User login
Large cohort study IDs prognostic factors in thromboangiitis obliterans
CHICAGO – Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection at diagnosis predict vascular events in patients with thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO), and the latter also predicts amputation, which occurs within 10 years of diagnosis in nearly a third of patients, according to findings from a large retrospective French cohort study.
After a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 58.9% of 224 patients with TAO – also known as Buerger’s disease – experienced a vascular event, 21.4% experienced at least one amputation, and 1.3% died, Alexandre Le Joncour, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The 5- and 15-year vascular event-free survival rates were 45% and 28%, respectively, and the 10- and 15-year amputation-free survival rates were 74%, and 66%, respectively, said Dr. Le Joncour of Sorbonne University, Paris.
Of note, no significant difference was seen in the vascular event-free survival rates based on tobacco use levels (more than 22 pack-years vs. 22 or fewer pack-years; HR, 1.2), he said.
Patient characteristics and clinical factors found to independently predict vascular events included nonwhite ethnicity (hazard ratio, 2.35; P = .005) and limb infection at diagnosis (HR, 3.29; P = .045). Limb infection at diagnosis also independently predicted amputation (HR, 12.1; P less than .001), he said.
“But there was no significant [association with amputation] in patients who had claudication, critical ischemia, or ischemic ulcers/necrosis,” he noted, adding that a comparison of white and nonwhite patients showed that the groups were similar with respect to epidemiologic and cardiovascular factors, clinical symptom distribution, and rates of addiction to tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs.
It was also clear that patients who quit using tobacco had a significantly lower risk of amputation than did those who continued using tobacco (P = .001), he said, explaining that 43 of the 48 patients who experienced amputation were current smokers, and 5 were ex-smokers at the time of amputation.
Dr. Le Joncour and his colleagues included TAO patients diagnosed between 1967 and 2016 at a median age of 36 years at the time of first symptoms, with a median of 12 months from symptom onset until diagnosis. About 76% were men, and about 83% were white. Patients with diabetes, atherosclerosis, arterial emboli, connective tissue disease, and/or thrombophilia were excluded.
Vascular events in this study were defined as “an acute worsening of the disease course requiring treatment modifications,” and included critical ischemia (35% of cases), ulcers/necrosis (33%), claudication worsening (16%), deep vein thrombosis (3%), superficial phlebitis (7%), limb infection (4%), and “other” events (2%).
Major amputation was defined as “an amputation involving the tibio-tarsian articulation for lower limbs and the metacarpophalangeal articulation for upper limbs,” he explained.
The median time to amputation was 4 years, and patients who experienced amputation had a median age of 39 years. Half of the 48 patients who experienced amputation had one amputation, nearly a third had two amputations, and 19% had three amputations. About two-thirds had minor amputations and a third had major amputations.
The findings provide important prognostic information regarding TAO, Dr. Le Joncour said, noting that long-term data on outcomes in TAO patients have been lacking.
“We found specific characteristics that identified those at highest risk for subsequent vascular complications, and these factors are not only important predictors of vascular complications or relapse, but may also serve to adjust more aggressive management and close follow-up of these patients,” he concluded.
Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
CHICAGO – Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection at diagnosis predict vascular events in patients with thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO), and the latter also predicts amputation, which occurs within 10 years of diagnosis in nearly a third of patients, according to findings from a large retrospective French cohort study.
After a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 58.9% of 224 patients with TAO – also known as Buerger’s disease – experienced a vascular event, 21.4% experienced at least one amputation, and 1.3% died, Alexandre Le Joncour, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The 5- and 15-year vascular event-free survival rates were 45% and 28%, respectively, and the 10- and 15-year amputation-free survival rates were 74%, and 66%, respectively, said Dr. Le Joncour of Sorbonne University, Paris.
Of note, no significant difference was seen in the vascular event-free survival rates based on tobacco use levels (more than 22 pack-years vs. 22 or fewer pack-years; HR, 1.2), he said.
Patient characteristics and clinical factors found to independently predict vascular events included nonwhite ethnicity (hazard ratio, 2.35; P = .005) and limb infection at diagnosis (HR, 3.29; P = .045). Limb infection at diagnosis also independently predicted amputation (HR, 12.1; P less than .001), he said.
“But there was no significant [association with amputation] in patients who had claudication, critical ischemia, or ischemic ulcers/necrosis,” he noted, adding that a comparison of white and nonwhite patients showed that the groups were similar with respect to epidemiologic and cardiovascular factors, clinical symptom distribution, and rates of addiction to tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs.
It was also clear that patients who quit using tobacco had a significantly lower risk of amputation than did those who continued using tobacco (P = .001), he said, explaining that 43 of the 48 patients who experienced amputation were current smokers, and 5 were ex-smokers at the time of amputation.
Dr. Le Joncour and his colleagues included TAO patients diagnosed between 1967 and 2016 at a median age of 36 years at the time of first symptoms, with a median of 12 months from symptom onset until diagnosis. About 76% were men, and about 83% were white. Patients with diabetes, atherosclerosis, arterial emboli, connective tissue disease, and/or thrombophilia were excluded.
Vascular events in this study were defined as “an acute worsening of the disease course requiring treatment modifications,” and included critical ischemia (35% of cases), ulcers/necrosis (33%), claudication worsening (16%), deep vein thrombosis (3%), superficial phlebitis (7%), limb infection (4%), and “other” events (2%).
Major amputation was defined as “an amputation involving the tibio-tarsian articulation for lower limbs and the metacarpophalangeal articulation for upper limbs,” he explained.
The median time to amputation was 4 years, and patients who experienced amputation had a median age of 39 years. Half of the 48 patients who experienced amputation had one amputation, nearly a third had two amputations, and 19% had three amputations. About two-thirds had minor amputations and a third had major amputations.
The findings provide important prognostic information regarding TAO, Dr. Le Joncour said, noting that long-term data on outcomes in TAO patients have been lacking.
“We found specific characteristics that identified those at highest risk for subsequent vascular complications, and these factors are not only important predictors of vascular complications or relapse, but may also serve to adjust more aggressive management and close follow-up of these patients,” he concluded.
Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
CHICAGO – Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection at diagnosis predict vascular events in patients with thromboangiitis obliterans (TAO), and the latter also predicts amputation, which occurs within 10 years of diagnosis in nearly a third of patients, according to findings from a large retrospective French cohort study.
After a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 58.9% of 224 patients with TAO – also known as Buerger’s disease – experienced a vascular event, 21.4% experienced at least one amputation, and 1.3% died, Alexandre Le Joncour, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The 5- and 15-year vascular event-free survival rates were 45% and 28%, respectively, and the 10- and 15-year amputation-free survival rates were 74%, and 66%, respectively, said Dr. Le Joncour of Sorbonne University, Paris.
Of note, no significant difference was seen in the vascular event-free survival rates based on tobacco use levels (more than 22 pack-years vs. 22 or fewer pack-years; HR, 1.2), he said.
Patient characteristics and clinical factors found to independently predict vascular events included nonwhite ethnicity (hazard ratio, 2.35; P = .005) and limb infection at diagnosis (HR, 3.29; P = .045). Limb infection at diagnosis also independently predicted amputation (HR, 12.1; P less than .001), he said.
“But there was no significant [association with amputation] in patients who had claudication, critical ischemia, or ischemic ulcers/necrosis,” he noted, adding that a comparison of white and nonwhite patients showed that the groups were similar with respect to epidemiologic and cardiovascular factors, clinical symptom distribution, and rates of addiction to tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs.
It was also clear that patients who quit using tobacco had a significantly lower risk of amputation than did those who continued using tobacco (P = .001), he said, explaining that 43 of the 48 patients who experienced amputation were current smokers, and 5 were ex-smokers at the time of amputation.
Dr. Le Joncour and his colleagues included TAO patients diagnosed between 1967 and 2016 at a median age of 36 years at the time of first symptoms, with a median of 12 months from symptom onset until diagnosis. About 76% were men, and about 83% were white. Patients with diabetes, atherosclerosis, arterial emboli, connective tissue disease, and/or thrombophilia were excluded.
Vascular events in this study were defined as “an acute worsening of the disease course requiring treatment modifications,” and included critical ischemia (35% of cases), ulcers/necrosis (33%), claudication worsening (16%), deep vein thrombosis (3%), superficial phlebitis (7%), limb infection (4%), and “other” events (2%).
Major amputation was defined as “an amputation involving the tibio-tarsian articulation for lower limbs and the metacarpophalangeal articulation for upper limbs,” he explained.
The median time to amputation was 4 years, and patients who experienced amputation had a median age of 39 years. Half of the 48 patients who experienced amputation had one amputation, nearly a third had two amputations, and 19% had three amputations. About two-thirds had minor amputations and a third had major amputations.
The findings provide important prognostic information regarding TAO, Dr. Le Joncour said, noting that long-term data on outcomes in TAO patients have been lacking.
“We found specific characteristics that identified those at highest risk for subsequent vascular complications, and these factors are not only important predictors of vascular complications or relapse, but may also serve to adjust more aggressive management and close follow-up of these patients,” he concluded.
Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Nonwhite ethnicity and limb infection predict poor prognosis in TAO.
Major finding: Ethnicity predicts vascular events (HR, 2.35); limb infection at diagnosis predicts vascular events and amputation (HR, 3.29 and 12.1, respectively).
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 224 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Le Joncour reported having no disclosures.
Source: Le Joncour A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 1885.
Filgotinib shows efficacy, safety in RA phase 3 and PsA phase 2 trials
CHICAGO – The selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor filgotinib showed efficacy and safety for patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a phase 3 trial, and efficacy and safety for treating patients with psoriatic arthritis in results from a phase 2 study in two separate reports at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
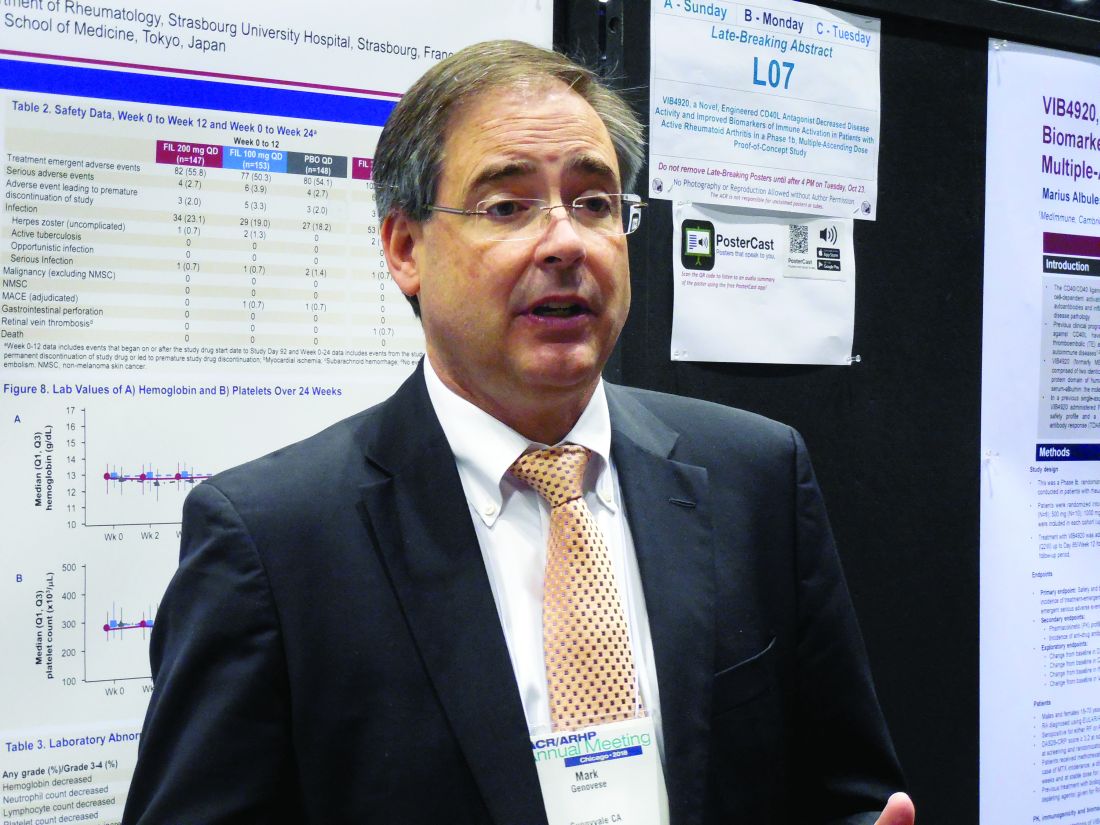
In the phase 3 study, treatment with filgotinib at an oral dosage of 200 mg once daily led to a 66% incidence of American College of Rheumatology 20 (ACR20) responses after 16 weeks of treatment in 147 patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), compared with a 31% rate among 148 patients randomized to receive placebo, a statistically significant improvement for the study’s primary efficacy endpoint, Mark C. Genovese, MD, reported in a poster at the meeting. The rate of ACR20 responses among the 153 RA patients who received 100 mg/day filgotinib was 58%, reported Dr. Genovese, professor of medicine and director of the rheumatology clinic at Stanford (Calif.) University.
After 24 weeks of daily treatment, the longest duration studied in the trial, ACR20 rates were 69%, 55%, and 35% in the 200-mg, 100-mg, and placebo patients, respectively. Dr. Genovese also reported that after 24 weeks on treatment, the rates of patients achieving low disease activity measured by their disease activity score based on 28 joints and C-reactive protein level (DAS28-CRP) were 48%, 38%, and 21%, respectively, and the percentages of patients achieving complete remission at 24 weeks based on their DAS28-CRP scores were 31%, 26%, and 12%, respectively.
“We were incredibly fortunate to see such positive results. The drug worked very well in very-challenging-to-treat patients,” Dr. Genovese said in an interview. All of the RA patients enrolled in the study had not previously responded to or were intolerant of prior treatment with at least one biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), and almost a quarter of enrolled patients had failed prior treatment with at least three different biologic DMARDs. The number of biologic DMARDs a patient had previously received showed no relationship to how well patients responded to filgotinib, he noted.
Dr. Genovese also highlighted the relatively high percentage of patients who achieved low disease activity and remission. The 48% and 31% rates, respectively, of low disease activity and remission among patients treated with the higher filgotinib dosage for 24 weeks “is fairly impressive in patients who did not previously respond to a biologic DMARD,” the researcher said. These findings are similar to data previously reported for upadacitinib, another Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that, like filgotinib, is selective for the JAK1 receptor, noted Dr. Genovese, who also was the lead investigator for a phase 3 study of upadacitinib in RA patients (Lancet. 2018 June 23;391[10139]:2513-24).
The filgotinib data he presented came from the FINCH 2 (Filgotinib Versus Placebo in Adults With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Have an Inadequate Response to Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug[s] Treatment) trial, which was run at 104 sites in 15 countries, including the United States. The results also showed a “favorable safety profile and stable laboratory parameters,” Dr. Genovese reported. Results from two additional phase 3 trials in RA patients are expected in 2019, he said.
Filgotinib studied in psoriatic arthritis
The separate, phase 2 study of filgotinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) reported during the meeting showed safety “in line with previous reports without new safety signals” in a multicenter trial with 131 patients randomized to receive oral filgotinib 200 mg daily for 16 weeks or placebo, Philip J. Mease, MD, reported in a talk at the meeting. For the primary endpoint of achievement of ACR20 response after 16 weeks, the rate was 80% of the filgotinib-treated patients and 33% of patients in the placebo group, a statistically significant difference, said Dr. Mease, a rheumatologist at Swedish Medical Center in Seattle.
EQUATOR (A Study to Assess Efficacy and Safety of Filgotinib in Active Psoriatic Arthritis) enrolled patients at sites in seven European countries who had “very active” PsA and either a history of or current plaque psoriasis. All patients had to have a history of either insufficient response to or intolerance of at least one conventional synthetic DMARD. The enrollment criteria had no specifications for prior use of an anti–tumor necrosis factor drug, and about 15% of patients had used least one of these drugs. At entry, about three-quarters of patients were on treatment with a conventional synthetic DMARD and about a quarter received treatment with a glucocorticoid.
The results showed statistically significant benefits from filgotinib, compared with placebo, for several other measures of arthritis activity, as well as measures of psoriasis, enthesitis, and pain, Dr. Mease reported. He also highlighted a “lack of meaningful changes in hemoglobin” or other laboratory measures that, along with the efficacy findings, make filgotinib “a promising first step” for patients with PsA. Dr. Mease also noted that roughly concurrently with his report, a separate group of researchers published results from a phase 2 study of filgotinib in patients with ankylosing spondylitis that also found evidence for efficacy and safety during 12 weeks of treating 116 randomized patients (Lancet. 2018 Oct 22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]32463-2).
FINCH 2 was sponsored by Galapagos and Gilead, the two companies developing filgotinib. Dr. Genovese has had financial relationships with Galapagos and Gilead and also with AbbVie, Lilly, and Pfizer. Dr. Mease has had financial relationships with Galapagos and Gilead and a dozen other companies.
SOURCES: Genovese M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L06; Mease P et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 1821.
CHICAGO – The selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor filgotinib showed efficacy and safety for patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a phase 3 trial, and efficacy and safety for treating patients with psoriatic arthritis in results from a phase 2 study in two separate reports at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In the phase 3 study, treatment with filgotinib at an oral dosage of 200 mg once daily led to a 66% incidence of American College of Rheumatology 20 (ACR20) responses after 16 weeks of treatment in 147 patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), compared with a 31% rate among 148 patients randomized to receive placebo, a statistically significant improvement for the study’s primary efficacy endpoint, Mark C. Genovese, MD, reported in a poster at the meeting. The rate of ACR20 responses among the 153 RA patients who received 100 mg/day filgotinib was 58%, reported Dr. Genovese, professor of medicine and director of the rheumatology clinic at Stanford (Calif.) University.
After 24 weeks of daily treatment, the longest duration studied in the trial, ACR20 rates were 69%, 55%, and 35% in the 200-mg, 100-mg, and placebo patients, respectively. Dr. Genovese also reported that after 24 weeks on treatment, the rates of patients achieving low disease activity measured by their disease activity score based on 28 joints and C-reactive protein level (DAS28-CRP) were 48%, 38%, and 21%, respectively, and the percentages of patients achieving complete remission at 24 weeks based on their DAS28-CRP scores were 31%, 26%, and 12%, respectively.
“We were incredibly fortunate to see such positive results. The drug worked very well in very-challenging-to-treat patients,” Dr. Genovese said in an interview. All of the RA patients enrolled in the study had not previously responded to or were intolerant of prior treatment with at least one biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), and almost a quarter of enrolled patients had failed prior treatment with at least three different biologic DMARDs. The number of biologic DMARDs a patient had previously received showed no relationship to how well patients responded to filgotinib, he noted.
