User login
From the Department of Medicine, University of California San Diego (Dr. Haponyuk), Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Tennessee (Dr. Dejong), the Department of Family Medicine, University of New Mexico (Dr. Gutfrucht), and the Department of Internal Medicine, University of New Mexico (Dr. Barrett)
Objective: Naloxone availability can reduce the risk of death from opioid overdoses, although prescriber, legislative, and payment barriers to accessing this life-saving medication exist. A previously underreported barrier involves same-day availability, the lack of which may force patients to travel to multiple pharmacies and having delays in access or risking not filling their prescription. This study sought to determine same-day availability of naloxone in pharmacies in the state of New Mexico.
Methods: Same-day availability of naloxone was assessed via an audit survey.
Results: Of the 183 pharamacies screened, only 84.7% had same-day availability, including only 72% in Albuquerque, the state’s most populous city/municipality.
Conclusion: These results highlight the extent of a previously underexplored challenge to patient care and barrier to patient safety, and future directions for more patient-centered care.
Keywords: naloxone; barriers to care; opioid overdose prevention.
The US is enduring an ongoing epidemic of deaths due to opioid use, which have increased in frequency since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.1 One strategy to reduce the risk of mortality from opioid use is to ensure the widespread availability of naloxone. Individual states have implemented harm reduction strategies to increase access to naloxone, including improving availability via a statewide standing order that it may be dispensed without a prescription.2,3 Such naloxone access laws are being widely adopted and are believed to reduce overdose deaths.4
There are many barriers to patients receiving naloxone despite their clinicians providing a prescription for it, including stigmatization, financial cost, and local availability.5-9 However, the stigma associated with naloxone extends to both patients and pharmacists. Pharmacists in West Virginia, for example, showed widespread concerns about having naloxone available for patients to purchase over the counter, for fear that increasing naloxone access may increase overdoses.6 A study in Tennessee also found pharmacists hesitant to recommend naloxone.7 Another study of rural pharmacies in Georgia found that just over half carried naloxone despite a state law that naloxone be available without a prescription.8 Challenges are not limited to rural areas, however; a study in Philadelphia found that more than one-third of pharmacies required a prescription to dispense naloxone, contrary to state law.9 Thus, in a rapidly changing regulatory environment, there are many evolving barriers to patients receiving naloxone.
New Mexico has an opioid overdose rate higher than the national average, coming in 15th out of 50 states when last ranked in 2018, with overdose rates that vary across demographic variables.10 Consequently, New Mexico state law added language requiring clinicians prescribing opioids for 5 days or longer to co-prescribe naloxone along with written information on how to administer the opioid antagonist.11 New Mexico is also a geographically large state with a relatively low overall population characterized by striking health disparities, particularly as related to access to care.
The purpose of this study is to describe the same-day availability of naloxone throughout the state of New Mexico after a change in state law requiring co-prescription was enacted, to help identify challenges to patients receiving it. Comprehensive examination of barriers to patients accessing this life-saving medication can advise strategies to both improve patient-centered care and potentially reduce deaths.
Methods
To better understand barriers to patients obtaining naloxone, in July and August of 2019 we performed an audit (“secret shopper”) study of all pharmacies in the state, posing as patients wishing to obtain naloxone. A publicly available list of every pharmacy in New Mexico was used to identify 89 pharmacies in Albuquerque (the most populous city in New Mexico) and 106 pharmacies throughout the rest of the state.12
Every pharmacy was called via a publicly available phone number during business hours (confirmed via an internet search), at least 2 hours prior to closing. One of 3 researchers telephoned pharmacies posing as a patient and inquired whether naloxone would be available for pick up the same day. If the pharmacy confirmed it was available that day, the call concluded. If naloxone was unavailable for same day pick up, researchers asked when it would be next available. Each pharmacy was called once, and neither insurance information nor cost was offered or requested. All questions were asked in English by native English speakers.
All responses were recorded in a secure spreadsheet. Once all responses were received and reviewed, they were characterized in discrete response categories: same day, within 1 to 2 days, within 3 to 4 days, within a week, or unsure/unknown. Naloxone availability was also tracked by city/municipality, and this was compared to the state’s population distribution.
No personally identifiable information was obtained. This study was Institutional Review Board exempt.
