User login
How Clinicians Can Help Patients Navigate Psychedelics/Microdosing
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When Is Sexual Behavior Out of Control?
A 25-year-old man comes in with a pulled muscle. You ask if he has anything else to discuss. Sheepishly, he says he is concerned about his use of pornography.
A 45-year-old woman struggling with depression finds herself persistently seeking sex outside the bounds of her long-term relationship. Her partner is threatening to leave. She is devastated and tells you she doesn’t understand her own behavior.
Do these patients have some form of sex addiction? How should a primary care clinician intervene? Is a referral to a 12-step program for sex addiction the right choice? What other options exist? Is a diagnosis — let alone treatment — possible or appropriate?
‘Who Are You Calling “Abnormal” ’?
Normal is not a meaningful concept in human sexual behavior. To quote the sex therapist Marty Klein, PhD: “Normal is just a setting on the dryer.”
The same goes among partners: What is “normal” for one person in a sexual relationship may discomfit another. In partnerships, we have differences around all sorts of issues, from finances to parenting to how to load the dishwasher. Why should sex, sexual desire, and sexual frequency be different?
Remember: Shame, fear, and secrecy often play a role in perpetuating behaviors that cause distress. Helping our patients accept and embrace their whole selves can provide important healing, relief from anxiety, and may even help them regulate their actions. Feeling less shame, fear, and secrecy may facilitate safer choices about sex, as well as testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections.
The International Classification of Diseases-11 includes compulsive sexual behavior disorder (CSBD)as an attempt to create consensus around a complicated, and hotly debated, problem to facilitate diagnosis and research. Syndromes similar to CSBD have had many names: “hypersexual disorder,” “sexual addiction,” “sexual compulsivity,” and “out-of-control sexual behavior.” A sizable cohort of the sexuality research community casts doubt on whether CSBD is even a discrete diagnosis.
According to the ICD-11, CSBD is characterized by “intense, repetitive sexual impulses or urges that are experienced as irresistible or uncontrollable” and result in significant distress or functional impairment.
This diagnosis has several important rule-outs. First, paraphilias, defined as a set of nonconsensual sexual behaviors and interests, are excluded. Another is that distress exclusively related to moral judgment or social disapproval is not sufficient for a diagnosis of CSBD. Finally, the diagnosis hinges on distress and does not rely on frequency of any type of sexual behavior. Some people experience significant distress over behaviors in which they engage infrequently, whereas others may have no distress from activities in which they engage quite frequently.
In one study from Germany, 5% of men and 3% of women met criteria for CSBD. A small US study found the number to be 10% and 7%, respectively. The diagnosis is not simple. Compulsive sexual behavior can be secondary to other mental health or medical conditions. Behaviors sometimes confused with CSBD can result from neurologic diseases, such as frontal brain lesions or frontotemporal dementia, as well as the use of substances and medications that enhance dopaminergic activity.
Impaired control over sexual impulses occurs in manic and hypomanic episodes. Compulsive sexual behavior frequently co-occurs with mood disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and substance use disorders. Those meeting criteria for CSBD may engage in sexual behaviors as a way of coping with depression, anxiety, boredom, loneliness, or other negative affective states.
The diagnosis of CSBD may be useful for clinicians. However, many, perhaps most, patients who present with concerns about their sexual behavior will fail to meet most criteria for CSBD. Their problem is of shorter duration, related to morality, external disapproval, lack of sexual health information, and anxiety about diverse erotic interests. It may be helpful for them to understand that they are not in the grip of a lifelong disorder but are experiencing common life challenges.
Societal concerns about sexually explicit media, often called pornography, are complex, conflicting, and catastrophizing. Some studies indicate that sexually explicit media are positive for both individual and relational sexual satisfaction; other studies have found negative effects on sexual function. Concerns about pornography often are conflated with taboos about solo sexual activity. Ironically, use of pornography is associated with fear of addiction to pornography, creating a spiral of negative self-perception.
Consequences of sexual behavior may induce distress, even if a person doesn’t meet criteria for CSBD, such as potential dissolution of a marriage, loss of a job, excessive spending, sexually transmitted infections, other health concerns, and even legal problems. Sexual behavior might not be the central issue but rather an offshoot of relational distress, a mental health disorder, or a dysfunctional coping style.
Guilt and shame can act as potent contributors to maintaining the behaviors as well as promoting secrecy around them. Sexual medicine experts recommend avoiding interventions that increase the experience of discrimination and stigma and avoiding the pathologization of the behaviors of sexually diverse individuals. As in so many aspects of medical care, we must walk in our patients’ shoes and avoid imposing on them our own moral or religious values.
What Can a Primary Care Provider Do?
When a patient is concerned about sexual behavior that feels out of control, primary care providers have an important role in evaluating for neurologic disease or side effects related to the use of medication or other substances, and facilitating psychiatric assessment to evaluate for mental health comorbidities, past trauma, and associated attachment disorders.
Our patients need resources to tease out the individual and relational problems that may arise. Seek out well-trained sex therapy colleagues in your community. The American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors, and Therapists (AASECT) is one certifying body in the United States for sex therapy.
Because of the heterogeneity of those who present with out-of-control sexual behavior, no one treatment fits all. Twelve-step programs, especially those with a focus on sexual “abstinence,” may not be the best choice. Many psychotherapeutic modalities are effective and often focus on addressing underlying or unrecognized mental health concerns, provide training on self-regulation and urge management, and relationship skills. Most important, the therapist needs to be sexologically informed and aware of their own biases around sexuality. Medical treatments are not recommended without concurrent psychological intervention.
Relational sex therapy can help couples create clear relational agreements that work for both parties (or, in polyamorous relationships, everyone involved). Relational distress also may be a stimulus for individual psychotherapy.
Back to these two patients.
The 25-year-old could be counseled that use of sexually explicit media and solo sex are not inherently bad or damaging. When used for pleasure and enjoyment, they do not lead to problems with partnered sex or cause sexual dysfunction. Counseling him to move toward social engagement and life goals, rather than away from pornography, may be all that is necessary.
Our second patient probably will need more intensive treatment, including medication management for her mood and referral to a certified sex therapist who has expertise in working with out-of-control sexual behavior. When she returns to see you in follow-up, she ideally expresses reduced shame, more autonomy, and renewed connection to her values, and she is keeping her relational agreements without sacrificing her sexual needs.
Dr. Kranz is medical director, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness; assistant professor of Clinical Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York. Dr. Kranz has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rosen is director of Behavioral Health, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness, Rochester, New York. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A 25-year-old man comes in with a pulled muscle. You ask if he has anything else to discuss. Sheepishly, he says he is concerned about his use of pornography.
A 45-year-old woman struggling with depression finds herself persistently seeking sex outside the bounds of her long-term relationship. Her partner is threatening to leave. She is devastated and tells you she doesn’t understand her own behavior.
Do these patients have some form of sex addiction? How should a primary care clinician intervene? Is a referral to a 12-step program for sex addiction the right choice? What other options exist? Is a diagnosis — let alone treatment — possible or appropriate?
‘Who Are You Calling “Abnormal” ’?
Normal is not a meaningful concept in human sexual behavior. To quote the sex therapist Marty Klein, PhD: “Normal is just a setting on the dryer.”
The same goes among partners: What is “normal” for one person in a sexual relationship may discomfit another. In partnerships, we have differences around all sorts of issues, from finances to parenting to how to load the dishwasher. Why should sex, sexual desire, and sexual frequency be different?
Remember: Shame, fear, and secrecy often play a role in perpetuating behaviors that cause distress. Helping our patients accept and embrace their whole selves can provide important healing, relief from anxiety, and may even help them regulate their actions. Feeling less shame, fear, and secrecy may facilitate safer choices about sex, as well as testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections.
The International Classification of Diseases-11 includes compulsive sexual behavior disorder (CSBD)as an attempt to create consensus around a complicated, and hotly debated, problem to facilitate diagnosis and research. Syndromes similar to CSBD have had many names: “hypersexual disorder,” “sexual addiction,” “sexual compulsivity,” and “out-of-control sexual behavior.” A sizable cohort of the sexuality research community casts doubt on whether CSBD is even a discrete diagnosis.
According to the ICD-11, CSBD is characterized by “intense, repetitive sexual impulses or urges that are experienced as irresistible or uncontrollable” and result in significant distress or functional impairment.
This diagnosis has several important rule-outs. First, paraphilias, defined as a set of nonconsensual sexual behaviors and interests, are excluded. Another is that distress exclusively related to moral judgment or social disapproval is not sufficient for a diagnosis of CSBD. Finally, the diagnosis hinges on distress and does not rely on frequency of any type of sexual behavior. Some people experience significant distress over behaviors in which they engage infrequently, whereas others may have no distress from activities in which they engage quite frequently.
In one study from Germany, 5% of men and 3% of women met criteria for CSBD. A small US study found the number to be 10% and 7%, respectively. The diagnosis is not simple. Compulsive sexual behavior can be secondary to other mental health or medical conditions. Behaviors sometimes confused with CSBD can result from neurologic diseases, such as frontal brain lesions or frontotemporal dementia, as well as the use of substances and medications that enhance dopaminergic activity.
Impaired control over sexual impulses occurs in manic and hypomanic episodes. Compulsive sexual behavior frequently co-occurs with mood disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and substance use disorders. Those meeting criteria for CSBD may engage in sexual behaviors as a way of coping with depression, anxiety, boredom, loneliness, or other negative affective states.
The diagnosis of CSBD may be useful for clinicians. However, many, perhaps most, patients who present with concerns about their sexual behavior will fail to meet most criteria for CSBD. Their problem is of shorter duration, related to morality, external disapproval, lack of sexual health information, and anxiety about diverse erotic interests. It may be helpful for them to understand that they are not in the grip of a lifelong disorder but are experiencing common life challenges.
Societal concerns about sexually explicit media, often called pornography, are complex, conflicting, and catastrophizing. Some studies indicate that sexually explicit media are positive for both individual and relational sexual satisfaction; other studies have found negative effects on sexual function. Concerns about pornography often are conflated with taboos about solo sexual activity. Ironically, use of pornography is associated with fear of addiction to pornography, creating a spiral of negative self-perception.
Consequences of sexual behavior may induce distress, even if a person doesn’t meet criteria for CSBD, such as potential dissolution of a marriage, loss of a job, excessive spending, sexually transmitted infections, other health concerns, and even legal problems. Sexual behavior might not be the central issue but rather an offshoot of relational distress, a mental health disorder, or a dysfunctional coping style.
Guilt and shame can act as potent contributors to maintaining the behaviors as well as promoting secrecy around them. Sexual medicine experts recommend avoiding interventions that increase the experience of discrimination and stigma and avoiding the pathologization of the behaviors of sexually diverse individuals. As in so many aspects of medical care, we must walk in our patients’ shoes and avoid imposing on them our own moral or religious values.
What Can a Primary Care Provider Do?
When a patient is concerned about sexual behavior that feels out of control, primary care providers have an important role in evaluating for neurologic disease or side effects related to the use of medication or other substances, and facilitating psychiatric assessment to evaluate for mental health comorbidities, past trauma, and associated attachment disorders.
Our patients need resources to tease out the individual and relational problems that may arise. Seek out well-trained sex therapy colleagues in your community. The American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors, and Therapists (AASECT) is one certifying body in the United States for sex therapy.
Because of the heterogeneity of those who present with out-of-control sexual behavior, no one treatment fits all. Twelve-step programs, especially those with a focus on sexual “abstinence,” may not be the best choice. Many psychotherapeutic modalities are effective and often focus on addressing underlying or unrecognized mental health concerns, provide training on self-regulation and urge management, and relationship skills. Most important, the therapist needs to be sexologically informed and aware of their own biases around sexuality. Medical treatments are not recommended without concurrent psychological intervention.
Relational sex therapy can help couples create clear relational agreements that work for both parties (or, in polyamorous relationships, everyone involved). Relational distress also may be a stimulus for individual psychotherapy.
Back to these two patients.
The 25-year-old could be counseled that use of sexually explicit media and solo sex are not inherently bad or damaging. When used for pleasure and enjoyment, they do not lead to problems with partnered sex or cause sexual dysfunction. Counseling him to move toward social engagement and life goals, rather than away from pornography, may be all that is necessary.
Our second patient probably will need more intensive treatment, including medication management for her mood and referral to a certified sex therapist who has expertise in working with out-of-control sexual behavior. When she returns to see you in follow-up, she ideally expresses reduced shame, more autonomy, and renewed connection to her values, and she is keeping her relational agreements without sacrificing her sexual needs.
Dr. Kranz is medical director, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness; assistant professor of Clinical Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York. Dr. Kranz has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rosen is director of Behavioral Health, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness, Rochester, New York. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A 25-year-old man comes in with a pulled muscle. You ask if he has anything else to discuss. Sheepishly, he says he is concerned about his use of pornography.
A 45-year-old woman struggling with depression finds herself persistently seeking sex outside the bounds of her long-term relationship. Her partner is threatening to leave. She is devastated and tells you she doesn’t understand her own behavior.
Do these patients have some form of sex addiction? How should a primary care clinician intervene? Is a referral to a 12-step program for sex addiction the right choice? What other options exist? Is a diagnosis — let alone treatment — possible or appropriate?
‘Who Are You Calling “Abnormal” ’?
Normal is not a meaningful concept in human sexual behavior. To quote the sex therapist Marty Klein, PhD: “Normal is just a setting on the dryer.”
The same goes among partners: What is “normal” for one person in a sexual relationship may discomfit another. In partnerships, we have differences around all sorts of issues, from finances to parenting to how to load the dishwasher. Why should sex, sexual desire, and sexual frequency be different?
Remember: Shame, fear, and secrecy often play a role in perpetuating behaviors that cause distress. Helping our patients accept and embrace their whole selves can provide important healing, relief from anxiety, and may even help them regulate their actions. Feeling less shame, fear, and secrecy may facilitate safer choices about sex, as well as testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections.
The International Classification of Diseases-11 includes compulsive sexual behavior disorder (CSBD)as an attempt to create consensus around a complicated, and hotly debated, problem to facilitate diagnosis and research. Syndromes similar to CSBD have had many names: “hypersexual disorder,” “sexual addiction,” “sexual compulsivity,” and “out-of-control sexual behavior.” A sizable cohort of the sexuality research community casts doubt on whether CSBD is even a discrete diagnosis.
According to the ICD-11, CSBD is characterized by “intense, repetitive sexual impulses or urges that are experienced as irresistible or uncontrollable” and result in significant distress or functional impairment.
This diagnosis has several important rule-outs. First, paraphilias, defined as a set of nonconsensual sexual behaviors and interests, are excluded. Another is that distress exclusively related to moral judgment or social disapproval is not sufficient for a diagnosis of CSBD. Finally, the diagnosis hinges on distress and does not rely on frequency of any type of sexual behavior. Some people experience significant distress over behaviors in which they engage infrequently, whereas others may have no distress from activities in which they engage quite frequently.
In one study from Germany, 5% of men and 3% of women met criteria for CSBD. A small US study found the number to be 10% and 7%, respectively. The diagnosis is not simple. Compulsive sexual behavior can be secondary to other mental health or medical conditions. Behaviors sometimes confused with CSBD can result from neurologic diseases, such as frontal brain lesions or frontotemporal dementia, as well as the use of substances and medications that enhance dopaminergic activity.
Impaired control over sexual impulses occurs in manic and hypomanic episodes. Compulsive sexual behavior frequently co-occurs with mood disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and substance use disorders. Those meeting criteria for CSBD may engage in sexual behaviors as a way of coping with depression, anxiety, boredom, loneliness, or other negative affective states.
The diagnosis of CSBD may be useful for clinicians. However, many, perhaps most, patients who present with concerns about their sexual behavior will fail to meet most criteria for CSBD. Their problem is of shorter duration, related to morality, external disapproval, lack of sexual health information, and anxiety about diverse erotic interests. It may be helpful for them to understand that they are not in the grip of a lifelong disorder but are experiencing common life challenges.
Societal concerns about sexually explicit media, often called pornography, are complex, conflicting, and catastrophizing. Some studies indicate that sexually explicit media are positive for both individual and relational sexual satisfaction; other studies have found negative effects on sexual function. Concerns about pornography often are conflated with taboos about solo sexual activity. Ironically, use of pornography is associated with fear of addiction to pornography, creating a spiral of negative self-perception.
Consequences of sexual behavior may induce distress, even if a person doesn’t meet criteria for CSBD, such as potential dissolution of a marriage, loss of a job, excessive spending, sexually transmitted infections, other health concerns, and even legal problems. Sexual behavior might not be the central issue but rather an offshoot of relational distress, a mental health disorder, or a dysfunctional coping style.
Guilt and shame can act as potent contributors to maintaining the behaviors as well as promoting secrecy around them. Sexual medicine experts recommend avoiding interventions that increase the experience of discrimination and stigma and avoiding the pathologization of the behaviors of sexually diverse individuals. As in so many aspects of medical care, we must walk in our patients’ shoes and avoid imposing on them our own moral or religious values.
What Can a Primary Care Provider Do?
When a patient is concerned about sexual behavior that feels out of control, primary care providers have an important role in evaluating for neurologic disease or side effects related to the use of medication or other substances, and facilitating psychiatric assessment to evaluate for mental health comorbidities, past trauma, and associated attachment disorders.
Our patients need resources to tease out the individual and relational problems that may arise. Seek out well-trained sex therapy colleagues in your community. The American Association of Sexuality Educators, Counselors, and Therapists (AASECT) is one certifying body in the United States for sex therapy.
Because of the heterogeneity of those who present with out-of-control sexual behavior, no one treatment fits all. Twelve-step programs, especially those with a focus on sexual “abstinence,” may not be the best choice. Many psychotherapeutic modalities are effective and often focus on addressing underlying or unrecognized mental health concerns, provide training on self-regulation and urge management, and relationship skills. Most important, the therapist needs to be sexologically informed and aware of their own biases around sexuality. Medical treatments are not recommended without concurrent psychological intervention.
Relational sex therapy can help couples create clear relational agreements that work for both parties (or, in polyamorous relationships, everyone involved). Relational distress also may be a stimulus for individual psychotherapy.
Back to these two patients.
The 25-year-old could be counseled that use of sexually explicit media and solo sex are not inherently bad or damaging. When used for pleasure and enjoyment, they do not lead to problems with partnered sex or cause sexual dysfunction. Counseling him to move toward social engagement and life goals, rather than away from pornography, may be all that is necessary.
Our second patient probably will need more intensive treatment, including medication management for her mood and referral to a certified sex therapist who has expertise in working with out-of-control sexual behavior. When she returns to see you in follow-up, she ideally expresses reduced shame, more autonomy, and renewed connection to her values, and she is keeping her relational agreements without sacrificing her sexual needs.
Dr. Kranz is medical director, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness; assistant professor of Clinical Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York. Dr. Kranz has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rosen is director of Behavioral Health, Rochester Center for Sexual Wellness, Rochester, New York. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Avoidance Predicts Worse Long-term Outcomes From Intensive OCD Treatment
BOSTON — , a new analysis shows.
Although avoidant patients with OCD reported symptom improvement immediately after treatment, baseline avoidance was associated with significantly worse outcomes 1 year later.
“Avoidance is often overlooked in OCD,” said lead investigator Michael Wheaton, PhD, an assistant professor of psychology at Barnard College in New York. “It’s really important clinically to focus on that.”