Dr. Genovese also highlighted the relatively high percentage of patients who achieved low disease activity and remission. The 48% and 31% rates, respectively, of low disease activity and remission among patients treated with the higher filgotinib dosage for 24 weeks “is fairly impressive in patients who did not previously respond to a biologic DMARD,” the researcher said. These findings are similar to data previously reported for upadacitinib, another Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that, like filgotinib, is selective for the JAK1 receptor, noted Dr. Genovese, who also was the lead investigator for a phase 3 study of upadacitinib in RA patients (Lancet. 2018 June 23;391[10139]:2513-24).
The filgotinib data he presented came from the FINCH 2 (Filgotinib Versus Placebo in Adults With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Have an Inadequate Response to Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug[s] Treatment) trial, which was run at 104 sites in 15 countries, including the United States. The results also showed a “favorable safety profile and stable laboratory parameters,” Dr. Genovese reported. Results from two additional phase 3 trials in RA patients are expected in 2019, he said.
Filgotinib studied in psoriatic arthritis
The separate, phase 2 study of filgotinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) reported during the meeting showed safety “in line with previous reports without new safety signals” in a multicenter trial with 131 patients randomized to receive oral filgotinib 200 mg daily for 16 weeks or placebo, Philip J. Mease, MD, reported in a talk at the meeting. For the primary endpoint of achievement of ACR20 response after 16 weeks, the rate was 80% of the filgotinib-treated patients and 33% of patients in the placebo group, a statistically significant difference, said Dr. Mease, a rheumatologist at Swedish Medical Center in Seattle.
EQUATOR (A Study to Assess Efficacy and Safety of Filgotinib in Active Psoriatic Arthritis) enrolled patients at sites in seven European countries who had “very active” PsA and either a history of or current plaque psoriasis. All patients had to have a history of either insufficient response to or intolerance of at least one conventional synthetic DMARD. The enrollment criteria had no specifications for prior use of an anti–tumor necrosis factor drug, and about 15% of patients had used least one of these drugs. At entry, about three-quarters of patients were on treatment with a conventional synthetic DMARD and about a quarter received treatment with a glucocorticoid.
The results showed statistically significant benefits from filgotinib, compared with placebo, for several other measures of arthritis activity, as well as measures of psoriasis, enthesitis, and pain, Dr. Mease reported. He also highlighted a “lack of meaningful changes in hemoglobin” or other laboratory measures that, along with the efficacy findings, make filgotinib “a promising first step” for patients with PsA. Dr. Mease also noted that roughly concurrently with his report, a separate group of researchers published results from a phase 2 study of filgotinib in patients with ankylosing spondylitis that also found evidence for efficacy and safety during 12 weeks of treating 116 randomized patients (Lancet. 2018 Oct 22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]32463-2).
FINCH 2 was sponsored by Galapagos and Gilead, the two companies developing filgotinib. Dr. Genovese has had financial relationships with Galapagos and Gilead and also with AbbVie, Lilly, and Pfizer. Dr. Mease has had financial relationships with Galapagos and Gilead and a dozen other companies.
SOURCES: Genovese M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L06; Mease P et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 1821.
CHICAGO – The selective Janus kinase 1 inhibitor filgotinib showed efficacy and safety for patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a phase 3 trial, and efficacy and safety for treating patients with psoriatic arthritis in results from a phase 2 study in two separate reports at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
In the phase 3 study, treatment with filgotinib at an oral dosage of 200 mg once daily led to a 66% incidence of American College of Rheumatology 20 (ACR20) responses after 16 weeks of treatment in 147 patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), compared with a 31% rate among 148 patients randomized to receive placebo, a statistically significant improvement for the study’s primary efficacy endpoint, Mark C. Genovese, MD, reported in a poster at the meeting. The rate of ACR20 responses among the 153 RA patients who received 100 mg/day filgotinib was 58%, reported Dr. Genovese, professor of medicine and director of the rheumatology clinic at Stanford (Calif.) University.
After 24 weeks of daily treatment, the longest duration studied in the trial, ACR20 rates were 69%, 55%, and 35% in the 200-mg, 100-mg, and placebo patients, respectively. Dr. Genovese also reported that after 24 weeks on treatment, the rates of patients achieving low disease activity measured by their disease activity score based on 28 joints and C-reactive protein level (DAS28-CRP) were 48%, 38%, and 21%, respectively, and the percentages of patients achieving complete remission at 24 weeks based on their DAS28-CRP scores were 31%, 26%, and 12%, respectively.
“We were incredibly fortunate to see such positive results. The drug worked very well in very-challenging-to-treat patients,” Dr. Genovese said in an interview. All of the RA patients enrolled in the study had not previously responded to or were intolerant of prior treatment with at least one biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), and almost a quarter of enrolled patients had failed prior treatment with at least three different biologic DMARDs. The number of biologic DMARDs a patient had previously received showed no relationship to how well patients responded to filgotinib, he noted.
Dr. Genovese also highlighted the relatively high percentage of patients who achieved low disease activity and remission. The 48% and 31% rates, respectively, of low disease activity and remission among patients treated with the higher filgotinib dosage for 24 weeks “is fairly impressive in patients who did not previously respond to a biologic DMARD,” the researcher said. These findings are similar to data previously reported for upadacitinib, another Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that, like filgotinib, is selective for the JAK1 receptor, noted Dr. Genovese, who also was the lead investigator for a phase 3 study of upadacitinib in RA patients (Lancet. 2018 June 23;391[10139]:2513-24).
The filgotinib data he presented came from the FINCH 2 (Filgotinib Versus Placebo in Adults With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Have an Inadequate Response to Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug[s] Treatment) trial, which was run at 104 sites in 15 countries, including the United States. The results also showed a “favorable safety profile and stable laboratory parameters,” Dr. Genovese reported. Results from two additional phase 3 trials in RA patients are expected in 2019, he said.
Filgotinib studied in psoriatic arthritis
The separate, phase 2 study of filgotinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) reported during the meeting showed safety “in line with previous reports without new safety signals” in a multicenter trial with 131 patients randomized to receive oral filgotinib 200 mg daily for 16 weeks or placebo, Philip J. Mease, MD, reported in a talk at the meeting. For the primary endpoint of achievement of ACR20 response after 16 weeks, the rate was 80% of the filgotinib-treated patients and 33% of patients in the placebo group, a statistically significant difference, said Dr. Mease, a rheumatologist at Swedish Medical Center in Seattle.
EQUATOR (A Study to Assess Efficacy and Safety of Filgotinib in Active Psoriatic Arthritis) enrolled patients at sites in seven European countries who had “very active” PsA and either a history of or current plaque psoriasis. All patients had to have a history of either insufficient response to or intolerance of at least one conventional synthetic DMARD. The enrollment criteria had no specifications for prior use of an anti–tumor necrosis factor drug, and about 15% of patients had used least one of these drugs. At entry, about three-quarters of patients were on treatment with a conventional synthetic DMARD and about a quarter received treatment with a glucocorticoid.
The results showed statistically significant benefits from filgotinib, compared with placebo, for several other measures of arthritis activity, as well as measures of psoriasis, enthesitis, and pain, Dr. Mease reported. He also highlighted a “lack of meaningful changes in hemoglobin” or other laboratory measures that, along with the efficacy findings, make filgotinib “a promising first step” for patients with PsA. Dr. Mease also noted that roughly concurrently with his report, a separate group of researchers published results from a phase 2 study of filgotinib in patients with ankylosing spondylitis that also found evidence for efficacy and safety during 12 weeks of treating 116 randomized patients (Lancet. 2018 Oct 22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]32463-2).
FINCH 2 was sponsored by Galapagos and Gilead, the two companies developing filgotinib. Dr. Genovese has had financial relationships with Galapagos and Gilead and also with AbbVie, Lilly, and Pfizer. Dr. Mease has had financial relationships with Galapagos and Gilead and a dozen other companies.
SOURCES: Genovese M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L06; Mease P et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 1821.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
RELIEF: In Behçet’s, apremilast improves oral ulcers for up to 28 weeks
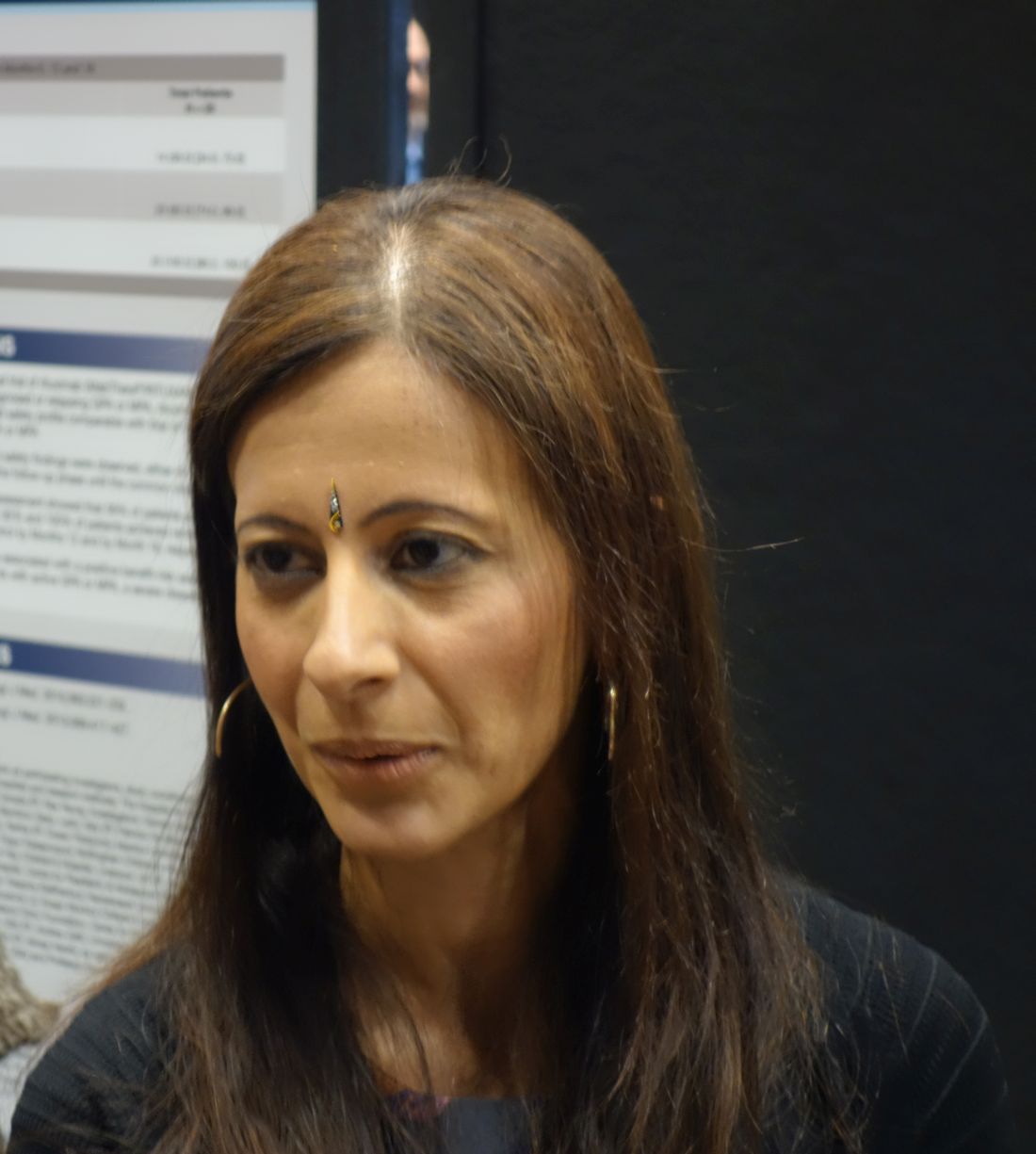
CHICAGO – Apremilast was effective and well tolerated for up to 28 weeks for the treatment of oral ulcers in patients with active Behçet’s disease, based on findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 RELIEF trial.
At baseline, mean oral ulcer counts were 4.2 in 104 patients randomized to receive the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor and 3.9 in 103 patients in the placebo group. Mean visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores were 61.2 and 60.8 in the two groups, respectively.
The primary study endpoint of area under the curve for total number of oral ulcers over a 12-week period (AUCWk0-12) – a measure that reflects the number of oral ulcers that occur over time and also accounts for the recurring-remitting course of oral ulcers – was achieved. AUCWk0-12 was significantly lower in the apremilast group than in the placebo group (129.54 vs. 222.14, respectively; P less than .0001), Gulen Hatemi, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
From baseline to week 12, apremilast treatment also resulted in a significantly lower number of oral ulcers (mean of 1.1 vs. 2.0 for placebo at 12 weeks) and significantly reduced pain from oral ulcers at every visit from week 1 through week 12 of the study, compared with placebo (mean VAS score change from baseline, –40.7 vs. –15.9), said Dr. Hatemi, a professor of medicine at Istanbul University.
“The [12-week] complete response rate ... was 53% in the apremilast group and 22.3% in the placebo group. The [12-week] partial response rate ...was 76% in the apremilast group and 48% in the placebo group,” she said, adding that the efficacy of apremilast was sustained with continued treatment through 28 weeks.
Study participants were adults (mean age, 40 years) with active Behçet’s disease and three or more oral ulcers at randomization or two or more at screening and at randomization. All had been previously treated with at least one nonbiologic medication for oral ulcers and were allowed to have received previous biologic therapies for other disease manifestations. Those with active major organ involvement were excluded.
Treatment included a 30-mg dose of apremilast twice daily for 12 weeks or placebo. After 12 weeks, all patients received apremilast through at least 28 weeks of the 64-week study.
At the 28-week analysis, patients who were initially randomized to placebo and who switched to apremilast after week 12 had benefits comparable with those seen in those randomized to apremilast at the start of the study. A complete response was seen in 59% and 62% of patients in the groups, respectively, and a partial response was seen in 90% and 85%, respectively. Additionally, the mean change in the VAS score for oral ulcer pain in the groups at that time was –40.6 and –41.9, Dr. Hatemi said.
Apremilast was well tolerated in this study; the incidence of adverse events was comparable in the treatment and placebo groups during the 12-week placebo-controlled phase of the study – 78.8% and 71.8%, respectively. The most common events were diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory tract infection, she said.
“These were generally mild to moderate, and only two patients had to discontinue the study due to gastrointestinal adverse events,” she said, noting that no new safety signals were observed.
Behçet’s disease is a chronic, relapsing, multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent oral ulcers that can be disabling and have a substantial effect on quality of life. These findings, which include efficacy data up to 28 weeks and safety data for at least 100 patients exposed to apremilast for at least 1 year, demonstrate the efficacy of apremilast for the treatment oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease, she said, noting that “the safety findings were consistent with the known safety profile of apremilast.”
The RELIEF study was supported by Celgene. Dr. Hatemi reported receiving grant/research support from Celgene and serving as a speaker for AbbVie, Mustafa Nevzet Pharmaceuticals, and UCB.
SOURCE: Hatemi G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 2789.
CHICAGO – Apremilast was effective and well tolerated for up to 28 weeks for the treatment of oral ulcers in patients with active Behçet’s disease, based on findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 RELIEF trial.
At baseline, mean oral ulcer counts were 4.2 in 104 patients randomized to receive the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor and 3.9 in 103 patients in the placebo group. Mean visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores were 61.2 and 60.8 in the two groups, respectively.
The primary study endpoint of area under the curve for total number of oral ulcers over a 12-week period (AUCWk0-12) – a measure that reflects the number of oral ulcers that occur over time and also accounts for the recurring-remitting course of oral ulcers – was achieved. AUCWk0-12 was significantly lower in the apremilast group than in the placebo group (129.54 vs. 222.14, respectively; P less than .0001), Gulen Hatemi, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
From baseline to week 12, apremilast treatment also resulted in a significantly lower number of oral ulcers (mean of 1.1 vs. 2.0 for placebo at 12 weeks) and significantly reduced pain from oral ulcers at every visit from week 1 through week 12 of the study, compared with placebo (mean VAS score change from baseline, –40.7 vs. –15.9), said Dr. Hatemi, a professor of medicine at Istanbul University.
“The [12-week] complete response rate ... was 53% in the apremilast group and 22.3% in the placebo group. The [12-week] partial response rate ...was 76% in the apremilast group and 48% in the placebo group,” she said, adding that the efficacy of apremilast was sustained with continued treatment through 28 weeks.
Study participants were adults (mean age, 40 years) with active Behçet’s disease and three or more oral ulcers at randomization or two or more at screening and at randomization. All had been previously treated with at least one nonbiologic medication for oral ulcers and were allowed to have received previous biologic therapies for other disease manifestations. Those with active major organ involvement were excluded.
Treatment included a 30-mg dose of apremilast twice daily for 12 weeks or placebo. After 12 weeks, all patients received apremilast through at least 28 weeks of the 64-week study.
At the 28-week analysis, patients who were initially randomized to placebo and who switched to apremilast after week 12 had benefits comparable with those seen in those randomized to apremilast at the start of the study. A complete response was seen in 59% and 62% of patients in the groups, respectively, and a partial response was seen in 90% and 85%, respectively. Additionally, the mean change in the VAS score for oral ulcer pain in the groups at that time was –40.6 and –41.9, Dr. Hatemi said.
Apremilast was well tolerated in this study; the incidence of adverse events was comparable in the treatment and placebo groups during the 12-week placebo-controlled phase of the study – 78.8% and 71.8%, respectively. The most common events were diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory tract infection, she said.
“These were generally mild to moderate, and only two patients had to discontinue the study due to gastrointestinal adverse events,” she said, noting that no new safety signals were observed.
Behçet’s disease is a chronic, relapsing, multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent oral ulcers that can be disabling and have a substantial effect on quality of life. These findings, which include efficacy data up to 28 weeks and safety data for at least 100 patients exposed to apremilast for at least 1 year, demonstrate the efficacy of apremilast for the treatment oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease, she said, noting that “the safety findings were consistent with the known safety profile of apremilast.”
The RELIEF study was supported by Celgene. Dr. Hatemi reported receiving grant/research support from Celgene and serving as a speaker for AbbVie, Mustafa Nevzet Pharmaceuticals, and UCB.
SOURCE: Hatemi G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 2789.
CHICAGO – Apremilast was effective and well tolerated for up to 28 weeks for the treatment of oral ulcers in patients with active Behçet’s disease, based on findings from the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 RELIEF trial.
At baseline, mean oral ulcer counts were 4.2 in 104 patients randomized to receive the oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor and 3.9 in 103 patients in the placebo group. Mean visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores were 61.2 and 60.8 in the two groups, respectively.
