User login
Pseudomyogenic Hemangioendothelioma
Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (PMHE), also referred to as epithelioid sarcoma–like hemangioendothelioma,1 is a rare soft tissue tumor that was described in 1992 by Mirra et al2 as a fibromalike variant of epithelioid sarcoma. It predominantly affects males between the second and fifth decades of life and most commonly presents as multiple nodules that may involve either the superficial or deep soft tissues of the legs and less often the arms. It also can arise on the trunk. We present a case of PMHE occurring in a young man and briefly review the literature on clinical presentation and histologic differentiation of this unique tumor, comparing these findings to its mimickers.
Case Report
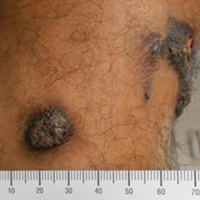
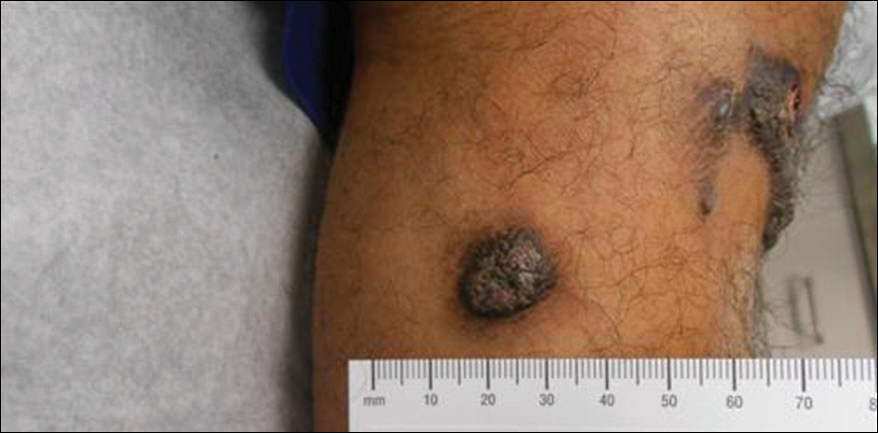
A 20-year-old man presented with skin lesions on the left leg that had been present for 1 year. The patient described the lesions as tender pimples that would drain yellow discharge on occasion but had now transformed into large brown plaques. Physical examination showed 4 verrucous plaques ranging in size from 1 to 3 cm with hyperpigmentation and a central crust (Figure 1). Initially, the patient thought the lesions appeared due to shaving his legs for sports. He presented to the emergency department multiple times over the past year; pain control was provided and local skin care was recommended. Culture of the discharge had been performed 6 months prior to biopsy with negative results. No biopsy was performed on initial presentation and the lesions were diagnosed in the emergency department clinically as boils.
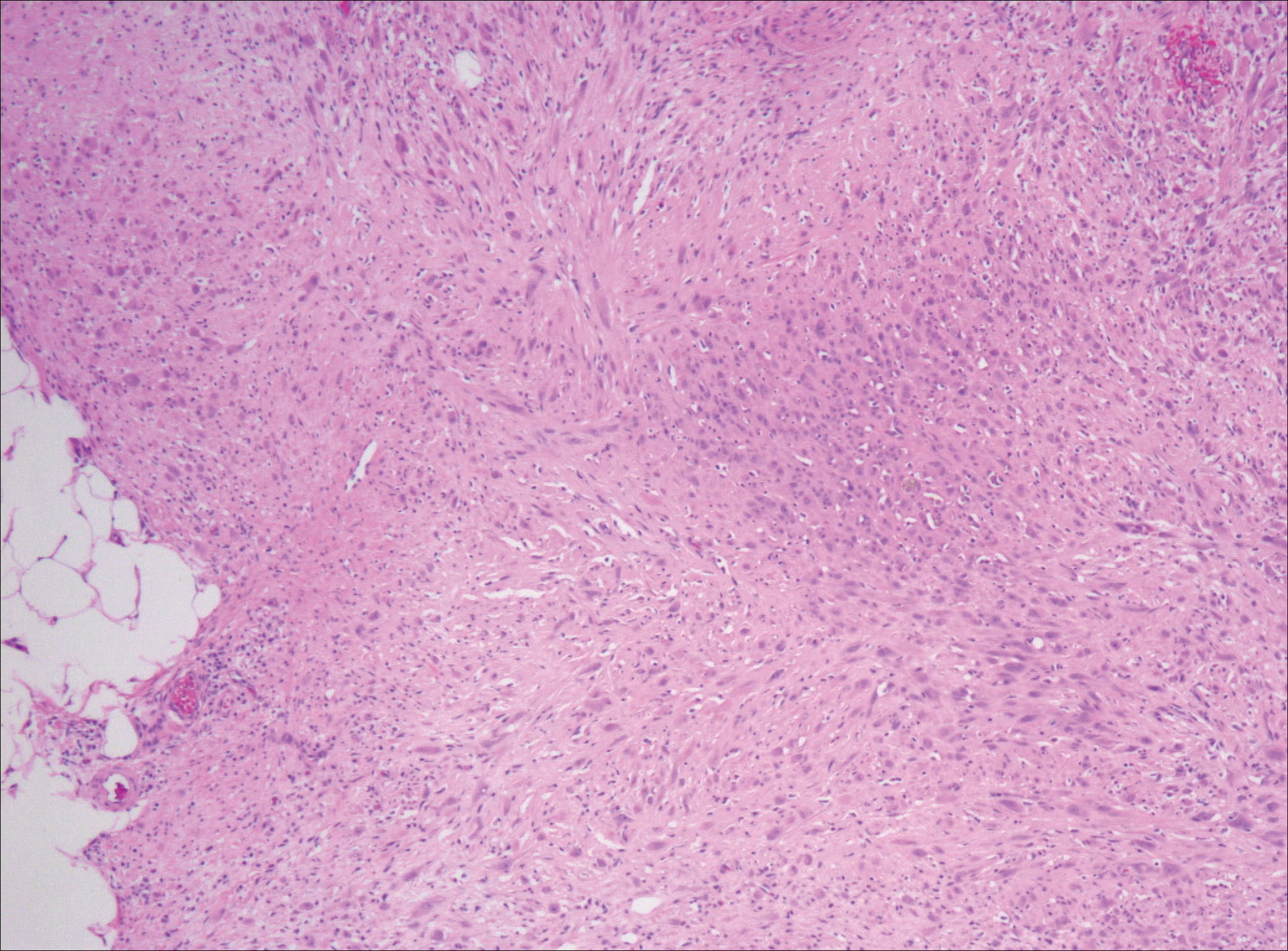
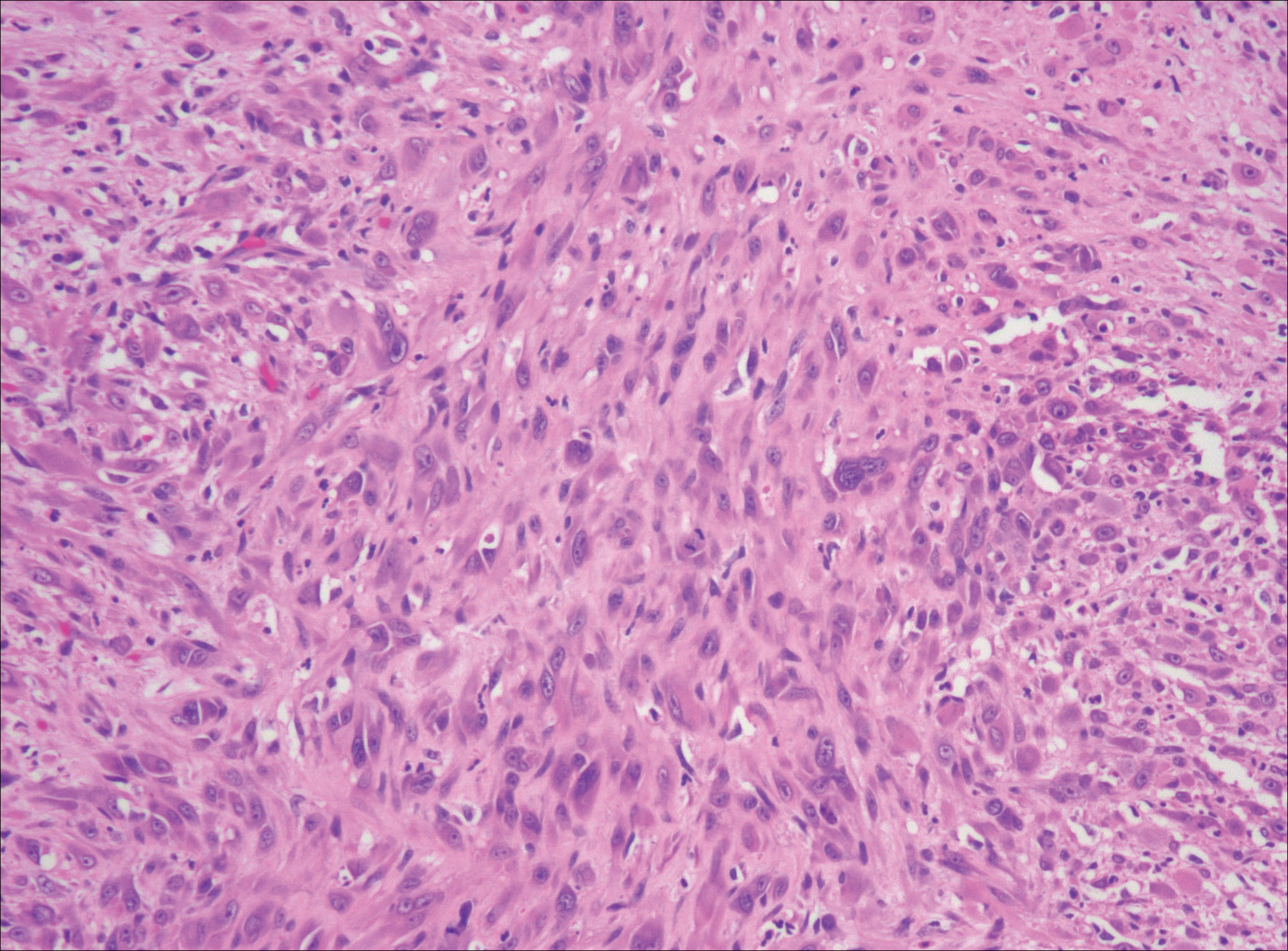
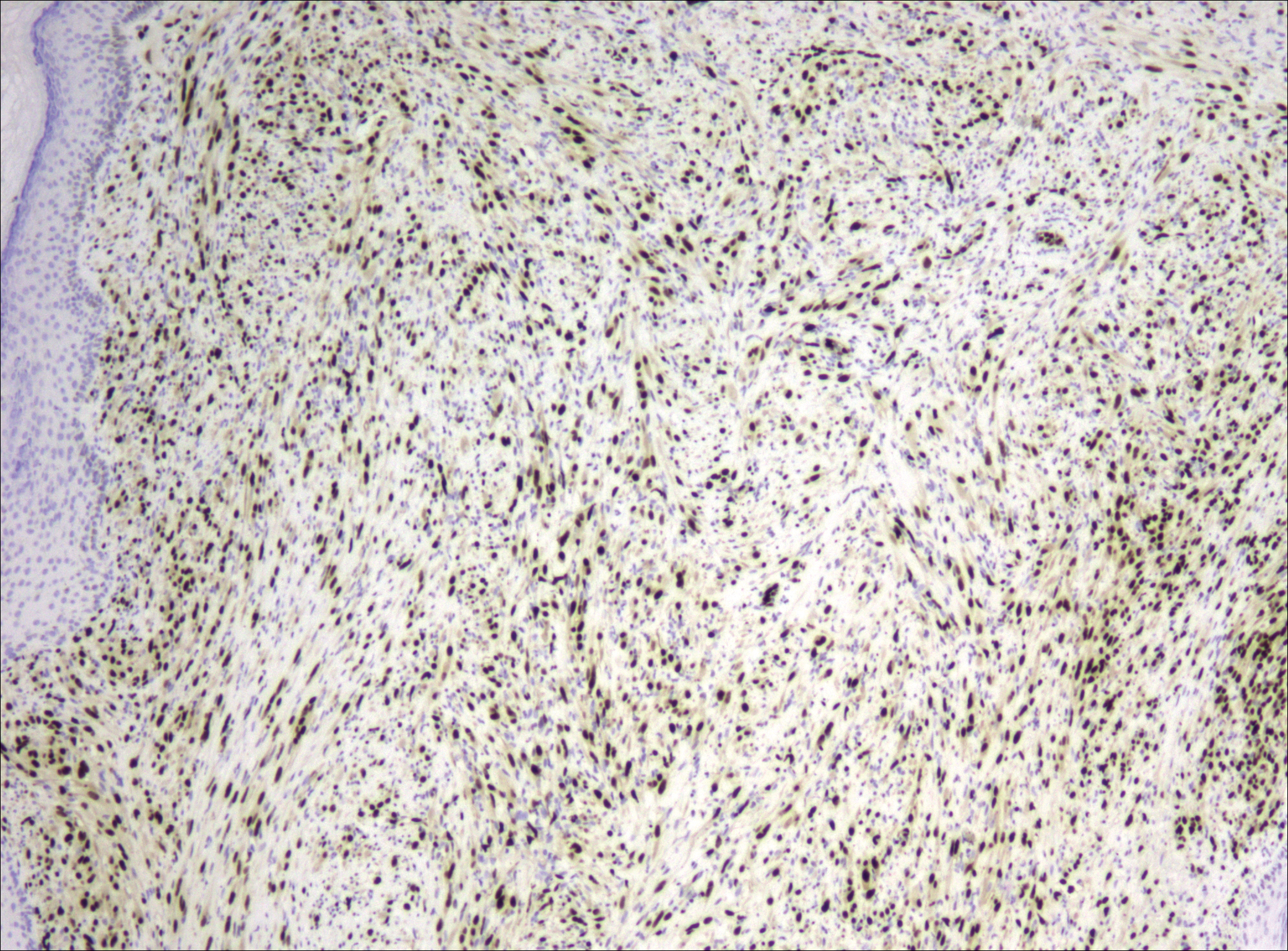
