User login
Anidulafungin effectively treated invasive pediatric candidiasis in open-label trial
SAN DIEGO – The intravenous echinocandin anidulafungin effectively treated invasive candidiasis in a single-arm, multicenter, open-label trial of 47 children aged 2-17 years.
The overall global response rate of 72% resembled that from the prior adult registry study (76%), Emmanuel Roilides, MD, PhD, and his associates reported in a poster presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
At 6-week follow-up, two patients (4%) had relapsed, both with Candida parapsilosis, which was more resistant to treatment with anidulafungin (Eraxis) than other Candida species, the researchers reported. Treating the children with 3.0 mg/kg anidulafungin on day 1, followed by 1.5 mg/kg every 24 hours, yielded similar pharmacokinetics as the 200/100 mg regimen used in adults. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included diarrhea (23%), vomiting (23%), and fever (19%), which also reflected findings in adults, the investigators said. Five patients (10%) developed at least one severe treatment-emergent adverse event, including neutropenia, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, increased hepatic transaminases, hyponatremia, and myalgia. The study (NCT00761267) is ongoing and continues to recruit patients in 11 states in the United States and nine other countries, with final top-line results expected in 2019.
Although rates of invasive candidiasis appear to be decreasing in children overall, the population at risk is expanding, experts have noted. Relevant guidelines from the Infectious Disease Society of America and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases list amphotericin B, echinocandins, and azoles as treatment options, but these recommendations are extrapolated mainly from adult studies, noted Dr. Roilides, who is a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Aristotle University School of Health Sciences and Hippokration General Hospital in Thessaloniki, Greece.
To better characterize the safety and efficacy of anidulafungin in children, the researchers enrolled patients up to 17 years of age who had signs and symptoms of invasive candidiasis and Candida cultured from a normally sterile site. Patients received intravenous anidulafungin (3 mg/kg on day 1, followed by 1.5 mg/kg every 24 hours) for at least 10 days, after which they could switch to oral fluconazole. Treatment continued for at least 14 days after blood cultures were negative and signs and symptoms resolved.
At interim data cutoff in October 2016, patients were exposed to anidulafungin for a median of 11.5 days (range, 1-28 days). Among 47 patients who received at least one dose of anidulafungin, about two-thirds were male, about 70% were white, and the average age was 8 years (standard deviation, 4.7 years). Rates of global success – a combination of clinical and microbiological response – were 82% in patients up to 5 years old and 67% in older children. Children whose baseline neutrophil count was at least 500 per mm3 had a 78% global response rate versus 50% among those with more severe neutropenia. C. parapsilosis had higher minimum inhibitory concentrations than other Candida species, and in vitro susceptibility rates of 85% for C. parapsilosis versus 100% for other species.
All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse effect. In addition to diarrhea, vomiting, and pyrexia, adverse events affecting more than 10% of patients included epistaxis (17%), headache (15%), and abdominal pain (13%). Half of patients switched to oral fluconazole. Four patients stopped treatment because of vomiting, generalized pruritus, or increased transaminases. A total of 15% of patients died, although no deaths were considered treatment related. The patient who stopped treatment because of pruritus later died of septic shock secondary to invasive candidiasis, despite having started treatment with fluconazole and micafungin, the investigators reported at the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
Nearly all patients had bloodstream infections, and catheters also cultured positive in more than two-thirds of cases, the researchers said. Many patients had multiple risk factors for infection such as central venous catheters, broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy, total parenteral nutrition, and chemotherapy. Cultures were most often positive for Candida albicans (38%), followed by C. parapsilosis (26%) and C. tropicalis (13%).
Pfizer makes anidulafungin and sponsored the study. Dr. Roilides disclosed research grants and advisory relationships with Pfizer, Astellas, Gilead, and Merck.
SAN DIEGO – The intravenous echinocandin anidulafungin effectively treated invasive candidiasis in a single-arm, multicenter, open-label trial of 47 children aged 2-17 years.
The overall global response rate of 72% resembled that from the prior adult registry study (76%), Emmanuel Roilides, MD, PhD, and his associates reported in a poster presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
At 6-week follow-up, two patients (4%) had relapsed, both with Candida parapsilosis, which was more resistant to treatment with anidulafungin (Eraxis) than other Candida species, the researchers reported. Treating the children with 3.0 mg/kg anidulafungin on day 1, followed by 1.5 mg/kg every 24 hours, yielded similar pharmacokinetics as the 200/100 mg regimen used in adults. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included diarrhea (23%), vomiting (23%), and fever (19%), which also reflected findings in adults, the investigators said. Five patients (10%) developed at least one severe treatment-emergent adverse event, including neutropenia, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, increased hepatic transaminases, hyponatremia, and myalgia. The study (NCT00761267) is ongoing and continues to recruit patients in 11 states in the United States and nine other countries, with final top-line results expected in 2019.
Although rates of invasive candidiasis appear to be decreasing in children overall, the population at risk is expanding, experts have noted. Relevant guidelines from the Infectious Disease Society of America and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases list amphotericin B, echinocandins, and azoles as treatment options, but these recommendations are extrapolated mainly from adult studies, noted Dr. Roilides, who is a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Aristotle University School of Health Sciences and Hippokration General Hospital in Thessaloniki, Greece.
To better characterize the safety and efficacy of anidulafungin in children, the researchers enrolled patients up to 17 years of age who had signs and symptoms of invasive candidiasis and Candida cultured from a normally sterile site. Patients received intravenous anidulafungin (3 mg/kg on day 1, followed by 1.5 mg/kg every 24 hours) for at least 10 days, after which they could switch to oral fluconazole. Treatment continued for at least 14 days after blood cultures were negative and signs and symptoms resolved.
At interim data cutoff in October 2016, patients were exposed to anidulafungin for a median of 11.5 days (range, 1-28 days). Among 47 patients who received at least one dose of anidulafungin, about two-thirds were male, about 70% were white, and the average age was 8 years (standard deviation, 4.7 years). Rates of global success – a combination of clinical and microbiological response – were 82% in patients up to 5 years old and 67% in older children. Children whose baseline neutrophil count was at least 500 per mm3 had a 78% global response rate versus 50% among those with more severe neutropenia. C. parapsilosis had higher minimum inhibitory concentrations than other Candida species, and in vitro susceptibility rates of 85% for C. parapsilosis versus 100% for other species.
All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse effect. In addition to diarrhea, vomiting, and pyrexia, adverse events affecting more than 10% of patients included epistaxis (17%), headache (15%), and abdominal pain (13%). Half of patients switched to oral fluconazole. Four patients stopped treatment because of vomiting, generalized pruritus, or increased transaminases. A total of 15% of patients died, although no deaths were considered treatment related. The patient who stopped treatment because of pruritus later died of septic shock secondary to invasive candidiasis, despite having started treatment with fluconazole and micafungin, the investigators reported at the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
Nearly all patients had bloodstream infections, and catheters also cultured positive in more than two-thirds of cases, the researchers said. Many patients had multiple risk factors for infection such as central venous catheters, broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy, total parenteral nutrition, and chemotherapy. Cultures were most often positive for Candida albicans (38%), followed by C. parapsilosis (26%) and C. tropicalis (13%).
Pfizer makes anidulafungin and sponsored the study. Dr. Roilides disclosed research grants and advisory relationships with Pfizer, Astellas, Gilead, and Merck.
SAN DIEGO – The intravenous echinocandin anidulafungin effectively treated invasive candidiasis in a single-arm, multicenter, open-label trial of 47 children aged 2-17 years.
The overall global response rate of 72% resembled that from the prior adult registry study (76%), Emmanuel Roilides, MD, PhD, and his associates reported in a poster presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
At 6-week follow-up, two patients (4%) had relapsed, both with Candida parapsilosis, which was more resistant to treatment with anidulafungin (Eraxis) than other Candida species, the researchers reported. Treating the children with 3.0 mg/kg anidulafungin on day 1, followed by 1.5 mg/kg every 24 hours, yielded similar pharmacokinetics as the 200/100 mg regimen used in adults. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included diarrhea (23%), vomiting (23%), and fever (19%), which also reflected findings in adults, the investigators said. Five patients (10%) developed at least one severe treatment-emergent adverse event, including neutropenia, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, increased hepatic transaminases, hyponatremia, and myalgia. The study (NCT00761267) is ongoing and continues to recruit patients in 11 states in the United States and nine other countries, with final top-line results expected in 2019.
Although rates of invasive candidiasis appear to be decreasing in children overall, the population at risk is expanding, experts have noted. Relevant guidelines from the Infectious Disease Society of America and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases list amphotericin B, echinocandins, and azoles as treatment options, but these recommendations are extrapolated mainly from adult studies, noted Dr. Roilides, who is a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Aristotle University School of Health Sciences and Hippokration General Hospital in Thessaloniki, Greece.
To better characterize the safety and efficacy of anidulafungin in children, the researchers enrolled patients up to 17 years of age who had signs and symptoms of invasive candidiasis and Candida cultured from a normally sterile site. Patients received intravenous anidulafungin (3 mg/kg on day 1, followed by 1.5 mg/kg every 24 hours) for at least 10 days, after which they could switch to oral fluconazole. Treatment continued for at least 14 days after blood cultures were negative and signs and symptoms resolved.
At interim data cutoff in October 2016, patients were exposed to anidulafungin for a median of 11.5 days (range, 1-28 days). Among 47 patients who received at least one dose of anidulafungin, about two-thirds were male, about 70% were white, and the average age was 8 years (standard deviation, 4.7 years). Rates of global success – a combination of clinical and microbiological response – were 82% in patients up to 5 years old and 67% in older children. Children whose baseline neutrophil count was at least 500 per mm3 had a 78% global response rate versus 50% among those with more severe neutropenia. C. parapsilosis had higher minimum inhibitory concentrations than other Candida species, and in vitro susceptibility rates of 85% for C. parapsilosis versus 100% for other species.