Results
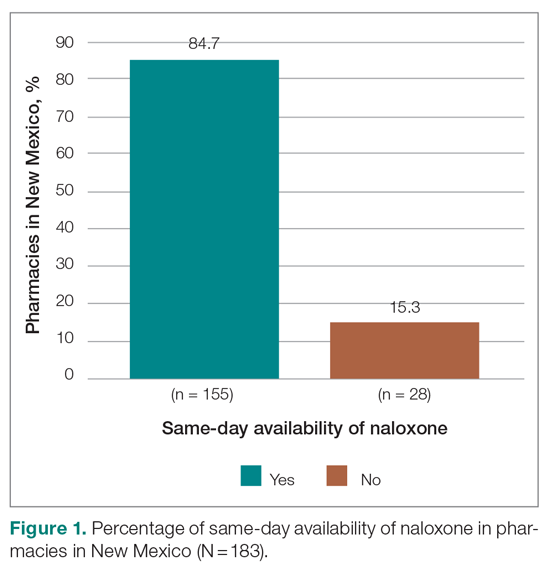
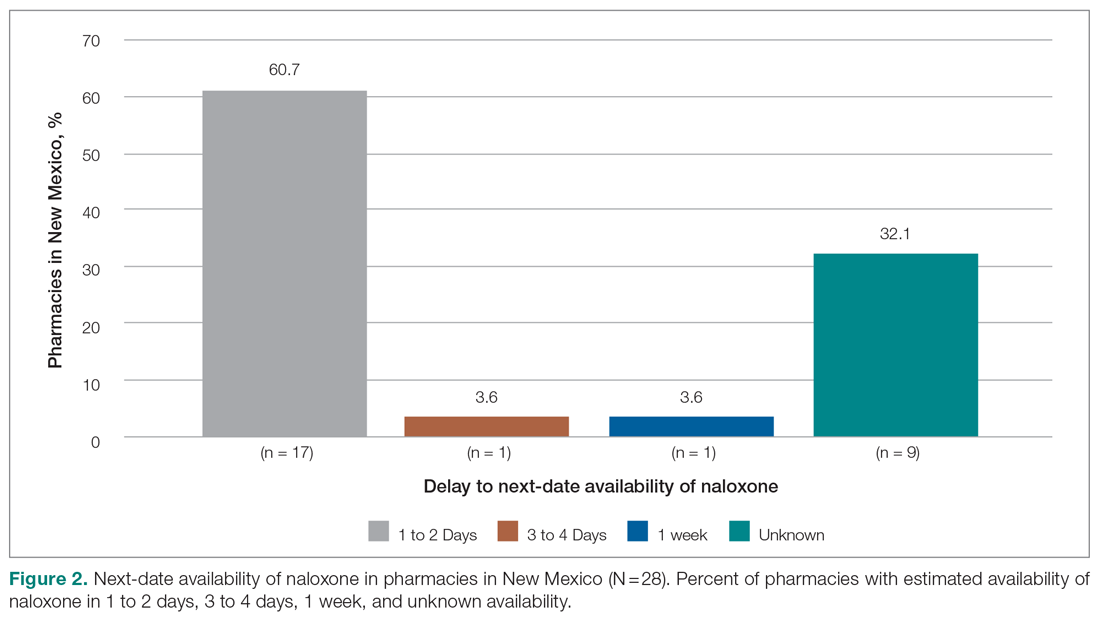
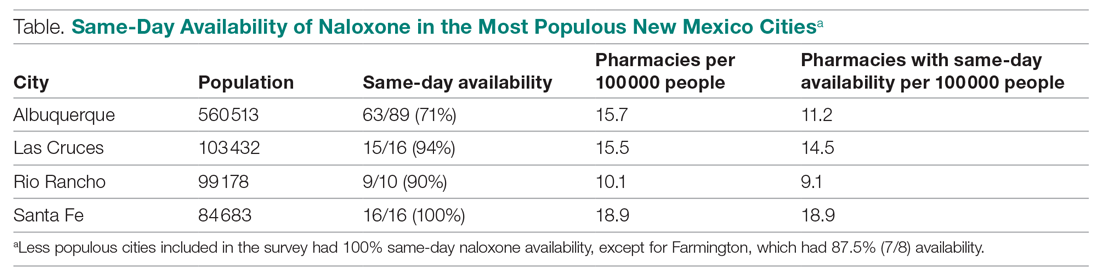
Responses were recorded from 183 pharmacies. Seventeen locations were eliminated from our analysis because their phone system was inoperable or the pharmacy was permanently closed. Of the pharmacies reached, 84.7% (155/183) reported they have naloxone available for pick up on the same day (Figure 1). Of the 15.3% (28) pharmacies that did not have same-day availability, 60.7% (17 pharmacies) reported availability in 1 to 2 days, 3.6% had availability in 3 to 4 days, 3.6% had availability in 1 week, and 32.1% were unsure of next availability (Figure 2). More than one-third of the state’s patients reside in municipalities where naloxone is immediately available in at least 72% of pharmacies (Table).13
Discussion
Increased access to naloxone at the state and community level is associated with reduced risk for death from overdose, and, consequently, widespread availability is recommended.14-17 Statewide real-time pharmacy availability of naloxone—as patients would experience availability—has not been previously reported. These findings suggest unpredictable same-day availability that may affect experience and care outcomes. That other studies have found similar challenges in naloxone availability in other municipalities and regions suggests this barrier to access is widespread,6-9 and likely affects patients throughout the country.
