis, hepatitis, liver function, complete blood cell counts (CBCs), and lipid panels within 6 months before treatment initiation and during the first 2 years of treatment. The median age of the study population was 49 years, and 52.1% were male.
A CBC was the most common pretreatment test across treatments, performed in 41%-69% of patients before starting treatment. Tuberculosis screening occurred in 11%-59% of patients within 6 months of initiating treatment, and 3%-26% had updated tests after 1 year. Similarly, 13%-41% of patients underwent hepatitis screening prior to treatment.
The highest levels of pretreatment testing occurred for TNF-alpha inhibitors, ustekinumab, IL-17A inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, with similar patterns, while the lowest levels of testing occurred with apremilast and dupilumab.
Testing prevalence before starting apremilast and after a year of treatment was 15%-45% and 9%-36%, respectively. Testing before initiation and a year into treatment with dupilumab was 11%-41% and 3%-25%, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors including the descriptive design, which does not allow for evaluation of the testing practices, the researchers said.
However, the results show the extent of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases (CISDs) who do not undergo pretreatment testing, and research is needed to create testing practices on the basis of recommendations for each agent and incorporating each patient’s history and clinical profile, they concluded.
“The finding that less than 60% of patients received recommended pretreatment testing was initially somewhat surprising,” Shay said in the interview. “However, the context provided by higher rates of baseline testing within the 6-12 months before treatment initiation and the potential for additional testing not captured by the dataset — such as hospital stays — suggests that the gap may not be as large as this estimate,” he said.
“The key message for clinicians is that there are considerable variations in laboratory testing practices with regard to the initiation of systemic immunomodulatory agents in patients with CISDs,” Shay said. “This represents a divergence from existing testing guidelines.”
“Further research is needed to understand the reasons for the variations in pretreatment testing practices and whether this heterogeneity affects patient outcomes,” he added.
Resist Routine Testing
The study findings represent a call to action in the form of ongoing assessment of the safety, clinical utility, and cost-effectiveness of pretreatment testing, wrote Clinton W. Enos, MD, Ana Ormaza Vera, MD, and Abby S. Van Voorhees, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, in an accompanying editorial.
The data in the current study suggesting less frequent laboratory testing compared with current guidelines could stem from a high comfort level with many of the therapies that have been available and in use for many years, they noted. Clinicians’ lack of knowledge of the laboratory screening and monitoring guidelines also may play a role, they said.
However, the authors cautioned against routine checking of laboratory results “without purpose” and without attention to their clinical utility and cost. “A thorough medical history is essential and can serve as a sensitive indicator of which patients are more at risk for diseases such as TB or hepatitis, thereby allowing for more meaningful laboratory screening use,” they said.
Evidence supporting prescreening labs for the spectrum of systemic agents used in dermatology varies considerably, “some trapped in time and carried forward for decades until finally questioned, others rooted in treatment mechanism and clinical data,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
The study elucidated the current state of clinical practice, said Friedman, who was not involved with the study. This includes screening even if the label says it is not necessary and letting screening slide when guidelines say otherwise — even if the guidelines are outdated and insurance requires certain metrics prior to approval, he said.
Looking ahead, “we need better consensus and even better communication/education on said guidance,” Dr. Friedman said. “Clear, concise, evidenced-based, and expert-validated guidance to ensure we are meaningfully using medical resources” is what is needed, he added. “It will certainly take a village, and close collaboration between the industry and practitioners is key to success.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Shay had no financial conflicts to disclose. Lead author Dr. Schneeweiss disclosed grants from UCB Pharma and AbbVie to Brigham and Women’s Hospital outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving personal fees from Aetion and grants from UCB Pharma and Takeda outside the submitted work; grants from Amarin, Kowa, Novartis, and Pfizer outside the submitted work; and personal fees from Hims & Hers, AbbVie, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Digital Diagnostics, Lilly, Equillium, ASLAN, Boehringer Ingelheim, ACOM, Olaplex, and Legacy Healthcare during the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Editorial author Dr. Enos disclosed serving as an investigator for Amgen and Castle Biosciences and receiving grants from Arcutis Biotherapeutics outside the submitted work. Dr. Van Voorhees disclosed an honorarium outside the submitted work.