All patients experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse effect. In addition to diarrhea, vomiting, and pyrexia, adverse events affecting more than 10% of patients included epistaxis (17%), headache (15%), and abdominal pain (13%). Half of patients switched to oral fluconazole. Four patients stopped treatment because of vomiting, generalized pruritus, or increased transaminases. A total of 15% of patients died, although no deaths were considered treatment related. The patient who stopped treatment because of pruritus later died of septic shock secondary to invasive candidiasis, despite having started treatment with fluconazole and micafungin, the investigators reported at the combined annual meetings of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, the HIV Medicine Association, and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society.
Nearly all patients had bloodstream infections, and catheters also cultured positive in more than two-thirds of cases, the researchers said. Many patients had multiple risk factors for infection such as central venous catheters, broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy, total parenteral nutrition, and chemotherapy. Cultures were most often positive for Candida albicans (38%), followed by C. parapsilosis (26%) and C. tropicalis (13%).
Pfizer makes anidulafungin and sponsored the study. Dr. Roilides disclosed research grants and advisory relationships with Pfizer, Astellas, Gilead, and Merck.
AT IDWEEK 2017
Key clinical point: The intravenous echinocandin anidulafungin effectively treated invasive candidiasis in children, with a safety profile resembling what has been previously reported for adults.
Major finding: The overall global response rate was 72%. The most common treatment-emergent adverse effects included diarrhea (23%), vomiting (23%), and fever (19%). Five patients (10%) developed at least one severe treatment-emergent adverse event.
Data source: A multicenter, single-arm, open-label study of 47 patients aged 2-17 years.
Disclosures: Pfizer makes anidulafungin and sponsored the study. Dr. Roilides disclosed research grants and advisory relationships with Pfizer, Astellas, Gilead, and Merck.
Safety data review finds no increased risk of infection from abatacept
MADRID – Abatacept doesn’t appear to increase the risk of opportunistic infections among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Kevin Winthrop, MD, reported at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
After reviewing all of the extant safety data on the drug – all of its clinical trial and open-label study data, and case reports of abatacept-associated adverse events – Dr. Winthrop concluded that infections, including tuberculosis, fungal overgrowth, herpes simplex and herpes zoster, occur either with similar frequency or less often than among those taking placebo.
“In fact, there is a sense that abatacept is actually safer,” than some other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs,” said Dr. Winthrop, an infectious disease specialist at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland. However, there are few data comparing safety among the agents – something he said should be examined in more detail.
His review encompassed 16 clinical trials comprising 7,044 patients who took the drug (21,330 patient/years of abatacept exposure) and 1,485 patients who took placebo. He conducted two analyses: one for opportunistic bacterial and fungal infections, and one for herpes simplex and herpes zoster.
The first analysis found 45 opportunistic bacterial or fungal infections among those taking abatacept – an incidence rate of 0.21/ 100 person-years. There were seven such infections in the placebo group – an incidence rate of 0.56/100 person-years. This difference was statistically significant.
In the abatacept cohort, there were two cases of bronchopulmonary aspergilliosis (IR 0.01) and three fungal eye infections (IR 0.01). There was also one case of gastrointestinal candidiasis; one fungal esophagitis; one cryptococcal meningitis; two pneumonias (one pseudomonal and one caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii); and two cases of respiratory monoliasis. All of these infections had an incidence rate of less than 0.01/100 person-years.
There were 17 tuberculosis cases (IR 0.08/100 person-years). Three cases were latent. Six of the cases were pulmonary and five were extrapulmonary. Two cases were unspecified. All occurred in regions with high or moderate endemic tuberculosis levels.
A meta-regression analysis examined the risk of opportunistic infections in the patients taken from the placebo-controlled clinical trials only (2,653 abatacept, 1,485 placebo). The estimated frequency of an opportunistic infection was 0.15% among those taking the drug and 0.48% among those taking placebo.
The herpes analysis examined the placebo-controlled clinical trial population as well. There were 57 cases of herpes simplex (IR 2.5/100 person-years) among those taking abatacept and 22 among those taking placebo (IR 1.8/100 person-years). The difference was not statistically significant.
There were 44 cases of herpes zoster among those taking abatacept (IR 1.9/100 person-years) and 21 among those taking placebo (IR 1.7/100 person-years).
“Basically, I think what we’re seeing here is a whole lot of nothing,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Dr. Winthrop has been a consultant for Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB Pharma, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, Galapagos, and Eli Lilly.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @Alz_gal
MADRID – Abatacept doesn’t appear to increase the risk of opportunistic infections among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Kevin Winthrop, MD, reported at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
After reviewing all of the extant safety data on the drug – all of its clinical trial and open-label study data, and case reports of abatacept-associated adverse events – Dr. Winthrop concluded that infections, including tuberculosis, fungal overgrowth, herpes simplex and herpes zoster, occur either with similar frequency or less often than among those taking placebo.
“In fact, there is a sense that abatacept is actually safer,” than some other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs,” said Dr. Winthrop, an infectious disease specialist at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland. However, there are few data comparing safety among the agents – something he said should be examined in more detail.
His review encompassed 16 clinical trials comprising 7,044 patients who took the drug (21,330 patient/years of abatacept exposure) and 1,485 patients who took placebo. He conducted two analyses: one for opportunistic bacterial and fungal infections, and one for herpes simplex and herpes zoster.
The first analysis found 45 opportunistic bacterial or fungal infections among those taking abatacept – an incidence rate of 0.21/ 100 person-years. There were seven such infections in the placebo group – an incidence rate of 0.56/100 person-years. This difference was statistically significant.
In the abatacept cohort, there were two cases of bronchopulmonary aspergilliosis (IR 0.01) and three fungal eye infections (IR 0.01). There was also one case of gastrointestinal candidiasis; one fungal esophagitis; one cryptococcal meningitis; two pneumonias (one pseudomonal and one caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii); and two cases of respiratory monoliasis. All of these infections had an incidence rate of less than 0.01/100 person-years.
There were 17 tuberculosis cases (IR 0.08/100 person-years). Three cases were latent. Six of the cases were pulmonary and five were extrapulmonary. Two cases were unspecified. All occurred in regions with high or moderate endemic tuberculosis levels.
A meta-regression analysis examined the risk of opportunistic infections in the patients taken from the placebo-controlled clinical trials only (2,653 abatacept, 1,485 placebo). The estimated frequency of an opportunistic infection was 0.15% among those taking the drug and 0.48% among those taking placebo.
The herpes analysis examined the placebo-controlled clinical trial population as well. There were 57 cases of herpes simplex (IR 2.5/100 person-years) among those taking abatacept and 22 among those taking placebo (IR 1.8/100 person-years). The difference was not statistically significant.
There were 44 cases of herpes zoster among those taking abatacept (IR 1.9/100 person-years) and 21 among those taking placebo (IR 1.7/100 person-years).
“Basically, I think what we’re seeing here is a whole lot of nothing,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Dr. Winthrop has been a consultant for Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB Pharma, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, Galapagos, and Eli Lilly.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @Alz_gal
MADRID – Abatacept doesn’t appear to increase the risk of opportunistic infections among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Kevin Winthrop, MD, reported at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
After reviewing all of the extant safety data on the drug – all of its clinical trial and open-label study data, and case reports of abatacept-associated adverse events – Dr. Winthrop concluded that infections, including tuberculosis, fungal overgrowth, herpes simplex and herpes zoster, occur either with similar frequency or less often than among those taking placebo.
“In fact, there is a sense that abatacept is actually safer,” than some other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs,” said Dr. Winthrop, an infectious disease specialist at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland. However, there are few data comparing safety among the agents – something he said should be examined in more detail.
His review encompassed 16 clinical trials comprising 7,044 patients who took the drug (21,330 patient/years of abatacept exposure) and 1,485 patients who took placebo. He conducted two analyses: one for opportunistic bacterial and fungal infections, and one for herpes simplex and herpes zoster.
The first analysis found 45 opportunistic bacterial or fungal infections among those taking abatacept – an incidence rate of 0.21/ 100 person-years. There were seven such infections in the placebo group – an incidence rate of 0.56/100 person-years. This difference was statistically significant.
In the abatacept cohort, there were two cases of bronchopulmonary aspergilliosis (IR 0.01) and three fungal eye infections (IR 0.01). There was also one case of gastrointestinal candidiasis; one fungal esophagitis; one cryptococcal meningitis; two pneumonias (one pseudomonal and one caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii); and two cases of respiratory monoliasis. All of these infections had an incidence rate of less than 0.01/100 person-years.
There were 17 tuberculosis cases (IR 0.08/100 person-years). Three cases were latent. Six of the cases were pulmonary and five were extrapulmonary. Two cases were unspecified. All occurred in regions with high or moderate endemic tuberculosis levels.
A meta-regression analysis examined the risk of opportunistic infections in the patients taken from the placebo-controlled clinical trials only (2,653 abatacept, 1,485 placebo). The estimated frequency of an opportunistic infection was 0.15% among those taking the drug and 0.48% among those taking placebo.
The herpes analysis examined the placebo-controlled clinical trial population as well. There were 57 cases of herpes simplex (IR 2.5/100 person-years) among those taking abatacept and 22 among those taking placebo (IR 1.8/100 person-years). The difference was not statistically significant.
There were 44 cases of herpes zoster among those taking abatacept (IR 1.9/100 person-years) and 21 among those taking placebo (IR 1.7/100 person-years).
“Basically, I think what we’re seeing here is a whole lot of nothing,” Dr. Winthrop said.
Dr. Winthrop has been a consultant for Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB Pharma, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, Galapagos, and Eli Lilly.
msullivan@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @Alz_gal
AT EULAR 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall incidence rate for opportunistic infection was 0.21/100 person-years for abatacept and 0.56 for placebo.
Data source: The review comprised 7,044 who took abatacept and 1,485 who took placebo.
Disclosures: Dr. Winthrop has been a consultant for Pfizer, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB Pharma, Roche/Genentech, Amgen, Galapagos, and Eli Lilly.