The findings were presented at the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) annual conference and published online in the Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders.
The Avoidance Question
Although ERP is often included in treatment for OCD, between 38% and 60% of patients have residual symptoms after treatment and as many as a quarter don’t respond at all, Dr. Wheaton said.
Severe pretreatment avoidance could affect the efficacy of ERP, which involves exposing patients to situations and stimuli they may usually avoid. But prior research to identify predictors of ERP outcomes have largely excluded severity of pretreatment avoidance as a factor.
The new study analyzed data from 161 Norwegian adults with treatment-resistant OCD who participated in a concentrated ERP therapy called the Bergen 4-day Exposure and Response Prevention (B4DT) treatment. This method delivers intensive treatment over 4 consecutive days in small groups with a 1:1 ratio of therapists to patients.
B4DT is common throughout Norway, with the treatment offered at 55 clinics, and has been trialed in other countries including the United States, Nepal, Ecuador, and Kenya.
Symptom severity was measured using the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (YBOCS) at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 3 and 12 months later. Functional impairment was measured 12 months after treatment using the Work and Social Adjustment Scale.
Although the formal scoring of the YBOCS does not include any questions about avoidance, one question in the auxiliary items does: “Have you been avoiding doing anything, going anyplace or being with anyone because of obsessional thoughts or out of a need to perform compulsions?”
Dr. Wheaton used this response, which is rated on a five-point scale, to measure avoidance. Overall, 18.8% of participants had no deliberate avoidance, 15% were rated as having mild avoidance, 36% moderate, 23% severe, and 6.8% extreme.
Long-Term Outcomes
Overall, 84% of participants responded to treatment, with a change in mean YBOCS scores from 26.98 at baseline to 12.28 immediately after treatment. Acute outcomes were similar between avoidant and nonavoidant patients.
But at 12-month follow-up, even after controlling for pretreatment OCD severity, patients with more extensive avoidance at baseline had worse long-term outcomes — both more severe OCD symptoms (P = .031) and greater functional impairment (P = .002).
Across all patients, average avoidance decreased significantly immediately after the concentrated ERP treatment. Average avoidance increased somewhat at 3- and 12-month follow-up but remained significantly improved from pretreatment.
Interestingly, patients’ change in avoidance immediately post-treatment to 3 months post-treatment predicted worsening of OCD severity at 12 months. This change could potentially identify people at risk of relapse, Dr. Wheaton said.
Previous research has shown that pretreatment OCD severity, measured using the YBOCS, does not significantly predict ERP outcomes, and this study found the same.
Relapse Prevention
“The fact that they did equally well in the short run I think was great,” Dr. Wheaton said.
Previous research, including 2018 and 2023 papers from Wheaton’s team, has shown that more avoidant patients have worse outcomes from standard 12-week ERP programs.
One possible explanation for this difference is that in the Bergen treatment, most exposures happen during face-to-face time with a therapist instead of as homework, which may be easier to avoid, he said.
“But then the finding was that their symptoms were worsening over time — their avoidance was sliding back into old habits,” said Dr. Wheaton.
He would like to see the study replicated in diverse populations outside Norway and in treatment-naive people. Dr. Wheaton also noted that the study assessed avoidance with only a single item.
Future work is needed to test ways to improve relapse prevention. For example, clinicians may be able to monitor for avoidance behaviors post-treatment, which could be the start of a relapse, said Dr. Wheaton.
Although clinicians consider avoidance when treating phobias, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder, “somehow avoidance got relegated to item 11 on the YBOCS that isn’t scored,” Helen Blair Simpson, MD, PhD, director of the Center for OCD and Related Disorders at Columbia University, New York, New York, said during the presentation.
A direct implication of Dr. Wheaton’s findings to clinical practice is to “talk to people about their avoidance right up front,” said Dr. Simpson, who was not part of the study.
Clinicians who deliver ERP in their practices “can apply this tomorrow,” Dr. Simpson added.
Dr. Wheaton reported no disclosures. Dr. Simpson reported a stipend from the American Medical Association for serving as associate editor of JAMA Psychiatry and royalties from UpToDate, Inc for articles on OCD and from Cambridge University Press for editing a book on anxiety disorders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — , a new analysis shows.
Although avoidant patients with OCD reported symptom improvement immediately after treatment, baseline avoidance was associated with significantly worse outcomes 1 year later.
“Avoidance is often overlooked in OCD,” said lead investigator Michael Wheaton, PhD, an assistant professor of psychology at Barnard College in New York. “It’s really important clinically to focus on that.”
The findings were presented at the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) annual conference and published online in the Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders.
The Avoidance Question
Although ERP is often included in treatment for OCD, between 38% and 60% of patients have residual symptoms after treatment and as many as a quarter don’t respond at all, Dr. Wheaton said.
Severe pretreatment avoidance could affect the efficacy of ERP, which involves exposing patients to situations and stimuli they may usually avoid. But prior research to identify predictors of ERP outcomes have largely excluded severity of pretreatment avoidance as a factor.
The new study analyzed data from 161 Norwegian adults with treatment-resistant OCD who participated in a concentrated ERP therapy called the Bergen 4-day Exposure and Response Prevention (B4DT) treatment. This method delivers intensive treatment over 4 consecutive days in small groups with a 1:1 ratio of therapists to patients.
B4DT is common throughout Norway, with the treatment offered at 55 clinics, and has been trialed in other countries including the United States, Nepal, Ecuador, and Kenya.
Symptom severity was measured using the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (YBOCS) at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 3 and 12 months later. Functional impairment was measured 12 months after treatment using the Work and Social Adjustment Scale.
Although the formal scoring of the YBOCS does not include any questions about avoidance, one question in the auxiliary items does: “Have you been avoiding doing anything, going anyplace or being with anyone because of obsessional thoughts or out of a need to perform compulsions?”
Dr. Wheaton used this response, which is rated on a five-point scale, to measure avoidance. Overall, 18.8% of participants had no deliberate avoidance, 15% were rated as having mild avoidance, 36% moderate, 23% severe, and 6.8% extreme.
Long-Term Outcomes
Overall, 84% of participants responded to treatment, with a change in mean YBOCS scores from 26.98 at baseline to 12.28 immediately after treatment. Acute outcomes were similar between avoidant and nonavoidant patients.
But at 12-month follow-up, even after controlling for pretreatment OCD severity, patients with more extensive avoidance at baseline had worse long-term outcomes — both more severe OCD symptoms (P = .031) and greater functional impairment (P = .002).
Across all patients, average avoidance decreased significantly immediately after the concentrated ERP treatment. Average avoidance increased somewhat at 3- and 12-month follow-up but remained significantly improved from pretreatment.
Interestingly, patients’ change in avoidance immediately post-treatment to 3 months post-treatment predicted worsening of OCD severity at 12 months. This change could potentially identify people at risk of relapse, Dr. Wheaton said.
Previous research has shown that pretreatment OCD severity, measured using the YBOCS, does not significantly predict ERP outcomes, and this study found the same.
Relapse Prevention
“The fact that they did equally well in the short run I think was great,” Dr. Wheaton said.
Previous research, including 2018 and 2023 papers from Wheaton’s team, has shown that more avoidant patients have worse outcomes from standard 12-week ERP programs.
One possible explanation for this difference is that in the Bergen treatment, most exposures happen during face-to-face time with a therapist instead of as homework, which may be easier to avoid, he said.
“But then the finding was that their symptoms were worsening over time — their avoidance was sliding back into old habits,” said Dr. Wheaton.
He would like to see the study replicated in diverse populations outside Norway and in treatment-naive people. Dr. Wheaton also noted that the study assessed avoidance with only a single item.
Future work is needed to test ways to improve relapse prevention. For example, clinicians may be able to monitor for avoidance behaviors post-treatment, which could be the start of a relapse, said Dr. Wheaton.
Although clinicians consider avoidance when treating phobias, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder, “somehow avoidance got relegated to item 11 on the YBOCS that isn’t scored,” Helen Blair Simpson, MD, PhD, director of the Center for OCD and Related Disorders at Columbia University, New York, New York, said during the presentation.
A direct implication of Dr. Wheaton’s findings to clinical practice is to “talk to people about their avoidance right up front,” said Dr. Simpson, who was not part of the study.
Clinicians who deliver ERP in their practices “can apply this tomorrow,” Dr. Simpson added.
Dr. Wheaton reported no disclosures. Dr. Simpson reported a stipend from the American Medical Association for serving as associate editor of JAMA Psychiatry and royalties from UpToDate, Inc for articles on OCD and from Cambridge University Press for editing a book on anxiety disorders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — , a new analysis shows.
Although avoidant patients with OCD reported symptom improvement immediately after treatment, baseline avoidance was associated with significantly worse outcomes 1 year later.
“Avoidance is often overlooked in OCD,” said lead investigator Michael Wheaton, PhD, an assistant professor of psychology at Barnard College in New York. “It’s really important clinically to focus on that.”
The findings were presented at the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) annual conference and published online in the Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders.
The Avoidance Question
Although ERP is often included in treatment for OCD, between 38% and 60% of patients have residual symptoms after treatment and as many as a quarter don’t respond at all, Dr. Wheaton said.
Severe pretreatment avoidance could affect the efficacy of ERP, which involves exposing patients to situations and stimuli they may usually avoid. But prior research to identify predictors of ERP outcomes have largely excluded severity of pretreatment avoidance as a factor.
The new study analyzed data from 161 Norwegian adults with treatment-resistant OCD who participated in a concentrated ERP therapy called the Bergen 4-day Exposure and Response Prevention (B4DT) treatment. This method delivers intensive treatment over 4 consecutive days in small groups with a 1:1 ratio of therapists to patients.
B4DT is common throughout Norway, with the treatment offered at 55 clinics, and has been trialed in other countries including the United States, Nepal, Ecuador, and Kenya.
Symptom severity was measured using the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (YBOCS) at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 3 and 12 months later. Functional impairment was measured 12 months after treatment using the Work and Social Adjustment Scale.
Although the formal scoring of the YBOCS does not include any questions about avoidance, one question in the auxiliary items does: “Have you been avoiding doing anything, going anyplace or being with anyone because of obsessional thoughts or out of a need to perform compulsions?”
Dr. Wheaton used this response, which is rated on a five-point scale, to measure avoidance. Overall, 18.8% of participants had no deliberate avoidance, 15% were rated as having mild avoidance, 36% moderate, 23% severe, and 6.8% extreme.
Long-Term Outcomes
Overall, 84% of participants responded to treatment, with a change in mean YBOCS scores from 26.98 at baseline to 12.28 immediately after treatment. Acute outcomes were similar between avoidant and nonavoidant patients.
But at 12-month follow-up, even after controlling for pretreatment OCD severity, patients with more extensive avoidance at baseline had worse long-term outcomes — both more severe OCD symptoms (P = .031) and greater functional impairment (P = .002).
Across all patients, average avoidance decreased significantly immediately after the concentrated ERP treatment. Average avoidance increased somewhat at 3- and 12-month follow-up but remained significantly improved from pretreatment.
Interestingly, patients’ change in avoidance immediately post-treatment to 3 months post-treatment predicted worsening of OCD severity at 12 months. This change could potentially identify people at risk of relapse, Dr. Wheaton said.
Previous research has shown that pretreatment OCD severity, measured using the YBOCS, does not significantly predict ERP outcomes, and this study found the same.
Relapse Prevention
“The fact that they did equally well in the short run I think was great,” Dr. Wheaton said.
Previous research, including 2018 and 2023 papers from Wheaton’s team, has shown that more avoidant patients have worse outcomes from standard 12-week ERP programs.
One possible explanation for this difference is that in the Bergen treatment, most exposures happen during face-to-face time with a therapist instead of as homework, which may be easier to avoid, he said.
“But then the finding was that their symptoms were worsening over time — their avoidance was sliding back into old habits,” said Dr. Wheaton.
He would like to see the study replicated in diverse populations outside Norway and in treatment-naive people. Dr. Wheaton also noted that the study assessed avoidance with only a single item.
Future work is needed to test ways to improve relapse prevention. For example, clinicians may be able to monitor for avoidance behaviors post-treatment, which could be the start of a relapse, said Dr. Wheaton.
Although clinicians consider avoidance when treating phobias, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder, “somehow avoidance got relegated to item 11 on the YBOCS that isn’t scored,” Helen Blair Simpson, MD, PhD, director of the Center for OCD and Related Disorders at Columbia University, New York, New York, said during the presentation.
A direct implication of Dr. Wheaton’s findings to clinical practice is to “talk to people about their avoidance right up front,” said Dr. Simpson, who was not part of the study.
Clinicians who deliver ERP in their practices “can apply this tomorrow,” Dr. Simpson added.
Dr. Wheaton reported no disclosures. Dr. Simpson reported a stipend from the American Medical Association for serving as associate editor of JAMA Psychiatry and royalties from UpToDate, Inc for articles on OCD and from Cambridge University Press for editing a book on anxiety disorders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADAA 2024
OCD Tied to a Twofold Increased Risk for All-Cause Mortality
TOPLINE:
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is linked to a twofold increased risk for all-cause mortality and a heightened risk for death from both natural and unnatural causes, a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators studied a population-based cohort (58% female) of 61,378 people with OCD and 613,780 unaffected individuals from several Swedish population registers and a sibling cohort of 34,085 people with OCD (58% female) and 47,874 unaffected full siblings (48% female).
- The median 8.1-year follow-up and median age at first diagnosis of OCD were 27 years.
- The researchers used Cox proportional hazard models, adjusting for birth year, sex, county, country of birth (Sweden vs abroad), and sociodemographic variables.
TAKEAWAY:
- (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.82; 95% CI, 1.76-1.89), an almost threefold higher risk for mortality due to unnatural causes (aHR, 3.30; 95% CI, 3.05-3.57), and a higher risk for mortality due to natural causes (aHR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.24-1.37).
- Of all the unnatural causes of death, suicide was most common (hazard ratio [HR], 4.90; 95% CI, 4.40-5.46), followed by accidents (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.68-2.19).
- Similar results were found in the sibling comparison, where the HR of all-cause mortality was 1.85 (95% CI, 1.67-2.03), death from natural causes was 1.51 (95% CI, 1.35-1.68), and death from unnatural causes was 3.10 (95% CI, 2.52-3.80).
- Natural causes of death that were higher in the OCD vs non-OCD cohort included endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases; mental and behavioral disorders; and diseases of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and genitourinary systems.
IN PRACTICE:
“Better surveillance, prevention, and early intervention strategies should be implemented to reduce the risk of fatal outcomes in people with OCD,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, of Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden, led the study, which was published online on January 17 in the British Medical Journal.
LIMITATIONS:
The study does not establish causality. Registry data used by the investigators only included diagnoses made in specialist care and may not have included diagnoses made in other settings. It is also unclear whether the findings, derived from a Swedish population, can be generalized to other populations, health systems, and medical practices.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Swedish Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, Region Stockholm, the Swedish Society of Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. Dr. de la Cruz received royalties for contributing articles to UpToDate and Wolters Kluwer Health and for editorial work from Elsevier outside the submitted work. See the paper for disclosures of the other authors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is linked to a twofold increased risk for all-cause mortality and a heightened risk for death from both natural and unnatural causes, a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators studied a population-based cohort (58% female) of 61,378 people with OCD and 613,780 unaffected individuals from several Swedish population registers and a sibling cohort of 34,085 people with OCD (58% female) and 47,874 unaffected full siblings (48% female).
- The median 8.1-year follow-up and median age at first diagnosis of OCD were 27 years.
- The researchers used Cox proportional hazard models, adjusting for birth year, sex, county, country of birth (Sweden vs abroad), and sociodemographic variables.
TAKEAWAY:
- (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.82; 95% CI, 1.76-1.89), an almost threefold higher risk for mortality due to unnatural causes (aHR, 3.30; 95% CI, 3.05-3.57), and a higher risk for mortality due to natural causes (aHR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.24-1.37).
- Of all the unnatural causes of death, suicide was most common (hazard ratio [HR], 4.90; 95% CI, 4.40-5.46), followed by accidents (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.68-2.19).
- Similar results were found in the sibling comparison, where the HR of all-cause mortality was 1.85 (95% CI, 1.67-2.03), death from natural causes was 1.51 (95% CI, 1.35-1.68), and death from unnatural causes was 3.10 (95% CI, 2.52-3.80).
- Natural causes of death that were higher in the OCD vs non-OCD cohort included endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases; mental and behavioral disorders; and diseases of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and genitourinary systems.
IN PRACTICE:
“Better surveillance, prevention, and early intervention strategies should be implemented to reduce the risk of fatal outcomes in people with OCD,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, of Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden, led the study, which was published online on January 17 in the British Medical Journal.
LIMITATIONS:
The study does not establish causality. Registry data used by the investigators only included diagnoses made in specialist care and may not have included diagnoses made in other settings. It is also unclear whether the findings, derived from a Swedish population, can be generalized to other populations, health systems, and medical practices.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Swedish Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, Region Stockholm, the Swedish Society of Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. Dr. de la Cruz received royalties for contributing articles to UpToDate and Wolters Kluwer Health and for editorial work from Elsevier outside the submitted work. See the paper for disclosures of the other authors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is linked to a twofold increased risk for all-cause mortality and a heightened risk for death from both natural and unnatural causes, a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators studied a population-based cohort (58% female) of 61,378 people with OCD and 613,780 unaffected individuals from several Swedish population registers and a sibling cohort of 34,085 people with OCD (58% female) and 47,874 unaffected full siblings (48% female).
- The median 8.1-year follow-up and median age at first diagnosis of OCD were 27 years.
- The researchers used Cox proportional hazard models, adjusting for birth year, sex, county, country of birth (Sweden vs abroad), and sociodemographic variables.
TAKEAWAY:
- (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.82; 95% CI, 1.76-1.89), an almost threefold higher risk for mortality due to unnatural causes (aHR, 3.30; 95% CI, 3.05-3.57), and a higher risk for mortality due to natural causes (aHR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.24-1.37).
- Of all the unnatural causes of death, suicide was most common (hazard ratio [HR], 4.90; 95% CI, 4.40-5.46), followed by accidents (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.68-2.19).
- Similar results were found in the sibling comparison, where the HR of all-cause mortality was 1.85 (95% CI, 1.67-2.03), death from natural causes was 1.51 (95% CI, 1.35-1.68), and death from unnatural causes was 3.10 (95% CI, 2.52-3.80).
- Natural causes of death that were higher in the OCD vs non-OCD cohort included endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases; mental and behavioral disorders; and diseases of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and genitourinary systems.
IN PRACTICE:
“Better surveillance, prevention, and early intervention strategies should be implemented to reduce the risk of fatal outcomes in people with OCD,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, of Karolinska Institutet, Solna, Sweden, led the study, which was published online on January 17 in the British Medical Journal.