Dr. Friedman had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a national commercial insurance claims database.
Because of concerns for the potential reactivation of tuberculosis or hepatitis B or C, or for an increased risk for infections, myelosuppression, and hepatoxicity in the wake of immunomodulator use, some medical societies recommend screening patients for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and tuberculosis before starting these medications, wrote Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
“Conducting this study was crucial because of the increasing use of systemic immunomodulatory agents for chronic inflammatory skin diseases and the recognized need for pretreatment testing to prevent complications,” coauthor Denys Shay, a PhD candidate in population health sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, said in an interview.
“Despite recommendations from professional societies, there was a lack of clarity on how consistently these guidelines were being followed in the United States. This study aimed to fill that gap in knowledge, providing a comprehensive view of current practices and highlighting areas for improvement,” he said.
In the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology, he and his coauthors identified 122,308 adults in the United States with psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, or atopic dermatitis who started an immunomodulatory agent, including methotrexate (28,684 patients), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors (40,965), ustekinumab (12,841), interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors (6116), IL-17A inhibitors (9799), dupilumab (7787), and apremilast (16,116). The data were from a commercial insurance claims database from December 31, 2002, to December 31, 2020.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who underwent recommended screening lab tests including tuberculosis, hepatitis, liver function, complete blood cell counts (CBCs), and lipid panels within 6 months before treatment initiation and during the first 2 years of treatment. The median age of the study population was 49 years, and 52.1% were male.
A CBC was the most common pretreatment test across treatments, performed in 41%-69% of patients before starting treatment. Tuberculosis screening occurred in 11%-59% of patients within 6 months of initiating treatment, and 3%-26% had updated tests after 1 year. Similarly, 13%-41% of patients underwent hepatitis screening prior to treatment.
The highest levels of pretreatment testing occurred for TNF-alpha inhibitors, ustekinumab, IL-17A inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, with similar patterns, while the lowest levels of testing occurred with apremilast and dupilumab.
Testing prevalence before starting apremilast and after a year of treatment was 15%-45% and 9%-36%, respectively. Testing before initiation and a year into treatment with dupilumab was 11%-41% and 3%-25%, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors including the descriptive design, which does not allow for evaluation of the testing practices, the researchers said.
However, the results show the extent of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases (CISDs) who do not undergo pretreatment testing, and research is needed to create testing practices on the basis of recommendations for each agent and incorporating each patient’s history and clinical profile, they concluded.
“The finding that less than 60% of patients received recommended pretreatment testing was initially somewhat surprising,” Shay said in the interview. “However, the context provided by higher rates of baseline testing within the 6-12 months before treatment initiation and the potential for additional testing not captured by the dataset — such as hospital stays — suggests that the gap may not be as large as this estimate,” he said.
“The key message for clinicians is that there are considerable variations in laboratory testing practices with regard to the initiation of systemic immunomodulatory agents in patients with CISDs,” Shay said. “This represents a divergence from existing testing guidelines.”
“Further research is needed to understand the reasons for the variations in pretreatment testing practices and whether this heterogeneity affects patient outcomes,” he added.
Resist Routine Testing
The study findings represent a call to action in the form of ongoing assessment of the safety, clinical utility, and cost-effectiveness of pretreatment testing, wrote Clinton W. Enos, MD, Ana Ormaza Vera, MD, and Abby S. Van Voorhees, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, in an accompanying editorial.
The data in the current study suggesting less frequent laboratory testing compared with current guidelines could stem from a high comfort level with many of the therapies that have been available and in use for many years, they noted. Clinicians’ lack of knowledge of the laboratory screening and monitoring guidelines also may play a role, they said.
However, the authors cautioned against routine checking of laboratory results “without purpose” and without attention to their clinical utility and cost. “A thorough medical history is essential and can serve as a sensitive indicator of which patients are more at risk for diseases such as TB or hepatitis, thereby allowing for more meaningful laboratory screening use,” they said.