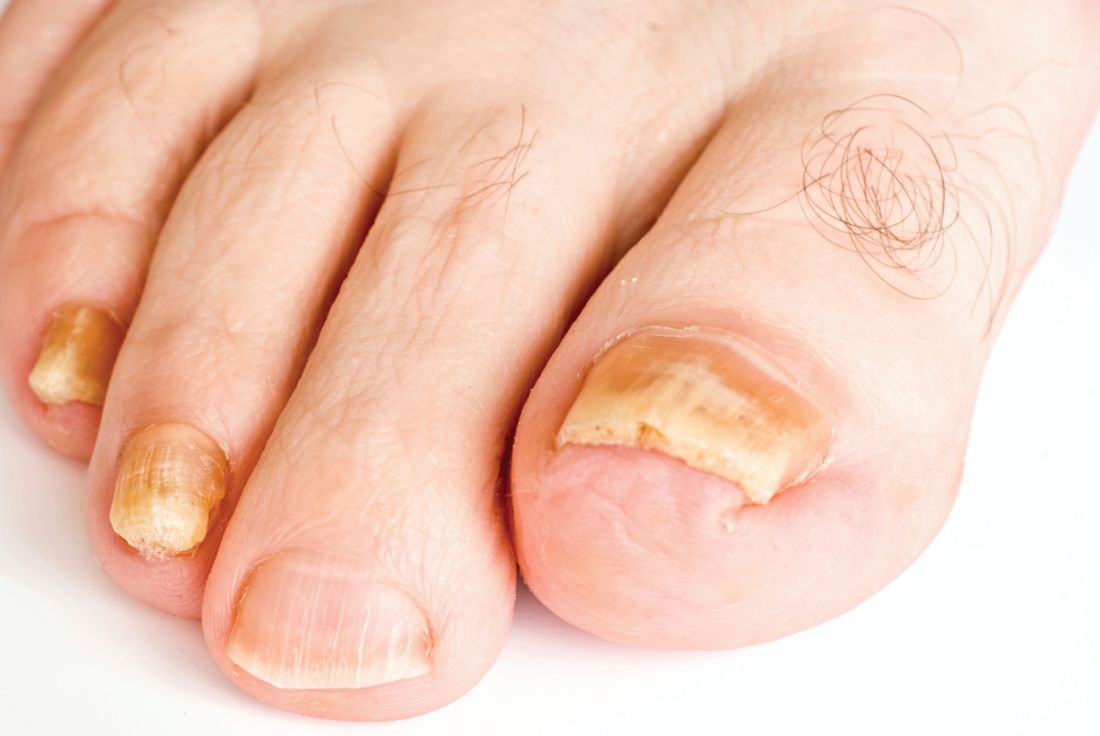
Limitations with molecular techniques in detecting onychomycosis
Real-time PCR techniques for identifying the pathogens responsible for onychomycosis can offer some advantages over conventional diagnostic approaches but also have their limitations, say the authors of a study published in Mycoses.
Anissa Z. Hafirassou of Frères-Mentouri, Constantine University, Algeria, and colleagues analyzed nail samples from 70 patients with clinical signs of onychomycosis and 15 healthy controls using four different real-time PCR assays – a panfungal, a pandermatophyte, an assay for Candida and one for Aspergillus – and conventional methods.
Most samples were of Trichophyton species and were found in patients with proven onychomycosis. In contrast, the sequencing results from the healthy samples were all negative.
The pandermatophyte analysis found dermatophyte DNA in 60% of cases – most of were proven cases of onychomycosis – representing a sensitivity of 90% compared to positive culture. This analysis showed 90% sensitivity compared to cultures, but there was no correlation between culture results and pandermatophyte RT-PCR in nine cases.
This technique also detected Trichophyton cases in 15 patients who had negative culture results, but found amplification products in three of the control subjects, two of which were Penicillium chrysogenum. However two culture-positive samples showed up as negative with both the panfungal and pandermatophyte methods.
“Due to the low sensitivity of the panfungal assay and the lack of correlation between cultures and PCR results, the possibility of the presence of environmental and colonizing species together with pathological species in nail samples, was studied,” the authors wrote.
Twenty-five fingernail samples that were negative on the panfungal analysis were also tested for Candida and Aspergillus. Candida species were detected in 76% of these samples, and Aspergillus in 60%, while 64% contained mixed populations. Ten samples contained more than one species of Candida and one had two species of Aspergillus.
“Conventional diagnostic methods have several limitations such as time-cost, low sensitivity and the need of skilled personnel,” the authors wrote, noting that the molecular methods also had limitations to their usefulness.
The panfungal method showed low sensitivity, which may have been due to the mix of fungal populations that was found even in healthy controls, the researchers added.
“The pandermatophyte assay was sensitive and specific but only detected dermatophyte species and did not allow differentiation among them,” they wrote.
The role of nondermatophyte species isolated from onychomycosis should be considered carefully, as these are also found in healthy nails, the researchers noted.
The study and one author were supported by the Spanish Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Real-time PCR techniques for identifying the pathogens responsible for onychomycosis can offer some advantages over conventional diagnostic approaches but also have their limitations, say the authors of a study published in Mycoses.
Anissa Z. Hafirassou of Frères-Mentouri, Constantine University, Algeria, and colleagues analyzed nail samples from 70 patients with clinical signs of onychomycosis and 15 healthy controls using four different real-time PCR assays – a panfungal, a pandermatophyte, an assay for Candida and one for Aspergillus – and conventional methods.
Most samples were of Trichophyton species and were found in patients with proven onychomycosis. In contrast, the sequencing results from the healthy samples were all negative.
The pandermatophyte analysis found dermatophyte DNA in 60% of cases – most of were proven cases of onychomycosis – representing a sensitivity of 90% compared to positive culture. This analysis showed 90% sensitivity compared to cultures, but there was no correlation between culture results and pandermatophyte RT-PCR in nine cases.
This technique also detected Trichophyton cases in 15 patients who had negative culture results, but found amplification products in three of the control subjects, two of which were Penicillium chrysogenum. However two culture-positive samples showed up as negative with both the panfungal and pandermatophyte methods.
“Due to the low sensitivity of the panfungal assay and the lack of correlation between cultures and PCR results, the possibility of the presence of environmental and colonizing species together with pathological species in nail samples, was studied,” the authors wrote.
Twenty-five fingernail samples that were negative on the panfungal analysis were also tested for Candida and Aspergillus. Candida species were detected in 76% of these samples, and Aspergillus in 60%, while 64% contained mixed populations. Ten samples contained more than one species of Candida and one had two species of Aspergillus.
“Conventional diagnostic methods have several limitations such as time-cost, low sensitivity and the need of skilled personnel,” the authors wrote, noting that the molecular methods also had limitations to their usefulness.
The panfungal method showed low sensitivity, which may have been due to the mix of fungal populations that was found even in healthy controls, the researchers added.
“The pandermatophyte assay was sensitive and specific but only detected dermatophyte species and did not allow differentiation among them,” they wrote.
The role of nondermatophyte species isolated from onychomycosis should be considered carefully, as these are also found in healthy nails, the researchers noted.
The study and one author were supported by the Spanish Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Real-time PCR techniques for identifying the pathogens responsible for onychomycosis can offer some advantages over conventional diagnostic approaches but also have their limitations, say the authors of a study published in Mycoses.
Anissa Z. Hafirassou of Frères-Mentouri, Constantine University, Algeria, and colleagues analyzed nail samples from 70 patients with clinical signs of onychomycosis and 15 healthy controls using four different real-time PCR assays – a panfungal, a pandermatophyte, an assay for Candida and one for Aspergillus – and conventional methods.
Most samples were of Trichophyton species and were found in patients with proven onychomycosis. In contrast, the sequencing results from the healthy samples were all negative.
The pandermatophyte analysis found dermatophyte DNA in 60% of cases – most of were proven cases of onychomycosis – representing a sensitivity of 90% compared to positive culture. This analysis showed 90% sensitivity compared to cultures, but there was no correlation between culture results and pandermatophyte RT-PCR in nine cases.
This technique also detected Trichophyton cases in 15 patients who had negative culture results, but found amplification products in three of the control subjects, two of which were Penicillium chrysogenum. However two culture-positive samples showed up as negative with both the panfungal and pandermatophyte methods.
“Due to the low sensitivity of the panfungal assay and the lack of correlation between cultures and PCR results, the possibility of the presence of environmental and colonizing species together with pathological species in nail samples, was studied,” the authors wrote.
Twenty-five fingernail samples that were negative on the panfungal analysis were also tested for Candida and Aspergillus. Candida species were detected in 76% of these samples, and Aspergillus in 60%, while 64% contained mixed populations. Ten samples contained more than one species of Candida and one had two species of Aspergillus.
“Conventional diagnostic methods have several limitations such as time-cost, low sensitivity and the need of skilled personnel,” the authors wrote, noting that the molecular methods also had limitations to their usefulness.
The panfungal method showed low sensitivity, which may have been due to the mix of fungal populations that was found even in healthy controls, the researchers added.
“The pandermatophyte assay was sensitive and specific but only detected dermatophyte species and did not allow differentiation among them,” they wrote.
The role of nondermatophyte species isolated from onychomycosis should be considered carefully, as these are also found in healthy nails, the researchers noted.
The study and one author were supported by the Spanish Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. No conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM MYCOSES
Key clinical point: Real-time PCR techniques for identifying the pathogens in onychomycosis have some advantages over culture but also have their limitations.
Major finding: Panfungal real-time PCR had a sensitivity of 47% and pandermatophyte RT-PCR had a sensitivity of 90% compared to positive culture.
Data source: Analysis of toenail samples from 70 patients with onychomycosis and 15 healthy controls.
Disclosures: The study and one author were supported by the Spanish Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Direct microscopy plus nail clipping identifies onychomycosis
In the absence of a typical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis, according to a report published in Mycoses.
It is often difficult to diagnose nail diseases based solely on clinical features, and laboratory techniques for diagnosing onychomycoses in particular “remain a challenge,” said Fernanda G. Lavorato, MD, of Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, and her associates.
Isolating filamentous fungi in cultures is considered the preferred method for diagnosing the disorder, but this method lacks sensitivity and is not always accessible, since some dermatologic centers don’t have a mycology laboratory with personnel trained in sample collection and fungal processing.
The mean patient age was 58.8 years (range, 27-86 years). Most study participants (77.8%) had more than 1 affected nail. Many (29.7%) also had symptoms or signs of cutaneous lesions on the palm, sole, or interdigital region.
Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis. In contrast, cultures identified only 34.4% of cases. This low sensitivity for culture testing was expected, and was “likely due to the rapid growth of fungi and bacteria comprising the local microbiota, which often prevents the growth of pathogenic fungi, particularly of slow-growing dermatophytes,” Dr. Lavorato and her associates said (Mycoses. 2017 May 15. doi:10.1111/myc.12633).
Histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases. “Nail clipping histopathologic analysis complements the [microscopic] examination, particularly in cases of strong clinical suspicion but repeatedly negative mycological tests,” the investigators noted.
Direct microscopy showed greater accuracy with nondermatophytes, while nail clipping showed greater accuracy for dermatophytes, they added.
In this study, Trichophyton rubrum and T. mentagrophytes were the most frequently isolated dermatophytes, found in 70% and 23% of cases, respectively. Neoscytalidium dimidatum and Fusarium species were the most frequently isolated nondermatophytes, found in 44% and 28% of cases, respectively. In addition, Candida yeasts were isolated in samples from 14% of patients, and bacterial colonies were isolated in 70%.
The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
In the absence of a typical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis, according to a report published in Mycoses.
It is often difficult to diagnose nail diseases based solely on clinical features, and laboratory techniques for diagnosing onychomycoses in particular “remain a challenge,” said Fernanda G. Lavorato, MD, of Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, and her associates.
Isolating filamentous fungi in cultures is considered the preferred method for diagnosing the disorder, but this method lacks sensitivity and is not always accessible, since some dermatologic centers don’t have a mycology laboratory with personnel trained in sample collection and fungal processing.
The mean patient age was 58.8 years (range, 27-86 years). Most study participants (77.8%) had more than 1 affected nail. Many (29.7%) also had symptoms or signs of cutaneous lesions on the palm, sole, or interdigital region.
Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis. In contrast, cultures identified only 34.4% of cases. This low sensitivity for culture testing was expected, and was “likely due to the rapid growth of fungi and bacteria comprising the local microbiota, which often prevents the growth of pathogenic fungi, particularly of slow-growing dermatophytes,” Dr. Lavorato and her associates said (Mycoses. 2017 May 15. doi:10.1111/myc.12633).
Histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases. “Nail clipping histopathologic analysis complements the [microscopic] examination, particularly in cases of strong clinical suspicion but repeatedly negative mycological tests,” the investigators noted.
Direct microscopy showed greater accuracy with nondermatophytes, while nail clipping showed greater accuracy for dermatophytes, they added.
In this study, Trichophyton rubrum and T. mentagrophytes were the most frequently isolated dermatophytes, found in 70% and 23% of cases, respectively. Neoscytalidium dimidatum and Fusarium species were the most frequently isolated nondermatophytes, found in 44% and 28% of cases, respectively. In addition, Candida yeasts were isolated in samples from 14% of patients, and bacterial colonies were isolated in 70%.
The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
In the absence of a typical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis, according to a report published in Mycoses.
It is often difficult to diagnose nail diseases based solely on clinical features, and laboratory techniques for diagnosing onychomycoses in particular “remain a challenge,” said Fernanda G. Lavorato, MD, of Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, and her associates.
Isolating filamentous fungi in cultures is considered the preferred method for diagnosing the disorder, but this method lacks sensitivity and is not always accessible, since some dermatologic centers don’t have a mycology laboratory with personnel trained in sample collection and fungal processing.
The mean patient age was 58.8 years (range, 27-86 years). Most study participants (77.8%) had more than 1 affected nail. Many (29.7%) also had symptoms or signs of cutaneous lesions on the palm, sole, or interdigital region.
Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis. In contrast, cultures identified only 34.4% of cases. This low sensitivity for culture testing was expected, and was “likely due to the rapid growth of fungi and bacteria comprising the local microbiota, which often prevents the growth of pathogenic fungi, particularly of slow-growing dermatophytes,” Dr. Lavorato and her associates said (Mycoses. 2017 May 15. doi:10.1111/myc.12633).
Histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases. “Nail clipping histopathologic analysis complements the [microscopic] examination, particularly in cases of strong clinical suspicion but repeatedly negative mycological tests,” the investigators noted.
Direct microscopy showed greater accuracy with nondermatophytes, while nail clipping showed greater accuracy for dermatophytes, they added.
In this study, Trichophyton rubrum and T. mentagrophytes were the most frequently isolated dermatophytes, found in 70% and 23% of cases, respectively. Neoscytalidium dimidatum and Fusarium species were the most frequently isolated nondermatophytes, found in 44% and 28% of cases, respectively. In addition, Candida yeasts were isolated in samples from 14% of patients, and bacterial colonies were isolated in 70%.
The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM MYCOSES
Key clinical point: In the absence of a typical clinical presentation, combining direct microscopy plus nail clipping histopathology – two diagnostic tests with different sensitivities and specificities – raises the likelihood of correctly diagnosing onychomycosis.
Major finding: Direct microscopy was the most sensitive diagnostic test, correctly identifying 100% of the 122 cases of onychomycosis, while histopathology of nail clippings was the most specific diagnostic test, correctly identifying 77% of cases.
Data source: A single-center prospective cross-sectional study involving 212 adults suspected of having onychomycosis during a 2-year period.
Disclosures: The Mycology Laboratory at Pedro Ernesto University Hospital supported the study. Dr. Lavorato and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Physical treatment plus antifungal best for chromoblastomycosis, review finds
SYDNEY – Chromoblastomycosis is best managed with a combination of surgery or cryotherapy, with an antifungal, based on a systematic review of 37 studies.
The results of these studies, none of which was randomized or controlled, highlighted challenges in the management of chromoblastomycosis, such as low cure rates and high relapse rates, particularly with chronic and extensive disease. “This is due to the indolent nature of the disease, which leads to a delayed diagnosis, so then the patient develops lymphedema and fibrosis, and the drug isn’t able to penetrate the sites of the lesion,” said Antonia Laino, MD, of the dermatology research center, University of Queensland (Australia).
Noncompliance was also found to be an issue because of side effects and the cost of long-term treatment.
Surgical and pharmacologic options were among the treatments used. Based on the results, Dr. Laino said surgery was recommended as the best treatment for small lesions, and could achieve cure rates of 100% for very small lesions. Cryotherapy was also used to treat chromoblastomycosis lesions, with variable success rates that were dependent on the size of the lesion and the frequency of freezing cycles. However, she suggested that larger lesions should be treated in serial sections, and warned of the risk of retractile scars with treatment over joints.
The most commonly reported drug therapies for chromoblastomycosis were itraconazole and terbinafine. With itraconazole, cure rates ranged from 15% to 80% over an average of 8.5 months of treatment. Pulsed itraconazole therapy, involving 1 week on and 3 weeks off treatment, achieved cure rates of 67%-100% across the studies. With terbinafine treatment, cure rates ranged from 40% to 75% over an average of 9 months of treatment.
In an interview, Dr. Laino said randomized controlled trials were needed to establish best practices for the treatment of chromoblastomycosis.
“I would also say that an antifungal plus a physical method [surgery or cryotherapy] is the way to go,” she said in the interview. As for pharmacotherapy, currently, “there’s the most support for use of itraconazole,” she said, but other antifungals that are being developed will also probably become good options, as studies of those become available. Refractory cases and very severe disease could be treated with a combination of itraconazole and terbinafine.
Chromoblastomycosis is a subcutaneous mycotic infection that is endemic worldwide, but is more common in tropical regions. It usually develops after injury to the skin, which allows entry of any one of several fungal pathogens including Fonsecaea pedrosoi, Phialophora verrucosa, and Cladophialophora carrionii. “Chromoblastomycosis can present with many different lesions, but the early lesions usually resemble a dermatophyte infection or begin as a papule,” Dr. Laino said. “Over time, the lesions will progress into the nodular, tumorous verrucous, cicatricial, and plaque types, and in advanced cases … you’ll see a lot of different lesions in one patient.”
No conflicts of interest were declared.
SYDNEY – Chromoblastomycosis is best managed with a combination of surgery or cryotherapy, with an antifungal, based on a systematic review of 37 studies.
The results of these studies, none of which was randomized or controlled, highlighted challenges in the management of chromoblastomycosis, such as low cure rates and high relapse rates, particularly with chronic and extensive disease. “This is due to the indolent nature of the disease, which leads to a delayed diagnosis, so then the patient develops lymphedema and fibrosis, and the drug isn’t able to penetrate the sites of the lesion,” said Antonia Laino, MD, of the dermatology research center, University of Queensland (Australia).
Noncompliance was also found to be an issue because of side effects and the cost of long-term treatment.
Surgical and pharmacologic options were among the treatments used. Based on the results, Dr. Laino said surgery was recommended as the best treatment for small lesions, and could achieve cure rates of 100% for very small lesions. Cryotherapy was also used to treat chromoblastomycosis lesions, with variable success rates that were dependent on the size of the lesion and the frequency of freezing cycles. However, she suggested that larger lesions should be treated in serial sections, and warned of the risk of retractile scars with treatment over joints.
The most commonly reported drug therapies for chromoblastomycosis were itraconazole and terbinafine. With itraconazole, cure rates ranged from 15% to 80% over an average of 8.5 months of treatment. Pulsed itraconazole therapy, involving 1 week on and 3 weeks off treatment, achieved cure rates of 67%-100% across the studies. With terbinafine treatment, cure rates ranged from 40% to 75% over an average of 9 months of treatment.
In an interview, Dr. Laino said randomized controlled trials were needed to establish best practices for the treatment of chromoblastomycosis.
“I would also say that an antifungal plus a physical method [surgery or cryotherapy] is the way to go,” she said in the interview. As for pharmacotherapy, currently, “there’s the most support for use of itraconazole,” she said, but other antifungals that are being developed will also probably become good options, as studies of those become available. Refractory cases and very severe disease could be treated with a combination of itraconazole and terbinafine.
