User login
Scleromyxedema in a Patient With Thyroid Disease: An Atypical Case or a Case for Revised Criteria?
Scleromyxedema (SM) is a generalized papular and sclerodermoid form of lichen myxedematosus (LM), commonly referred to as papular mucinosis. It is a rare progressive disease of unknown etiology with systemic manifestations that cause serious morbidity and mortality. Diagnostic criteria were initially created by Montgomery and Underwood1 in 1953 and revised by Rongioletti and Rebora2 in 2001 as follows: (1) generalized papular and sclerodermoid eruption; (2) histologic triad of mucin deposition, fibroblast proliferation, and fibrosis; (3) monoclonal gammopathy; and (4) absence of thyroid disease. There are several reports of LM in association with hypothyroidism, most of which can be characterized as atypical.3-8 We present a case of SM in a patient with Hashimoto thyroiditis and propose that the presence of thyroid disease should not preclude the diagnosis of SM.
Case Report
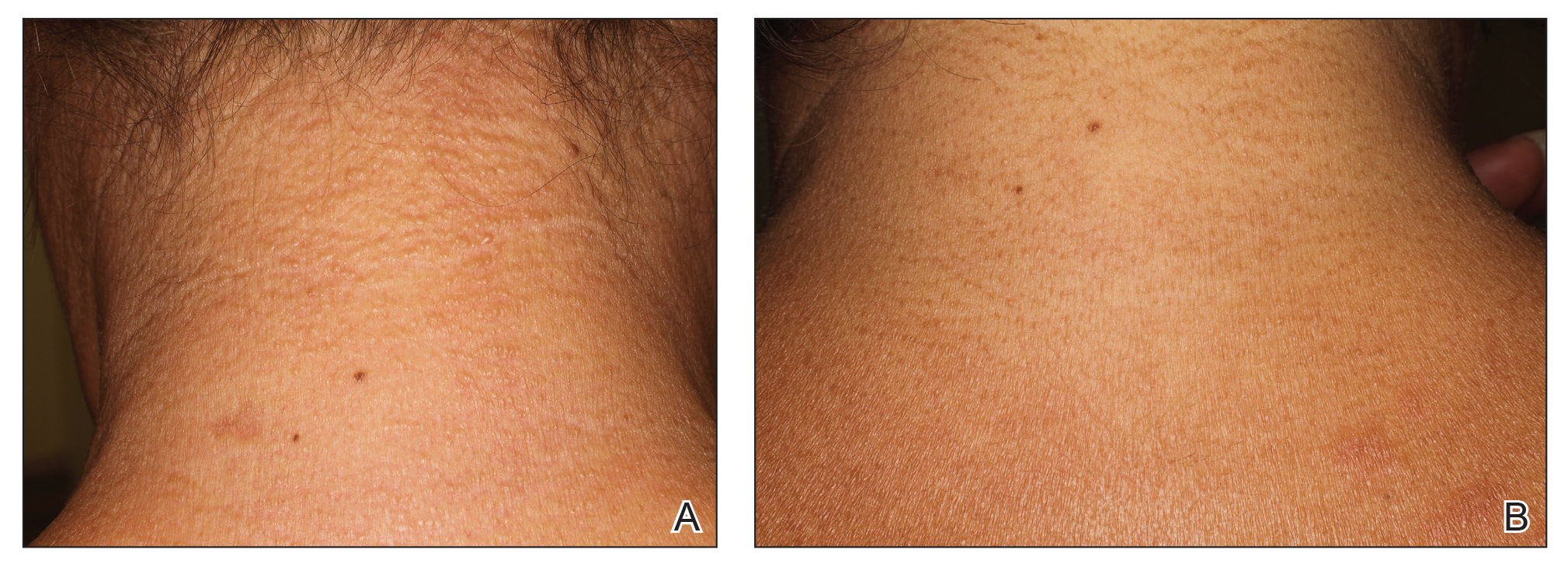
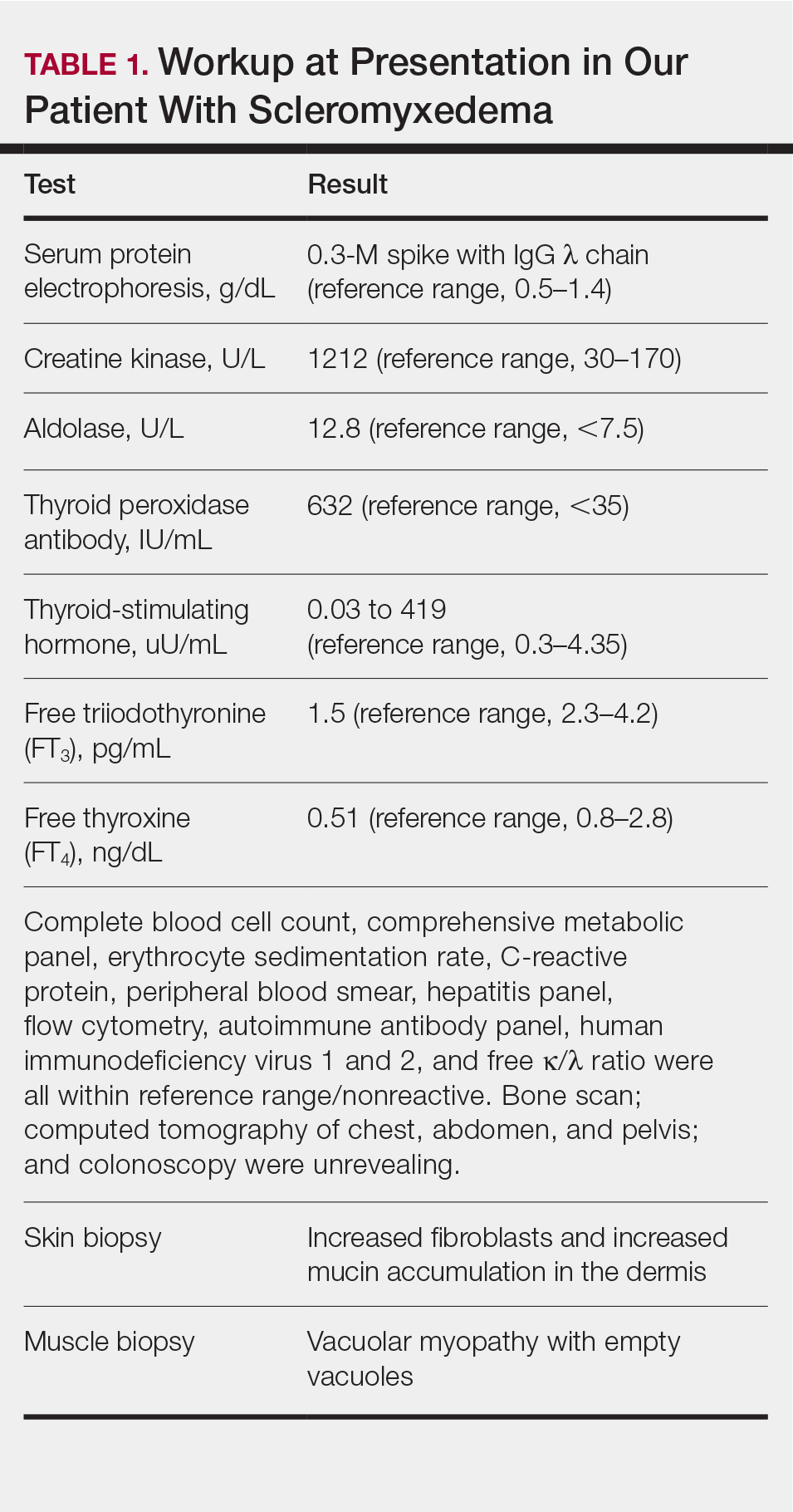
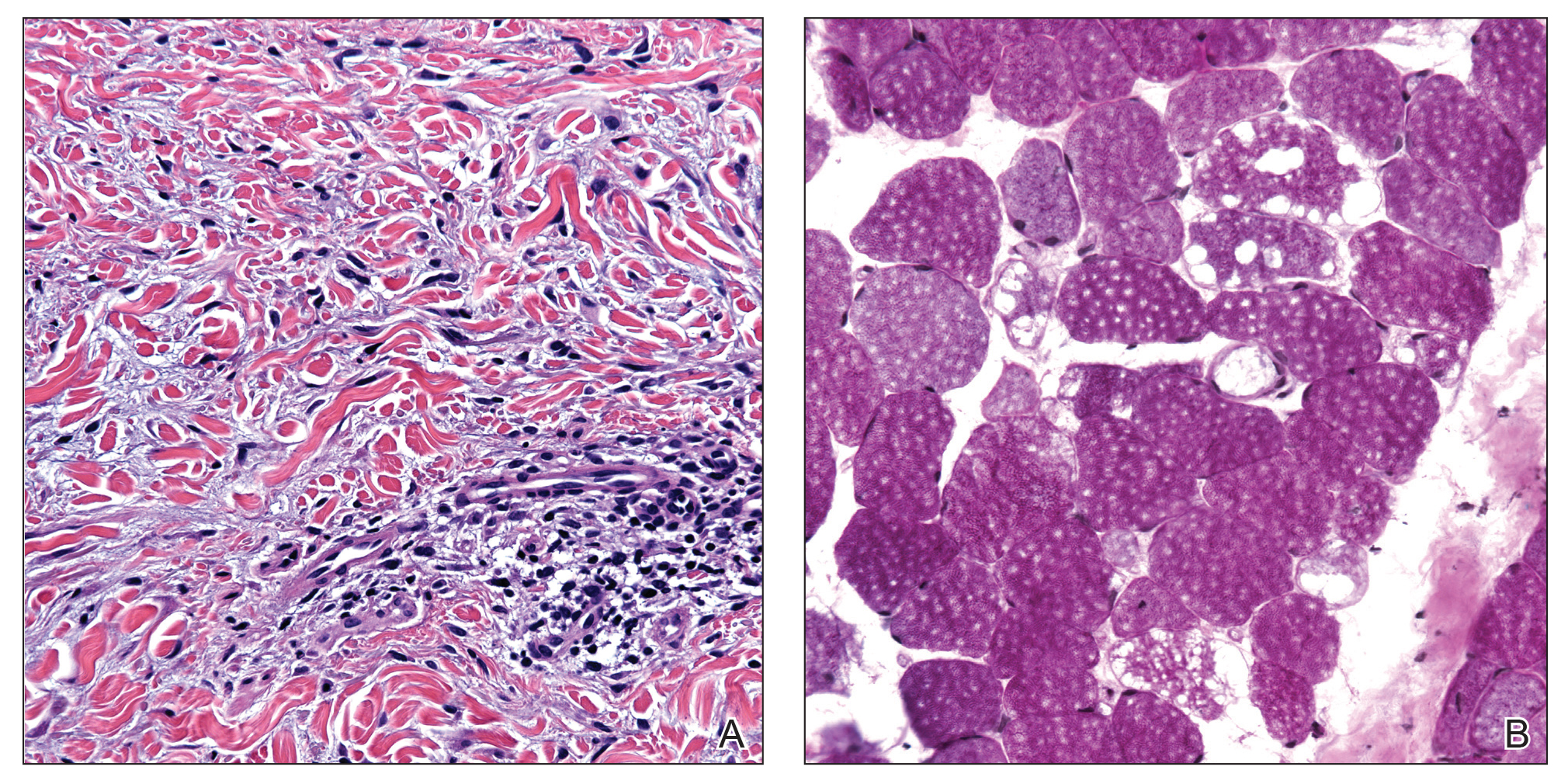
A 44-year-old woman presented with a progressive eruption of thickened skin and papules spanning many months. The papules ranged from flesh colored to erythematous and covered more than 80% of the body surface area, most notably involving the face, neck, ears, arms, chest, abdomen, and thighs (Figures 1A and 2A). Review of systems was notable for pruritus, muscle pain but no weakness, dysphagia, and