Many patients have misgivings about naloxone, and it places an undue burden on them to travel to multiple pharmacies or take repeated trips to fill prescriptions. Additionally, patients without reliable transportation may be unable to return at a later date. Although we found most pharmacies in New Mexico without immediate availability of naloxone reported they could have it within several days, such a delay may reduce the likelihood that patients will fill their prescription at all. It is also concerning that many pharmacies are unsure of when naloxone will be available, particularly when some of these may be the only pharmacy easily accessible to patients or the one where they regularly fill their prescriptions.
Barriers to naloxone availability requires further study due to possible negative consequences for patient safety and risks for exacerbating health disparities among vulnerable populations. Further research may focus on examining the effects on patients when naloxone dispensing is delayed or impossible, why there is variability in naloxone availability between different pharmacies and municipalities, the reasons for uncertainty when naloxone will be available, and effective solutions. Expanded naloxone distribution in community locations and in clinics offers one potential patient-centered solution that should be explored, but it is likely that more widespread and systemic solutions will require policy and regulatory changes at the state and national levels.
Limitations of this study include that the findings may be relevant for solely 1 state, such as in the case of state-specific barriers to keeping naloxone in stock that we are unaware of. However, it is unclear why that would be the case, and it is more likely that similar barriers are pervasive. Additionally, repeat phone calls, which we did not follow up with, may have yielded more pharmacies with naloxone availability. However, due to the stigma associated with obtaining naloxone, it may be that patients will not make multiple calls either—highlighting how important real-time availability is.
Conclusion
Urgent solutions are needed to address the epidemic of deaths from opioid overdoses. Naloxone availability is an important tool for reducing these deaths, resulting in numerous state laws attempting to increase access. Despite this, there are persistent barriers to patients receiving naloxone, including a lack of same-day availability at pharmacies. Our results suggest that this underexplored barrier is widespread. Improving both availability and accessibility of naloxone may include legislative policy solutions as well as patient-oriented solutions, such as distribution in clinics and hospitals when opioid prescriptions are first written. Further research should be conducted to determine patient-centered, effective solutions that can improve outcomes.
Corresponding author: Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, Department of Internal Medicine, University of New Mexico; ebarrett@salud.unm.edu.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Mason M, Welch SB, Arunkumar P, et al. Notes from the field: opioid overdose deaths before, during, and after an 11-week COVID-19 stay-at-home order—Cook County, Illinois, January 1, 2018–October 6, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(10):362-363. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7010a3
2. Kaiser Family Foundation. Opioid overdose death rates and all drug overdose death rates per 100,000 population (age-adjusted). Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.kff.org/other/state-indicator/opioid-overdose-death
3. Sohn M, Talbert JC, Huang Z, et al. Association of naloxone coprescription laws with naloxone prescription dispensing in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(6):e196215. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.6215
4. Smart R, Pardo B, Davis CS. Systematic review of the emerging literature on the effectiveness of naloxone access laws in the United States. Addiction. 2021;116(1):6-17. doi:10.1111/add.15163
5. Mueller SR, Koester S, Glanz JM, et al. Attitudes toward naloxone prescribing in clinical settings: a qualitative study of patients prescribed high dose opioids for chronic non-cancer pain. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(3):277-283. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3895-8
6. Thornton JD, Lyvers E, Scott VGG, Dwibedi N. Pharmacists’ readiness to provide naloxone in community pharmacies in West Virginia. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2017;57(2S):S12-S18.e4. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2016.12.070
7. Spivey C, Wilder A, Chisholm-Burns MA, et al. Evaluation of naloxone access, pricing, and barriers to dispensing in Tennessee retail community pharmacies. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020;60(5):694-701.e1. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2020.01.030
8. Nguyen JL, Gilbert LR, Beasley L, et al. Availability of naloxone at rural Georgia pharmacies, 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1921227. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.21227
9. Guadamuz JS, Alexander GC, Chaudhri T, et al. Availability and cost of naloxone nasal spray at pharmacies in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(6):e195388. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.5388
10. Edge K. Changes in drug overdose mortality in New Mexico. New Mexico Epidemiology. July 2020 (3). https://www.nmhealth.org/data/view/report/2402/
11. Senate Bill 221. 54th Legislature, State of New Mexico, First Session, 2019 (introduced by William P. Soules). Accessed October 6, 2021. https://nmlegis.gov/Sessions/19%20Regular/bills/senate/SB0221.pdf
12. GoodRx. Find pharmacies in New Mexico. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.goodrx.com/pharmacy-near-me/all/nm
13. U.S. Census Bureau. QuickFacts: New Mexico. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/NM
14. Linas BP, Savinkina A, Madushani RWMA, et al. Projected estimates of opioid mortality after community-level interventions. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037259. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37259
15. You HS, Ha J, Kang CY, et al. Regional variation in states’ naloxone accessibility laws in association with opioid overdose death rates—observational study (STROBE compliant). Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(22):e20033. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000020033
16. Pew Charitable Trusts. Expanded access to naloxone can curb opioid overdose deaths. October 20, 2020. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.