Chromoblastomycosis is a subcutaneous mycotic infection that is endemic worldwide, but is more common in tropical regions. It usually develops after injury to the skin, which allows entry of any one of several fungal pathogens including Fonsecaea pedrosoi, Phialophora verrucosa, and Cladophialophora carrionii. “Chromoblastomycosis can present with many different lesions, but the early lesions usually resemble a dermatophyte infection or begin as a papule,” Dr. Laino said. “Over time, the lesions will progress into the nodular, tumorous verrucous, cicatricial, and plaque types, and in advanced cases … you’ll see a lot of different lesions in one patient.”
No conflicts of interest were declared.
SYDNEY – Chromoblastomycosis is best managed with a combination of surgery or cryotherapy, with an antifungal, based on a systematic review of 37 studies.
The results of these studies, none of which was randomized or controlled, highlighted challenges in the management of chromoblastomycosis, such as low cure rates and high relapse rates, particularly with chronic and extensive disease. “This is due to the indolent nature of the disease, which leads to a delayed diagnosis, so then the patient develops lymphedema and fibrosis, and the drug isn’t able to penetrate the sites of the lesion,” said Antonia Laino, MD, of the dermatology research center, University of Queensland (Australia).
Noncompliance was also found to be an issue because of side effects and the cost of long-term treatment.
Surgical and pharmacologic options were among the treatments used. Based on the results, Dr. Laino said surgery was recommended as the best treatment for small lesions, and could achieve cure rates of 100% for very small lesions. Cryotherapy was also used to treat chromoblastomycosis lesions, with variable success rates that were dependent on the size of the lesion and the frequency of freezing cycles. However, she suggested that larger lesions should be treated in serial sections, and warned of the risk of retractile scars with treatment over joints.
The most commonly reported drug therapies for chromoblastomycosis were itraconazole and terbinafine. With itraconazole, cure rates ranged from 15% to 80% over an average of 8.5 months of treatment. Pulsed itraconazole therapy, involving 1 week on and 3 weeks off treatment, achieved cure rates of 67%-100% across the studies. With terbinafine treatment, cure rates ranged from 40% to 75% over an average of 9 months of treatment.
In an interview, Dr. Laino said randomized controlled trials were needed to establish best practices for the treatment of chromoblastomycosis.
“I would also say that an antifungal plus a physical method [surgery or cryotherapy] is the way to go,” she said in the interview. As for pharmacotherapy, currently, “there’s the most support for use of itraconazole,” she said, but other antifungals that are being developed will also probably become good options, as studies of those become available. Refractory cases and very severe disease could be treated with a combination of itraconazole and terbinafine.
Chromoblastomycosis is a subcutaneous mycotic infection that is endemic worldwide, but is more common in tropical regions. It usually develops after injury to the skin, which allows entry of any one of several fungal pathogens including Fonsecaea pedrosoi, Phialophora verrucosa, and Cladophialophora carrionii. “Chromoblastomycosis can present with many different lesions, but the early lesions usually resemble a dermatophyte infection or begin as a papule,” Dr. Laino said. “Over time, the lesions will progress into the nodular, tumorous verrucous, cicatricial, and plaque types, and in advanced cases … you’ll see a lot of different lesions in one patient.”
No conflicts of interest were declared.
AT ACDASM 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Surgery in combination with an antifungal was the most effective management approach for chromoblastomycosis.
Data source: A systematic review of 37 studies of patients with chromoblastomycosis.
Disclosures: No conflicts of interest were declared.
Novel antifungal had favorable safety, efficacy profile for onychomycosis in phase IIB study
ORLANDO – A novel orally administered antifungal showed a favorable safety and efficacy profile in the treatment of distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, in a phase IIB study presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
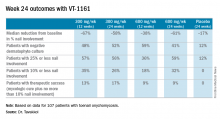
In the RENOVATE (Restoring Nail: An Oral VT-1161 Tablet Evaluation) study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial, 259 adults with moderate to severe distal lateral subungual onychomycosis of the large toenail were assigned to either one of four treatment arms. They were given the antifungal, currently named VT-1161, a selective CYP51 inhibitor, at doses of 300 mg or 600 mg once weekly for 10 or 22 weeks, after receiving daily loading doses for the initial 2 weeks. The trial evaluated two dose levels of VT-1161 (300 mg and 600 mg) administered once weekly for either 10 or 22 weeks following an initial 2-week, once-daily loading dose period.
At baseline, the average involvement of the large toenail was 46%, with an average of 4.6 toenails affected. In the intent-to-treat analysis, at 48 weeks, complete cure rates in the four study drug arms ranged from 32% to 42%, compared with 0% in the placebo arm.
Amir Tavakkol, PhD, chief development officer at Viamet Pharmaceuticals, which is developing VT01161, presented the study findings during a late breaking clinical session at the meeting.
Adverse event rates and discontinuation rates were comparable to placebo through week 60, with no patients discontinuing due to any laboratory abnormalities. Nausea and muscle spasms were the most commonly reported adverse events, which Dr. Tavakkol said seemed to occur in patients given the higher doses. VT-1161 is also being studied for treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. In October 2016, the FDA granted the drug Qualified Infectious Disease Product and Fast Track designations for the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, according to the company.
Viamet sponsored the study and Dr. Tavakkol is an employee of the company.
ORLANDO – A novel orally administered antifungal showed a favorable safety and efficacy profile in the treatment of distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, in a phase IIB study presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In the RENOVATE (Restoring Nail: An Oral VT-1161 Tablet Evaluation) study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial, 259 adults with moderate to severe distal lateral subungual onychomycosis of the large toenail were assigned to either one of four treatment arms. They were given the antifungal, currently named VT-1161, a selective CYP51 inhibitor, at doses of 300 mg or 600 mg once weekly for 10 or 22 weeks, after receiving daily loading doses for the initial 2 weeks. The trial evaluated two dose levels of VT-1161 (300 mg and 600 mg) administered once weekly for either 10 or 22 weeks following an initial 2-week, once-daily loading dose period.
At baseline, the average involvement of the large toenail was 46%, with an average of 4.6 toenails affected. In the intent-to-treat analysis, at 48 weeks, complete cure rates in the four study drug arms ranged from 32% to 42%, compared with 0% in the placebo arm.
Amir Tavakkol, PhD, chief development officer at Viamet Pharmaceuticals, which is developing VT01161, presented the study findings during a late breaking clinical session at the meeting.
Adverse event rates and discontinuation rates were comparable to placebo through week 60, with no patients discontinuing due to any laboratory abnormalities. Nausea and muscle spasms were the most commonly reported adverse events, which Dr. Tavakkol said seemed to occur in patients given the higher doses. VT-1161 is also being studied for treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. In October 2016, the FDA granted the drug Qualified Infectious Disease Product and Fast Track designations for the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, according to the company.
Viamet sponsored the study and Dr. Tavakkol is an employee of the company.
ORLANDO – A novel orally administered antifungal showed a favorable safety and efficacy profile in the treatment of distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, in a phase IIB study presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In the RENOVATE (Restoring Nail: An Oral VT-1161 Tablet Evaluation) study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial, 259 adults with moderate to severe distal lateral subungual onychomycosis of the large toenail were assigned to either one of four treatment arms. They were given the antifungal, currently named VT-1161, a selective CYP51 inhibitor, at doses of 300 mg or 600 mg once weekly for 10 or 22 weeks, after receiving daily loading doses for the initial 2 weeks. The trial evaluated two dose levels of VT-1161 (300 mg and 600 mg) administered once weekly for either 10 or 22 weeks following an initial 2-week, once-daily loading dose period.
At baseline, the average involvement of the large toenail was 46%, with an average of 4.6 toenails affected. In the intent-to-treat analysis, at 48 weeks, complete cure rates in the four study drug arms ranged from 32% to 42%, compared with 0% in the placebo arm.
Amir Tavakkol, PhD, chief development officer at Viamet Pharmaceuticals, which is developing VT01161, presented the study findings during a late breaking clinical session at the meeting.
Adverse event rates and discontinuation rates were comparable to placebo through week 60, with no patients discontinuing due to any laboratory abnormalities. Nausea and muscle spasms were the most commonly reported adverse events, which Dr. Tavakkol said seemed to occur in patients given the higher doses. VT-1161 is also being studied for treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. In October 2016, the FDA granted the drug Qualified Infectious Disease Product and Fast Track designations for the treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, according to the company.
Viamet sponsored the study and Dr. Tavakkol is an employee of the company.
AT AAD 17
Key clinical point:
Major finding: A new selective CYP51 inhibitor, administered orally, met the primary endpoint of complete cure rates at 48 weeks.
Data source: A phase IIB, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of 259 adults with moderate-to-severe distal lateral subungual onychomycosis of the large toenail.
Disclosures: Dr. Tavakkol is the chief development officer of Viamet Pharmaceuticals, the sponsor of this trial.
C. auris forms biofilms, enhancing its virulence, resistance
The emerging multidrug-resistant yeast organism Candida auris forms biofilms that enhance both its resistance and its virulence, according to in vitro analyses.
C. auris first attracted attention in 2009 because of its resistance to azoles and amphotericin B. Since then, it has been identified as the cause of life-threatening invasive infections worldwide, including hospital outbreaks across Asia and South America, wrote Leighann Sherry, PhD, a medical mycologist at the University of Glasgow, and her associates.
To determine whether the pathogen has the capacity to form biofilms, the investigators propagated several different strains in the laboratory and examined their development. In three separate trials, eight samples of each strain grew biofilms, which constitute “a key driver of candida pathogenicity.” In antifungal susceptibility tests, caspofungin was completely ineffective, an unexpected finding because the agent usually is highly effective against other candida species. Amphotericin B, liposomal amphotericin B, and fluconazole also were ineffective; micafungin and chlorhexidine were the most effective at clearing C. auris.
Biofilm formation “contributes not only to C. auris virulence but also to its [resistance] in hospital environments, increasing its ability to cause outbreaks,” Dr. Sherry and her associates said (Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017 Feb;23[2]:328-31).
“Our findings suggest it is improbable that the spread and prevalence of C. auris can be controlled with antifungal stewardship approaches alone,” they noted, adding that “infection-prevention measures targeting C. auris biofilms in patients, on medical devices, and in the hospital environment will be required,” they noted.