constipation. Her medical history included childhood atopic dermatitis and Hashimoto thyroiditis. Hypothyroidism was diagnosed with support of a thyroid ultrasound and thyroid peroxidase antibodies. It was treated with oral levothyroxine for 2 years prior to the skin eruption. Thyroid biopsy was not performed. Her thyroid-stimulating hormone levels notably fluctuated in the year prior to presentation despite close clinical and laboratory monitoring by an endocrinologist. Laboratory results are summarized in Table 1. Both skin and muscle9 biopsies were consistent with SM (Figure 3) and are summarized in Table 1.
Shortly after presentation to our clinic the patient developed acute concerns of confusion and muscle weakness. She was admitted for further inpatient management due to concern for dermato-neuro syndrome, a rare but potentially fatal decline in neurological status that can progress to coma and death, rather than myxedema coma. On admission, a thyroid function test showed subclinical hypothyroidism with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level of 6.35 uU/mL (reference range, 0.3–4.35 uU/mL) and free thyroxine (FT4) level of 1.5 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8–2.8 ng/dL). While hospitalized she was started on intravenous levothyroxine, systemic steroids, and a course of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatment consisting of 2 g/kg divided over 5 days. On this regimen, her mental status quickly returned to baseline and other symptoms improved, including the skin eruption (Figures 1B and 2B). She has been maintained on lenalidomide 25 mg/d for the first 3 weeks of each month as well as monthly IVIg infusions. Her thyroid levels have persistently fluctuated despite intramuscular levothyroxine dosing, but her skin has remained clear with continued SM-directed therapy.
Comment
Classification
Lichen myxedematosus is differentiated into localized and generalized forms. The former is limited to the skin and lacks monoclonal gammopathy. The latter, also known as SM, is associated with monoclonal gammopathy and systemic symptoms. Atypical LM is an umbrella term for intermediate cases.
Clinical Presentation
Skin manifestations of SM are described as 1- to 3-mm, firm, waxy, dome-shaped papules that commonly affect the hands, forearms, face, neck, trunk, and thighs. The surrounding skin may be reddish brown and edematous with evidence of skin thickening. Extracutaneous manifestations in SM are numerous and unpredictable. Any organ system can be involved, but gastrointestinal, rheumatologic, pulmonary, and cardiovascular complications are most common.10 A comprehensive multidisciplinary evaluation is necessary based on clinical symptoms and laboratory findings.
Management
Many treatments have been proposed for SM in case reports and case series. Prior treatments have had little success. Most recently, in one of the largest case series on SM, Rongioletti et al10 demonstrated IVIg to be a safe and effective treatment modality.