Evidence supporting prescreening labs for the spectrum of systemic agents used in dermatology varies considerably, “some trapped in time and carried forward for decades until finally questioned, others rooted in treatment mechanism and clinical data,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
The study elucidated the current state of clinical practice, said Friedman, who was not involved with the study. This includes screening even if the label says it is not necessary and letting screening slide when guidelines say otherwise — even if the guidelines are outdated and insurance requires certain metrics prior to approval, he said.
Looking ahead, “we need better consensus and even better communication/education on said guidance,” Dr. Friedman said. “Clear, concise, evidenced-based, and expert-validated guidance to ensure we are meaningfully using medical resources” is what is needed, he added. “It will certainly take a village, and close collaboration between the industry and practitioners is key to success.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Shay had no financial conflicts to disclose. Lead author Dr. Schneeweiss disclosed grants from UCB Pharma and AbbVie to Brigham and Women’s Hospital outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving personal fees from Aetion and grants from UCB Pharma and Takeda outside the submitted work; grants from Amarin, Kowa, Novartis, and Pfizer outside the submitted work; and personal fees from Hims & Hers, AbbVie, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Digital Diagnostics, Lilly, Equillium, ASLAN, Boehringer Ingelheim, ACOM, Olaplex, and Legacy Healthcare during the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Editorial author Dr. Enos disclosed serving as an investigator for Amgen and Castle Biosciences and receiving grants from Arcutis Biotherapeutics outside the submitted work. Dr. Van Voorhees disclosed an honorarium outside the submitted work.
Dr. Friedman had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
in a national commercial insurance claims database.
Because of concerns for the potential reactivation of tuberculosis or hepatitis B or C, or for an increased risk for infections, myelosuppression, and hepatoxicity in the wake of immunomodulator use, some medical societies recommend screening patients for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and tuberculosis before starting these medications, wrote Maria C. Schneeweiss, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and colleagues.
“Conducting this study was crucial because of the increasing use of systemic immunomodulatory agents for chronic inflammatory skin diseases and the recognized need for pretreatment testing to prevent complications,” coauthor Denys Shay, a PhD candidate in population health sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, said in an interview.
“Despite recommendations from professional societies, there was a lack of clarity on how consistently these guidelines were being followed in the United States. This study aimed to fill that gap in knowledge, providing a comprehensive view of current practices and highlighting areas for improvement,” he said.
In the study, published online in JAMA Dermatology, he and his coauthors identified 122,308 adults in the United States with psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, or atopic dermatitis who started an immunomodulatory agent, including methotrexate (28,684 patients), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha inhibitors (40,965), ustekinumab (12,841), interleukin (IL)-23 inhibitors (6116), IL-17A inhibitors (9799), dupilumab (7787), and apremilast (16,116). The data were from a commercial insurance claims database from December 31, 2002, to December 31, 2020.
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who underwent recommended screening lab tests including tuberculosis, hepatitis, liver function, complete blood cell counts (CBCs), and lipid panels within 6 months before treatment initiation and during the first 2 years of treatment. The median age of the study population was 49 years, and 52.1% were male.
A CBC was the most common pretreatment test across treatments, performed in 41%-69% of patients before starting treatment. Tuberculosis screening occurred in 11%-59% of patients within 6 months of initiating treatment, and 3%-26% had updated tests after 1 year. Similarly, 13%-41% of patients underwent hepatitis screening prior to treatment.
The highest levels of pretreatment testing occurred for TNF-alpha inhibitors, ustekinumab, IL-17A inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, with similar patterns, while the lowest levels of testing occurred with apremilast and dupilumab.
Testing prevalence before starting apremilast and after a year of treatment was 15%-45% and 9%-36%, respectively. Testing before initiation and a year into treatment with dupilumab was 11%-41% and 3%-25%, respectively.
The findings were limited by several factors including the descriptive design, which does not allow for evaluation of the testing practices, the researchers said.
However, the results show the extent of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases (CISDs) who do not undergo pretreatment testing, and research is needed to create testing practices on the basis of recommendations for each agent and incorporating each patient’s history and clinical profile, they concluded.