The emerging multidrug-resistant yeast organism Candida auris forms biofilms that enhance both its resistance and its virulence, according to in vitro analyses.
C. auris first attracted attention in 2009 because of its resistance to azoles and amphotericin B. Since then, it has been identified as the cause of life-threatening invasive infections worldwide, including hospital outbreaks across Asia and South America, wrote Leighann Sherry, PhD, a medical mycologist at the University of Glasgow, and her associates.
To determine whether the pathogen has the capacity to form biofilms, the investigators propagated several different strains in the laboratory and examined their development. In three separate trials, eight samples of each strain grew biofilms, which constitute “a key driver of candida pathogenicity.” In antifungal susceptibility tests, caspofungin was completely ineffective, an unexpected finding because the agent usually is highly effective against other candida species. Amphotericin B, liposomal amphotericin B, and fluconazole also were ineffective; micafungin and chlorhexidine were the most effective at clearing C. auris.
Biofilm formation “contributes not only to C. auris virulence but also to its [resistance] in hospital environments, increasing its ability to cause outbreaks,” Dr. Sherry and her associates said (Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017 Feb;23[2]:328-31).
“Our findings suggest it is improbable that the spread and prevalence of C. auris can be controlled with antifungal stewardship approaches alone,” they noted, adding that “infection-prevention measures targeting C. auris biofilms in patients, on medical devices, and in the hospital environment will be required,” they noted.
The emerging multidrug-resistant yeast organism Candida auris forms biofilms that enhance both its resistance and its virulence, according to in vitro analyses.
C. auris first attracted attention in 2009 because of its resistance to azoles and amphotericin B. Since then, it has been identified as the cause of life-threatening invasive infections worldwide, including hospital outbreaks across Asia and South America, wrote Leighann Sherry, PhD, a medical mycologist at the University of Glasgow, and her associates.
To determine whether the pathogen has the capacity to form biofilms, the investigators propagated several different strains in the laboratory and examined their development. In three separate trials, eight samples of each strain grew biofilms, which constitute “a key driver of candida pathogenicity.” In antifungal susceptibility tests, caspofungin was completely ineffective, an unexpected finding because the agent usually is highly effective against other candida species. Amphotericin B, liposomal amphotericin B, and fluconazole also were ineffective; micafungin and chlorhexidine were the most effective at clearing C. auris.
Biofilm formation “contributes not only to C. auris virulence but also to its [resistance] in hospital environments, increasing its ability to cause outbreaks,” Dr. Sherry and her associates said (Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017 Feb;23[2]:328-31).
“Our findings suggest it is improbable that the spread and prevalence of C. auris can be controlled with antifungal stewardship approaches alone,” they noted, adding that “infection-prevention measures targeting C. auris biofilms in patients, on medical devices, and in the hospital environment will be required,” they noted.
FROM EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Key clinical point: The emerging multidrug-resistant yeast organism Candida auris forms biofilms that enhance both its resistance and its virulence.
Major finding: In three separate trials, eight samples of each strain of C. auris grew biofilms that constitute “a key driver of Candida pathogenicity.”
Data source: In-vitro analyses of C. auris growth.
Disclosures: No funding source(s) or financial disclosures were provided.
VIDEO: Don’t miss reservoirs when treating recurrent onychomycosis
WAILEA, HAWAII – Patients attribute every nail problem to nail fungus, but part of the problem with nails is concomitant tinea pedis, tinea corporis, and other reservoirs of infection, according to Neal Bhatia, MD, director of clinical dermatology at Therapeutics Clinical Research in San Diego.
Failure to locate and treat these other reservoirs can lead to recurrence of the nail infection, Dr. Bhatia said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“If we aren’t treating the skin as well as the nails, it is creating a reservoir effect that reaccumulates in the nail itself,” he said. Similarly, the nails can serve as a reservoir of infection for the skin.
“That makes it all the more important” to treat both skin and nails and “treat through the disease state,” he commented in a video interview. Cost can influence treatment decisions, and there is a role for both topical and systemic therapy, he said. However, “if there’s not adequate testing or if there’s not a good proof of the diagnosis, we are just losing out no matter what we use,” he cautioned.
Dr. Bhatia disclosed relationships with companies including Actavis, Aqua, Allergan, Anacor, Bayer, Biofrontera, Biopharmx, Dermira, Dusa, Exceltis, Ferndale, Foamix, Galderma, Intraderm, ISDIN, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Novartis, Sanofi, and Valeant.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
WAILEA, HAWAII – Patients attribute every nail problem to nail fungus, but part of the problem with nails is concomitant tinea pedis, tinea corporis, and other reservoirs of infection, according to Neal Bhatia, MD, director of clinical dermatology at Therapeutics Clinical Research in San Diego.
Failure to locate and treat these other reservoirs can lead to recurrence of the nail infection, Dr. Bhatia said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“If we aren’t treating the skin as well as the nails, it is creating a reservoir effect that reaccumulates in the nail itself,” he said. Similarly, the nails can serve as a reservoir of infection for the skin.
“That makes it all the more important” to treat both skin and nails and “treat through the disease state,” he commented in a video interview. Cost can influence treatment decisions, and there is a role for both topical and systemic therapy, he said. However, “if there’s not adequate testing or if there’s not a good proof of the diagnosis, we are just losing out no matter what we use,” he cautioned.
Dr. Bhatia disclosed relationships with companies including Actavis, Aqua, Allergan, Anacor, Bayer, Biofrontera, Biopharmx, Dermira, Dusa, Exceltis, Ferndale, Foamix, Galderma, Intraderm, ISDIN, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Novartis, Sanofi, and Valeant.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
WAILEA, HAWAII – Patients attribute every nail problem to nail fungus, but part of the problem with nails is concomitant tinea pedis, tinea corporis, and other reservoirs of infection, according to Neal Bhatia, MD, director of clinical dermatology at Therapeutics Clinical Research in San Diego.
Failure to locate and treat these other reservoirs can lead to recurrence of the nail infection, Dr. Bhatia said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
“If we aren’t treating the skin as well as the nails, it is creating a reservoir effect that reaccumulates in the nail itself,” he said. Similarly, the nails can serve as a reservoir of infection for the skin.
“That makes it all the more important” to treat both skin and nails and “treat through the disease state,” he commented in a video interview. Cost can influence treatment decisions, and there is a role for both topical and systemic therapy, he said. However, “if there’s not adequate testing or if there’s not a good proof of the diagnosis, we are just losing out no matter what we use,” he cautioned.
Dr. Bhatia disclosed relationships with companies including Actavis, Aqua, Allergan, Anacor, Bayer, Biofrontera, Biopharmx, Dermira, Dusa, Exceltis, Ferndale, Foamix, Galderma, Intraderm, ISDIN, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Novartis, Sanofi, and Valeant.
SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
AT SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Survey shines new light on weighty comorbidity burden in adult atopic dermatitis
VIENNA – Newly enhanced appreciation of the profound burden of comorbidities associated with adult atopic dermatitis (AD) is provided by the Liberty AD-AWARE study, investigators said at a joint program of the International Eczema Council and the International Psoriasis Council held in conjunction with the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“I think the only reason we thought psoriasis is a systemic disease and atopic dermatitis is not is because people were researching it much more in psoriasis. I think atopic dermatitis will emerge as potentially more systemic than psoriasis, including the comorbidities. It’s just a matter of time before the evidence is put forth for atopic dermatitis,” predicted Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and vice chair of the department of dermatology at Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky noted that 85% of cases of AD begin before 5 years of age. Many cases resolve later in childhood, but for others it becomes a chronic lifelong condition. And while the burden of AD has been well characterized in the pediatric population, that’s not so in affected adults. This was the impetus for the Liberty AD-AWARE (Adults With Atopic Dermatitis Reporting on their Experience) study, an Internet-based cross-sectional survey of more than 1,500 adults with AD receiving their care from dermatologists at eight major U.S. academic medical centers.
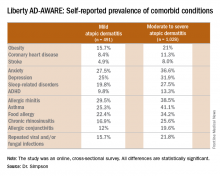
Eric L. Simpson, MD, a coinvestigator with Dr. Guttman-Yassky in Liberty AD-AWARE, observed that the study documented self-reported high rates of a range of psychiatric, cardiovascular, allergic, respiratory, and infectious diseases in participants. And while a cross-sectional study can’t establish causality, it’s important to appreciate that rates of these comorbidities were across the board significantly higher in the 1,028 patients with moderate to severe AD over the prior 12 months than in the 491 classified as having mild AD.
These associations between AD and mental health problems have been confirmed in other studies. For example, a recent analysis of data on more than 354,000 children and nearly 35,000 adults in the United States demonstrated that AD was independently associated with a 14% increased likelihood of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and a 61% increased risk in adults. Those risks of ADHD rose far higher in individuals with severe AD and sleep disruption (Br J Dermatol. 2016 Nov;175[5]:920-9).
A number of theories have been put forth to explain these associations, including altered brain development stemming from early exposure to inflammatory cytokines or perhaps shared genetic predisposition, but Dr. Simpson proposed a simpler explanation which carries more optimistic implications.
“I suspect the mental health problems associated with adult atopic dermatitis are probably nonspecific sequelae of any chronic skin disorder involving severe itch and sleep disturbances,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Moreover, there is good reason to believe that novel therapies targeting inflammation more effectively than what’s been available to date may help improve mental health outcomes, as well as asthma in affected adults with AD, he added. He cited a phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study for which he was lead investigator. In this trial, 16 weeks of treatment with dupilumab, a first-in-class investigational blocker of the interleukin-4/interleukin-13 signaling pathway, not only resulted in significant reductions in itch and sleep problems, it also decreased anxiety and depression symptoms and improved multiple validated measures of health-related quality of life (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75[3]:506-15).
Liberty AD-AWARE provides hints of the profound cumulative negative impact moderate to severe AD can have on a patient’s life course. Among the group with moderate to severe disease, 7.5% said AD had a large negative effect on their pursuit of an education, 10.7% said their disease had influenced their career choice “a lot/very much,” 13.3% were unemployed for reasons other than being retired or a student, and 17.1% reported an annual family income of less than $25,000. All these rates were multifold higher than in patients with mild AD in the study, which didn’t include a non-AD control group.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky observed that 42% of the moderate to severe AD group in Liberty AD-AWARE reported their current treatments were ineffective at controlling their disease, even though study participants were presumably receiving high-quality care at academic medical centers. Twenty-eight percent of patients with inadequately controlled AD had used phototherapy or an immunomodulatory drug within the past 7 days, underscoring the limitations of those forms of therapy in patients with more severe AD as well as the need for new and better treatments.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky has played a key role in the paradigm shift regarding understanding of the pathogenesis of AD as involving not just disordered skin barrier function but also immunologic impairment. She was senior author of a study that showed the nonlesional skin of patients with AD is characterized by high-level expression of inflammatory cytokines, whereas the nonlesional skin of psoriasis patients is not, an observation that serves to highlight the need for proactive treatments for AD (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Apr;127[4]:954-64.e1-4). Later, she and her coworkers demonstrated that AD is characterized by greater levels of T-cell activation among central and effector CD4+ and CD8+CLA+ and CD8+CLA– memory cell subsets (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Jul;136[1]:208-11).
More recently, she was also senior author of a landmark study that provides a mechanism to account for the reason AD patients would potentially have more comorbid illnesses than psoriasis patients. The investigators demonstrated that AD is accompanied by systemic expansion of transitional and chronically activated memory B cells, plasmablasts, and IgE-expressing memory B cells in both skin and blood. In other words, AD is characterized by a greater level of systemic immune activation, compared with psoriasis, where activated T cells are largely confined to the skin, and activated central memory B cells don’t figure prominently (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jan;137[1]:118-29.e5).
The Liberty AD-AWARE study was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron. Dr. Simpson and Dr. Guttman-Yassky reported receiving research grants from and serving as consultants to those and other pharmaceutical companies.
VIENNA – Newly enhanced appreciation of the profound burden of comorbidities associated with adult atopic dermatitis (AD) is provided by the Liberty AD-AWARE study, investigators said at a joint program of the International Eczema Council and the International Psoriasis Council held in conjunction with the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“I think the only reason we thought psoriasis is a systemic disease and atopic dermatitis is not is because people were researching it much more in psoriasis. I think atopic dermatitis will emerge as potentially more systemic than psoriasis, including the comorbidities. It’s just a matter of time before the evidence is put forth for atopic dermatitis,” predicted Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and vice chair of the department of dermatology at Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky noted that 85% of cases of AD begin before 5 years of age. Many cases resolve later in childhood, but for others it becomes a chronic lifelong condition. And while the burden of AD has been well characterized in the pediatric population, that’s not so in affected adults. This was the impetus for the Liberty AD-AWARE (Adults With Atopic Dermatitis Reporting on their Experience) study, an Internet-based cross-sectional survey of more than 1,500 adults with AD receiving their care from dermatologists at eight major U.S. academic medical centers.
Eric L. Simpson, MD, a coinvestigator with Dr. Guttman-Yassky in Liberty AD-AWARE, observed that the study documented self-reported high rates of a range of psychiatric, cardiovascular, allergic, respiratory, and infectious diseases in participants. And while a cross-sectional study can’t establish causality, it’s important to appreciate that rates of these comorbidities were across the board significantly higher in the 1,028 patients with moderate to severe AD over the prior 12 months than in the 491 classified as having mild AD.
These associations between AD and mental health problems have been confirmed in other studies. For example, a recent analysis of data on more than 354,000 children and nearly 35,000 adults in the United States demonstrated that AD was independently associated with a 14% increased likelihood of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and a 61% increased risk in adults. Those risks of ADHD rose far higher in individuals with severe AD and sleep disruption (Br J Dermatol. 2016 Nov;175[5]:920-9).
A number of theories have been put forth to explain these associations, including altered brain development stemming from early exposure to inflammatory cytokines or perhaps shared genetic predisposition, but Dr. Simpson proposed a simpler explanation which carries more optimistic implications.
“I suspect the mental health problems associated with adult atopic dermatitis are probably nonspecific sequelae of any chronic skin disorder involving severe itch and sleep disturbances,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Moreover, there is good reason to believe that novel therapies targeting inflammation more effectively than what’s been available to date may help improve mental health outcomes, as well as asthma in affected adults with AD, he added. He cited a phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study for which he was lead investigator. In this trial, 16 weeks of treatment with dupilumab, a first-in-class investigational blocker of the interleukin-4/interleukin-13 signaling pathway, not only resulted in significant reductions in itch and sleep problems, it also decreased anxiety and depression symptoms and improved multiple validated measures of health-related quality of life (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75[3]:506-15).
Liberty AD-AWARE provides hints of the profound cumulative negative impact moderate to severe AD can have on a patient’s life course. Among the group with moderate to severe disease, 7.5% said AD had a large negative effect on their pursuit of an education, 10.7% said their disease had influenced their career choice “a lot/very much,” 13.3% were unemployed for reasons other than being retired or a student, and 17.1% reported an annual family income of less than $25,000. All these rates were multifold higher than in patients with mild AD in the study, which didn’t include a non-AD control group.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky observed that 42% of the moderate to severe AD group in Liberty AD-AWARE reported their current treatments were ineffective at controlling their disease, even though study participants were presumably receiving high-quality care at academic medical centers. Twenty-eight percent of patients with inadequately controlled AD had used phototherapy or an immunomodulatory drug within the past 7 days, underscoring the limitations of those forms of therapy in patients with more severe AD as well as the need for new and better treatments.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky has played a key role in the paradigm shift regarding understanding of the pathogenesis of AD as involving not just disordered skin barrier function but also immunologic impairment. She was senior author of a study that showed the nonlesional skin of patients with AD is characterized by high-level expression of inflammatory cytokines, whereas the nonlesional skin of psoriasis patients is not, an observation that serves to highlight the need for proactive treatments for AD (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Apr;127[4]:954-64.e1-4). Later, she and her coworkers demonstrated that AD is characterized by greater levels of T-cell activation among central and effector CD4+ and CD8+CLA+ and CD8+CLA– memory cell subsets (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Jul;136[1]:208-11).
More recently, she was also senior author of a landmark study that provides a mechanism to account for the reason AD patients would potentially have more comorbid illnesses than psoriasis patients. The investigators demonstrated that AD is accompanied by systemic expansion of transitional and chronically activated memory B cells, plasmablasts, and IgE-expressing memory B cells in both skin and blood. In other words, AD is characterized by a greater level of systemic immune activation, compared with psoriasis, where activated T cells are largely confined to the skin, and activated central memory B cells don’t figure prominently (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jan;137[1]:118-29.e5).
The Liberty AD-AWARE study was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron. Dr. Simpson and Dr. Guttman-Yassky reported receiving research grants from and serving as consultants to those and other pharmaceutical companies.
VIENNA – Newly enhanced appreciation of the profound burden of comorbidities associated with adult atopic dermatitis (AD) is provided by the Liberty AD-AWARE study, investigators said at a joint program of the International Eczema Council and the International Psoriasis Council held in conjunction with the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“I think the only reason we thought psoriasis is a systemic disease and atopic dermatitis is not is because people were researching it much more in psoriasis. I think atopic dermatitis will emerge as potentially more systemic than psoriasis, including the comorbidities. It’s just a matter of time before the evidence is put forth for atopic dermatitis,” predicted Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, professor and vice chair of the department of dermatology at Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky noted that 85% of cases of AD begin before 5 years of age. Many cases resolve later in childhood, but for others it becomes a chronic lifelong condition. And while the burden of AD has been well characterized in the pediatric population, that’s not so in affected adults. This was the impetus for the Liberty AD-AWARE (Adults With Atopic Dermatitis Reporting on their Experience) study, an Internet-based cross-sectional survey of more than 1,500 adults with AD receiving their care from dermatologists at eight major U.S. academic medical centers.
Eric L. Simpson, MD, a coinvestigator with Dr. Guttman-Yassky in Liberty AD-AWARE, observed that the study documented self-reported high rates of a range of psychiatric, cardiovascular, allergic, respiratory, and infectious diseases in participants. And while a cross-sectional study can’t establish causality, it’s important to appreciate that rates of these comorbidities were across the board significantly higher in the 1,028 patients with moderate to severe AD over the prior 12 months than in the 491 classified as having mild AD.
These associations between AD and mental health problems have been confirmed in other studies. For example, a recent analysis of data on more than 354,000 children and nearly 35,000 adults in the United States demonstrated that AD was independently associated with a 14% increased likelihood of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and a 61% increased risk in adults. Those risks of ADHD rose far higher in individuals with severe AD and sleep disruption (Br J Dermatol. 2016 Nov;175[5]:920-9).
A number of theories have been put forth to explain these associations, including altered brain development stemming from early exposure to inflammatory cytokines or perhaps shared genetic predisposition, but Dr. Simpson proposed a simpler explanation which carries more optimistic implications.
“I suspect the mental health problems associated with adult atopic dermatitis are probably nonspecific sequelae of any chronic skin disorder involving severe itch and sleep disturbances,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Moreover, there is good reason to believe that novel therapies targeting inflammation more effectively than what’s been available to date may help improve mental health outcomes, as well as asthma in affected adults with AD, he added. He cited a phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study for which he was lead investigator. In this trial, 16 weeks of treatment with dupilumab, a first-in-class investigational blocker of the interleukin-4/interleukin-13 signaling pathway, not only resulted in significant reductions in itch and sleep problems, it also decreased anxiety and depression symptoms and improved multiple validated measures of health-related quality of life (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75[3]:506-15).
Liberty AD-AWARE provides hints of the profound cumulative negative impact moderate to severe AD can have on a patient’s life course. Among the group with moderate to severe disease, 7.5% said AD had a large negative effect on their pursuit of an education, 10.7% said their disease had influenced their career choice “a lot/very much,” 13.3% were unemployed for reasons other than being retired or a student, and 17.1% reported an annual family income of less than $25,000. All these rates were multifold higher than in patients with mild AD in the study, which didn’t include a non-AD control group.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky observed that 42% of the moderate to severe AD group in Liberty AD-AWARE reported their current treatments were ineffective at controlling their disease, even though study participants were presumably receiving high-quality care at academic medical centers. Twenty-eight percent of patients with inadequately controlled AD had used phototherapy or an immunomodulatory drug within the past 7 days, underscoring the limitations of those forms of therapy in patients with more severe AD as well as the need for new and better treatments.
Dr. Guttman-Yassky has played a key role in the paradigm shift regarding understanding of the pathogenesis of AD as involving not just disordered skin barrier function but also immunologic impairment. She was senior author of a study that showed the nonlesional skin of patients with AD is characterized by high-level expression of inflammatory cytokines, whereas the nonlesional skin of psoriasis patients is not, an observation that serves to highlight the need for proactive treatments for AD (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Apr;127[4]:954-64.e1-4). Later, she and her coworkers demonstrated that AD is characterized by greater levels of T-cell activation among central and effector CD4+ and CD8+CLA+ and CD8+CLA– memory cell subsets (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Jul;136[1]:208-11).
More recently, she was also senior author of a landmark study that provides a mechanism to account for the reason AD patients would potentially have more comorbid illnesses than psoriasis patients. The investigators demonstrated that AD is accompanied by systemic expansion of transitional and chronically activated memory B cells, plasmablasts, and IgE-expressing memory B cells in both skin and blood. In other words, AD is characterized by a greater level of systemic immune activation, compared with psoriasis, where activated T cells are largely confined to the skin, and activated central memory B cells don’t figure prominently (J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jan;137[1]:118-29.e5).
The Liberty AD-AWARE study was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron. Dr. Simpson and Dr. Guttman-Yassky reported receiving research grants from and serving as consultants to those and other pharmaceutical companies.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Novel oral antifungal headed to phase III for onychomycosis
VIENNA – A once-weekly oral antifungal drug known as VT-1161 will move into phase III clinical testing in 2017 based on its impressive performance in an interim analysis of a phase IIb study, Amir Tavakkol, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“We saw robust evidence of clinical and mycologic efficacy in patients with moderate to severe onychomycosis. This was true even in patients with nails considered very difficult to treat because of dermatophytomas and spikes, which are usually poor prognostic elements,” said Dr. Tavakkol, chief development officer at Viamet Pharmaceuticals in Durham, N.C., which is developing VT-1161.
He reported on 107 patients with toenail onychomycosis who enrolled in the phase IIb, double-blind, placebo-controlled RENOVATE (Restoring Nail: An Oral VT-1161 Tablet Evaluation) study. At enrollment they averaged 47% disease involvement of the big toenail, the target nail for the trial. Participants in the five study arms had an average of 4.2-5.0 affected toenails. Both the percentage of nail involvement and the number of diseased toenails were roughly twice as great as is typical in studies of topical antifungals, underscoring that participants in the VT-1161 trial had fairly severe onychomycosis.
Patients were assigned to one of five study arms: 300 mg of VT-1161 once weekly for 12 weeks, then 12 weeks of placebo; 600 mg of VT-1161 once weekly for 12 weeks, followed by 12 weeks of placebo; either 300 or 600 mg of the antifungal agent once weekly for the full 24 weeks; or 24 weeks of once-per-week placebo. Immediately prior to the formal start of the study, however, everyone received 14 days of a once-daily loading dose of VT-1161 or placebo at the dose they would subsequently take once weekly during the trial.
The primary outcome in the ongoing study is the percentage of patients with a complete cure, both mycologic and clinical, at 48 weeks. Those data aren’t in yet, but Dr. Tavakkol presented the results of the prespecified interim analysis at 24 weeks.
“Please keep in mind that this is only at most 24 weeks of therapy. Given the rate of nail growth at 1 mm per month when it is healthy, these are remarkable data. Ten percent or less nail involvement is basically 1-2 mm at the distal end. I believe a substantial percentage of these patients will reach clinical cure by 48 weeks,” he said.
VT-1161, a molecule with high selectivity for fungal CYP51, blocks the production of ergosterol, a key component of the fungal cell membrane, according to the company. It has no known drug interactions. At all doses studied in the trial, it was safe and well tolerated, with no abnormal liver function tests, no effect on bilirubin, and no change in QTc interval. Only 8 of the 107 patients reported adverse events deemed possibly related to the study drug by blinded investigators. No one dropped out of the study.
“VT-1161 is also being developed for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. The results there are outstanding, too,” Dr. Tavakkol said.
The trial was funded by Viamet, where he is employed.
VIENNA – A once-weekly oral antifungal drug known as VT-1161 will move into phase III clinical testing in 2017 based on its impressive performance in an interim analysis of a phase IIb study, Amir Tavakkol, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“We saw robust evidence of clinical and mycologic efficacy in patients with moderate to severe onychomycosis. This was true even in patients with nails considered very difficult to treat because of dermatophytomas and spikes, which are usually poor prognostic elements,” said Dr. Tavakkol, chief development officer at Viamet Pharmaceuticals in Durham, N.C., which is developing VT-1161.
He reported on 107 patients with toenail onychomycosis who enrolled in the phase IIb, double-blind, placebo-controlled RENOVATE (Restoring Nail: An Oral VT-1161 Tablet Evaluation) study. At enrollment they averaged 47% disease involvement of the big toenail, the target nail for the trial. Participants in the five study arms had an average of 4.2-5.0 affected toenails. Both the percentage of nail involvement and the number of diseased toenails were roughly twice as great as is typical in studies of topical antifungals, underscoring that participants in the VT-1161 trial had fairly severe onychomycosis.
Patients were assigned to one of five study arms: 300 mg of VT-1161 once weekly for 12 weeks, then 12 weeks of placebo; 600 mg of VT-1161 once weekly for 12 weeks, followed by 12 weeks of placebo; either 300 or 600 mg of the antifungal agent once weekly for the full 24 weeks; or 24 weeks of once-per-week placebo. Immediately prior to the formal start of the study, however, everyone received 14 days of a once-daily loading dose of VT-1161 or placebo at the dose they would subsequently take once weekly during the trial.
The primary outcome in the ongoing study is the percentage of patients with a complete cure, both mycologic and clinical, at 48 weeks. Those data aren’t in yet, but Dr. Tavakkol presented the results of the prespecified interim analysis at 24 weeks.
“Please keep in mind that this is only at most 24 weeks of therapy. Given the rate of nail growth at 1 mm per month when it is healthy, these are remarkable data. Ten percent or less nail involvement is basically 1-2 mm at the distal end. I believe a substantial percentage of these patients will reach clinical cure by 48 weeks,” he said.
VT-1161, a molecule with high selectivity for fungal CYP51, blocks the production of ergosterol, a key component of the fungal cell membrane, according to the company. It has no known drug interactions. At all doses studied in the trial, it was safe and well tolerated, with no abnormal liver function tests, no effect on bilirubin, and no change in QTc interval. Only 8 of the 107 patients reported adverse events deemed possibly related to the study drug by blinded investigators. No one dropped out of the study.
“VT-1161 is also being developed for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. The results there are outstanding, too,” Dr. Tavakkol said.
The trial was funded by Viamet, where he is employed.
VIENNA – A once-weekly oral antifungal drug known as VT-1161 will move into phase III clinical testing in 2017 based on its impressive performance in an interim analysis of a phase IIb study, Amir Tavakkol, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“We saw robust evidence of clinical and mycologic efficacy in patients with moderate to severe onychomycosis. This was true even in patients with nails considered very difficult to treat because of dermatophytomas and spikes, which are usually poor prognostic elements,” said Dr. Tavakkol, chief development officer at Viamet Pharmaceuticals in Durham, N.C., which is developing VT-1161.
He reported on 107 patients with toenail onychomycosis who enrolled in the phase IIb, double-blind, placebo-controlled RENOVATE (Restoring Nail: An Oral VT-1161 Tablet Evaluation) study. At enrollment they averaged 47% disease involvement of the big toenail, the target nail for the trial. Participants in the five study arms had an average of 4.2-5.0 affected toenails. Both the percentage of nail involvement and the number of diseased toenails were roughly twice as great as is typical in studies of topical antifungals, underscoring that participants in the VT-1161 trial had fairly severe onychomycosis.
Patients were assigned to one of five study arms: 300 mg of VT-1161 once weekly for 12 weeks, then 12 weeks of placebo; 600 mg of VT-1161 once weekly for 12 weeks, followed by 12 weeks of placebo; either 300 or 600 mg of the antifungal agent once weekly for the full 24 weeks; or 24 weeks of once-per-week placebo. Immediately prior to the formal start of the study, however, everyone received 14 days of a once-daily loading dose of VT-1161 or placebo at the dose they would subsequently take once weekly during the trial.
The primary outcome in the ongoing study is the percentage of patients with a complete cure, both mycologic and clinical, at 48 weeks. Those data aren’t in yet, but Dr. Tavakkol presented the results of the prespecified interim analysis at 24 weeks.
“Please keep in mind that this is only at most 24 weeks of therapy. Given the rate of nail growth at 1 mm per month when it is healthy, these are remarkable data. Ten percent or less nail involvement is basically 1-2 mm at the distal end. I believe a substantial percentage of these patients will reach clinical cure by 48 weeks,” he said.
VT-1161, a molecule with high selectivity for fungal CYP51, blocks the production of ergosterol, a key component of the fungal cell membrane, according to the company. It has no known drug interactions. At all doses studied in the trial, it was safe and well tolerated, with no abnormal liver function tests, no effect on bilirubin, and no change in QTc interval. Only 8 of the 107 patients reported adverse events deemed possibly related to the study drug by blinded investigators. No one dropped out of the study.
“VT-1161 is also being developed for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. The results there are outstanding, too,” Dr. Tavakkol said.
The trial was funded by Viamet, where he is employed.
AT THE EADV CONGRESS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Among onychomycosis patients with an average 47% target toenail involvement at baseline, 35% had improved to no more than 10% nail involvement at 24 weeks after 12 weeks of once-weekly VT-1161 followed by 12 weeks of placebo.
Data source: A double-blind, randomized, phase IIb clinical trial involving 107 patients with toenail onychomycosis.
Disclosures: The trial was funded by Viamet Pharmaceuticals, where the study presenter is employed.