17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Still not enough naloxone where it’s most needed. August 6, 2019. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2019/p0806-naloxone.html
From the Department of Medicine, University of California San Diego (Dr. Haponyuk), Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Tennessee (Dr. Dejong), the Department of Family Medicine, University of New Mexico (Dr. Gutfrucht), and the Department of Internal Medicine, University of New Mexico (Dr. Barrett)
Objective: Naloxone availability can reduce the risk of death from opioid overdoses, although prescriber, legislative, and payment barriers to accessing this life-saving medication exist. A previously underreported barrier involves same-day availability, the lack of which may force patients to travel to multiple pharmacies and having delays in access or risking not filling their prescription. This study sought to determine same-day availability of naloxone in pharmacies in the state of New Mexico.
Methods: Same-day availability of naloxone was assessed via an audit survey.
Results: Of the 183 pharamacies screened, only 84.7% had same-day availability, including only 72% in Albuquerque, the state’s most populous city/municipality.
Conclusion: These results highlight the extent of a previously underexplored challenge to patient care and barrier to patient safety, and future directions for more patient-centered care.
Keywords: naloxone; barriers to care; opioid overdose prevention.
The US is enduring an ongoing epidemic of deaths due to opioid use, which have increased in frequency since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.1 One strategy to reduce the risk of mortality from opioid use is to ensure the widespread availability of naloxone. Individual states have implemented harm reduction strategies to increase access to naloxone, including improving availability via a statewide standing order that it may be dispensed without a prescription.2,3 Such naloxone access laws are being widely adopted and are believed to reduce overdose deaths.4
There are many barriers to patients receiving naloxone despite their clinicians providing a prescription for it, including stigmatization, financial cost, and local availability.5-9 However, the stigma associated with naloxone extends to both patients and pharmacists. Pharmacists in West Virginia, for example, showed widespread concerns about having naloxone available for patients to purchase over the counter, for fear that increasing naloxone access may increase overdoses.6 A study in Tennessee also found pharmacists hesitant to recommend naloxone.7 Another study of rural pharmacies in Georgia found that just over half carried naloxone despite a state law that naloxone be available without a prescription.8 Challenges are not limited to rural areas, however; a study in Philadelphia found that more than one-third of pharmacies required a prescription to dispense naloxone, contrary to state law.9 Thus, in a rapidly changing regulatory environment, there are many evolving barriers to patients receiving naloxone.
New Mexico has an opioid overdose rate higher than the national average, coming in 15th out of 50 states when last ranked in 2018, with overdose rates that vary across demographic variables.10 Consequently, New Mexico state law added language requiring clinicians prescribing opioids for 5 days or longer to co-prescribe naloxone along with written information on how to administer the opioid antagonist.11 New Mexico is also a geographically large state with a relatively low overall population characterized by striking health disparities, particularly as related to access to care.
The purpose of this study is to describe the same-day availability of naloxone throughout the state of New Mexico after a change in state law requiring co-prescription was enacted, to help identify challenges to patients receiving it. Comprehensive examination of barriers to patients accessing this life-saving medication can advise strategies to both improve patient-centered care and potentially reduce deaths.