The primary study endpoint of area under the curve for total number of oral ulcers over a 12-week period (AUCWk0-12) – a measure that reflects the number of oral ulcers that occur over time and also accounts for the recurring-remitting course of oral ulcers – was achieved. AUCWk0-12 was significantly lower in the apremilast group than in the placebo group (129.54 vs. 222.14, respectively; P less than .0001), Gulen Hatemi, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
From baseline to week 12, apremilast treatment also resulted in a significantly lower number of oral ulcers (mean of 1.1 vs. 2.0 for placebo at 12 weeks) and significantly reduced pain from oral ulcers at every visit from week 1 through week 12 of the study, compared with placebo (mean VAS score change from baseline, –40.7 vs. –15.9), said Dr. Hatemi, a professor of medicine at Istanbul University.
“The [12-week] complete response rate ... was 53% in the apremilast group and 22.3% in the placebo group. The [12-week] partial response rate ...was 76% in the apremilast group and 48% in the placebo group,” she said, adding that the efficacy of apremilast was sustained with continued treatment through 28 weeks.
Study participants were adults (mean age, 40 years) with active Behçet’s disease and three or more oral ulcers at randomization or two or more at screening and at randomization. All had been previously treated with at least one nonbiologic medication for oral ulcers and were allowed to have received previous biologic therapies for other disease manifestations. Those with active major organ involvement were excluded.
Treatment included a 30-mg dose of apremilast twice daily for 12 weeks or placebo. After 12 weeks, all patients received apremilast through at least 28 weeks of the 64-week study.
At the 28-week analysis, patients who were initially randomized to placebo and who switched to apremilast after week 12 had benefits comparable with those seen in those randomized to apremilast at the start of the study. A complete response was seen in 59% and 62% of patients in the groups, respectively, and a partial response was seen in 90% and 85%, respectively. Additionally, the mean change in the VAS score for oral ulcer pain in the groups at that time was –40.6 and –41.9, Dr. Hatemi said.
Apremilast was well tolerated in this study; the incidence of adverse events was comparable in the treatment and placebo groups during the 12-week placebo-controlled phase of the study – 78.8% and 71.8%, respectively. The most common events were diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory tract infection, she said.
“These were generally mild to moderate, and only two patients had to discontinue the study due to gastrointestinal adverse events,” she said, noting that no new safety signals were observed.
Behçet’s disease is a chronic, relapsing, multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent oral ulcers that can be disabling and have a substantial effect on quality of life. These findings, which include efficacy data up to 28 weeks and safety data for at least 100 patients exposed to apremilast for at least 1 year, demonstrate the efficacy of apremilast for the treatment oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease, she said, noting that “the safety findings were consistent with the known safety profile of apremilast.”
The RELIEF study was supported by Celgene. Dr. Hatemi reported receiving grant/research support from Celgene and serving as a speaker for AbbVie, Mustafa Nevzet Pharmaceuticals, and UCB.
SOURCE: Hatemi G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 2789.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Apremilast is safe and effective for treating oral ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease.
Major finding: The AUCWk0-12 was significantly lower with apremilast (129.54) versus placebo (222.14).
Study details: A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study of 207 patients.
Disclosures: The RELIEF study was supported by Celgene. Dr. Hatemi reported receiving grant/research support from Celgene and serving as a speaker for AbbVie, Mustafa Nevzet Pharmaceuticals, and UCB.
Source: Hatemi G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract 2789
DMARDs improve vascular abnormalities in early RA
, Maya H. Buch, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
She presented a study of 71 treatment-naive patients with recently diagnosed RA and no history of cardiovascular disease. Patients were randomized to either etanercept plus methotrexate or methotrexate with treat-to-target escalation to triple nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy by week 12. Patients in the latter group were switched to etanercept plus methotrexate at week 24 if at that point they had a Disease Activity Score 28 of 2.6 or more.
All participants underwent cardiovascular MRI at baseline and again after 1 and 2 years in order to measure change in aortic stiffness, the primary study endpoint chosen because it is clinically meaningful and can reliably and reproducibly be measured by MRI.
The study was designed to shed light on possible mechanisms for the epidemiologic observation that effective treatment with methotrexate and/or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors curbs the excess risk of cardiovascular events that accompanies RA. The thinking is that abnormal aortic distensibility represents an early harbinger of the increased cardiovascular risk associated with this form of inflammatory arthritis, explained Dr. Buch, professor of rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England) and section head of clinical and translational rheumatology at the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
The mean aortic distensibility at baseline, when the study population was treatment naive, was 2.99 x 10–3 mm Hg–1. This value is abnormally low when compared with values seen in healthy age- and sex-matched controls. After 1 year of treatment, however, mean aortic distensibility improved significantly to 3.59 x 10–3 mm Hg–1. This improvement was maintained at year 2, when the mean value was 3.55.
Interestingly, neither treatment response status or disease activity was associated with the improvement in aortic stiffness. However, in a prespecified exploratory comparison between the 20 responders to etanercept plus methotrexate and the 10 responders to first-line methotrexate who never received etanercept, the group on biologic therapy had a 16% greater improvement in aortic distensibility at 1 year.
“It’s not a statistically significant difference. The study wasn’t powered for that,” she said in an interview. “But these data suggest that an anti-TNF treatment strategy may confer additional benefit. Of course, that will need to be confirmed in a larger trial. And if it is confirmed, it would suggest a role for etanercept plus methotrexate in personalizing tailored therapy in early RA patients at particularly high cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Buch reported receiving funding from Pfizer, Roche, UCB, AbbVie, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Sandoz, but reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding this study, which was sponsored by the U.K. National Institute for Healthcare Research.
SOURCE: Buch MH et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L05.
, Maya H. Buch, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
She presented a study of 71 treatment-naive patients with recently diagnosed RA and no history of cardiovascular disease. Patients were randomized to either etanercept plus methotrexate or methotrexate with treat-to-target escalation to triple nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy by week 12. Patients in the latter group were switched to etanercept plus methotrexate at week 24 if at that point they had a Disease Activity Score 28 of 2.6 or more.
All participants underwent cardiovascular MRI at baseline and again after 1 and 2 years in order to measure change in aortic stiffness, the primary study endpoint chosen because it is clinically meaningful and can reliably and reproducibly be measured by MRI.
The study was designed to shed light on possible mechanisms for the epidemiologic observation that effective treatment with methotrexate and/or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors curbs the excess risk of cardiovascular events that accompanies RA. The thinking is that abnormal aortic distensibility represents an early harbinger of the increased cardiovascular risk associated with this form of inflammatory arthritis, explained Dr. Buch, professor of rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England) and section head of clinical and translational rheumatology at the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
The mean aortic distensibility at baseline, when the study population was treatment naive, was 2.99 x 10–3 mm Hg–1. This value is abnormally low when compared with values seen in healthy age- and sex-matched controls. After 1 year of treatment, however, mean aortic distensibility improved significantly to 3.59 x 10–3 mm Hg–1. This improvement was maintained at year 2, when the mean value was 3.55.
Interestingly, neither treatment response status or disease activity was associated with the improvement in aortic stiffness. However, in a prespecified exploratory comparison between the 20 responders to etanercept plus methotrexate and the 10 responders to first-line methotrexate who never received etanercept, the group on biologic therapy had a 16% greater improvement in aortic distensibility at 1 year.
“It’s not a statistically significant difference. The study wasn’t powered for that,” she said in an interview. “But these data suggest that an anti-TNF treatment strategy may confer additional benefit. Of course, that will need to be confirmed in a larger trial. And if it is confirmed, it would suggest a role for etanercept plus methotrexate in personalizing tailored therapy in early RA patients at particularly high cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Buch reported receiving funding from Pfizer, Roche, UCB, AbbVie, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Sandoz, but reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding this study, which was sponsored by the U.K. National Institute for Healthcare Research.
SOURCE: Buch MH et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L05.
, Maya H. Buch, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
She presented a study of 71 treatment-naive patients with recently diagnosed RA and no history of cardiovascular disease. Patients were randomized to either etanercept plus methotrexate or methotrexate with treat-to-target escalation to triple nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy by week 12. Patients in the latter group were switched to etanercept plus methotrexate at week 24 if at that point they had a Disease Activity Score 28 of 2.6 or more.
All participants underwent cardiovascular MRI at baseline and again after 1 and 2 years in order to measure change in aortic stiffness, the primary study endpoint chosen because it is clinically meaningful and can reliably and reproducibly be measured by MRI.
The study was designed to shed light on possible mechanisms for the epidemiologic observation that effective treatment with methotrexate and/or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors curbs the excess risk of cardiovascular events that accompanies RA. The thinking is that abnormal aortic distensibility represents an early harbinger of the increased cardiovascular risk associated with this form of inflammatory arthritis, explained Dr. Buch, professor of rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England) and section head of clinical and translational rheumatology at the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine.
The mean aortic distensibility at baseline, when the study population was treatment naive, was 2.99 x 10–3 mm Hg–1. This value is abnormally low when compared with values seen in healthy age- and sex-matched controls. After 1 year of treatment, however, mean aortic distensibility improved significantly to 3.59 x 10–3 mm Hg–1. This improvement was maintained at year 2, when the mean value was 3.55.
Interestingly, neither treatment response status or disease activity was associated with the improvement in aortic stiffness. However, in a prespecified exploratory comparison between the 20 responders to etanercept plus methotrexate and the 10 responders to first-line methotrexate who never received etanercept, the group on biologic therapy had a 16% greater improvement in aortic distensibility at 1 year.
“It’s not a statistically significant difference. The study wasn’t powered for that,” she said in an interview. “But these data suggest that an anti-TNF treatment strategy may confer additional benefit. Of course, that will need to be confirmed in a larger trial. And if it is confirmed, it would suggest a role for etanercept plus methotrexate in personalizing tailored therapy in early RA patients at particularly high cardiovascular risk.”
Dr. Buch reported receiving funding from Pfizer, Roche, UCB, AbbVie, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Sandoz, but reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding this study, which was sponsored by the U.K. National Institute for Healthcare Research.
SOURCE: Buch MH et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L05.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Abnormal aortic stiffness is present in patients with newly diagnosed RA but improves with disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy.
Major finding: Mean aortic distensibility in patients with early RA improved from an abnormally low 2.99 x 10–3 mm Hg–1 prior to treatment to a more robust 3.59 x 10–3 mm Hg–1 after 1 year of disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy.
Study details: This study included 71 patients with newly diagnosed RA whose aortic stiffness was measured serially via cardiovascular MRI over a 2-year period.
Disclosures: The presenter reported receiving funding from Pfizer, Roche, UCB, AbbVie, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Sandoz, but reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding this study, which was sponsored by the U.K. National Institute for Healthcare Research.
Source: Buch MH et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L05.
Hamstring tendinopathy implicated in persistent Lyme arthritis
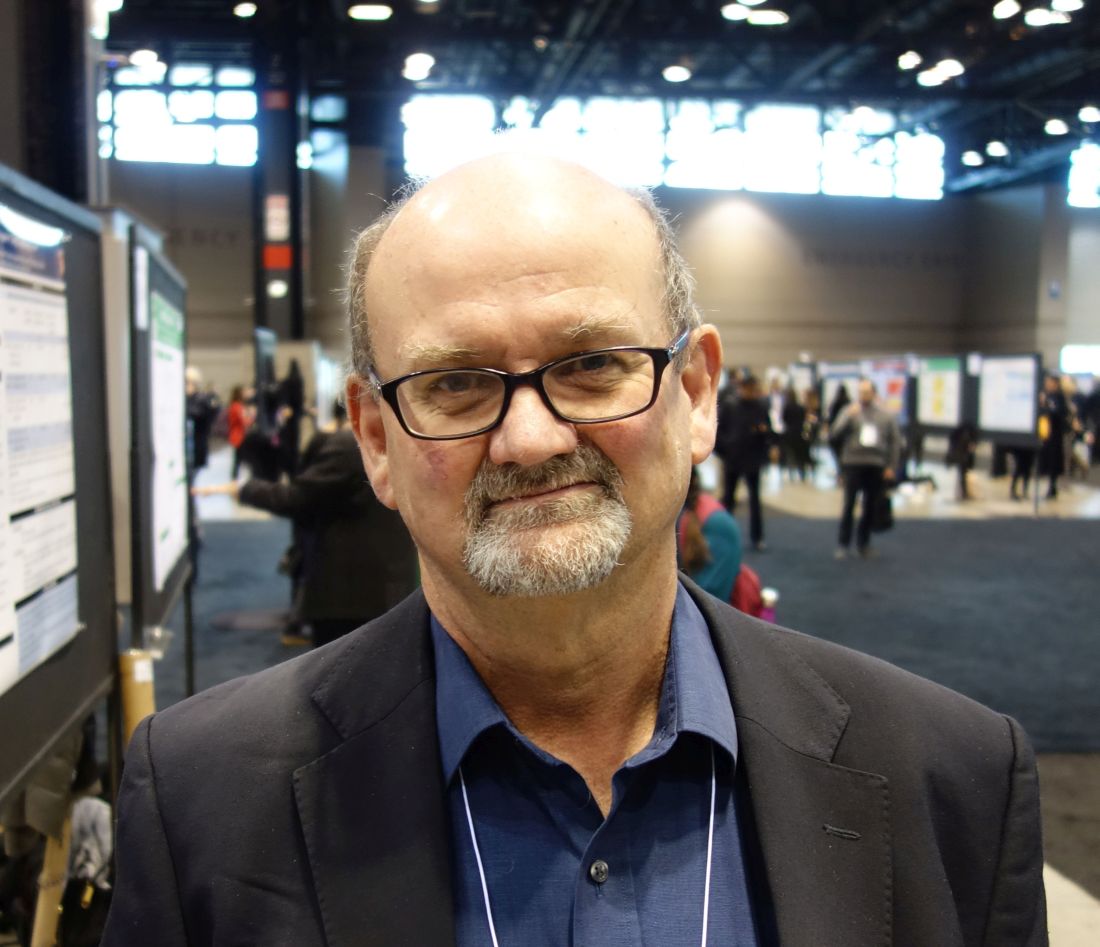
CHICAGO – The big news regarding Lyme disease at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology was a report that hamstring tendon calcification is extremely common among patients who have persistent Lyme arthritis despite having undergone appropriate antibiotic therapy.
“This is a fascinating study,” Robert A. Kalish, MD, a Lyme disease expert not involved in the research, said regarding the report by Sheila L. Arvikar, MD, and her coworkers at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
One implication of this finding by a renowned group of Lyme disease researchers is that persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis may in many cases be due to ongoing immunostimulation by spirochete remains located in hamstring tendons, a privileged, relatively avascular site where the foreign material may be able to evade immune clearance.
Also, as Dr. Arvikar pointed out in her presentation, calcific tendinopathy implies prior inflammation or degenerative changes. Thus, these calcific hamstring abnormalities implicate the hamstring tendons as a potential initial site of infection by hematogenously-spread Borrelia burgdorferi during the prearthritis phase of Lyme disease.
A further implication of the study is the possibility that hamstring tendon calcification could serve as a useful diagnostic aid in distinguishing Lyme arthritis from arthritis due to other causes. In the study, hamstring calcific tendinopathy was found in 28 of 31 adults and children with Lyme arthritis, 3 of 22 with knee osteoarthritis, and 1 of 14 patients with inflammatory arthritis, Dr. Arvikar noted.
She and her coinvestigators evaluated tendon pathology in their retrospective study of patients at the Massachusetts General Hospital Rheumatology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Clinic. They used ultrasound because they have found it offers far better spatial resolution of calcification than does MRI or x-rays. The semimembranosus tendon was the hamstring tendon that most commonly exhibited calcification, although 11 patients with Lyme arthritis also had involvement of the semitendinosus tendon, compared with none of the controls with osteoarthritis or inflammatory arthritis.
In the eight patients with serial ultrasound evaluations over a period of up to 12 months, the calcification persisted but the symptoms of tendinitis and synovitis improved.
Dr. Arvikar and her colleagues are expanding the scope of their ongoing study by examining patients whose Lyme arthritis is milder than that of the initial population, including patients who haven’t yet received antibiotics. They are also evaluating more controls with inflammatory arthritis.
In a separate presentation, Dr. Kalish noted that Lyme arthritis, the manifestation of Lyme disease of greatest interest to rheumatologists, occurs in about 60% of untreated patients, with onset a mean of 6 months after the tick bite. It typically entails recurrent mono- or oligoarthritis of large joints. The knee is involved in roughly 95% of cases.
The natural history of untreated Lyme arthritis is a spontaneous resolution rate of 10%-20% per year. Since the 1980s, however, 4 weeks of oral doxycycline or amoxicillin has been the treatment of choice. About 10% of patients with Lyme arthritis continue to have active synovitis 3 months after their course of antibiotics.
“There are some patients you give the treatment to and their arthritis just melts away in a month, but some, no matter what you do with antibiotics, continue to have synovitis, often developing a highly proliferative palpable synovitis that is really gunked up and features obliterative microvascular lesions,” observed Dr. Kalish, a rheumatologist at Tufts University in Boston.
Dr. Kalish said that persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis is most often due to a self-perpetuating immune response after the spirochete has been killed by antibiotics. He noted that patients with certain HLA-DRB1 haplotypes are more likely to experience persistent Lyme arthritis after standard recommended courses of antibiotics, and these DRB1 alleles correlate closely with the shared epitope associated with increased susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Several candidate autoantigens have already been identified.
He noted that the Massachusetts General group, in an earlier study, demonstrated that the presence of B. burgdorferi DNA by PCR in synovial fluid from patients with persistent Lyme arthritis after antibiotic therapy was not a reliable indicator of active joint infection (Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Aug;63[8]:2238-47).
“This was a paradigm change for me in seeing this study, because prior to that I had used PCR somewhat to guide treatment and make management decisions,” Dr. Kalish said.
What’s a reasonable treatment strategy in patients with persistent Lyme arthritis despite 30 days of oral antibiotics? Dr. Kalish favors an algorithm similar to one published by Dr. Arvikar and Allen C. Steere, MD (Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015 Jun;29[2]:269-80). In the case of mild persistent arthritis, he opts for another 30 days of oral doxycycline. If the arthritis is moderate or severe, he goes with either another 30 days of doxycycline or 30 days of intravenous ceftriaxone.
If the arthritis still hasn’t resolved despite two 30-day rounds of antibiotic therapy, he prescribes an NSAID or hydroxychloroquine if the persistent arthritis is mild, or methotrexate if it’s moderate to severe. And if the arthritis still persists after 3-6 months of disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy, he’ll consider synovectomy, which has a good success rate.
Neither Dr. Arvikar nor Dr. Kalish reported having any financial conflicts regarding their presentations.
SOURCE: Arvikar SL et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 950.
CHICAGO – The big news regarding Lyme disease at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology was a report that hamstring tendon calcification is extremely common among patients who have persistent Lyme arthritis despite having undergone appropriate antibiotic therapy.
“This is a fascinating study,” Robert A. Kalish, MD, a Lyme disease expert not involved in the research, said regarding the report by Sheila L. Arvikar, MD, and her coworkers at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
One implication of this finding by a renowned group of Lyme disease researchers is that persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis may in many cases be due to ongoing immunostimulation by spirochete remains located in hamstring tendons, a privileged, relatively avascular site where the foreign material may be able to evade immune clearance.