LIMITATIONS:
The study does not establish causality. Registry data used by the investigators only included diagnoses made in specialist care and may not have included diagnoses made in other settings. It is also unclear whether the findings, derived from a Swedish population, can be generalized to other populations, health systems, and medical practices.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Swedish Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, Region Stockholm, the Swedish Society of Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. Dr. de la Cruz received royalties for contributing articles to UpToDate and Wolters Kluwer Health and for editorial work from Elsevier outside the submitted work. See the paper for disclosures of the other authors.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Catch and Treat a Stealth Diagnosis: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
“Allie” is a 16-year-old African American female, presenting to her primary care provider for a routine well-child visit. She gets straight As in school, has a boyfriend, and works as a lifeguard. She is always on her phone using Snapchat, TikTok, and Instagram. Over the past year, it’s been taking her longer to turn off the phone and electronics at night. She needs to close the apps one by one and check the power sources a number of times. In the past few months, this ritual has become longer, includes more checks, and is interfering with sleep. She reports knowing this is abnormal and thinking she is “just kind of crazy” but she cannot stop. Her parents reassure her each evening. They now help her doublecheck that her devices are plugged in at least twice.
Unlike its depiction in the movies, many symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) happen internally. Often patients are aware that these are “not normal” and cover up their experiences. It can be hard for treaters to learn about these challenges. Children spend years suffering from OCD and even regularly attend nonspecific therapy without being diagnosed. However,
OCD impacts 2.3% of the population in their lifetime but more than 28% of people report symptoms consistent with OCD traits.1 OCD symptoms have increased since the pandemic2 so it is showing up in primary care more frequently. Younger patients meet criteria when their symptoms on the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS) are sufficiently present, and impact the ability to function. The youngest patients with OCD are more likely to be male1 and children are most likely to be identified between ages 8-12 and during the later teenage years,3 although symptoms can occur at any time in life.
Usually, symptom onset happens gradually and then waxes and wanes. Often OCD has been present over months to years but not identified until they reach a functional tipping point. Alternatively, symptoms caused by PANDAS/PANS occur out of the blue and should be treated according to infectious disease/autoimmune workup protocols. Other differential diagnosis for OCD include other anxiety disorders, mood disorders, eating disorders, psychotic disorders, and other compulsive behaviors. OCD, tics, and ADHD are a combination seen more frequently in younger patients.4 Comorbidities frequently occur, including anxiety disorders, mood disorders, impulse control disorders, and substance use disorders.1 PTSD frequently presents with comorbid OCD symptoms.1 Finding the underlying cause is key to effective treatment.
How do I identify OCD in primary care?
Administer the CY-BOCS if these symptoms cause inability to function. The cut off for moderate symptoms is a score of 16 or above. Like all mental health screening, clinical judgment should be used to interpret the score. Many therapists do not screen for OCD.
How do I treat OCD in primary care?
Exposure Therapy with Response Prevention (ERP) is the gold-standard therapy and medication management is most effective when paired with ERP. ERP helps patients list their obsessions and compulsions in order of how much anxiety they cause, then work on gradual exposure starting with those that cause the least amount of anxiety. Picking up on any sneaky internal or external “responses” is important. An example response could include externally checking the rearview mirror to make sure the patient didn’t run over a puppy after they hit a pothole, or internally reassuring themselves. This “response prevention” can be the trickiest part of the therapy and is key to efficacy.
How to access ERP?
The International OCD Foundation offers a list of therapists trained in ERP, and most states’ psychiatry access lines can help primary care providers find available targeted resources. Despite these resources, it can be frustrating to help a family try find any available therapist who takes insurance, let alone a specialist. A recent JAMA article review found that IInternet-based treatment with both therapist- and non-therapist–guided interventions resulted in symptom improvements.2 Interventions that include parents are most helpful for children.
Other therapy options include:
- MGH/McLean/ (iocd.org) hosts an online, low cost ($65 per family) OCD camp for those age 6-17 and caregivers found here.
- Many workbooks are available, Standing Up to OCD Workbook for Kids by Tyson Reuter, PhD, is one good option.
- A book for parents about how not to accidentally reinforce anxiety is Anxious Kids, Anxious Parents: 7 Ways to Stop the Worry Cycle by Lynn Lyons and Reid Wilson.
- Sometimes a therapist without expertise can work with families using workbooks and other supports to help with ERP.
Medication options
Medications alone do not cure OCD, but can help patients better participate in ERP therapy. When the most likely cause of OCD symptoms is OCD (ruling out family history of bipolar or other psychiatric illness), using SSRIs to treat symptoms is the gold standard for medications. There is FDA approval for sertraline (≥ age 6) and fluoxetine (≥ age 7) as first-line options. If tolerated, up-titrate to efficacy. Clomipramine and fluvoxamine also have FDA approval but have more side effects so are not first line. Citalopram has randomized clinical trial support.5
Allie’s primary care provider administered and scored the CY-BOCS, started her on an SSRI, and up-titrated to efficacy over 4 months. The family signed up for an online OCD camp and learned more about OCD at iocdf.org. They talked with her therapist and worked through an OCD workbook together as no specialist was available. Her parents decreased their reassurances. Because of her primary care provider’s intervention, Allie got the care she required and was better prepared to face future exacerbations.
Dr. Spottswood is a child psychiatrist practicing in an integrated care clinic at the Community Health Centers of Burlington, Vermont. She is the medical director of the Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program and a clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont.
References
1. Ruscio AM et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010 Jan;15(1):53-63. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.94.
2. Lattie EG, Stamatis CA. Focusing on accessibility of evidence-based treatments for obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(3):e221978. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.1978.
3. International OCD Foundation pediatric OCD for professionals. https://kids.iocdf.org/professionals/md/pediatric-ocd/. Accessed December 27, 2023.
4. American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). 2013. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596. Accessed December 27, 2023.5. Hilt RJ, Nussbaum AM. DSM-5 pocket guide to child and adolescent mental health. Arlington, Virginia: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2015.
“Allie” is a 16-year-old African American female, presenting to her primary care provider for a routine well-child visit. She gets straight As in school, has a boyfriend, and works as a lifeguard. She is always on her phone using Snapchat, TikTok, and Instagram. Over the past year, it’s been taking her longer to turn off the phone and electronics at night. She needs to close the apps one by one and check the power sources a number of times. In the past few months, this ritual has become longer, includes more checks, and is interfering with sleep. She reports knowing this is abnormal and thinking she is “just kind of crazy” but she cannot stop. Her parents reassure her each evening. They now help her doublecheck that her devices are plugged in at least twice.
Unlike its depiction in the movies, many symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) happen internally. Often patients are aware that these are “not normal” and cover up their experiences. It can be hard for treaters to learn about these challenges. Children spend years suffering from OCD and even regularly attend nonspecific therapy without being diagnosed. However,
OCD impacts 2.3% of the population in their lifetime but more than 28% of people report symptoms consistent with OCD traits.1 OCD symptoms have increased since the pandemic2 so it is showing up in primary care more frequently. Younger patients meet criteria when their symptoms on the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS) are sufficiently present, and impact the ability to function. The youngest patients with OCD are more likely to be male1 and children are most likely to be identified between ages 8-12 and during the later teenage years,3 although symptoms can occur at any time in life.
Usually, symptom onset happens gradually and then waxes and wanes. Often OCD has been present over months to years but not identified until they reach a functional tipping point. Alternatively, symptoms caused by PANDAS/PANS occur out of the blue and should be treated according to infectious disease/autoimmune workup protocols. Other differential diagnosis for OCD include other anxiety disorders, mood disorders, eating disorders, psychotic disorders, and other compulsive behaviors. OCD, tics, and ADHD are a combination seen more frequently in younger patients.4 Comorbidities frequently occur, including anxiety disorders, mood disorders, impulse control disorders, and substance use disorders.1 PTSD frequently presents with comorbid OCD symptoms.1 Finding the underlying cause is key to effective treatment.
How do I identify OCD in primary care?
Administer the CY-BOCS if these symptoms cause inability to function. The cut off for moderate symptoms is a score of 16 or above. Like all mental health screening, clinical judgment should be used to interpret the score. Many therapists do not screen for OCD.
How do I treat OCD in primary care?
Exposure Therapy with Response Prevention (ERP) is the gold-standard therapy and medication management is most effective when paired with ERP. ERP helps patients list their obsessions and compulsions in order of how much anxiety they cause, then work on gradual exposure starting with those that cause the least amount of anxiety. Picking up on any sneaky internal or external “responses” is important. An example response could include externally checking the rearview mirror to make sure the patient didn’t run over a puppy after they hit a pothole, or internally reassuring themselves. This “response prevention” can be the trickiest part of the therapy and is key to efficacy.
How to access ERP?
The International OCD Foundation offers a list of therapists trained in ERP, and most states’ psychiatry access lines can help primary care providers find available targeted resources. Despite these resources, it can be frustrating to help a family try find any available therapist who takes insurance, let alone a specialist. A recent JAMA article review found that IInternet-based treatment with both therapist- and non-therapist–guided interventions resulted in symptom improvements.2 Interventions that include parents are most helpful for children.
Other therapy options include:
- MGH/McLean/ (iocd.org) hosts an online, low cost ($65 per family) OCD camp for those age 6-17 and caregivers found here.
- Many workbooks are available, Standing Up to OCD Workbook for Kids by Tyson Reuter, PhD, is one good option.
- A book for parents about how not to accidentally reinforce anxiety is Anxious Kids, Anxious Parents: 7 Ways to Stop the Worry Cycle by Lynn Lyons and Reid Wilson.
- Sometimes a therapist without expertise can work with families using workbooks and other supports to help with ERP.
Medication options
Medications alone do not cure OCD, but can help patients better participate in ERP therapy. When the most likely cause of OCD symptoms is OCD (ruling out family history of bipolar or other psychiatric illness), using SSRIs to treat symptoms is the gold standard for medications. There is FDA approval for sertraline (≥ age 6) and fluoxetine (≥ age 7) as first-line options. If tolerated, up-titrate to efficacy. Clomipramine and fluvoxamine also have FDA approval but have more side effects so are not first line. Citalopram has randomized clinical trial support.5
Allie’s primary care provider administered and scored the CY-BOCS, started her on an SSRI, and up-titrated to efficacy over 4 months. The family signed up for an online OCD camp and learned more about OCD at iocdf.org. They talked with her therapist and worked through an OCD workbook together as no specialist was available. Her parents decreased their reassurances. Because of her primary care provider’s intervention, Allie got the care she required and was better prepared to face future exacerbations.
Dr. Spottswood is a child psychiatrist practicing in an integrated care clinic at the Community Health Centers of Burlington, Vermont. She is the medical director of the Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program and a clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont.
References
1. Ruscio AM et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010 Jan;15(1):53-63. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.94.
2. Lattie EG, Stamatis CA. Focusing on accessibility of evidence-based treatments for obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(3):e221978. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.1978.
3. International OCD Foundation pediatric OCD for professionals. https://kids.iocdf.org/professionals/md/pediatric-ocd/. Accessed December 27, 2023.
4. American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). 2013. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596. Accessed December 27, 2023.5. Hilt RJ, Nussbaum AM. DSM-5 pocket guide to child and adolescent mental health. Arlington, Virginia: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2015.
“Allie” is a 16-year-old African American female, presenting to her primary care provider for a routine well-child visit. She gets straight As in school, has a boyfriend, and works as a lifeguard. She is always on her phone using Snapchat, TikTok, and Instagram. Over the past year, it’s been taking her longer to turn off the phone and electronics at night. She needs to close the apps one by one and check the power sources a number of times. In the past few months, this ritual has become longer, includes more checks, and is interfering with sleep. She reports knowing this is abnormal and thinking she is “just kind of crazy” but she cannot stop. Her parents reassure her each evening. They now help her doublecheck that her devices are plugged in at least twice.
Unlike its depiction in the movies, many symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) happen internally. Often patients are aware that these are “not normal” and cover up their experiences. It can be hard for treaters to learn about these challenges. Children spend years suffering from OCD and even regularly attend nonspecific therapy without being diagnosed. However,
OCD impacts 2.3% of the population in their lifetime but more than 28% of people report symptoms consistent with OCD traits.1 OCD symptoms have increased since the pandemic2 so it is showing up in primary care more frequently. Younger patients meet criteria when their symptoms on the Children’s Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (CY-BOCS) are sufficiently present, and impact the ability to function. The youngest patients with OCD are more likely to be male1 and children are most likely to be identified between ages 8-12 and during the later teenage years,3 although symptoms can occur at any time in life.
Usually, symptom onset happens gradually and then waxes and wanes. Often OCD has been present over months to years but not identified until they reach a functional tipping point. Alternatively, symptoms caused by PANDAS/PANS occur out of the blue and should be treated according to infectious disease/autoimmune workup protocols. Other differential diagnosis for OCD include other anxiety disorders, mood disorders, eating disorders, psychotic disorders, and other compulsive behaviors. OCD, tics, and ADHD are a combination seen more frequently in younger patients.4 Comorbidities frequently occur, including anxiety disorders, mood disorders, impulse control disorders, and substance use disorders.1 PTSD frequently presents with comorbid OCD symptoms.1 Finding the underlying cause is key to effective treatment.
How do I identify OCD in primary care?
Administer the CY-BOCS if these symptoms cause inability to function. The cut off for moderate symptoms is a score of 16 or above. Like all mental health screening, clinical judgment should be used to interpret the score. Many therapists do not screen for OCD.
How do I treat OCD in primary care?
Exposure Therapy with Response Prevention (ERP) is the gold-standard therapy and medication management is most effective when paired with ERP. ERP helps patients list their obsessions and compulsions in order of how much anxiety they cause, then work on gradual exposure starting with those that cause the least amount of anxiety. Picking up on any sneaky internal or external “responses” is important. An example response could include externally checking the rearview mirror to make sure the patient didn’t run over a puppy after they hit a pothole, or internally reassuring themselves. This “response prevention” can be the trickiest part of the therapy and is key to efficacy.
How to access ERP?
The International OCD Foundation offers a list of therapists trained in ERP, and most states’ psychiatry access lines can help primary care providers find available targeted resources. Despite these resources, it can be frustrating to help a family try find any available therapist who takes insurance, let alone a specialist. A recent JAMA article review found that IInternet-based treatment with both therapist- and non-therapist–guided interventions resulted in symptom improvements.2 Interventions that include parents are most helpful for children.
Other therapy options include:
- MGH/McLean/ (iocd.org) hosts an online, low cost ($65 per family) OCD camp for those age 6-17 and caregivers found here.
- Many workbooks are available, Standing Up to OCD Workbook for Kids by Tyson Reuter, PhD, is one good option.
- A book for parents about how not to accidentally reinforce anxiety is Anxious Kids, Anxious Parents: 7 Ways to Stop the Worry Cycle by Lynn Lyons and Reid Wilson.
- Sometimes a therapist without expertise can work with families using workbooks and other supports to help with ERP.
Medication options
Medications alone do not cure OCD, but can help patients better participate in ERP therapy. When the most likely cause of OCD symptoms is OCD (ruling out family history of bipolar or other psychiatric illness), using SSRIs to treat symptoms is the gold standard for medications. There is FDA approval for sertraline (≥ age 6) and fluoxetine (≥ age 7) as first-line options. If tolerated, up-titrate to efficacy. Clomipramine and fluvoxamine also have FDA approval but have more side effects so are not first line. Citalopram has randomized clinical trial support.5
Allie’s primary care provider administered and scored the CY-BOCS, started her on an SSRI, and up-titrated to efficacy over 4 months. The family signed up for an online OCD camp and learned more about OCD at iocdf.org. They talked with her therapist and worked through an OCD workbook together as no specialist was available. Her parents decreased their reassurances. Because of her primary care provider’s intervention, Allie got the care she required and was better prepared to face future exacerbations.
Dr. Spottswood is a child psychiatrist practicing in an integrated care clinic at the Community Health Centers of Burlington, Vermont. She is the medical director of the Vermont Child Psychiatry Access Program and a clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont.
References
1. Ruscio AM et al. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry. 2010 Jan;15(1):53-63. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.94.
2. Lattie EG, Stamatis CA. Focusing on accessibility of evidence-based treatments for obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(3):e221978. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.1978.
3. International OCD Foundation pediatric OCD for professionals. https://kids.iocdf.org/professionals/md/pediatric-ocd/. Accessed December 27, 2023.
4. American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). 2013. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596. Accessed December 27, 2023.5. Hilt RJ, Nussbaum AM. DSM-5 pocket guide to child and adolescent mental health. Arlington, Virginia: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2015.
Symptoms of psychosis and OCD in a patient with postpartum depression
CASE Thoughts of harming baby
Ms. A, age 37, is G4P2, 4 months postpartum, and breastfeeding. She has major depressive disorder (MDD) with peripartum onset, posttraumatic stress disorder, and mild intellectual disability. For years she has been stable on fluoxetine 40 mg/d and prazosin 2 mg/d. Despite recent titration of her medications, at her most recent outpatient appointment Ms. A reports having a depressed mood with frequent crying, insomnia, a lack of desire to bond with her baby, and feelings of shame. She also says she has had auditory hallucinations and thoughts of harming her baby. Ms. A’s outpatient physician makes an urgent request for her to be evaluated at the psychiatric emergency department (ED).
HISTORY Depression and possible auditory hallucinations
Ms. A developed MDD following the birth of her first child, for which her care team initiated fluoxetine at 20 mg/d and titrated it to 40 mg/d,which was effective. At that time, her outpatient physician documented potential psychotic features, including vague descriptions of derogatory auditory hallucinations. However, it was unclear if these auditory hallucinations were more representative of a distressing inner monologue without the quality of an external voice. The team determined that Ms. A was not at acute risk for harm to herself or her baby and was appropriate for outpatient care. Because the nature of these possible auditory hallucinations was mild, nondistressing, and nonthreatening, the treatment team did not initiate an antipsychotic and Ms. A was not hospitalized. She has no history of hypomanic/manic episodes and has never met criteria for a psychotic disorder.
EVALUATION Distressing thoughts and discontinued medications
During the evaluation by psychiatric emergency services, Ms. A reports that 2 weeks after giving birth she experienced a worsening of her depressive symptoms. She says she began hearing voices telling her to harm herself and her baby and describes frequent distressing thoughts, such as stabbing her baby with a knife and running over her baby with a car. Ms. A says she repeatedly wakes up at night to check on her baby’s breathing, overfeeds her baby due to a fear of inadequate nutrition, and notes intermittent feelings of confusion. Afraid of being alone with her infant, Ms. A asks her partner and mother to move in with her. Additionally, she says 2 weeks ago she discontinued all her medications at the suggestion of her partner, who recommended herbal supplements. Ms. A’s initial routine laboratory results are unremarkable and her urine drug screen is negative for all substances.
[polldaddy:13041928]
The authors’ observations
Approximately 85% of birthing parents experience some form of postpartum mood disturbance; 10% to 15% develop more significant symptoms of anxiety or depression.3 The etiology of postpartum illness is multifactorial, and includes psychiatric personal/family history, insomnia, acute and chronic psychosocial stressors, and rapid hormone fluctuations.1 As a result, the postpartum period represents a vulnerable time for birthing parents, particularly those with previously established psychiatric illness.
Ms. A’s initial presentation was concerning for a possible diagnosis of postpartum psychosis vs obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) with postpartum onset; other differential diagnoses included MDD with peripartum onset and psychotic features (Table1-6). Ms. A’s subjective clinical history was significant for critical pertinent findings of both OCD with postpartum onset (ie, egodystonic intrusive thoughts, checking behaviors, feelings of shame, and seeking reassurance) and postpartum psychosis (ie, command auditory hallucinations and waxing/waning confusion), which added to diagnostic complexity.