Methods
To better understand barriers to patients obtaining naloxone, in July and August of 2019 we performed an audit (“secret shopper”) study of all pharmacies in the state, posing as patients wishing to obtain naloxone. A publicly available list of every pharmacy in New Mexico was used to identify 89 pharmacies in Albuquerque (the most populous city in New Mexico) and 106 pharmacies throughout the rest of the state.12
Every pharmacy was called via a publicly available phone number during business hours (confirmed via an internet search), at least 2 hours prior to closing. One of 3 researchers telephoned pharmacies posing as a patient and inquired whether naloxone would be available for pick up the same day. If the pharmacy confirmed it was available that day, the call concluded. If naloxone was unavailable for same day pick up, researchers asked when it would be next available. Each pharmacy was called once, and neither insurance information nor cost was offered or requested. All questions were asked in English by native English speakers.
All responses were recorded in a secure spreadsheet. Once all responses were received and reviewed, they were characterized in discrete response categories: same day, within 1 to 2 days, within 3 to 4 days, within a week, or unsure/unknown. Naloxone availability was also tracked by city/municipality, and this was compared to the state’s population distribution.
No personally identifiable information was obtained. This study was Institutional Review Board exempt.
Results
Responses were recorded from 183 pharmacies. Seventeen locations were eliminated from our analysis because their phone system was inoperable or the pharmacy was permanently closed. Of the pharmacies reached, 84.7% (155/183) reported they have naloxone available for pick up on the same day (Figure 1). Of the 15.3% (28) pharmacies that did not have same-day availability, 60.7% (17 pharmacies) reported availability in 1 to 2 days, 3.6% had availability in 3 to 4 days, 3.6% had availability in 1 week, and 32.1% were unsure of next availability (Figure 2). More than one-third of the state’s patients reside in municipalities where naloxone is immediately available in at least 72% of pharmacies (Table).13
Discussion
Increased access to naloxone at the state and community level is associated with reduced risk for death from overdose, and, consequently, widespread availability is recommended.14-17 Statewide real-time pharmacy availability of naloxone—as patients would experience availability—has not been previously reported. These findings suggest unpredictable same-day availability that may affect experience and care outcomes. That other studies have found similar challenges in naloxone availability in other municipalities and regions suggests this barrier to access is widespread,6-9 and likely affects patients throughout the country.
Many patients have misgivings about naloxone, and it places an undue burden on them to travel to multiple pharmacies or take repeated trips to fill prescriptions. Additionally, patients without reliable transportation may be unable to return at a later date. Although we found most pharmacies in New Mexico without immediate availability of naloxone reported they could have it within several days, such a delay may reduce the likelihood that patients will fill their prescription at all. It is also concerning that many pharmacies are unsure of when naloxone will be available, particularly when some of these may be the only pharmacy easily accessible to patients or the one where they regularly fill their prescriptions.
Barriers to naloxone availability requires further study due to possible negative consequences for patient safety and risks for exacerbating health disparities among vulnerable populations. Further research may focus on examining the effects on patients when naloxone dispensing is delayed or impossible, why there is variability in naloxone availability between different pharmacies and municipalities, the reasons for uncertainty when naloxone will be available, and effective solutions. Expanded naloxone distribution in community locations and in clinics offers one potential patient-centered solution that should be explored, but it is likely that more widespread and systemic solutions will require policy and regulatory changes at the state and national levels.
Limitations of this study include that the findings may be relevant for solely 1 state, such as in the case of state-specific barriers to keeping naloxone in stock that we are unaware of. However, it is unclear why that would be the case, and it is more likely that similar barriers are pervasive. Additionally, repeat phone calls, which we did not follow up with, may have yielded more pharmacies with naloxone availability. However, due to the stigma associated with obtaining naloxone, it may be that patients will not make multiple calls either—highlighting how important real-time availability is.
Conclusion
Urgent solutions are needed to address the epidemic of deaths from opioid overdoses. Naloxone availability is an important tool for reducing these deaths, resulting in numerous state laws attempting to increase access. Despite this, there are persistent barriers to patients receiving naloxone, including a lack of same-day availability at pharmacies. Our results suggest that this underexplored barrier is widespread. Improving both availability and accessibility of naloxone may include legislative policy solutions as well as patient-oriented solutions, such as distribution in clinics and hospitals when opioid prescriptions are first written. Further research should be conducted to determine patient-centered, effective solutions that can improve outcomes.
Corresponding author: Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, Department of Internal Medicine, University of New Mexico; ebarrett@salud.unm.edu.
Financial disclosures: None.
