User login
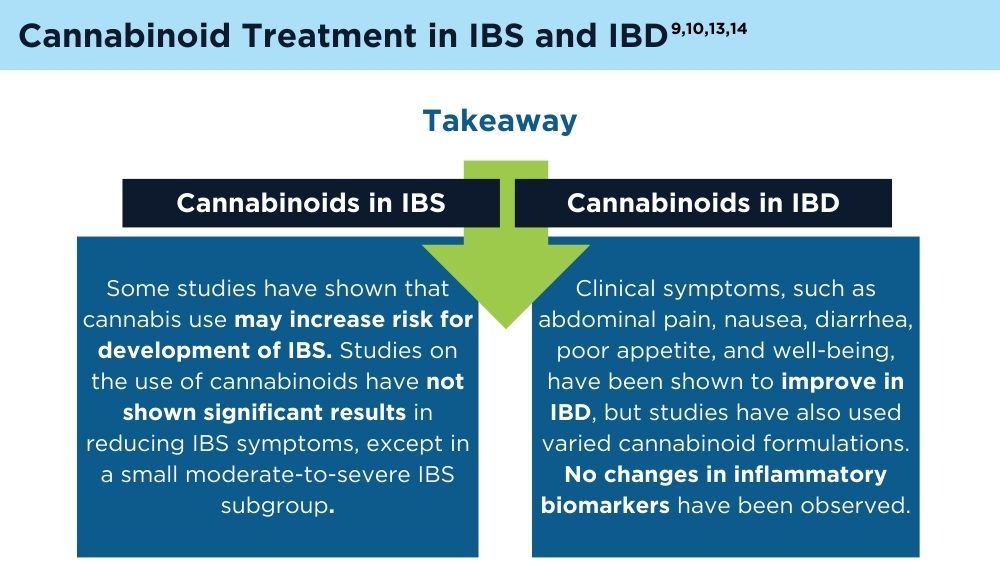
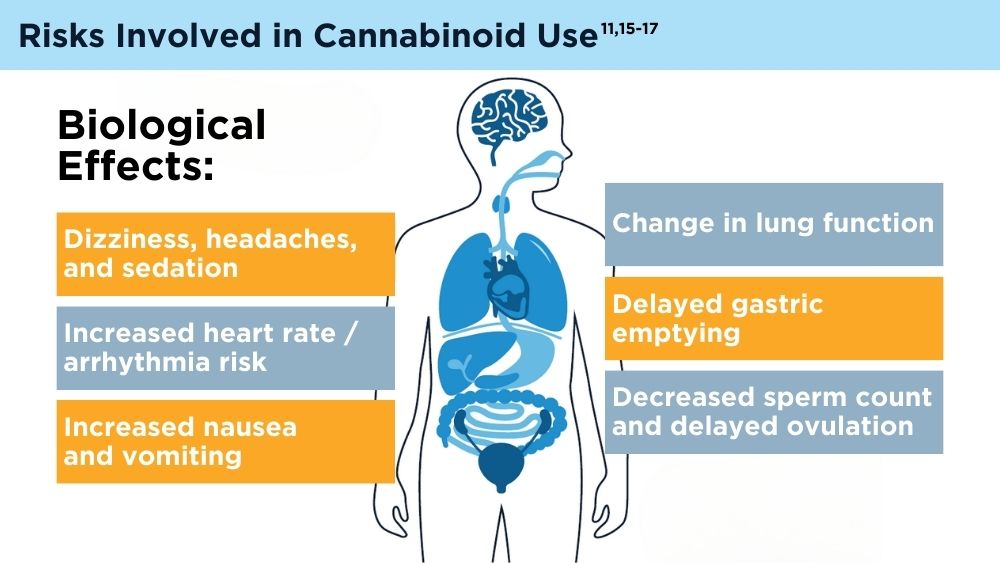
Cannabinoids and Digestive Disorders
- Leung J, Chan G, Stjepanović D, Chung JYC, Hall W, Hammond D. Prevalence and self-reported reasons of cannabis use for medical purposes in USA and Canada. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022;239(5):1509-1519. doi:10.1007/s00213-021-06047-8
- Ahmed W, Katz S. Therapeutic use of cannabis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016;12(11):668-679.
- Ravikoff Allegretti J, Courtwright A, Lucci M, Korzenik JR, Levine J. Marijuana use patterns among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19(13):2809-2814. doi:10.1097/01.MIB.0000435851.94391.37
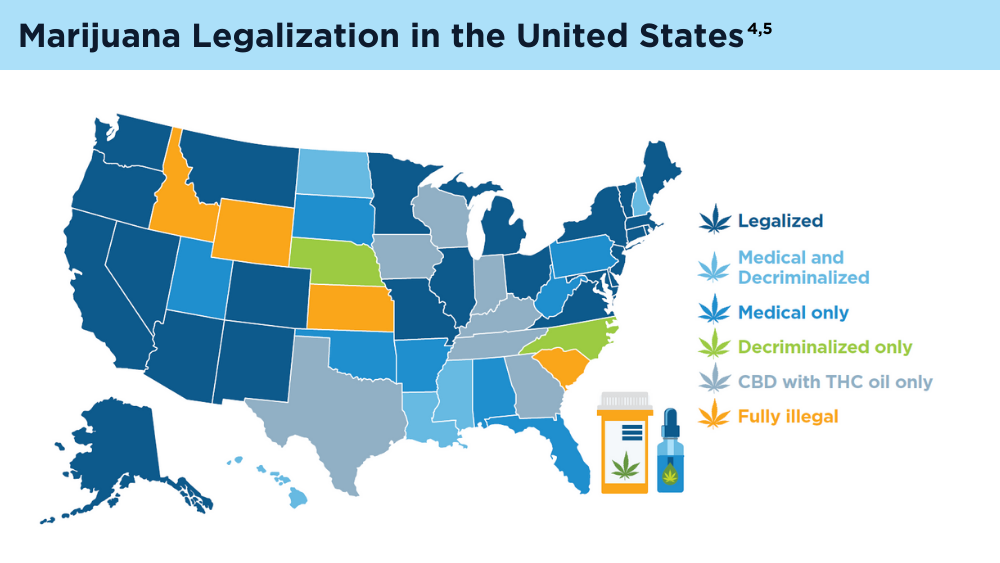
- Marijuana legality by state - updated February 1, 2024. DISA. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://disa.com/marijuana-legality-by-state
- The Cannigma Staff. Where is weed legal around the globe? The Cannigma. Updated July 3, 2022. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://cannigma.com/regulation/cannabis-regulation-around-the-world/
- Zou S, Kumar U. Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):833. doi:10.3390/ijms19030833
- Maselli DB, Camilleri M. Pharmacology, clinical effects, and therapeutic potential of cannabinoids for gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(9):1748-1758.e2. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.020
- Buckley MC, Kumar A, Swaminath A. Inflammatory bowel disease and cannabis: a practical approach for clinicians. Adv Ther. 2021;38(7):4152- 4161. doi:10.1007/s12325-021-01805-8
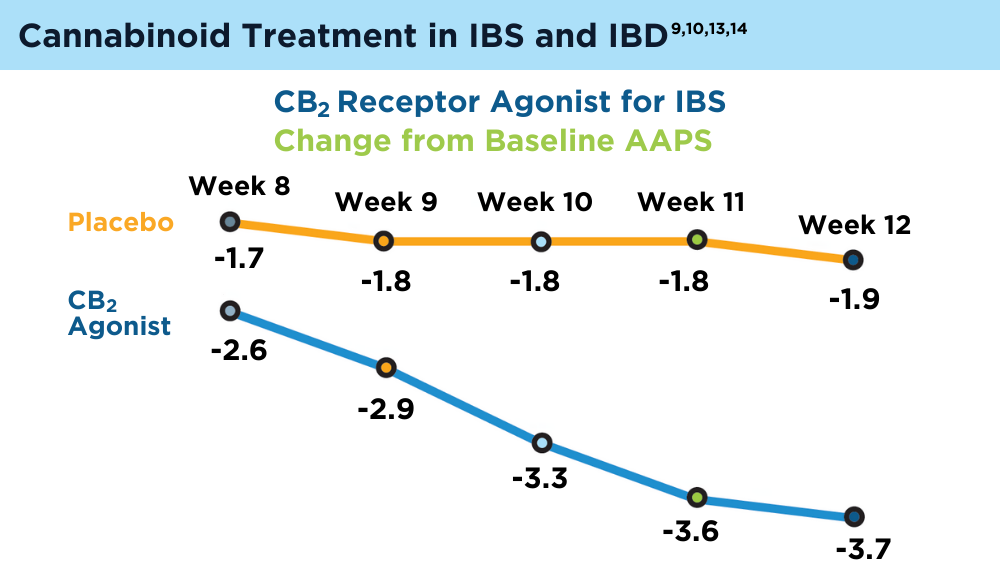
- Chang L, Cash BD, Lembo A, et al. Efficacy and safety of olorinab, a full agonist of the cannabinoid receptor 2, for the treatment of abdominal pain in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: results from a phase 2b randomized placebo-controlled trial (CAPTIVATE). Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023;35(5):e14539. doi:10.1111/nmo.14539
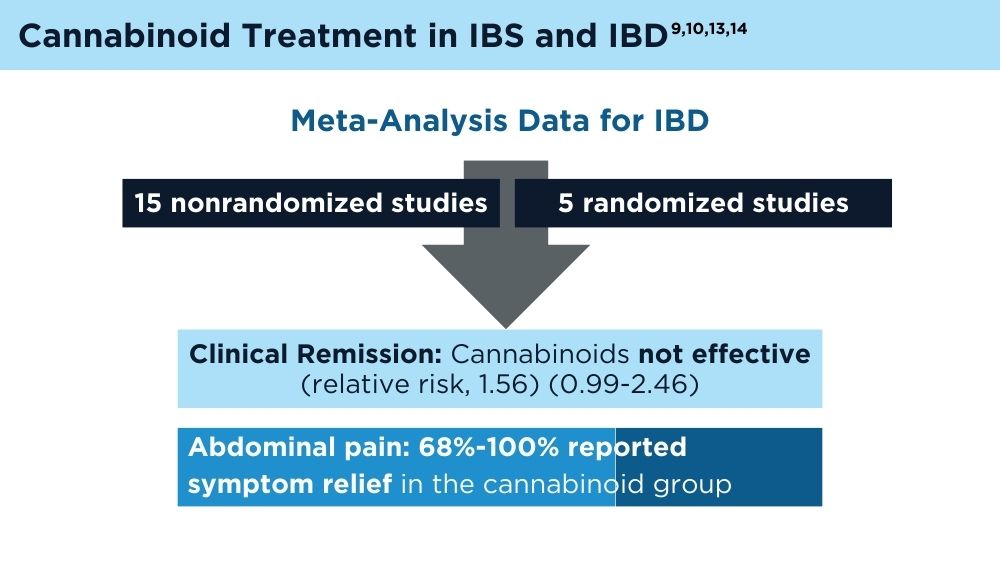
- Doeve BH, van de Meeberg MM, van Schaik FDM, Fidder HH. A systematic review with meta-analysis of the efficacy of cannabis and cannabinoids for inflammatory bowel disease: what can we learn from randomized and nonrandomized studies? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021;55(9):798-809. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000001393
- Gotfried J, Naftali T, Schey R. Role of cannabis and its derivatives in gastrointestinal and hepatic disease [published correction appears in Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5):1904]. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):62-80. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.087
- Goyal H, Singla U, Gupta U, May E. Role of cannabis in digestive disorders. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(2):135-143. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000779
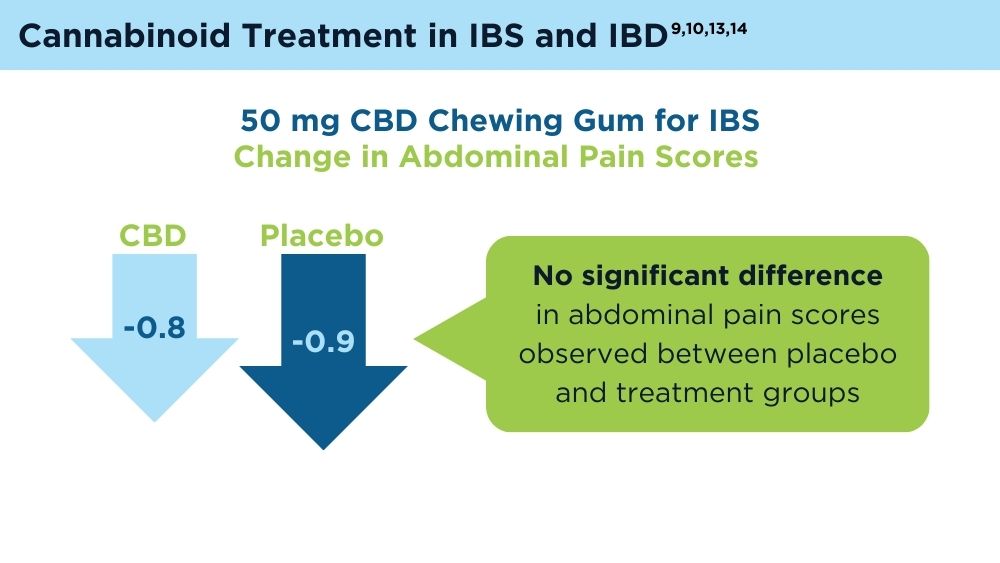
- van Orten-Luiten AB, de Roos NM, Majait S, Witteman BJM, Witkamp RF. Effects of cannabidiol chewing gum on perceived pain and well-being of irritable bowel syndrome patients: a placebo-controlled crossover exploratory intervention study with symptom-driven dosing. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2022;7(4):436-444. doi:10.1089/can.2020.0087
- Adejumo AC, Ajayi TO, Adegbala OM, Bukong TN. Higher odds of irritable bowel syndrome among hospitalized patients using cannabis: a propensity matched analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;31(7):756-765. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001382
- Antoniou T, Bodkin J, Ho JM. Drug interactions with cannabinoids. CMAJ. 2020;192(9):E206. doi:10.1503/cmaj.191097
- Karila L, Roux P, Rolland B, et al. Acute and long-term effects of cannabis use: a review. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(25):4112-4118. doi:10.2174/13816128113199990620
- Venkatesan T, Levinthal DJ, Li BUK, et al. Role of chronic cannabis use: cyclic vomiting syndrome vs cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019;31(suppl 2):e13606. doi:10.1111/nmo.13606
- Leung J, Chan G, Stjepanović D, Chung JYC, Hall W, Hammond D. Prevalence and self-reported reasons of cannabis use for medical purposes in USA and Canada. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022;239(5):1509-1519. doi:10.1007/s00213-021-06047-8
- Ahmed W, Katz S. Therapeutic use of cannabis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016;12(11):668-679.
- Ravikoff Allegretti J, Courtwright A, Lucci M, Korzenik JR, Levine J. Marijuana use patterns among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19(13):2809-2814. doi:10.1097/01.MIB.0000435851.94391.37
- Marijuana legality by state - updated February 1, 2024. DISA. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://disa.com/marijuana-legality-by-state
- The Cannigma Staff. Where is weed legal around the globe? The Cannigma. Updated July 3, 2022. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://cannigma.com/regulation/cannabis-regulation-around-the-world/
- Zou S, Kumar U. Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):833. doi:10.3390/ijms19030833
- Maselli DB, Camilleri M. Pharmacology, clinical effects, and therapeutic potential of cannabinoids for gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(9):1748-1758.e2. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.020
- Buckley MC, Kumar A, Swaminath A. Inflammatory bowel disease and cannabis: a practical approach for clinicians. Adv Ther. 2021;38(7):4152- 4161. doi:10.1007/s12325-021-01805-8
- Chang L, Cash BD, Lembo A, et al. Efficacy and safety of olorinab, a full agonist of the cannabinoid receptor 2, for the treatment of abdominal pain in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: results from a phase 2b randomized placebo-controlled trial (CAPTIVATE). Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023;35(5):e14539. doi:10.1111/nmo.14539
- Doeve BH, van de Meeberg MM, van Schaik FDM, Fidder HH. A systematic review with meta-analysis of the efficacy of cannabis and cannabinoids for inflammatory bowel disease: what can we learn from randomized and nonrandomized studies? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021;55(9):798-809. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000001393
- Gotfried J, Naftali T, Schey R. Role of cannabis and its derivatives in gastrointestinal and hepatic disease [published correction appears in Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5):1904]. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):62-80. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.087
- Goyal H, Singla U, Gupta U, May E. Role of cannabis in digestive disorders. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(2):135-143. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000779
- van Orten-Luiten AB, de Roos NM, Majait S, Witteman BJM, Witkamp RF. Effects of cannabidiol chewing gum on perceived pain and well-being of irritable bowel syndrome patients: a placebo-controlled crossover exploratory intervention study with symptom-driven dosing. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2022;7(4):436-444. doi:10.1089/can.2020.0087
- Adejumo AC, Ajayi TO, Adegbala OM, Bukong TN. Higher odds of irritable bowel syndrome among hospitalized patients using cannabis: a propensity matched analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;31(7):756-765. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001382
- Antoniou T, Bodkin J, Ho JM. Drug interactions with cannabinoids. CMAJ. 2020;192(9):E206. doi:10.1503/cmaj.191097
- Karila L, Roux P, Rolland B, et al. Acute and long-term effects of cannabis use: a review. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(25):4112-4118. doi:10.2174/13816128113199990620
- Venkatesan T, Levinthal DJ, Li BUK, et al. Role of chronic cannabis use: cyclic vomiting syndrome vs cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019;31(suppl 2):e13606. doi:10.1111/nmo.13606
- Leung J, Chan G, Stjepanović D, Chung JYC, Hall W, Hammond D. Prevalence and self-reported reasons of cannabis use for medical purposes in USA and Canada. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022;239(5):1509-1519. doi:10.1007/s00213-021-06047-8
- Ahmed W, Katz S. Therapeutic use of cannabis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016;12(11):668-679.