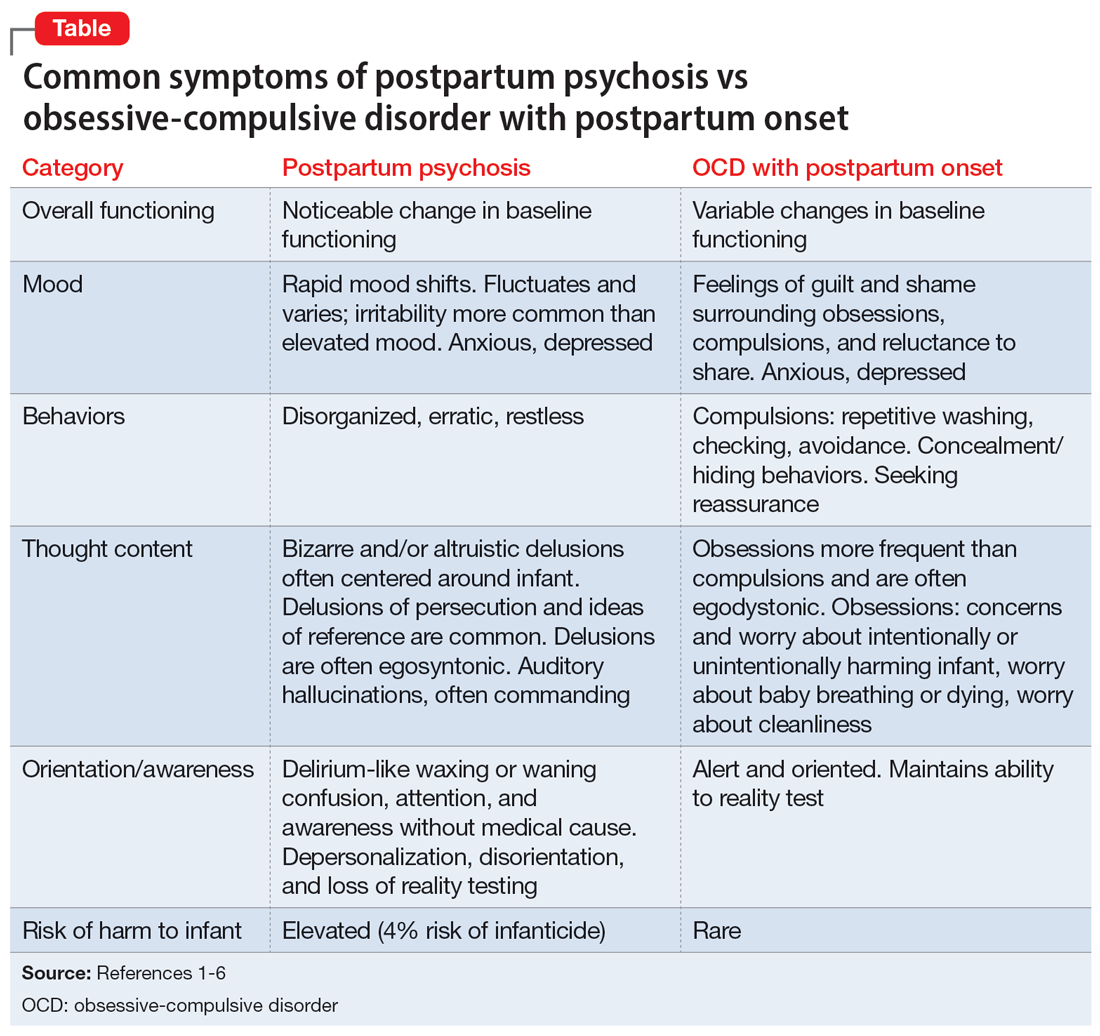
Although postpartum psychosis is rare (1 to 2 cases per 1,000 women),5 it is considered a psychiatric emergency because it has significant potential for infanticide, morbidity, and mortality. Most symptoms develop within the first 2 weeks of the postpartum period.2 There are many risk factors for the development of postpartum psychosis; however, in first-time pregnancies, a previous diagnosis of BD I is the single most important risk factor.1 Approximately 20% to 30% of women with BD experience postpartum psychosis.4
For many patients (approximately 56.7%, according to 1 meta-analysis7), postpartum psychosis denotes an episode of BD, representing a more severe form of illness with increased risk of recurrence. Most manic or mixed mood episodes reoccur within the first year removed from the perinatal period. In contrast, for some patients (approximately 43.5% according to the same meta-analysis), the episode denotes “isolated postpartum psychosis.”7 Isolated postpartum psychosis is a psychotic episode that occurs only in the postpartum period with no recurrence of psychosis or recurrence of psychosis exclusive to postpartum periods. If treated, this type of postpartum psychosis has a more favorable prognosis than postpartum psychosis in a patient with BD.7 As such, a BD diagnosis should not be established at the onset of a patient’s first postpartum psychosis presentation. Regardless of type, all presentations of postpartum psychosis are considered a psychiatry emergency.
Continue to: The prevalence of OCD...
The prevalence of OCD with postpartum onset varies. One study estimated it occurs in 2.43% of cases.4 However, the true prevalence is likely underreported due to feelings of guilt or shame associated with intrusive thoughts, and fear of stigmatization and separation from the baby. Approximately 70.6% of women experiencing OCD with postpartum onset have a comorbid depressive disorder.4
Ms. A’s presentation to the psychiatric ED carried with it diagnostic complexity and uncertainty. Her initial presentation was concerning for elements of both postpartum psychosis and OCD with postpartum onset. After her evaluation in the psychiatric ED, there remained a lack of clear and convincing evidence for a diagnosis of OCD with postpartum onset, which eliminated the possibility of discharging Ms. A with robust safety planning and reinitiation of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
Additionally, because auditory hallucinations are atypical in OCD, the treatment team remained concerned for a diagnosis of postpartum psychosis, which would warrant hospitalization. With assistance from the institution’s reproductive psychiatrists, the treatment team discussed the importance of inpatient hospitalization for risk mitigation, close observation, and thorough evaluation for greater diagnostic clarity and certainty.
TREATMENT Involuntary hospitalization
The treatment team counsels Ms. A and her partner on her differential diagnoses, including the elevated acute risk of harm to herself and her baby if she has postpartum psychosis, as well as the need for continued observation and evaluation. When alone with a clinician, Ms. A says she understands and agrees to voluntary hospitalization. However, following a subsequent risk-benefit discussion with her partner, they both grew increasingly concerned about her separation from the baby and reinitiating her medications. Amid these concerns, the treatment team notices that Ms. A attempts to minimize her symptoms. Ms. A changes her mind and no longer consents to hospitalization. She is placed on a psychiatric hold for involuntary hospitalization on the psychiatric inpatient unit.
On the inpatient unit, the inpatient clinicians and a reproductive psychiatrist continue to evaluate Ms. A. Though her diagnosis remains unclear, Ms. A agrees to start a trial of quetiapine 100 mg/d titrated to 150 mg/d to manage her potential postpartum psychosis, depressed mood, insomnia (off-label), anxiety (off-label), and OCD (off-label). Lithium is deferred because Ms. A is breastfeeding.
[polldaddy:13041932]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Due to an elevated acute risk of suicide and infanticide, postpartum psychosis represents a psychiatric emergency and often requires hospitalization. The Figure outlines steps in evaluating a patient with concerns for postpartum psychosis in a psychiatric emergency service setting. Due to the waxing and waning nature of symptoms, patients may appear psychiatrically stable at any time but remain at an overall elevated acute risk of harm to self and/or their baby.
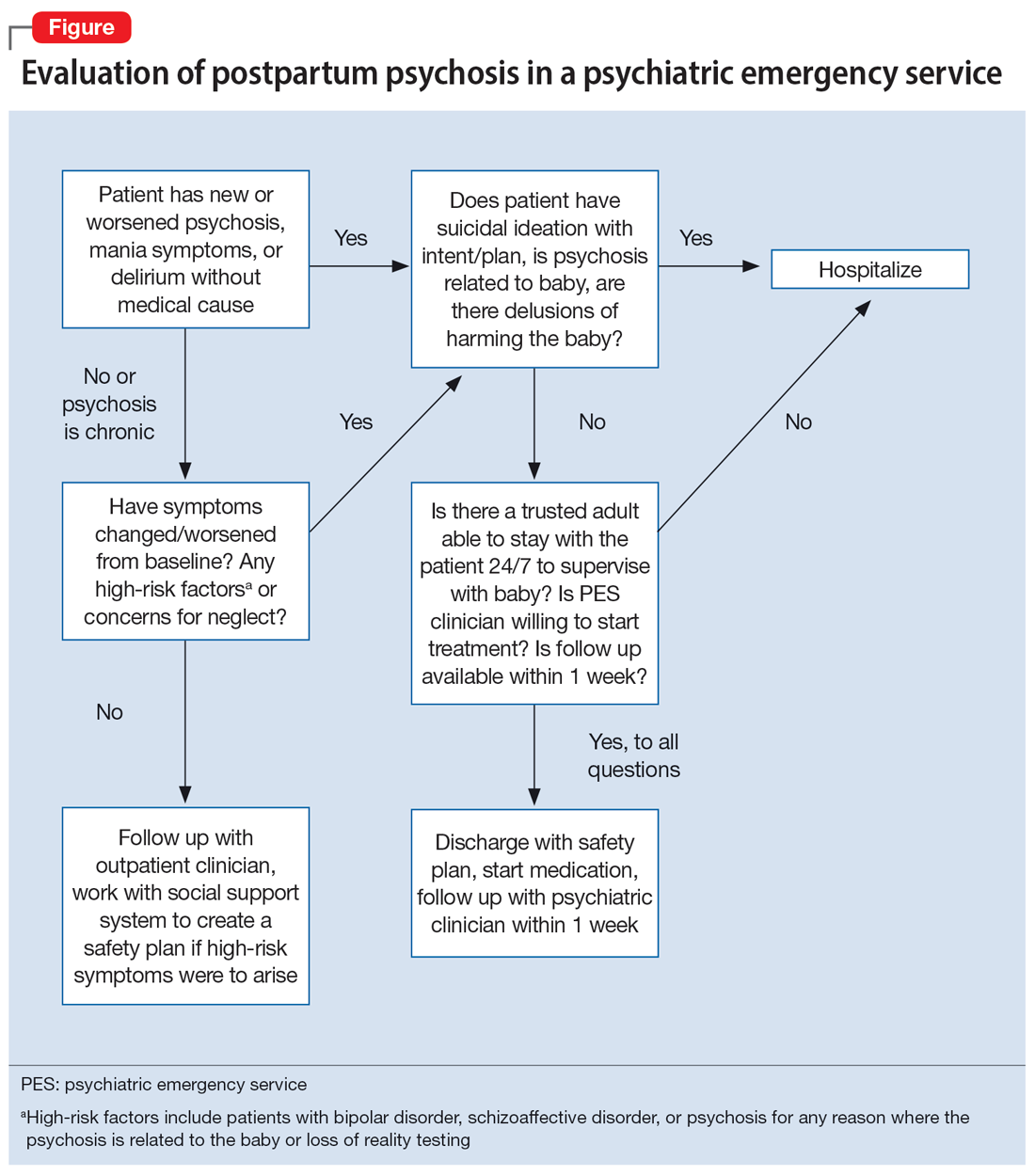
If a patient is being considered for discharge based on yes answers to all questions in Step 2 of the Figure, the emergency psychiatric clinician must initiate appropriate psychotropic medications and complete robust safety planning with the patient and a trusted adult who will provide direct supervision. Safety planning may include (but is not limited to) strict return precautions, education on concerning symptoms and behaviors, psychotropic education and agreement of compliance, and detailed instructions on outpatient follow-up within 1 week. Ideally—and as was the case for Ms. A—a reproductive psychiatrist should be consulted in the emergency setting for shared decision-making on admission vs discharge, medication management, and outpatient follow-up considerations.
Because postpartum psychosis carries significant risks and hospitalization generally results in separating the patient from their baby, initiating psychotropics should not be delayed. Clinicians must consider the patient’s psychiatric history, allergies, and breastfeeding status.
Based on current evidence, first-line treatment for postpartum psychosis includes a mood stabilizer, an antipsychotic, and possibly a benzodiazepine.6 Thus, an appropriate initial treatment regimen would be a benzodiazepine (particularly lorazepam due to its relatively shorter half-life) and an antipsychotic (eg, haloperidol, olanzapine, or quetiapine) for acute psychosis, plus lithium for mood stabilization.1,5
If the postpartum psychosis represents an episode of BD, use of a long-term mood stabilizer may be required. In contrast, for isolated postpartum psychosis, clinicians may consider initiating psychotropics only in the immediate postpartum period, with an eventual slow taper. In future pregnancies, psychotropics may be reintroduced postpartum, which will avoid peripartum fetal exposure.8 If the patient is breastfeeding, lithium may be deferred in an acute care setting. For patients with evidence of catatonia, severe suicidality, refusal of oral intake with compromised nutrition, severe agitation, or treatment resistance, electroconvulsive therapy remains a safe and effective treatment option.6 Additionally, the safety of continued breastfeeding in acute psychosis must be considered, with the potential for recommending discontinuation, which would decrease sleep disruptions at night and increase the ability of others to feed the baby. Comprehensive care requires nonpharmacologic interventions, including psychoeducation for the patient and their family, individual psychotherapy, and expansion of psychosocial supports.
Continue to: Patients who have experienced...
Patients who have experienced an episode of postpartum psychosis are predisposed to another episode in future pregnancies.1 Current research recommends prophylaxis of recurrence with lithium monotherapy.1,2,5,6 Similar to other psychotropics in reproductive psychiatry, maintenance therapy on lithium requires a thorough “risk vs risk” discussion with the patient. The risk of lithium use while pregnant and/or breastfeeding must be weighed against the risks associated with postpartum psychosis (ie, infanticide, suicide, poor peripartum care, or poor infant bonding).
OUTCOME Improved mood
After 7 days of inpatient treatment with quetiapine, Ms. A demonstrates improvement in the targeted depressive symptoms (including improved motivation/energy and insomnia, decreased feelings of guilt, and denial of ongoing suicidal ideation). Additionally, the thoughts of harming her baby are less frequent, and command auditory hallucinations resolve. Upon discharge, Ms. A and her partner meet with inpatient clinicians for continued counseling, safety planning, and plans for outpatient follow-up with the institution’s reproductive psychiatrist.
The authors’ observations
Many aspects of Ms. A’s initial presentation in the psychiatric ED were challenging. Given the presence of symptoms of both psychosis and OCD, a diagnosis was difficult to ascertain in the emergency setting. Since command auditory hallucinations are atypical in patients with postpartum OCD, the treatment team maintained high suspicion for postpartum psychosis, which represented an emergency requiring inpatient care.
Hospitalization separated Ms. A from her baby, for whom she was the primary caregiver. Additional considerations for inpatient admission and psychotropic initiation were necessary, because Ms. A was breastfeeding. Although Ms. A’s partner was able to provide full-time childcare, the patient ultimately did not agree to hospitalization and required an emergency hold for involuntary admission, which was an additional barrier to care. Furthermore, her partner held unfavorable beliefs regarding psychotropic medications and Ms. A’s need for hospital admission, which required ongoing patient and partner education in the emergency, inpatient, and outpatient settings. Moreover, if Ms. A’s symptoms were ultimately attributable to postpartum OCD, the patient’s involuntary hospitalization might have increased the risk of stigmatization of mental illness and treatment with psychotropics.
Bottom Line
The peripartum period is a vulnerable time for patients, particularly those with previously diagnosed psychiatric illnesses. Postpartum psychosis is the most severe form of postpartum psychiatric illness and often represents an episode of bipolar disorder. Due to an elevated acute risk of suicide and infanticide, postpartum psychosis is a psychiatric emergency and warrants inpatient hospitalization for immediate intervention.
Related Resources
- Sharma V. Does your patient have postpartum OCD? Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(5):9-10.
- Hatters Friedman S, Prakash C, Nagel-Yang S. Postpartum psychosis: protecting mother and infant. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):12-21.
Drug Brand Names
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Prazosin • Minipress
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakene
1. Raza SK, Raza S. Postpartum Psychosis. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated June 26, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544304/
2. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. What Is Postpartum Psychosis: This Is What You Need to Know. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Published November 15, 2019. Accessed June 22, 2023. https://womensmentalhealth.org/posts/postpartum-psychosis-ten-things-need-know-2/
3. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Postpartum Psychiatric Disorders. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Accessed October 7, 2023. https://womensmentalhealth.org/specialty-clinics-2/postpartum-psychiatric-disorders-2/
4. Sharma V, Sommerdyk C. Obsessive-compulsive disorder in the postpartum period: diagnosis, differential diagnosis and management. Womens Health (Lond). 2015;11(4):543-552. doi:10.2217/whe.15.20
5. Osborne LM. Recognizing and managing postpartum psychosis: a clinical guide for obstetric providers. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2018;45(3):455-468. doi:10.1016/j.ogc.2018.04.005
6. Hutner LA, Catapano LA, Nagle-Yang SM, et al, eds. Textbook of Women’s Reproductive Mental Health. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
7. Gilden J, Kamperman AM, Munk-Olsen T, et al. Long-term outcomes of postpartum psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(2):19r12906. doi:10.4088/JCP.19r12906
8. Bergink V, Boyce P, Munk-Olsen T. Postpartum psychosis: a valuable misnomer. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2015;49(2):102-103. doi:10.1177/0004867414564698
CASE Thoughts of harming baby
Ms. A, age 37, is G4P2, 4 months postpartum, and breastfeeding. She has major depressive disorder (MDD) with peripartum onset, posttraumatic stress disorder, and mild intellectual disability. For years she has been stable on fluoxetine 40 mg/d and prazosin 2 mg/d. Despite recent titration of her medications, at her most recent outpatient appointment Ms. A reports having a depressed mood with frequent crying, insomnia, a lack of desire to bond with her baby, and feelings of shame. She also says she has had auditory hallucinations and thoughts of harming her baby. Ms. A’s outpatient physician makes an urgent request for her to be evaluated at the psychiatric emergency department (ED).
HISTORY Depression and possible auditory hallucinations
Ms. A developed MDD following the birth of her first child, for which her care team initiated fluoxetine at 20 mg/d and titrated it to 40 mg/d,which was effective. At that time, her outpatient physician documented potential psychotic features, including vague descriptions of derogatory auditory hallucinations. However, it was unclear if these auditory hallucinations were more representative of a distressing inner monologue without the quality of an external voice. The team determined that Ms. A was not at acute risk for harm to herself or her baby and was appropriate for outpatient care. Because the nature of these possible auditory hallucinations was mild, nondistressing, and nonthreatening, the treatment team did not initiate an antipsychotic and Ms. A was not hospitalized. She has no history of hypomanic/manic episodes and has never met criteria for a psychotic disorder.
EVALUATION Distressing thoughts and discontinued medications
During the evaluation by psychiatric emergency services, Ms. A reports that 2 weeks after giving birth she experienced a worsening of her depressive symptoms. She says she began hearing voices telling her to harm herself and her baby and describes frequent distressing thoughts, such as stabbing her baby with a knife and running over her baby with a car. Ms. A says she repeatedly wakes up at night to check on her baby’s breathing, overfeeds her baby due to a fear of inadequate nutrition, and notes intermittent feelings of confusion. Afraid of being alone with her infant, Ms. A asks her partner and mother to move in with her. Additionally, she says 2 weeks ago she discontinued all her medications at the suggestion of her partner, who recommended herbal supplements. Ms. A’s initial routine laboratory results are unremarkable and her urine drug screen is negative for all substances.