“The finding that less than 60% of patients received recommended pretreatment testing was initially somewhat surprising,” Shay said in the interview. “However, the context provided by higher rates of baseline testing within the 6-12 months before treatment initiation and the potential for additional testing not captured by the dataset — such as hospital stays — suggests that the gap may not be as large as this estimate,” he said.
“The key message for clinicians is that there are considerable variations in laboratory testing practices with regard to the initiation of systemic immunomodulatory agents in patients with CISDs,” Shay said. “This represents a divergence from existing testing guidelines.”
“Further research is needed to understand the reasons for the variations in pretreatment testing practices and whether this heterogeneity affects patient outcomes,” he added.
Resist Routine Testing
The study findings represent a call to action in the form of ongoing assessment of the safety, clinical utility, and cost-effectiveness of pretreatment testing, wrote Clinton W. Enos, MD, Ana Ormaza Vera, MD, and Abby S. Van Voorhees, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, in an accompanying editorial.
The data in the current study suggesting less frequent laboratory testing compared with current guidelines could stem from a high comfort level with many of the therapies that have been available and in use for many years, they noted. Clinicians’ lack of knowledge of the laboratory screening and monitoring guidelines also may play a role, they said.
However, the authors cautioned against routine checking of laboratory results “without purpose” and without attention to their clinical utility and cost. “A thorough medical history is essential and can serve as a sensitive indicator of which patients are more at risk for diseases such as TB or hepatitis, thereby allowing for more meaningful laboratory screening use,” they said.
Evidence supporting prescreening labs for the spectrum of systemic agents used in dermatology varies considerably, “some trapped in time and carried forward for decades until finally questioned, others rooted in treatment mechanism and clinical data,” Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chief of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, said in an interview.
The study elucidated the current state of clinical practice, said Friedman, who was not involved with the study. This includes screening even if the label says it is not necessary and letting screening slide when guidelines say otherwise — even if the guidelines are outdated and insurance requires certain metrics prior to approval, he said.
Looking ahead, “we need better consensus and even better communication/education on said guidance,” Dr. Friedman said. “Clear, concise, evidenced-based, and expert-validated guidance to ensure we are meaningfully using medical resources” is what is needed, he added. “It will certainly take a village, and close collaboration between the industry and practitioners is key to success.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Shay had no financial conflicts to disclose. Lead author Dr. Schneeweiss disclosed grants from UCB Pharma and AbbVie to Brigham and Women’s Hospital outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving personal fees from Aetion and grants from UCB Pharma and Takeda outside the submitted work; grants from Amarin, Kowa, Novartis, and Pfizer outside the submitted work; and personal fees from Hims & Hers, AbbVie, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Digital Diagnostics, Lilly, Equillium, ASLAN, Boehringer Ingelheim, ACOM, Olaplex, and Legacy Healthcare during the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Editorial author Dr. Enos disclosed serving as an investigator for Amgen and Castle Biosciences and receiving grants from Arcutis Biotherapeutics outside the submitted work. Dr. Van Voorhees disclosed an honorarium outside the submitted work.
Dr. Friedman had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Oral IL-23 Inhibitor Calms Moderate to Severe Psoriasis
A novel oral drug for plaque psoriasis that targets the same inflammatory pathway as currently available parenteral therapies showed promise for treating moderate to severe disease in a phase 2 dose-finding trial.
Among 255 at week 16 of at least 75% (PASI 75) compared with 9% of patients assigned to placebo, reported Robert Bissonnette, MD, from Innovaderm Research in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“The level of reduction of psoriasis that was observed with higher doses of JNJ-77242113 at week 16 was similar in magnitude to the responses seen with several of the injectable biologics that are currently approved for psoriasis,” investigators in the FRONTIER 1 trial wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The investigators noted that among patients assigned to the 100-mg dose of the active drug, 60% had a PASI 90 response, which compares favorably with that seen in phase 3 trials of two other orally available therapies for psoriasis, deucravacitinib (Sotyktu) and apremilast (Otezla). They cautioned, however, against drawing any further inferences from these data, because these agents have not been tested head-to-head against JNJ-77242113 in comparison trials.