From the Department of Medicine, University of California San Diego (Dr. Haponyuk), Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Tennessee (Dr. Dejong), the Department of Family Medicine, University of New Mexico (Dr. Gutfrucht), and the Department of Internal Medicine, University of New Mexico (Dr. Barrett)
Objective: Naloxone availability can reduce the risk of death from opioid overdoses, although prescriber, legislative, and payment barriers to accessing this life-saving medication exist. A previously underreported barrier involves same-day availability, the lack of which may force patients to travel to multiple pharmacies and having delays in access or risking not filling their prescription. This study sought to determine same-day availability of naloxone in pharmacies in the state of New Mexico.
Methods: Same-day availability of naloxone was assessed via an audit survey.
Results: Of the 183 pharamacies screened, only 84.7% had same-day availability, including only 72% in Albuquerque, the state’s most populous city/municipality.
Conclusion: These results highlight the extent of a previously underexplored challenge to patient care and barrier to patient safety, and future directions for more patient-centered care.
Keywords: naloxone; barriers to care; opioid overdose prevention.
The US is enduring an ongoing epidemic of deaths due to opioid use, which have increased in frequency since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.1 One strategy to reduce the risk of mortality from opioid use is to ensure the widespread availability of naloxone. Individual states have implemented harm reduction strategies to increase access to naloxone, including improving availability via a statewide standing order that it may be dispensed without a prescription.2,3 Such naloxone access laws are being widely adopted and are believed to reduce overdose deaths.4
There are many barriers to patients receiving naloxone despite their clinicians providing a prescription for it, including stigmatization, financial cost, and local availability.5-9 However, the stigma associated with naloxone extends to both patients and pharmacists. Pharmacists in West Virginia, for example, showed widespread concerns about having naloxone available for patients to purchase over the counter, for fear that increasing naloxone access may increase overdoses.6 A study in Tennessee also found pharmacists hesitant to recommend naloxone.7 Another study of rural pharmacies in Georgia found that just over half carried naloxone despite a state law that naloxone be available without a prescription.8 Challenges are not limited to rural areas, however; a study in Philadelphia found that more than one-third of pharmacies required a prescription to dispense naloxone, contrary to state law.9 Thus, in a rapidly changing regulatory environment, there are many evolving barriers to patients receiving naloxone.
New Mexico has an opioid overdose rate higher than the national average, coming in 15th out of 50 states when last ranked in 2018, with overdose rates that vary across demographic variables.10 Consequently, New Mexico state law added language requiring clinicians prescribing opioids for 5 days or longer to co-prescribe naloxone along with written information on how to administer the opioid antagonist.11 New Mexico is also a geographically large state with a relatively low overall population characterized by striking health disparities, particularly as related to access to care.
The purpose of this study is to describe the same-day availability of naloxone throughout the state of New Mexico after a change in state law requiring co-prescription was enacted, to help identify challenges to patients receiving it. Comprehensive examination of barriers to patients accessing this life-saving medication can advise strategies to both improve patient-centered care and potentially reduce deaths.
Methods
To better understand barriers to patients obtaining naloxone, in July and August of 2019 we performed an audit (“secret shopper”) study of all pharmacies in the state, posing as patients wishing to obtain naloxone. A publicly available list of every pharmacy in New Mexico was used to identify 89 pharmacies in Albuquerque (the most populous city in New Mexico) and 106 pharmacies throughout the rest of the state.12
Every pharmacy was called via a publicly available phone number during business hours (confirmed via an internet search), at least 2 hours prior to closing. One of 3 researchers telephoned pharmacies posing as a patient and inquired whether naloxone would be available for pick up the same day. If the pharmacy confirmed it was available that day, the call concluded. If naloxone was unavailable for same day pick up, researchers asked when it would be next available. Each pharmacy was called once, and neither insurance information nor cost was offered or requested. All questions were asked in English by native English speakers.
All responses were recorded in a secure spreadsheet. Once all responses were received and reviewed, they were characterized in discrete response categories: same day, within 1 to 2 days, within 3 to 4 days, within a week, or unsure/unknown. Naloxone availability was also tracked by city/municipality, and this was compared to the state’s population distribution.
No personally identifiable information was obtained. This study was Institutional Review Board exempt.