Differential Diagnosis
An important differential diagnosis is generalized myxedema, which is seen in long-standing hypothyroidism and may present with cutaneous mucinosis and systemic symptoms that resemble SM. Hypothyroid myxedema is associated with a widespread slowing of the body’s metabolic processes and deposition of mucin in various organs, including the skin, creating a generalized nonpitting edema. Classic clinical signs include macroglossia, periorbital puffiness, thick lips, and acral swelling. The skin tends to be cold, dry, and pale. Hair is characterized as being coarse, dry, and brittle with diffuse partial alopecia. Histologically, there is hyperkeratosis with follicular plugging and diffuse mucin and edema splaying between collagen fibers spanning the entire dermis.11 In contradistinction with SM, there is no fibroblast proliferation. The treatment is thyroid replacement therapy. Hyperthyroidism has distinct clinical and histologic changes. Clinically, there is moist and smooth skin with soft, fine, and sometimes alopecic hair. Graves disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, is further characterized by Graves ophthalmopathy and pretibial myxedema, or pink to brown, raised, firm, indurated, asymmetric plaques most commonly affecting the shins. Histologically there is increased mucin in the lower to mid dermis without fibroblast proliferation. The epidermis can be hyperkeratotic, which will clinically correlate with verrucous lesions.12
Hypothyroid encephalopathy is a rare disorder that can cause a change in mental status. It is a steroid-responsive autoimmune process characterized by encephalopathy that is associated with cognitive impairment and psychiatric features. It is a diagnosis of exclusion and should be suspected in women with a history of autoimmune disease, especially antithyroid peroxidase antibodies, a negative infectious workup, and encephalitis with behavioral changes. Although typically highly responsive to systemic steroids, IVIg also has shown efficacy.13
Presence of Thyroid Disease
According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms scleromyxedema and lichen myxedematosus, there are 7 cases in the literature that potentially describe LM associated with hypothyroidism (Table 2).3-8 The majority of these cases lack monoclonal gammopathy; improved with thyroid replacement therapy; or had severely atypical clinical presentations, rendering them cases of atypical LM or atypical thyroid dermopathy.3-6 Macnab and Kenny7 presented a case of subclinical hypothyroidism with a generalized papular eruption, monoclonal gammopathy, and consistent histologic changes that responded to IVIg therapy. These findings are suggestive of SM, but limited to the current diagnostic criteria, the patient was diagnosed with atypical LM.7 Shenoy et al8 described 2 cases of LM with hypothyroidism. One patient had biopsy-proven SM that was responsive to IVIg as well as Hashimoto thyroiditis with delayed onset of monoclonal gammopathy. The second patient had a medical history of hypothyroidism and Hodgkin lymphoma with active rheumatoid arthritis and biopsy-proven LM that was responsive to systemic steroids.8
Current literature states that thyroid disorder precludes the diagnosis of SM. However, historic literature would suggest otherwise. Because of inconsistent reports and theories regarding the pathogenesis of various sclerodermoid and mucin deposition diseases, in 1953 Montgomery and Underwood1 sought to differentiate LM from scleroderma and generalized myxedema. They stressed clinical appearance and proposed diagnostic criteria for LM as generalized papular mucinosis in which “[n]o relation to disturbance of the thyroid or other endocrine glands is apparent,” whereas generalized myxedema was defined as a “[t]rue cutaneous myxedema, with diffuse edema and the usual commonly recognized changes” in patients with endocrine abnormalities.1 With this classification, the authors made a clear distinction between mucinosis caused by thyroid abnormalities and LM, which is not caused by a thyroid disorder. Since this original description was published, associations with monoclonal gammopathy and fibroblast proliferation have been made, ultimately culminating into the current 2001 criteria that incorporate the absence of thyroid disease.2
Conclusion
We believe our case is consistent with the classification initially proposed by Montgomery and Underwood1 and is strengthened with the more recent associations with monoclonal gammopathy and specific histopathologic findings. Although there is no definitive way to rule out myxedema coma or Hashimoto encephalopathy to describe our patient’s transient neurologic decline, her clinical symptoms, laboratory findings, and biopsy results all supported the diagnosis of SM. Furthermore, her response to SM-directed therapy, despite fluctuating thyroid function test results, also supported the diagnosis. In the setting of cutaneous mucinosis with conflicting findings for hypothyroid myxedema, LM should be ruled out. Given the features presented in this report and others, diagnostic criteria should allow for SM and thyroid dysfunction to be concurrent diagnoses. Most importantly, we believe it is essential to identify and diagnose SM in a timely manner to facilitate SM-directed therapy, namely IVIg, to potentially minimize the disease’s notable morbidity and mortality.
- Montgomery H, Underwood LJ. Lichen myxedematosus; differentiation from cutaneous myxedemas or mucoid states. J Invest Dermatol. 1953;20:213-236.
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Updated classification of papular mucinosis, lichen myxedematosus and scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:273-281.
- Archibald GC, Calvert HT. Hypothyroidsm and lichen myxedematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:684.
- Schaeffer D, Bruce S, Rosen T. Cutaneous mucinosis associated with thyroid dysfunction. Cutis. 1983;11:449-456.
- Martin-Ezquerra G, Sanchez-Regaña M, Massana-Gil J, et al. Papular mucinosis associated with subclinical hypothyroidism: improvement with thyroxine therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1340-1341.
- Volpato MB, Jaime TJ, Proença MP, et al. Papular mucinosis associated with hypothyroidism. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:89-92.
- Macnab M, Kenny P. Successful intravenous immunoglobulin treatment of atypical lichen myxedematosus associated with hypothyroidism and central nervous system. involvement: case report and discussion of the literature. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17:69-73.
- Shenoy A, Steixner J, Beltrani V, et al. Discrete papular lichen myxedematosus and scleromyxedema with hypothyroidism: a report of two cases. Case Rep Dermatol. 2019;11:64-70.
- Helfrich DJ, Walker ER, Martinez AJ, et al. Scleromyxedema myopathy: case report and review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:1437-1441.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Jackson EM, English JC 3rd. Diffuse cutaneous mucinoses. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:493-501.