[polldaddy:13041928]
The authors’ observations
Approximately 85% of birthing parents experience some form of postpartum mood disturbance; 10% to 15% develop more significant symptoms of anxiety or depression.3 The etiology of postpartum illness is multifactorial, and includes psychiatric personal/family history, insomnia, acute and chronic psychosocial stressors, and rapid hormone fluctuations.1 As a result, the postpartum period represents a vulnerable time for birthing parents, particularly those with previously established psychiatric illness.
Ms. A’s initial presentation was concerning for a possible diagnosis of postpartum psychosis vs obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) with postpartum onset; other differential diagnoses included MDD with peripartum onset and psychotic features (Table1-6). Ms. A’s subjective clinical history was significant for critical pertinent findings of both OCD with postpartum onset (ie, egodystonic intrusive thoughts, checking behaviors, feelings of shame, and seeking reassurance) and postpartum psychosis (ie, command auditory hallucinations and waxing/waning confusion), which added to diagnostic complexity.

Although postpartum psychosis is rare (1 to 2 cases per 1,000 women),5 it is considered a psychiatric emergency because it has significant potential for infanticide, morbidity, and mortality. Most symptoms develop within the first 2 weeks of the postpartum period.2 There are many risk factors for the development of postpartum psychosis; however, in first-time pregnancies, a previous diagnosis of BD I is the single most important risk factor.1 Approximately 20% to 30% of women with BD experience postpartum psychosis.4
For many patients (approximately 56.7%, according to 1 meta-analysis7), postpartum psychosis denotes an episode of BD, representing a more severe form of illness with increased risk of recurrence. Most manic or mixed mood episodes reoccur within the first year removed from the perinatal period. In contrast, for some patients (approximately 43.5% according to the same meta-analysis), the episode denotes “isolated postpartum psychosis.”7 Isolated postpartum psychosis is a psychotic episode that occurs only in the postpartum period with no recurrence of psychosis or recurrence of psychosis exclusive to postpartum periods. If treated, this type of postpartum psychosis has a more favorable prognosis than postpartum psychosis in a patient with BD.7 As such, a BD diagnosis should not be established at the onset of a patient’s first postpartum psychosis presentation. Regardless of type, all presentations of postpartum psychosis are considered a psychiatry emergency.
Continue to: The prevalence of OCD...
The prevalence of OCD with postpartum onset varies. One study estimated it occurs in 2.43% of cases.4 However, the true prevalence is likely underreported due to feelings of guilt or shame associated with intrusive thoughts, and fear of stigmatization and separation from the baby. Approximately 70.6% of women experiencing OCD with postpartum onset have a comorbid depressive disorder.4
Ms. A’s presentation to the psychiatric ED carried with it diagnostic complexity and uncertainty. Her initial presentation was concerning for elements of both postpartum psychosis and OCD with postpartum onset. After her evaluation in the psychiatric ED, there remained a lack of clear and convincing evidence for a diagnosis of OCD with postpartum onset, which eliminated the possibility of discharging Ms. A with robust safety planning and reinitiation of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
Additionally, because auditory hallucinations are atypical in OCD, the treatment team remained concerned for a diagnosis of postpartum psychosis, which would warrant hospitalization. With assistance from the institution’s reproductive psychiatrists, the treatment team discussed the importance of inpatient hospitalization for risk mitigation, close observation, and thorough evaluation for greater diagnostic clarity and certainty.
TREATMENT Involuntary hospitalization
The treatment team counsels Ms. A and her partner on her differential diagnoses, including the elevated acute risk of harm to herself and her baby if she has postpartum psychosis, as well as the need for continued observation and evaluation. When alone with a clinician, Ms. A says she understands and agrees to voluntary hospitalization. However, following a subsequent risk-benefit discussion with her partner, they both grew increasingly concerned about her separation from the baby and reinitiating her medications. Amid these concerns, the treatment team notices that Ms. A attempts to minimize her symptoms. Ms. A changes her mind and no longer consents to hospitalization. She is placed on a psychiatric hold for involuntary hospitalization on the psychiatric inpatient unit.
On the inpatient unit, the inpatient clinicians and a reproductive psychiatrist continue to evaluate Ms. A. Though her diagnosis remains unclear, Ms. A agrees to start a trial of quetiapine 100 mg/d titrated to 150 mg/d to manage her potential postpartum psychosis, depressed mood, insomnia (off-label), anxiety (off-label), and OCD (off-label). Lithium is deferred because Ms. A is breastfeeding.
[polldaddy:13041932]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Due to an elevated acute risk of suicide and infanticide, postpartum psychosis represents a psychiatric emergency and often requires hospitalization. The Figure outlines steps in evaluating a patient with concerns for postpartum psychosis in a psychiatric emergency service setting. Due to the waxing and waning nature of symptoms, patients may appear psychiatrically stable at any time but remain at an overall elevated acute risk of harm to self and/or their baby.

If a patient is being considered for discharge based on yes answers to all questions in Step 2 of the Figure, the emergency psychiatric clinician must initiate appropriate psychotropic medications and complete robust safety planning with the patient and a trusted adult who will provide direct supervision. Safety planning may include (but is not limited to) strict return precautions, education on concerning symptoms and behaviors, psychotropic education and agreement of compliance, and detailed instructions on outpatient follow-up within 1 week. Ideally—and as was the case for Ms. A—a reproductive psychiatrist should be consulted in the emergency setting for shared decision-making on admission vs discharge, medication management, and outpatient follow-up considerations.
Because postpartum psychosis carries significant risks and hospitalization generally results in separating the patient from their baby, initiating psychotropics should not be delayed. Clinicians must consider the patient’s psychiatric history, allergies, and breastfeeding status.
Based on current evidence, first-line treatment for postpartum psychosis includes a mood stabilizer, an antipsychotic, and possibly a benzodiazepine.6 Thus, an appropriate initial treatment regimen would be a benzodiazepine (particularly lorazepam due to its relatively shorter half-life) and an antipsychotic (eg, haloperidol, olanzapine, or quetiapine) for acute psychosis, plus lithium for mood stabilization.1,5
If the postpartum psychosis represents an episode of BD, use of a long-term mood stabilizer may be required. In contrast, for isolated postpartum psychosis, clinicians may consider initiating psychotropics only in the immediate postpartum period, with an eventual slow taper. In future pregnancies, psychotropics may be reintroduced postpartum, which will avoid peripartum fetal exposure.8 If the patient is breastfeeding, lithium may be deferred in an acute care setting. For patients with evidence of catatonia, severe suicidality, refusal of oral intake with compromised nutrition, severe agitation, or treatment resistance, electroconvulsive therapy remains a safe and effective treatment option.6 Additionally, the safety of continued breastfeeding in acute psychosis must be considered, with the potential for recommending discontinuation, which would decrease sleep disruptions at night and increase the ability of others to feed the baby. Comprehensive care requires nonpharmacologic interventions, including psychoeducation for the patient and their family, individual psychotherapy, and expansion of psychosocial supports.
Continue to: Patients who have experienced...
Patients who have experienced an episode of postpartum psychosis are predisposed to another episode in future pregnancies.1 Current research recommends prophylaxis of recurrence with lithium monotherapy.1,2,5,6 Similar to other psychotropics in reproductive psychiatry, maintenance therapy on lithium requires a thorough “risk vs risk” discussion with the patient. The risk of lithium use while pregnant and/or breastfeeding must be weighed against the risks associated with postpartum psychosis (ie, infanticide, suicide, poor peripartum care, or poor infant bonding).
OUTCOME Improved mood
After 7 days of inpatient treatment with quetiapine, Ms. A demonstrates improvement in the targeted depressive symptoms (including improved motivation/energy and insomnia, decreased feelings of guilt, and denial of ongoing suicidal ideation). Additionally, the thoughts of harming her baby are less frequent, and command auditory hallucinations resolve. Upon discharge, Ms. A and her partner meet with inpatient clinicians for continued counseling, safety planning, and plans for outpatient follow-up with the institution’s reproductive psychiatrist.
The authors’ observations
Many aspects of Ms. A’s initial presentation in the psychiatric ED were challenging. Given the presence of symptoms of both psychosis and OCD, a diagnosis was difficult to ascertain in the emergency setting. Since command auditory hallucinations are atypical in patients with postpartum OCD, the treatment team maintained high suspicion for postpartum psychosis, which represented an emergency requiring inpatient care.
Hospitalization separated Ms. A from her baby, for whom she was the primary caregiver. Additional considerations for inpatient admission and psychotropic initiation were necessary, because Ms. A was breastfeeding. Although Ms. A’s partner was able to provide full-time childcare, the patient ultimately did not agree to hospitalization and required an emergency hold for involuntary admission, which was an additional barrier to care. Furthermore, her partner held unfavorable beliefs regarding psychotropic medications and Ms. A’s need for hospital admission, which required ongoing patient and partner education in the emergency, inpatient, and outpatient settings. Moreover, if Ms. A’s symptoms were ultimately attributable to postpartum OCD, the patient’s involuntary hospitalization might have increased the risk of stigmatization of mental illness and treatment with psychotropics.
Bottom Line
The peripartum period is a vulnerable time for patients, particularly those with previously diagnosed psychiatric illnesses. Postpartum psychosis is the most severe form of postpartum psychiatric illness and often represents an episode of bipolar disorder. Due to an elevated acute risk of suicide and infanticide, postpartum psychosis is a psychiatric emergency and warrants inpatient hospitalization for immediate intervention.
Related Resources
- Sharma V. Does your patient have postpartum OCD? Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(5):9-10.
- Hatters Friedman S, Prakash C, Nagel-Yang S. Postpartum psychosis: protecting mother and infant. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):12-21.
Drug Brand Names
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Prazosin • Minipress
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakene
CASE Thoughts of harming baby
Ms. A, age 37, is G4P2, 4 months postpartum, and breastfeeding. She has major depressive disorder (MDD) with peripartum onset, posttraumatic stress disorder, and mild intellectual disability. For years she has been stable on fluoxetine 40 mg/d and prazosin 2 mg/d. Despite recent titration of her medications, at her most recent outpatient appointment Ms. A reports having a depressed mood with frequent crying, insomnia, a lack of desire to bond with her baby, and feelings of shame. She also says she has had auditory hallucinations and thoughts of harming her baby. Ms. A’s outpatient physician makes an urgent request for her to be evaluated at the psychiatric emergency department (ED).
HISTORY Depression and possible auditory hallucinations
Ms. A developed MDD following the birth of her first child, for which her care team initiated fluoxetine at 20 mg/d and titrated it to 40 mg/d,which was effective. At that time, her outpatient physician documented potential psychotic features, including vague descriptions of derogatory auditory hallucinations. However, it was unclear if these auditory hallucinations were more representative of a distressing inner monologue without the quality of an external voice. The team determined that Ms. A was not at acute risk for harm to herself or her baby and was appropriate for outpatient care. Because the nature of these possible auditory hallucinations was mild, nondistressing, and nonthreatening, the treatment team did not initiate an antipsychotic and Ms. A was not hospitalized. She has no history of hypomanic/manic episodes and has never met criteria for a psychotic disorder.
EVALUATION Distressing thoughts and discontinued medications
During the evaluation by psychiatric emergency services, Ms. A reports that 2 weeks after giving birth she experienced a worsening of her depressive symptoms. She says she began hearing voices telling her to harm herself and her baby and describes frequent distressing thoughts, such as stabbing her baby with a knife and running over her baby with a car. Ms. A says she repeatedly wakes up at night to check on her baby’s breathing, overfeeds her baby due to a fear of inadequate nutrition, and notes intermittent feelings of confusion. Afraid of being alone with her infant, Ms. A asks her partner and mother to move in with her. Additionally, she says 2 weeks ago she discontinued all her medications at the suggestion of her partner, who recommended herbal supplements. Ms. A’s initial routine laboratory results are unremarkable and her urine drug screen is negative for all substances.
[polldaddy:13041928]
The authors’ observations
Approximately 85% of birthing parents experience some form of postpartum mood disturbance; 10% to 15% develop more significant symptoms of anxiety or depression.3 The etiology of postpartum illness is multifactorial, and includes psychiatric personal/family history, insomnia, acute and chronic psychosocial stressors, and rapid hormone fluctuations.1 As a result, the postpartum period represents a vulnerable time for birthing parents, particularly those with previously established psychiatric illness.
Ms. A’s initial presentation was concerning for a possible diagnosis of postpartum psychosis vs obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) with postpartum onset; other differential diagnoses included MDD with peripartum onset and psychotic features (Table1-6). Ms. A’s subjective clinical history was significant for critical pertinent findings of both OCD with postpartum onset (ie, egodystonic intrusive thoughts, checking behaviors, feelings of shame, and seeking reassurance) and postpartum psychosis (ie, command auditory hallucinations and waxing/waning confusion), which added to diagnostic complexity.

Although postpartum psychosis is rare (1 to 2 cases per 1,000 women),5 it is considered a psychiatric emergency because it has significant potential for infanticide, morbidity, and mortality. Most symptoms develop within the first 2 weeks of the postpartum period.2 There are many risk factors for the development of postpartum psychosis; however, in first-time pregnancies, a previous diagnosis of BD I is the single most important risk factor.1 Approximately 20% to 30% of women with BD experience postpartum psychosis.4
For many patients (approximately 56.7%, according to 1 meta-analysis7), postpartum psychosis denotes an episode of BD, representing a more severe form of illness with increased risk of recurrence. Most manic or mixed mood episodes reoccur within the first year removed from the perinatal period. In contrast, for some patients (approximately 43.5% according to the same meta-analysis), the episode denotes “isolated postpartum psychosis.”7 Isolated postpartum psychosis is a psychotic episode that occurs only in the postpartum period with no recurrence of psychosis or recurrence of psychosis exclusive to postpartum periods. If treated, this type of postpartum psychosis has a more favorable prognosis than postpartum psychosis in a patient with BD.7 As such, a BD diagnosis should not be established at the onset of a patient’s first postpartum psychosis presentation. Regardless of type, all presentations of postpartum psychosis are considered a psychiatry emergency.
Continue to: The prevalence of OCD...
The prevalence of OCD with postpartum onset varies. One study estimated it occurs in 2.43% of cases.4 However, the true prevalence is likely underreported due to feelings of guilt or shame associated with intrusive thoughts, and fear of stigmatization and separation from the baby. Approximately 70.6% of women experiencing OCD with postpartum onset have a comorbid depressive disorder.4
Ms. A’s presentation to the psychiatric ED carried with it diagnostic complexity and uncertainty. Her initial presentation was concerning for elements of both postpartum psychosis and OCD with postpartum onset. After her evaluation in the psychiatric ED, there remained a lack of clear and convincing evidence for a diagnosis of OCD with postpartum onset, which eliminated the possibility of discharging Ms. A with robust safety planning and reinitiation of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
Additionally, because auditory hallucinations are atypical in OCD, the treatment team remained concerned for a diagnosis of postpartum psychosis, which would warrant hospitalization. With assistance from the institution’s reproductive psychiatrists, the treatment team discussed the importance of inpatient hospitalization for risk mitigation, close observation, and thorough evaluation for greater diagnostic clarity and certainty.
TREATMENT Involuntary hospitalization
The treatment team counsels Ms. A and her partner on her differential diagnoses, including the elevated acute risk of harm to herself and her baby if she has postpartum psychosis, as well as the need for continued observation and evaluation. When alone with a clinician, Ms. A says she understands and agrees to voluntary hospitalization. However, following a subsequent risk-benefit discussion with her partner, they both grew increasingly concerned about her separation from the baby and reinitiating her medications. Amid these concerns, the treatment team notices that Ms. A attempts to minimize her symptoms. Ms. A changes her mind and no longer consents to hospitalization. She is placed on a psychiatric hold for involuntary hospitalization on the psychiatric inpatient unit.
On the inpatient unit, the inpatient clinicians and a reproductive psychiatrist continue to evaluate Ms. A. Though her diagnosis remains unclear, Ms. A agrees to start a trial of quetiapine 100 mg/d titrated to 150 mg/d to manage her potential postpartum psychosis, depressed mood, insomnia (off-label), anxiety (off-label), and OCD (off-label). Lithium is deferred because Ms. A is breastfeeding.
[polldaddy:13041932]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Due to an elevated acute risk of suicide and infanticide, postpartum psychosis represents a psychiatric emergency and often requires hospitalization. The Figure outlines steps in evaluating a patient with concerns for postpartum psychosis in a psychiatric emergency service setting. Due to the waxing and waning nature of symptoms, patients may appear psychiatrically stable at any time but remain at an overall elevated acute risk of harm to self and/or their baby.

If a patient is being considered for discharge based on yes answers to all questions in Step 2 of the Figure, the emergency psychiatric clinician must initiate appropriate psychotropic medications and complete robust safety planning with the patient and a trusted adult who will provide direct supervision. Safety planning may include (but is not limited to) strict return precautions, education on concerning symptoms and behaviors, psychotropic education and agreement of compliance, and detailed instructions on outpatient follow-up within 1 week. Ideally—and as was the case for Ms. A—a reproductive psychiatrist should be consulted in the emergency setting for shared decision-making on admission vs discharge, medication management, and outpatient follow-up considerations.
Because postpartum psychosis carries significant risks and hospitalization generally results in separating the patient from their baby, initiating psychotropics should not be delayed. Clinicians must consider the patient’s psychiatric history, allergies, and breastfeeding status.
Based on current evidence, first-line treatment for postpartum psychosis includes a mood stabilizer, an antipsychotic, and possibly a benzodiazepine.6 Thus, an appropriate initial treatment regimen would be a benzodiazepine (particularly lorazepam due to its relatively shorter half-life) and an antipsychotic (eg, haloperidol, olanzapine, or quetiapine) for acute psychosis, plus lithium for mood stabilization.1,5
If the postpartum psychosis represents an episode of BD, use of a long-term mood stabilizer may be required. In contrast, for isolated postpartum psychosis, clinicians may consider initiating psychotropics only in the immediate postpartum period, with an eventual slow taper. In future pregnancies, psychotropics may be reintroduced postpartum, which will avoid peripartum fetal exposure.8 If the patient is breastfeeding, lithium may be deferred in an acute care setting. For patients with evidence of catatonia, severe suicidality, refusal of oral intake with compromised nutrition, severe agitation, or treatment resistance, electroconvulsive therapy remains a safe and effective treatment option.6 Additionally, the safety of continued breastfeeding in acute psychosis must be considered, with the potential for recommending discontinuation, which would decrease sleep disruptions at night and increase the ability of others to feed the baby. Comprehensive care requires nonpharmacologic interventions, including psychoeducation for the patient and their family, individual psychotherapy, and expansion of psychosocial supports.
Continue to: Patients who have experienced...
Patients who have experienced an episode of postpartum psychosis are predisposed to another episode in future pregnancies.1 Current research recommends prophylaxis of recurrence with lithium monotherapy.1,2,5,6 Similar to other psychotropics in reproductive psychiatry, maintenance therapy on lithium requires a thorough “risk vs risk” discussion with the patient. The risk of lithium use while pregnant and/or breastfeeding must be weighed against the risks associated with postpartum psychosis (ie, infanticide, suicide, poor peripartum care, or poor infant bonding).