Results
Responses were recorded from 183 pharmacies. Seventeen locations were eliminated from our analysis because their phone system was inoperable or the pharmacy was permanently closed. Of the pharmacies reached, 84.7% (155/183) reported they have naloxone available for pick up on the same day (Figure 1). Of the 15.3% (28) pharmacies that did not have same-day availability, 60.7% (17 pharmacies) reported availability in 1 to 2 days, 3.6% had availability in 3 to 4 days, 3.6% had availability in 1 week, and 32.1% were unsure of next availability (Figure 2). More than one-third of the state’s patients reside in municipalities where naloxone is immediately available in at least 72% of pharmacies (Table).13
Discussion
Increased access to naloxone at the state and community level is associated with reduced risk for death from overdose, and, consequently, widespread availability is recommended.14-17 Statewide real-time pharmacy availability of naloxone—as patients would experience availability—has not been previously reported. These findings suggest unpredictable same-day availability that may affect experience and care outcomes. That other studies have found similar challenges in naloxone availability in other municipalities and regions suggests this barrier to access is widespread,6-9 and likely affects patients throughout the country.
Many patients have misgivings about naloxone, and it places an undue burden on them to travel to multiple pharmacies or take repeated trips to fill prescriptions. Additionally, patients without reliable transportation may be unable to return at a later date. Although we found most pharmacies in New Mexico without immediate availability of naloxone reported they could have it within several days, such a delay may reduce the likelihood that patients will fill their prescription at all. It is also concerning that many pharmacies are unsure of when naloxone will be available, particularly when some of these may be the only pharmacy easily accessible to patients or the one where they regularly fill their prescriptions.
Barriers to naloxone availability requires further study due to possible negative consequences for patient safety and risks for exacerbating health disparities among vulnerable populations. Further research may focus on examining the effects on patients when naloxone dispensing is delayed or impossible, why there is variability in naloxone availability between different pharmacies and municipalities, the reasons for uncertainty when naloxone will be available, and effective solutions. Expanded naloxone distribution in community locations and in clinics offers one potential patient-centered solution that should be explored, but it is likely that more widespread and systemic solutions will require policy and regulatory changes at the state and national levels.
Limitations of this study include that the findings may be relevant for solely 1 state, such as in the case of state-specific barriers to keeping naloxone in stock that we are unaware of. However, it is unclear why that would be the case, and it is more likely that similar barriers are pervasive. Additionally, repeat phone calls, which we did not follow up with, may have yielded more pharmacies with naloxone availability. However, due to the stigma associated with obtaining naloxone, it may be that patients will not make multiple calls either—highlighting how important real-time availability is.
Conclusion
Urgent solutions are needed to address the epidemic of deaths from opioid overdoses. Naloxone availability is an important tool for reducing these deaths, resulting in numerous state laws attempting to increase access. Despite this, there are persistent barriers to patients receiving naloxone, including a lack of same-day availability at pharmacies. Our results suggest that this underexplored barrier is widespread. Improving both availability and accessibility of naloxone may include legislative policy solutions as well as patient-oriented solutions, such as distribution in clinics and hospitals when opioid prescriptions are first written. Further research should be conducted to determine patient-centered, effective solutions that can improve outcomes.
Corresponding author: Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, Department of Internal Medicine, University of New Mexico; ebarrett@salud.unm.edu.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Mason M, Welch SB, Arunkumar P, et al. Notes from the field: opioid overdose deaths before, during, and after an 11-week COVID-19 stay-at-home order—Cook County, Illinois, January 1, 2018–October 6, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(10):362-363. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7010a3
2. Kaiser Family Foundation. Opioid overdose death rates and all drug overdose death rates per 100,000 population (age-adjusted). Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.kff.org/other/state-indicator/opioid-overdose-death
3. Sohn M, Talbert JC, Huang Z, et al. Association of naloxone coprescription laws with naloxone prescription dispensing in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(6):e196215. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.6215
4. Smart R, Pardo B, Davis CS. Systematic review of the emerging literature on the effectiveness of naloxone access laws in the United States. Addiction. 2021;116(1):6-17. doi:10.1111/add.15163
5. Mueller SR, Koester S, Glanz JM, et al. Attitudes toward naloxone prescribing in clinical settings: a qualitative study of patients prescribed high dose opioids for chronic non-cancer pain. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(3):277-283. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3895-8
6. Thornton JD, Lyvers E, Scott VGG, Dwibedi N. Pharmacists’ readiness to provide naloxone in community pharmacies in West Virginia. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2017;57(2S):S12-S18.e4. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2016.12.070
7. Spivey C, Wilder A, Chisholm-Burns MA, et al. Evaluation of naloxone access, pricing, and barriers to dispensing in Tennessee retail community pharmacies. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020;60(5):694-701.e1. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2020.01.030
8. Nguyen JL, Gilbert LR, Beasley L, et al. Availability of naloxone at rural Georgia pharmacies, 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1921227. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.21227
9. Guadamuz JS, Alexander GC, Chaudhri T, et al. Availability and cost of naloxone nasal spray at pharmacies in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(6):e195388. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.5388
10. Edge K. Changes in drug overdose mortality in New Mexico. New Mexico Epidemiology. July 2020 (3). https://www.nmhealth.org/data/view/report/2402/
11. Senate Bill 221. 54th Legislature, State of New Mexico, First Session, 2019 (introduced by William P. Soules). Accessed October 6, 2021. https://nmlegis.gov/Sessions/19%20Regular/bills/senate/SB0221.pdf
12. GoodRx. Find pharmacies in New Mexico. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.goodrx.com/pharmacy-near-me/all/nm
13. U.S. Census Bureau. QuickFacts: New Mexico. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/NM
14. Linas BP, Savinkina A, Madushani RWMA, et al. Projected estimates of opioid mortality after community-level interventions. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037259. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37259
15. You HS, Ha J, Kang CY, et al. Regional variation in states’ naloxone accessibility laws in association with opioid overdose death rates—observational study (STROBE compliant). Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(22):e20033. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000020033
16. Pew Charitable Trusts. Expanded access to naloxone can curb opioid overdose deaths. October 20, 2020. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.
17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Still not enough naloxone where it’s most needed. August 6, 2019. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2019/p0806-naloxone.html
1. Mason M, Welch SB, Arunkumar P, et al. Notes from the field: opioid overdose deaths before, during, and after an 11-week COVID-19 stay-at-home order—Cook County, Illinois, January 1, 2018–October 6, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(10):362-363. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7010a3
2. Kaiser Family Foundation. Opioid overdose death rates and all drug overdose death rates per 100,000 population (age-adjusted). Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.kff.org/other/state-indicator/opioid-overdose-death
3. Sohn M, Talbert JC, Huang Z, et al. Association of naloxone coprescription laws with naloxone prescription dispensing in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(6):e196215. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.6215
4. Smart R, Pardo B, Davis CS. Systematic review of the emerging literature on the effectiveness of naloxone access laws in the United States. Addiction. 2021;116(1):6-17. doi:10.1111/add.15163
5. Mueller SR, Koester S, Glanz JM, et al. Attitudes toward naloxone prescribing in clinical settings: a qualitative study of patients prescribed high dose opioids for chronic non-cancer pain. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(3):277-283. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3895-8
6. Thornton JD, Lyvers E, Scott VGG, Dwibedi N. Pharmacists’ readiness to provide naloxone in community pharmacies in West Virginia. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2017;57(2S):S12-S18.e4. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2016.12.070
7. Spivey C, Wilder A, Chisholm-Burns MA, et al. Evaluation of naloxone access, pricing, and barriers to dispensing in Tennessee retail community pharmacies. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020;60(5):694-701.e1. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2020.01.030
8. Nguyen JL, Gilbert LR, Beasley L, et al. Availability of naloxone at rural Georgia pharmacies, 2019. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1921227. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.21227
9. Guadamuz JS, Alexander GC, Chaudhri T, et al. Availability and cost of naloxone nasal spray at pharmacies in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(6):e195388. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.5388
10. Edge K. Changes in drug overdose mortality in New Mexico. New Mexico Epidemiology. July 2020 (3). https://www.nmhealth.org/data/view/report/2402/
11. Senate Bill 221. 54th Legislature, State of New Mexico, First Session, 2019 (introduced by William P. Soules). Accessed October 6, 2021. https://nmlegis.gov/Sessions/19%20Regular/bills/senate/SB0221.pdf
12. GoodRx. Find pharmacies in New Mexico. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.goodrx.com/pharmacy-near-me/all/nm
13. U.S. Census Bureau. QuickFacts: New Mexico. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/NM
14. Linas BP, Savinkina A, Madushani RWMA, et al. Projected estimates of opioid mortality after community-level interventions. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037259. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37259
15. You HS, Ha J, Kang CY, et al. Regional variation in states’ naloxone accessibility laws in association with opioid overdose death rates—observational study (STROBE compliant). Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(22):e20033. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000020033
16. Pew Charitable Trusts. Expanded access to naloxone can curb opioid overdose deaths. October 20, 2020. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.
17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Still not enough naloxone where it’s most needed. August 6, 2019. Accessed October 6, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2019/p0806-naloxone.html