- Leonhardt JM, Heymann WR. Thyroid disease and the skin. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:473-481.
- Zhou JY, Xu B, Lopes J, et al. Hashimoto encephalopathy: literature review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;135:285-290.
Scleromyxedema (SM) is a generalized papular and sclerodermoid form of lichen myxedematosus (LM), commonly referred to as papular mucinosis. It is a rare progressive disease of unknown etiology with systemic manifestations that cause serious morbidity and mortality. Diagnostic criteria were initially created by Montgomery and Underwood1 in 1953 and revised by Rongioletti and Rebora2 in 2001 as follows: (1) generalized papular and sclerodermoid eruption; (2) histologic triad of mucin deposition, fibroblast proliferation, and fibrosis; (3) monoclonal gammopathy; and (4) absence of thyroid disease. There are several reports of LM in association with hypothyroidism, most of which can be characterized as atypical.3-8 We present a case of SM in a patient with Hashimoto thyroiditis and propose that the presence of thyroid disease should not preclude the diagnosis of SM.
Case Report
A 44-year-old woman presented with a progressive eruption of thickened skin and papules spanning many months. The papules ranged from flesh colored to erythematous and covered more than 80% of the body surface area, most notably involving the face, neck, ears, arms, chest, abdomen, and thighs (Figures 1A and 2A). Review of systems was notable for pruritus, muscle pain but no weakness, dysphagia, and constipation. Her medical history included childhood atopic dermatitis and Hashimoto thyroiditis. Hypothyroidism was diagnosed with support of a thyroid ultrasound and thyroid peroxidase antibodies. It was treated with oral levothyroxine for 2 years prior to the skin eruption. Thyroid biopsy was not performed. Her thyroid-stimulating hormone levels notably fluctuated in the year prior to presentation despite close clinical and laboratory monitoring by an endocrinologist. Laboratory results are summarized in Table 1. Both skin and muscle9 biopsies were consistent with SM (Figure 3) and are summarized in Table 1.
Shortly after presentation to our clinic the patient developed acute concerns of confusion and muscle weakness. She was admitted for further inpatient management due to concern for dermato-neuro syndrome, a rare but potentially fatal decline in neurological status that can progress to coma and death, rather than myxedema coma. On admission, a thyroid function test showed subclinical hypothyroidism with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level of 6.35 uU/mL (reference range, 0.3–4.35 uU/mL) and free thyroxine (FT4) level of 1.5 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8–2.8 ng/dL). While hospitalized she was started on intravenous levothyroxine, systemic steroids, and a course of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatment consisting of 2 g/kg divided over 5 days. On this regimen, her mental status quickly returned to baseline and other symptoms improved, including the skin eruption (Figures 1B and 2B). She has been maintained on lenalidomide 25 mg/d for the first 3 weeks of each month as well as monthly IVIg infusions. Her thyroid levels have persistently fluctuated despite intramuscular levothyroxine dosing, but her skin has remained clear with continued SM-directed therapy.
Comment
Classification
Lichen myxedematosus is differentiated into localized and generalized forms. The former is limited to the skin and lacks monoclonal gammopathy. The latter, also known as SM, is associated with monoclonal gammopathy and systemic symptoms. Atypical LM is an umbrella term for intermediate cases.
Clinical Presentation
Skin manifestations of SM are described as 1- to 3-mm, firm, waxy, dome-shaped papules that commonly affect the hands, forearms, face, neck, trunk, and thighs. The surrounding skin may be reddish brown and edematous with evidence of skin thickening. Extracutaneous manifestations in SM are numerous and unpredictable. Any organ system can be involved, but gastrointestinal, rheumatologic, pulmonary, and cardiovascular complications are most common.10 A comprehensive multidisciplinary evaluation is necessary based on clinical symptoms and laboratory findings.
Management
Many treatments have been proposed for SM in case reports and case series. Prior treatments have had little success. Most recently, in one of the largest case series on SM, Rongioletti et al10 demonstrated IVIg to be a safe and effective treatment modality.