Targets IL-23 and IL-17
The investigational agent is an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that selectively blocks IL-23 proximal signaling as well as the production of downstream inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, according to the authors.
“Modulation of the interleukin-23 pathway with the use of monoclonal antibodies has shown efficacy in the treatment of psoriasis and is considered to be associated with a more favorable safety profile than older oral therapies (eg, cyclosporine, acitretin, methotrexate, and dimethyl fumarate),” the investigators wrote.
Currently available biologic agents targeting IL-23 include guselkumab (Tremfya), risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tildrakizumab (Ilumya). These agents require intravenous or subcutaneous administration, whereas JNJ-77242113 is taken orally, giving it a theoretical advantage in terms of patient preference.
The novel drug must be taken twice daily on an empty stomach at least 2 hours before food or drink, and those who take it must wait an additional 30 minutes to eat or drink after taking the drug. (This news organization has learned that in planned phase 3 studies, patients will be instructed to take a double daily dose on awakening and then wait 30 minutes for eating or drinking.)
‘Profoundly Effective’
The results of this study have convinced at least one former skeptic of the efficacy of the novel agent.
“They asked me to do the trial, and I turned it down, because I didn’t believe it would work,” said Mark G. Lebwohl, MD, dean for Clinical Therapeutics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai Medicine in New York, NY.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Lebwohl said that he was initially dubious that a peptide, a short chain of amino acids directed against a receptor, could be effective because it would likely be digested in the intestinal tract.
“Indeed, more than 99% of it is digested, but the data show that the tiny amount that gets through is profoundly effective,” he said.
“I would never have believed that this was going to work – and it did,” Dr. Lebwohl added.
He has signed on as an investigator in the currently recruiting phase 3 ICONIC-LEAD trial, in which JNJ-77242113 will be tested against placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
In an editorial accompanying the study in the NEJM, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, vice chair of clinical research and medical director of the Dermatology Clinical Studies Unit at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, noted that if confirmed in larger studies, the PASI 90 rate at the highest dose “would be similar to the most effective injectable biologics,” with no evidence of increased adverse events at higher doses.
“However, two occurrences of infection (COVID-19 and an infected cyst) and a suicide attempt were reported as serious adverse events; larger trials will be needed to determine whether such events are attributable to chance, psoriasis itself, or inhibition of interleukin-23 signaling,” cautioned Dr. Gelfand, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania.
In an interview, Dr. Lebwohl said that currently available IL-23 signaling inhibitors have an excellent safety profile and that the investigational oral agent also appears to be very safe. “It’s seeing a target whose effects are known, and the effects are all good and not bad,” he said.
FRONTIER-1 Details
The investigators enrolled eligible adults aged 18 years or older who had moderate to severe plaque psoriasis as defined by an Investigator’s Global Assessment score ≥ 3, a total body-surface area of psoriasis involvement of at least 10%, and a PASI score ≥ 12 who had received their diagnosis of plaque psoriasis at least 6 months before starting the trial. The participants had to be candidates for phototherapy or systemic psoriasis therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned to the active agent at doses of 25 mg once or twice daily, 50 mg once daily, or 100 mg once or twice daily for 16 weeks.
There was a clear dose response, with 37% of patients assigned to 25-mg once-daily dose meeting the primary endpoint of a PASI 75 response at week 16 compared with 51% of those assigned to the 25-mg twice-daily dose, 58% assigned to 50-mg once-daily dose, 65% assigned to 100-mg once-daily dose, and 79% assigned to 100-mg twice-daily dose (P for dose response < .001).
As noted previously, 9% of patients in the placebo group had a PASI 75 response at week 16.
After a mean duration of 15.9 weeks, adverse events after the first dose of JNJ-77242113 (all dose groups were pooled for the safety analysis) were reported in 47% of patients on the 25-mg once-daily dose, 49% on 25-mg twice-daily dose, 60% on 50-mg once-daily dose, 44% on 100-mg once-daily dose, and 62% on 100-mg twice-daily dose. Adverse events after the first dose occurred in 51% of patients assigned to placebo.
The incidence of adverse events did not increase significantly with successively higher dose levels.