After failing to improve, the patient was seen by an outside dermatologist and the clinical differential diagnosis included deep fungal infection, atypical mycobacterial infection, and keloids. A 4-mm punch biopsy was taken from the periphery of one of the lesions and demonstrated hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis (Figure 2). Within the superficial and deep dermis and focally extending into the subcutaneous tissue, there were sheets of spindled to epithelioid-appearing cells with moderate cytologic atypia (Figure 3). The tumor showed infiltrative margins. There was moderate cellularity. The individual cells had a rhabdoid appearance with large eccentric vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 4). No definitive evidence of glandular, squamous, or vascular differentiation was present. There was an associated moderate inflammatory host response composed of neutrophils and lymphocytes. Occasional extravasated red blood cells were present. Immunohistochemistry staining was performed and the atypical cells demonstrated diffuse positive staining for friend leukemia integration 1 transcription factor (FLI-1), erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming sequence-related gene (ERG)(Figure 5), CD31, and CD68. There was patchy positive staining for cytokeratin AE1/AE3, CD10, and factor VIII. There was no remarkable staining for human herpesvirus 8, epithelial membrane antigen, S-100, CD34, cytokeratin 903, and desmin. Overall, the histologic features in conjunction with the immunohistochemistry staining were consistent with a diagnosis of PMHE.

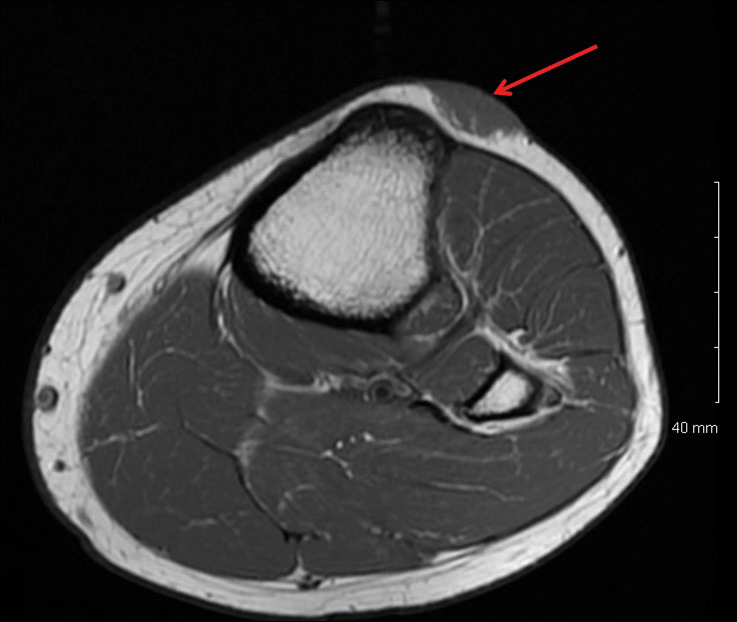
Magnetic resonance imaging was then performed to evaluate the depth and extent of the lesions for surgical excision planning (Figure 6), which showed 5 nodular lesions within the dermis and subcutis adjacent to the proximal aspect of the left tibia and medial aspect of the left knee. An additional lesion was noted between the sartorius and semimembranosus muscles, which was thought to represent either a lymph node or an additional neoplastic lesion. Chest computed tomography also displayed indeterminate lesions in the lungs.
Excision of the superficial lesions was performed. All of the lesions demonstrated similar histologic changes to the previously described biopsy specimen. The tumor was limited to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. The patient was lost to follow-up and the etiology of the lung lesions was unknown.
Comment
Nomenclature
Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma is a relatively new type of vascular tumor that has been included in the updated 2013 edition of the World Health Organization classification as an intermediate malignant tumor that rarely metastasizes.3 It typically involves multiple tissue planes, most notably the dermis and subcutaneous layers but also muscle and bone.4 The term pseudomyogenic refers to the histologic resemblance of some of the cells to rhabdomyoblasts; however, these tumors are negative for all immunohistochemical muscle markers, most notably myogenin, desmin, and α-smooth muscle actin.5
Clinical Presentation
Gross features of PMHE typically include multiple firm nodules with ill-defined margins. The tumor was initially described in 1992 by Mirra et al2 as a fibromalike variant of epithelioid sarcoma. In 2003, a series of 7 cases of PMHE was reported by Billings et al6 under the term epithelioid sarcomalike hemangioendothelioma. Other than the predominance of an epithelioid morphology, the cases reported as epithelioid sarcomalike hemangioendothelioma had similar clinical features and immunophenotype to what has been reported as PMHE.
Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma, the 2 largest case series were reported by Pradhan et al7 (N=8) in 2017 and Hornick and Fletcher4 (N=50) in 2011. Hornick and Fletcher4 reported a male (41/50 [82.0%]) to female (9/50 [18.0%]) ratio of 4.6 to 1, and an average age at presentation of 31 years with 82% (41/50) of patients 40 years or younger. Pradhan et al7 also reported a male predominance (7/8 [87.5%]) with a similar average age at presentation of 29 years (age range, 9–62 years). The size of individual tumors ranged from 0.3 to 5.5 cm (mean size, 1.9 cm) in the series by Hornick and Fletcher4 and 0.3 to 6.0 com in the series by Pradhan et al.7 Hornick and Fletcher4 reported the most common site of involvement was the leg (27/50 [54.0%]), followed by the arm (12/50 [24.0%]), trunk (9/50 [18.0%]), and head and neck (2/50 [4.0%]). The leg (6/8 [75.0%]) also was the most common site of involvement in the series by Pradhan et al,7 with 2 cases occurring on the arm. In the series by Hornick and Fletcher,4 the tumors typically involved the dermis and subcutaneous tissue (26/50 [52%]) with a smaller number involving skeletal muscle (17/50 [34%]) and bone (7/50 [14%]). They reported 66% of their patients (33/50) had multifocal disease at presentation.4 Pradhan et al7 also reported 2 (25.0%) cases being limited to the superficial soft tissue, 2 (25.0%) being limited to the deep soft tissue, and 4 (50.0%) involving the bone; 5 (62.5%) patients had multifocal disease at presentation. The presentation of our patient in regards to gender, age, and tumor characteristics is consistent with other published cases.5-10
Histopathology
Microscopic features of PMHE include sheets of spindled to epithelioid-appearing cells with mild to moderate nuclear atypia and eosinophilic cytoplasm. The tumor has an infiltrative growth pattern. Some of the cells may resemble rhabdomyoblastlike cells, hence the moniker pseudomyogenic. There is no recapitulation of vascular structures or remarkable cytoplasmic vacuolization. Mitotic rate is low and there is no tumor necrosis.4 The tumor cells do not appear to arise from a vessel or display an angiocentric growth pattern. Many cases report the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate containing neutrophils interspersed within the tumor.4,5,7 The overlying epidermis will commonly show hyperkeratosis, epidermal hyperplasia, and acanthosis.4,11
Differential Diagnosis
The histopathologic differential diagnosis would include epithelioid sarcoma, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, and to a lesser extent dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and rhabdomyosarcoma. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is the most commonly encountered of these tumors. Histologically, DFSP is characterized by a cellular proliferation of small spindle cells with plump nuclei arranged in a storiform or cartwheel pattern. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans tends to be limited to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue and only rarely involves underlying skeletal muscle. The presence of the storiform growth pattern in conjunction with the lack of rhabdoid changes would favor a diagnosis of DFSP. Another characteristic histologic finding typically only associated with DFSP is the interdigitating growth pattern of the spindle cells within the lobules of the subcutaneous tissue, creating a lacelike or honeycomb appearance.
Immunohistochemistry staining is necessary to help differentiate PMHE from other tumors in the differential diagnosis. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma stains positive for cytokeratin AE1/AE3; integrase interactor 1; and vascular markers FLI-1, CD31, and ERG, and negative for CD34.4,6,12-15 In contrast to epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, DFSP, and to a lesser extent epithelioid sarcoma, all of which are positive for CD34, epithelioid sarcoma is negative for both CD31 and integrase interactor 1. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is negative for cytokeratin AE1/AE3. Rhabdomyosarcomas are positive for myogenic markers such as MyoD1 and myogenin, unlike any of the other tumors mentioned. Histologically, epithelioid sarcomas will tend to have a granulomalike growth pattern with central necrosis, unlike PMHE.12 Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma often will have a cordlike growth pattern in a myxochondroid background. Unlike PMHE, these tumors often will appear to be arising from vessels, and intracytoplasmic vacuoles are common. Three cases of PMHE have been reported to have a t(7;19)(q22;q13) chromosomal anomaly, which is not consistent with every case.16
Treatment Options
Standard treatment typically includes wide excision of the lesions, as was done in our case. Because of the substantial risk of local recurrence, which was up to 58% in the series by Hornick and Fletcher,4 adjuvant therapy may be considered if positive margins are found on excision. Metastasis to lymph nodes and the lungs has been reported but is rare.2,4 Most cases have been shown to have a favorable prognosis; however, local recurrence seems to be common. Rarely, amputation of the limb may be required.5 In contrast, epithelioid sarcomas have been found to spread to lymph nodes and the lungs in up to 50% of cases with a 5-year survival rate of 10% to 30%.13
Conclusion
In summary, we describe a case of PMHE involving the lower leg in a 20-year-old man. These tumors often are multinodular and multiplanar, with the dermis and subcutaneous tissues being the most common areas affected. It has a high rate of local recurrence but rarely has distant metastasis. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma, similar to other soft tissue tumors, can be difficult to diagnose on shave biopsy or superficial punch biopsy not extending into subcutaneous tissue. Deep incisional or punch biopsies are required to more definitively diagnose these types of tumors. The diagnosis of PMHE versus other soft tissue tumors requires correlation of histology and immunohistochemistry staining with clinical information and radiographic findings.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma (pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma). Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:1088; author reply 1088-1089.
- Mirra JM, Kessler S, Bhuta S, et al. The fibroma-like variant of epithelioid sarcoma. a fibrohistiocytic/myoid cell lesion often confused with benign and malignant spindle cell tumors. Cancer. 1992;69:1382-1395.
- Jo VY, Fletcher CD. WHO classification of soft tissue tumours: an update based on the 2013 (4th) edition. Pathology. 2014;46:95-104.
- Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma: a distinctive, often multicentric tumor with indolent behavior. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:190-201.
- Sheng W, Pan Y, Wang J. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma: report of an additional case with aggressive clinical course. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:597-600.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:48-57.
- Pradhan D, Schoedel K, McGough RL, et al. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma of skin, bone and soft tissue—a clinicopathological, immunohistochemical and fluorescence in situ hybridization study [published online November 2, 2017]. Hum Pathol. 2017. doi:0.1016/j.humpath.2017.10.023.
- Requena L, Santonja C, Martinez-Amo JL, et al. Cutaneous epithelioid sarcoma like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma: a little-known low-grade cutaneous vascular neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:459-465.
- McGinity M, Bartanusz V, Dengler B, et al. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma, fibroma-like variant of epithelioid sarcoma) of the thoracic spine. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(suppl 3):S506-S511.
- Stuart LN, Gardner JM, Lauer SR, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma-like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma, clinically mimicking dermatofibroma, diagnosed by skin biopsy in a 30-year-old man. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:909-913.
- Amary MF, O’Donnell P, Berisha F, et al. Pseudomyogenic (epithelioid sarcoma-like) hemangioendothelioma: characterization of five cases. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:947-957.
- Hornick JL, Dal Cin P, Fletcher CD. Loss of INI1 expression is characteristic of both conventional and proximal-type epithelioid sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:542-550.
- Chbani L, Guillou L, Terrier P, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 106 cases from the French Sarcoma Group. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;131:222-227.
- Fisher C. Epithelioid sarcoma of Enzinger. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:114-121.
- Requena L, Santonja C, Martinez-Amo JL, et al. Cutaneous epithelioid sarcoma like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma: a little-known low-grade cutaneous vascular neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:459-465.
- Trombetta D, Magnusson L, von Steyern FV, et al. Translocation t(7;19)(q22;q13)—a recurrent chromosome aberration in pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma? Cancer Genet. 2011;204:211-215.
Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (PMHE), also referred to as epithelioid sarcoma–like hemangioendothelioma,1 is a rare soft tissue tumor that was described in 1992 by Mirra et al2 as a fibromalike variant of epithelioid sarcoma. It predominantly affects males between the second and fifth decades of life and most commonly presents as multiple nodules that may involve either the superficial or deep soft tissues of the legs and less often the arms. It also can arise on the trunk. We present a case of PMHE occurring in a young man and briefly review the literature on clinical presentation and histologic differentiation of this unique tumor, comparing these findings to its mimickers.
Case Report
A 20-year-old man presented with skin lesions on the left leg that had been present for 1 year. The patient described the lesions as tender pimples that would drain yellow discharge on occasion but had now transformed into large brown plaques. Physical examination showed 4 verrucous plaques ranging in size from 1 to 3 cm with hyperpigmentation and a central crust (Figure 1). Initially, the patient thought the lesions appeared due to shaving his legs for sports. He presented to the emergency department multiple times over the past year; pain control was provided and local skin care was recommended. Culture of the discharge had been performed 6 months prior to biopsy with negative results. No biopsy was performed on initial presentation and the lesions were diagnosed in the emergency department clinically as boils.

After failing to improve, the patient was seen by an outside dermatologist and the clinical differential diagnosis included deep fungal infection, atypical mycobacterial infection, and keloids. A 4-mm punch biopsy was taken from the periphery of one of the lesions and demonstrated hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis (Figure 2). Within the superficial and deep dermis and focally extending into the subcutaneous tissue, there were sheets of spindled to epithelioid-appearing cells with moderate cytologic atypia (Figure 3). The tumor showed infiltrative margins. There was moderate cellularity. The individual cells had a rhabdoid appearance with large eccentric vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 4). No definitive evidence of glandular, squamous, or vascular differentiation was present. There was an associated moderate inflammatory host response composed of neutrophils and lymphocytes. Occasional extravasated red blood cells were present. Immunohistochemistry staining was performed and the atypical cells demonstrated diffuse positive staining for friend leukemia integration 1 transcription factor (FLI-1), erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming sequence-related gene (ERG)(Figure 5), CD31, and CD68. There was patchy positive staining for cytokeratin AE1/AE3, CD10, and factor VIII. There was no remarkable staining for human herpesvirus 8, epithelial membrane antigen, S-100, CD34, cytokeratin 903, and desmin. Overall, the histologic features in conjunction with the immunohistochemistry staining were consistent with a diagnosis of PMHE.




Magnetic resonance imaging was then performed to evaluate the depth and extent of the lesions for surgical excision planning (Figure 6), which showed 5 nodular lesions within the dermis and subcutis adjacent to the proximal aspect of the left tibia and medial aspect of the left knee. An additional lesion was noted between the sartorius and semimembranosus muscles, which was thought to represent either a lymph node or an additional neoplastic lesion. Chest computed tomography also displayed indeterminate lesions in the lungs.

Excision of the superficial lesions was performed. All of the lesions demonstrated similar histologic changes to the previously described biopsy specimen. The tumor was limited to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. The patient was lost to follow-up and the etiology of the lung lesions was unknown.
Comment
Nomenclature
Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma is a relatively new type of vascular tumor that has been included in the updated 2013 edition of the World Health Organization classification as an intermediate malignant tumor that rarely metastasizes.3 It typically involves multiple tissue planes, most notably the dermis and subcutaneous layers but also muscle and bone.4 The term pseudomyogenic refers to the histologic resemblance of some of the cells to rhabdomyoblasts; however, these tumors are negative for all immunohistochemical muscle markers, most notably myogenin, desmin, and α-smooth muscle actin.5
Clinical Presentation
Gross features of PMHE typically include multiple firm nodules with ill-defined margins. The tumor was initially described in 1992 by Mirra et al2 as a fibromalike variant of epithelioid sarcoma. In 2003, a series of 7 cases of PMHE was reported by Billings et al6 under the term epithelioid sarcomalike hemangioendothelioma. Other than the predominance of an epithelioid morphology, the cases reported as epithelioid sarcomalike hemangioendothelioma had similar clinical features and immunophenotype to what has been reported as PMHE.
Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma, the 2 largest case series were reported by Pradhan et al7 (N=8) in 2017 and Hornick and Fletcher4 (N=50) in 2011. Hornick and Fletcher4 reported a male (41/50 [82.0%]) to female (9/50 [18.0%]) ratio of 4.6 to 1, and an average age at presentation of 31 years with 82% (41/50) of patients 40 years or younger. Pradhan et al7 also reported a male predominance (7/8 [87.5%]) with a similar average age at presentation of 29 years (age range, 9–62 years). The size of individual tumors ranged from 0.3 to 5.5 cm (mean size, 1.9 cm) in the series by Hornick and Fletcher4 and 0.3 to 6.0 com in the series by Pradhan et al.7 Hornick and Fletcher4 reported the most common site of involvement was the leg (27/50 [54.0%]), followed by the arm (12/50 [24.0%]), trunk (9/50 [18.0%]), and head and neck (2/50 [4.0%]). The leg (6/8 [75.0%]) also was the most common site of involvement in the series by Pradhan et al,7 with 2 cases occurring on the arm. In the series by Hornick and Fletcher,4 the tumors typically involved the dermis and subcutaneous tissue (26/50 [52%]) with a smaller number involving skeletal muscle (17/50 [34%]) and bone (7/50 [14%]). They reported 66% of their patients (33/50) had multifocal disease at presentation.4 Pradhan et al7 also reported 2 (25.0%) cases being limited to the superficial soft tissue, 2 (25.0%) being limited to the deep soft tissue, and 4 (50.0%) involving the bone; 5 (62.5%) patients had multifocal disease at presentation. The presentation of our patient in regards to gender, age, and tumor characteristics is consistent with other published cases.5-10
Histopathology
Microscopic features of PMHE include sheets of spindled to epithelioid-appearing cells with mild to moderate nuclear atypia and eosinophilic cytoplasm. The tumor has an infiltrative growth pattern. Some of the cells may resemble rhabdomyoblastlike cells, hence the moniker pseudomyogenic. There is no recapitulation of vascular structures or remarkable cytoplasmic vacuolization. Mitotic rate is low and there is no tumor necrosis.4 The tumor cells do not appear to arise from a vessel or display an angiocentric growth pattern. Many cases report the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate containing neutrophils interspersed within the tumor.4,5,7 The overlying epidermis will commonly show hyperkeratosis, epidermal hyperplasia, and acanthosis.4,11
Differential Diagnosis
The histopathologic differential diagnosis would include epithelioid sarcoma, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, and to a lesser extent dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and rhabdomyosarcoma. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is the most commonly encountered of these tumors. Histologically, DFSP is characterized by a cellular proliferation of small spindle cells with plump nuclei arranged in a storiform or cartwheel pattern. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans tends to be limited to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue and only rarely involves underlying skeletal muscle. The presence of the storiform growth pattern in conjunction with the lack of rhabdoid changes would favor a diagnosis of DFSP. Another characteristic histologic finding typically only associated with DFSP is the interdigitating growth pattern of the spindle cells within the lobules of the subcutaneous tissue, creating a lacelike or honeycomb appearance.
Immunohistochemistry staining is necessary to help differentiate PMHE from other tumors in the differential diagnosis. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma stains positive for cytokeratin AE1/AE3; integrase interactor 1; and vascular markers FLI-1, CD31, and ERG, and negative for CD34.4,6,12-15 In contrast to epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, DFSP, and to a lesser extent epithelioid sarcoma, all of which are positive for CD34, epithelioid sarcoma is negative for both CD31 and integrase interactor 1. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is negative for cytokeratin AE1/AE3. Rhabdomyosarcomas are positive for myogenic markers such as MyoD1 and myogenin, unlike any of the other tumors mentioned. Histologically, epithelioid sarcomas will tend to have a granulomalike growth pattern with central necrosis, unlike PMHE.12 Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma often will have a cordlike growth pattern in a myxochondroid background. Unlike PMHE, these tumors often will appear to be arising from vessels, and intracytoplasmic vacuoles are common. Three cases of PMHE have been reported to have a t(7;19)(q22;q13) chromosomal anomaly, which is not consistent with every case.16
Treatment Options
Standard treatment typically includes wide excision of the lesions, as was done in our case. Because of the substantial risk of local recurrence, which was up to 58% in the series by Hornick and Fletcher,4 adjuvant therapy may be considered if positive margins are found on excision. Metastasis to lymph nodes and the lungs has been reported but is rare.2,4 Most cases have been shown to have a favorable prognosis; however, local recurrence seems to be common. Rarely, amputation of the limb may be required.5 In contrast, epithelioid sarcomas have been found to spread to lymph nodes and the lungs in up to 50% of cases with a 5-year survival rate of 10% to 30%.13
Conclusion
In summary, we describe a case of PMHE involving the lower leg in a 20-year-old man. These tumors often are multinodular and multiplanar, with the dermis and subcutaneous tissues being the most common areas affected. It has a high rate of local recurrence but rarely has distant metastasis. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma, similar to other soft tissue tumors, can be difficult to diagnose on shave biopsy or superficial punch biopsy not extending into subcutaneous tissue. Deep incisional or punch biopsies are required to more definitively diagnose these types of tumors. The diagnosis of PMHE versus other soft tissue tumors requires correlation of histology and immunohistochemistry staining with clinical information and radiographic findings.
Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (PMHE), also referred to as epithelioid sarcoma–like hemangioendothelioma,1 is a rare soft tissue tumor that was described in 1992 by Mirra et al2 as a fibromalike variant of epithelioid sarcoma. It predominantly affects males between the second and fifth decades of life and most commonly presents as multiple nodules that may involve either the superficial or deep soft tissues of the legs and less often the arms. It also can arise on the trunk. We present a case of PMHE occurring in a young man and briefly review the literature on clinical presentation and histologic differentiation of this unique tumor, comparing these findings to its mimickers.
Case Report
A 20-year-old man presented with skin lesions on the left leg that had been present for 1 year. The patient described the lesions as tender pimples that would drain yellow discharge on occasion but had now transformed into large brown plaques. Physical examination showed 4 verrucous plaques ranging in size from 1 to 3 cm with hyperpigmentation and a central crust (Figure 1). Initially, the patient thought the lesions appeared due to shaving his legs for sports. He presented to the emergency department multiple times over the past year; pain control was provided and local skin care was recommended. Culture of the discharge had been performed 6 months prior to biopsy with negative results. No biopsy was performed on initial presentation and the lesions were diagnosed in the emergency department clinically as boils.

After failing to improve, the patient was seen by an outside dermatologist and the clinical differential diagnosis included deep fungal infection, atypical mycobacterial infection, and keloids. A 4-mm punch biopsy was taken from the periphery of one of the lesions and demonstrated hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis (Figure 2). Within the superficial and deep dermis and focally extending into the subcutaneous tissue, there were sheets of spindled to epithelioid-appearing cells with moderate cytologic atypia (Figure 3). The tumor showed infiltrative margins. There was moderate cellularity. The individual cells had a rhabdoid appearance with large eccentric vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 4). No definitive evidence of glandular, squamous, or vascular differentiation was present. There was an associated moderate inflammatory host response composed of neutrophils and lymphocytes. Occasional extravasated red blood cells were present. Immunohistochemistry staining was performed and the atypical cells demonstrated diffuse positive staining for friend leukemia integration 1 transcription factor (FLI-1), erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming sequence-related gene (ERG)(Figure 5), CD31, and CD68. There was patchy positive staining for cytokeratin AE1/AE3, CD10, and factor VIII. There was no remarkable staining for human herpesvirus 8, epithelial membrane antigen, S-100, CD34, cytokeratin 903, and desmin. Overall, the histologic features in conjunction with the immunohistochemistry staining were consistent with a diagnosis of PMHE.




Magnetic resonance imaging was then performed to evaluate the depth and extent of the lesions for surgical excision planning (Figure 6), which showed 5 nodular lesions within the dermis and subcutis adjacent to the proximal aspect of the left tibia and medial aspect of the left knee. An additional lesion was noted between the sartorius and semimembranosus muscles, which was thought to represent either a lymph node or an additional neoplastic lesion. Chest computed tomography also displayed indeterminate lesions in the lungs.

Excision of the superficial lesions was performed. All of the lesions demonstrated similar histologic changes to the previously described biopsy specimen. The tumor was limited to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. The patient was lost to follow-up and the etiology of the lung lesions was unknown.
Comment
Nomenclature
Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma is a relatively new type of vascular tumor that has been included in the updated 2013 edition of the World Health Organization classification as an intermediate malignant tumor that rarely metastasizes.3 It typically involves multiple tissue planes, most notably the dermis and subcutaneous layers but also muscle and bone.4 The term pseudomyogenic refers to the histologic resemblance of some of the cells to rhabdomyoblasts; however, these tumors are negative for all immunohistochemical muscle markers, most notably myogenin, desmin, and α-smooth muscle actin.5
Clinical Presentation
Gross features of PMHE typically include multiple firm nodules with ill-defined margins. The tumor was initially described in 1992 by Mirra et al2 as a fibromalike variant of epithelioid sarcoma. In 2003, a series of 7 cases of PMHE was reported by Billings et al6 under the term epithelioid sarcomalike hemangioendothelioma. Other than the predominance of an epithelioid morphology, the cases reported as epithelioid sarcomalike hemangioendothelioma had similar clinical features and immunophenotype to what has been reported as PMHE.
Based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma, the 2 largest case series were reported by Pradhan et al7 (N=8) in 2017 and Hornick and Fletcher4 (N=50) in 2011. Hornick and Fletcher4 reported a male (41/50 [82.0%]) to female (9/50 [18.0%]) ratio of 4.6 to 1, and an average age at presentation of 31 years with 82% (41/50) of patients 40 years or younger. Pradhan et al7 also reported a male predominance (7/8 [87.5%]) with a similar average age at presentation of 29 years (age range, 9–62 years). The size of individual tumors ranged from 0.3 to 5.5 cm (mean size, 1.9 cm) in the series by Hornick and Fletcher4 and 0.3 to 6.0 com in the series by Pradhan et al.7 Hornick and Fletcher4 reported the most common site of involvement was the leg (27/50 [54.0%]), followed by the arm (12/50 [24.0%]), trunk (9/50 [18.0%]), and head and neck (2/50 [4.0%]). The leg (6/8 [75.0%]) also was the most common site of involvement in the series by Pradhan et al,7 with 2 cases occurring on the arm. In the series by Hornick and Fletcher,4 the tumors typically involved the dermis and subcutaneous tissue (26/50 [52%]) with a smaller number involving skeletal muscle (17/50 [34%]) and bone (7/50 [14%]). They reported 66% of their patients (33/50) had multifocal disease at presentation.4 Pradhan et al7 also reported 2 (25.0%) cases being limited to the superficial soft tissue, 2 (25.0%) being limited to the deep soft tissue, and 4 (50.0%) involving the bone; 5 (62.5%) patients had multifocal disease at presentation. The presentation of our patient in regards to gender, age, and tumor characteristics is consistent with other published cases.5-10
Histopathology
Microscopic features of PMHE include sheets of spindled to epithelioid-appearing cells with mild to moderate nuclear atypia and eosinophilic cytoplasm. The tumor has an infiltrative growth pattern. Some of the cells may resemble rhabdomyoblastlike cells, hence the moniker pseudomyogenic. There is no recapitulation of vascular structures or remarkable cytoplasmic vacuolization. Mitotic rate is low and there is no tumor necrosis.4 The tumor cells do not appear to arise from a vessel or display an angiocentric growth pattern. Many cases report the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate containing neutrophils interspersed within the tumor.4,5,7 The overlying epidermis will commonly show hyperkeratosis, epidermal hyperplasia, and acanthosis.4,11
Differential Diagnosis
The histopathologic differential diagnosis would include epithelioid sarcoma, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, and to a lesser extent dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and rhabdomyosarcoma. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is the most commonly encountered of these tumors. Histologically, DFSP is characterized by a cellular proliferation of small spindle cells with plump nuclei arranged in a storiform or cartwheel pattern. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans tends to be limited to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue and only rarely involves underlying skeletal muscle. The presence of the storiform growth pattern in conjunction with the lack of rhabdoid changes would favor a diagnosis of DFSP. Another characteristic histologic finding typically only associated with DFSP is the interdigitating growth pattern of the spindle cells within the lobules of the subcutaneous tissue, creating a lacelike or honeycomb appearance.
Immunohistochemistry staining is necessary to help differentiate PMHE from other tumors in the differential diagnosis. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma stains positive for cytokeratin AE1/AE3; integrase interactor 1; and vascular markers FLI-1, CD31, and ERG, and negative for CD34.4,6,12-15 In contrast to epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, DFSP, and to a lesser extent epithelioid sarcoma, all of which are positive for CD34, epithelioid sarcoma is negative for both CD31 and integrase interactor 1. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is negative for cytokeratin AE1/AE3. Rhabdomyosarcomas are positive for myogenic markers such as MyoD1 and myogenin, unlike any of the other tumors mentioned. Histologically, epithelioid sarcomas will tend to have a granulomalike growth pattern with central necrosis, unlike PMHE.12 Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma often will have a cordlike growth pattern in a myxochondroid background. Unlike PMHE, these tumors often will appear to be arising from vessels, and intracytoplasmic vacuoles are common. Three cases of PMHE have been reported to have a t(7;19)(q22;q13) chromosomal anomaly, which is not consistent with every case.16
Treatment Options
Standard treatment typically includes wide excision of the lesions, as was done in our case. Because of the substantial risk of local recurrence, which was up to 58% in the series by Hornick and Fletcher,4 adjuvant therapy may be considered if positive margins are found on excision. Metastasis to lymph nodes and the lungs has been reported but is rare.2,4 Most cases have been shown to have a favorable prognosis; however, local recurrence seems to be common. Rarely, amputation of the limb may be required.5 In contrast, epithelioid sarcomas have been found to spread to lymph nodes and the lungs in up to 50% of cases with a 5-year survival rate of 10% to 30%.13
Conclusion
In summary, we describe a case of PMHE involving the lower leg in a 20-year-old man. These tumors often are multinodular and multiplanar, with the dermis and subcutaneous tissues being the most common areas affected. It has a high rate of local recurrence but rarely has distant metastasis. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma, similar to other soft tissue tumors, can be difficult to diagnose on shave biopsy or superficial punch biopsy not extending into subcutaneous tissue. Deep incisional or punch biopsies are required to more definitively diagnose these types of tumors. The diagnosis of PMHE versus other soft tissue tumors requires correlation of histology and immunohistochemistry staining with clinical information and radiographic findings.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma (pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma). Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:1088; author reply 1088-1089.
- Mirra JM, Kessler S, Bhuta S, et al. The fibroma-like variant of epithelioid sarcoma. a fibrohistiocytic/myoid cell lesion often confused with benign and malignant spindle cell tumors. Cancer. 1992;69:1382-1395.
- Jo VY, Fletcher CD. WHO classification of soft tissue tumours: an update based on the 2013 (4th) edition. Pathology. 2014;46:95-104.
- Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma: a distinctive, often multicentric tumor with indolent behavior. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:190-201.
- Sheng W, Pan Y, Wang J. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma: report of an additional case with aggressive clinical course. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:597-600.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:48-57.
- Pradhan D, Schoedel K, McGough RL, et al. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma of skin, bone and soft tissue—a clinicopathological, immunohistochemical and fluorescence in situ hybridization study [published online November 2, 2017]. Hum Pathol. 2017. doi:0.1016/j.humpath.2017.10.023.
- Requena L, Santonja C, Martinez-Amo JL, et al. Cutaneous epithelioid sarcoma like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma: a little-known low-grade cutaneous vascular neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:459-465.
- McGinity M, Bartanusz V, Dengler B, et al. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma, fibroma-like variant of epithelioid sarcoma) of the thoracic spine. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(suppl 3):S506-S511.
- Stuart LN, Gardner JM, Lauer SR, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma-like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma, clinically mimicking dermatofibroma, diagnosed by skin biopsy in a 30-year-old man. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:909-913.
- Amary MF, O’Donnell P, Berisha F, et al. Pseudomyogenic (epithelioid sarcoma-like) hemangioendothelioma: characterization of five cases. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:947-957.
- Hornick JL, Dal Cin P, Fletcher CD. Loss of INI1 expression is characteristic of both conventional and proximal-type epithelioid sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:542-550.
- Chbani L, Guillou L, Terrier P, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 106 cases from the French Sarcoma Group. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;131:222-227.
- Fisher C. Epithelioid sarcoma of Enzinger. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:114-121.
- Requena L, Santonja C, Martinez-Amo JL, et al. Cutaneous epithelioid sarcoma like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma: a little-known low-grade cutaneous vascular neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:459-465.
- Trombetta D, Magnusson L, von Steyern FV, et al. Translocation t(7;19)(q22;q13)—a recurrent chromosome aberration in pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma? Cancer Genet. 2011;204:211-215.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma (pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma). Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:1088; author reply 1088-1089.
- Mirra JM, Kessler S, Bhuta S, et al. The fibroma-like variant of epithelioid sarcoma. a fibrohistiocytic/myoid cell lesion often confused with benign and malignant spindle cell tumors. Cancer. 1992;69:1382-1395.
- Jo VY, Fletcher CD. WHO classification of soft tissue tumours: an update based on the 2013 (4th) edition. Pathology. 2014;46:95-104.
- Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma: a distinctive, often multicentric tumor with indolent behavior. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35:190-201.
- Sheng W, Pan Y, Wang J. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma: report of an additional case with aggressive clinical course. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:597-600.
- Billings SD, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:48-57.
- Pradhan D, Schoedel K, McGough RL, et al. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma of skin, bone and soft tissue—a clinicopathological, immunohistochemical and fluorescence in situ hybridization study [published online November 2, 2017]. Hum Pathol. 2017. doi:0.1016/j.humpath.2017.10.023.
- Requena L, Santonja C, Martinez-Amo JL, et al. Cutaneous epithelioid sarcoma like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma: a little-known low-grade cutaneous vascular neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:459-465.
- McGinity M, Bartanusz V, Dengler B, et al. Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (epithelioid sarcoma-like hemangioendothelioma, fibroma-like variant of epithelioid sarcoma) of the thoracic spine. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(suppl 3):S506-S511.
- Stuart LN, Gardner JM, Lauer SR, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma-like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma, clinically mimicking dermatofibroma, diagnosed by skin biopsy in a 30-year-old man. J Cutan Pathol. 2013;40:909-913.
- Amary MF, O’Donnell P, Berisha F, et al. Pseudomyogenic (epithelioid sarcoma-like) hemangioendothelioma: characterization of five cases. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:947-957.
- Hornick JL, Dal Cin P, Fletcher CD. Loss of INI1 expression is characteristic of both conventional and proximal-type epithelioid sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:542-550.
- Chbani L, Guillou L, Terrier P, et al. Epithelioid sarcoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 106 cases from the French Sarcoma Group. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;131:222-227.
- Fisher C. Epithelioid sarcoma of Enzinger. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:114-121.
- Requena L, Santonja C, Martinez-Amo JL, et al. Cutaneous epithelioid sarcoma like (pseudomyogenic) hemangioendothelioma: a little-known low-grade cutaneous vascular neoplasm. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:459-465.
- Trombetta D, Magnusson L, von Steyern FV, et al. Translocation t(7;19)(q22;q13)—a recurrent chromosome aberration in pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma? Cancer Genet. 2011;204:211-215.
Practice Points
- Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma (PMHE) is an uncommon vascular tumor that most often presents as multiple distinct nodules on the legs in young men.
- Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma has an unusual immunohistochemistry staining pattern, with positive staining for cytokeratin AE1/AE3, CD31, and ERG but negative for CD34.
- Although local reoccurrence is common, PMHE metastasis is very uncommon.