- Ravikoff Allegretti J, Courtwright A, Lucci M, Korzenik JR, Levine J. Marijuana use patterns among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19(13):2809-2814. doi:10.1097/01.MIB.0000435851.94391.37
- Marijuana legality by state - updated February 1, 2024. DISA. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://disa.com/marijuana-legality-by-state
- The Cannigma Staff. Where is weed legal around the globe? The Cannigma. Updated July 3, 2022. Accessed March 1, 2024. https://cannigma.com/regulation/cannabis-regulation-around-the-world/
- Zou S, Kumar U. Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):833. doi:10.3390/ijms19030833
- Maselli DB, Camilleri M. Pharmacology, clinical effects, and therapeutic potential of cannabinoids for gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(9):1748-1758.e2. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.020
- Buckley MC, Kumar A, Swaminath A. Inflammatory bowel disease and cannabis: a practical approach for clinicians. Adv Ther. 2021;38(7):4152- 4161. doi:10.1007/s12325-021-01805-8
- Chang L, Cash BD, Lembo A, et al. Efficacy and safety of olorinab, a full agonist of the cannabinoid receptor 2, for the treatment of abdominal pain in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: results from a phase 2b randomized placebo-controlled trial (CAPTIVATE). Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023;35(5):e14539. doi:10.1111/nmo.14539
- Doeve BH, van de Meeberg MM, van Schaik FDM, Fidder HH. A systematic review with meta-analysis of the efficacy of cannabis and cannabinoids for inflammatory bowel disease: what can we learn from randomized and nonrandomized studies? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021;55(9):798-809. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000001393
- Gotfried J, Naftali T, Schey R. Role of cannabis and its derivatives in gastrointestinal and hepatic disease [published correction appears in Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5):1904]. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):62-80. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.087
- Goyal H, Singla U, Gupta U, May E. Role of cannabis in digestive disorders. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(2):135-143. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000779
- van Orten-Luiten AB, de Roos NM, Majait S, Witteman BJM, Witkamp RF. Effects of cannabidiol chewing gum on perceived pain and well-being of irritable bowel syndrome patients: a placebo-controlled crossover exploratory intervention study with symptom-driven dosing. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2022;7(4):436-444. doi:10.1089/can.2020.0087
- Adejumo AC, Ajayi TO, Adegbala OM, Bukong TN. Higher odds of irritable bowel syndrome among hospitalized patients using cannabis: a propensity matched analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;31(7):756-765. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001382
- Antoniou T, Bodkin J, Ho JM. Drug interactions with cannabinoids. CMAJ. 2020;192(9):E206. doi:10.1503/cmaj.191097
- Karila L, Roux P, Rolland B, et al. Acute and long-term effects of cannabis use: a review. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(25):4112-4118. doi:10.2174/13816128113199990620
- Venkatesan T, Levinthal DJ, Li BUK, et al. Role of chronic cannabis use: cyclic vomiting syndrome vs cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019;31(suppl 2):e13606. doi:10.1111/nmo.13606
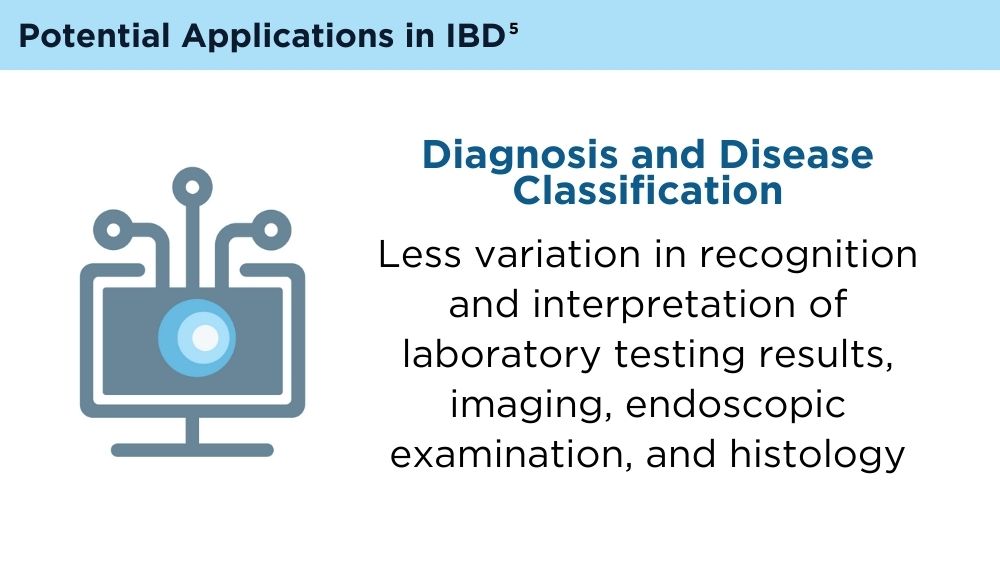
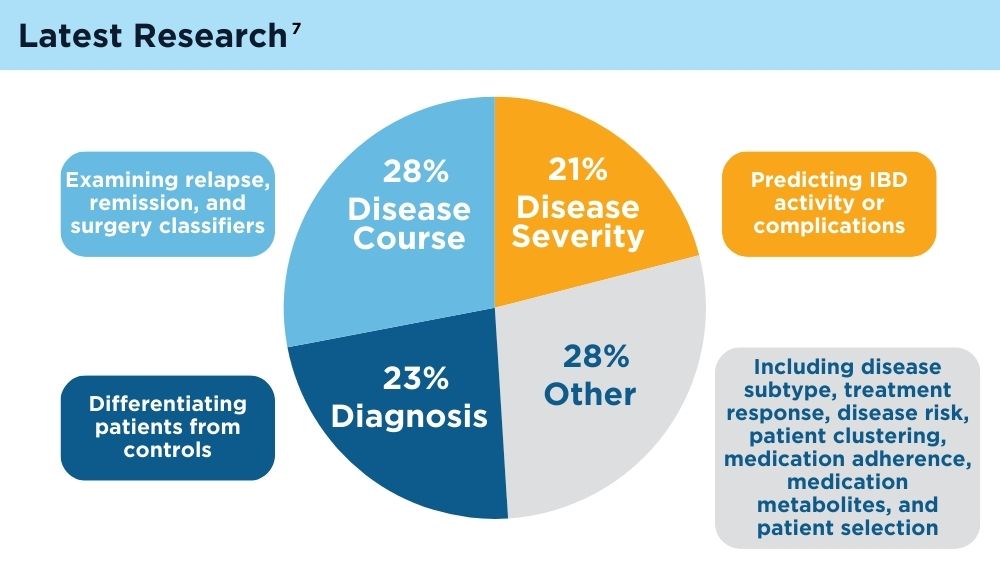
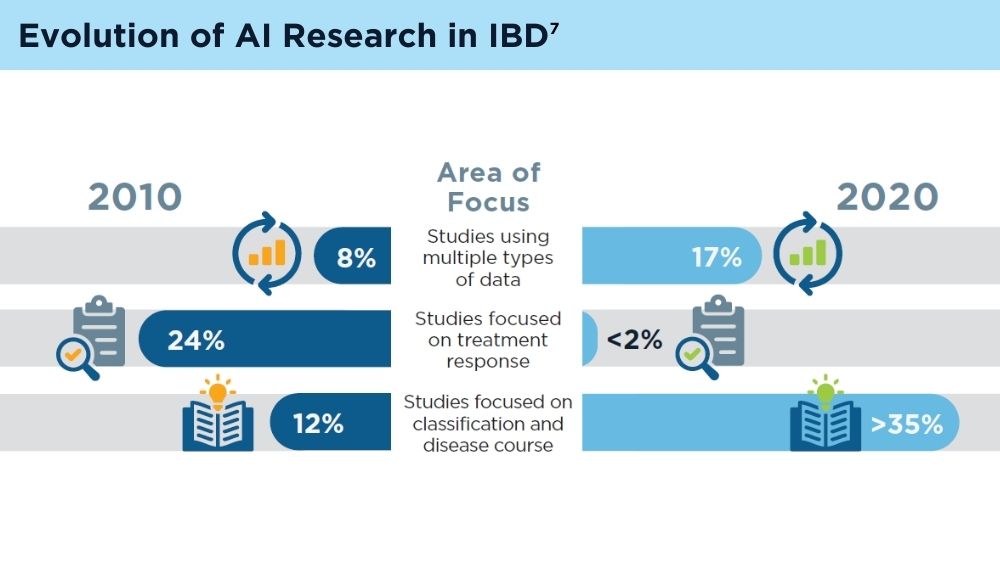
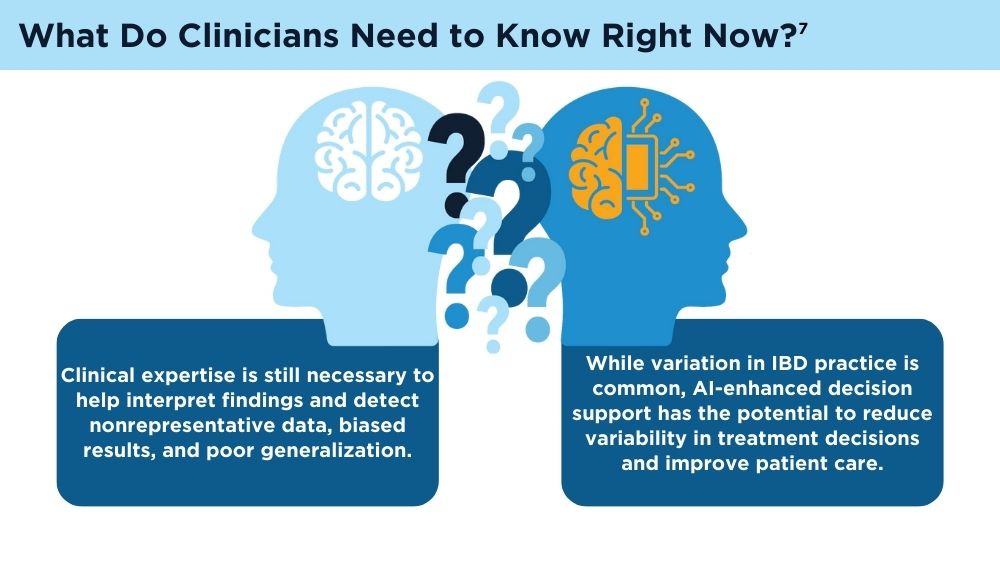
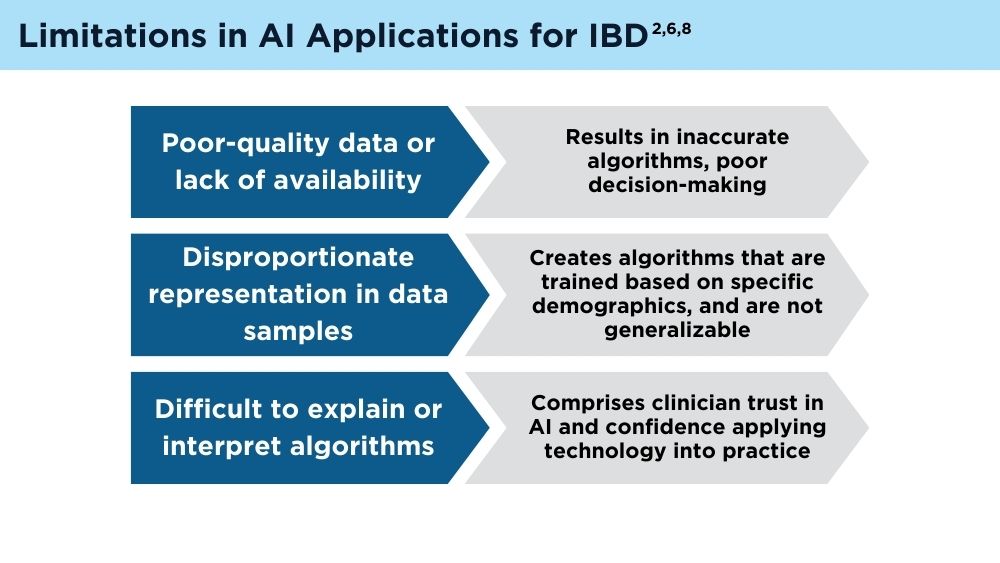
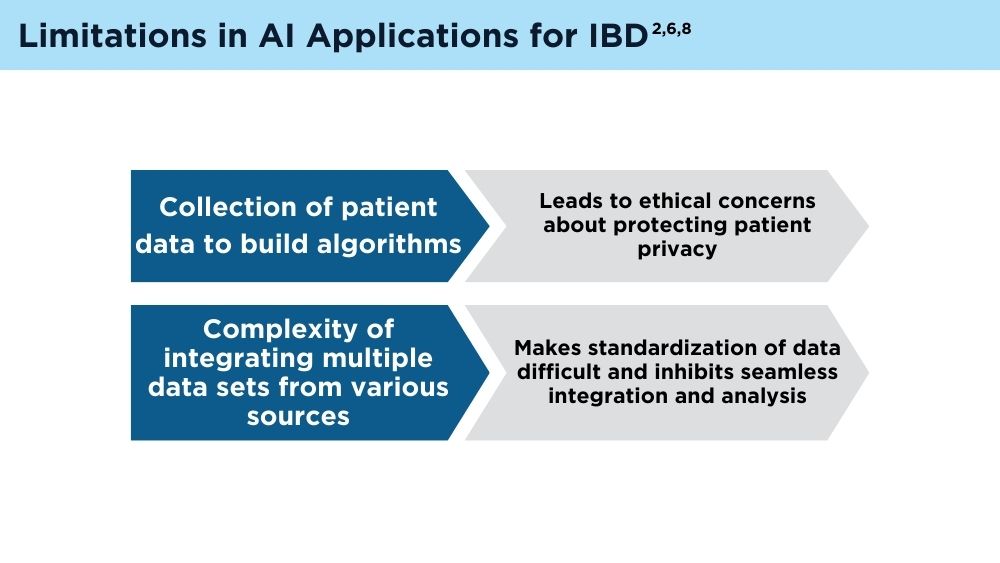
AI and Machine Learning in IBD: Promising Applications and Remaining Challenges
- Lewis JD, Parlett LE, Jonsson Funk ML, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and racial and ethnic distribution of inflammatory bowel disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2023;165(5):1197-1205.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.07.003
- Sharma P. AI shows promise in diagnosis, treatment of IBD, but limitations, concerns remain. Healio. Published June 19, 2023. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.healio.com/news/gastroenterology/20230606/ai-shows-promise-in-diagnosis-treatment-of-ibd-but-limitations-concerns-remain
- Artificial intelligence (AI) vs. machine learning. Columbia Engineering.Accessed January 5, 2024. https://ai.engineering.columbia.edu/ai-vs-machine-learning/
- Zhang B, Shi H, Wang H. Machine learning and AI in cancer prognosis, prediction, and treatment selection: a critical approach. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023;16:1779-1791. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S410301
- Cohen-Mekelburg S, Berry S, Stidham RW, Zhu J, Waljee AK. Clinical applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning-based methods in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(2):279-285. doi:10.1111/jgh.15405
- Uche-Anya E, Anyane-Yeboa A, Berzin TM, Ghassemi M, May FP. Artificial intelligence in gastroenterology and hepatology: how to advance clinical practice while ensuring health equity. Gut. 2022;71(9):1909-1915. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326271
- Stafford IS, Gosink MM, Mossotto E, Ennis S, Hauben M. A systematic review of artificial intelligence and machine learning applications to inflammatory bowel disease, with practical guidelines for interpretation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022;28(10):1573-1583. doi:10.1093/ibd/izac115
- Gubatan J, Levitte S, Patel A, Balabanis T, Wei MT, Sinha SR. Artificial intelligence applications in inflammatory bowel disease: emerging technologies and future directions. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27(17):1920-1935. doi:10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1920
- Lewis JD, Parlett LE, Jonsson Funk ML, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and racial and ethnic distribution of inflammatory bowel disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2023;165(5):1197-1205.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.07.003
- Sharma P. AI shows promise in diagnosis, treatment of IBD, but limitations, concerns remain. Healio. Published June 19, 2023. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.healio.com/news/gastroenterology/20230606/ai-shows-promise-in-diagnosis-treatment-of-ibd-but-limitations-concerns-remain
- Artificial intelligence (AI) vs. machine learning. Columbia Engineering.Accessed January 5, 2024. https://ai.engineering.columbia.edu/ai-vs-machine-learning/
- Zhang B, Shi H, Wang H. Machine learning and AI in cancer prognosis, prediction, and treatment selection: a critical approach. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023;16:1779-1791. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S410301
- Cohen-Mekelburg S, Berry S, Stidham RW, Zhu J, Waljee AK. Clinical applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning-based methods in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(2):279-285. doi:10.1111/jgh.15405
- Uche-Anya E, Anyane-Yeboa A, Berzin TM, Ghassemi M, May FP. Artificial intelligence in gastroenterology and hepatology: how to advance clinical practice while ensuring health equity. Gut. 2022;71(9):1909-1915. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326271
- Stafford IS, Gosink MM, Mossotto E, Ennis S, Hauben M. A systematic review of artificial intelligence and machine learning applications to inflammatory bowel disease, with practical guidelines for interpretation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022;28(10):1573-1583. doi:10.1093/ibd/izac115
- Gubatan J, Levitte S, Patel A, Balabanis T, Wei MT, Sinha SR. Artificial intelligence applications in inflammatory bowel disease: emerging technologies and future directions. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27(17):1920-1935. doi:10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1920
- Lewis JD, Parlett LE, Jonsson Funk ML, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and racial and ethnic distribution of inflammatory bowel disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2023;165(5):1197-1205.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.07.003
- Sharma P. AI shows promise in diagnosis, treatment of IBD, but limitations, concerns remain. Healio. Published June 19, 2023. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.healio.com/news/gastroenterology/20230606/ai-shows-promise-in-diagnosis-treatment-of-ibd-but-limitations-concerns-remain
- Artificial intelligence (AI) vs. machine learning. Columbia Engineering.Accessed January 5, 2024. https://ai.engineering.columbia.edu/ai-vs-machine-learning/
- Zhang B, Shi H, Wang H. Machine learning and AI in cancer prognosis, prediction, and treatment selection: a critical approach. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023;16:1779-1791. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S410301
- Cohen-Mekelburg S, Berry S, Stidham RW, Zhu J, Waljee AK. Clinical applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning-based methods in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(2):279-285. doi:10.1111/jgh.15405
- Uche-Anya E, Anyane-Yeboa A, Berzin TM, Ghassemi M, May FP. Artificial intelligence in gastroenterology and hepatology: how to advance clinical practice while ensuring health equity. Gut. 2022;71(9):1909-1915. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326271
- Stafford IS, Gosink MM, Mossotto E, Ennis S, Hauben M. A systematic review of artificial intelligence and machine learning applications to inflammatory bowel disease, with practical guidelines for interpretation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022;28(10):1573-1583. doi:10.1093/ibd/izac115
- Gubatan J, Levitte S, Patel A, Balabanis T, Wei MT, Sinha SR. Artificial intelligence applications in inflammatory bowel disease: emerging technologies and future directions. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27(17):1920-1935. doi:10.3748/wjg.v27.i17.1920
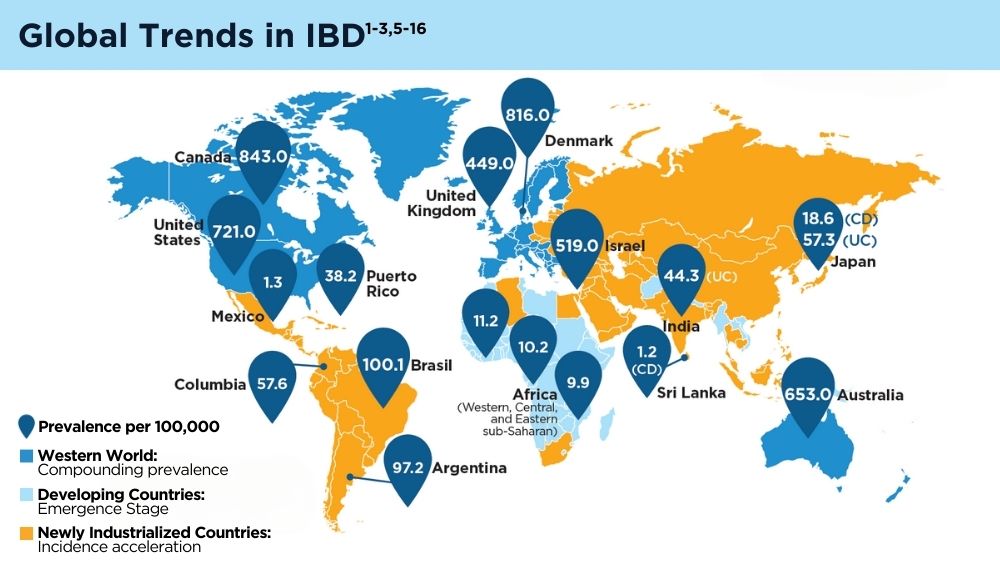
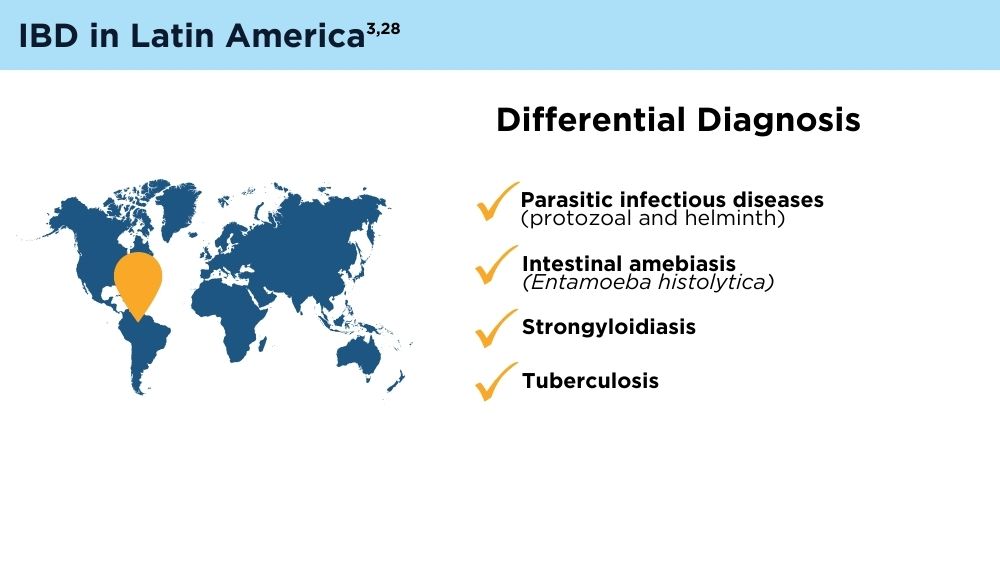
The Changing Face of IBD: Beyond the Western World
- Kaplan GG, Windsor JW. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(1):56-66. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-00360-x
- Kaplan GG, Ng SC. Understanding and preventing the global increase of inflammatory bowel disease [published correction appears in Gastroenterology. 2017;152(8):2084]. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(2):313-321.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.020