Also, as Dr. Arvikar pointed out in her presentation, calcific tendinopathy implies prior inflammation or degenerative changes. Thus, these calcific hamstring abnormalities implicate the hamstring tendons as a potential initial site of infection by hematogenously-spread Borrelia burgdorferi during the prearthritis phase of Lyme disease.
A further implication of the study is the possibility that hamstring tendon calcification could serve as a useful diagnostic aid in distinguishing Lyme arthritis from arthritis due to other causes. In the study, hamstring calcific tendinopathy was found in 28 of 31 adults and children with Lyme arthritis, 3 of 22 with knee osteoarthritis, and 1 of 14 patients with inflammatory arthritis, Dr. Arvikar noted.
She and her coinvestigators evaluated tendon pathology in their retrospective study of patients at the Massachusetts General Hospital Rheumatology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Clinic. They used ultrasound because they have found it offers far better spatial resolution of calcification than does MRI or x-rays. The semimembranosus tendon was the hamstring tendon that most commonly exhibited calcification, although 11 patients with Lyme arthritis also had involvement of the semitendinosus tendon, compared with none of the controls with osteoarthritis or inflammatory arthritis.
In the eight patients with serial ultrasound evaluations over a period of up to 12 months, the calcification persisted but the symptoms of tendinitis and synovitis improved.
Dr. Arvikar and her colleagues are expanding the scope of their ongoing study by examining patients whose Lyme arthritis is milder than that of the initial population, including patients who haven’t yet received antibiotics. They are also evaluating more controls with inflammatory arthritis.
In a separate presentation, Dr. Kalish noted that Lyme arthritis, the manifestation of Lyme disease of greatest interest to rheumatologists, occurs in about 60% of untreated patients, with onset a mean of 6 months after the tick bite. It typically entails recurrent mono- or oligoarthritis of large joints. The knee is involved in roughly 95% of cases.
The natural history of untreated Lyme arthritis is a spontaneous resolution rate of 10%-20% per year. Since the 1980s, however, 4 weeks of oral doxycycline or amoxicillin has been the treatment of choice. About 10% of patients with Lyme arthritis continue to have active synovitis 3 months after their course of antibiotics.
“There are some patients you give the treatment to and their arthritis just melts away in a month, but some, no matter what you do with antibiotics, continue to have synovitis, often developing a highly proliferative palpable synovitis that is really gunked up and features obliterative microvascular lesions,” observed Dr. Kalish, a rheumatologist at Tufts University in Boston.
Dr. Kalish said that persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis is most often due to a self-perpetuating immune response after the spirochete has been killed by antibiotics. He noted that patients with certain HLA-DRB1 haplotypes are more likely to experience persistent Lyme arthritis after standard recommended courses of antibiotics, and these DRB1 alleles correlate closely with the shared epitope associated with increased susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Several candidate autoantigens have already been identified.
He noted that the Massachusetts General group, in an earlier study, demonstrated that the presence of B. burgdorferi DNA by PCR in synovial fluid from patients with persistent Lyme arthritis after antibiotic therapy was not a reliable indicator of active joint infection (Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Aug;63[8]:2238-47).
“This was a paradigm change for me in seeing this study, because prior to that I had used PCR somewhat to guide treatment and make management decisions,” Dr. Kalish said.
What’s a reasonable treatment strategy in patients with persistent Lyme arthritis despite 30 days of oral antibiotics? Dr. Kalish favors an algorithm similar to one published by Dr. Arvikar and Allen C. Steere, MD (Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015 Jun;29[2]:269-80). In the case of mild persistent arthritis, he opts for another 30 days of oral doxycycline. If the arthritis is moderate or severe, he goes with either another 30 days of doxycycline or 30 days of intravenous ceftriaxone.
If the arthritis still hasn’t resolved despite two 30-day rounds of antibiotic therapy, he prescribes an NSAID or hydroxychloroquine if the persistent arthritis is mild, or methotrexate if it’s moderate to severe. And if the arthritis still persists after 3-6 months of disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy, he’ll consider synovectomy, which has a good success rate.
Neither Dr. Arvikar nor Dr. Kalish reported having any financial conflicts regarding their presentations.
SOURCE: Arvikar SL et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 950.
CHICAGO – The big news regarding Lyme disease at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology was a report that hamstring tendon calcification is extremely common among patients who have persistent Lyme arthritis despite having undergone appropriate antibiotic therapy.
“This is a fascinating study,” Robert A. Kalish, MD, a Lyme disease expert not involved in the research, said regarding the report by Sheila L. Arvikar, MD, and her coworkers at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
One implication of this finding by a renowned group of Lyme disease researchers is that persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis may in many cases be due to ongoing immunostimulation by spirochete remains located in hamstring tendons, a privileged, relatively avascular site where the foreign material may be able to evade immune clearance.
Also, as Dr. Arvikar pointed out in her presentation, calcific tendinopathy implies prior inflammation or degenerative changes. Thus, these calcific hamstring abnormalities implicate the hamstring tendons as a potential initial site of infection by hematogenously-spread Borrelia burgdorferi during the prearthritis phase of Lyme disease.
A further implication of the study is the possibility that hamstring tendon calcification could serve as a useful diagnostic aid in distinguishing Lyme arthritis from arthritis due to other causes. In the study, hamstring calcific tendinopathy was found in 28 of 31 adults and children with Lyme arthritis, 3 of 22 with knee osteoarthritis, and 1 of 14 patients with inflammatory arthritis, Dr. Arvikar noted.
She and her coinvestigators evaluated tendon pathology in their retrospective study of patients at the Massachusetts General Hospital Rheumatology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Clinic. They used ultrasound because they have found it offers far better spatial resolution of calcification than does MRI or x-rays. The semimembranosus tendon was the hamstring tendon that most commonly exhibited calcification, although 11 patients with Lyme arthritis also had involvement of the semitendinosus tendon, compared with none of the controls with osteoarthritis or inflammatory arthritis.
In the eight patients with serial ultrasound evaluations over a period of up to 12 months, the calcification persisted but the symptoms of tendinitis and synovitis improved.
Dr. Arvikar and her colleagues are expanding the scope of their ongoing study by examining patients whose Lyme arthritis is milder than that of the initial population, including patients who haven’t yet received antibiotics. They are also evaluating more controls with inflammatory arthritis.
In a separate presentation, Dr. Kalish noted that Lyme arthritis, the manifestation of Lyme disease of greatest interest to rheumatologists, occurs in about 60% of untreated patients, with onset a mean of 6 months after the tick bite. It typically entails recurrent mono- or oligoarthritis of large joints. The knee is involved in roughly 95% of cases.
The natural history of untreated Lyme arthritis is a spontaneous resolution rate of 10%-20% per year. Since the 1980s, however, 4 weeks of oral doxycycline or amoxicillin has been the treatment of choice. About 10% of patients with Lyme arthritis continue to have active synovitis 3 months after their course of antibiotics.
“There are some patients you give the treatment to and their arthritis just melts away in a month, but some, no matter what you do with antibiotics, continue to have synovitis, often developing a highly proliferative palpable synovitis that is really gunked up and features obliterative microvascular lesions,” observed Dr. Kalish, a rheumatologist at Tufts University in Boston.
Dr. Kalish said that persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis is most often due to a self-perpetuating immune response after the spirochete has been killed by antibiotics. He noted that patients with certain HLA-DRB1 haplotypes are more likely to experience persistent Lyme arthritis after standard recommended courses of antibiotics, and these DRB1 alleles correlate closely with the shared epitope associated with increased susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Several candidate autoantigens have already been identified.
He noted that the Massachusetts General group, in an earlier study, demonstrated that the presence of B. burgdorferi DNA by PCR in synovial fluid from patients with persistent Lyme arthritis after antibiotic therapy was not a reliable indicator of active joint infection (Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Aug;63[8]:2238-47).
“This was a paradigm change for me in seeing this study, because prior to that I had used PCR somewhat to guide treatment and make management decisions,” Dr. Kalish said.
What’s a reasonable treatment strategy in patients with persistent Lyme arthritis despite 30 days of oral antibiotics? Dr. Kalish favors an algorithm similar to one published by Dr. Arvikar and Allen C. Steere, MD (Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015 Jun;29[2]:269-80). In the case of mild persistent arthritis, he opts for another 30 days of oral doxycycline. If the arthritis is moderate or severe, he goes with either another 30 days of doxycycline or 30 days of intravenous ceftriaxone.
If the arthritis still hasn’t resolved despite two 30-day rounds of antibiotic therapy, he prescribes an NSAID or hydroxychloroquine if the persistent arthritis is mild, or methotrexate if it’s moderate to severe. And if the arthritis still persists after 3-6 months of disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy, he’ll consider synovectomy, which has a good success rate.
Neither Dr. Arvikar nor Dr. Kalish reported having any financial conflicts regarding their presentations.
SOURCE: Arvikar SL et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 950.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Ultrasound evidence of hamstring calcific tendinopathy was found in 28 of 31 patients with persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis, compared with 3 of 22 patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Study details: This was a retrospective imaging study of hamstring tendon status in 31 patients with persistent posttreatment Lyme arthritis, 22 patients with osteoarthritis, and 14 with inflammatory arthritis.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, conducted free of commercial support.
Source: Arvikar SL et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 950.
Weight loss cuts risk of psoriatic arthritis
CHICAGO – Overweight and obese psoriasis patients have it within their power to reduce their risk of developing psoriatic arthritis through weight loss, according to a large British longitudinal study.
Of the three modifiable lifestyle factors evaluated in the study as potential risk factors for the development of psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis patients – body mass index, smoking, and alcohol intake – reduction in BMI over time was clearly the winning strategy, Neil McHugh, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The message from this study of 90,189 incident cases of psoriasis identified in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink was unequivocal: “If you’re overweight and have psoriasis and you lose weight, you reduce your chance of developing a nasty form of arthritis,” said Dr. McHugh, professor of pharmacoepidemiology and a rheumatologist at the University of Bath, England.
“As psoriatic arthritis affects around 20% of people with psoriasis, weight reduction amongst those who are obese may have the potential to greatly reduce their risk of psoriatic arthritis in addition to providing additional health benefits,” he added.
Among the more than 90,000 patients diagnosed with psoriasis, 1,409 subsequently developed psoriatic arthritis, with an overall incidence rate of 2.72 cases per 1,000 person-years. Baseline BMI was strongly associated in stepwise fashion with subsequent psoriatic arthritis. Psoriasis patients with a baseline BMI of 25-29.9 kg/m2 were at an adjusted 1.76-fold increased risk of later developing psoriatic arthritis, compared with psoriasis patients having a BMI of less than 25. For those with a BMI of 30-34.9 kg/m2, the risk of subsequent psoriatic arthritis was increased 2.04-fold. And for those with a baseline BMI of 35 kg/m2 or more, the risk was increased 2.42-fold in analyses adjusted for age, sex, psoriasis duration and severity, history of trauma, and diabetes.
In contrast, the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis wasn’t significantly different between psoriasis patients who were nonsmokers, ex-smokers, or current smokers. And while there was a significantly increased risk of developing psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis patients who were current drinkers, compared with nondrinkers, the risk in ex-drinkers and heavy drinkers was similar to that in nondrinkers, a counterintuitive finding Dr. McHugh suspects was a distortion due to small numbers.
While the observed relationship between baseline BMI and subsequent risk of psoriatic arthritis was informative, it only tells part of the story, since body weight so often changes over time. Dr. McHugh and his coinvestigators had data on change in BMI over the course of 10 years of follow-up in 15,627 psoriasis patients free of psoriatic arthritis at the time their psoriasis was diagnosed. The researchers developed a BMI risk calculator that expressed the effect of change in BMI over time on the cumulative risk of developing psoriatic arthritis.
“We were able to show that if, for instance, you started with a BMI of 25 at baseline and ended up with a BMI of 30, your risk of psoriatic arthritis goes up by 13%, whereas if you start at 30 and come down to 25, your risk decreases by 13%. And the more weight you lose, the greater you reduce your risk of developing psoriatic arthritis,” the rheumatologist explained in an interview.
Indeed, with more extreme changes in BMI over the course of a decade following diagnosis of psoriasis – for example, dropping from a baseline BMI of 36 kg/m2 to 23 kg/m2 – the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis fell by close to 30%.
Dr. McHugh reported having no financial conflicts regarding this study, funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research.
SOURCE: Green A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 2134.
CHICAGO – Overweight and obese psoriasis patients have it within their power to reduce their risk of developing psoriatic arthritis through weight loss, according to a large British longitudinal study.
Of the three modifiable lifestyle factors evaluated in the study as potential risk factors for the development of psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis patients – body mass index, smoking, and alcohol intake – reduction in BMI over time was clearly the winning strategy, Neil McHugh, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The message from this study of 90,189 incident cases of psoriasis identified in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink was unequivocal: “If you’re overweight and have psoriasis and you lose weight, you reduce your chance of developing a nasty form of arthritis,” said Dr. McHugh, professor of pharmacoepidemiology and a rheumatologist at the University of Bath, England.
“As psoriatic arthritis affects around 20% of people with psoriasis, weight reduction amongst those who are obese may have the potential to greatly reduce their risk of psoriatic arthritis in addition to providing additional health benefits,” he added.
Among the more than 90,000 patients diagnosed with psoriasis, 1,409 subsequently developed psoriatic arthritis, with an overall incidence rate of 2.72 cases per 1,000 person-years. Baseline BMI was strongly associated in stepwise fashion with subsequent psoriatic arthritis. Psoriasis patients with a baseline BMI of 25-29.9 kg/m2 were at an adjusted 1.76-fold increased risk of later developing psoriatic arthritis, compared with psoriasis patients having a BMI of less than 25. For those with a BMI of 30-34.9 kg/m2, the risk of subsequent psoriatic arthritis was increased 2.04-fold. And for those with a baseline BMI of 35 kg/m2 or more, the risk was increased 2.42-fold in analyses adjusted for age, sex, psoriasis duration and severity, history of trauma, and diabetes.
In contrast, the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis wasn’t significantly different between psoriasis patients who were nonsmokers, ex-smokers, or current smokers. And while there was a significantly increased risk of developing psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis patients who were current drinkers, compared with nondrinkers, the risk in ex-drinkers and heavy drinkers was similar to that in nondrinkers, a counterintuitive finding Dr. McHugh suspects was a distortion due to small numbers.
While the observed relationship between baseline BMI and subsequent risk of psoriatic arthritis was informative, it only tells part of the story, since body weight so often changes over time. Dr. McHugh and his coinvestigators had data on change in BMI over the course of 10 years of follow-up in 15,627 psoriasis patients free of psoriatic arthritis at the time their psoriasis was diagnosed. The researchers developed a BMI risk calculator that expressed the effect of change in BMI over time on the cumulative risk of developing psoriatic arthritis.
“We were able to show that if, for instance, you started with a BMI of 25 at baseline and ended up with a BMI of 30, your risk of psoriatic arthritis goes up by 13%, whereas if you start at 30 and come down to 25, your risk decreases by 13%. And the more weight you lose, the greater you reduce your risk of developing psoriatic arthritis,” the rheumatologist explained in an interview.
Indeed, with more extreme changes in BMI over the course of a decade following diagnosis of psoriasis – for example, dropping from a baseline BMI of 36 kg/m2 to 23 kg/m2 – the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis fell by close to 30%.
Dr. McHugh reported having no financial conflicts regarding this study, funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research.
SOURCE: Green A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 2134.
CHICAGO – Overweight and obese psoriasis patients have it within their power to reduce their risk of developing psoriatic arthritis through weight loss, according to a large British longitudinal study.
Of the three modifiable lifestyle factors evaluated in the study as potential risk factors for the development of psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis patients – body mass index, smoking, and alcohol intake – reduction in BMI over time was clearly the winning strategy, Neil McHugh, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
The message from this study of 90,189 incident cases of psoriasis identified in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink was unequivocal: “If you’re overweight and have psoriasis and you lose weight, you reduce your chance of developing a nasty form of arthritis,” said Dr. McHugh, professor of pharmacoepidemiology and a rheumatologist at the University of Bath, England.
“As psoriatic arthritis affects around 20% of people with psoriasis, weight reduction amongst those who are obese may have the potential to greatly reduce their risk of psoriatic arthritis in addition to providing additional health benefits,” he added.
Among the more than 90,000 patients diagnosed with psoriasis, 1,409 subsequently developed psoriatic arthritis, with an overall incidence rate of 2.72 cases per 1,000 person-years. Baseline BMI was strongly associated in stepwise fashion with subsequent psoriatic arthritis. Psoriasis patients with a baseline BMI of 25-29.9 kg/m2 were at an adjusted 1.76-fold increased risk of later developing psoriatic arthritis, compared with psoriasis patients having a BMI of less than 25. For those with a BMI of 30-34.9 kg/m2, the risk of subsequent psoriatic arthritis was increased 2.04-fold. And for those with a baseline BMI of 35 kg/m2 or more, the risk was increased 2.42-fold in analyses adjusted for age, sex, psoriasis duration and severity, history of trauma, and diabetes.
In contrast, the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis wasn’t significantly different between psoriasis patients who were nonsmokers, ex-smokers, or current smokers. And while there was a significantly increased risk of developing psoriatic arthritis in psoriasis patients who were current drinkers, compared with nondrinkers, the risk in ex-drinkers and heavy drinkers was similar to that in nondrinkers, a counterintuitive finding Dr. McHugh suspects was a distortion due to small numbers.
While the observed relationship between baseline BMI and subsequent risk of psoriatic arthritis was informative, it only tells part of the story, since body weight so often changes over time. Dr. McHugh and his coinvestigators had data on change in BMI over the course of 10 years of follow-up in 15,627 psoriasis patients free of psoriatic arthritis at the time their psoriasis was diagnosed. The researchers developed a BMI risk calculator that expressed the effect of change in BMI over time on the cumulative risk of developing psoriatic arthritis.
“We were able to show that if, for instance, you started with a BMI of 25 at baseline and ended up with a BMI of 30, your risk of psoriatic arthritis goes up by 13%, whereas if you start at 30 and come down to 25, your risk decreases by 13%. And the more weight you lose, the greater you reduce your risk of developing psoriatic arthritis,” the rheumatologist explained in an interview.
Indeed, with more extreme changes in BMI over the course of a decade following diagnosis of psoriasis – for example, dropping from a baseline BMI of 36 kg/m2 to 23 kg/m2 – the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis fell by close to 30%.
Dr. McHugh reported having no financial conflicts regarding this study, funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research.
SOURCE: Green A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 2134.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: A psoriasis patient’s risk of developing psoriatic arthritis increases stepwise with greater body mass index, and the converse is true as well.
Study details: This study included more than 90,000 patients with a diagnosis of psoriasis in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding this study, funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research.
Source: Green A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 2134.