OUTCOME Improved mood
After 7 days of inpatient treatment with quetiapine, Ms. A demonstrates improvement in the targeted depressive symptoms (including improved motivation/energy and insomnia, decreased feelings of guilt, and denial of ongoing suicidal ideation). Additionally, the thoughts of harming her baby are less frequent, and command auditory hallucinations resolve. Upon discharge, Ms. A and her partner meet with inpatient clinicians for continued counseling, safety planning, and plans for outpatient follow-up with the institution’s reproductive psychiatrist.
The authors’ observations
Many aspects of Ms. A’s initial presentation in the psychiatric ED were challenging. Given the presence of symptoms of both psychosis and OCD, a diagnosis was difficult to ascertain in the emergency setting. Since command auditory hallucinations are atypical in patients with postpartum OCD, the treatment team maintained high suspicion for postpartum psychosis, which represented an emergency requiring inpatient care.
Hospitalization separated Ms. A from her baby, for whom she was the primary caregiver. Additional considerations for inpatient admission and psychotropic initiation were necessary, because Ms. A was breastfeeding. Although Ms. A’s partner was able to provide full-time childcare, the patient ultimately did not agree to hospitalization and required an emergency hold for involuntary admission, which was an additional barrier to care. Furthermore, her partner held unfavorable beliefs regarding psychotropic medications and Ms. A’s need for hospital admission, which required ongoing patient and partner education in the emergency, inpatient, and outpatient settings. Moreover, if Ms. A’s symptoms were ultimately attributable to postpartum OCD, the patient’s involuntary hospitalization might have increased the risk of stigmatization of mental illness and treatment with psychotropics.
Bottom Line
The peripartum period is a vulnerable time for patients, particularly those with previously diagnosed psychiatric illnesses. Postpartum psychosis is the most severe form of postpartum psychiatric illness and often represents an episode of bipolar disorder. Due to an elevated acute risk of suicide and infanticide, postpartum psychosis is a psychiatric emergency and warrants inpatient hospitalization for immediate intervention.
Related Resources
- Sharma V. Does your patient have postpartum OCD? Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(5):9-10.
- Hatters Friedman S, Prakash C, Nagel-Yang S. Postpartum psychosis: protecting mother and infant. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):12-21.
Drug Brand Names
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Haloperidol • Haldol
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lorazepam • Ativan
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Prazosin • Minipress
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakene
1. Raza SK, Raza S. Postpartum Psychosis. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated June 26, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544304/
2. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. What Is Postpartum Psychosis: This Is What You Need to Know. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Published November 15, 2019. Accessed June 22, 2023. https://womensmentalhealth.org/posts/postpartum-psychosis-ten-things-need-know-2/
3. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Postpartum Psychiatric Disorders. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Accessed October 7, 2023. https://womensmentalhealth.org/specialty-clinics-2/postpartum-psychiatric-disorders-2/
4. Sharma V, Sommerdyk C. Obsessive-compulsive disorder in the postpartum period: diagnosis, differential diagnosis and management. Womens Health (Lond). 2015;11(4):543-552. doi:10.2217/whe.15.20
5. Osborne LM. Recognizing and managing postpartum psychosis: a clinical guide for obstetric providers. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2018;45(3):455-468. doi:10.1016/j.ogc.2018.04.005
6. Hutner LA, Catapano LA, Nagle-Yang SM, et al, eds. Textbook of Women’s Reproductive Mental Health. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
7. Gilden J, Kamperman AM, Munk-Olsen T, et al. Long-term outcomes of postpartum psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(2):19r12906. doi:10.4088/JCP.19r12906
8. Bergink V, Boyce P, Munk-Olsen T. Postpartum psychosis: a valuable misnomer. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2015;49(2):102-103. doi:10.1177/0004867414564698
1. Raza SK, Raza S. Postpartum Psychosis. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated June 26, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544304/
2. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. What Is Postpartum Psychosis: This Is What You Need to Know. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Published November 15, 2019. Accessed June 22, 2023. https://womensmentalhealth.org/posts/postpartum-psychosis-ten-things-need-know-2/
3. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Postpartum Psychiatric Disorders. MGH Center for Women’s Mental Health. Accessed October 7, 2023. https://womensmentalhealth.org/specialty-clinics-2/postpartum-psychiatric-disorders-2/
4. Sharma V, Sommerdyk C. Obsessive-compulsive disorder in the postpartum period: diagnosis, differential diagnosis and management. Womens Health (Lond). 2015;11(4):543-552. doi:10.2217/whe.15.20
5. Osborne LM. Recognizing and managing postpartum psychosis: a clinical guide for obstetric providers. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2018;45(3):455-468. doi:10.1016/j.ogc.2018.04.005
6. Hutner LA, Catapano LA, Nagle-Yang SM, et al, eds. Textbook of Women’s Reproductive Mental Health. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
7. Gilden J, Kamperman AM, Munk-Olsen T, et al. Long-term outcomes of postpartum psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2020;81(2):19r12906. doi:10.4088/JCP.19r12906
8. Bergink V, Boyce P, Munk-Olsen T. Postpartum psychosis: a valuable misnomer. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2015;49(2):102-103. doi:10.1177/0004867414564698
Brain volume patterns vary across psychiatric disorders
A large brain imaging study of adults with six different psychiatric illnesses shows that heterogeneity in regional gray matter volume deviations is a general feature of psychiatric illness, but that these regionally heterogeneous areas are often embedded within common functional circuits and networks.
study investigator Ashlea Segal said in an email.
The findings also suggest that it’s “unlikely that a single cause or mechanism of a given disorder exists, and that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to treatment is likely only appropriate for a small subset of individuals. In fact, one size doesn’t fit all. It probably doesn’t even fit most,” said Ms. Segal, a PhD candidate with the Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health’s Neural Systems and Behaviour Lab at Monash University in Melbourne.
“Focusing on brain alterations at an individual level allows us to develop more personally tailored treatments,” Ms. Segal added.
Regional heterogeneity, the authors write, “thus offers a plausible explanation for the well-described clinical heterogeneity observed in psychiatric disorders, while circuit- and network-level aggregation of deviations is a putative neural substrate for phenotypic similarities between patients assigned the same diagnosis.”
The study was published online in Nature Neuroscience
Beyond group averages
For decades, researchers have mapped brain areas showing reduced gray matter volume (GMV) in people diagnosed with a variety of mental illnesses, but these maps have only been generated at the level of group averages, Ms. Segal explained.
“This means that we understand how the brains of people with, say, schizophrenia, differ from those without schizophrenia on average, but we can’t really say much about individual people,” Ms. Segal said.
For their study, the researchers used new statistical techniques developed by Andre Marquand, PhD, who co-led the project, to characterize the heterogeneity of GMV differences in 1,294 individuals diagnosed with one of six psychiatric conditions and 1,465 matched controls. Dr. Marquand is affiliated with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition, and Behavior in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
These techniques “allow us to benchmark the size of over 1,000 different brain regions in any given person relative to what we should expect to see in the general population. In this way, we can identify, for any person, brain regions showing unusually small or large volumes, given that person’s age and sex,” Ms. Segal told this news organization.
The clinical sample included 202 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 153 with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 228 with bipolar disorder, 161 with major depressive disorder, 167 with obsessive-compulsive disorder, and 383 individuals with schizophrenia.
Confirming earlier findings, those with psychiatric illness showed more GMV deviations than healthy controls, the researchers found.
However, at the individual level, deviations from population expectations for regional gray matter volumes were “highly heterogeneous,” affecting the same area in less than 7% of people with the same diagnosis, they note. “This result means that it is difficult to pinpoint treatment targets or causal mechanisms by focusing on group averages alone,” Alex Fornito, PhD, of Monash University, who led the research team, said in a statement.
“It may also explain why people with the same diagnosis show wide variability in their symptom profiles and treatment outcomes,” Dr. Fornito added.
Yet, despite considerable heterogeneity at the regional level across different diagnoses, these deviations were embedded within common functional circuits and networks in up to 56% of cases.
The salience-ventral attention network, for example, which plays a central role in cognitive control, interoceptive awareness, and switching between internally and externally focused attention, was implicated across diagnoses, with other neural networks selectively involved in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
The researchers say the approach they developed opens new opportunities for mapping brain changes in mental illness.
“The framework we have developed allows us to understand the diversity of brain changes in people with mental illness at different levels, from individual regions through to more widespread brain circuits and networks, offering a deeper insight into how the brain is affected in individual people,” Dr. Fornito said in a statement.
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Segal, Dr. Fornito, and Dr. Marquand report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large brain imaging study of adults with six different psychiatric illnesses shows that heterogeneity in regional gray matter volume deviations is a general feature of psychiatric illness, but that these regionally heterogeneous areas are often embedded within common functional circuits and networks.
study investigator Ashlea Segal said in an email.
The findings also suggest that it’s “unlikely that a single cause or mechanism of a given disorder exists, and that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to treatment is likely only appropriate for a small subset of individuals. In fact, one size doesn’t fit all. It probably doesn’t even fit most,” said Ms. Segal, a PhD candidate with the Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health’s Neural Systems and Behaviour Lab at Monash University in Melbourne.
“Focusing on brain alterations at an individual level allows us to develop more personally tailored treatments,” Ms. Segal added.
Regional heterogeneity, the authors write, “thus offers a plausible explanation for the well-described clinical heterogeneity observed in psychiatric disorders, while circuit- and network-level aggregation of deviations is a putative neural substrate for phenotypic similarities between patients assigned the same diagnosis.”
The study was published online in Nature Neuroscience
Beyond group averages
For decades, researchers have mapped brain areas showing reduced gray matter volume (GMV) in people diagnosed with a variety of mental illnesses, but these maps have only been generated at the level of group averages, Ms. Segal explained.
“This means that we understand how the brains of people with, say, schizophrenia, differ from those without schizophrenia on average, but we can’t really say much about individual people,” Ms. Segal said.
For their study, the researchers used new statistical techniques developed by Andre Marquand, PhD, who co-led the project, to characterize the heterogeneity of GMV differences in 1,294 individuals diagnosed with one of six psychiatric conditions and 1,465 matched controls. Dr. Marquand is affiliated with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition, and Behavior in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
These techniques “allow us to benchmark the size of over 1,000 different brain regions in any given person relative to what we should expect to see in the general population. In this way, we can identify, for any person, brain regions showing unusually small or large volumes, given that person’s age and sex,” Ms. Segal told this news organization.
The clinical sample included 202 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 153 with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 228 with bipolar disorder, 161 with major depressive disorder, 167 with obsessive-compulsive disorder, and 383 individuals with schizophrenia.
Confirming earlier findings, those with psychiatric illness showed more GMV deviations than healthy controls, the researchers found.
However, at the individual level, deviations from population expectations for regional gray matter volumes were “highly heterogeneous,” affecting the same area in less than 7% of people with the same diagnosis, they note. “This result means that it is difficult to pinpoint treatment targets or causal mechanisms by focusing on group averages alone,” Alex Fornito, PhD, of Monash University, who led the research team, said in a statement.
“It may also explain why people with the same diagnosis show wide variability in their symptom profiles and treatment outcomes,” Dr. Fornito added.
Yet, despite considerable heterogeneity at the regional level across different diagnoses, these deviations were embedded within common functional circuits and networks in up to 56% of cases.
The salience-ventral attention network, for example, which plays a central role in cognitive control, interoceptive awareness, and switching between internally and externally focused attention, was implicated across diagnoses, with other neural networks selectively involved in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
The researchers say the approach they developed opens new opportunities for mapping brain changes in mental illness.
“The framework we have developed allows us to understand the diversity of brain changes in people with mental illness at different levels, from individual regions through to more widespread brain circuits and networks, offering a deeper insight into how the brain is affected in individual people,” Dr. Fornito said in a statement.
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Segal, Dr. Fornito, and Dr. Marquand report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A large brain imaging study of adults with six different psychiatric illnesses shows that heterogeneity in regional gray matter volume deviations is a general feature of psychiatric illness, but that these regionally heterogeneous areas are often embedded within common functional circuits and networks.
study investigator Ashlea Segal said in an email.
The findings also suggest that it’s “unlikely that a single cause or mechanism of a given disorder exists, and that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to treatment is likely only appropriate for a small subset of individuals. In fact, one size doesn’t fit all. It probably doesn’t even fit most,” said Ms. Segal, a PhD candidate with the Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health’s Neural Systems and Behaviour Lab at Monash University in Melbourne.
“Focusing on brain alterations at an individual level allows us to develop more personally tailored treatments,” Ms. Segal added.
Regional heterogeneity, the authors write, “thus offers a plausible explanation for the well-described clinical heterogeneity observed in psychiatric disorders, while circuit- and network-level aggregation of deviations is a putative neural substrate for phenotypic similarities between patients assigned the same diagnosis.”
The study was published online in Nature Neuroscience
Beyond group averages
For decades, researchers have mapped brain areas showing reduced gray matter volume (GMV) in people diagnosed with a variety of mental illnesses, but these maps have only been generated at the level of group averages, Ms. Segal explained.
“This means that we understand how the brains of people with, say, schizophrenia, differ from those without schizophrenia on average, but we can’t really say much about individual people,” Ms. Segal said.
For their study, the researchers used new statistical techniques developed by Andre Marquand, PhD, who co-led the project, to characterize the heterogeneity of GMV differences in 1,294 individuals diagnosed with one of six psychiatric conditions and 1,465 matched controls. Dr. Marquand is affiliated with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition, and Behavior in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
These techniques “allow us to benchmark the size of over 1,000 different brain regions in any given person relative to what we should expect to see in the general population. In this way, we can identify, for any person, brain regions showing unusually small or large volumes, given that person’s age and sex,” Ms. Segal told this news organization.
The clinical sample included 202 individuals with autism spectrum disorder, 153 with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), 228 with bipolar disorder, 161 with major depressive disorder, 167 with obsessive-compulsive disorder, and 383 individuals with schizophrenia.
Confirming earlier findings, those with psychiatric illness showed more GMV deviations than healthy controls, the researchers found.
However, at the individual level, deviations from population expectations for regional gray matter volumes were “highly heterogeneous,” affecting the same area in less than 7% of people with the same diagnosis, they note. “This result means that it is difficult to pinpoint treatment targets or causal mechanisms by focusing on group averages alone,” Alex Fornito, PhD, of Monash University, who led the research team, said in a statement.
“It may also explain why people with the same diagnosis show wide variability in their symptom profiles and treatment outcomes,” Dr. Fornito added.
Yet, despite considerable heterogeneity at the regional level across different diagnoses, these deviations were embedded within common functional circuits and networks in up to 56% of cases.
The salience-ventral attention network, for example, which plays a central role in cognitive control, interoceptive awareness, and switching between internally and externally focused attention, was implicated across diagnoses, with other neural networks selectively involved in depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
The researchers say the approach they developed opens new opportunities for mapping brain changes in mental illness.
“The framework we have developed allows us to understand the diversity of brain changes in people with mental illness at different levels, from individual regions through to more widespread brain circuits and networks, offering a deeper insight into how the brain is affected in individual people,” Dr. Fornito said in a statement.
The study had no commercial funding. Ms. Segal, Dr. Fornito, and Dr. Marquand report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
Prescribing lifestyle changes: When medicine isn’t enough
In psychiatry, patients come to us with their list of symptoms, often a diagnosis they’ve made themselves, and the expectation that they will be given medication to fix their problem. Their diagnoses are often right on target – people often know if they are depressed or anxious, and Doctor Google may provide useful information.
Sometimes they want a specific medication, one they saw in a TV ad, or one that helped them in the past or has helped someone they know. As psychiatrists have focused more on their strengths as psychopharmacologists and less on psychotherapy, it gets easy for both the patient and the doctor to look to medication, cocktails, and titration as the only thing we do.
“My medicine stopped working,” is a line I commonly hear. Often the patient is on a complicated regimen that has been serving them well, and it seems unlikely that the five psychotropic medications they are taking have suddenly “stopped working.” An obvious exception is the SSRI “poop out” that can occur 6-12 months or more after beginning treatment. In addition, it’s important to make sure patients are taking their medications as prescribed, and that the generic formulations have not changed.
But as rates of mental illness increase, some of it spurred on by difficult times,
This is not to devalue our medications, but to help the patient see symptoms as having multiple factors and give them some means to intervene, in addition to medications. At the beginning of therapy, it is important to “prescribe” lifestyle changes that will facilitate the best possible outcomes.
Nonpharmaceutical prescriptions
Early in my career, people with alcohol use problems were told they needed to be substance free before they were candidates for antidepressants. While we no longer do that, it is still important to emphasize abstinence from addictive substances, and to recommend specific treatment when necessary.
Patients are often reluctant to see their use of alcohol, marijuana (it’s medical! It’s part of wellness!), or their pain medications as part of the problem, and this can be difficult. There have been times, after multiple medications have failed to help their symptoms, when I have said, “If you don’t get treatment for this problem, I am not going to be able to help you feel better” and that has been motivating for the patient.
There are other “prescriptions” to write. Regular sleep is essential for people with mood disorders, and this can be difficult for many patients, especially those who do shift work, or who have regular disruptions to their sleep from noise, pets, and children. Exercise is wonderful for the cardiovascular system, calms anxiety, and maintains strength, endurance, mobility, and quality of life as people age. But it can be a hard sell to people in a mental health crisis.
Nature is healing, and sunshine helps with maintaining circadian rhythms. For those who don’t exercise, I often “prescribe” 20 to 30 minutes a day of walking, preferably outside, during daylight hours, in a park or natural setting. For people with anxiety, it is important to check their caffeine consumption and to suggest ways to moderate it – moving to decaffeinated beverages or titrating down by mixing decaf with caffeinated.
Meditation is something that many people find helpful. For anxious people, it can be very difficult, and I will prescribe a specific instructional video course that I like on the well-being app InsightTimer – Sarah Blondin’s Learn How to Meditate in Seven Days. The sessions are approximately 10 minutes long, and that seems like the right amount of time for a beginner.
When people are very ill and don’t want to go into the hospital, I talk with them about things that happen in the hospital that are helpful, things they can try to mimic at home. In the hospital, patients don’t go to work, they don’t spend hours a day on the computer, and they are given a pass from dealing with the routine stresses of daily life.
I ask them to take time off work, to avoid as much stress as possible, to spend time with loved ones who give them comfort, and to avoid the people who leave them feeling drained or distressed. I ask them to engage in activities they find healing, to eat well, exercise, and avoid social media. In the hospital, I emphasize, they wake patients up in the morning, ask them to get out of bed and engage in therapeutic activities. They are fed and kept from intoxicants.
When it comes to nutrition, we know so little about how food affects mental health. I feel like it can’t hurt to ask people to avoid fast foods, soft drinks, and processed foods, and so I do.
And what about compliance? Of course, not everyone complies; not everyone is interested in making changes and these can be hard changes. I’ve recently started to recommend the book Atomic Habits by James Clear. Sometimes a bit of motivational interviewing can also be helpful in getting people to look at slowly moving toward making changes.
In prescribing lifestyle changes, it is important to offer most of these changes as suggestions, not as things we insist on, or that will leave the patient feeling ashamed if he doesn’t follow through. They should be discussed early in treatment so that patients don’t feel blamed for their illness or relapses. As with all the things we prescribe, some of these behavior changes help some of the people some of the time. Suggesting them, however, makes the strong statement that treating psychiatric disorders can be about more than passively swallowing a pill.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
In psychiatry, patients come to us with their list of symptoms, often a diagnosis they’ve made themselves, and the expectation that they will be given medication to fix their problem. Their diagnoses are often right on target – people often know if they are depressed or anxious, and Doctor Google may provide useful information.