As noted by Dr. Gelfand in his editorial, there were three serious adverse events, all occurring in patients on the active drug: a case of COVID-19 in one patient and a suicide attempt in one patient, both in the 100-mg once-daily dose group, and an infected cyst in the 50-mg once-daily group. All three events were determined by the principal investigator and the sponsor to be unrelated to JNJ-77242113.
There were no reports of deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events, or incident cancers during the trial.
The study was supported by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Bissonnette disclosed institutional research funding and advisory board participation and honoraria with Janssen. Dr. Gelfand disclosed consulting for Janssen Biotech. Dr. Lebwohl disclosed institutional research funding from Janssen but no personal fees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel oral drug for plaque psoriasis that targets the same inflammatory pathway as currently available parenteral therapies showed promise for treating moderate to severe disease in a phase 2 dose-finding trial.
Among 255 at week 16 of at least 75% (PASI 75) compared with 9% of patients assigned to placebo, reported Robert Bissonnette, MD, from Innovaderm Research in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“The level of reduction of psoriasis that was observed with higher doses of JNJ-77242113 at week 16 was similar in magnitude to the responses seen with several of the injectable biologics that are currently approved for psoriasis,” investigators in the FRONTIER 1 trial wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The investigators noted that among patients assigned to the 100-mg dose of the active drug, 60% had a PASI 90 response, which compares favorably with that seen in phase 3 trials of two other orally available therapies for psoriasis, deucravacitinib (Sotyktu) and apremilast (Otezla). They cautioned, however, against drawing any further inferences from these data, because these agents have not been tested head-to-head against JNJ-77242113 in comparison trials.
Targets IL-23 and IL-17
The investigational agent is an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that selectively blocks IL-23 proximal signaling as well as the production of downstream inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, according to the authors.
“Modulation of the interleukin-23 pathway with the use of monoclonal antibodies has shown efficacy in the treatment of psoriasis and is considered to be associated with a more favorable safety profile than older oral therapies (eg, cyclosporine, acitretin, methotrexate, and dimethyl fumarate),” the investigators wrote.
Currently available biologic agents targeting IL-23 include guselkumab (Tremfya), risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tildrakizumab (Ilumya). These agents require intravenous or subcutaneous administration, whereas JNJ-77242113 is taken orally, giving it a theoretical advantage in terms of patient preference.
The novel drug must be taken twice daily on an empty stomach at least 2 hours before food or drink, and those who take it must wait an additional 30 minutes to eat or drink after taking the drug. (This news organization has learned that in planned phase 3 studies, patients will be instructed to take a double daily dose on awakening and then wait 30 minutes for eating or drinking.)
‘Profoundly Effective’
The results of this study have convinced at least one former skeptic of the efficacy of the novel agent.
“They asked me to do the trial, and I turned it down, because I didn’t believe it would work,” said Mark G. Lebwohl, MD, dean for Clinical Therapeutics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai Medicine in New York, NY.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Lebwohl said that he was initially dubious that a peptide, a short chain of amino acids directed against a receptor, could be effective because it would likely be digested in the intestinal tract.
“Indeed, more than 99% of it is digested, but the data show that the tiny amount that gets through is profoundly effective,” he said.
“I would never have believed that this was going to work – and it did,” Dr. Lebwohl added.
He has signed on as an investigator in the currently recruiting phase 3 ICONIC-LEAD trial, in which JNJ-77242113 will be tested against placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
In an editorial accompanying the study in the NEJM, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, vice chair of clinical research and medical director of the Dermatology Clinical Studies Unit at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, noted that if confirmed in larger studies, the PASI 90 rate at the highest dose “would be similar to the most effective injectable biologics,” with no evidence of increased adverse events at higher doses.
“However, two occurrences of infection (COVID-19 and an infected cyst) and a suicide attempt were reported as serious adverse events; larger trials will be needed to determine whether such events are attributable to chance, psoriasis itself, or inhibition of interleukin-23 signaling,” cautioned Dr. Gelfand, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania.
In an interview, Dr. Lebwohl said that currently available IL-23 signaling inhibitors have an excellent safety profile and that the investigational oral agent also appears to be very safe. “It’s seeing a target whose effects are known, and the effects are all good and not bad,” he said.