Intra-articular Wnt inhibitor for knee OA sails through phase 2
CHICAGO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel drug known for now as SMO4690 resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain and physical function through 6 months of follow-up in a phase 2b study including 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA, Yusuf Yazici, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based on the encouraging results of this and another large phase 2 study, two pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials are due to start in the spring of 2019. If the results are positive, SMO4690 could become the first approved disease-modifying OA drug (DMOAD), something that’s been a long-sought, high-priority goal in rheumatology, noted Dr. Yazici, chief medical officer at San Diego–based Samumed, which is developing the drug, and a rheumatologist at New York University.
SMO4690 is a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway. The drug has two distinct mechanisms of action for treatment of knee OA: It has an anti-inflammatory effect and it protects cartilage from degeneration, as demonstrated by a clinically significant improvement in joint space width by x-ray, compared with placebo at 12 months of follow-up after a single baseline injection in the earlier 455-patient, phase 2 study. Also, animal studies suggest SMO4690 generates cartilage, an exciting possibility now being evaluated in two ongoing serial MRI studies in knee OA patients.
Dr. Yazici presented patient-reported outcomes from the 695-patient, 24-week, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study, which evaluated four different concentrations of SMO4690. The 0.07- and 0.23-mg per 2-mL injection doses proved significantly better than placebo at 12 weeks – the primary endpoint – for all patient-reported outcomes.
The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 remained superior to placebo for all four patient-reported outcomes at subsequent assessments at weeks 16, 20, and 24. The 0.07-mg dose remained significantly better than placebo through week 20.
As in the earlier phase 2 study, SMO4690 raised no significant safety concerns. Adverse events were similar in type and frequency in the active-treatment and placebo groups.
The study was sponsored by Samumed, where Dr. Yazici is employed as chief medical officer.
SOURCE: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.
CHICAGO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel drug known for now as SMO4690 resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain and physical function through 6 months of follow-up in a phase 2b study including 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA, Yusuf Yazici, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based on the encouraging results of this and another large phase 2 study, two pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials are due to start in the spring of 2019. If the results are positive, SMO4690 could become the first approved disease-modifying OA drug (DMOAD), something that’s been a long-sought, high-priority goal in rheumatology, noted Dr. Yazici, chief medical officer at San Diego–based Samumed, which is developing the drug, and a rheumatologist at New York University.
SMO4690 is a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway. The drug has two distinct mechanisms of action for treatment of knee OA: It has an anti-inflammatory effect and it protects cartilage from degeneration, as demonstrated by a clinically significant improvement in joint space width by x-ray, compared with placebo at 12 months of follow-up after a single baseline injection in the earlier 455-patient, phase 2 study. Also, animal studies suggest SMO4690 generates cartilage, an exciting possibility now being evaluated in two ongoing serial MRI studies in knee OA patients.
Dr. Yazici presented patient-reported outcomes from the 695-patient, 24-week, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study, which evaluated four different concentrations of SMO4690. The 0.07- and 0.23-mg per 2-mL injection doses proved significantly better than placebo at 12 weeks – the primary endpoint – for all patient-reported outcomes.
The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 remained superior to placebo for all four patient-reported outcomes at subsequent assessments at weeks 16, 20, and 24. The 0.07-mg dose remained significantly better than placebo through week 20.
As in the earlier phase 2 study, SMO4690 raised no significant safety concerns. Adverse events were similar in type and frequency in the active-treatment and placebo groups.
The study was sponsored by Samumed, where Dr. Yazici is employed as chief medical officer.
SOURCE: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.
CHICAGO – A single intra-articular injection of a novel drug known for now as SMO4690 resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain and physical function through 6 months of follow-up in a phase 2b study including 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA, Yusuf Yazici, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based on the encouraging results of this and another large phase 2 study, two pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials are due to start in the spring of 2019. If the results are positive, SMO4690 could become the first approved disease-modifying OA drug (DMOAD), something that’s been a long-sought, high-priority goal in rheumatology, noted Dr. Yazici, chief medical officer at San Diego–based Samumed, which is developing the drug, and a rheumatologist at New York University.
SMO4690 is a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway. The drug has two distinct mechanisms of action for treatment of knee OA: It has an anti-inflammatory effect and it protects cartilage from degeneration, as demonstrated by a clinically significant improvement in joint space width by x-ray, compared with placebo at 12 months of follow-up after a single baseline injection in the earlier 455-patient, phase 2 study. Also, animal studies suggest SMO4690 generates cartilage, an exciting possibility now being evaluated in two ongoing serial MRI studies in knee OA patients.
Dr. Yazici presented patient-reported outcomes from the 695-patient, 24-week, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study, which evaluated four different concentrations of SMO4690. The 0.07- and 0.23-mg per 2-mL injection doses proved significantly better than placebo at 12 weeks – the primary endpoint – for all patient-reported outcomes.
The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 remained superior to placebo for all four patient-reported outcomes at subsequent assessments at weeks 16, 20, and 24. The 0.07-mg dose remained significantly better than placebo through week 20.
As in the earlier phase 2 study, SMO4690 raised no significant safety concerns. Adverse events were similar in type and frequency in the active-treatment and placebo groups.
The study was sponsored by Samumed, where Dr. Yazici is employed as chief medical officer.
SOURCE: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The 0.23-mg dose of SMO4690 proved superior to placebo for four key patient-reported outcomes.
Study details: This was a 24-week, randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2b study in 695 patients with moderately to severely symptomatic knee OA.
Disclosures: The presenter is chief medical officer at Samumed, the study sponsor.
Source: Yazici Y et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10), Abstract L03.
Three drugs disappoint in SSc trials, but show some promise
CHICAGO – Recent randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of tocilizumab, abatacept, and riociguat for the treatment of systemic sclerosis each failed to reach its primary endpoint of change from baseline in modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS).
Still, findings with respect to secondary endpoints and certain exploratory outcomes suggest each of the agents holds some promise in the systemic sclerosis (SSc) arena, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
In the double-blind portion of the phase 3 focuSSced trial of 212 patients with SSc, numerical improvement was observed for the primary endpoint of mean change in mRSS from baseline to week 48 with tocilizumab versus placebo (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points, respectively). The change in the treatment group was comparable with what was seen in the phase 2 faSScinate trial, but the decline in mRSS in the placebo group was much greater in phase 3 than in phase 2, and so the difference between the groups in the current study failed to reach statistical significance (P = .098), reported Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody was previously shown in the faSScinate trial to lead to numeric improvements in skin thickening as measured by the mRSS, as well as to clinically meaningful lung function preservation as measured by percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC).
In the current phase 3 study, key secondary end points also appeared to favor tocilizumab, but since the primary endpoint for mRSS was not met, all other P values cannot be considered statistically significant despite the strength of the evidence and were reported for informational purposes only, he noted.
The median cumulative distribution of change from baseline to week 48 in percent predicted FVC with tocilizumab versus placebo was –0.6 vs. –3.9, respectively (descriptive P = .0015), and the mean change from baseline in FVC at week 48 was –24 mL vs. –190 mL (difference of 167 mL in favor of tocilizumab; descriptive P = .0001).
Time to treatment failure also favored tocilizumab, he said (hazard ratio, 0.63; descriptive P = .082), he said.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either weekly 162-mg injections of subcutaneous tocilizumab or placebo for 48 weeks. Escape therapy was allowed beginning at week 16 if patients experienced declines in FVC or beginning at week 24 if they experienced worsened mRSS or worsened SSc complications, Dr. Khanna said.
“The key part is that no immunotherapy was allowed. ... So it’s a true randomized, placebo-controlled trial,” he said.
Most (81%) of the patients were women, and they had a mean age of 48 years, mean SSc duration of 23 months, mean mRSS of 20.4 units on a 0-51 scale, and a normal mean percent predicted FVC of 82.1%.
“HAQ-DI showed moderate disability of 1.2,” he noted.
Safety in the study was consistent with that seen in prior tocilizumab studies; no new safety signals were identified. Serious adverse events occurred in 13% and 17% of tocilizumab and placebo group patients , respectively, and serious infections were reported by 7% and 2%.
Although clinically meaningful and consistent differences in FVC favoring tocilizumab were shown in this study, the primary endpoint was not met, Dr. Khanna said.
“There were no statistically significant differences, largely driven by unexpected improvement in the placebo group, which was different than what we found in [the faSScinate] trial,” he said, noting, however, that the FVC findings in the current study were clinically meaningful.
Also, in a separate presentation at the meeting, he explained that the differences favoring tocilizumab were statistically significant when patient-level data from the trial were analyzed based on the ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS). Those findings provide validation of the novel outcomes measure, he said.
Abatacept (Orencia)
Dr. Khanna also reported results of the 12-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 ASSET trial of abatacept, which showed no significant difference in mRSS in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc (dfSSc) who were treated with 125 mg of the recombinant fusion protein weekly and those who received placebo. However, certain secondary outcomes favored abatacept. No concomitant immunotherapy was allowed.
The adjusted mean decrease in the mRSS among patients who completed the 12-month treatment period was –6.24 vs. –4.49 in 34 patients in the abatacept group and 35 in the placebo group, respectively (P = .28).
The secondary outcome measures of mean change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), patients global assessment, physician global assessment, and ACR CRISS scores were statistically significant or showed numerical results favoring abatacept over placebo: mean decrease in HAQ-DI, –0.17 vs. –0.11 (P = .05), respectively; mean change in physician global assessment scores, –1.30 vs. –0.35 (P = .03); median ACR CRISS index, 0.68 vs. 0.01 (P = .03), decline in percent predicted FVC of 4.13% and 1.34% (P = .11).
Escape therapy was allowed at 6 months for worsening SSc, but it did not change the outcomes trajectory, he said. A larger proportion of placebo vs. abatacept subjects required escape immunosuppressive therapy (36% vs. 16%; P = .03).
Patients were enrolled between 2014 and 2018 at 27 U.S., Canadian, and U.K. sites. At baseline, participants had a mean age of 49 years, 75% were women, and mean disease duration was very short at 1.59 years, with 60% having disease duration of 18 months or less. The mean baseline mRSS was 22.4, mean percent predicted FVC was 85.3%, and mean HAQ-DI was 1.0.
Compliance with both treatments was greater than 98%. Abatacept was well tolerated with comparable adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, and AEs of special interest such as infections and malignancies between treatments, Dr. Khanna said, noting that two deaths occurred in the abatacept group (caused by scleroderma renal crisis in both cases at days 11 and 46) and one occurred in a placebo group patient who experienced sudden cardiac arrest at day 310.
Of note, mRSS showed large variability, despite recruiting an early dcSSc population, Dr. Khanna said.
The finding with respect to the primary outcome is consistent with other recent trials because of improvement in mRSS that’s part of the natural history of the disease, including the tocilizumab findings that he reported at the meeting. The findings with respect to secondary endpoints and safety show promise.
“Stay tuned for robust ongoing work on the relationship between clinical changes and ongoing mechanistic work,” he said.
Riociguat (Adempas)
Similarly, in the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b RISE-SSc study comparing riociguat and placebo for early dcSSc, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change in mRSS did not reach statistical significance, but exploratory data suggested that the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator prevented disease progression in patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, head of the connective tissue diseases program at University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland).
The mean mRSS at baseline was comparable in 60 patients randomized to receive riociguat and 61 in the placebo group (16.8 and 16.71, respectively). These mean values at week 52 dropped to 14.63 vs. 15.73, respectively (P = .08).
“So it was close, but it didn’t reach significance,” he said.
The difference in the mRSS progression rate, however, suggested significant effects favoring riociguat (descriptive P = .02), he said.
Further, mean change from baseline to week 52 in percent predicted FVC was not different overall between the groups, but a large difference favoring riociguat was seen among patients with scleroderma interstitial lung disease at baseline (mean change of –2.7 vs. –8.9), he said.
No differences were seen between the groups in HAQ-DI or patient and physician global assessment. The proportion of patients with probability of improvement at 52 weeks as measured using ACR CRISS was also the same at 18% in both treatment arms, he noted, ”but the CRISS is designed more for assessing disease regression than for assessing prevention of progression.”
Treatment was, however, well tolerated. At week 52, fewer serious adverse events occurred with riociguat group than in the placebo group (15% vs. 25%, respectively), and no new safety signals were observed, he said.
Riociguat has previously shown antifibrotic effects in animal models and efficacy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease, so it was hypothesized that patients with dcSSc might benefit from riociguat therapy, Dr. Distler explained.
Study subjects had very early dcSSc (duration of 18 months or less; mean of 9 months), mRSS of 10-22 units, FVC of 45% predicted or greater, and diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide of at least 40% of predicted at screening.
Riociguat was given at an individually adjusted dose between 0.5 mg and 2.5 mg three times daily.
The findings demonstrate a numeric decrease in mRSS over time with riociguat versus placebo and a prevention of progression with riociguat; the failure to reach the primary endpoint may be related to the small study size and the higher than expected regression rate in the placebo group, Dr. Distler said.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. In addition, he has a patent on mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis.
SOURCES: Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 898 and Abstract 900; Distler O et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 903.
CHICAGO – Recent randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of tocilizumab, abatacept, and riociguat for the treatment of systemic sclerosis each failed to reach its primary endpoint of change from baseline in modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS).
Still, findings with respect to secondary endpoints and certain exploratory outcomes suggest each of the agents holds some promise in the systemic sclerosis (SSc) arena, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
In the double-blind portion of the phase 3 focuSSced trial of 212 patients with SSc, numerical improvement was observed for the primary endpoint of mean change in mRSS from baseline to week 48 with tocilizumab versus placebo (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points, respectively). The change in the treatment group was comparable with what was seen in the phase 2 faSScinate trial, but the decline in mRSS in the placebo group was much greater in phase 3 than in phase 2, and so the difference between the groups in the current study failed to reach statistical significance (P = .098), reported Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody was previously shown in the faSScinate trial to lead to numeric improvements in skin thickening as measured by the mRSS, as well as to clinically meaningful lung function preservation as measured by percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC).
In the current phase 3 study, key secondary end points also appeared to favor tocilizumab, but since the primary endpoint for mRSS was not met, all other P values cannot be considered statistically significant despite the strength of the evidence and were reported for informational purposes only, he noted.
The median cumulative distribution of change from baseline to week 48 in percent predicted FVC with tocilizumab versus placebo was –0.6 vs. –3.9, respectively (descriptive P = .0015), and the mean change from baseline in FVC at week 48 was –24 mL vs. –190 mL (difference of 167 mL in favor of tocilizumab; descriptive P = .0001).
Time to treatment failure also favored tocilizumab, he said (hazard ratio, 0.63; descriptive P = .082), he said.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either weekly 162-mg injections of subcutaneous tocilizumab or placebo for 48 weeks. Escape therapy was allowed beginning at week 16 if patients experienced declines in FVC or beginning at week 24 if they experienced worsened mRSS or worsened SSc complications, Dr. Khanna said.
“The key part is that no immunotherapy was allowed. ... So it’s a true randomized, placebo-controlled trial,” he said.
Most (81%) of the patients were women, and they had a mean age of 48 years, mean SSc duration of 23 months, mean mRSS of 20.4 units on a 0-51 scale, and a normal mean percent predicted FVC of 82.1%.
“HAQ-DI showed moderate disability of 1.2,” he noted.
Safety in the study was consistent with that seen in prior tocilizumab studies; no new safety signals were identified. Serious adverse events occurred in 13% and 17% of tocilizumab and placebo group patients , respectively, and serious infections were reported by 7% and 2%.
Although clinically meaningful and consistent differences in FVC favoring tocilizumab were shown in this study, the primary endpoint was not met, Dr. Khanna said.
“There were no statistically significant differences, largely driven by unexpected improvement in the placebo group, which was different than what we found in [the faSScinate] trial,” he said, noting, however, that the FVC findings in the current study were clinically meaningful.
Also, in a separate presentation at the meeting, he explained that the differences favoring tocilizumab were statistically significant when patient-level data from the trial were analyzed based on the ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS). Those findings provide validation of the novel outcomes measure, he said.
Abatacept (Orencia)
Dr. Khanna also reported results of the 12-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 ASSET trial of abatacept, which showed no significant difference in mRSS in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc (dfSSc) who were treated with 125 mg of the recombinant fusion protein weekly and those who received placebo. However, certain secondary outcomes favored abatacept. No concomitant immunotherapy was allowed.
The adjusted mean decrease in the mRSS among patients who completed the 12-month treatment period was –6.24 vs. –4.49 in 34 patients in the abatacept group and 35 in the placebo group, respectively (P = .28).
The secondary outcome measures of mean change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), patients global assessment, physician global assessment, and ACR CRISS scores were statistically significant or showed numerical results favoring abatacept over placebo: mean decrease in HAQ-DI, –0.17 vs. –0.11 (P = .05), respectively; mean change in physician global assessment scores, –1.30 vs. –0.35 (P = .03); median ACR CRISS index, 0.68 vs. 0.01 (P = .03), decline in percent predicted FVC of 4.13% and 1.34% (P = .11).
Escape therapy was allowed at 6 months for worsening SSc, but it did not change the outcomes trajectory, he said. A larger proportion of placebo vs. abatacept subjects required escape immunosuppressive therapy (36% vs. 16%; P = .03).
Patients were enrolled between 2014 and 2018 at 27 U.S., Canadian, and U.K. sites. At baseline, participants had a mean age of 49 years, 75% were women, and mean disease duration was very short at 1.59 years, with 60% having disease duration of 18 months or less. The mean baseline mRSS was 22.4, mean percent predicted FVC was 85.3%, and mean HAQ-DI was 1.0.
Compliance with both treatments was greater than 98%. Abatacept was well tolerated with comparable adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, and AEs of special interest such as infections and malignancies between treatments, Dr. Khanna said, noting that two deaths occurred in the abatacept group (caused by scleroderma renal crisis in both cases at days 11 and 46) and one occurred in a placebo group patient who experienced sudden cardiac arrest at day 310.
Of note, mRSS showed large variability, despite recruiting an early dcSSc population, Dr. Khanna said.
The finding with respect to the primary outcome is consistent with other recent trials because of improvement in mRSS that’s part of the natural history of the disease, including the tocilizumab findings that he reported at the meeting. The findings with respect to secondary endpoints and safety show promise.
“Stay tuned for robust ongoing work on the relationship between clinical changes and ongoing mechanistic work,” he said.
Riociguat (Adempas)
Similarly, in the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b RISE-SSc study comparing riociguat and placebo for early dcSSc, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change in mRSS did not reach statistical significance, but exploratory data suggested that the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator prevented disease progression in patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, head of the connective tissue diseases program at University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland).
The mean mRSS at baseline was comparable in 60 patients randomized to receive riociguat and 61 in the placebo group (16.8 and 16.71, respectively). These mean values at week 52 dropped to 14.63 vs. 15.73, respectively (P = .08).
“So it was close, but it didn’t reach significance,” he said.
The difference in the mRSS progression rate, however, suggested significant effects favoring riociguat (descriptive P = .02), he said.
Further, mean change from baseline to week 52 in percent predicted FVC was not different overall between the groups, but a large difference favoring riociguat was seen among patients with scleroderma interstitial lung disease at baseline (mean change of –2.7 vs. –8.9), he said.
No differences were seen between the groups in HAQ-DI or patient and physician global assessment. The proportion of patients with probability of improvement at 52 weeks as measured using ACR CRISS was also the same at 18% in both treatment arms, he noted, ”but the CRISS is designed more for assessing disease regression than for assessing prevention of progression.”
Treatment was, however, well tolerated. At week 52, fewer serious adverse events occurred with riociguat group than in the placebo group (15% vs. 25%, respectively), and no new safety signals were observed, he said.
Riociguat has previously shown antifibrotic effects in animal models and efficacy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease, so it was hypothesized that patients with dcSSc might benefit from riociguat therapy, Dr. Distler explained.
Study subjects had very early dcSSc (duration of 18 months or less; mean of 9 months), mRSS of 10-22 units, FVC of 45% predicted or greater, and diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide of at least 40% of predicted at screening.
Riociguat was given at an individually adjusted dose between 0.5 mg and 2.5 mg three times daily.
The findings demonstrate a numeric decrease in mRSS over time with riociguat versus placebo and a prevention of progression with riociguat; the failure to reach the primary endpoint may be related to the small study size and the higher than expected regression rate in the placebo group, Dr. Distler said.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. In addition, he has a patent on mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis.
SOURCES: Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 898 and Abstract 900; Distler O et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 903.
CHICAGO – Recent randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of tocilizumab, abatacept, and riociguat for the treatment of systemic sclerosis each failed to reach its primary endpoint of change from baseline in modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS).
Still, findings with respect to secondary endpoints and certain exploratory outcomes suggest each of the agents holds some promise in the systemic sclerosis (SSc) arena, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Tocilizumab (Actemra)
In the double-blind portion of the phase 3 focuSSced trial of 212 patients with SSc, numerical improvement was observed for the primary endpoint of mean change in mRSS from baseline to week 48 with tocilizumab versus placebo (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points, respectively). The change in the treatment group was comparable with what was seen in the phase 2 faSScinate trial, but the decline in mRSS in the placebo group was much greater in phase 3 than in phase 2, and so the difference between the groups in the current study failed to reach statistical significance (P = .098), reported Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody was previously shown in the faSScinate trial to lead to numeric improvements in skin thickening as measured by the mRSS, as well as to clinically meaningful lung function preservation as measured by percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC).
In the current phase 3 study, key secondary end points also appeared to favor tocilizumab, but since the primary endpoint for mRSS was not met, all other P values cannot be considered statistically significant despite the strength of the evidence and were reported for informational purposes only, he noted.
The median cumulative distribution of change from baseline to week 48 in percent predicted FVC with tocilizumab versus placebo was –0.6 vs. –3.9, respectively (descriptive P = .0015), and the mean change from baseline in FVC at week 48 was –24 mL vs. –190 mL (difference of 167 mL in favor of tocilizumab; descriptive P = .0001).
Time to treatment failure also favored tocilizumab, he said (hazard ratio, 0.63; descriptive P = .082), he said.
Patients were randomly assigned to receive either weekly 162-mg injections of subcutaneous tocilizumab or placebo for 48 weeks. Escape therapy was allowed beginning at week 16 if patients experienced declines in FVC or beginning at week 24 if they experienced worsened mRSS or worsened SSc complications, Dr. Khanna said.
“The key part is that no immunotherapy was allowed. ... So it’s a true randomized, placebo-controlled trial,” he said.
Most (81%) of the patients were women, and they had a mean age of 48 years, mean SSc duration of 23 months, mean mRSS of 20.4 units on a 0-51 scale, and a normal mean percent predicted FVC of 82.1%.
“HAQ-DI showed moderate disability of 1.2,” he noted.
Safety in the study was consistent with that seen in prior tocilizumab studies; no new safety signals were identified. Serious adverse events occurred in 13% and 17% of tocilizumab and placebo group patients , respectively, and serious infections were reported by 7% and 2%.
Although clinically meaningful and consistent differences in FVC favoring tocilizumab were shown in this study, the primary endpoint was not met, Dr. Khanna said.
“There were no statistically significant differences, largely driven by unexpected improvement in the placebo group, which was different than what we found in [the faSScinate] trial,” he said, noting, however, that the FVC findings in the current study were clinically meaningful.
Also, in a separate presentation at the meeting, he explained that the differences favoring tocilizumab were statistically significant when patient-level data from the trial were analyzed based on the ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS). Those findings provide validation of the novel outcomes measure, he said.
Abatacept (Orencia)
Dr. Khanna also reported results of the 12-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 ASSET trial of abatacept, which showed no significant difference in mRSS in patients with early diffuse cutaneous SSc (dfSSc) who were treated with 125 mg of the recombinant fusion protein weekly and those who received placebo. However, certain secondary outcomes favored abatacept. No concomitant immunotherapy was allowed.
The adjusted mean decrease in the mRSS among patients who completed the 12-month treatment period was –6.24 vs. –4.49 in 34 patients in the abatacept group and 35 in the placebo group, respectively (P = .28).
The secondary outcome measures of mean change in Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), patients global assessment, physician global assessment, and ACR CRISS scores were statistically significant or showed numerical results favoring abatacept over placebo: mean decrease in HAQ-DI, –0.17 vs. –0.11 (P = .05), respectively; mean change in physician global assessment scores, –1.30 vs. –0.35 (P = .03); median ACR CRISS index, 0.68 vs. 0.01 (P = .03), decline in percent predicted FVC of 4.13% and 1.34% (P = .11).
Escape therapy was allowed at 6 months for worsening SSc, but it did not change the outcomes trajectory, he said. A larger proportion of placebo vs. abatacept subjects required escape immunosuppressive therapy (36% vs. 16%; P = .03).
Patients were enrolled between 2014 and 2018 at 27 U.S., Canadian, and U.K. sites. At baseline, participants had a mean age of 49 years, 75% were women, and mean disease duration was very short at 1.59 years, with 60% having disease duration of 18 months or less. The mean baseline mRSS was 22.4, mean percent predicted FVC was 85.3%, and mean HAQ-DI was 1.0.
Compliance with both treatments was greater than 98%. Abatacept was well tolerated with comparable adverse events (AEs), serious AEs, and AEs of special interest such as infections and malignancies between treatments, Dr. Khanna said, noting that two deaths occurred in the abatacept group (caused by scleroderma renal crisis in both cases at days 11 and 46) and one occurred in a placebo group patient who experienced sudden cardiac arrest at day 310.
Of note, mRSS showed large variability, despite recruiting an early dcSSc population, Dr. Khanna said.
The finding with respect to the primary outcome is consistent with other recent trials because of improvement in mRSS that’s part of the natural history of the disease, including the tocilizumab findings that he reported at the meeting. The findings with respect to secondary endpoints and safety show promise.
“Stay tuned for robust ongoing work on the relationship between clinical changes and ongoing mechanistic work,” he said.
Riociguat (Adempas)
Similarly, in the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b RISE-SSc study comparing riociguat and placebo for early dcSSc, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change in mRSS did not reach statistical significance, but exploratory data suggested that the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator prevented disease progression in patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, head of the connective tissue diseases program at University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland).
The mean mRSS at baseline was comparable in 60 patients randomized to receive riociguat and 61 in the placebo group (16.8 and 16.71, respectively). These mean values at week 52 dropped to 14.63 vs. 15.73, respectively (P = .08).
“So it was close, but it didn’t reach significance,” he said.
The difference in the mRSS progression rate, however, suggested significant effects favoring riociguat (descriptive P = .02), he said.
Further, mean change from baseline to week 52 in percent predicted FVC was not different overall between the groups, but a large difference favoring riociguat was seen among patients with scleroderma interstitial lung disease at baseline (mean change of –2.7 vs. –8.9), he said.
No differences were seen between the groups in HAQ-DI or patient and physician global assessment. The proportion of patients with probability of improvement at 52 weeks as measured using ACR CRISS was also the same at 18% in both treatment arms, he noted, ”but the CRISS is designed more for assessing disease regression than for assessing prevention of progression.”
Treatment was, however, well tolerated. At week 52, fewer serious adverse events occurred with riociguat group than in the placebo group (15% vs. 25%, respectively), and no new safety signals were observed, he said.
Riociguat has previously shown antifibrotic effects in animal models and efficacy in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease, so it was hypothesized that patients with dcSSc might benefit from riociguat therapy, Dr. Distler explained.
Study subjects had very early dcSSc (duration of 18 months or less; mean of 9 months), mRSS of 10-22 units, FVC of 45% predicted or greater, and diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide of at least 40% of predicted at screening.
Riociguat was given at an individually adjusted dose between 0.5 mg and 2.5 mg three times daily.
The findings demonstrate a numeric decrease in mRSS over time with riociguat versus placebo and a prevention of progression with riociguat; the failure to reach the primary endpoint may be related to the small study size and the higher than expected regression rate in the placebo group, Dr. Distler said.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. In addition, he has a patent on mir-29 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis.
SOURCES: Khanna D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 898 and Abstract 900; Distler O et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract 903.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
ACR CRISS: A way forward for scleroderma treatment trials?
CHICAGO – At least three phase 3 randomized scleroderma treatment trials presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology failed to meet modified Rodnan Skin Score–based primary endpoints, but a different story emerged when data from the trials were analyzed using the novel ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS).
The differences highlight the limitations of individual outcome measures like the modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) and underscore the need for new measures that capture the complexity of systemic sclerosis (SSc) and are more sensitive to changes in disease severity, according to Robert Spiera, MD, director of the vasculitis and scleroderma program at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York.
Such measures are needed to better assess the effects of treatment interventions in scleroderma trials, Dr. Spiera said in an interview.
The ACR CRISS
Development of the ACR CRISS was led by Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He and his colleagues described the measure in 2016 (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;68[2]:299-311. doi: 10.1002/art.39501).
Its use involves a two-step process of identifying any significant disease worsening or new end-organ damage, and then calculating the probability of patient improvement after 1 year of treatment on a 0- to 1-point scale based on changes from baseline in five variables: the mRSS, percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC), patient and physician global assessments, and the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI).
A CRISS score of 0.6 or higher indicates likelihood that a patient improved on treatment. Of note, subjects with significant worsening of renal or cardiopulmonary involvement are classified as not improved (score of 0), regardless of improvements in other core items.
To devise the CRISS, the investigators compiled 150 patient profiles with standardized clinical outcome elements using patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc). The profiles were assessed by 40 scleroderma experts who rated patient improvement or lack thereof over 12 months.
Using the 79% of profiles for which a consensus was reached, the investigators “fit logistic regression models in which the binary outcome referred to whether the patient was improved or not, and the changes in the core set items from baseline to follow-up were entered as covariates,” they explained.
This led to the selection of the five measures included in the final version, which was found to have sensitivity of 0.982 and specificity of 0.931. When evaluated in a previously completed 1-year randomized controlled trial, the index differentiated the effect of methotrexate from the effect of placebo (P = .02), they reported.
Based on these findings, the ACR board of directors granted “provisional” endorsement of the CRISS for use in SSc clinical studies, signifying that it had been quantitatively validated using patient data, but had not undergone validation using an external data set.
New data presented at the 2018 ACR meeting will likely lead to full approval of the measure once the studies validating the measure are published, according to Dr. Spiera.
The focuSSced study of tocilizumab
For example, in the phase 3 focuSSced study comparing the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody tocilizumab (Actemra) with placebo in patients with SSc, the primary endpoint of mean change from baseline in mRSS was not met (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points with tocilizumab vs. placebo, respectively; P = .098), Dr. Khanna said during a report of findings from the double-blind portion of the study.
However, when the CRISS was applied and its performance prospectively assessed as an exploratory outcome at week 48 in the focuSSced trial, the differences between the groups were statistically significant. Dr. Khanna reported those findings in a separate presentation at the meeting, noting that they marked the first prospective evaluation of the ACR CRISS in a phase 3 trial in SSc.
The CRISS was applied – using a blinded review of adverse events and serious adverse events to complete step 1 – in all patients who received study treatment, stratified by baseline IL-6 levels.
Of 104 patients in the tocilizumab arm and 106 in the placebo arm, 6 and 13 patients, respectively, had cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement and therefore received a score of 0.
Using the ACR CRISS as a continuous measure, scores favored tocilizumab over placebo at week 48 with a median increase of 0.89 vs. 0.25 points (P = .023), and using the binary form of CRISS, 51% vs. 37% of patients in the treatment and placebo arms achieved the score cutoff of 0.60 or higher at week 48 (P = .035), he said.
“The focuSSced study validates the ACR CRISS endpoint for the first time in an independent prospective clinical trial and highlights the importance of step 1 as an indicator of reduced organ progression during 48 weeks of treatment,” Dr. Khanna concluded.
The ASSET trial of abatacept
Dr. Khanna also reported results from the 12-month phase 2 ASSET trial comparing abatacept (Orencia) and placebo in early dcSSc.
Again, the change from baseline in mRSS – the primary endpoint of the study – did not differ significantly with treatment vs. placebo (–6.24 vs. –4.49; P = .28).
And again, as presented separately in a poster session at ACR, application of CRISS at 12 months – a secondary outcome measure in the trial – showed a significant difference between the groups.
The investigators prospectively performed step 1 of the CRISS using a case report form. Of 63 patients with complete data available for relevant outcomes at 12 months, 10 (5 in each group) had cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement and thus were given a score of 0.
Overall, there was evidence of significantly improved CRISS scores in the abatacept group vs. the placebo group (P = .03), he said.
Most of the individual CRISS variables, except HAQ-DI and patient global assessment, had statistically significant correlations with the CRISS, he noted, adding that “although the degree of correlation is high between the mRSS and CRISS, there is evidence that CRISS may be more sensitive to clinically meaningful treatment changes than the standard skin score endpoint.”
“This suggests further validation of CRISS as an independent primary endpoint for scleroderma clinical trials,” he concluded.
The phase 2b RISE-SSc study of riociguat
As in the focuSSced and ASSET studies, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change from baseline in mRSS was not met in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled RISE-SSc study evaluating the safety and efficacy of the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator riociguat (Adempas) vs. placebo in 121 patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, a professor at University Hospital Zurich.
The mean change in mRSS at 52 weeks was 2.25 vs. 0.97 with riociguat vs. placebo, respectively (P = .08), although the difference in mRSS progression rate showed significant effects favoring riociguat (P = .02), he noted.
In this study, however, the proportion of patients with ACR CRISS probability of improvement (score of 0.60 or higher) at week 52 – a secondary study outcome – was the same at 18% in both arms, Dr. Distler said.
In a way, it’s helpful that the CRISS findings as well as the mRSS outcome in the RISE-SSc study were negative because it shows that “not everything comes up positive using the CRISS,” Dr. Spiera said.
An open-label extension trial of lenabasum
In the open-label extension of a phase 2 trial of lenabasum, Dr. Spiera and his colleagues also found the CRISS useful for assessing response in 36 patients. Lenabasum is a synthetic, nonimunosuppressive, selective cannabinoid receptor type 2 agonist that activates resolution of innate immune responses.
The agent continued to demonstrate acceptable safety and tolerability in dcSSc with no severe or serious adverse events or study discontinuations related to treatment during 12 months of open-label extension dosing, both from baseline and from the start of the extension, they reported in a poster at the ACR meeting. These assessments were based on ACR CRISS score, mRSS, physician global assessment, and multiple patient-reported outcomes.
The median CRISS score was 92% at week 52, and mRSS declined by a mean of 9.4 points (41.3% from baseline). More than a third of patients (35%) achieved a low mRSS of 10 or less.
The investigators noted, however, that definitive attribution of the findings to lenabasum is limited by the use of background therapy, the potential for spontaneous improvement in patients, and open-label dosing.
Evaluating immunosuppressive therapy in SSc
In another study presented at the ACR meeting, Boyang Zheng, MD, a second-year rheumatology fellow at McGill University in Montreal and his colleagues evaluated the effect of current immunosuppressive therapy on the ACR CRISS in 301 adult dcSSc patients without prior immunosuppression who were part of the Canadian Scleroderma Research Group (CSRG) registry.
Patients newly treated with methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate and/or cyclophosphamide for at least 2 years (47 patients) were considered “exposed patients,” and untreated patients with at least the same follow-up duration were considered control subjects (254 patients).
Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was performed to balance potential confounders in the two groups, including age, sex, disease duration, and CRISS variables, in an effort “to create a statistical cohort that would resemble a randomized, controlled trial,” Dr Zheng explained.
Prior to IPTW, treated patients trended towards more improvement after 1 year, but with “unimpressive absolute values.”
“But [after IPTW], when you look at overall CRISS at 1 year, more of the treated patients had actually improved – 23% vs. 11.8% in the untreated patients. After adjusting for age, sex, and disease duration, immunosuppression was associated with an almost twofold higher likelihood of improvement, although this was not statistically significant,” he said.
“Most importantly, after our balancing in the statistical cohort – so after balancing and adjusting for covariates ... immunosuppression use was still associated with a higher likelihood of improving [with an] odds ratio of 1.85 and P-value of 0.018,” he said.
The treated patients were sicker, and the CRISS was still able to capture individual patient improvement, he added.
Though limited by the observational design and the fact that “IPTW balancing cannot correct for all possible confounders,” the findings “provide novel evidence to support the use of immunosuppression in diffuse systemic sclerosis, and this reassures us in our current practice; it provides evidence that the CRISS seems to have better sensitivity to change than the mean of individual disease measures,” he said.
However, it also shows that “we have a long way to go to have better treatment for our patients,” he added, noting that only a minority (23%) of the patients in this study improved on the CRISS.
Moving forward in systemic sclerosis
Indeed, in order to move forward in developing better treatment for SSc, it is important to have the best possible means for assessing the effects of the potential new treatments, Dr. Spiera said.
“The mRSS is a good, reliable outcome measure in terms of intra- and inter-rater reliability, and we know it has meaning in the real world; in a patient with rapidly progressive skin thickening and a skin score that is getting higher and higher, we know they have worse prognosis in terms of function and even survival,” he said. “On the other hand, it’s just one piece of this very complicated story when you’re dealing with patients with systemic sclerosis, some of whom can have important internal organ involvement and not even have skin involvement.”
The main challenge with the skin score is how it performs in clinical trials when it comes to demonstrating whether a drug works, he added.
“This is particularly relevant in an era where our better understanding of the disease has led to candidate therapeutic agents that we have reason to think might work, but where clinical trials haven’t shown a significant difference between the groups using the skin score.”
Conversely, there have been studies in which skin scores improve, but the patient is doing terribly, he noted.
“That patient would not be [shown to be] doing well using the CRISS,” he said, explaining that the complex formula used to determine the CRISS score, which is “heavily weighted toward skin score,” allows for an overall score that is “greater than the sum of its parts.” That is, if a patient is improving in multiple domains indicating that the patient is responding to therapy, more credit is given for each of those parts.
“So my sense, and I think it’s the consensus in the community of clinical investigators, is that the skin score is not adequately sensitive to change in the context of a trial and doesn’t capture the disease holistically enough to be the optimal measure for scleroderma clinical trials,” he said. “We think the CRISS score works better in terms of capturing improvement in the course of a trial, and also in capturing other outcomes that are really, really important to patients and to their physicians, like disability or lung function.”
The hope is that, given the evidence, regulatory agencies will look favorably on the ACR CRISS as an outcome measure in clinical trials moving forward, and that understanding of its use and value will increase across the rheumatology community, he said.
Dr. Spiera has received research grants, consulting fees, and/or other payments from many companies involved in SSc treatments, including Roche/Genentech, which markets tocilizumab, and Corbus Pharmaceuticals, which is developing lenabasum.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an NIH/NIAID Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. He also has a patent for a treatment for systemic sclerosis.
Dr. Zheng reported having no disclosures.
sworcester@mdedge.com
CHICAGO – At least three phase 3 randomized scleroderma treatment trials presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology failed to meet modified Rodnan Skin Score–based primary endpoints, but a different story emerged when data from the trials were analyzed using the novel ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS).
The differences highlight the limitations of individual outcome measures like the modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) and underscore the need for new measures that capture the complexity of systemic sclerosis (SSc) and are more sensitive to changes in disease severity, according to Robert Spiera, MD, director of the vasculitis and scleroderma program at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York.
Such measures are needed to better assess the effects of treatment interventions in scleroderma trials, Dr. Spiera said in an interview.
The ACR CRISS
Development of the ACR CRISS was led by Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He and his colleagues described the measure in 2016 (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;68[2]:299-311. doi: 10.1002/art.39501).
Its use involves a two-step process of identifying any significant disease worsening or new end-organ damage, and then calculating the probability of patient improvement after 1 year of treatment on a 0- to 1-point scale based on changes from baseline in five variables: the mRSS, percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC), patient and physician global assessments, and the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI).
A CRISS score of 0.6 or higher indicates likelihood that a patient improved on treatment. Of note, subjects with significant worsening of renal or cardiopulmonary involvement are classified as not improved (score of 0), regardless of improvements in other core items.
To devise the CRISS, the investigators compiled 150 patient profiles with standardized clinical outcome elements using patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc). The profiles were assessed by 40 scleroderma experts who rated patient improvement or lack thereof over 12 months.
Using the 79% of profiles for which a consensus was reached, the investigators “fit logistic regression models in which the binary outcome referred to whether the patient was improved or not, and the changes in the core set items from baseline to follow-up were entered as covariates,” they explained.
This led to the selection of the five measures included in the final version, which was found to have sensitivity of 0.982 and specificity of 0.931. When evaluated in a previously completed 1-year randomized controlled trial, the index differentiated the effect of methotrexate from the effect of placebo (P = .02), they reported.
Based on these findings, the ACR board of directors granted “provisional” endorsement of the CRISS for use in SSc clinical studies, signifying that it had been quantitatively validated using patient data, but had not undergone validation using an external data set.
New data presented at the 2018 ACR meeting will likely lead to full approval of the measure once the studies validating the measure are published, according to Dr. Spiera.
The focuSSced study of tocilizumab
For example, in the phase 3 focuSSced study comparing the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody tocilizumab (Actemra) with placebo in patients with SSc, the primary endpoint of mean change from baseline in mRSS was not met (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points with tocilizumab vs. placebo, respectively; P = .098), Dr. Khanna said during a report of findings from the double-blind portion of the study.
However, when the CRISS was applied and its performance prospectively assessed as an exploratory outcome at week 48 in the focuSSced trial, the differences between the groups were statistically significant. Dr. Khanna reported those findings in a separate presentation at the meeting, noting that they marked the first prospective evaluation of the ACR CRISS in a phase 3 trial in SSc.
The CRISS was applied – using a blinded review of adverse events and serious adverse events to complete step 1 – in all patients who received study treatment, stratified by baseline IL-6 levels.
Of 104 patients in the tocilizumab arm and 106 in the placebo arm, 6 and 13 patients, respectively, had cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement and therefore received a score of 0.
Using the ACR CRISS as a continuous measure, scores favored tocilizumab over placebo at week 48 with a median increase of 0.89 vs. 0.25 points (P = .023), and using the binary form of CRISS, 51% vs. 37% of patients in the treatment and placebo arms achieved the score cutoff of 0.60 or higher at week 48 (P = .035), he said.
“The focuSSced study validates the ACR CRISS endpoint for the first time in an independent prospective clinical trial and highlights the importance of step 1 as an indicator of reduced organ progression during 48 weeks of treatment,” Dr. Khanna concluded.
The ASSET trial of abatacept
Dr. Khanna also reported results from the 12-month phase 2 ASSET trial comparing abatacept (Orencia) and placebo in early dcSSc.
Again, the change from baseline in mRSS – the primary endpoint of the study – did not differ significantly with treatment vs. placebo (–6.24 vs. –4.49; P = .28).
And again, as presented separately in a poster session at ACR, application of CRISS at 12 months – a secondary outcome measure in the trial – showed a significant difference between the groups.
The investigators prospectively performed step 1 of the CRISS using a case report form. Of 63 patients with complete data available for relevant outcomes at 12 months, 10 (5 in each group) had cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement and thus were given a score of 0.
Overall, there was evidence of significantly improved CRISS scores in the abatacept group vs. the placebo group (P = .03), he said.
Most of the individual CRISS variables, except HAQ-DI and patient global assessment, had statistically significant correlations with the CRISS, he noted, adding that “although the degree of correlation is high between the mRSS and CRISS, there is evidence that CRISS may be more sensitive to clinically meaningful treatment changes than the standard skin score endpoint.”
“This suggests further validation of CRISS as an independent primary endpoint for scleroderma clinical trials,” he concluded.
The phase 2b RISE-SSc study of riociguat
As in the focuSSced and ASSET studies, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change from baseline in mRSS was not met in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled RISE-SSc study evaluating the safety and efficacy of the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator riociguat (Adempas) vs. placebo in 121 patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, a professor at University Hospital Zurich.
The mean change in mRSS at 52 weeks was 2.25 vs. 0.97 with riociguat vs. placebo, respectively (P = .08), although the difference in mRSS progression rate showed significant effects favoring riociguat (P = .02), he noted.
In this study, however, the proportion of patients with ACR CRISS probability of improvement (score of 0.60 or higher) at week 52 – a secondary study outcome – was the same at 18% in both arms, Dr. Distler said.
In a way, it’s helpful that the CRISS findings as well as the mRSS outcome in the RISE-SSc study were negative because it shows that “not everything comes up positive using the CRISS,” Dr. Spiera said.
An open-label extension trial of lenabasum
In the open-label extension of a phase 2 trial of lenabasum, Dr. Spiera and his colleagues also found the CRISS useful for assessing response in 36 patients. Lenabasum is a synthetic, nonimunosuppressive, selective cannabinoid receptor type 2 agonist that activates resolution of innate immune responses.
The agent continued to demonstrate acceptable safety and tolerability in dcSSc with no severe or serious adverse events or study discontinuations related to treatment during 12 months of open-label extension dosing, both from baseline and from the start of the extension, they reported in a poster at the ACR meeting. These assessments were based on ACR CRISS score, mRSS, physician global assessment, and multiple patient-reported outcomes.
The median CRISS score was 92% at week 52, and mRSS declined by a mean of 9.4 points (41.3% from baseline). More than a third of patients (35%) achieved a low mRSS of 10 or less.
The investigators noted, however, that definitive attribution of the findings to lenabasum is limited by the use of background therapy, the potential for spontaneous improvement in patients, and open-label dosing.
Evaluating immunosuppressive therapy in SSc
In another study presented at the ACR meeting, Boyang Zheng, MD, a second-year rheumatology fellow at McGill University in Montreal and his colleagues evaluated the effect of current immunosuppressive therapy on the ACR CRISS in 301 adult dcSSc patients without prior immunosuppression who were part of the Canadian Scleroderma Research Group (CSRG) registry.
Patients newly treated with methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate and/or cyclophosphamide for at least 2 years (47 patients) were considered “exposed patients,” and untreated patients with at least the same follow-up duration were considered control subjects (254 patients).
Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was performed to balance potential confounders in the two groups, including age, sex, disease duration, and CRISS variables, in an effort “to create a statistical cohort that would resemble a randomized, controlled trial,” Dr Zheng explained.
Prior to IPTW, treated patients trended towards more improvement after 1 year, but with “unimpressive absolute values.”
“But [after IPTW], when you look at overall CRISS at 1 year, more of the treated patients had actually improved – 23% vs. 11.8% in the untreated patients. After adjusting for age, sex, and disease duration, immunosuppression was associated with an almost twofold higher likelihood of improvement, although this was not statistically significant,” he said.
“Most importantly, after our balancing in the statistical cohort – so after balancing and adjusting for covariates ... immunosuppression use was still associated with a higher likelihood of improving [with an] odds ratio of 1.85 and P-value of 0.018,” he said.
The treated patients were sicker, and the CRISS was still able to capture individual patient improvement, he added.
Though limited by the observational design and the fact that “IPTW balancing cannot correct for all possible confounders,” the findings “provide novel evidence to support the use of immunosuppression in diffuse systemic sclerosis, and this reassures us in our current practice; it provides evidence that the CRISS seems to have better sensitivity to change than the mean of individual disease measures,” he said.
However, it also shows that “we have a long way to go to have better treatment for our patients,” he added, noting that only a minority (23%) of the patients in this study improved on the CRISS.
Moving forward in systemic sclerosis
Indeed, in order to move forward in developing better treatment for SSc, it is important to have the best possible means for assessing the effects of the potential new treatments, Dr. Spiera said.
“The mRSS is a good, reliable outcome measure in terms of intra- and inter-rater reliability, and we know it has meaning in the real world; in a patient with rapidly progressive skin thickening and a skin score that is getting higher and higher, we know they have worse prognosis in terms of function and even survival,” he said. “On the other hand, it’s just one piece of this very complicated story when you’re dealing with patients with systemic sclerosis, some of whom can have important internal organ involvement and not even have skin involvement.”
The main challenge with the skin score is how it performs in clinical trials when it comes to demonstrating whether a drug works, he added.
“This is particularly relevant in an era where our better understanding of the disease has led to candidate therapeutic agents that we have reason to think might work, but where clinical trials haven’t shown a significant difference between the groups using the skin score.”
Conversely, there have been studies in which skin scores improve, but the patient is doing terribly, he noted.
“That patient would not be [shown to be] doing well using the CRISS,” he said, explaining that the complex formula used to determine the CRISS score, which is “heavily weighted toward skin score,” allows for an overall score that is “greater than the sum of its parts.” That is, if a patient is improving in multiple domains indicating that the patient is responding to therapy, more credit is given for each of those parts.
“So my sense, and I think it’s the consensus in the community of clinical investigators, is that the skin score is not adequately sensitive to change in the context of a trial and doesn’t capture the disease holistically enough to be the optimal measure for scleroderma clinical trials,” he said. “We think the CRISS score works better in terms of capturing improvement in the course of a trial, and also in capturing other outcomes that are really, really important to patients and to their physicians, like disability or lung function.”
The hope is that, given the evidence, regulatory agencies will look favorably on the ACR CRISS as an outcome measure in clinical trials moving forward, and that understanding of its use and value will increase across the rheumatology community, he said.
Dr. Spiera has received research grants, consulting fees, and/or other payments from many companies involved in SSc treatments, including Roche/Genentech, which markets tocilizumab, and Corbus Pharmaceuticals, which is developing lenabasum.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an NIH/NIAID Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. He also has a patent for a treatment for systemic sclerosis.
Dr. Zheng reported having no disclosures.
sworcester@mdedge.com
CHICAGO – At least three phase 3 randomized scleroderma treatment trials presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology failed to meet modified Rodnan Skin Score–based primary endpoints, but a different story emerged when data from the trials were analyzed using the novel ACR Composite Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS).
The differences highlight the limitations of individual outcome measures like the modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) and underscore the need for new measures that capture the complexity of systemic sclerosis (SSc) and are more sensitive to changes in disease severity, according to Robert Spiera, MD, director of the vasculitis and scleroderma program at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York.
Such measures are needed to better assess the effects of treatment interventions in scleroderma trials, Dr. Spiera said in an interview.
The ACR CRISS
Development of the ACR CRISS was led by Dinesh Khanna, MBBS, a professor of medicine and director of the scleroderma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He and his colleagues described the measure in 2016 (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;68[2]:299-311. doi: 10.1002/art.39501).
Its use involves a two-step process of identifying any significant disease worsening or new end-organ damage, and then calculating the probability of patient improvement after 1 year of treatment on a 0- to 1-point scale based on changes from baseline in five variables: the mRSS, percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC), patient and physician global assessments, and the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI).
A CRISS score of 0.6 or higher indicates likelihood that a patient improved on treatment. Of note, subjects with significant worsening of renal or cardiopulmonary involvement are classified as not improved (score of 0), regardless of improvements in other core items.
To devise the CRISS, the investigators compiled 150 patient profiles with standardized clinical outcome elements using patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc). The profiles were assessed by 40 scleroderma experts who rated patient improvement or lack thereof over 12 months.
Using the 79% of profiles for which a consensus was reached, the investigators “fit logistic regression models in which the binary outcome referred to whether the patient was improved or not, and the changes in the core set items from baseline to follow-up were entered as covariates,” they explained.
This led to the selection of the five measures included in the final version, which was found to have sensitivity of 0.982 and specificity of 0.931. When evaluated in a previously completed 1-year randomized controlled trial, the index differentiated the effect of methotrexate from the effect of placebo (P = .02), they reported.
Based on these findings, the ACR board of directors granted “provisional” endorsement of the CRISS for use in SSc clinical studies, signifying that it had been quantitatively validated using patient data, but had not undergone validation using an external data set.
New data presented at the 2018 ACR meeting will likely lead to full approval of the measure once the studies validating the measure are published, according to Dr. Spiera.
The focuSSced study of tocilizumab
For example, in the phase 3 focuSSced study comparing the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor–alpha antibody tocilizumab (Actemra) with placebo in patients with SSc, the primary endpoint of mean change from baseline in mRSS was not met (–6.14 vs. –4.41 points with tocilizumab vs. placebo, respectively; P = .098), Dr. Khanna said during a report of findings from the double-blind portion of the study.
However, when the CRISS was applied and its performance prospectively assessed as an exploratory outcome at week 48 in the focuSSced trial, the differences between the groups were statistically significant. Dr. Khanna reported those findings in a separate presentation at the meeting, noting that they marked the first prospective evaluation of the ACR CRISS in a phase 3 trial in SSc.
The CRISS was applied – using a blinded review of adverse events and serious adverse events to complete step 1 – in all patients who received study treatment, stratified by baseline IL-6 levels.
Of 104 patients in the tocilizumab arm and 106 in the placebo arm, 6 and 13 patients, respectively, had cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement and therefore received a score of 0.
Using the ACR CRISS as a continuous measure, scores favored tocilizumab over placebo at week 48 with a median increase of 0.89 vs. 0.25 points (P = .023), and using the binary form of CRISS, 51% vs. 37% of patients in the treatment and placebo arms achieved the score cutoff of 0.60 or higher at week 48 (P = .035), he said.
“The focuSSced study validates the ACR CRISS endpoint for the first time in an independent prospective clinical trial and highlights the importance of step 1 as an indicator of reduced organ progression during 48 weeks of treatment,” Dr. Khanna concluded.
The ASSET trial of abatacept
Dr. Khanna also reported results from the 12-month phase 2 ASSET trial comparing abatacept (Orencia) and placebo in early dcSSc.
Again, the change from baseline in mRSS – the primary endpoint of the study – did not differ significantly with treatment vs. placebo (–6.24 vs. –4.49; P = .28).
And again, as presented separately in a poster session at ACR, application of CRISS at 12 months – a secondary outcome measure in the trial – showed a significant difference between the groups.
The investigators prospectively performed step 1 of the CRISS using a case report form. Of 63 patients with complete data available for relevant outcomes at 12 months, 10 (5 in each group) had cardio-pulmonary-renal involvement and thus were given a score of 0.
Overall, there was evidence of significantly improved CRISS scores in the abatacept group vs. the placebo group (P = .03), he said.
Most of the individual CRISS variables, except HAQ-DI and patient global assessment, had statistically significant correlations with the CRISS, he noted, adding that “although the degree of correlation is high between the mRSS and CRISS, there is evidence that CRISS may be more sensitive to clinically meaningful treatment changes than the standard skin score endpoint.”
“This suggests further validation of CRISS as an independent primary endpoint for scleroderma clinical trials,” he concluded.
The phase 2b RISE-SSc study of riociguat
As in the focuSSced and ASSET studies, the primary efficacy endpoint of mean change from baseline in mRSS was not met in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled RISE-SSc study evaluating the safety and efficacy of the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator riociguat (Adempas) vs. placebo in 121 patients with early dcSSc, reported Oliver Distler, MD, a professor at University Hospital Zurich.
The mean change in mRSS at 52 weeks was 2.25 vs. 0.97 with riociguat vs. placebo, respectively (P = .08), although the difference in mRSS progression rate showed significant effects favoring riociguat (P = .02), he noted.
In this study, however, the proportion of patients with ACR CRISS probability of improvement (score of 0.60 or higher) at week 52 – a secondary study outcome – was the same at 18% in both arms, Dr. Distler said.
In a way, it’s helpful that the CRISS findings as well as the mRSS outcome in the RISE-SSc study were negative because it shows that “not everything comes up positive using the CRISS,” Dr. Spiera said.
An open-label extension trial of lenabasum
In the open-label extension of a phase 2 trial of lenabasum, Dr. Spiera and his colleagues also found the CRISS useful for assessing response in 36 patients. Lenabasum is a synthetic, nonimunosuppressive, selective cannabinoid receptor type 2 agonist that activates resolution of innate immune responses.
The agent continued to demonstrate acceptable safety and tolerability in dcSSc with no severe or serious adverse events or study discontinuations related to treatment during 12 months of open-label extension dosing, both from baseline and from the start of the extension, they reported in a poster at the ACR meeting. These assessments were based on ACR CRISS score, mRSS, physician global assessment, and multiple patient-reported outcomes.
The median CRISS score was 92% at week 52, and mRSS declined by a mean of 9.4 points (41.3% from baseline). More than a third of patients (35%) achieved a low mRSS of 10 or less.
The investigators noted, however, that definitive attribution of the findings to lenabasum is limited by the use of background therapy, the potential for spontaneous improvement in patients, and open-label dosing.
Evaluating immunosuppressive therapy in SSc
In another study presented at the ACR meeting, Boyang Zheng, MD, a second-year rheumatology fellow at McGill University in Montreal and his colleagues evaluated the effect of current immunosuppressive therapy on the ACR CRISS in 301 adult dcSSc patients without prior immunosuppression who were part of the Canadian Scleroderma Research Group (CSRG) registry.
Patients newly treated with methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate and/or cyclophosphamide for at least 2 years (47 patients) were considered “exposed patients,” and untreated patients with at least the same follow-up duration were considered control subjects (254 patients).
Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was performed to balance potential confounders in the two groups, including age, sex, disease duration, and CRISS variables, in an effort “to create a statistical cohort that would resemble a randomized, controlled trial,” Dr Zheng explained.
Prior to IPTW, treated patients trended towards more improvement after 1 year, but with “unimpressive absolute values.”
“But [after IPTW], when you look at overall CRISS at 1 year, more of the treated patients had actually improved – 23% vs. 11.8% in the untreated patients. After adjusting for age, sex, and disease duration, immunosuppression was associated with an almost twofold higher likelihood of improvement, although this was not statistically significant,” he said.
“Most importantly, after our balancing in the statistical cohort – so after balancing and adjusting for covariates ... immunosuppression use was still associated with a higher likelihood of improving [with an] odds ratio of 1.85 and P-value of 0.018,” he said.
The treated patients were sicker, and the CRISS was still able to capture individual patient improvement, he added.
Though limited by the observational design and the fact that “IPTW balancing cannot correct for all possible confounders,” the findings “provide novel evidence to support the use of immunosuppression in diffuse systemic sclerosis, and this reassures us in our current practice; it provides evidence that the CRISS seems to have better sensitivity to change than the mean of individual disease measures,” he said.
However, it also shows that “we have a long way to go to have better treatment for our patients,” he added, noting that only a minority (23%) of the patients in this study improved on the CRISS.
Moving forward in systemic sclerosis
Indeed, in order to move forward in developing better treatment for SSc, it is important to have the best possible means for assessing the effects of the potential new treatments, Dr. Spiera said.
“The mRSS is a good, reliable outcome measure in terms of intra- and inter-rater reliability, and we know it has meaning in the real world; in a patient with rapidly progressive skin thickening and a skin score that is getting higher and higher, we know they have worse prognosis in terms of function and even survival,” he said. “On the other hand, it’s just one piece of this very complicated story when you’re dealing with patients with systemic sclerosis, some of whom can have important internal organ involvement and not even have skin involvement.”
The main challenge with the skin score is how it performs in clinical trials when it comes to demonstrating whether a drug works, he added.
“This is particularly relevant in an era where our better understanding of the disease has led to candidate therapeutic agents that we have reason to think might work, but where clinical trials haven’t shown a significant difference between the groups using the skin score.”
Conversely, there have been studies in which skin scores improve, but the patient is doing terribly, he noted.
“That patient would not be [shown to be] doing well using the CRISS,” he said, explaining that the complex formula used to determine the CRISS score, which is “heavily weighted toward skin score,” allows for an overall score that is “greater than the sum of its parts.” That is, if a patient is improving in multiple domains indicating that the patient is responding to therapy, more credit is given for each of those parts.
“So my sense, and I think it’s the consensus in the community of clinical investigators, is that the skin score is not adequately sensitive to change in the context of a trial and doesn’t capture the disease holistically enough to be the optimal measure for scleroderma clinical trials,” he said. “We think the CRISS score works better in terms of capturing improvement in the course of a trial, and also in capturing other outcomes that are really, really important to patients and to their physicians, like disability or lung function.”
The hope is that, given the evidence, regulatory agencies will look favorably on the ACR CRISS as an outcome measure in clinical trials moving forward, and that understanding of its use and value will increase across the rheumatology community, he said.
Dr. Spiera has received research grants, consulting fees, and/or other payments from many companies involved in SSc treatments, including Roche/Genentech, which markets tocilizumab, and Corbus Pharmaceuticals, which is developing lenabasum.
Dr. Khanna is a consultant to Roche/Genentech and Bayer, which markets riociguat, and other companies. He has received research grants from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which markets abatacept), and Pfizer. The ASSET trial he presented was sponsored by an NIH/NIAID Clinical ACE grant and an investigator-initiated grant by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Dr. Distler has a consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding from Bayer, Roche/Genentech, and other companies. He also has a patent for a treatment for systemic sclerosis.
Dr. Zheng reported having no disclosures.
sworcester@mdedge.com
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Glucocorticoid elimination works for 2/3 of RA patients on tocilizumab
CHICAGO – while remaining in at least low disease activity in a multicenter, randomized trial with 259 patients.
The results also showed that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients randomized to maintain prednisone treatment at 5 mg/day along with tocilizumab fared even better. After 24 weeks of the glucocorticoid-tapering regimen, by which time patients in the tapered arm had their prednisone dosage down to 0 mg, the average change from baseline in their disease activity score 28 with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) was an increase of 0.538, compared with an average drop of 0.075 among untapered patients, a statistically significant difference for the study’s primary endpoint, Gerd R. Burmester, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
But while the results definitively showed that RA patients treated with the anti-interleukin 6 agent tocilizumab (Actemra) as their primary drug benefited from continued, additional treatment with low-dose prednisone, the results also showed that many patients could come off prednisone without immediate downside. Among the 131 randomized to a forced taper and eventual prednisone discontinuation, 85 (65%) went through this process without flaring and maintained at least low disease activity and sometimes remission, said Dr. Burmester, a professor and director of rheumatology and clinical immunology at Charité Hospital in Berlin. In contrast, 99 of 128 patients (77%) maintained on tocilizumab plus 5 mg/day of prednisone were free from any flares and had at least low disease activity after 24 weeks, a statistically significant between-group difference.
These findings “have potential to inform clinical practice and aid in conversations with patients. RA patients who achieve at least low disease activity while receiving tocilizumab and long-term glucocorticoid treatment at 5 mg/day should be considered for tapering of their glucocorticoid dosage, ideally targeting discontinuation,” Dr. Burmester said.
Addressing a comment from the audience that it’s common knowledge that patients who are well controlled on a potent immunomodulating drug like tocilizumab can often successfully wean off a glucocorticoid, Dr. Burmester insisted that it was important to show this in a randomized, blinded trial.
“When they discontinue [a glucocorticoid] patients can develop myalgias or other symptoms and we haven’t known whether that was real or psychological. In this study patients did not know whether they were being discontinued, so the psychological element was gone,” he said. The new findings confirm in a rigorous way that “we could discontinue a substantial number of patients who probably no longer need a glucocorticoid. It’s an important discussion” for clinicians to have with patients.
The SEMIRA (Steroid Elimination in RA) trial enrolled 68 patients who had already begun tocilizumab treatment and 191 patients new to the drug who had a 24-week run-in on tocilizumab, all of whom also received 5 mg prednisone daily. The trial included 46 sites in five European countries plus Russia and Tunisia. During the main 24-week phase of the study, 128 patients remained on their entry regimen of tocilizumab and prednisone, with 112 completers; 131 others went through a forced taper that culminated in no prednisone administered during the final 8 weeks, with 114 completers. Patients averaged about 54 years old, and just over three-quarters were women. Almost two-thirds of patients also received a nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug.
A time-trend analysis of changes in DAS28-ERS showed that, while the difference in change from baseline in disease activity between the two treatment arms separated early in the taper process, the biggest uptick in DAS28-ESR in the patients coming off prednisone occurred once the final 1 mg/day dose was stopped.
The results also showed that tapering led to a statistically significant rise in the clinical disease activity index for RA, compared with that seen with not tapering, and tapering also was linked significantly with an increase in serum markers of bone turnover. The safety analysis showed no striking between-group differences in adverse events and in serious adverse events, and no patients developed confirmed adrenal insufficiency that required replacement therapy.
SOURCE: Burmester G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10): Abstract L18.
Tapering well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis patients off glucocorticoid treatment is often attempted in clinical practice, but until now no evidence base existed to justify this approach. While the results reported by Dr. Burmester from the SEMIRA study are not unexpected, it’s very helpful to see these data from a well-designed study.
What remains unclear is the generalizability of the findings: Do they only apply to patients receiving tocilizumab as their primary antirheumatic drug or does glucocorticoid tapering work the same way in RA patients on different drugs?
The results also confirm another impression that many clinicians have had but until now was unsubstantiated: Eliminating the final 1 mg of daily glucocorticoid treatment is the most difficult part of tapering patients down to complete corticosteroid withdrawal. What often happens in practice is that patients get down to the last 1 or 2 mg of daily glucocorticoid treatment but further reduction beyond that causes a flare or a manifestation of steroid-withdrawal syndrome.
The results from this study give clinicians a better context for discussing glucocorticoid tapering with patients. Even with a potent antirheumatic drug like tocilizumab, it’s hard for some patients to completely withdraw from a glucocorticoid. Even at very low dosages glucocorticoids still have a very meaningful effect on some patients.
David S. Pisetsky, MD , is a professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C. He has been a consultant to Celgene, Celltrion, GlaxoSmithKline, and Lilly, and he has received research support from Pfizer. He made these comments in an interview.
Tapering well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis patients off glucocorticoid treatment is often attempted in clinical practice, but until now no evidence base existed to justify this approach. While the results reported by Dr. Burmester from the SEMIRA study are not unexpected, it’s very helpful to see these data from a well-designed study.
What remains unclear is the generalizability of the findings: Do they only apply to patients receiving tocilizumab as their primary antirheumatic drug or does glucocorticoid tapering work the same way in RA patients on different drugs?
The results also confirm another impression that many clinicians have had but until now was unsubstantiated: Eliminating the final 1 mg of daily glucocorticoid treatment is the most difficult part of tapering patients down to complete corticosteroid withdrawal. What often happens in practice is that patients get down to the last 1 or 2 mg of daily glucocorticoid treatment but further reduction beyond that causes a flare or a manifestation of steroid-withdrawal syndrome.
The results from this study give clinicians a better context for discussing glucocorticoid tapering with patients. Even with a potent antirheumatic drug like tocilizumab, it’s hard for some patients to completely withdraw from a glucocorticoid. Even at very low dosages glucocorticoids still have a very meaningful effect on some patients.
David S. Pisetsky, MD , is a professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C. He has been a consultant to Celgene, Celltrion, GlaxoSmithKline, and Lilly, and he has received research support from Pfizer. He made these comments in an interview.
Tapering well-controlled rheumatoid arthritis patients off glucocorticoid treatment is often attempted in clinical practice, but until now no evidence base existed to justify this approach. While the results reported by Dr. Burmester from the SEMIRA study are not unexpected, it’s very helpful to see these data from a well-designed study.
What remains unclear is the generalizability of the findings: Do they only apply to patients receiving tocilizumab as their primary antirheumatic drug or does glucocorticoid tapering work the same way in RA patients on different drugs?
The results also confirm another impression that many clinicians have had but until now was unsubstantiated: Eliminating the final 1 mg of daily glucocorticoid treatment is the most difficult part of tapering patients down to complete corticosteroid withdrawal. What often happens in practice is that patients get down to the last 1 or 2 mg of daily glucocorticoid treatment but further reduction beyond that causes a flare or a manifestation of steroid-withdrawal syndrome.
The results from this study give clinicians a better context for discussing glucocorticoid tapering with patients. Even with a potent antirheumatic drug like tocilizumab, it’s hard for some patients to completely withdraw from a glucocorticoid. Even at very low dosages glucocorticoids still have a very meaningful effect on some patients.
David S. Pisetsky, MD , is a professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C. He has been a consultant to Celgene, Celltrion, GlaxoSmithKline, and Lilly, and he has received research support from Pfizer. He made these comments in an interview.
CHICAGO – while remaining in at least low disease activity in a multicenter, randomized trial with 259 patients.
The results also showed that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients randomized to maintain prednisone treatment at 5 mg/day along with tocilizumab fared even better. After 24 weeks of the glucocorticoid-tapering regimen, by which time patients in the tapered arm had their prednisone dosage down to 0 mg, the average change from baseline in their disease activity score 28 with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) was an increase of 0.538, compared with an average drop of 0.075 among untapered patients, a statistically significant difference for the study’s primary endpoint, Gerd R. Burmester, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
But while the results definitively showed that RA patients treated with the anti-interleukin 6 agent tocilizumab (Actemra) as their primary drug benefited from continued, additional treatment with low-dose prednisone, the results also showed that many patients could come off prednisone without immediate downside. Among the 131 randomized to a forced taper and eventual prednisone discontinuation, 85 (65%) went through this process without flaring and maintained at least low disease activity and sometimes remission, said Dr. Burmester, a professor and director of rheumatology and clinical immunology at Charité Hospital in Berlin. In contrast, 99 of 128 patients (77%) maintained on tocilizumab plus 5 mg/day of prednisone were free from any flares and had at least low disease activity after 24 weeks, a statistically significant between-group difference.
These findings “have potential to inform clinical practice and aid in conversations with patients. RA patients who achieve at least low disease activity while receiving tocilizumab and long-term glucocorticoid treatment at 5 mg/day should be considered for tapering of their glucocorticoid dosage, ideally targeting discontinuation,” Dr. Burmester said.
Addressing a comment from the audience that it’s common knowledge that patients who are well controlled on a potent immunomodulating drug like tocilizumab can often successfully wean off a glucocorticoid, Dr. Burmester insisted that it was important to show this in a randomized, blinded trial.
“When they discontinue [a glucocorticoid] patients can develop myalgias or other symptoms and we haven’t known whether that was real or psychological. In this study patients did not know whether they were being discontinued, so the psychological element was gone,” he said. The new findings confirm in a rigorous way that “we could discontinue a substantial number of patients who probably no longer need a glucocorticoid. It’s an important discussion” for clinicians to have with patients.
The SEMIRA (Steroid Elimination in RA) trial enrolled 68 patients who had already begun tocilizumab treatment and 191 patients new to the drug who had a 24-week run-in on tocilizumab, all of whom also received 5 mg prednisone daily. The trial included 46 sites in five European countries plus Russia and Tunisia. During the main 24-week phase of the study, 128 patients remained on their entry regimen of tocilizumab and prednisone, with 112 completers; 131 others went through a forced taper that culminated in no prednisone administered during the final 8 weeks, with 114 completers. Patients averaged about 54 years old, and just over three-quarters were women. Almost two-thirds of patients also received a nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug.
A time-trend analysis of changes in DAS28-ERS showed that, while the difference in change from baseline in disease activity between the two treatment arms separated early in the taper process, the biggest uptick in DAS28-ESR in the patients coming off prednisone occurred once the final 1 mg/day dose was stopped.
The results also showed that tapering led to a statistically significant rise in the clinical disease activity index for RA, compared with that seen with not tapering, and tapering also was linked significantly with an increase in serum markers of bone turnover. The safety analysis showed no striking between-group differences in adverse events and in serious adverse events, and no patients developed confirmed adrenal insufficiency that required replacement therapy.
SOURCE: Burmester G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10): Abstract L18.
CHICAGO – while remaining in at least low disease activity in a multicenter, randomized trial with 259 patients.
The results also showed that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients randomized to maintain prednisone treatment at 5 mg/day along with tocilizumab fared even better. After 24 weeks of the glucocorticoid-tapering regimen, by which time patients in the tapered arm had their prednisone dosage down to 0 mg, the average change from baseline in their disease activity score 28 with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) was an increase of 0.538, compared with an average drop of 0.075 among untapered patients, a statistically significant difference for the study’s primary endpoint, Gerd R. Burmester, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
But while the results definitively showed that RA patients treated with the anti-interleukin 6 agent tocilizumab (Actemra) as their primary drug benefited from continued, additional treatment with low-dose prednisone, the results also showed that many patients could come off prednisone without immediate downside. Among the 131 randomized to a forced taper and eventual prednisone discontinuation, 85 (65%) went through this process without flaring and maintained at least low disease activity and sometimes remission, said Dr. Burmester, a professor and director of rheumatology and clinical immunology at Charité Hospital in Berlin. In contrast, 99 of 128 patients (77%) maintained on tocilizumab plus 5 mg/day of prednisone were free from any flares and had at least low disease activity after 24 weeks, a statistically significant between-group difference.
These findings “have potential to inform clinical practice and aid in conversations with patients. RA patients who achieve at least low disease activity while receiving tocilizumab and long-term glucocorticoid treatment at 5 mg/day should be considered for tapering of their glucocorticoid dosage, ideally targeting discontinuation,” Dr. Burmester said.
Addressing a comment from the audience that it’s common knowledge that patients who are well controlled on a potent immunomodulating drug like tocilizumab can often successfully wean off a glucocorticoid, Dr. Burmester insisted that it was important to show this in a randomized, blinded trial.
“When they discontinue [a glucocorticoid] patients can develop myalgias or other symptoms and we haven’t known whether that was real or psychological. In this study patients did not know whether they were being discontinued, so the psychological element was gone,” he said. The new findings confirm in a rigorous way that “we could discontinue a substantial number of patients who probably no longer need a glucocorticoid. It’s an important discussion” for clinicians to have with patients.
The SEMIRA (Steroid Elimination in RA) trial enrolled 68 patients who had already begun tocilizumab treatment and 191 patients new to the drug who had a 24-week run-in on tocilizumab, all of whom also received 5 mg prednisone daily. The trial included 46 sites in five European countries plus Russia and Tunisia. During the main 24-week phase of the study, 128 patients remained on their entry regimen of tocilizumab and prednisone, with 112 completers; 131 others went through a forced taper that culminated in no prednisone administered during the final 8 weeks, with 114 completers. Patients averaged about 54 years old, and just over three-quarters were women. Almost two-thirds of patients also received a nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug.
A time-trend analysis of changes in DAS28-ERS showed that, while the difference in change from baseline in disease activity between the two treatment arms separated early in the taper process, the biggest uptick in DAS28-ESR in the patients coming off prednisone occurred once the final 1 mg/day dose was stopped.
The results also showed that tapering led to a statistically significant rise in the clinical disease activity index for RA, compared with that seen with not tapering, and tapering also was linked significantly with an increase in serum markers of bone turnover. The safety analysis showed no striking between-group differences in adverse events and in serious adverse events, and no patients developed confirmed adrenal insufficiency that required replacement therapy.
SOURCE: Burmester G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10): Abstract L18.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point: Many rheumatoid arthritis patients with low disease activity on tocilizumab plus a glucocorticoid can taper off the corticosteroid without flaring.
Major finding: In RA patients with low disease activity on tocilizumab plus prednisone, 65% came off the glucocorticoid without flaring or relapse.
Study details: SEMIRA, a multicenter, randomized study with 259 rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Disclosures: SEMIRA was funded by Hoffmann-La Roche. Dr. Burmester has been a consultant to and speaker on behalf of Roche and Sanofi-Genzyme.
Source: Burmester G et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10): Abstract L18.