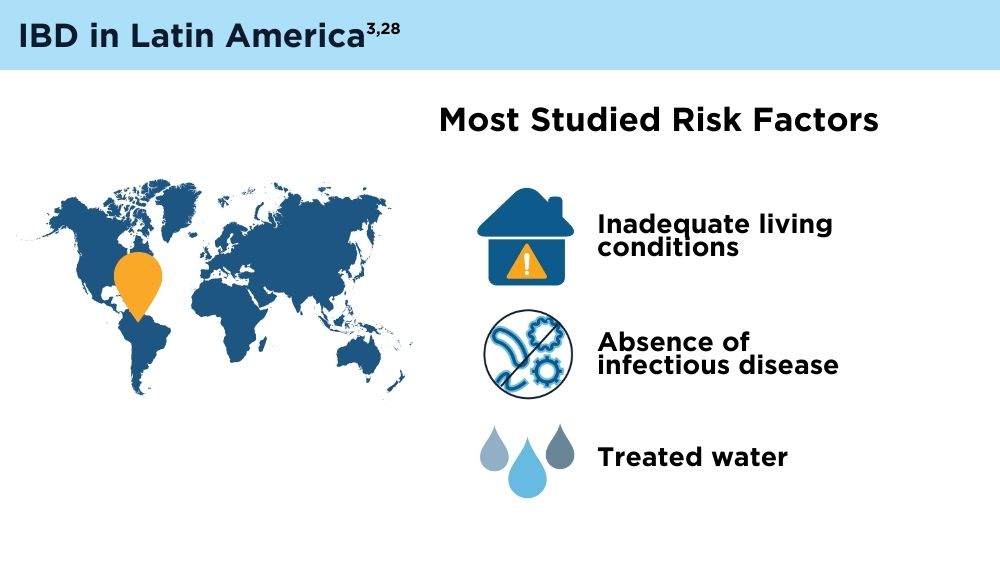
- Balderramo D, Quaresma AB, Olivera PA, et al. Challenges in diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in Latin America. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024; 9(3):263-272. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00284-4
- Song EM, Na SY, Hong SN, Ng SC, Hisamatsu T, Ye BD. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease–Asian perspectives: the results of a multinational web-based survey in the 8th Asian Organization for Crohn’s and Colitis meeting. Intest Res. 2023;21(3):339-352. doi:10.5217/ir.2022.00135
- GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(1):17-30. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30333-4
- Chen X, Xiang X, Xia W, et al. Evolving trends and burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia, 1990-2019: a comprehensive analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2023;13(4):725-739. doi:10.1007/s44197-023-00145-w
- Zhao M, Feng R, Ben-Horin S, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: environmental and dietary differences of inflammatory bowel disease in Eastern and Western populations. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55(3):266-276. doi:10.1111/apt.16703
- Lewis JD, Parlett LE, Jonsson Funk ML, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and racial and ethnic distribution of inflammatory bowel disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2023;165(5):1197-1205.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.07.003
- Quaresma AB, Damiao AOMC, Coy CSR, et al. Temporal trends in the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel diseases in the public healthcare system in Brazil: a large population-based study. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022;13:100298. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100298
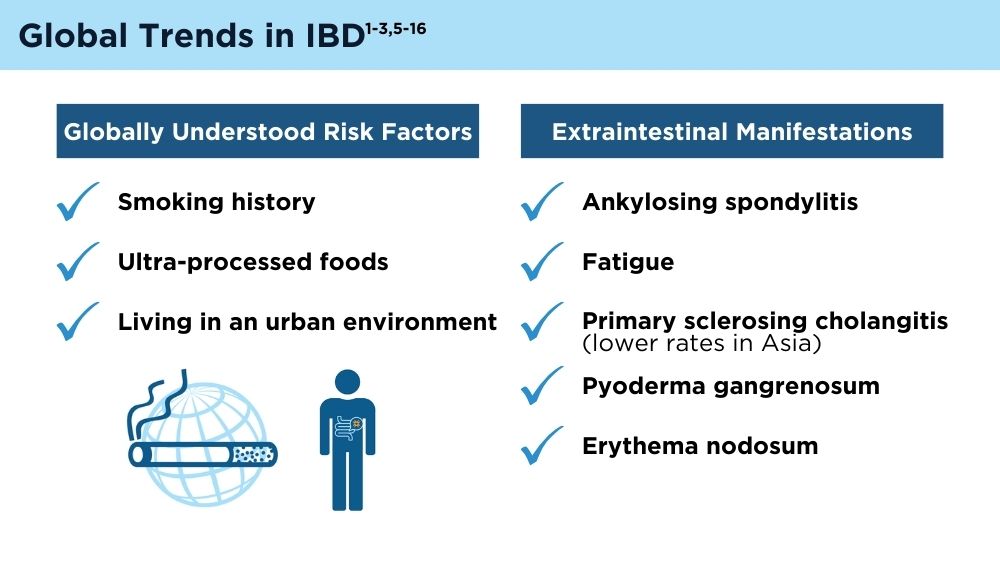
- Gordon H, Burisch J, Ellul P, et al. ECCO guidelines on extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2024;18(1):1-37. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad108
- Coward S, Benchimol EI, Bernstein CN, et al; Canadian Gastro-Intestinal Epidemiology Consortium (CanGIEC). Forecasting the Incidence and Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Canadian Nationwide Analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 18. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000002687. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38299598.
- Dorn-Rasmussen M, Lo B, Zhao M, Kaplan GG, Malham M, Wewer V, Burisch J. The Incidence and Prevalence of Paediatric- and Adult-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Denmark During a 37-Year Period: A Nationwide Cohort Study (1980-2017). J Crohns Colitis. 2023;17(2):259- 268. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac138. PMID: 36125076.
- Watermeyer G, Katsidzira L, Setshedi M, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease in sub-Saharan Africa: epidemiology, risk factors, and challenges in diagnosis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7(10):952-961. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00047-4
- Stulman MY, Asayag N, Focht G, et al. Epidemiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases in Israel: A Nationwide Epi-Israeli IBD Research Nucleus Study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(11):1784-1794. doi:10.1093/ibd/izaa341
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies [published correction appears in Lancet. 2020;396(10256):e56]. Lancet. 2017;390(10114):2769-2778. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0
- Busingye D, Pollack A, Chidwick K. Prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the Australian general practice population: A cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0252458. Published 2021 May 27. doi:10.1371/ journal.pone.0252458
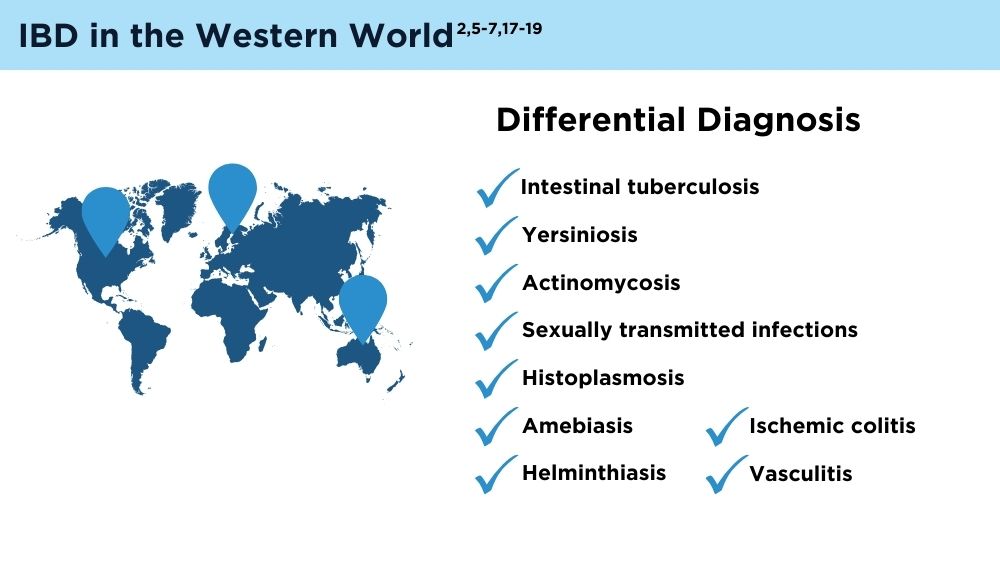
- Gecse KB, Vermeire S. Differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease: imitations and complications. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(9):644-653. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30159-6
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): comorbidities. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last reviewed April 14, 2022. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/data-and-statistics/comorbidities.html
- Mosli MH, Alsahafi M, Alsanea MN, Alhasani F, Ahmed M, Saadah O. Multimorbidity among inflammatory bowel disease patients in a tertiary care center: a retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22(1):487. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02578-2
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mayo Clinic. September 3, 2022. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inflammatory-bowel-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353320
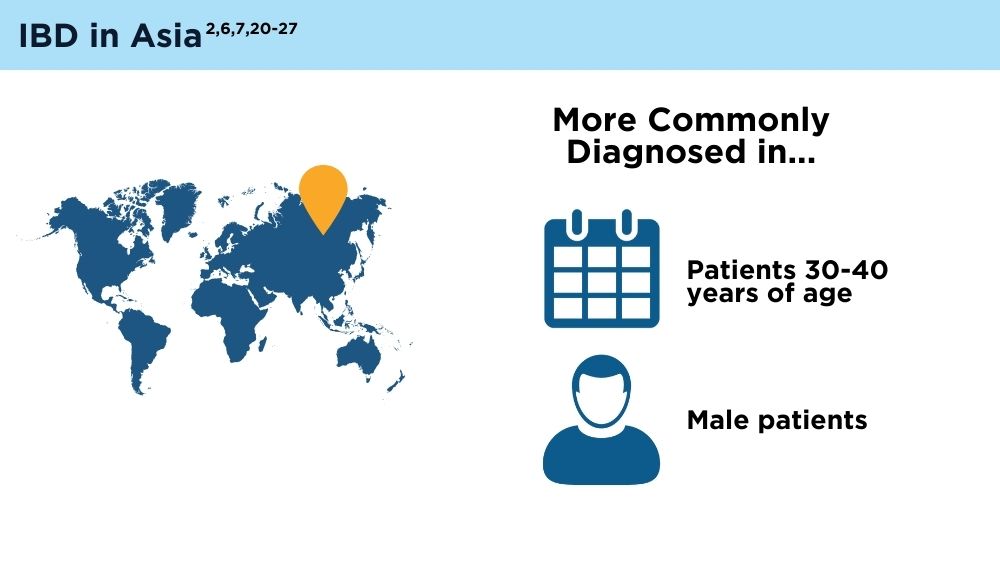
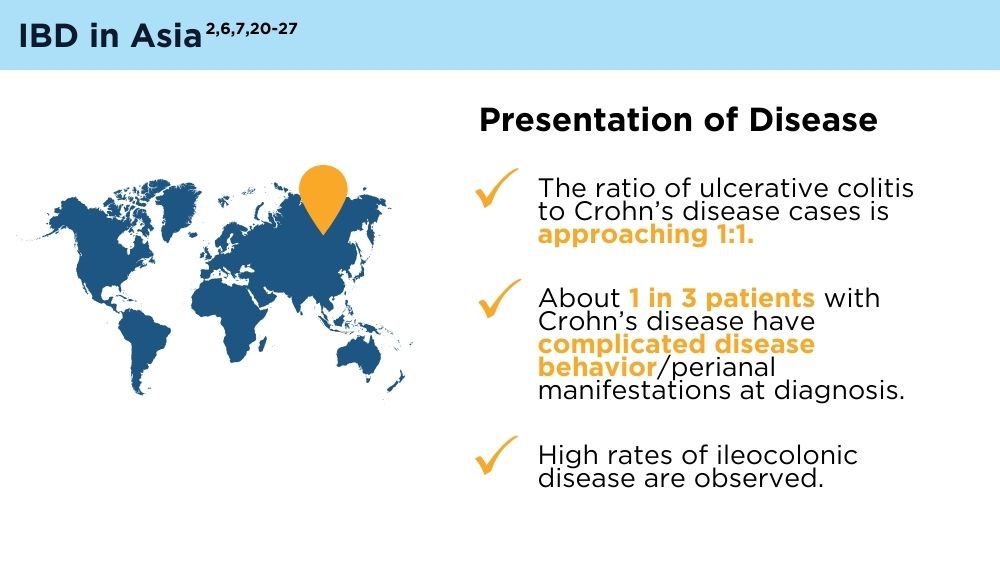
- Ng SC, Tang W, Ching JY, et al. Incidence and phenotype of inflammatory bowel disease based on results from the Asia-pacific Crohn’s and Colitis Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):158-165.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.007
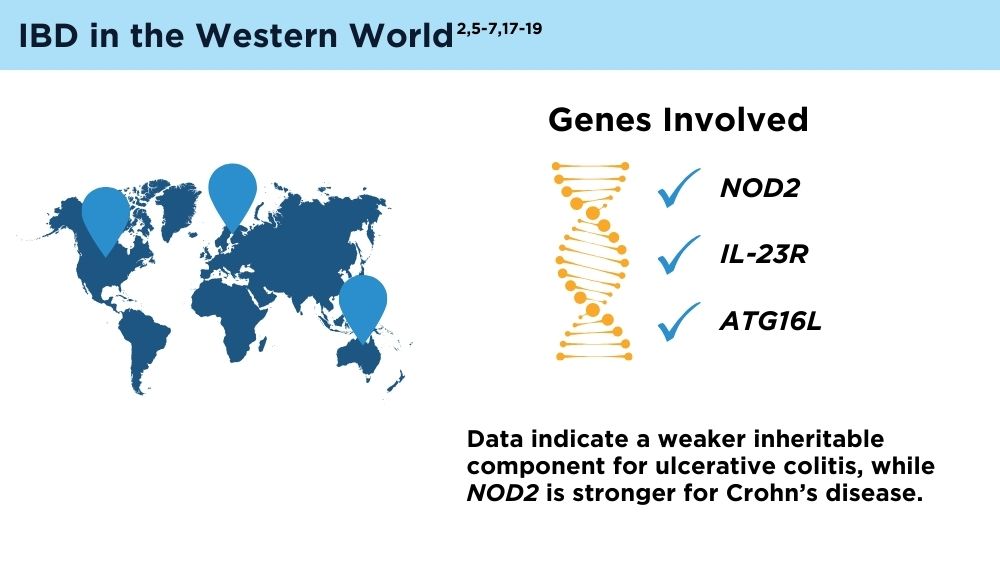
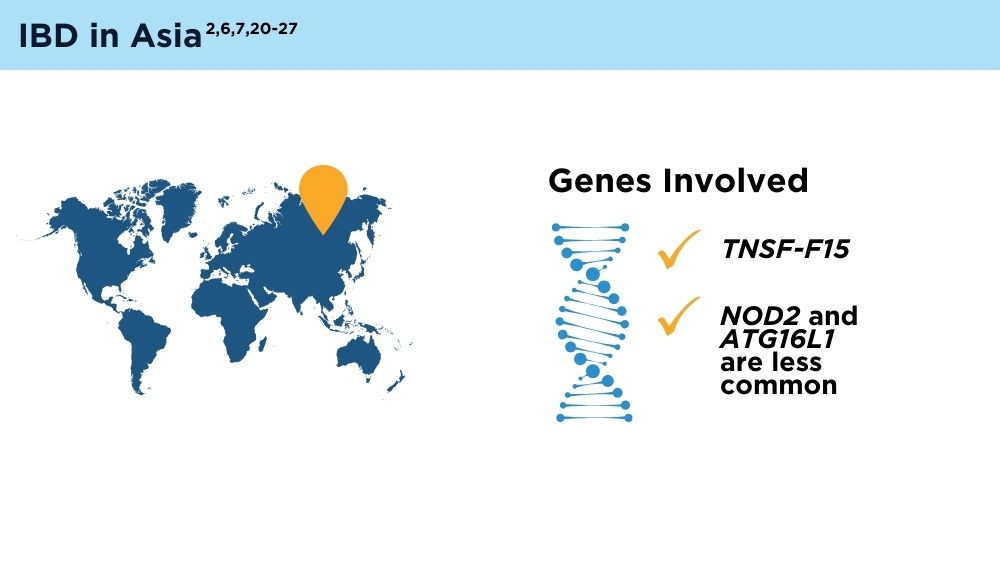
- Ng SC, Tsoi KK, Kamm MA, et al. Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18(6):1164-1176. doi:10.1002/ibd.21845
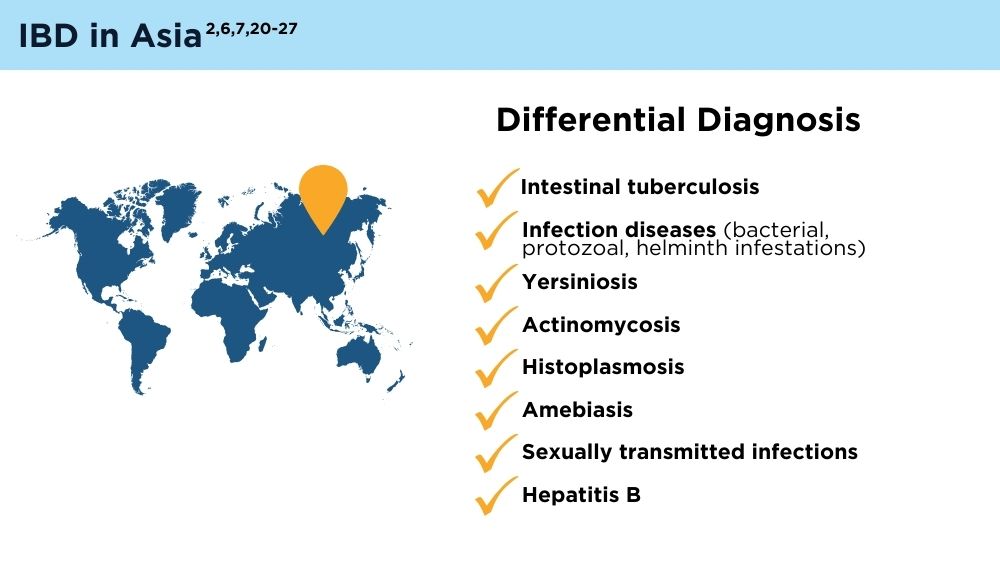
- Banerjee R, Pal P, Mak JWY, Ng SC. Challenges in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease in resource-limited settings in Asia. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(12):1076-1088. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30299-5
- Ng SC, Mak JWY, Pal P, Banerjee R. Optimising management strategies of inflammatory bowel disease in resource-limited settings in Asia. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(12):1089-1100. 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30298-3
- Ng SC. Emerging trends of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016;12(3):193-196. PMID: 27231449
- Ran Z, Wu K, Matsuoka K, et al. Asian Organization for Crohn’s and Colitis and Asia Pacific Association of Gastroenterology practice recommendations for medical management and monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(3):637-645. doi:10.1111/jgh.15185
- Liu JZ, van Sommeren S, Huang H, et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat Genet. 2015;47(9):979-986. doi:10.1038/ng.3359
- Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Parra-Holguín NN, Juliao-Baños F, et al; for the EPILATAM study group. Clinical differentiation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Latin America and the Caribbean. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(3):e28624. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000028624
- Kaplan GG, Windsor JW. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(1):56-66. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-00360-x
- Kaplan GG, Ng SC. Understanding and preventing the global increase of inflammatory bowel disease [published correction appears in Gastroenterology. 2017;152(8):2084]. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(2):313-321.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.020
- Balderramo D, Quaresma AB, Olivera PA, et al. Challenges in diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in Latin America. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024; 9(3):263-272. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00284-4
- Song EM, Na SY, Hong SN, Ng SC, Hisamatsu T, Ye BD. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease–Asian perspectives: the results of a multinational web-based survey in the 8th Asian Organization for Crohn’s and Colitis meeting. Intest Res. 2023;21(3):339-352. doi:10.5217/ir.2022.00135
- GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(1):17-30. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30333-4
- Chen X, Xiang X, Xia W, et al. Evolving trends and burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia, 1990-2019: a comprehensive analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2023;13(4):725-739. doi:10.1007/s44197-023-00145-w
- Zhao M, Feng R, Ben-Horin S, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: environmental and dietary differences of inflammatory bowel disease in Eastern and Western populations. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55(3):266-276. doi:10.1111/apt.16703
- Lewis JD, Parlett LE, Jonsson Funk ML, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and racial and ethnic distribution of inflammatory bowel disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2023;165(5):1197-1205.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.07.003
- Quaresma AB, Damiao AOMC, Coy CSR, et al. Temporal trends in the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel diseases in the public healthcare system in Brazil: a large population-based study. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022;13:100298. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100298
- Gordon H, Burisch J, Ellul P, et al. ECCO guidelines on extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2024;18(1):1-37. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad108
- Coward S, Benchimol EI, Bernstein CN, et al; Canadian Gastro-Intestinal Epidemiology Consortium (CanGIEC). Forecasting the Incidence and Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Canadian Nationwide Analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 18. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000002687. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38299598.
- Dorn-Rasmussen M, Lo B, Zhao M, Kaplan GG, Malham M, Wewer V, Burisch J. The Incidence and Prevalence of Paediatric- and Adult-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Denmark During a 37-Year Period: A Nationwide Cohort Study (1980-2017). J Crohns Colitis. 2023;17(2):259- 268. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac138. PMID: 36125076.
- Watermeyer G, Katsidzira L, Setshedi M, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease in sub-Saharan Africa: epidemiology, risk factors, and challenges in diagnosis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7(10):952-961. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00047-4
- Stulman MY, Asayag N, Focht G, et al. Epidemiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases in Israel: A Nationwide Epi-Israeli IBD Research Nucleus Study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(11):1784-1794. doi:10.1093/ibd/izaa341