FRONTIER-1 Details
The investigators enrolled eligible adults aged 18 years or older who had moderate to severe plaque psoriasis as defined by an Investigator’s Global Assessment score ≥ 3, a total body-surface area of psoriasis involvement of at least 10%, and a PASI score ≥ 12 who had received their diagnosis of plaque psoriasis at least 6 months before starting the trial. The participants had to be candidates for phototherapy or systemic psoriasis therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned to the active agent at doses of 25 mg once or twice daily, 50 mg once daily, or 100 mg once or twice daily for 16 weeks.
There was a clear dose response, with 37% of patients assigned to 25-mg once-daily dose meeting the primary endpoint of a PASI 75 response at week 16 compared with 51% of those assigned to the 25-mg twice-daily dose, 58% assigned to 50-mg once-daily dose, 65% assigned to 100-mg once-daily dose, and 79% assigned to 100-mg twice-daily dose (P for dose response < .001).
As noted previously, 9% of patients in the placebo group had a PASI 75 response at week 16.
After a mean duration of 15.9 weeks, adverse events after the first dose of JNJ-77242113 (all dose groups were pooled for the safety analysis) were reported in 47% of patients on the 25-mg once-daily dose, 49% on 25-mg twice-daily dose, 60% on 50-mg once-daily dose, 44% on 100-mg once-daily dose, and 62% on 100-mg twice-daily dose. Adverse events after the first dose occurred in 51% of patients assigned to placebo.
The incidence of adverse events did not increase significantly with successively higher dose levels.
As noted by Dr. Gelfand in his editorial, there were three serious adverse events, all occurring in patients on the active drug: a case of COVID-19 in one patient and a suicide attempt in one patient, both in the 100-mg once-daily dose group, and an infected cyst in the 50-mg once-daily group. All three events were determined by the principal investigator and the sponsor to be unrelated to JNJ-77242113.
There were no reports of deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events, or incident cancers during the trial.
The study was supported by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Bissonnette disclosed institutional research funding and advisory board participation and honoraria with Janssen. Dr. Gelfand disclosed consulting for Janssen Biotech. Dr. Lebwohl disclosed institutional research funding from Janssen but no personal fees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel oral drug for plaque psoriasis that targets the same inflammatory pathway as currently available parenteral therapies showed promise for treating moderate to severe disease in a phase 2 dose-finding trial.
Among 255 at week 16 of at least 75% (PASI 75) compared with 9% of patients assigned to placebo, reported Robert Bissonnette, MD, from Innovaderm Research in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“The level of reduction of psoriasis that was observed with higher doses of JNJ-77242113 at week 16 was similar in magnitude to the responses seen with several of the injectable biologics that are currently approved for psoriasis,” investigators in the FRONTIER 1 trial wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The investigators noted that among patients assigned to the 100-mg dose of the active drug, 60% had a PASI 90 response, which compares favorably with that seen in phase 3 trials of two other orally available therapies for psoriasis, deucravacitinib (Sotyktu) and apremilast (Otezla). They cautioned, however, against drawing any further inferences from these data, because these agents have not been tested head-to-head against JNJ-77242113 in comparison trials.
Targets IL-23 and IL-17
The investigational agent is an oral IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide that selectively blocks IL-23 proximal signaling as well as the production of downstream inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17, according to the authors.
“Modulation of the interleukin-23 pathway with the use of monoclonal antibodies has shown efficacy in the treatment of psoriasis and is considered to be associated with a more favorable safety profile than older oral therapies (eg, cyclosporine, acitretin, methotrexate, and dimethyl fumarate),” the investigators wrote.
Currently available biologic agents targeting IL-23 include guselkumab (Tremfya), risankizumab (Skyrizi) and tildrakizumab (Ilumya). These agents require intravenous or subcutaneous administration, whereas JNJ-77242113 is taken orally, giving it a theoretical advantage in terms of patient preference.