Differential Diagnosis
An important differential diagnosis is generalized myxedema, which is seen in long-standing hypothyroidism and may present with cutaneous mucinosis and systemic symptoms that resemble SM. Hypothyroid myxedema is associated with a widespread slowing of the body’s metabolic processes and deposition of mucin in various organs, including the skin, creating a generalized nonpitting edema. Classic clinical signs include macroglossia, periorbital puffiness, thick lips, and acral swelling. The skin tends to be cold, dry, and pale. Hair is characterized as being coarse, dry, and brittle with diffuse partial alopecia. Histologically, there is hyperkeratosis with follicular plugging and diffuse mucin and edema splaying between collagen fibers spanning the entire dermis.11 In contradistinction with SM, there is no fibroblast proliferation. The treatment is thyroid replacement therapy. Hyperthyroidism has distinct clinical and histologic changes. Clinically, there is moist and smooth skin with soft, fine, and sometimes alopecic hair. Graves disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, is further characterized by Graves ophthalmopathy and pretibial myxedema, or pink to brown, raised, firm, indurated, asymmetric plaques most commonly affecting the shins. Histologically there is increased mucin in the lower to mid dermis without fibroblast proliferation. The epidermis can be hyperkeratotic, which will clinically correlate with verrucous lesions.12
Hypothyroid encephalopathy is a rare disorder that can cause a change in mental status. It is a steroid-responsive autoimmune process characterized by encephalopathy that is associated with cognitive impairment and psychiatric features. It is a diagnosis of exclusion and should be suspected in women with a history of autoimmune disease, especially antithyroid peroxidase antibodies, a negative infectious workup, and encephalitis with behavioral changes. Although typically highly responsive to systemic steroids, IVIg also has shown efficacy.13
Presence of Thyroid Disease
According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms scleromyxedema and lichen myxedematosus, there are 7 cases in the literature that potentially describe LM associated with hypothyroidism (Table 2).3-8 The majority of these cases lack monoclonal gammopathy; improved with thyroid replacement therapy; or had severely atypical clinical presentations, rendering them cases of atypical LM or atypical thyroid dermopathy.3-6 Macnab and Kenny7 presented a case of subclinical hypothyroidism with a generalized papular eruption, monoclonal gammopathy, and consistent histologic changes that responded to IVIg therapy. These findings are suggestive of SM, but limited to the current diagnostic criteria, the patient was diagnosed with atypical LM.7 Shenoy et al8 described 2 cases of LM with hypothyroidism. One patient had biopsy-proven SM that was responsive to IVIg as well as Hashimoto thyroiditis with delayed onset of monoclonal gammopathy. The second patient had a medical history of hypothyroidism and Hodgkin lymphoma with active rheumatoid arthritis and biopsy-proven LM that was responsive to systemic steroids.8
Current literature states that thyroid disorder precludes the diagnosis of SM. However, historic literature would suggest otherwise. Because of inconsistent reports and theories regarding the pathogenesis of various sclerodermoid and mucin deposition diseases, in 1953 Montgomery and Underwood1 sought to differentiate LM from scleroderma and generalized myxedema. They stressed clinical appearance and proposed diagnostic criteria for LM as generalized papular mucinosis in which “[n]o relation to disturbance of the thyroid or other endocrine glands is apparent,” whereas generalized myxedema was defined as a “[t]rue cutaneous myxedema, with diffuse edema and the usual commonly recognized changes” in patients with endocrine abnormalities.1 With this classification, the authors made a clear distinction between mucinosis caused by thyroid abnormalities and LM, which is not caused by a thyroid disorder. Since this original description was published, associations with monoclonal gammopathy and fibroblast proliferation have been made, ultimately culminating into the current 2001 criteria that incorporate the absence of thyroid disease.2
Conclusion
We believe our case is consistent with the classification initially proposed by Montgomery and Underwood1 and is strengthened with the more recent associations with monoclonal gammopathy and specific histopathologic findings. Although there is no definitive way to rule out myxedema coma or Hashimoto encephalopathy to describe our patient’s transient neurologic decline, her clinical symptoms, laboratory findings, and biopsy results all supported the diagnosis of SM. Furthermore, her response to SM-directed therapy, despite fluctuating thyroid function test results, also supported the diagnosis. In the setting of cutaneous mucinosis with conflicting findings for hypothyroid myxedema, LM should be ruled out. Given the features presented in this report and others, diagnostic criteria should allow for SM and thyroid dysfunction to be concurrent diagnoses. Most importantly, we believe it is essential to identify and diagnose SM in a timely manner to facilitate SM-directed therapy, namely IVIg, to potentially minimize the disease’s notable morbidity and mortality.
Scleromyxedema (SM) is a generalized papular and sclerodermoid form of lichen myxedematosus (LM), commonly referred to as papular mucinosis. It is a rare progressive disease of unknown etiology with systemic manifestations that cause serious morbidity and mortality. Diagnostic criteria were initially created by Montgomery and Underwood1 in 1953 and revised by Rongioletti and Rebora2 in 2001 as follows: (1) generalized papular and sclerodermoid eruption; (2) histologic triad of mucin deposition, fibroblast proliferation, and fibrosis; (3) monoclonal gammopathy; and (4) absence of thyroid disease. There are several reports of LM in association with hypothyroidism, most of which can be characterized as atypical.3-8 We present a case of SM in a patient with Hashimoto thyroiditis and propose that the presence of thyroid disease should not preclude the diagnosis of SM.
Case Report
A 44-year-old woman presented with a progressive eruption of thickened skin and papules spanning many months. The papules ranged from flesh colored to erythematous and covered more than 80% of the body surface area, most notably involving the face, neck, ears, arms, chest, abdomen, and thighs (Figures 1A and 2A). Review of systems was notable for pruritus, muscle pain but no weakness, dysphagia, and constipation. Her medical history included childhood atopic dermatitis and Hashimoto thyroiditis. Hypothyroidism was diagnosed with support of a thyroid ultrasound and thyroid peroxidase antibodies. It was treated with oral levothyroxine for 2 years prior to the skin eruption. Thyroid biopsy was not performed. Her thyroid-stimulating hormone levels notably fluctuated in the year prior to presentation despite close clinical and laboratory monitoring by an endocrinologist. Laboratory results are summarized in Table 1. Both skin and muscle9 biopsies were consistent with SM (Figure 3) and are summarized in Table 1.
Shortly after presentation to our clinic the patient developed acute concerns of confusion and muscle weakness. She was admitted for further inpatient management due to concern for dermato-neuro syndrome, a rare but potentially fatal decline in neurological status that can progress to coma and death, rather than myxedema coma. On admission, a thyroid function test showed subclinical hypothyroidism with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level of 6.35 uU/mL (reference range, 0.3–4.35 uU/mL) and free thyroxine (FT4) level of 1.5 ng/dL (reference range, 0.8–2.8 ng/dL). While hospitalized she was started on intravenous levothyroxine, systemic steroids, and a course of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatment consisting of 2 g/kg divided over 5 days. On this regimen, her mental status quickly returned to baseline and other symptoms improved, including the skin eruption (Figures 1B and 2B). She has been maintained on lenalidomide 25 mg/d for the first 3 weeks of each month as well as monthly IVIg infusions. Her thyroid levels have persistently fluctuated despite intramuscular levothyroxine dosing, but her skin has remained clear with continued SM-directed therapy.
Comment
Classification
Lichen myxedematosus is differentiated into localized and generalized forms. The former is limited to the skin and lacks monoclonal gammopathy. The latter, also known as SM, is associated with monoclonal gammopathy and systemic symptoms. Atypical LM is an umbrella term for intermediate cases.
Clinical Presentation
Skin manifestations of SM are described as 1- to 3-mm, firm, waxy, dome-shaped papules that commonly affect the hands, forearms, face, neck, trunk, and thighs. The surrounding skin may be reddish brown and edematous with evidence of skin thickening. Extracutaneous manifestations in SM are numerous and unpredictable. Any organ system can be involved, but gastrointestinal, rheumatologic, pulmonary, and cardiovascular complications are most common.10 A comprehensive multidisciplinary evaluation is necessary based on clinical symptoms and laboratory findings.
Management
Many treatments have been proposed for SM in case reports and case series. Prior treatments have had little success. Most recently, in one of the largest case series on SM, Rongioletti et al10 demonstrated IVIg to be a safe and effective treatment modality.
Differential Diagnosis
An important differential diagnosis is generalized myxedema, which is seen in long-standing hypothyroidism and may present with cutaneous mucinosis and systemic symptoms that resemble SM. Hypothyroid myxedema is associated with a widespread slowing of the body’s metabolic processes and deposition of mucin in various organs, including the skin, creating a generalized nonpitting edema. Classic clinical signs include macroglossia, periorbital puffiness, thick lips, and acral swelling. The skin tends to be cold, dry, and pale. Hair is characterized as being coarse, dry, and brittle with diffuse partial alopecia. Histologically, there is hyperkeratosis with follicular plugging and diffuse mucin and edema splaying between collagen fibers spanning the entire dermis.11 In contradistinction with SM, there is no fibroblast proliferation. The treatment is thyroid replacement therapy. Hyperthyroidism has distinct clinical and histologic changes. Clinically, there is moist and smooth skin with soft, fine, and sometimes alopecic hair. Graves disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, is further characterized by Graves ophthalmopathy and pretibial myxedema, or pink to brown, raised, firm, indurated, asymmetric plaques most commonly affecting the shins. Histologically there is increased mucin in the lower to mid dermis without fibroblast proliferation. The epidermis can be hyperkeratotic, which will clinically correlate with verrucous lesions.12
Hypothyroid encephalopathy is a rare disorder that can cause a change in mental status. It is a steroid-responsive autoimmune process characterized by encephalopathy that is associated with cognitive impairment and psychiatric features. It is a diagnosis of exclusion and should be suspected in women with a history of autoimmune disease, especially antithyroid peroxidase antibodies, a negative infectious workup, and encephalitis with behavioral changes. Although typically highly responsive to systemic steroids, IVIg also has shown efficacy.13
Presence of Thyroid Disease
According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms scleromyxedema and lichen myxedematosus, there are 7 cases in the literature that potentially describe LM associated with hypothyroidism (Table 2).3-8 The majority of these cases lack monoclonal gammopathy; improved with thyroid replacement therapy; or had severely atypical clinical presentations, rendering them cases of atypical LM or atypical thyroid dermopathy.3-6 Macnab and Kenny7 presented a case of subclinical hypothyroidism with a generalized papular eruption, monoclonal gammopathy, and consistent histologic changes that responded to IVIg therapy. These findings are suggestive of SM, but limited to the current diagnostic criteria, the patient was diagnosed with atypical LM.7 Shenoy et al8 described 2 cases of LM with hypothyroidism. One patient had biopsy-proven SM that was responsive to IVIg as well as Hashimoto thyroiditis with delayed onset of monoclonal gammopathy. The second patient had a medical history of hypothyroidism and Hodgkin lymphoma with active rheumatoid arthritis and biopsy-proven LM that was responsive to systemic steroids.8
Current literature states that thyroid disorder precludes the diagnosis of SM. However, historic literature would suggest otherwise. Because of inconsistent reports and theories regarding the pathogenesis of various sclerodermoid and mucin deposition diseases, in 1953 Montgomery and Underwood1 sought to differentiate LM from scleroderma and generalized myxedema. They stressed clinical appearance and proposed diagnostic criteria for LM as generalized papular mucinosis in which “[n]o relation to disturbance of the thyroid or other endocrine glands is apparent,” whereas generalized myxedema was defined as a “[t]rue cutaneous myxedema, with diffuse edema and the usual commonly recognized changes” in patients with endocrine abnormalities.1 With this classification, the authors made a clear distinction between mucinosis caused by thyroid abnormalities and LM, which is not caused by a thyroid disorder. Since this original description was published, associations with monoclonal gammopathy and fibroblast proliferation have been made, ultimately culminating into the current 2001 criteria that incorporate the absence of thyroid disease.2
Conclusion
We believe our case is consistent with the classification initially proposed by Montgomery and Underwood1 and is strengthened with the more recent associations with monoclonal gammopathy and specific histopathologic findings. Although there is no definitive way to rule out myxedema coma or Hashimoto encephalopathy to describe our patient’s transient neurologic decline, her clinical symptoms, laboratory findings, and biopsy results all supported the diagnosis of SM. Furthermore, her response to SM-directed therapy, despite fluctuating thyroid function test results, also supported the diagnosis. In the setting of cutaneous mucinosis with conflicting findings for hypothyroid myxedema, LM should be ruled out. Given the features presented in this report and others, diagnostic criteria should allow for SM and thyroid dysfunction to be concurrent diagnoses. Most importantly, we believe it is essential to identify and diagnose SM in a timely manner to facilitate SM-directed therapy, namely IVIg, to potentially minimize the disease’s notable morbidity and mortality.
- Montgomery H, Underwood LJ. Lichen myxedematosus; differentiation from cutaneous myxedemas or mucoid states. J Invest Dermatol. 1953;20:213-236.
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Updated classification of papular mucinosis, lichen myxedematosus and scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:273-281.
- Archibald GC, Calvert HT. Hypothyroidsm and lichen myxedematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:684.
- Schaeffer D, Bruce S, Rosen T. Cutaneous mucinosis associated with thyroid dysfunction. Cutis. 1983;11:449-456.
- Martin-Ezquerra G, Sanchez-Regaña M, Massana-Gil J, et al. Papular mucinosis associated with subclinical hypothyroidism: improvement with thyroxine therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1340-1341.
- Volpato MB, Jaime TJ, Proença MP, et al. Papular mucinosis associated with hypothyroidism. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:89-92.
- Macnab M, Kenny P. Successful intravenous immunoglobulin treatment of atypical lichen myxedematosus associated with hypothyroidism and central nervous system. involvement: case report and discussion of the literature. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17:69-73.
- Shenoy A, Steixner J, Beltrani V, et al. Discrete papular lichen myxedematosus and scleromyxedema with hypothyroidism: a report of two cases. Case Rep Dermatol. 2019;11:64-70.
- Helfrich DJ, Walker ER, Martinez AJ, et al. Scleromyxedema myopathy: case report and review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:1437-1441.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Jackson EM, English JC 3rd. Diffuse cutaneous mucinoses. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:493-501.
- Leonhardt JM, Heymann WR. Thyroid disease and the skin. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:473-481.
- Zhou JY, Xu B, Lopes J, et al. Hashimoto encephalopathy: literature review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;135:285-290.
- Montgomery H, Underwood LJ. Lichen myxedematosus; differentiation from cutaneous myxedemas or mucoid states. J Invest Dermatol. 1953;20:213-236.
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Updated classification of papular mucinosis, lichen myxedematosus and scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:273-281.
- Archibald GC, Calvert HT. Hypothyroidsm and lichen myxedematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:684.
- Schaeffer D, Bruce S, Rosen T. Cutaneous mucinosis associated with thyroid dysfunction. Cutis. 1983;11:449-456.
- Martin-Ezquerra G, Sanchez-Regaña M, Massana-Gil J, et al. Papular mucinosis associated with subclinical hypothyroidism: improvement with thyroxine therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:1340-1341.
- Volpato MB, Jaime TJ, Proença MP, et al. Papular mucinosis associated with hypothyroidism. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:89-92.
- Macnab M, Kenny P. Successful intravenous immunoglobulin treatment of atypical lichen myxedematosus associated with hypothyroidism and central nervous system. involvement: case report and discussion of the literature. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17:69-73.
- Shenoy A, Steixner J, Beltrani V, et al. Discrete papular lichen myxedematosus and scleromyxedema with hypothyroidism: a report of two cases. Case Rep Dermatol. 2019;11:64-70.
- Helfrich DJ, Walker ER, Martinez AJ, et al. Scleromyxedema myopathy: case report and review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:1437-1441.
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, et al. Scleromyxedema: a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:66-72.
- Jackson EM, English JC 3rd. Diffuse cutaneous mucinoses. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:493-501.
- Leonhardt JM, Heymann WR. Thyroid disease and the skin. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:473-481.
- Zhou JY, Xu B, Lopes J, et al. Hashimoto encephalopathy: literature review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;135:285-290.
Practice Points
- Scleromyxedema (SM) is progressive disease of unknown etiology with unpredictable behavior.
- Systemic manifestations associated with SM can cause serious morbidity and mortality.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin is the most effective treatment modality in SM.
- The presence of thyroid disease should not preclude the diagnosis of SM.