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies [published correction appears in Lancet. 2020;396(10256):e56]. Lancet. 2017;390(10114):2769-2778. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0
- Busingye D, Pollack A, Chidwick K. Prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the Australian general practice population: A cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0252458. Published 2021 May 27. doi:10.1371/ journal.pone.0252458
- Gecse KB, Vermeire S. Differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease: imitations and complications. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(9):644-653. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30159-6
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): comorbidities. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last reviewed April 14, 2022. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/data-and-statistics/comorbidities.html
- Mosli MH, Alsahafi M, Alsanea MN, Alhasani F, Ahmed M, Saadah O. Multimorbidity among inflammatory bowel disease patients in a tertiary care center: a retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22(1):487. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02578-2
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mayo Clinic. September 3, 2022. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inflammatory-bowel-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353320
- Ng SC, Tang W, Ching JY, et al. Incidence and phenotype of inflammatory bowel disease based on results from the Asia-pacific Crohn’s and Colitis Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):158-165.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.007
- Ng SC, Tsoi KK, Kamm MA, et al. Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18(6):1164-1176. doi:10.1002/ibd.21845
- Banerjee R, Pal P, Mak JWY, Ng SC. Challenges in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease in resource-limited settings in Asia. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(12):1076-1088. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30299-5
- Ng SC, Mak JWY, Pal P, Banerjee R. Optimising management strategies of inflammatory bowel disease in resource-limited settings in Asia. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(12):1089-1100. 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30298-3
- Ng SC. Emerging trends of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016;12(3):193-196. PMID: 27231449
- Ran Z, Wu K, Matsuoka K, et al. Asian Organization for Crohn’s and Colitis and Asia Pacific Association of Gastroenterology practice recommendations for medical management and monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(3):637-645. doi:10.1111/jgh.15185
- Liu JZ, van Sommeren S, Huang H, et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat Genet. 2015;47(9):979-986. doi:10.1038/ng.3359
- Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Parra-Holguín NN, Juliao-Baños F, et al; for the EPILATAM study group. Clinical differentiation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Latin America and the Caribbean. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(3):e28624. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000028624
- Kaplan GG, Windsor JW. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(1):56-66. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-00360-x
- Kaplan GG, Ng SC. Understanding and preventing the global increase of inflammatory bowel disease [published correction appears in Gastroenterology. 2017;152(8):2084]. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(2):313-321.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.020
- Balderramo D, Quaresma AB, Olivera PA, et al. Challenges in diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in Latin America. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024; 9(3):263-272. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00284-4
- Song EM, Na SY, Hong SN, Ng SC, Hisamatsu T, Ye BD. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease–Asian perspectives: the results of a multinational web-based survey in the 8th Asian Organization for Crohn’s and Colitis meeting. Intest Res. 2023;21(3):339-352. doi:10.5217/ir.2022.00135
- GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(1):17-30. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30333-4
- Chen X, Xiang X, Xia W, et al. Evolving trends and burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia, 1990-2019: a comprehensive analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2023;13(4):725-739. doi:10.1007/s44197-023-00145-w
- Zhao M, Feng R, Ben-Horin S, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: environmental and dietary differences of inflammatory bowel disease in Eastern and Western populations. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55(3):266-276. doi:10.1111/apt.16703
- Lewis JD, Parlett LE, Jonsson Funk ML, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and racial and ethnic distribution of inflammatory bowel disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2023;165(5):1197-1205.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.07.003
- Quaresma AB, Damiao AOMC, Coy CSR, et al. Temporal trends in the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel diseases in the public healthcare system in Brazil: a large population-based study. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022;13:100298. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100298
- Gordon H, Burisch J, Ellul P, et al. ECCO guidelines on extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2024;18(1):1-37. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad108
- Coward S, Benchimol EI, Bernstein CN, et al; Canadian Gastro-Intestinal Epidemiology Consortium (CanGIEC). Forecasting the Incidence and Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Canadian Nationwide Analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 18. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000002687. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38299598.
- Dorn-Rasmussen M, Lo B, Zhao M, Kaplan GG, Malham M, Wewer V, Burisch J. The Incidence and Prevalence of Paediatric- and Adult-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Denmark During a 37-Year Period: A Nationwide Cohort Study (1980-2017). J Crohns Colitis. 2023;17(2):259- 268. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac138. PMID: 36125076.
- Watermeyer G, Katsidzira L, Setshedi M, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease in sub-Saharan Africa: epidemiology, risk factors, and challenges in diagnosis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7(10):952-961. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00047-4
- Stulman MY, Asayag N, Focht G, et al. Epidemiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases in Israel: A Nationwide Epi-Israeli IBD Research Nucleus Study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27(11):1784-1794. doi:10.1093/ibd/izaa341
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies [published correction appears in Lancet. 2020;396(10256):e56]. Lancet. 2017;390(10114):2769-2778. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0
- Busingye D, Pollack A, Chidwick K. Prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the Australian general practice population: A cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0252458. Published 2021 May 27. doi:10.1371/ journal.pone.0252458
- Gecse KB, Vermeire S. Differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease: imitations and complications. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(9):644-653. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30159-6
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): comorbidities. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last reviewed April 14, 2022. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/data-and-statistics/comorbidities.html
- Mosli MH, Alsahafi M, Alsanea MN, Alhasani F, Ahmed M, Saadah O. Multimorbidity among inflammatory bowel disease patients in a tertiary care center: a retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22(1):487. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02578-2
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mayo Clinic. September 3, 2022. Accessed February 21, 2024. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inflammatory-bowel-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353320
- Ng SC, Tang W, Ching JY, et al. Incidence and phenotype of inflammatory bowel disease based on results from the Asia-pacific Crohn’s and Colitis Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(1):158-165.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.007
- Ng SC, Tsoi KK, Kamm MA, et al. Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18(6):1164-1176. doi:10.1002/ibd.21845
- Banerjee R, Pal P, Mak JWY, Ng SC. Challenges in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease in resource-limited settings in Asia. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(12):1076-1088. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30299-5
- Ng SC, Mak JWY, Pal P, Banerjee R. Optimising management strategies of inflammatory bowel disease in resource-limited settings in Asia. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(12):1089-1100. 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30298-3
- Ng SC. Emerging trends of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016;12(3):193-196. PMID: 27231449
- Ran Z, Wu K, Matsuoka K, et al. Asian Organization for Crohn’s and Colitis and Asia Pacific Association of Gastroenterology practice recommendations for medical management and monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(3):637-645. doi:10.1111/jgh.15185
- Liu JZ, van Sommeren S, Huang H, et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat Genet. 2015;47(9):979-986. doi:10.1038/ng.3359
- Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Parra-Holguín NN, Juliao-Baños F, et al; for the EPILATAM study group. Clinical differentiation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Latin America and the Caribbean. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(3):e28624. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000028624
Spondyloarthritis Screening Study Finds ‘High Burden of Need’ in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
More than 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) screened positive for joint pain symptomatic of spondyloarthritis (SpA), according to a new study.
Of these patients, 75% did not have any history of arthritis.
“What we know is that a substantial proportion of patients with IBD do report musculoskeletal symptoms, and inflammatory back pain stands out as being one of the more frequent symptoms reported,” said Reem Jan, MBBS, a rheumatologist at the University of Chicago Medicine. She presented the study findings during the annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN) in Cleveland.
“Yet a minority of these patients are evaluated by rheumatologists. So that suggests there’s a high burden of need in the IBD population to have this joint pain evaluated and addressed,” she said during her presentation.
She presented preliminary data from an ongoing project to better understand the prevalence of inflammatory arthritis in IBD — estimates range from 17% to 39%— and the risk factors for developing arthritis in this patient population.
Study Details
Researchers enrolled patients from outpatient gastroenterology clinics or procedure units at NYU Langone Health, New York City; Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado; Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota; University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago; and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City. Additional patients were recruited from Mercy Health, a community health system in Ohio.
Upon entry into the study, participants completed a survey documenting their history with joint pain. The survey combined questions from the DETAIL and the IBIS questionnaires.
Between January 2021 and December 2022, 669 patients joined the study. In total, 41% of patients (n = 275) screened positive.
“What really stood out to us was that of all the positive screens, only about a quarter of those patients were known to have SpA,” Dr. Jan said during her presentation. “[This] means 75% of the patients who screened positive were not known to have any type of arthritic disease.”
In addition, only 24% (n = 65) of all patients who screened positive — including those with a SpA diagnosis — had seen a rheumatologist in the previous year.
Among these patients, inflammatory back pain was the most commonly reported symptom, followed by painful swelling of peripheral joints and heel pain.
Excluding patients with a SpA diagnosis, researchers also investigated which characteristics were associated with a higher likelihood of screening positive in the questionnaire. The analysis, including 588 patients, identified the following risk factors:
- Female sex: Odds ratio (OR), 2.0; 95% CI, 1.4-2.9
- Older age: OR, 1.02; 95% CI, 1.01-1.4
- History of smoking: OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.1-2.6
- History of prior IBD-related surgery: OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.1-2.5
- History of biologic or small molecule therapy: OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-4.0
Future Directions
Commenting on the study, Mark Hwang, MD, a rheumatologist at UTHealth Houston, noted that it was “very interesting to see the fairly large, positive rates” of joint pain in patients with IBD, which certainly have clinical implications. However, it is not yet known if any of these patients went on to be diagnosed with SpA.
Jan noted that potential next steps include a follow-up analysis of patients who screened positive to see how many went on to see a rheumatologist and which patients were ultimately diagnosed with SpA or other inflammatory arthritis conditions.
These findings are a first step, Dr. Hwang said, and will likely “help further establish some of the validity of these questionnaires by testing in different patient populations,” he noted.
The ultimate goal is to “develop really good strategies to risk stratify IBD patients with the greatest need of rheumatologist consultation,” Dr. Jan said. “We certainly don’t want to see all these patients, so how can we figure out who really needs to be seen?”
Funding information was not available for this study. Dr. Hwang is conducting two clinical trials for psoriatic arthritis sponsored by Janssen and Eli Lilly. Dr. Jan reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) screened positive for joint pain symptomatic of spondyloarthritis (SpA), according to a new study.
Of these patients, 75% did not have any history of arthritis.
“What we know is that a substantial proportion of patients with IBD do report musculoskeletal symptoms, and inflammatory back pain stands out as being one of the more frequent symptoms reported,” said Reem Jan, MBBS, a rheumatologist at the University of Chicago Medicine. She presented the study findings during the annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN) in Cleveland.
“Yet a minority of these patients are evaluated by rheumatologists. So that suggests there’s a high burden of need in the IBD population to have this joint pain evaluated and addressed,” she said during her presentation.
She presented preliminary data from an ongoing project to better understand the prevalence of inflammatory arthritis in IBD — estimates range from 17% to 39%— and the risk factors for developing arthritis in this patient population.
Study Details
Researchers enrolled patients from outpatient gastroenterology clinics or procedure units at NYU Langone Health, New York City; Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado; Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota; University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago; and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City. Additional patients were recruited from Mercy Health, a community health system in Ohio.
Upon entry into the study, participants completed a survey documenting their history with joint pain. The survey combined questions from the DETAIL and the IBIS questionnaires.
Between January 2021 and December 2022, 669 patients joined the study. In total, 41% of patients (n = 275) screened positive.
“What really stood out to us was that of all the positive screens, only about a quarter of those patients were known to have SpA,” Dr. Jan said during her presentation. “[This] means 75% of the patients who screened positive were not known to have any type of arthritic disease.”
In addition, only 24% (n = 65) of all patients who screened positive — including those with a SpA diagnosis — had seen a rheumatologist in the previous year.
Among these patients, inflammatory back pain was the most commonly reported symptom, followed by painful swelling of peripheral joints and heel pain.
Excluding patients with a SpA diagnosis, researchers also investigated which characteristics were associated with a higher likelihood of screening positive in the questionnaire. The analysis, including 588 patients, identified the following risk factors:
- Female sex: Odds ratio (OR), 2.0; 95% CI, 1.4-2.9
- Older age: OR, 1.02; 95% CI, 1.01-1.4
- History of smoking: OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.1-2.6
- History of prior IBD-related surgery: OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.1-2.5
- History of biologic or small molecule therapy: OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-4.0
Future Directions
Commenting on the study, Mark Hwang, MD, a rheumatologist at UTHealth Houston, noted that it was “very interesting to see the fairly large, positive rates” of joint pain in patients with IBD, which certainly have clinical implications. However, it is not yet known if any of these patients went on to be diagnosed with SpA.
Jan noted that potential next steps include a follow-up analysis of patients who screened positive to see how many went on to see a rheumatologist and which patients were ultimately diagnosed with SpA or other inflammatory arthritis conditions.
These findings are a first step, Dr. Hwang said, and will likely “help further establish some of the validity of these questionnaires by testing in different patient populations,” he noted.
The ultimate goal is to “develop really good strategies to risk stratify IBD patients with the greatest need of rheumatologist consultation,” Dr. Jan said. “We certainly don’t want to see all these patients, so how can we figure out who really needs to be seen?”
Funding information was not available for this study. Dr. Hwang is conducting two clinical trials for psoriatic arthritis sponsored by Janssen and Eli Lilly. Dr. Jan reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) screened positive for joint pain symptomatic of spondyloarthritis (SpA), according to a new study.
Of these patients, 75% did not have any history of arthritis.
“What we know is that a substantial proportion of patients with IBD do report musculoskeletal symptoms, and inflammatory back pain stands out as being one of the more frequent symptoms reported,” said Reem Jan, MBBS, a rheumatologist at the University of Chicago Medicine. She presented the study findings during the annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN) in Cleveland.
“Yet a minority of these patients are evaluated by rheumatologists. So that suggests there’s a high burden of need in the IBD population to have this joint pain evaluated and addressed,” she said during her presentation.
She presented preliminary data from an ongoing project to better understand the prevalence of inflammatory arthritis in IBD — estimates range from 17% to 39%— and the risk factors for developing arthritis in this patient population.
Study Details
Researchers enrolled patients from outpatient gastroenterology clinics or procedure units at NYU Langone Health, New York City; Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston; University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado; Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota; University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago; and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City. Additional patients were recruited from Mercy Health, a community health system in Ohio.
Upon entry into the study, participants completed a survey documenting their history with joint pain. The survey combined questions from the DETAIL and the IBIS questionnaires.
Between January 2021 and December 2022, 669 patients joined the study. In total, 41% of patients (n = 275) screened positive.
“What really stood out to us was that of all the positive screens, only about a quarter of those patients were known to have SpA,” Dr. Jan said during her presentation. “[This] means 75% of the patients who screened positive were not known to have any type of arthritic disease.”
In addition, only 24% (n = 65) of all patients who screened positive — including those with a SpA diagnosis — had seen a rheumatologist in the previous year.
Among these patients, inflammatory back pain was the most commonly reported symptom, followed by painful swelling of peripheral joints and heel pain.
Excluding patients with a SpA diagnosis, researchers also investigated which characteristics were associated with a higher likelihood of screening positive in the questionnaire. The analysis, including 588 patients, identified the following risk factors:
- Female sex: Odds ratio (OR), 2.0; 95% CI, 1.4-2.9
- Older age: OR, 1.02; 95% CI, 1.01-1.4
- History of smoking: OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.1-2.6
- History of prior IBD-related surgery: OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.1-2.5
- History of biologic or small molecule therapy: OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-4.0
Future Directions
Commenting on the study, Mark Hwang, MD, a rheumatologist at UTHealth Houston, noted that it was “very interesting to see the fairly large, positive rates” of joint pain in patients with IBD, which certainly have clinical implications. However, it is not yet known if any of these patients went on to be diagnosed with SpA.
Jan noted that potential next steps include a follow-up analysis of patients who screened positive to see how many went on to see a rheumatologist and which patients were ultimately diagnosed with SpA or other inflammatory arthritis conditions.
These findings are a first step, Dr. Hwang said, and will likely “help further establish some of the validity of these questionnaires by testing in different patient populations,” he noted.
The ultimate goal is to “develop really good strategies to risk stratify IBD patients with the greatest need of rheumatologist consultation,” Dr. Jan said. “We certainly don’t want to see all these patients, so how can we figure out who really needs to be seen?”
Funding information was not available for this study. Dr. Hwang is conducting two clinical trials for psoriatic arthritis sponsored by Janssen and Eli Lilly. Dr. Jan reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPARTAN 2024
Healthy Sleep Linked to Lower Odds for Digestive Diseases
TOPLINE:
Healthier sleep is associated with lower odds of developing a wide range of gastrointestinal conditions, regardless of genetic susceptibility, new research revealed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Due to the widespread prevalence of sleep issues and a growing burden of digestive diseases globally, researchers investigated the association between sleep quality and digestive disorders in a prospective cohort study of 410,586 people in the UK Biobank.
- Five individual sleep behaviors were assessed: sleep duration, insomnia, snoring, daytime sleepiness, and chronotype.
- A healthy sleep was defined as a morning chronotype, 7-8 hours of sleep duration, no self-reported snoring, never or rare insomnia, and a low frequency of daytime sleepiness, for a score of 5/5.
- The study investigators tracked the development of 16 digestive diseases over a mean period of 13.2 years.
- As well as looking at healthy sleep scores, researchers considered genetic susceptibility to gastrointestinal conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 16 digestive diseases looked at, the reduction of risk was highest for irritable bowel syndrome at 50% (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.45-0.57).
- A healthy sleep score was also associated with 37% reduced odds for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.55-0.71), 35% lower chance for peptic ulcer (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.058-0.74), 34% reduced chance for dyspepsia (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.58-0.75), and a 25% lower risk for diverticulosis (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.71-0.80).
- High genetic risk and poor sleep scores were also associated with increased odds (53% to > 200%) of developing digestive diseases.
- However, healthy sleep reduced the risk for digestive diseases regardless of genetic susceptibility.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings underscore the potential holistic impact of different sleep behaviors in mitigating the risk of digestive diseases in clinical practice,” wrote Shiyi Yu, MD, of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
Poor sleep can also change our gut microbiome, Dr. Yu told this news organization. If you don’t sleep well, the repair of the gut lining cannot be finished during the night.
SOURCE:
The study was presented at the Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), 2024, annual meeting.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Yu had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Healthier sleep is associated with lower odds of developing a wide range of gastrointestinal conditions, regardless of genetic susceptibility, new research revealed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Due to the widespread prevalence of sleep issues and a growing burden of digestive diseases globally, researchers investigated the association between sleep quality and digestive disorders in a prospective cohort study of 410,586 people in the UK Biobank.
- Five individual sleep behaviors were assessed: sleep duration, insomnia, snoring, daytime sleepiness, and chronotype.
- A healthy sleep was defined as a morning chronotype, 7-8 hours of sleep duration, no self-reported snoring, never or rare insomnia, and a low frequency of daytime sleepiness, for a score of 5/5.
- The study investigators tracked the development of 16 digestive diseases over a mean period of 13.2 years.
- As well as looking at healthy sleep scores, researchers considered genetic susceptibility to gastrointestinal conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 16 digestive diseases looked at, the reduction of risk was highest for irritable bowel syndrome at 50% (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.45-0.57).
- A healthy sleep score was also associated with 37% reduced odds for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.55-0.71), 35% lower chance for peptic ulcer (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.058-0.74), 34% reduced chance for dyspepsia (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.58-0.75), and a 25% lower risk for diverticulosis (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.71-0.80).
- High genetic risk and poor sleep scores were also associated with increased odds (53% to > 200%) of developing digestive diseases.
- However, healthy sleep reduced the risk for digestive diseases regardless of genetic susceptibility.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings underscore the potential holistic impact of different sleep behaviors in mitigating the risk of digestive diseases in clinical practice,” wrote Shiyi Yu, MD, of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
Poor sleep can also change our gut microbiome, Dr. Yu told this news organization. If you don’t sleep well, the repair of the gut lining cannot be finished during the night.
SOURCE:
The study was presented at the Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), 2024, annual meeting.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Yu had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Healthier sleep is associated with lower odds of developing a wide range of gastrointestinal conditions, regardless of genetic susceptibility, new research revealed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Due to the widespread prevalence of sleep issues and a growing burden of digestive diseases globally, researchers investigated the association between sleep quality and digestive disorders in a prospective cohort study of 410,586 people in the UK Biobank.
- Five individual sleep behaviors were assessed: sleep duration, insomnia, snoring, daytime sleepiness, and chronotype.
- A healthy sleep was defined as a morning chronotype, 7-8 hours of sleep duration, no self-reported snoring, never or rare insomnia, and a low frequency of daytime sleepiness, for a score of 5/5.
- The study investigators tracked the development of 16 digestive diseases over a mean period of 13.2 years.
- As well as looking at healthy sleep scores, researchers considered genetic susceptibility to gastrointestinal conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 16 digestive diseases looked at, the reduction of risk was highest for irritable bowel syndrome at 50% (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.45-0.57).
- A healthy sleep score was also associated with 37% reduced odds for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.55-0.71), 35% lower chance for peptic ulcer (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.058-0.74), 34% reduced chance for dyspepsia (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.58-0.75), and a 25% lower risk for diverticulosis (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.71-0.80).
- High genetic risk and poor sleep scores were also associated with increased odds (53% to > 200%) of developing digestive diseases.
- However, healthy sleep reduced the risk for digestive diseases regardless of genetic susceptibility.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings underscore the potential holistic impact of different sleep behaviors in mitigating the risk of digestive diseases in clinical practice,” wrote Shiyi Yu, MD, of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
Poor sleep can also change our gut microbiome, Dr. Yu told this news organization. If you don’t sleep well, the repair of the gut lining cannot be finished during the night.
SOURCE:
The study was presented at the Digestive Disease Week® (DDW), 2024, annual meeting.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Yu had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Maintenance Treatment With Guselkumab for Ulcerative Colitis Meets All Endpoints: QUASAR
WASHINGTON —
The primary outcome of clinical remission at 44 weeks was greater with either of two dose regimens of guselkumab than with placebo, David Rubin, MD, AGAF, reported as part of his presentation (Abstract 759) at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
Guselkumab is not the only biologic approved or in development for UC, but it is unique because of its dual action. It is an interleukin (IL)-23p19 subunit inhibitor that blocks IL-23 and also binds to the CD64 receptor on cells that produce IL-23.
Dr. Rubin, who is chief of the Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago, said he was unsure at the beginning of the trial if this dual activity “might have any value.”
Targeting both the IL-23 circulating in the tissue and the receptor remains to be proven, “but nonetheless seems reasonable,” he said.
The study included 568 people, about 42% of whom had an inadequate response or were intolerant to prior advanced therapy, and 42.5% of whom had failed two or more advanced therapy classes.
Clinical responders from two prior guselkumab induction studies were enrolled in this randomized withdrawal, double-blind maintenance trial. At either 12 weeks or 24 weeks of induction, patients were randomly assigned to subcutaneous 200-mg guselkumab every 4 weeks (n = 190), 100-mg guselkumab every 8 weeks (n = 188), or placebo (n = 190). The placebo group served as a guselkumab withdrawal group.
Participants had a mean age of 41 years and a mean disease duration of 7.8 years. The 40% using oral corticosteroids were tapered off during the study.
A total of 45.2% of the 100-mg guselkumab group and 50.0% of the 200-mg guselkumab group met the primary outcome of clinical remission at week 44 compared with 18.9% with placebo.
“It was interesting to note that the 200 mg every 4 weeks was similar in efficacy at week 44 to the 100 mg every 8 weeks. It’s much less medicine, but you get similar results,” Dr. Rubin said.
Secondary Outcomes Also Superior
“The bottom line is not only did it work, but it worked when you look at some secondary endpoints, including endoscopic remission, where the bowel is completely healed,” Dr. Rubin said in an interview.
Overall, 34% of all participants who received guselkumab achieved this outcome, “which is a very high rate,” he said. “We haven’t seen a Mayo score of zero — meaning endoscopic remission — at that rate with any of our other therapies currently.”
Among the participants who achieved clinical remission, 69% of them also showed complete remission on endoscopy.
Other secondary outcomes significantly better at week 44 vs placebo included corticosteroid-free clinical remission, maintenance of clinical remission, clinical response, symptomatic remission, endoscopic improvement, histo-endoscopic mucosal improvement, endoscopic normalization, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire remission, and fatigue response.
“It was a great study. I think it’s very promising data,” said session co-moderator Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MBBS, MPH, AGAF, director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“As we get more data from these more selective interleukins, we’ll get a better sense of how that plays out” vs other similar agents in development, he added.
IL-23 Target Seems Safe
One or more adverse events were reported by 70% of the higher-dose guselkumab group, 65% of the lower-dose guselkumab group, and 68% of the placebo group.
The most common adverse events in a combined 200-mg and 100-mg guselkumab group were lower than in the placebo group: 11.2% vs 14.1% reported COVID-19, 11.2% vs 29.7% reported exacerbation of UC, and 6.1% vs 6.8% experienced arthralgia, respectively.
No cases of active tuberculosis, opportunistic infection, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, Hy’s law, or serious hepatic issues were reported. One patient had clear cell renal carcinoma, another had rectal adenocarcinoma, and one hemorrhagic stroke was reported in the treatment groups. No patients died during the trial.
A higher proportion of people in the placebo group (13.7%) discontinued the study than those in the 100-mg guselkumab group (10.6%) and the 200-mg guselkumab group (11.6%).
“In general, we have accepted that the IL-23 target seems to be a very safe one,” Dr. Rubin said.
A leading theory is that unlike some interleukins, IL-23 is only expressed where the body has inflammation; therefore, targeting IL-23 does not affect other areas, he explained.
If approved by the Food and Drug Administration, it would expand the official indications for guselkumab, which was approved in 2020 for psoriatic arthritis and in 2017 for plaque psoriasis.
The study was supported by Janssen Research & Development, LLC. Dr. Rubin is a consultant for Janssen. Dr. Ananthakrishnan had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON —
The primary outcome of clinical remission at 44 weeks was greater with either of two dose regimens of guselkumab than with placebo, David Rubin, MD, AGAF, reported as part of his presentation (Abstract 759) at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
Guselkumab is not the only biologic approved or in development for UC, but it is unique because of its dual action. It is an interleukin (IL)-23p19 subunit inhibitor that blocks IL-23 and also binds to the CD64 receptor on cells that produce IL-23.
Dr. Rubin, who is chief of the Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago, said he was unsure at the beginning of the trial if this dual activity “might have any value.”
Targeting both the IL-23 circulating in the tissue and the receptor remains to be proven, “but nonetheless seems reasonable,” he said.
The study included 568 people, about 42% of whom had an inadequate response or were intolerant to prior advanced therapy, and 42.5% of whom had failed two or more advanced therapy classes.
Clinical responders from two prior guselkumab induction studies were enrolled in this randomized withdrawal, double-blind maintenance trial. At either 12 weeks or 24 weeks of induction, patients were randomly assigned to subcutaneous 200-mg guselkumab every 4 weeks (n = 190), 100-mg guselkumab every 8 weeks (n = 188), or placebo (n = 190). The placebo group served as a guselkumab withdrawal group.
Participants had a mean age of 41 years and a mean disease duration of 7.8 years. The 40% using oral corticosteroids were tapered off during the study.
A total of 45.2% of the 100-mg guselkumab group and 50.0% of the 200-mg guselkumab group met the primary outcome of clinical remission at week 44 compared with 18.9% with placebo.
“It was interesting to note that the 200 mg every 4 weeks was similar in efficacy at week 44 to the 100 mg every 8 weeks. It’s much less medicine, but you get similar results,” Dr. Rubin said.
Secondary Outcomes Also Superior
“The bottom line is not only did it work, but it worked when you look at some secondary endpoints, including endoscopic remission, where the bowel is completely healed,” Dr. Rubin said in an interview.
Overall, 34% of all participants who received guselkumab achieved this outcome, “which is a very high rate,” he said. “We haven’t seen a Mayo score of zero — meaning endoscopic remission — at that rate with any of our other therapies currently.”
Among the participants who achieved clinical remission, 69% of them also showed complete remission on endoscopy.
Other secondary outcomes significantly better at week 44 vs placebo included corticosteroid-free clinical remission, maintenance of clinical remission, clinical response, symptomatic remission, endoscopic improvement, histo-endoscopic mucosal improvement, endoscopic normalization, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire remission, and fatigue response.
“It was a great study. I think it’s very promising data,” said session co-moderator Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MBBS, MPH, AGAF, director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“As we get more data from these more selective interleukins, we’ll get a better sense of how that plays out” vs other similar agents in development, he added.
IL-23 Target Seems Safe
One or more adverse events were reported by 70% of the higher-dose guselkumab group, 65% of the lower-dose guselkumab group, and 68% of the placebo group.
The most common adverse events in a combined 200-mg and 100-mg guselkumab group were lower than in the placebo group: 11.2% vs 14.1% reported COVID-19, 11.2% vs 29.7% reported exacerbation of UC, and 6.1% vs 6.8% experienced arthralgia, respectively.
No cases of active tuberculosis, opportunistic infection, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, Hy’s law, or serious hepatic issues were reported. One patient had clear cell renal carcinoma, another had rectal adenocarcinoma, and one hemorrhagic stroke was reported in the treatment groups. No patients died during the trial.
A higher proportion of people in the placebo group (13.7%) discontinued the study than those in the 100-mg guselkumab group (10.6%) and the 200-mg guselkumab group (11.6%).
“In general, we have accepted that the IL-23 target seems to be a very safe one,” Dr. Rubin said.
A leading theory is that unlike some interleukins, IL-23 is only expressed where the body has inflammation; therefore, targeting IL-23 does not affect other areas, he explained.
If approved by the Food and Drug Administration, it would expand the official indications for guselkumab, which was approved in 2020 for psoriatic arthritis and in 2017 for plaque psoriasis.
The study was supported by Janssen Research & Development, LLC. Dr. Rubin is a consultant for Janssen. Dr. Ananthakrishnan had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON —
The primary outcome of clinical remission at 44 weeks was greater with either of two dose regimens of guselkumab than with placebo, David Rubin, MD, AGAF, reported as part of his presentation (Abstract 759) at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
Guselkumab is not the only biologic approved or in development for UC, but it is unique because of its dual action. It is an interleukin (IL)-23p19 subunit inhibitor that blocks IL-23 and also binds to the CD64 receptor on cells that produce IL-23.
Dr. Rubin, who is chief of the Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago, said he was unsure at the beginning of the trial if this dual activity “might have any value.”
Targeting both the IL-23 circulating in the tissue and the receptor remains to be proven, “but nonetheless seems reasonable,” he said.
The study included 568 people, about 42% of whom had an inadequate response or were intolerant to prior advanced therapy, and 42.5% of whom had failed two or more advanced therapy classes.
Clinical responders from two prior guselkumab induction studies were enrolled in this randomized withdrawal, double-blind maintenance trial. At either 12 weeks or 24 weeks of induction, patients were randomly assigned to subcutaneous 200-mg guselkumab every 4 weeks (n = 190), 100-mg guselkumab every 8 weeks (n = 188), or placebo (n = 190). The placebo group served as a guselkumab withdrawal group.
Participants had a mean age of 41 years and a mean disease duration of 7.8 years. The 40% using oral corticosteroids were tapered off during the study.
A total of 45.2% of the 100-mg guselkumab group and 50.0% of the 200-mg guselkumab group met the primary outcome of clinical remission at week 44 compared with 18.9% with placebo.
“It was interesting to note that the 200 mg every 4 weeks was similar in efficacy at week 44 to the 100 mg every 8 weeks. It’s much less medicine, but you get similar results,” Dr. Rubin said.
Secondary Outcomes Also Superior
“The bottom line is not only did it work, but it worked when you look at some secondary endpoints, including endoscopic remission, where the bowel is completely healed,” Dr. Rubin said in an interview.
Overall, 34% of all participants who received guselkumab achieved this outcome, “which is a very high rate,” he said. “We haven’t seen a Mayo score of zero — meaning endoscopic remission — at that rate with any of our other therapies currently.”
Among the participants who achieved clinical remission, 69% of them also showed complete remission on endoscopy.
Other secondary outcomes significantly better at week 44 vs placebo included corticosteroid-free clinical remission, maintenance of clinical remission, clinical response, symptomatic remission, endoscopic improvement, histo-endoscopic mucosal improvement, endoscopic normalization, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire remission, and fatigue response.
“It was a great study. I think it’s very promising data,” said session co-moderator Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MBBS, MPH, AGAF, director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“As we get more data from these more selective interleukins, we’ll get a better sense of how that plays out” vs other similar agents in development, he added.
IL-23 Target Seems Safe
One or more adverse events were reported by 70% of the higher-dose guselkumab group, 65% of the lower-dose guselkumab group, and 68% of the placebo group.
The most common adverse events in a combined 200-mg and 100-mg guselkumab group were lower than in the placebo group: 11.2% vs 14.1% reported COVID-19, 11.2% vs 29.7% reported exacerbation of UC, and 6.1% vs 6.8% experienced arthralgia, respectively.
No cases of active tuberculosis, opportunistic infection, anaphylaxis, serum sickness, Hy’s law, or serious hepatic issues were reported. One patient had clear cell renal carcinoma, another had rectal adenocarcinoma, and one hemorrhagic stroke was reported in the treatment groups. No patients died during the trial.
A higher proportion of people in the placebo group (13.7%) discontinued the study than those in the 100-mg guselkumab group (10.6%) and the 200-mg guselkumab group (11.6%).
“In general, we have accepted that the IL-23 target seems to be a very safe one,” Dr. Rubin said.
A leading theory is that unlike some interleukins, IL-23 is only expressed where the body has inflammation; therefore, targeting IL-23 does not affect other areas, he explained.
If approved by the Food and Drug Administration, it would expand the official indications for guselkumab, which was approved in 2020 for psoriatic arthritis and in 2017 for plaque psoriasis.
The study was supported by Janssen Research & Development, LLC. Dr. Rubin is a consultant for Janssen. Dr. Ananthakrishnan had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DDW 2024
In IBD Patients, Statin Use Associated with Lower Risk of Developing PSC
WASHINGTON — , according to a study presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
Statin use was associated with an 86% risk reduction, and only .09% of IBD patients who took statins developed PSC.
“We all take care of patients with liver disease, and we know what a significant burden PSC is. These patients have a significantly elevated risk of enhanced fibrosis and cirrhosis, multiple cancers, and cholangitis and sepsis,” said lead author Chiraag Kulkarni, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford (California) University Medical School.
“Despite this, we have to date no proven effective medical care for PSC,” he said. “However, over the last decade, there is growing evidence that statins may be beneficial in liver disease, and we see this evidence base stretching from basic science to clinical data.”
Dr. Kulkarni pointed to numerous studies that indicate statins may slow disease progression in steatotic liver disease, viral hepatitis, and cirrhosis. But could statins prevent the onset of PSC?
Because PSC incidence is low, Dr. Kulkarni and colleagues focused on a patient population with higher prevalence — those with IBD, who have an overall lifetime risk of 2% to 7%. The research team followed patients from the date of IBD diagnosis.
Among 33,813 patients with IBD in a national dataset from 2018 onward, 8813 used statins. Statin users tended to be older than non–statin users.
Overall, 181 patients developed new onset PSC during a median follow-up of about 45 months after initial IBD diagnosis. Only eight statin users (.09%) developed PSC, compared with 173 patients (.69%) in the control group.
In a propensity score-matched analysis, statin therapy was associated with a significantly lower risk of developing PSC (HR .14, P < .001). The associated E-value was 5.5, which suggested a robust finding and unlikely to be due to non-visible confounding.
The findings were consistent across secondary and sensitivity analyses, including by age, duration of statin use, and type of statin. For instance, for patients under age 50 where PSC is more likely to occur, statins were associated with a 90% reduction in PSC risk.
“We take away two things from this. First, it’s suggested that a protective effect occurs at ages where PSC is most likely to occur,” Dr. Kulkarni said. “Second, in combination with our propensity score-matched analysis, the results we are observing are not due to a survival bias, where the patients who survive to an age where statins are prescribed simply have a biologically different predilection for developing PSC.”
Statins also protected against PSC in both ulcerative colitis (HR .21) and Crohn’s disease (HR .15), as well as both women (HR .16) and men (HR .22).
Given the uncertainty about the optimal duration of statin therapy for a protective effect, Dr. Kulkarni and colleagues looked at a lag time of 12 months. They found statins were associated with an 84% risk reduction (HR .16), which was similar to the primary analysis.
The study was limited by the inability to capture dosage data or medication adherence. The findings raised several questions, Dr. Kulkarni said, such as the underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. For instance, the underlying mechanisms appear to be related to the pleiotropic effect of statins, modulation of gut inflammation, and alterations in bile acid profiles.
“This is really fascinating and interesting. I wonder about this as a primary prevention strategy in those who have normal cholesterol. Could this work or not?” said Gyongyi Szabo, MD, AGAF, chief academic officer at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, who was a moderator for the Liver & Biliary Section Distinguished Abstract Plenary Session.
Dr. Kulkarni noted that these findings wouldn’t change clinical practice alone, but based on existing literature around statin hesitancy among patients with cardiovascular disease, the risk reduction for PSC could provide another reason to encourage patients to take them.
“To move this to a place where you can actually think about primary prevention, I think the biological mechanisms need to be teased out a little bit more,” Dr. Kulkarni said. “Then I think you probably still need to identify a higher-risk group than IBD alone.”
Dr. Kulkarni declared no disclosures.
WASHINGTON — , according to a study presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
Statin use was associated with an 86% risk reduction, and only .09% of IBD patients who took statins developed PSC.
“We all take care of patients with liver disease, and we know what a significant burden PSC is. These patients have a significantly elevated risk of enhanced fibrosis and cirrhosis, multiple cancers, and cholangitis and sepsis,” said lead author Chiraag Kulkarni, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford (California) University Medical School.
“Despite this, we have to date no proven effective medical care for PSC,” he said. “However, over the last decade, there is growing evidence that statins may be beneficial in liver disease, and we see this evidence base stretching from basic science to clinical data.”
Dr. Kulkarni pointed to numerous studies that indicate statins may slow disease progression in steatotic liver disease, viral hepatitis, and cirrhosis. But could statins prevent the onset of PSC?
Because PSC incidence is low, Dr. Kulkarni and colleagues focused on a patient population with higher prevalence — those with IBD, who have an overall lifetime risk of 2% to 7%. The research team followed patients from the date of IBD diagnosis.
Among 33,813 patients with IBD in a national dataset from 2018 onward, 8813 used statins. Statin users tended to be older than non–statin users.
Overall, 181 patients developed new onset PSC during a median follow-up of about 45 months after initial IBD diagnosis. Only eight statin users (.09%) developed PSC, compared with 173 patients (.69%) in the control group.
In a propensity score-matched analysis, statin therapy was associated with a significantly lower risk of developing PSC (HR .14, P < .001). The associated E-value was 5.5, which suggested a robust finding and unlikely to be due to non-visible confounding.
The findings were consistent across secondary and sensitivity analyses, including by age, duration of statin use, and type of statin. For instance, for patients under age 50 where PSC is more likely to occur, statins were associated with a 90% reduction in PSC risk.
“We take away two things from this. First, it’s suggested that a protective effect occurs at ages where PSC is most likely to occur,” Dr. Kulkarni said. “Second, in combination with our propensity score-matched analysis, the results we are observing are not due to a survival bias, where the patients who survive to an age where statins are prescribed simply have a biologically different predilection for developing PSC.”
Statins also protected against PSC in both ulcerative colitis (HR .21) and Crohn’s disease (HR .15), as well as both women (HR .16) and men (HR .22).
Given the uncertainty about the optimal duration of statin therapy for a protective effect, Dr. Kulkarni and colleagues looked at a lag time of 12 months. They found statins were associated with an 84% risk reduction (HR .16), which was similar to the primary analysis.
The study was limited by the inability to capture dosage data or medication adherence. The findings raised several questions, Dr. Kulkarni said, such as the underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. For instance, the underlying mechanisms appear to be related to the pleiotropic effect of statins, modulation of gut inflammation, and alterations in bile acid profiles.
“This is really fascinating and interesting. I wonder about this as a primary prevention strategy in those who have normal cholesterol. Could this work or not?” said Gyongyi Szabo, MD, AGAF, chief academic officer at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, who was a moderator for the Liver & Biliary Section Distinguished Abstract Plenary Session.
Dr. Kulkarni noted that these findings wouldn’t change clinical practice alone, but based on existing literature around statin hesitancy among patients with cardiovascular disease, the risk reduction for PSC could provide another reason to encourage patients to take them.
“To move this to a place where you can actually think about primary prevention, I think the biological mechanisms need to be teased out a little bit more,” Dr. Kulkarni said. “Then I think you probably still need to identify a higher-risk group than IBD alone.”
Dr. Kulkarni declared no disclosures.
WASHINGTON — , according to a study presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
Statin use was associated with an 86% risk reduction, and only .09% of IBD patients who took statins developed PSC.
“We all take care of patients with liver disease, and we know what a significant burden PSC is. These patients have a significantly elevated risk of enhanced fibrosis and cirrhosis, multiple cancers, and cholangitis and sepsis,” said lead author Chiraag Kulkarni, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford (California) University Medical School.
“Despite this, we have to date no proven effective medical care for PSC,” he said. “However, over the last decade, there is growing evidence that statins may be beneficial in liver disease, and we see this evidence base stretching from basic science to clinical data.”
Dr. Kulkarni pointed to numerous studies that indicate statins may slow disease progression in steatotic liver disease, viral hepatitis, and cirrhosis. But could statins prevent the onset of PSC?
Because PSC incidence is low, Dr. Kulkarni and colleagues focused on a patient population with higher prevalence — those with IBD, who have an overall lifetime risk of 2% to 7%. The research team followed patients from the date of IBD diagnosis.
Among 33,813 patients with IBD in a national dataset from 2018 onward, 8813 used statins. Statin users tended to be older than non–statin users.
Overall, 181 patients developed new onset PSC during a median follow-up of about 45 months after initial IBD diagnosis. Only eight statin users (.09%) developed PSC, compared with 173 patients (.69%) in the control group.
In a propensity score-matched analysis, statin therapy was associated with a significantly lower risk of developing PSC (HR .14, P < .001). The associated E-value was 5.5, which suggested a robust finding and unlikely to be due to non-visible confounding.
The findings were consistent across secondary and sensitivity analyses, including by age, duration of statin use, and type of statin. For instance, for patients under age 50 where PSC is more likely to occur, statins were associated with a 90% reduction in PSC risk.
“We take away two things from this. First, it’s suggested that a protective effect occurs at ages where PSC is most likely to occur,” Dr. Kulkarni said. “Second, in combination with our propensity score-matched analysis, the results we are observing are not due to a survival bias, where the patients who survive to an age where statins are prescribed simply have a biologically different predilection for developing PSC.”
Statins also protected against PSC in both ulcerative colitis (HR .21) and Crohn’s disease (HR .15), as well as both women (HR .16) and men (HR .22).
Given the uncertainty about the optimal duration of statin therapy for a protective effect, Dr. Kulkarni and colleagues looked at a lag time of 12 months. They found statins were associated with an 84% risk reduction (HR .16), which was similar to the primary analysis.
The study was limited by the inability to capture dosage data or medication adherence. The findings raised several questions, Dr. Kulkarni said, such as the underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. For instance, the underlying mechanisms appear to be related to the pleiotropic effect of statins, modulation of gut inflammation, and alterations in bile acid profiles.
“This is really fascinating and interesting. I wonder about this as a primary prevention strategy in those who have normal cholesterol. Could this work or not?” said Gyongyi Szabo, MD, AGAF, chief academic officer at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, who was a moderator for the Liver & Biliary Section Distinguished Abstract Plenary Session.
Dr. Kulkarni noted that these findings wouldn’t change clinical practice alone, but based on existing literature around statin hesitancy among patients with cardiovascular disease, the risk reduction for PSC could provide another reason to encourage patients to take them.
“To move this to a place where you can actually think about primary prevention, I think the biological mechanisms need to be teased out a little bit more,” Dr. Kulkarni said. “Then I think you probably still need to identify a higher-risk group than IBD alone.”
Dr. Kulkarni declared no disclosures.
FROM DDW 2024
Mirikizumab Shows Promise for Moderate to Severe Crohn’s Disease
WASHINGTON — , according to results of the phase 3 randomized, double blind, treat-through VIVID-1 study.
Bruce E. Sands, MD, AGAF, chief of gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, reported the findings in a poster (Abstract Su1801) at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The FDA approved mirikizumab (Omvoh, Eli Lilly) to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis in October 2023.
Dr. Sands and a team of US and international collaborators studied 1065 adults with Crohn’s disease or fistulizing Crohn’s disease for 3 months or more, with a mean duration of more than 7 years. At baseline, participants had a Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD) of 7 or more and reported an inadequate response, lost response, or intolerance to other therapy.
A total of 579 people were randomly assigned to mirikizumab and another 199 to placebo. Another 287 patients received ustekinumab; though they were not included in this current analysis, the findings were presented separately at DDW 2024.
Mean age of study participants was 30 years, and men comprised 57%-59% of the groups. Nearly half (49%) of each group previously failed biologic therapy.
A primary composite endpoint was clinical response at 12 weeks according to patient reported outcome and endoscopic response at 52 weeks measured with the SES-CD. A second primary endpoint was clinical response at 12 weeks by patient reported outcome combined with clinical remission on Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) at 52 weeks.
Researchers also tracked 12 major secondary endpoints for mirikizumab vs placebo, including clinical response, endoscopic response, and clinical remission at week 12 and week 52.
Efficacy Findings
A higher percentage of participants in the mirikizumab group achieved 12-week secondary endpoints compared with placebo. In the treatment group, 32.5% reached endoscopic response vs 12.6% in the placebo group, a statistically significant difference (P < .000001). In addition, 17.6% achieved endoscopic remission in the treatment group vs 7.0% in the placebo group at 12 weeks (P < .000213).
The “treat-through” results at 52 weeks revealed that a higher proportion of the group taking mirikizumab met the co-primary endpoints compared with placebo. A total of 48.4% in the mirikizumab group vs 9.0% in the placebo group achieved endoscopic response (P < .000001). Similarly, a higher proportion met clinical remission on the CDAI, 54.1% in the treatment group vs 19.6% in the placebo group (P < .000001).
Overall, 38% of mirikizumab-treated patients vs 9% of the placebo group reached a composite endpoint of patient reported clinical response at week 12 and endoscopic response by SES-CD at week 52 (P < .000001).
Dr. Sands and colleagues also combined clinical response reported by patients at 12 weeks with CDAI findings for clinical remission at week 52. A total of 45.4% in the treatment group met the combined endpoint compared with 19.6% of the placebo group (P < .000001).
In an additional analysis, the researchers looked at this composite endpoint in patients in both groups who had failed or not failed a prior biologic for a total of 43.4% vs 12.4%, and 47.3% vs 26.5%, respectively.
“Mirikizumab demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements” in the study co-primary endpoints and secondary endpoints compared with placebo, the researchers concluded.
Safety Findings
Safety outcomes during the 52-week study were “consistent with the known safety profile” of mirikizumab, the researchers noted.
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 78.6% of mirikizumab participants vs 73.0% of the placebo group. The most common were COVID-19, anemia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events were reported in 10.3% of the mirikizumab group vs 17.1% of the placebo group. There were seven opportunistic infections in the treatment group, including herpes zoster and Candida, compared with none in the placebo group.
One person in the placebo cohort died of a pulmonary embolism; there were no deaths in the mirikizumab group.
People randomly assigned to placebo without a response at 12 weeks were switched over to mirikizumab. However, the findings from this group between 12 and 52 weeks were excluded from the 1-year data presented at DDW 2024, including one death from worsening Crohn’s disease during that time.
Mirikizumab looked particularly robust in this study, and it may turn out to be a critically important option for our patients, said Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH, co-director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at NYU Langone Health in New York City. Dr. Axelrad was not involved in this study.
Of importance, effect sizes were similar for “bio-naive and previously biologic-exposed patients,” he added.
These data “really underscore that therapies targeting IL-23 may be clinically useful for Crohn’s disease patients with prior biologic failure, representing a significant departure from our previous experience with other biologic classes,” Dr. Axelrad said.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Sands is a consultant and receives grant funding from Lilly. Dr. Axelrad had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , according to results of the phase 3 randomized, double blind, treat-through VIVID-1 study.
Bruce E. Sands, MD, AGAF, chief of gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, reported the findings in a poster (Abstract Su1801) at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The FDA approved mirikizumab (Omvoh, Eli Lilly) to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis in October 2023.
Dr. Sands and a team of US and international collaborators studied 1065 adults with Crohn’s disease or fistulizing Crohn’s disease for 3 months or more, with a mean duration of more than 7 years. At baseline, participants had a Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD) of 7 or more and reported an inadequate response, lost response, or intolerance to other therapy.
A total of 579 people were randomly assigned to mirikizumab and another 199 to placebo. Another 287 patients received ustekinumab; though they were not included in this current analysis, the findings were presented separately at DDW 2024.
Mean age of study participants was 30 years, and men comprised 57%-59% of the groups. Nearly half (49%) of each group previously failed biologic therapy.
A primary composite endpoint was clinical response at 12 weeks according to patient reported outcome and endoscopic response at 52 weeks measured with the SES-CD. A second primary endpoint was clinical response at 12 weeks by patient reported outcome combined with clinical remission on Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) at 52 weeks.
Researchers also tracked 12 major secondary endpoints for mirikizumab vs placebo, including clinical response, endoscopic response, and clinical remission at week 12 and week 52.
Efficacy Findings
A higher percentage of participants in the mirikizumab group achieved 12-week secondary endpoints compared with placebo. In the treatment group, 32.5% reached endoscopic response vs 12.6% in the placebo group, a statistically significant difference (P < .000001). In addition, 17.6% achieved endoscopic remission in the treatment group vs 7.0% in the placebo group at 12 weeks (P < .000213).
The “treat-through” results at 52 weeks revealed that a higher proportion of the group taking mirikizumab met the co-primary endpoints compared with placebo. A total of 48.4% in the mirikizumab group vs 9.0% in the placebo group achieved endoscopic response (P < .000001). Similarly, a higher proportion met clinical remission on the CDAI, 54.1% in the treatment group vs 19.6% in the placebo group (P < .000001).
Overall, 38% of mirikizumab-treated patients vs 9% of the placebo group reached a composite endpoint of patient reported clinical response at week 12 and endoscopic response by SES-CD at week 52 (P < .000001).
Dr. Sands and colleagues also combined clinical response reported by patients at 12 weeks with CDAI findings for clinical remission at week 52. A total of 45.4% in the treatment group met the combined endpoint compared with 19.6% of the placebo group (P < .000001).
In an additional analysis, the researchers looked at this composite endpoint in patients in both groups who had failed or not failed a prior biologic for a total of 43.4% vs 12.4%, and 47.3% vs 26.5%, respectively.
“Mirikizumab demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements” in the study co-primary endpoints and secondary endpoints compared with placebo, the researchers concluded.
Safety Findings
Safety outcomes during the 52-week study were “consistent with the known safety profile” of mirikizumab, the researchers noted.
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 78.6% of mirikizumab participants vs 73.0% of the placebo group. The most common were COVID-19, anemia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events were reported in 10.3% of the mirikizumab group vs 17.1% of the placebo group. There were seven opportunistic infections in the treatment group, including herpes zoster and Candida, compared with none in the placebo group.
One person in the placebo cohort died of a pulmonary embolism; there were no deaths in the mirikizumab group.
People randomly assigned to placebo without a response at 12 weeks were switched over to mirikizumab. However, the findings from this group between 12 and 52 weeks were excluded from the 1-year data presented at DDW 2024, including one death from worsening Crohn’s disease during that time.
Mirikizumab looked particularly robust in this study, and it may turn out to be a critically important option for our patients, said Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH, co-director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at NYU Langone Health in New York City. Dr. Axelrad was not involved in this study.
Of importance, effect sizes were similar for “bio-naive and previously biologic-exposed patients,” he added.
These data “really underscore that therapies targeting IL-23 may be clinically useful for Crohn’s disease patients with prior biologic failure, representing a significant departure from our previous experience with other biologic classes,” Dr. Axelrad said.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Sands is a consultant and receives grant funding from Lilly. Dr. Axelrad had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , according to results of the phase 3 randomized, double blind, treat-through VIVID-1 study.
Bruce E. Sands, MD, AGAF, chief of gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, reported the findings in a poster (Abstract Su1801) at the annual Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
The FDA approved mirikizumab (Omvoh, Eli Lilly) to treat moderate to severe ulcerative colitis in October 2023.
Dr. Sands and a team of US and international collaborators studied 1065 adults with Crohn’s disease or fistulizing Crohn’s disease for 3 months or more, with a mean duration of more than 7 years. At baseline, participants had a Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s Disease (SES-CD) of 7 or more and reported an inadequate response, lost response, or intolerance to other therapy.
A total of 579 people were randomly assigned to mirikizumab and another 199 to placebo. Another 287 patients received ustekinumab; though they were not included in this current analysis, the findings were presented separately at DDW 2024.
Mean age of study participants was 30 years, and men comprised 57%-59% of the groups. Nearly half (49%) of each group previously failed biologic therapy.
A primary composite endpoint was clinical response at 12 weeks according to patient reported outcome and endoscopic response at 52 weeks measured with the SES-CD. A second primary endpoint was clinical response at 12 weeks by patient reported outcome combined with clinical remission on Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) at 52 weeks.
Researchers also tracked 12 major secondary endpoints for mirikizumab vs placebo, including clinical response, endoscopic response, and clinical remission at week 12 and week 52.
Efficacy Findings
A higher percentage of participants in the mirikizumab group achieved 12-week secondary endpoints compared with placebo. In the treatment group, 32.5% reached endoscopic response vs 12.6% in the placebo group, a statistically significant difference (P < .000001). In addition, 17.6% achieved endoscopic remission in the treatment group vs 7.0% in the placebo group at 12 weeks (P < .000213).
The “treat-through” results at 52 weeks revealed that a higher proportion of the group taking mirikizumab met the co-primary endpoints compared with placebo. A total of 48.4% in the mirikizumab group vs 9.0% in the placebo group achieved endoscopic response (P < .000001). Similarly, a higher proportion met clinical remission on the CDAI, 54.1% in the treatment group vs 19.6% in the placebo group (P < .000001).
Overall, 38% of mirikizumab-treated patients vs 9% of the placebo group reached a composite endpoint of patient reported clinical response at week 12 and endoscopic response by SES-CD at week 52 (P < .000001).
Dr. Sands and colleagues also combined clinical response reported by patients at 12 weeks with CDAI findings for clinical remission at week 52. A total of 45.4% in the treatment group met the combined endpoint compared with 19.6% of the placebo group (P < .000001).
In an additional analysis, the researchers looked at this composite endpoint in patients in both groups who had failed or not failed a prior biologic for a total of 43.4% vs 12.4%, and 47.3% vs 26.5%, respectively.
“Mirikizumab demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements” in the study co-primary endpoints and secondary endpoints compared with placebo, the researchers concluded.
Safety Findings
Safety outcomes during the 52-week study were “consistent with the known safety profile” of mirikizumab, the researchers noted.
Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 78.6% of mirikizumab participants vs 73.0% of the placebo group. The most common were COVID-19, anemia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events were reported in 10.3% of the mirikizumab group vs 17.1% of the placebo group. There were seven opportunistic infections in the treatment group, including herpes zoster and Candida, compared with none in the placebo group.
One person in the placebo cohort died of a pulmonary embolism; there were no deaths in the mirikizumab group.
People randomly assigned to placebo without a response at 12 weeks were switched over to mirikizumab. However, the findings from this group between 12 and 52 weeks were excluded from the 1-year data presented at DDW 2024, including one death from worsening Crohn’s disease during that time.
Mirikizumab looked particularly robust in this study, and it may turn out to be a critically important option for our patients, said Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH, co-director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at NYU Langone Health in New York City. Dr. Axelrad was not involved in this study.
Of importance, effect sizes were similar for “bio-naive and previously biologic-exposed patients,” he added.
These data “really underscore that therapies targeting IL-23 may be clinically useful for Crohn’s disease patients with prior biologic failure, representing a significant departure from our previous experience with other biologic classes,” Dr. Axelrad said.
The study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. Dr. Sands is a consultant and receives grant funding from Lilly. Dr. Axelrad had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DDW 2024
Green Initiative Reduces Endoscopic Waste During Colonoscopies
WASHINGTON — As part of a quality improvement initiative, , according to a study presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
After discussing environmentally conscious practices during regular meetings, the odds of gastroenterologists using a single tool — either biopsy forceps or a snare — compared with multiple disposable tools was three times higher.
“The burden of waste is massive, with GI being the third-largest waste generator in healthcare. The number of procedures is increasing, which just means more waste, and we have to look at ways to reduce it,” said lead author Prateek Harne, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at the University of Texas Health Science Center.
Overall, the healthcare industry generates 8.5% of U.S. greenhouse emissions, with more than 70% coming from used instruments and supplies, he said. GI endoscopy generates 85,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide waste annually. That waste stems from high case volumes, patient travel, the decontamination process, and single-use devices.
After seeing the waste at his institution, Dr. Harne wondered how to reduce single-use device and nonrenewable waste, particularly the tools used during polypectomies. He and colleagues decided to focus on single-tool use and collected data about the tools used during screening colonoscopies for 8 weeks before an intervention.
As part of the intervention, Dr. Harne and colleagues discussed green endoscopy initiatives supported by North American gastrointestinal societies during a journal club meeting with gastroenterology faculty. They also discussed potential strategies to reduce waste in day-to-day practice during a monthly business meeting, particularly focused on being mindful of using tools during polypectomies. The meetings occurred 3 days apart.
Then Dr. Harne and colleagues collected data regarding tool use during screening colonoscopies, looking at the number and type of instruments used. Before the meetings, 210 patients underwent colonoscopies, including 34% that required no intervention, 32% that required one tool, and 33% that required multiple tools.
After the meetings, 112 patients underwent colonoscopies, including 34% that required no tools, 49% that used one tool, and 17% that used multiple tools. This represented a 17% increase in the use of one tool (P < .01) and a 16% decrease in the use of multiple tools (P < .01). The odds of using a single tool compared with multiple tools was 2.98, and there was a statistically significant increase in uptake of snare for polypectomy.
The study was limited by being at a single center, having a small sample size, and using a short-term assessment. At the same time, the findings show potential for a low-cost solution through open discussion with gastroenterologists.
“Sir Isaac Newton had two holes for two different sized cats in his home, but all of his cats ended up using the bigger hole,” Dr. Harne said in his conclusion. “Maybe we can do the same for polypectomies and use only the tools that we need.”