The novel drug must be taken twice daily on an empty stomach at least 2 hours before food or drink, and those who take it must wait an additional 30 minutes to eat or drink after taking the drug. (This news organization has learned that in planned phase 3 studies, patients will be instructed to take a double daily dose on awakening and then wait 30 minutes for eating or drinking.)
‘Profoundly Effective’
The results of this study have convinced at least one former skeptic of the efficacy of the novel agent.
“They asked me to do the trial, and I turned it down, because I didn’t believe it would work,” said Mark G. Lebwohl, MD, dean for Clinical Therapeutics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and professor and chairman emeritus of the Department of Dermatology at Mount Sinai Medicine in New York, NY.
In an interview with this news organization, Dr. Lebwohl said that he was initially dubious that a peptide, a short chain of amino acids directed against a receptor, could be effective because it would likely be digested in the intestinal tract.
“Indeed, more than 99% of it is digested, but the data show that the tiny amount that gets through is profoundly effective,” he said.
“I would never have believed that this was going to work – and it did,” Dr. Lebwohl added.
He has signed on as an investigator in the currently recruiting phase 3 ICONIC-LEAD trial, in which JNJ-77242113 will be tested against placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
In an editorial accompanying the study in the NEJM, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, vice chair of clinical research and medical director of the Dermatology Clinical Studies Unit at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, noted that if confirmed in larger studies, the PASI 90 rate at the highest dose “would be similar to the most effective injectable biologics,” with no evidence of increased adverse events at higher doses.
“However, two occurrences of infection (COVID-19 and an infected cyst) and a suicide attempt were reported as serious adverse events; larger trials will be needed to determine whether such events are attributable to chance, psoriasis itself, or inhibition of interleukin-23 signaling,” cautioned Dr. Gelfand, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center at the University of Pennsylvania.
In an interview, Dr. Lebwohl said that currently available IL-23 signaling inhibitors have an excellent safety profile and that the investigational oral agent also appears to be very safe. “It’s seeing a target whose effects are known, and the effects are all good and not bad,” he said.
FRONTIER-1 Details
The investigators enrolled eligible adults aged 18 years or older who had moderate to severe plaque psoriasis as defined by an Investigator’s Global Assessment score ≥ 3, a total body-surface area of psoriasis involvement of at least 10%, and a PASI score ≥ 12 who had received their diagnosis of plaque psoriasis at least 6 months before starting the trial. The participants had to be candidates for phototherapy or systemic psoriasis therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned to the active agent at doses of 25 mg once or twice daily, 50 mg once daily, or 100 mg once or twice daily for 16 weeks.
There was a clear dose response, with 37% of patients assigned to 25-mg once-daily dose meeting the primary endpoint of a PASI 75 response at week 16 compared with 51% of those assigned to the 25-mg twice-daily dose, 58% assigned to 50-mg once-daily dose, 65% assigned to 100-mg once-daily dose, and 79% assigned to 100-mg twice-daily dose (P for dose response < .001).
As noted previously, 9% of patients in the placebo group had a PASI 75 response at week 16.
After a mean duration of 15.9 weeks, adverse events after the first dose of JNJ-77242113 (all dose groups were pooled for the safety analysis) were reported in 47% of patients on the 25-mg once-daily dose, 49% on 25-mg twice-daily dose, 60% on 50-mg once-daily dose, 44% on 100-mg once-daily dose, and 62% on 100-mg twice-daily dose. Adverse events after the first dose occurred in 51% of patients assigned to placebo.
The incidence of adverse events did not increase significantly with successively higher dose levels.
As noted by Dr. Gelfand in his editorial, there were three serious adverse events, all occurring in patients on the active drug: a case of COVID-19 in one patient and a suicide attempt in one patient, both in the 100-mg once-daily dose group, and an infected cyst in the 50-mg once-daily group. All three events were determined by the principal investigator and the sponsor to be unrelated to JNJ-77242113.
There were no reports of deaths, major adverse cardiovascular events, or incident cancers during the trial.
The study was supported by Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Bissonnette disclosed institutional research funding and advisory board participation and honoraria with Janssen. Dr. Gelfand disclosed consulting for Janssen Biotech. Dr. Lebwohl disclosed institutional research funding from Janssen but no personal fees.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE


