User login
Blood Glucose Testing Lancet and Paper Clip as a Milia Extractor
Practice Gap
In low-resource settings, dermatologists may not have the preferred tools to evaluate a patient or perform a procedure. Commonplace affordable supplies can be substituted when needed.
Traditionally, tools readily available for comedone extraction in dermatology clinics include sterile disposable hypodermic needles to open the skin and either a comedone extractor or 2 cotton-tip applicators to apply pressure for extraction. However, when these tools are not available, resourceful techniques have been utilized. Ashique and Srinivas1 described a less-painful method for extracting conchae comedones that they called “pen punching,” which involved using the rim of the tip of a ballpoint pen to apply pressure to extract lesions. Mukhtar and Gupta2 used a 3-mL disposable syringe as a comedone extractor; the syringe was cut at the needle hub using a surgical blade, with one half at 30° to 45°. Kaya et al3 used sharp-tipped cautery to puncture closed macrocomedones. Cvancara and Meffert4 described how an autoclaved paper clip could be fashioned into a disposable comedone extractor, highlighting its potential use in humanitarian work or military deployments. A sterilized safety pin has been demonstrated to be an inexpensive tool to extract open and closed comedones without a surgical blade.5 We describe the use of a blood glucose testing lancet and a paper clip for comedone extraction.
Tools and Technique
A patient presented to a satellite clinic requesting extraction of multiple bothersome milia. A comedone extractor was unavailable at that location, and the patient’s access to care elsewhere was limited.
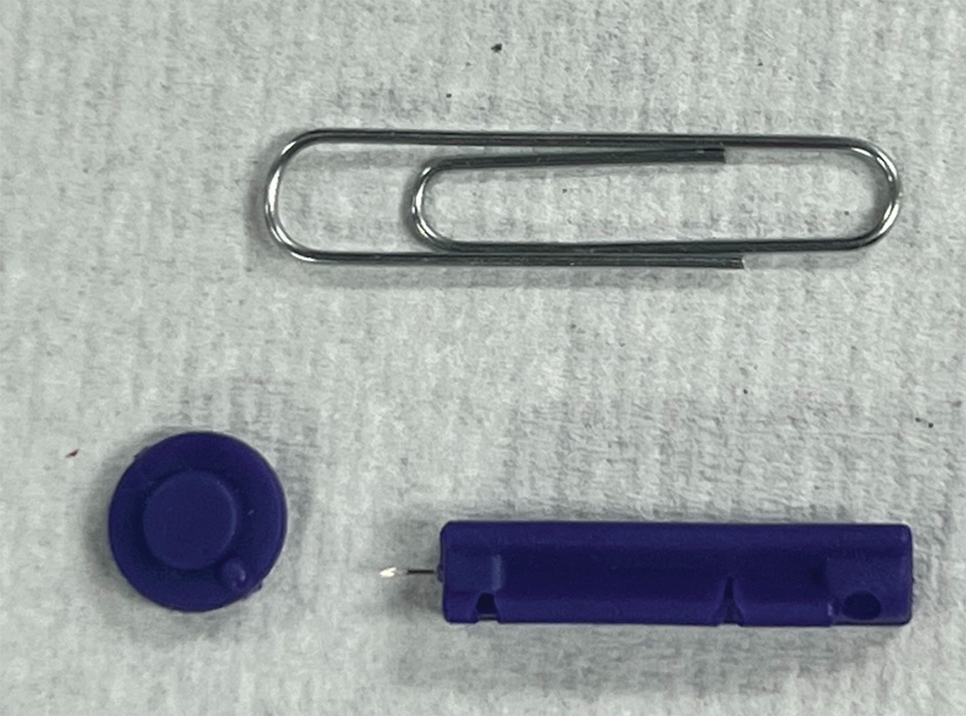
To perform extraction of milia in this case, we used a sterile, twist-top, stainless steel, 30-gauge blood glucose testing lancet and a paper clip sterilized with an isopropyl alcohol wipe (Figure). The beveled edge of the lancet was used to make a superficial opening to the skin, and the end loop of the paper clip was used as a comedone extractor. Applying moderate vertical pressure, 15 milia were expressed from the forearms. The patient tolerated the procedure well and reported minimal pain.
Practical Implications
The cost of the paper clip and lancet for our technique was $0.07. These materials are affordable, easy to use, and readily found in a variety of settings, making them a feasible option for performing this procedure.
- Ashique KT, Srinivas CR. Pen punching: an innovative technique for comedone extraction from the well of the concha. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E177. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.033
- Mukhtar M, Gupta S. Surgical pearl: disposable syringe as modified customized comedone extractor. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2022;15:185-186. doi:10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_112_21
- Kaya TI, Tursen U, Kokturk A, et al. An effective extraction technique for the treatment of closed macrocomedones. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:741-744. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29190.x
- Cvancara JL, Meffert JJ. Surgical pearl: versatile paper clip comedo extractor for acne surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:477-478. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70501-3
- Mukhtar M, Sharma R. Surgical pearl: the safety pin as a better alternative to the versatile paper clip comedo extractor. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:967-968. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02293.x
Practice Gap
In low-resource settings, dermatologists may not have the preferred tools to evaluate a patient or perform a procedure. Commonplace affordable supplies can be substituted when needed.
Traditionally, tools readily available for comedone extraction in dermatology clinics include sterile disposable hypodermic needles to open the skin and either a comedone extractor or 2 cotton-tip applicators to apply pressure for extraction. However, when these tools are not available, resourceful techniques have been utilized. Ashique and Srinivas1 described a less-painful method for extracting conchae comedones that they called “pen punching,” which involved using the rim of the tip of a ballpoint pen to apply pressure to extract lesions. Mukhtar and Gupta2 used a 3-mL disposable syringe as a comedone extractor; the syringe was cut at the needle hub using a surgical blade, with one half at 30° to 45°. Kaya et al3 used sharp-tipped cautery to puncture closed macrocomedones. Cvancara and Meffert4 described how an autoclaved paper clip could be fashioned into a disposable comedone extractor, highlighting its potential use in humanitarian work or military deployments. A sterilized safety pin has been demonstrated to be an inexpensive tool to extract open and closed comedones without a surgical blade.5 We describe the use of a blood glucose testing lancet and a paper clip for comedone extraction.
Tools and Technique
A patient presented to a satellite clinic requesting extraction of multiple bothersome milia. A comedone extractor was unavailable at that location, and the patient’s access to care elsewhere was limited.
To perform extraction of milia in this case, we used a sterile, twist-top, stainless steel, 30-gauge blood glucose testing lancet and a paper clip sterilized with an isopropyl alcohol wipe (Figure). The beveled edge of the lancet was used to make a superficial opening to the skin, and the end loop of the paper clip was used as a comedone extractor. Applying moderate vertical pressure, 15 milia were expressed from the forearms. The patient tolerated the procedure well and reported minimal pain.

Practical Implications
The cost of the paper clip and lancet for our technique was $0.07. These materials are affordable, easy to use, and readily found in a variety of settings, making them a feasible option for performing this procedure.
Practice Gap
In low-resource settings, dermatologists may not have the preferred tools to evaluate a patient or perform a procedure. Commonplace affordable supplies can be substituted when needed.
Traditionally, tools readily available for comedone extraction in dermatology clinics include sterile disposable hypodermic needles to open the skin and either a comedone extractor or 2 cotton-tip applicators to apply pressure for extraction. However, when these tools are not available, resourceful techniques have been utilized. Ashique and Srinivas1 described a less-painful method for extracting conchae comedones that they called “pen punching,” which involved using the rim of the tip of a ballpoint pen to apply pressure to extract lesions. Mukhtar and Gupta2 used a 3-mL disposable syringe as a comedone extractor; the syringe was cut at the needle hub using a surgical blade, with one half at 30° to 45°. Kaya et al3 used sharp-tipped cautery to puncture closed macrocomedones. Cvancara and Meffert4 described how an autoclaved paper clip could be fashioned into a disposable comedone extractor, highlighting its potential use in humanitarian work or military deployments. A sterilized safety pin has been demonstrated to be an inexpensive tool to extract open and closed comedones without a surgical blade.5 We describe the use of a blood glucose testing lancet and a paper clip for comedone extraction.
Tools and Technique
A patient presented to a satellite clinic requesting extraction of multiple bothersome milia. A comedone extractor was unavailable at that location, and the patient’s access to care elsewhere was limited.
To perform extraction of milia in this case, we used a sterile, twist-top, stainless steel, 30-gauge blood glucose testing lancet and a paper clip sterilized with an isopropyl alcohol wipe (Figure). The beveled edge of the lancet was used to make a superficial opening to the skin, and the end loop of the paper clip was used as a comedone extractor. Applying moderate vertical pressure, 15 milia were expressed from the forearms. The patient tolerated the procedure well and reported minimal pain.

Practical Implications
The cost of the paper clip and lancet for our technique was $0.07. These materials are affordable, easy to use, and readily found in a variety of settings, making them a feasible option for performing this procedure.
- Ashique KT, Srinivas CR. Pen punching: an innovative technique for comedone extraction from the well of the concha. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E177. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.033
- Mukhtar M, Gupta S. Surgical pearl: disposable syringe as modified customized comedone extractor. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2022;15:185-186. doi:10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_112_21
- Kaya TI, Tursen U, Kokturk A, et al. An effective extraction technique for the treatment of closed macrocomedones. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:741-744. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29190.x
- Cvancara JL, Meffert JJ. Surgical pearl: versatile paper clip comedo extractor for acne surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:477-478. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70501-3
- Mukhtar M, Sharma R. Surgical pearl: the safety pin as a better alternative to the versatile paper clip comedo extractor. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:967-968. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02293.x
- Ashique KT, Srinivas CR. Pen punching: an innovative technique for comedone extraction from the well of the concha. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:E177. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.033
- Mukhtar M, Gupta S. Surgical pearl: disposable syringe as modified customized comedone extractor. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2022;15:185-186. doi:10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_112_21
- Kaya TI, Tursen U, Kokturk A, et al. An effective extraction technique for the treatment of closed macrocomedones. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:741-744. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29190.x
- Cvancara JL, Meffert JJ. Surgical pearl: versatile paper clip comedo extractor for acne surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:477-478. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70501-3
- Mukhtar M, Sharma R. Surgical pearl: the safety pin as a better alternative to the versatile paper clip comedo extractor. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:967-968. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02293.x