Sometimes they want a specific medication, one they saw in a TV ad, or one that helped them in the past or has helped someone they know. As psychiatrists have focused more on their strengths as psychopharmacologists and less on psychotherapy, it gets easy for both the patient and the doctor to look to medication, cocktails, and titration as the only thing we do.
“My medicine stopped working,” is a line I commonly hear. Often the patient is on a complicated regimen that has been serving them well, and it seems unlikely that the five psychotropic medications they are taking have suddenly “stopped working.” An obvious exception is the SSRI “poop out” that can occur 6-12 months or more after beginning treatment. In addition, it’s important to make sure patients are taking their medications as prescribed, and that the generic formulations have not changed.
But as rates of mental illness increase, some of it spurred on by difficult times,
This is not to devalue our medications, but to help the patient see symptoms as having multiple factors and give them some means to intervene, in addition to medications. At the beginning of therapy, it is important to “prescribe” lifestyle changes that will facilitate the best possible outcomes.
Nonpharmaceutical prescriptions
Early in my career, people with alcohol use problems were told they needed to be substance free before they were candidates for antidepressants. While we no longer do that, it is still important to emphasize abstinence from addictive substances, and to recommend specific treatment when necessary.
Patients are often reluctant to see their use of alcohol, marijuana (it’s medical! It’s part of wellness!), or their pain medications as part of the problem, and this can be difficult. There have been times, after multiple medications have failed to help their symptoms, when I have said, “If you don’t get treatment for this problem, I am not going to be able to help you feel better” and that has been motivating for the patient.
There are other “prescriptions” to write. Regular sleep is essential for people with mood disorders, and this can be difficult for many patients, especially those who do shift work, or who have regular disruptions to their sleep from noise, pets, and children. Exercise is wonderful for the cardiovascular system, calms anxiety, and maintains strength, endurance, mobility, and quality of life as people age. But it can be a hard sell to people in a mental health crisis.
Nature is healing, and sunshine helps with maintaining circadian rhythms. For those who don’t exercise, I often “prescribe” 20 to 30 minutes a day of walking, preferably outside, during daylight hours, in a park or natural setting. For people with anxiety, it is important to check their caffeine consumption and to suggest ways to moderate it – moving to decaffeinated beverages or titrating down by mixing decaf with caffeinated.
Meditation is something that many people find helpful. For anxious people, it can be very difficult, and I will prescribe a specific instructional video course that I like on the well-being app InsightTimer – Sarah Blondin’s Learn How to Meditate in Seven Days. The sessions are approximately 10 minutes long, and that seems like the right amount of time for a beginner.
When people are very ill and don’t want to go into the hospital, I talk with them about things that happen in the hospital that are helpful, things they can try to mimic at home. In the hospital, patients don’t go to work, they don’t spend hours a day on the computer, and they are given a pass from dealing with the routine stresses of daily life.
I ask them to take time off work, to avoid as much stress as possible, to spend time with loved ones who give them comfort, and to avoid the people who leave them feeling drained or distressed. I ask them to engage in activities they find healing, to eat well, exercise, and avoid social media. In the hospital, I emphasize, they wake patients up in the morning, ask them to get out of bed and engage in therapeutic activities. They are fed and kept from intoxicants.
When it comes to nutrition, we know so little about how food affects mental health. I feel like it can’t hurt to ask people to avoid fast foods, soft drinks, and processed foods, and so I do.
And what about compliance? Of course, not everyone complies; not everyone is interested in making changes and these can be hard changes. I’ve recently started to recommend the book Atomic Habits by James Clear. Sometimes a bit of motivational interviewing can also be helpful in getting people to look at slowly moving toward making changes.
In prescribing lifestyle changes, it is important to offer most of these changes as suggestions, not as things we insist on, or that will leave the patient feeling ashamed if he doesn’t follow through. They should be discussed early in treatment so that patients don’t feel blamed for their illness or relapses. As with all the things we prescribe, some of these behavior changes help some of the people some of the time. Suggesting them, however, makes the strong statement that treating psychiatric disorders can be about more than passively swallowing a pill.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
In psychiatry, patients come to us with their list of symptoms, often a diagnosis they’ve made themselves, and the expectation that they will be given medication to fix their problem. Their diagnoses are often right on target – people often know if they are depressed or anxious, and Doctor Google may provide useful information.
Sometimes they want a specific medication, one they saw in a TV ad, or one that helped them in the past or has helped someone they know. As psychiatrists have focused more on their strengths as psychopharmacologists and less on psychotherapy, it gets easy for both the patient and the doctor to look to medication, cocktails, and titration as the only thing we do.
“My medicine stopped working,” is a line I commonly hear. Often the patient is on a complicated regimen that has been serving them well, and it seems unlikely that the five psychotropic medications they are taking have suddenly “stopped working.” An obvious exception is the SSRI “poop out” that can occur 6-12 months or more after beginning treatment. In addition, it’s important to make sure patients are taking their medications as prescribed, and that the generic formulations have not changed.
But as rates of mental illness increase, some of it spurred on by difficult times,
This is not to devalue our medications, but to help the patient see symptoms as having multiple factors and give them some means to intervene, in addition to medications. At the beginning of therapy, it is important to “prescribe” lifestyle changes that will facilitate the best possible outcomes.
Nonpharmaceutical prescriptions
Early in my career, people with alcohol use problems were told they needed to be substance free before they were candidates for antidepressants. While we no longer do that, it is still important to emphasize abstinence from addictive substances, and to recommend specific treatment when necessary.
Patients are often reluctant to see their use of alcohol, marijuana (it’s medical! It’s part of wellness!), or their pain medications as part of the problem, and this can be difficult. There have been times, after multiple medications have failed to help their symptoms, when I have said, “If you don’t get treatment for this problem, I am not going to be able to help you feel better” and that has been motivating for the patient.
There are other “prescriptions” to write. Regular sleep is essential for people with mood disorders, and this can be difficult for many patients, especially those who do shift work, or who have regular disruptions to their sleep from noise, pets, and children. Exercise is wonderful for the cardiovascular system, calms anxiety, and maintains strength, endurance, mobility, and quality of life as people age. But it can be a hard sell to people in a mental health crisis.
Nature is healing, and sunshine helps with maintaining circadian rhythms. For those who don’t exercise, I often “prescribe” 20 to 30 minutes a day of walking, preferably outside, during daylight hours, in a park or natural setting. For people with anxiety, it is important to check their caffeine consumption and to suggest ways to moderate it – moving to decaffeinated beverages or titrating down by mixing decaf with caffeinated.
Meditation is something that many people find helpful. For anxious people, it can be very difficult, and I will prescribe a specific instructional video course that I like on the well-being app InsightTimer – Sarah Blondin’s Learn How to Meditate in Seven Days. The sessions are approximately 10 minutes long, and that seems like the right amount of time for a beginner.
When people are very ill and don’t want to go into the hospital, I talk with them about things that happen in the hospital that are helpful, things they can try to mimic at home. In the hospital, patients don’t go to work, they don’t spend hours a day on the computer, and they are given a pass from dealing with the routine stresses of daily life.
I ask them to take time off work, to avoid as much stress as possible, to spend time with loved ones who give them comfort, and to avoid the people who leave them feeling drained or distressed. I ask them to engage in activities they find healing, to eat well, exercise, and avoid social media. In the hospital, I emphasize, they wake patients up in the morning, ask them to get out of bed and engage in therapeutic activities. They are fed and kept from intoxicants.
When it comes to nutrition, we know so little about how food affects mental health. I feel like it can’t hurt to ask people to avoid fast foods, soft drinks, and processed foods, and so I do.
And what about compliance? Of course, not everyone complies; not everyone is interested in making changes and these can be hard changes. I’ve recently started to recommend the book Atomic Habits by James Clear. Sometimes a bit of motivational interviewing can also be helpful in getting people to look at slowly moving toward making changes.
In prescribing lifestyle changes, it is important to offer most of these changes as suggestions, not as things we insist on, or that will leave the patient feeling ashamed if he doesn’t follow through. They should be discussed early in treatment so that patients don’t feel blamed for their illness or relapses. As with all the things we prescribe, some of these behavior changes help some of the people some of the time. Suggesting them, however, makes the strong statement that treating psychiatric disorders can be about more than passively swallowing a pill.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Clinical index predicts common postpartum mental health disorders
Developed by Canadian researchers, the easily implementable PMH CAREPLAN index “creates a framework for clinically actionable risk stratification that could assist patients and providers in determining an individual’s level of risk for common postpartum mental health disorders and direct them to appropriate intervention,” wrote a group led by Simone N. Vigod, MD, MSc, head of the department of psychiatry at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
After giving birth, women are especially vulnerable to major depression, anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, which have a general postpartum prevalence of 7%-20%.
Common PMH disorders are to be distinguished from the more rare but severe PMH disorders such as postpartum psychosis and bipolar disorder, the researchers stressed.
“We know there are interventions that can prevent these disorders, but these seem to work best in people who are at high risk for developing the illnesses, “ Dr. Vigod said. “So, we wanted to be able to determine the level of risk that a person might actually experience them.”
In an ideal world, she continued, physicians might be able to say to a patient: “You have a 50% chance of developing postpartum depression and anxiety, so it may be worth investing your time and resources in a course of preventive psychotherapy.” Or: “You have a 90% chance of developing these disorders, so it might be worth going back on your medications even though you are breastfeeding.” Or: “You have only a 1% chance of developing them, so probably it’s not worthwhile to go back on your medication prophylactically.”
A need for a new assessment tool, akin to the Framingham Risk Score for 10-year cardiovascular events and the FRAX scoring system for 10-year fracture risk, was evident since previous indices based largely on patient self-reporting have had moderate predictive capacity, and have not been adopted in clinical practice, Dr. Vigod and associates noted.
Split-cohort design
Using population-based health administrative data and hospital birth records from Ontario during 2012-2015, Dr. Vigod’s group created and internally validated a predictive model for common PMH disorders in a cohort of 152,362 mothers. They then converted it to a risk index after validation in an additional cohort of 75,772 mothers. The women had delivered live infants during 2012-2014.
A common PMH disorder occurred in 13,608 mothers, while 214,526 were unaffected.
Independently associated PMH variables were many: prenatal care provider, mental health diagnosis history and medications during pregnancy, psychiatric hospital admissions or ED visits, conception type and complications, and apprehension of newborn by child services. Other factors were region of maternal origin, extremes of gestational age at birth, primary maternal language, lactation intention, maternal age, and number of prenatal visits.
Based on a broad span of scores from 0 to 39, 1-year common PMH disorder risk ranged from 1.5% to 40.5%, with an overall 1-year prevalence of 6%, consistent with previous studies. That included 11,262 (5%) mothers with an anxiety or related disorder, 3,392 (1.5%) with a depressive episode, and 1,046 (0.5%) with both. The best trade-off of sensitivity/specificity for risk appeared to be at a screening threshold score of 17 or above.
Risk drivers
PMH-affected mothers were slightly younger than unaffected women (mean age, 29.9 years vs. 30.6 years), more likely to be primiparous (45.2% vs. 42%), and less likely to be recent immigrants (16.7% vs. 27.2%).
They were also more likely to have previously experienced postpartum depression (4.4% vs. 1.4%), any depression (15.3% vs. 4.4%), and any anxiety disorder (13.8% vs. 4.3%).
As to lifestyle, smoking was more common in women with PMH (15.0% vs. 10.2%), as were the use of nonprescribed substances (3% vs. 1.4%) and intimate partner violence in pregnancy (2.7% vs. 1.5%).
In addition, the affected group experienced more pregnancy complications than their unaffected peers (16% vs. 13.9%), preterm birth (8.2% vs. 6.8%), and Apgar scores below 7 at 1 or 5 minutes (10.5% vs. 7.6%).
Low income did not appear to have an impact since just over 20% in either group fell into the lowest neighborhood income quintile.
Commenting on the index but not involved in developing it, LaTasha D. Nelson, MD, an associate professor or medicine and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, doubted the Canadian model would work as well in the more fragmented U.S. health care system, compared with Canada’s universal model with its large provincial health databases.
She also found the large number of variables and broad score range potentially problematic, especially if the risk threshold is set at less than half the maximum score at 17, at which some low-risk mothers might get screening and perhaps intervention. “Are we going to use up the resources we have for those who might not need help, or are we going to treat someone who really needs it?” she asked.
Another concern is the postpartum timing of assessment. At Dr. Nelson’s center, mothers are checked for mental health at two points during pregnancy and those with higher scores are triaged for further care.
Dr. Nelson was also puzzled by the score-lowering impact of prenatal care given by a nurse practitioner and “other” provider : –5 and –2, respectively, versus +3 for a midwife and +1 for a family doctor. “This may capture more relaxed, easy-going multiparous mothers who felt comfortable turning to an NP,” she said.
It may indeed reflect that the risk level of a person who sees those providers is overall lower, Dr. Vigod agreed. “This is one reason why we would want to see replication of these results in other jurisdictions and by other ways of diagnosis before putting it out into clinical practice.”
As to the score-lowering effect of not speaking English as the primary tongue, Dr. Nelson wondered, “is that because we’re taking better care of mothers who speak the main language and missing those who speak other languages? Are they not getting the same level of interrogation?”
It may be that individuals in these groups were less likely to access mental health care, Dr. Vigod agreed, or it might reflect the so-called healthy immigrant effect or culturally different levels of postpartum support. “It might mean that there are more people who benefit from community-level protective factors in these groups. We know that social support is an important protective factor.”
Despite her reservations about the index, Dr. Nelson said that increasing attention to the pre- and postnatal mental health of mothers is an important part of maternal care. “This is an issue that needs to be recognized.”
The next step, Dr. Vigod said, is to determine whether the index holds up in other populations. “Then, we would want to test it out to see if recommending interventions based on a certain level of risk improves outcomes. At what percentage risk would starting an antidepressant medication result in a reduced risk for postpartum depression or anxiety – 90%, 80%, 70%, or less?”
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Data were analyzed by ICES, an independent nonprofit research organization that holds population-based data. Dr. Vigod reported royalties from UpToDate for materials related to depression and pregnancy. Dr. Nelson disclosed no relevant competing interests.
Developed by Canadian researchers, the easily implementable PMH CAREPLAN index “creates a framework for clinically actionable risk stratification that could assist patients and providers in determining an individual’s level of risk for common postpartum mental health disorders and direct them to appropriate intervention,” wrote a group led by Simone N. Vigod, MD, MSc, head of the department of psychiatry at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
After giving birth, women are especially vulnerable to major depression, anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, which have a general postpartum prevalence of 7%-20%.
Common PMH disorders are to be distinguished from the more rare but severe PMH disorders such as postpartum psychosis and bipolar disorder, the researchers stressed.
“We know there are interventions that can prevent these disorders, but these seem to work best in people who are at high risk for developing the illnesses, “ Dr. Vigod said. “So, we wanted to be able to determine the level of risk that a person might actually experience them.”
In an ideal world, she continued, physicians might be able to say to a patient: “You have a 50% chance of developing postpartum depression and anxiety, so it may be worth investing your time and resources in a course of preventive psychotherapy.” Or: “You have a 90% chance of developing these disorders, so it might be worth going back on your medications even though you are breastfeeding.” Or: “You have only a 1% chance of developing them, so probably it’s not worthwhile to go back on your medication prophylactically.”
A need for a new assessment tool, akin to the Framingham Risk Score for 10-year cardiovascular events and the FRAX scoring system for 10-year fracture risk, was evident since previous indices based largely on patient self-reporting have had moderate predictive capacity, and have not been adopted in clinical practice, Dr. Vigod and associates noted.
Split-cohort design
Using population-based health administrative data and hospital birth records from Ontario during 2012-2015, Dr. Vigod’s group created and internally validated a predictive model for common PMH disorders in a cohort of 152,362 mothers. They then converted it to a risk index after validation in an additional cohort of 75,772 mothers. The women had delivered live infants during 2012-2014.
A common PMH disorder occurred in 13,608 mothers, while 214,526 were unaffected.
Independently associated PMH variables were many: prenatal care provider, mental health diagnosis history and medications during pregnancy, psychiatric hospital admissions or ED visits, conception type and complications, and apprehension of newborn by child services. Other factors were region of maternal origin, extremes of gestational age at birth, primary maternal language, lactation intention, maternal age, and number of prenatal visits.
Based on a broad span of scores from 0 to 39, 1-year common PMH disorder risk ranged from 1.5% to 40.5%, with an overall 1-year prevalence of 6%, consistent with previous studies. That included 11,262 (5%) mothers with an anxiety or related disorder, 3,392 (1.5%) with a depressive episode, and 1,046 (0.5%) with both. The best trade-off of sensitivity/specificity for risk appeared to be at a screening threshold score of 17 or above.
Risk drivers
PMH-affected mothers were slightly younger than unaffected women (mean age, 29.9 years vs. 30.6 years), more likely to be primiparous (45.2% vs. 42%), and less likely to be recent immigrants (16.7% vs. 27.2%).
They were also more likely to have previously experienced postpartum depression (4.4% vs. 1.4%), any depression (15.3% vs. 4.4%), and any anxiety disorder (13.8% vs. 4.3%).
As to lifestyle, smoking was more common in women with PMH (15.0% vs. 10.2%), as were the use of nonprescribed substances (3% vs. 1.4%) and intimate partner violence in pregnancy (2.7% vs. 1.5%).
In addition, the affected group experienced more pregnancy complications than their unaffected peers (16% vs. 13.9%), preterm birth (8.2% vs. 6.8%), and Apgar scores below 7 at 1 or 5 minutes (10.5% vs. 7.6%).
Low income did not appear to have an impact since just over 20% in either group fell into the lowest neighborhood income quintile.
Commenting on the index but not involved in developing it, LaTasha D. Nelson, MD, an associate professor or medicine and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, doubted the Canadian model would work as well in the more fragmented U.S. health care system, compared with Canada’s universal model with its large provincial health databases.
She also found the large number of variables and broad score range potentially problematic, especially if the risk threshold is set at less than half the maximum score at 17, at which some low-risk mothers might get screening and perhaps intervention. “Are we going to use up the resources we have for those who might not need help, or are we going to treat someone who really needs it?” she asked.
Another concern is the postpartum timing of assessment. At Dr. Nelson’s center, mothers are checked for mental health at two points during pregnancy and those with higher scores are triaged for further care.
Dr. Nelson was also puzzled by the score-lowering impact of prenatal care given by a nurse practitioner and “other” provider : –5 and –2, respectively, versus +3 for a midwife and +1 for a family doctor. “This may capture more relaxed, easy-going multiparous mothers who felt comfortable turning to an NP,” she said.
It may indeed reflect that the risk level of a person who sees those providers is overall lower, Dr. Vigod agreed. “This is one reason why we would want to see replication of these results in other jurisdictions and by other ways of diagnosis before putting it out into clinical practice.”
As to the score-lowering effect of not speaking English as the primary tongue, Dr. Nelson wondered, “is that because we’re taking better care of mothers who speak the main language and missing those who speak other languages? Are they not getting the same level of interrogation?”