In an interview, Dr. Harne noted he spoke with the janitorial staff at his institution to learn more about endoscopy unit waste, including how much is recycled, how much is incinerated, and who handles the waste. He recognized the work being done in Europe to understand and reduce endoscopic waste and hopes U.S. groups begin to implement more measures.
“Gastroenterologists and their teams need to be more cognizant of the impact we have on the environment,” Dr. Harne said. “As our study shows, if providers are aware that they can and should use fewer tools to get the same results, it can lead to a statistically significant impact, just with a friendly reminder to reduce use.”
After the presentation, Dr. Harne discussed other shifts with conference attendees, such as not opening or unwrapping tools until needed during a procedure.
“Small changes could have big impacts. Everything that we do in QI [quality improvement] is meant to help patients and the environment,” said Amanda Krouse, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Diego, who was a moderator of the DDW session on GI fellow–directed QI projects.
In an interview, Alana Persaud, MD, an endoscopy fellow at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pennsylvania, also a moderator of the session, said: “Ultimately, the medical services we’re providing are for the longevity of our patients, but at the same time, we don’t want it to be to the detriment of the environment, so paying attention to green endoscopy when we can preserve and use more discretion with our devices is worth it so we can all thrive together.”
Dr. Harne did not have any disclosures.
WASHINGTON — As part of a quality improvement initiative, , according to a study presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
After discussing environmentally conscious practices during regular meetings, the odds of gastroenterologists using a single tool — either biopsy forceps or a snare — compared with multiple disposable tools was three times higher.
“The burden of waste is massive, with GI being the third-largest waste generator in healthcare. The number of procedures is increasing, which just means more waste, and we have to look at ways to reduce it,” said lead author Prateek Harne, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at the University of Texas Health Science Center.
Overall, the healthcare industry generates 8.5% of U.S. greenhouse emissions, with more than 70% coming from used instruments and supplies, he said. GI endoscopy generates 85,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide waste annually. That waste stems from high case volumes, patient travel, the decontamination process, and single-use devices.
After seeing the waste at his institution, Dr. Harne wondered how to reduce single-use device and nonrenewable waste, particularly the tools used during polypectomies. He and colleagues decided to focus on single-tool use and collected data about the tools used during screening colonoscopies for 8 weeks before an intervention.
As part of the intervention, Dr. Harne and colleagues discussed green endoscopy initiatives supported by North American gastrointestinal societies during a journal club meeting with gastroenterology faculty. They also discussed potential strategies to reduce waste in day-to-day practice during a monthly business meeting, particularly focused on being mindful of using tools during polypectomies. The meetings occurred 3 days apart.
Then Dr. Harne and colleagues collected data regarding tool use during screening colonoscopies, looking at the number and type of instruments used. Before the meetings, 210 patients underwent colonoscopies, including 34% that required no intervention, 32% that required one tool, and 33% that required multiple tools.
After the meetings, 112 patients underwent colonoscopies, including 34% that required no tools, 49% that used one tool, and 17% that used multiple tools. This represented a 17% increase in the use of one tool (P < .01) and a 16% decrease in the use of multiple tools (P < .01). The odds of using a single tool compared with multiple tools was 2.98, and there was a statistically significant increase in uptake of snare for polypectomy.
The study was limited by being at a single center, having a small sample size, and using a short-term assessment. At the same time, the findings show potential for a low-cost solution through open discussion with gastroenterologists.
“Sir Isaac Newton had two holes for two different sized cats in his home, but all of his cats ended up using the bigger hole,” Dr. Harne said in his conclusion. “Maybe we can do the same for polypectomies and use only the tools that we need.”
In an interview, Dr. Harne noted he spoke with the janitorial staff at his institution to learn more about endoscopy unit waste, including how much is recycled, how much is incinerated, and who handles the waste. He recognized the work being done in Europe to understand and reduce endoscopic waste and hopes U.S. groups begin to implement more measures.
“Gastroenterologists and their teams need to be more cognizant of the impact we have on the environment,” Dr. Harne said. “As our study shows, if providers are aware that they can and should use fewer tools to get the same results, it can lead to a statistically significant impact, just with a friendly reminder to reduce use.”
After the presentation, Dr. Harne discussed other shifts with conference attendees, such as not opening or unwrapping tools until needed during a procedure.
“Small changes could have big impacts. Everything that we do in QI [quality improvement] is meant to help patients and the environment,” said Amanda Krouse, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Diego, who was a moderator of the DDW session on GI fellow–directed QI projects.
In an interview, Alana Persaud, MD, an endoscopy fellow at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pennsylvania, also a moderator of the session, said: “Ultimately, the medical services we’re providing are for the longevity of our patients, but at the same time, we don’t want it to be to the detriment of the environment, so paying attention to green endoscopy when we can preserve and use more discretion with our devices is worth it so we can all thrive together.”
Dr. Harne did not have any disclosures.
WASHINGTON — As part of a quality improvement initiative, , according to a study presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW).
After discussing environmentally conscious practices during regular meetings, the odds of gastroenterologists using a single tool — either biopsy forceps or a snare — compared with multiple disposable tools was three times higher.
“The burden of waste is massive, with GI being the third-largest waste generator in healthcare. The number of procedures is increasing, which just means more waste, and we have to look at ways to reduce it,” said lead author Prateek Harne, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at the University of Texas Health Science Center.
Overall, the healthcare industry generates 8.5% of U.S. greenhouse emissions, with more than 70% coming from used instruments and supplies, he said. GI endoscopy generates 85,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide waste annually. That waste stems from high case volumes, patient travel, the decontamination process, and single-use devices.
After seeing the waste at his institution, Dr. Harne wondered how to reduce single-use device and nonrenewable waste, particularly the tools used during polypectomies. He and colleagues decided to focus on single-tool use and collected data about the tools used during screening colonoscopies for 8 weeks before an intervention.
As part of the intervention, Dr. Harne and colleagues discussed green endoscopy initiatives supported by North American gastrointestinal societies during a journal club meeting with gastroenterology faculty. They also discussed potential strategies to reduce waste in day-to-day practice during a monthly business meeting, particularly focused on being mindful of using tools during polypectomies. The meetings occurred 3 days apart.
Then Dr. Harne and colleagues collected data regarding tool use during screening colonoscopies, looking at the number and type of instruments used. Before the meetings, 210 patients underwent colonoscopies, including 34% that required no intervention, 32% that required one tool, and 33% that required multiple tools.
After the meetings, 112 patients underwent colonoscopies, including 34% that required no tools, 49% that used one tool, and 17% that used multiple tools. This represented a 17% increase in the use of one tool (P < .01) and a 16% decrease in the use of multiple tools (P < .01). The odds of using a single tool compared with multiple tools was 2.98, and there was a statistically significant increase in uptake of snare for polypectomy.
The study was limited by being at a single center, having a small sample size, and using a short-term assessment. At the same time, the findings show potential for a low-cost solution through open discussion with gastroenterologists.
“Sir Isaac Newton had two holes for two different sized cats in his home, but all of his cats ended up using the bigger hole,” Dr. Harne said in his conclusion. “Maybe we can do the same for polypectomies and use only the tools that we need.”
In an interview, Dr. Harne noted he spoke with the janitorial staff at his institution to learn more about endoscopy unit waste, including how much is recycled, how much is incinerated, and who handles the waste. He recognized the work being done in Europe to understand and reduce endoscopic waste and hopes U.S. groups begin to implement more measures.
“Gastroenterologists and their teams need to be more cognizant of the impact we have on the environment,” Dr. Harne said. “As our study shows, if providers are aware that they can and should use fewer tools to get the same results, it can lead to a statistically significant impact, just with a friendly reminder to reduce use.”
After the presentation, Dr. Harne discussed other shifts with conference attendees, such as not opening or unwrapping tools until needed during a procedure.
“Small changes could have big impacts. Everything that we do in QI [quality improvement] is meant to help patients and the environment,” said Amanda Krouse, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Diego, who was a moderator of the DDW session on GI fellow–directed QI projects.
In an interview, Alana Persaud, MD, an endoscopy fellow at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pennsylvania, also a moderator of the session, said: “Ultimately, the medical services we’re providing are for the longevity of our patients, but at the same time, we don’t want it to be to the detriment of the environment, so paying attention to green endoscopy when we can preserve and use more discretion with our devices is worth it so we can all thrive together.”
Dr. Harne did not have any disclosures.
FROM DDW 2024
Genes May Govern Intestinal Sites of Pediatric Crohn’s
, a small analysis in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology suggests.
Richard Kellermayer, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics in the Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, and colleagues compared the genetic makeup of patients based on their Crohn’s disease location — predominantly in the small bowel (L4) or predominantly in the colon (L2 and/or L3). They then generated bipartite networks of susceptibility genes to study the polygenic background of the disease subtypes. They hypothesize that such networks may govern where a patient develops Crohn’s disease.
According to current understanding, as Dr. Kellermayer told GI & Hepatology News, most autoimmune disorders, CD included, develop in people with a genetic predisposition after serial environmental insults between conception and young adulthood. “As opposed to single-gene-associated genetic disorders, autoimmune diseases are linked to several hundred genes in which subtle anomalies can work in concert to predispose someone to a certain disorder,” he said. “We hope our findings will guide the development of personalized treatments based on the disease location at diagnosis to advance precision medicine.”
CD cases
Eight cases of SB-CD and 11 of C-CD met the inclusion criteria. Mean age at CD diagnosis was about 11 years for both subtypes, while 36.3% of patients with C-CD were female vs 25% of those with SB-CD. Ethnicity was 72.2% White in the C-CD group and 87.5% in the SB-CD group.
As to the main ileocolonic locations according to the Paris Classification of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease, 54.5% in the C-CD group had involvement at L2 and 45.5% at L3. In SB-CD cases, 100% had disease at L4b, 37.5% at L4, and 50% at L1.
The researchers identified 115 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with a combined annotation-dependent depletion (CADD) score on Phil’s Read Editor (PHRED) of >10 that was associated with 97 genes. PHRED is a computer program measuring the quality of the identification of nucleobases generated by automated DNA sequencing and scores the deleteriousness of single-nucleotide variants. The identified genes in this study had a significantly (P < .01) different allele variation between C-CD and SB-CD.
Among the top 28 candidates was an SNP in the EFNA3 gene with a CADD score > 20 for differentiating between the two phenotypically distinct CD groups. Furthermore, the EFNA3 rs17723260 (predicted to be deleterious) was found to have a significantly lower allele frequency (4.5%) in C-CD compared with its allele frequency of 37.5% in SB-CD (chi square P = .0097).
“This finding indicates that EFNA3 might play a role in modulating colonic inflammation, in which a deleterious genetic defect might provide protection against colitis (and direct autoimmunity against the proximal small bowel) in the polygenic background of CD,” the investigators wrote.
EFNA3 has been linked to both CD and ulcerative colitis. Another four genes associated with the top five SNP candidates had already been connected with IBD or mammalian intestinal inflammation.
According to the authors, the biomedical literature and mouse model findings “implicate the translational relevance of our candidate gene compendium for directing colon- vs small-bowel–predominant CD development.” They hope the findings will be replicated in larger CD cohorts differentiated by disease location. “Our work may set the nidus for CD subtype–based precision medicine by guiding individualized treatment strategies,” they wrote.
This study was supported by the ProKIIDS Network of the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation and the Public Health Service. It was also supported by the Wagner, Frugoni, and Klaasmeyer families’ Gutsy Kids Fund and by the DR and GL Laws Fund. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
, a small analysis in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology suggests.
Richard Kellermayer, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics in the Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, and colleagues compared the genetic makeup of patients based on their Crohn’s disease location — predominantly in the small bowel (L4) or predominantly in the colon (L2 and/or L3). They then generated bipartite networks of susceptibility genes to study the polygenic background of the disease subtypes. They hypothesize that such networks may govern where a patient develops Crohn’s disease.
According to current understanding, as Dr. Kellermayer told GI & Hepatology News, most autoimmune disorders, CD included, develop in people with a genetic predisposition after serial environmental insults between conception and young adulthood. “As opposed to single-gene-associated genetic disorders, autoimmune diseases are linked to several hundred genes in which subtle anomalies can work in concert to predispose someone to a certain disorder,” he said. “We hope our findings will guide the development of personalized treatments based on the disease location at diagnosis to advance precision medicine.”
CD cases
Eight cases of SB-CD and 11 of C-CD met the inclusion criteria. Mean age at CD diagnosis was about 11 years for both subtypes, while 36.3% of patients with C-CD were female vs 25% of those with SB-CD. Ethnicity was 72.2% White in the C-CD group and 87.5% in the SB-CD group.
As to the main ileocolonic locations according to the Paris Classification of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease, 54.5% in the C-CD group had involvement at L2 and 45.5% at L3. In SB-CD cases, 100% had disease at L4b, 37.5% at L4, and 50% at L1.
The researchers identified 115 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with a combined annotation-dependent depletion (CADD) score on Phil’s Read Editor (PHRED) of >10 that was associated with 97 genes. PHRED is a computer program measuring the quality of the identification of nucleobases generated by automated DNA sequencing and scores the deleteriousness of single-nucleotide variants. The identified genes in this study had a significantly (P < .01) different allele variation between C-CD and SB-CD.
Among the top 28 candidates was an SNP in the EFNA3 gene with a CADD score > 20 for differentiating between the two phenotypically distinct CD groups. Furthermore, the EFNA3 rs17723260 (predicted to be deleterious) was found to have a significantly lower allele frequency (4.5%) in C-CD compared with its allele frequency of 37.5% in SB-CD (chi square P = .0097).
“This finding indicates that EFNA3 might play a role in modulating colonic inflammation, in which a deleterious genetic defect might provide protection against colitis (and direct autoimmunity against the proximal small bowel) in the polygenic background of CD,” the investigators wrote.
EFNA3 has been linked to both CD and ulcerative colitis. Another four genes associated with the top five SNP candidates had already been connected with IBD or mammalian intestinal inflammation.
According to the authors, the biomedical literature and mouse model findings “implicate the translational relevance of our candidate gene compendium for directing colon- vs small-bowel–predominant CD development.” They hope the findings will be replicated in larger CD cohorts differentiated by disease location. “Our work may set the nidus for CD subtype–based precision medicine by guiding individualized treatment strategies,” they wrote.
This study was supported by the ProKIIDS Network of the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation and the Public Health Service. It was also supported by the Wagner, Frugoni, and Klaasmeyer families’ Gutsy Kids Fund and by the DR and GL Laws Fund. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
, a small analysis in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology suggests.
Richard Kellermayer, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics in the Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, and colleagues compared the genetic makeup of patients based on their Crohn’s disease location — predominantly in the small bowel (L4) or predominantly in the colon (L2 and/or L3). They then generated bipartite networks of susceptibility genes to study the polygenic background of the disease subtypes. They hypothesize that such networks may govern where a patient develops Crohn’s disease.
According to current understanding, as Dr. Kellermayer told GI & Hepatology News, most autoimmune disorders, CD included, develop in people with a genetic predisposition after serial environmental insults between conception and young adulthood. “As opposed to single-gene-associated genetic disorders, autoimmune diseases are linked to several hundred genes in which subtle anomalies can work in concert to predispose someone to a certain disorder,” he said. “We hope our findings will guide the development of personalized treatments based on the disease location at diagnosis to advance precision medicine.”
CD cases
Eight cases of SB-CD and 11 of C-CD met the inclusion criteria. Mean age at CD diagnosis was about 11 years for both subtypes, while 36.3% of patients with C-CD were female vs 25% of those with SB-CD. Ethnicity was 72.2% White in the C-CD group and 87.5% in the SB-CD group.
As to the main ileocolonic locations according to the Paris Classification of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease, 54.5% in the C-CD group had involvement at L2 and 45.5% at L3. In SB-CD cases, 100% had disease at L4b, 37.5% at L4, and 50% at L1.
The researchers identified 115 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with a combined annotation-dependent depletion (CADD) score on Phil’s Read Editor (PHRED) of >10 that was associated with 97 genes. PHRED is a computer program measuring the quality of the identification of nucleobases generated by automated DNA sequencing and scores the deleteriousness of single-nucleotide variants. The identified genes in this study had a significantly (P < .01) different allele variation between C-CD and SB-CD.
Among the top 28 candidates was an SNP in the EFNA3 gene with a CADD score > 20 for differentiating between the two phenotypically distinct CD groups. Furthermore, the EFNA3 rs17723260 (predicted to be deleterious) was found to have a significantly lower allele frequency (4.5%) in C-CD compared with its allele frequency of 37.5% in SB-CD (chi square P = .0097).
“This finding indicates that EFNA3 might play a role in modulating colonic inflammation, in which a deleterious genetic defect might provide protection against colitis (and direct autoimmunity against the proximal small bowel) in the polygenic background of CD,” the investigators wrote.
EFNA3 has been linked to both CD and ulcerative colitis. Another four genes associated with the top five SNP candidates had already been connected with IBD or mammalian intestinal inflammation.
According to the authors, the biomedical literature and mouse model findings “implicate the translational relevance of our candidate gene compendium for directing colon- vs small-bowel–predominant CD development.” They hope the findings will be replicated in larger CD cohorts differentiated by disease location. “Our work may set the nidus for CD subtype–based precision medicine by guiding individualized treatment strategies,” they wrote.
This study was supported by the ProKIIDS Network of the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation and the Public Health Service. It was also supported by the Wagner, Frugoni, and Klaasmeyer families’ Gutsy Kids Fund and by the DR and GL Laws Fund. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY