User login
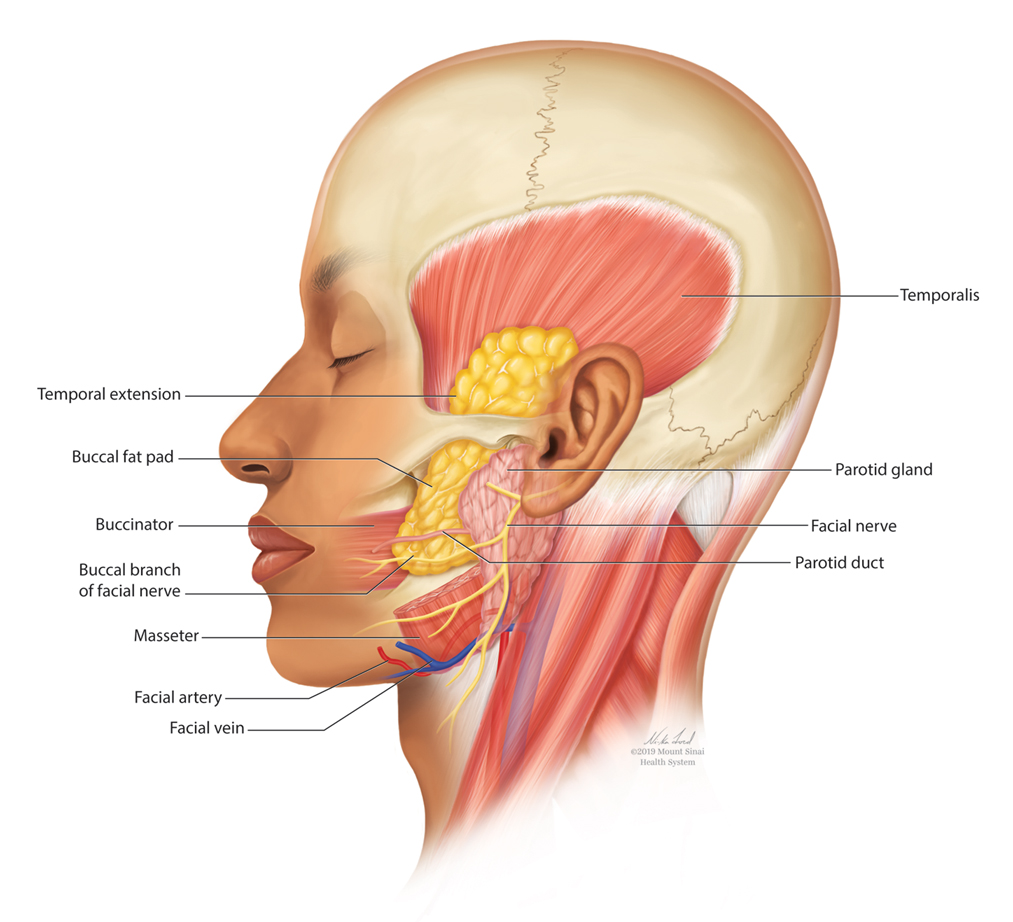
The buccal fat pad (Bichat fat pad) is a tubular-shaped collection of adipose tissue that occupies a prominent position in the midface. The buccal fat pad has been described as having 3 lobes: an anterior lobe, which is anterior to the masseter muscle; an intermediate lobe between the masseter and buccinator muscles; and a posterior lobe between the temporal masticatory space.1 There are 4 extensions from the body of the buccal fat pad: the buccal, the sublevator, the melolabial, and the pterygoid. It is the buccal extension and main body that are removed intraorally to achieve midfacial and lower facial contouring, as these support the contours of the cheeks. The deep fat pad within the temporal fossa is a true extension of the buccal fat pad (Figure).2 It has a complex relationship to the facial structures, with known variability in the positions of the buccal branch of the facial nerve and the parotid duct.3 The parotid duct travels over, superior to, or through the buccal extension 42%, 32%, and 26% of the time, respectively. The duct travels along the surface of the masseter, then pierces the buccinator to drain into the vestibule of the mouth at the second superior molar tooth. The buccal branch of the facial nerve travels on the surface of the buccal fat pad 73% of the time, whereas 27% of the time it travels deeper through the buccal extension.4 A study that used ultrasonography to map the surface anatomy path of the parotid duct in 50 healthy patients showed that the duct was within 1.5 cm of the middle half of a line between the lower border of the tragus and the oral commissure in 93% of individuals.5 We describe a technique in which part of the buccal fat pad is removed and the fat is transferred to the temple to achieve aesthetically pleasing facial contouring. We used a vertical line from the lateral canthus as a surface anatomy landmark to determine when the duct emerges from the gland and is most susceptible to injury.
Operative Technique
Correct instrumentation is important to obtain appropriate anatomic exposure for this procedure. The surgical tray should include 4-0 poliglecaprone 25 suture, bite guards, a needle driver, a hemostat, surgical scissors, toothed forceps, a Beaver surgical handle with #15 blade, a protected diathermy needle, cotton tip applicators, and gauze.
Fat Harvest—With the patient supine, bite blocks are placed, and the buccal fat pad incision line is marked with a surgical marker. A 1-cm line is drawn approximately 4 cm posterior to the oral commissure by the buccal bite marks. The location is verified by balloting externally on the buccal fat pad on the cheek. The incision line is then anesthetized transorally with lidocaine and epinephrine-containing solution. The cheek is retracted laterally with Caldwell-Luc retractors, and a 1-cm incision is made and carried through the mucosa and superficial muscle using the Colorado needle. Scissors are then used to spread the deeper muscle fibers to expose the deeper fascia and fat pads. Metzenbaum scissors are used to gently spread the fat while the surgeon places pressure on the external cheek, manipulating the fat into the wound. Without excess traction, the walnut-sized portion of the fat pad that protrudes is grasped with Debakey forceps, gently teased into the field, clamped at its base with a curved hemostat, and excised. The stump is electrocoagulated with an extendable protected Colorado needle, with care to prevent inadvertent cauterization of the lips. The wound is closed with a single 4-0 poliglecaprone-25 suture.
A 5-cc Luer lock syringe is preloaded with 2 cc of normal saline and attached to another 5-cc Luer lock syringe via a female-female attachment. The excised fat is then placed in a 5-cc Luer lock syringe by removing the plunger. The plunger is then reinstalled, and the fat is injected back and forth approximately 30 times. The fat is centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 3 minutes. The purified fat is then transferred to a 1-cc Luer lock syringe attached to an 18-gauge needle.
Fat Injection—The authors use an 18-gauge needle to perform depot injections into the temporal fossae above the periosteum. This is a relatively safe area of the face to inject, but care must be taken to avoid injury to the superficial temporal artery. Between 1.5 and 3 cc of high-quality fat usually are administered to each temple.
Aftercare Instructions—The patient is instructed to have a soft diet for 24 to 48 hours and can return to work the next day. The patient also is given prophylactic antibiotics with Gram-negative coverage for 7 days (amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for 7 days).
Candidates for Buccal Fat Pad Reduction
Buccal fat pad reduction has become an increasingly popular technique for midface and lower face shaping to decrease the appearance of a round face. To achieve an aesthetically pleasing midface, surgeons should consider enhancing zygomatic eminences while emphasizing the border between the zygomatic prominence and cheek hollow.6 Selection criteria for buccal fat pad reduction are not well established. One study recommended avoiding the procedure in pregnant or lactating patients, patients with chronic illnesses, patients on blood-thinning agents, and patients younger than 18 years. In addition, this study suggested ensuring the malar fullness is in the anteromedial portion of the face, as posterolateral fullness may be due to masseter hypertrophy.6
Complications From Buccal Fat Pad Reduction
Complications associated with buccal fat pad reduction include inadvertent damage to surrounding structures, including the buccal branch of the facial nerve and parotid duct. Because the location of the facial nerve in relation to the parotid duct is highly variable, surgeons must be aware of its anatomy to avoid unintentional damage. Hwang et al7 reported that the parotid duct and buccal branches of the facial nerves passed through the buccal extension in 26.3% of cadavers. The transbuccal approach is preferred over the sub–superficial muscular aponeurotic system approach largely because it avoids these structures. In addition, blunt dissection may further decrease chances of injury. Although the long-term effects are unknown, there is a potential risk for facial hollowing.3 The use of preprocedure ultrasonography to quantify the buccal fat pad may avoid overresection and enhanced potential for facial hollowing.6
Avoidance of Temporal Hollowing
Because the buccal fat pad extends into the temporal space, buccal fat pad reduction may lead to further temporal hollowing, contributing to an aged appearance. The authors’ technique addresses both midface and upper face contouring in one minimally invasive procedure. Temporal hollowing commonly has been corrected with autologous fat grafting from the thigh or abdomen, which leads to an additional scar at the donor site. Our technique relies on autologous adjacent fat transfer from previously removed buccal fat. In addition, compared with the use of hyaluronic acid fillers for temple reflation, fat transfer largely is safe and biocompatible. Major complications of autologous fat transfer to the temples include nodularity or fat clumping, fat necrosis, sensory or motor nerve damage, and edema or ecchymosis.4 Also, with time there will be ongoing hollowing of the temples as part of the aging process with soft tissue and bone resorption. Therefore, further volume restoration procedures may be required in the future to address these dynamic changes.
Conclusion
The buccal fat pad has been extensively used to reconstruct oral defects, including oroantral and cranial base defects, owing to its high vascularity.6 However, there also is great potential to utilize buccal fat for autologous fat transfer to improve temporal wasting. Further studies are needed to determine optimal technique as well as longer-term safety and efficacy of this procedure.
- Zhang HM, Yan YP, Qi KM, et al. Anatomical structure of the buccal fat pad and its clinical adaptations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109:2509-2518.
- Yousuf S, Tubbs RS, Wartmann CT, et al. A review of the gross anatomy, functions, pathology, and clinical uses of the buccal fat pad. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010;32:427-436.
- Benjamin M, Reish RG. Buccal fat pad excision: proceed with caution. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018;6:E1970.
- Tzikas TL. Fat grafting volume restoration to the brow and temporal regions. Facial Plast Surg. 2018;34:164-172.
- Stringer MD, Mirjalili SA, Meredith SJ, et al. Redefining the surface anatomy of the parotid duct: an in vivo ultrasound study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130:1032-1037.
- Sezgin B, Tatar S, Boge M, et al. The excision of the buccal fat pad for cheek refinement: volumetric considerations. Aesthet Surg J. 2019;39:585-592.
- Hwang K, Cho HJ, Battuvshin D, et al. Interrelated buccal fat pad with facial buccal branches and parotid duct. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16:658-660.
The buccal fat pad (Bichat fat pad) is a tubular-shaped collection of adipose tissue that occupies a prominent position in the midface. The buccal fat pad has been described as having 3 lobes: an anterior lobe, which is anterior to the masseter muscle; an intermediate lobe between the masseter and buccinator muscles; and a posterior lobe between the temporal masticatory space.1 There are 4 extensions from the body of the buccal fat pad: the buccal, the sublevator, the melolabial, and the pterygoid. It is the buccal extension and main body that are removed intraorally to achieve midfacial and lower facial contouring, as these support the contours of the cheeks. The deep fat pad within the temporal fossa is a true extension of the buccal fat pad (Figure).2 It has a complex relationship to the facial structures, with known variability in the positions of the buccal branch of the facial nerve and the parotid duct.3 The parotid duct travels over, superior to, or through the buccal extension 42%, 32%, and 26% of the time, respectively. The duct travels along the surface of the masseter, then pierces the buccinator to drain into the vestibule of the mouth at the second superior molar tooth. The buccal branch of the facial nerve travels on the surface of the buccal fat pad 73% of the time, whereas 27% of the time it travels deeper through the buccal extension.4 A study that used ultrasonography to map the surface anatomy path of the parotid duct in 50 healthy patients showed that the duct was within 1.5 cm of the middle half of a line between the lower border of the tragus and the oral commissure in 93% of individuals.5 We describe a technique in which part of the buccal fat pad is removed and the fat is transferred to the temple to achieve aesthetically pleasing facial contouring. We used a vertical line from the lateral canthus as a surface anatomy landmark to determine when the duct emerges from the gland and is most susceptible to injury.
Operative Technique
Correct instrumentation is important to obtain appropriate anatomic exposure for this procedure. The surgical tray should include 4-0 poliglecaprone 25 suture, bite guards, a needle driver, a hemostat, surgical scissors, toothed forceps, a Beaver surgical handle with #15 blade, a protected diathermy needle, cotton tip applicators, and gauze.
Fat Harvest—With the patient supine, bite blocks are placed, and the buccal fat pad incision line is marked with a surgical marker. A 1-cm line is drawn approximately 4 cm posterior to the oral commissure by the buccal bite marks. The location is verified by balloting externally on the buccal fat pad on the cheek. The incision line is then anesthetized transorally with lidocaine and epinephrine-containing solution. The cheek is retracted laterally with Caldwell-Luc retractors, and a 1-cm incision is made and carried through the mucosa and superficial muscle using the Colorado needle. Scissors are then used to spread the deeper muscle fibers to expose the deeper fascia and fat pads. Metzenbaum scissors are used to gently spread the fat while the surgeon places pressure on the external cheek, manipulating the fat into the wound. Without excess traction, the walnut-sized portion of the fat pad that protrudes is grasped with Debakey forceps, gently teased into the field, clamped at its base with a curved hemostat, and excised. The stump is electrocoagulated with an extendable protected Colorado needle, with care to prevent inadvertent cauterization of the lips. The wound is closed with a single 4-0 poliglecaprone-25 suture.
A 5-cc Luer lock syringe is preloaded with 2 cc of normal saline and attached to another 5-cc Luer lock syringe via a female-female attachment. The excised fat is then placed in a 5-cc Luer lock syringe by removing the plunger. The plunger is then reinstalled, and the fat is injected back and forth approximately 30 times. The fat is centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 3 minutes. The purified fat is then transferred to a 1-cc Luer lock syringe attached to an 18-gauge needle.
Fat Injection—The authors use an 18-gauge needle to perform depot injections into the temporal fossae above the periosteum. This is a relatively safe area of the face to inject, but care must be taken to avoid injury to the superficial temporal artery. Between 1.5 and 3 cc of high-quality fat usually are administered to each temple.
Aftercare Instructions—The patient is instructed to have a soft diet for 24 to 48 hours and can return to work the next day. The patient also is given prophylactic antibiotics with Gram-negative coverage for 7 days (amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for 7 days).
Candidates for Buccal Fat Pad Reduction
Buccal fat pad reduction has become an increasingly popular technique for midface and lower face shaping to decrease the appearance of a round face. To achieve an aesthetically pleasing midface, surgeons should consider enhancing zygomatic eminences while emphasizing the border between the zygomatic prominence and cheek hollow.6 Selection criteria for buccal fat pad reduction are not well established. One study recommended avoiding the procedure in pregnant or lactating patients, patients with chronic illnesses, patients on blood-thinning agents, and patients younger than 18 years. In addition, this study suggested ensuring the malar fullness is in the anteromedial portion of the face, as posterolateral fullness may be due to masseter hypertrophy.6
Complications From Buccal Fat Pad Reduction
Complications associated with buccal fat pad reduction include inadvertent damage to surrounding structures, including the buccal branch of the facial nerve and parotid duct. Because the location of the facial nerve in relation to the parotid duct is highly variable, surgeons must be aware of its anatomy to avoid unintentional damage. Hwang et al7 reported that the parotid duct and buccal branches of the facial nerves passed through the buccal extension in 26.3% of cadavers. The transbuccal approach is preferred over the sub–superficial muscular aponeurotic system approach largely because it avoids these structures. In addition, blunt dissection may further decrease chances of injury. Although the long-term effects are unknown, there is a potential risk for facial hollowing.3 The use of preprocedure ultrasonography to quantify the buccal fat pad may avoid overresection and enhanced potential for facial hollowing.6
Avoidance of Temporal Hollowing
Because the buccal fat pad extends into the temporal space, buccal fat pad reduction may lead to further temporal hollowing, contributing to an aged appearance. The authors’ technique addresses both midface and upper face contouring in one minimally invasive procedure. Temporal hollowing commonly has been corrected with autologous fat grafting from the thigh or abdomen, which leads to an additional scar at the donor site. Our technique relies on autologous adjacent fat transfer from previously removed buccal fat. In addition, compared with the use of hyaluronic acid fillers for temple reflation, fat transfer largely is safe and biocompatible. Major complications of autologous fat transfer to the temples include nodularity or fat clumping, fat necrosis, sensory or motor nerve damage, and edema or ecchymosis.4 Also, with time there will be ongoing hollowing of the temples as part of the aging process with soft tissue and bone resorption. Therefore, further volume restoration procedures may be required in the future to address these dynamic changes.
Conclusion
The buccal fat pad has been extensively used to reconstruct oral defects, including oroantral and cranial base defects, owing to its high vascularity.6 However, there also is great potential to utilize buccal fat for autologous fat transfer to improve temporal wasting. Further studies are needed to determine optimal technique as well as longer-term safety and efficacy of this procedure.
The buccal fat pad (Bichat fat pad) is a tubular-shaped collection of adipose tissue that occupies a prominent position in the midface. The buccal fat pad has been described as having 3 lobes: an anterior lobe, which is anterior to the masseter muscle; an intermediate lobe between the masseter and buccinator muscles; and a posterior lobe between the temporal masticatory space.1 There are 4 extensions from the body of the buccal fat pad: the buccal, the sublevator, the melolabial, and the pterygoid. It is the buccal extension and main body that are removed intraorally to achieve midfacial and lower facial contouring, as these support the contours of the cheeks. The deep fat pad within the temporal fossa is a true extension of the buccal fat pad (Figure).2 It has a complex relationship to the facial structures, with known variability in the positions of the buccal branch of the facial nerve and the parotid duct.3 The parotid duct travels over, superior to, or through the buccal extension 42%, 32%, and 26% of the time, respectively. The duct travels along the surface of the masseter, then pierces the buccinator to drain into the vestibule of the mouth at the second superior molar tooth. The buccal branch of the facial nerve travels on the surface of the buccal fat pad 73% of the time, whereas 27% of the time it travels deeper through the buccal extension.4 A study that used ultrasonography to map the surface anatomy path of the parotid duct in 50 healthy patients showed that the duct was within 1.5 cm of the middle half of a line between the lower border of the tragus and the oral commissure in 93% of individuals.5 We describe a technique in which part of the buccal fat pad is removed and the fat is transferred to the temple to achieve aesthetically pleasing facial contouring. We used a vertical line from the lateral canthus as a surface anatomy landmark to determine when the duct emerges from the gland and is most susceptible to injury.
Operative Technique
Correct instrumentation is important to obtain appropriate anatomic exposure for this procedure. The surgical tray should include 4-0 poliglecaprone 25 suture, bite guards, a needle driver, a hemostat, surgical scissors, toothed forceps, a Beaver surgical handle with #15 blade, a protected diathermy needle, cotton tip applicators, and gauze.
Fat Harvest—With the patient supine, bite blocks are placed, and the buccal fat pad incision line is marked with a surgical marker. A 1-cm line is drawn approximately 4 cm posterior to the oral commissure by the buccal bite marks. The location is verified by balloting externally on the buccal fat pad on the cheek. The incision line is then anesthetized transorally with lidocaine and epinephrine-containing solution. The cheek is retracted laterally with Caldwell-Luc retractors, and a 1-cm incision is made and carried through the mucosa and superficial muscle using the Colorado needle. Scissors are then used to spread the deeper muscle fibers to expose the deeper fascia and fat pads. Metzenbaum scissors are used to gently spread the fat while the surgeon places pressure on the external cheek, manipulating the fat into the wound. Without excess traction, the walnut-sized portion of the fat pad that protrudes is grasped with Debakey forceps, gently teased into the field, clamped at its base with a curved hemostat, and excised. The stump is electrocoagulated with an extendable protected Colorado needle, with care to prevent inadvertent cauterization of the lips. The wound is closed with a single 4-0 poliglecaprone-25 suture.
A 5-cc Luer lock syringe is preloaded with 2 cc of normal saline and attached to another 5-cc Luer lock syringe via a female-female attachment. The excised fat is then placed in a 5-cc Luer lock syringe by removing the plunger. The plunger is then reinstalled, and the fat is injected back and forth approximately 30 times. The fat is centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 3 minutes. The purified fat is then transferred to a 1-cc Luer lock syringe attached to an 18-gauge needle.
Fat Injection—The authors use an 18-gauge needle to perform depot injections into the temporal fossae above the periosteum. This is a relatively safe area of the face to inject, but care must be taken to avoid injury to the superficial temporal artery. Between 1.5 and 3 cc of high-quality fat usually are administered to each temple.
Aftercare Instructions—The patient is instructed to have a soft diet for 24 to 48 hours and can return to work the next day. The patient also is given prophylactic antibiotics with Gram-negative coverage for 7 days (amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for 7 days).
Candidates for Buccal Fat Pad Reduction
Buccal fat pad reduction has become an increasingly popular technique for midface and lower face shaping to decrease the appearance of a round face. To achieve an aesthetically pleasing midface, surgeons should consider enhancing zygomatic eminences while emphasizing the border between the zygomatic prominence and cheek hollow.6 Selection criteria for buccal fat pad reduction are not well established. One study recommended avoiding the procedure in pregnant or lactating patients, patients with chronic illnesses, patients on blood-thinning agents, and patients younger than 18 years. In addition, this study suggested ensuring the malar fullness is in the anteromedial portion of the face, as posterolateral fullness may be due to masseter hypertrophy.6
Complications From Buccal Fat Pad Reduction
Complications associated with buccal fat pad reduction include inadvertent damage to surrounding structures, including the buccal branch of the facial nerve and parotid duct. Because the location of the facial nerve in relation to the parotid duct is highly variable, surgeons must be aware of its anatomy to avoid unintentional damage. Hwang et al7 reported that the parotid duct and buccal branches of the facial nerves passed through the buccal extension in 26.3% of cadavers. The transbuccal approach is preferred over the sub–superficial muscular aponeurotic system approach largely because it avoids these structures. In addition, blunt dissection may further decrease chances of injury. Although the long-term effects are unknown, there is a potential risk for facial hollowing.3 The use of preprocedure ultrasonography to quantify the buccal fat pad may avoid overresection and enhanced potential for facial hollowing.6
Avoidance of Temporal Hollowing
Because the buccal fat pad extends into the temporal space, buccal fat pad reduction may lead to further temporal hollowing, contributing to an aged appearance. The authors’ technique addresses both midface and upper face contouring in one minimally invasive procedure. Temporal hollowing commonly has been corrected with autologous fat grafting from the thigh or abdomen, which leads to an additional scar at the donor site. Our technique relies on autologous adjacent fat transfer from previously removed buccal fat. In addition, compared with the use of hyaluronic acid fillers for temple reflation, fat transfer largely is safe and biocompatible. Major complications of autologous fat transfer to the temples include nodularity or fat clumping, fat necrosis, sensory or motor nerve damage, and edema or ecchymosis.4 Also, with time there will be ongoing hollowing of the temples as part of the aging process with soft tissue and bone resorption. Therefore, further volume restoration procedures may be required in the future to address these dynamic changes.
Conclusion
The buccal fat pad has been extensively used to reconstruct oral defects, including oroantral and cranial base defects, owing to its high vascularity.6 However, there also is great potential to utilize buccal fat for autologous fat transfer to improve temporal wasting. Further studies are needed to determine optimal technique as well as longer-term safety and efficacy of this procedure.
- Zhang HM, Yan YP, Qi KM, et al. Anatomical structure of the buccal fat pad and its clinical adaptations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109:2509-2518.
- Yousuf S, Tubbs RS, Wartmann CT, et al. A review of the gross anatomy, functions, pathology, and clinical uses of the buccal fat pad. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010;32:427-436.
- Benjamin M, Reish RG. Buccal fat pad excision: proceed with caution. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018;6:E1970.
- Tzikas TL. Fat grafting volume restoration to the brow and temporal regions. Facial Plast Surg. 2018;34:164-172.
- Stringer MD, Mirjalili SA, Meredith SJ, et al. Redefining the surface anatomy of the parotid duct: an in vivo ultrasound study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130:1032-1037.
- Sezgin B, Tatar S, Boge M, et al. The excision of the buccal fat pad for cheek refinement: volumetric considerations. Aesthet Surg J. 2019;39:585-592.
- Hwang K, Cho HJ, Battuvshin D, et al. Interrelated buccal fat pad with facial buccal branches and parotid duct. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16:658-660.
- Zhang HM, Yan YP, Qi KM, et al. Anatomical structure of the buccal fat pad and its clinical adaptations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109:2509-2518.
- Yousuf S, Tubbs RS, Wartmann CT, et al. A review of the gross anatomy, functions, pathology, and clinical uses of the buccal fat pad. Surg Radiol Anat. 2010;32:427-436.
- Benjamin M, Reish RG. Buccal fat pad excision: proceed with caution. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018;6:E1970.
- Tzikas TL. Fat grafting volume restoration to the brow and temporal regions. Facial Plast Surg. 2018;34:164-172.
- Stringer MD, Mirjalili SA, Meredith SJ, et al. Redefining the surface anatomy of the parotid duct: an in vivo ultrasound study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130:1032-1037.
- Sezgin B, Tatar S, Boge M, et al. The excision of the buccal fat pad for cheek refinement: volumetric considerations. Aesthet Surg J. 2019;39:585-592.
- Hwang K, Cho HJ, Battuvshin D, et al. Interrelated buccal fat pad with facial buccal branches and parotid duct. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16:658-660.
Practice Points
- Buccal fat pad reduction is an increasingly popular procedure for facial shaping.
- Buccal fat pad reduction in addition to natural aging can result in volume depletion of the temporal fossae.
- Removed buccal fat can be transferred to the temples for increased volume.