It may be that individuals in these groups were less likely to access mental health care, Dr. Vigod agreed, or it might reflect the so-called healthy immigrant effect or culturally different levels of postpartum support. “It might mean that there are more people who benefit from community-level protective factors in these groups. We know that social support is an important protective factor.”
Despite her reservations about the index, Dr. Nelson said that increasing attention to the pre- and postnatal mental health of mothers is an important part of maternal care. “This is an issue that needs to be recognized.”
The next step, Dr. Vigod said, is to determine whether the index holds up in other populations. “Then, we would want to test it out to see if recommending interventions based on a certain level of risk improves outcomes. At what percentage risk would starting an antidepressant medication result in a reduced risk for postpartum depression or anxiety – 90%, 80%, 70%, or less?”
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Data were analyzed by ICES, an independent nonprofit research organization that holds population-based data. Dr. Vigod reported royalties from UpToDate for materials related to depression and pregnancy. Dr. Nelson disclosed no relevant competing interests.
Developed by Canadian researchers, the easily implementable PMH CAREPLAN index “creates a framework for clinically actionable risk stratification that could assist patients and providers in determining an individual’s level of risk for common postpartum mental health disorders and direct them to appropriate intervention,” wrote a group led by Simone N. Vigod, MD, MSc, head of the department of psychiatry at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
After giving birth, women are especially vulnerable to major depression, anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, which have a general postpartum prevalence of 7%-20%.
Common PMH disorders are to be distinguished from the more rare but severe PMH disorders such as postpartum psychosis and bipolar disorder, the researchers stressed.
“We know there are interventions that can prevent these disorders, but these seem to work best in people who are at high risk for developing the illnesses, “ Dr. Vigod said. “So, we wanted to be able to determine the level of risk that a person might actually experience them.”
In an ideal world, she continued, physicians might be able to say to a patient: “You have a 50% chance of developing postpartum depression and anxiety, so it may be worth investing your time and resources in a course of preventive psychotherapy.” Or: “You have a 90% chance of developing these disorders, so it might be worth going back on your medications even though you are breastfeeding.” Or: “You have only a 1% chance of developing them, so probably it’s not worthwhile to go back on your medication prophylactically.”
A need for a new assessment tool, akin to the Framingham Risk Score for 10-year cardiovascular events and the FRAX scoring system for 10-year fracture risk, was evident since previous indices based largely on patient self-reporting have had moderate predictive capacity, and have not been adopted in clinical practice, Dr. Vigod and associates noted.
Split-cohort design
Using population-based health administrative data and hospital birth records from Ontario during 2012-2015, Dr. Vigod’s group created and internally validated a predictive model for common PMH disorders in a cohort of 152,362 mothers. They then converted it to a risk index after validation in an additional cohort of 75,772 mothers. The women had delivered live infants during 2012-2014.
A common PMH disorder occurred in 13,608 mothers, while 214,526 were unaffected.
Independently associated PMH variables were many: prenatal care provider, mental health diagnosis history and medications during pregnancy, psychiatric hospital admissions or ED visits, conception type and complications, and apprehension of newborn by child services. Other factors were region of maternal origin, extremes of gestational age at birth, primary maternal language, lactation intention, maternal age, and number of prenatal visits.
Based on a broad span of scores from 0 to 39, 1-year common PMH disorder risk ranged from 1.5% to 40.5%, with an overall 1-year prevalence of 6%, consistent with previous studies. That included 11,262 (5%) mothers with an anxiety or related disorder, 3,392 (1.5%) with a depressive episode, and 1,046 (0.5%) with both. The best trade-off of sensitivity/specificity for risk appeared to be at a screening threshold score of 17 or above.
Risk drivers
PMH-affected mothers were slightly younger than unaffected women (mean age, 29.9 years vs. 30.6 years), more likely to be primiparous (45.2% vs. 42%), and less likely to be recent immigrants (16.7% vs. 27.2%).
They were also more likely to have previously experienced postpartum depression (4.4% vs. 1.4%), any depression (15.3% vs. 4.4%), and any anxiety disorder (13.8% vs. 4.3%).
As to lifestyle, smoking was more common in women with PMH (15.0% vs. 10.2%), as were the use of nonprescribed substances (3% vs. 1.4%) and intimate partner violence in pregnancy (2.7% vs. 1.5%).
In addition, the affected group experienced more pregnancy complications than their unaffected peers (16% vs. 13.9%), preterm birth (8.2% vs. 6.8%), and Apgar scores below 7 at 1 or 5 minutes (10.5% vs. 7.6%).
Low income did not appear to have an impact since just over 20% in either group fell into the lowest neighborhood income quintile.
Commenting on the index but not involved in developing it, LaTasha D. Nelson, MD, an associate professor or medicine and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, doubted the Canadian model would work as well in the more fragmented U.S. health care system, compared with Canada’s universal model with its large provincial health databases.
She also found the large number of variables and broad score range potentially problematic, especially if the risk threshold is set at less than half the maximum score at 17, at which some low-risk mothers might get screening and perhaps intervention. “Are we going to use up the resources we have for those who might not need help, or are we going to treat someone who really needs it?” she asked.
Another concern is the postpartum timing of assessment. At Dr. Nelson’s center, mothers are checked for mental health at two points during pregnancy and those with higher scores are triaged for further care.
Dr. Nelson was also puzzled by the score-lowering impact of prenatal care given by a nurse practitioner and “other” provider : –5 and –2, respectively, versus +3 for a midwife and +1 for a family doctor. “This may capture more relaxed, easy-going multiparous mothers who felt comfortable turning to an NP,” she said.
It may indeed reflect that the risk level of a person who sees those providers is overall lower, Dr. Vigod agreed. “This is one reason why we would want to see replication of these results in other jurisdictions and by other ways of diagnosis before putting it out into clinical practice.”
As to the score-lowering effect of not speaking English as the primary tongue, Dr. Nelson wondered, “is that because we’re taking better care of mothers who speak the main language and missing those who speak other languages? Are they not getting the same level of interrogation?”
It may be that individuals in these groups were less likely to access mental health care, Dr. Vigod agreed, or it might reflect the so-called healthy immigrant effect or culturally different levels of postpartum support. “It might mean that there are more people who benefit from community-level protective factors in these groups. We know that social support is an important protective factor.”
Despite her reservations about the index, Dr. Nelson said that increasing attention to the pre- and postnatal mental health of mothers is an important part of maternal care. “This is an issue that needs to be recognized.”
The next step, Dr. Vigod said, is to determine whether the index holds up in other populations. “Then, we would want to test it out to see if recommending interventions based on a certain level of risk improves outcomes. At what percentage risk would starting an antidepressant medication result in a reduced risk for postpartum depression or anxiety – 90%, 80%, 70%, or less?”
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Data were analyzed by ICES, an independent nonprofit research organization that holds population-based data. Dr. Vigod reported royalties from UpToDate for materials related to depression and pregnancy. Dr. Nelson disclosed no relevant competing interests.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
OCD linked to adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes
In an observational study that followed almost 3 million pregnancies in two countries over 20 years, children of women with OCD were at increased risk for low Apgar score at 5 minutes in Sweden (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.62) and British Columbia, Canada (aRR, 2.30). The risks for adverse outcomes were greater among women with OCD who were taking serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), compared with those who were not.
“To me, the most relevant things to consider are the clinical implications of these findings,” lead author Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, principal researcher at Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, told this news organization. She noted that some of the outcomes, such as preeclampsia, can be prevented or improved with collaboration among clinicians and increased monitoring.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Increased risk
OCD affects roughly 1%-3% of the population. Although it is sometimes seen as a mild psychiatric disorder, OCD entails a range of adverse outcomes, and this research suggests that the adverse outcomes extend to maternal health, Dr. Fernández de la Cruz stressed.
The researchers drew data from population registers in Sweden and British Columbia for all singleton births over a roughly 20-year period ending in 2019, with subcohorts identified by formal OCD diagnosis and exposure to SRIs within 30 days before conception. Statistical analyses were performed on a range of pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal outcomes.
In an analysis adjusted for common risk factors such as age, BMI, and smoking, Swedish women with OCD had elevated risk for several adverse outcomes, including a 40% increased risk for gestational diabetes. In British Columbia, fewer adverse pregnancy outcomes for women were associated with an OCD diagnosis.
The study, which also tracked neonatal outcomes, found that infants of mothers with OCD in both Sweden and British Columbia had higher rates of preterm birth (Sweden: aRR, 1.33; BC: aRR, 1.58), low birth weight (Sweden: aRR, 1.28; BC: aRR, 1.40), and neonatal respiratory distress (Sweden: aRR, 1.63; BC: aRR, 1.47).
These results, the authors say, show a need for more monitoring of maternal OCD and collaboration among obstetricians and psychologists. “All this evidence shows that OCD should be detected and treated so that adverse outcomes can be prevented or properly handled,” said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz.
SRI medication
SRIs are frequently used to treat OCD. The subclass of selective SRIs, which includes common antidepressants, has been associated with worsened pregnancy outcomes, but it remains unclear whether all SRIs increase pregnancy risks.
To understand the role of SRIs better in this study, the authors compared the outcomes for women taking SRIs and those who were not prescribed the medication, which is a novel aspect of the study, according to Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Women who took the medication were at greater risk for several adverse outcomes, although all women with an OCD diagnosis were at higher risk than were those without the condition. The investigators hope to continue studying the role of OCD medication during pregnancy in more detail.
The rates of SRI use varied between the two cohorts: 81% of Canadian patients took the medication, compared with 37% of Swedish patients. The disparate rates, along with other clinical practices, may have contributed to differences in outcomes for the two cohorts.
It is also important to bear in mind, however, that patients taking the medication tend to have more severe cases of OCD, said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Thus, the increased risk may or may not result from the medication itself. “It is important to understand that there may be other variables besides medication explaining why one group had higher risks than the other,” she said.
‘Multifactorial’ reasons
In addition to medication, other factors may play a role in the association between OCD and adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes, including genetics, lifestyle, and psychiatric comorbidities. The authors addressed some of these potential confounders in additional analyses, including sister and cousin comparisons in the Swedish arm of the study, which found weakened associations, compared with population wide statistics.
Commenting on the research, Benicio Frey, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., said that acknowledging these confounding factors is a strength of the study. Psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety are common among patients with OCD. Of the patients with OCD in this study, 72% and 51% had other psychiatric diagnoses in Sweden and British Columbia, respectively. About 7% of the women without OCD had one of these conditions.
However, Dr. Frey said that the effect of adjusting for psychiatric comorbidities on some outcomes should be stated more clearly. “I see a clear difference,” he said. The relative risk for gestational diabetes among the Swedish cohort, for example, drops from a 40% increased risk to 19% increased when adjusted for mood and anxiety disorders.
Regardless of the cause, the results are important and demonstrate a need to provide additional care for pregnant women with psychiatric conditions, said Dr. Frey. “The important take-home message for policymakers and health care providers is to make sure that they assess for OCD and then monitor those individuals very closely. What I would suggest as a caution is that the reasons behind it are multifactorial.”
The study was supported by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare and by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Fernández de la Cruz and Dr. Frey reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an observational study that followed almost 3 million pregnancies in two countries over 20 years, children of women with OCD were at increased risk for low Apgar score at 5 minutes in Sweden (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.62) and British Columbia, Canada (aRR, 2.30). The risks for adverse outcomes were greater among women with OCD who were taking serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), compared with those who were not.
“To me, the most relevant things to consider are the clinical implications of these findings,” lead author Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, principal researcher at Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, told this news organization. She noted that some of the outcomes, such as preeclampsia, can be prevented or improved with collaboration among clinicians and increased monitoring.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Increased risk
OCD affects roughly 1%-3% of the population. Although it is sometimes seen as a mild psychiatric disorder, OCD entails a range of adverse outcomes, and this research suggests that the adverse outcomes extend to maternal health, Dr. Fernández de la Cruz stressed.
The researchers drew data from population registers in Sweden and British Columbia for all singleton births over a roughly 20-year period ending in 2019, with subcohorts identified by formal OCD diagnosis and exposure to SRIs within 30 days before conception. Statistical analyses were performed on a range of pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal outcomes.
In an analysis adjusted for common risk factors such as age, BMI, and smoking, Swedish women with OCD had elevated risk for several adverse outcomes, including a 40% increased risk for gestational diabetes. In British Columbia, fewer adverse pregnancy outcomes for women were associated with an OCD diagnosis.
The study, which also tracked neonatal outcomes, found that infants of mothers with OCD in both Sweden and British Columbia had higher rates of preterm birth (Sweden: aRR, 1.33; BC: aRR, 1.58), low birth weight (Sweden: aRR, 1.28; BC: aRR, 1.40), and neonatal respiratory distress (Sweden: aRR, 1.63; BC: aRR, 1.47).
These results, the authors say, show a need for more monitoring of maternal OCD and collaboration among obstetricians and psychologists. “All this evidence shows that OCD should be detected and treated so that adverse outcomes can be prevented or properly handled,” said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz.
SRI medication
SRIs are frequently used to treat OCD. The subclass of selective SRIs, which includes common antidepressants, has been associated with worsened pregnancy outcomes, but it remains unclear whether all SRIs increase pregnancy risks.
To understand the role of SRIs better in this study, the authors compared the outcomes for women taking SRIs and those who were not prescribed the medication, which is a novel aspect of the study, according to Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Women who took the medication were at greater risk for several adverse outcomes, although all women with an OCD diagnosis were at higher risk than were those without the condition. The investigators hope to continue studying the role of OCD medication during pregnancy in more detail.
The rates of SRI use varied between the two cohorts: 81% of Canadian patients took the medication, compared with 37% of Swedish patients. The disparate rates, along with other clinical practices, may have contributed to differences in outcomes for the two cohorts.
It is also important to bear in mind, however, that patients taking the medication tend to have more severe cases of OCD, said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Thus, the increased risk may or may not result from the medication itself. “It is important to understand that there may be other variables besides medication explaining why one group had higher risks than the other,” she said.
‘Multifactorial’ reasons
In addition to medication, other factors may play a role in the association between OCD and adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes, including genetics, lifestyle, and psychiatric comorbidities. The authors addressed some of these potential confounders in additional analyses, including sister and cousin comparisons in the Swedish arm of the study, which found weakened associations, compared with population wide statistics.
Commenting on the research, Benicio Frey, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., said that acknowledging these confounding factors is a strength of the study. Psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety are common among patients with OCD. Of the patients with OCD in this study, 72% and 51% had other psychiatric diagnoses in Sweden and British Columbia, respectively. About 7% of the women without OCD had one of these conditions.
However, Dr. Frey said that the effect of adjusting for psychiatric comorbidities on some outcomes should be stated more clearly. “I see a clear difference,” he said. The relative risk for gestational diabetes among the Swedish cohort, for example, drops from a 40% increased risk to 19% increased when adjusted for mood and anxiety disorders.
Regardless of the cause, the results are important and demonstrate a need to provide additional care for pregnant women with psychiatric conditions, said Dr. Frey. “The important take-home message for policymakers and health care providers is to make sure that they assess for OCD and then monitor those individuals very closely. What I would suggest as a caution is that the reasons behind it are multifactorial.”
The study was supported by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare and by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Fernández de la Cruz and Dr. Frey reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an observational study that followed almost 3 million pregnancies in two countries over 20 years, children of women with OCD were at increased risk for low Apgar score at 5 minutes in Sweden (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.62) and British Columbia, Canada (aRR, 2.30). The risks for adverse outcomes were greater among women with OCD who were taking serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), compared with those who were not.
“To me, the most relevant things to consider are the clinical implications of these findings,” lead author Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, principal researcher at Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, told this news organization. She noted that some of the outcomes, such as preeclampsia, can be prevented or improved with collaboration among clinicians and increased monitoring.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Increased risk
OCD affects roughly 1%-3% of the population. Although it is sometimes seen as a mild psychiatric disorder, OCD entails a range of adverse outcomes, and this research suggests that the adverse outcomes extend to maternal health, Dr. Fernández de la Cruz stressed.
The researchers drew data from population registers in Sweden and British Columbia for all singleton births over a roughly 20-year period ending in 2019, with subcohorts identified by formal OCD diagnosis and exposure to SRIs within 30 days before conception. Statistical analyses were performed on a range of pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal outcomes.
In an analysis adjusted for common risk factors such as age, BMI, and smoking, Swedish women with OCD had elevated risk for several adverse outcomes, including a 40% increased risk for gestational diabetes. In British Columbia, fewer adverse pregnancy outcomes for women were associated with an OCD diagnosis.
The study, which also tracked neonatal outcomes, found that infants of mothers with OCD in both Sweden and British Columbia had higher rates of preterm birth (Sweden: aRR, 1.33; BC: aRR, 1.58), low birth weight (Sweden: aRR, 1.28; BC: aRR, 1.40), and neonatal respiratory distress (Sweden: aRR, 1.63; BC: aRR, 1.47).
These results, the authors say, show a need for more monitoring of maternal OCD and collaboration among obstetricians and psychologists. “All this evidence shows that OCD should be detected and treated so that adverse outcomes can be prevented or properly handled,” said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz.
SRI medication
SRIs are frequently used to treat OCD. The subclass of selective SRIs, which includes common antidepressants, has been associated with worsened pregnancy outcomes, but it remains unclear whether all SRIs increase pregnancy risks.
To understand the role of SRIs better in this study, the authors compared the outcomes for women taking SRIs and those who were not prescribed the medication, which is a novel aspect of the study, according to Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Women who took the medication were at greater risk for several adverse outcomes, although all women with an OCD diagnosis were at higher risk than were those without the condition. The investigators hope to continue studying the role of OCD medication during pregnancy in more detail.
The rates of SRI use varied between the two cohorts: 81% of Canadian patients took the medication, compared with 37% of Swedish patients. The disparate rates, along with other clinical practices, may have contributed to differences in outcomes for the two cohorts.
It is also important to bear in mind, however, that patients taking the medication tend to have more severe cases of OCD, said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Thus, the increased risk may or may not result from the medication itself. “It is important to understand that there may be other variables besides medication explaining why one group had higher risks than the other,” she said.
‘Multifactorial’ reasons
In addition to medication, other factors may play a role in the association between OCD and adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes, including genetics, lifestyle, and psychiatric comorbidities. The authors addressed some of these potential confounders in additional analyses, including sister and cousin comparisons in the Swedish arm of the study, which found weakened associations, compared with population wide statistics.
Commenting on the research, Benicio Frey, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., said that acknowledging these confounding factors is a strength of the study. Psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety are common among patients with OCD. Of the patients with OCD in this study, 72% and 51% had other psychiatric diagnoses in Sweden and British Columbia, respectively. About 7% of the women without OCD had one of these conditions.
However, Dr. Frey said that the effect of adjusting for psychiatric comorbidities on some outcomes should be stated more clearly. “I see a clear difference,” he said. The relative risk for gestational diabetes among the Swedish cohort, for example, drops from a 40% increased risk to 19% increased when adjusted for mood and anxiety disorders.
Regardless of the cause, the results are important and demonstrate a need to provide additional care for pregnant women with psychiatric conditions, said Dr. Frey. “The important take-home message for policymakers and health care providers is to make sure that they assess for OCD and then monitor those individuals very closely. What I would suggest as a caution is that the reasons behind it are multifactorial.”
The study was supported by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare and by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Fernández de la Cruz and Dr. Frey reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN







