User login
Improving Colorectal Cancer Screening via Mailed Fecal Immunochemical Testing in a Veterans Affairs Health System
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
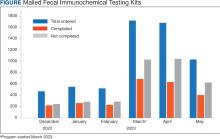
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Virtual Respiratory Urgent Clinics for COVID-19 Symptoms
Virtual care (VC) has emerged as an effective mode of health care delivery especially in settings where significant barriers to traditional in-person visits exist; a large systematic review supports feasibility of telemedicine in primary care and suggests that telemedicine is at least as effective as traditional care.1 Nevertheless, broad adoption of VC into practice has lagged, impeded by government and private insurance reimbursement requirements as well as the persistent belief that care can best be delivered in person.2-4 Before the COVID-19 pandemic, states that enacted parity legislation that required private insurance companies to provide reimbursement coverage for telehealth services saw a significant increase in the number of outpatient telehealth visits (about ≥ 30% odds compared with nonparity states).3
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, in-person medical appointments were converted to VC visits to reduce increased exposure risks to patients and health care workers.5 Prior government and private sector policies were suspended, and payment restrictions lifted, enabling adoption of VC modalities to rapidly accommodate the emergent need and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations for virtual care.6-11
The CDC guidelines on managing operations during the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need to provide care in the safest way for patients and health care personnel and emphasized the importance of optimizing telehealth services. The federal government facilitated telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic via temporary measures under the COVID-19 public health emergency declaration. This included Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act flexibility to use everyday technology for VC visits, regulatory changes to deliver services to Medicare and Medicaid patients, permission of telehealth services across state lines, and prescribing of controlled substances via telehealth without an in-person medical evaluation.7
In response, health care providers (HCPs) and health care organizations created or expanded on existing telehealth infrastructure, developing virtual urgent care centers and telephone-based programs to evaluate patients remotely via screening questions that triaged them to a correct level of response, with possible subsequent virtual physician evaluation if indicated.12,13
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) also shifted to a VC model in response to COVID-19 guided by a unique perspective from a well-developed prior VC experience.14-16 As a federally funded system, the VHA depends on workload documentation for budgeting. Since 2015, the VHA has provided workload credit and incentivized HCPs (via pay for performance) for the use of VC, including telephone visits, video visits, and secure messaging. These incentives resulted in higher rates of telehealth utilization before the COVID-19 pandemic compared with the private sector (with 4.2% and 0.7% of visits within the VHA being telephone and video visits, respectively, compared with telehealth utilization rates of 1.0% for Medicare recipients and 1.1% in an all-payer database).16
Historically, VHA care has successfully transitioned from in-person care models to exclusively virtual modalities to prevent suspension of medical services during natural disasters. Studies performed during these periods, specifically during the 2017 hurricane season (during which multiple VHA hospitals were closed or had limited in-person service available), supported telehealth as an efficient health care delivery method, and even recommended expanding telehealth services within non-VHA environments to accommodate needs of the general public during crises and postdisaster health care delivery.17
Armed with both a well-established telehealth infrastructure and prior knowledge gained from successful systemwide implementation of virtual care during times of disaster, US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) primary care quickly transitioned to a VC model in response to COVID-19.16 Early in the pandemic, a rapid transition to virtual care (RTVC) model was developed, including implementation of virtual respiratory urgent clinics (VRUCs), defined as virtual respiratory symptom triage clinics, staffed by primary care providers (PCPs) aimed at minimizing patient and health care worker exposure risk.
Methods
VACHS consists of 8 primary care sites, including a major tertiary care center, a smaller medical center with full ambulatory services, and 6 community-based outpatient clinics with only primary care and mental health. There are 80 individual PCPs delivering care to 58,058 veterans. VRUCs were established during the COVID-19 pandemic to cover patients across the entire health care system, using a rotational schedule of VA PCPs.
COVID-19 Urgent Clinics Program
Within the first few weeks of the pandemic, VACHS primary care established VRUCS to provide expeditious virtual assessment of respiratory or flu-like symptoms. Using the established telehealth system, the intervention aimed to provide emergent screening, testing, and care to those with potential COVID-19 infections. The model also was designed to minimize exposures to the health care workforce and patients.
Retrospective analysis was performed using information obtained from the electronic health record (EHR) database to describe the characteristics of patients who received care through the VRUCs, such as demographics, era of military service, COVID-19 testing rates and results, as well as subsequent emergency department (ED) visits and hospital admissions. A secondary aim included collection of additional qualitative data via a random sample chart review.
Virtual clinics were established January 22, 2020, and data were analyzed over the next 3 months. Data were retrieved and analyzed from the EHR, and codes were used to categorize the VRUCs.
Results
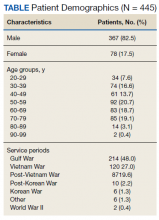
A total of 445 unique patients used these clinics during this period. Unique patients were defined as individual patients (some may have used a clinic more than once but were counted only once). Of this group, 82% were male, and 48% served in the Gulf War era (1990 to present). A total of 51% of patients received a COVID-19 test (clinics began before wide testing availability), and 10% tested positive. Of all patients using the clinics, approximately 5% were admitted to the hospital, and 18% had at least 1 subsequent ED visit (Table).
A secondary aim included review of a random sample of 99 patient charts to gain additional information regarding whether the patient was given appropriate isolation precautions, was in a high-exposure occupation (eg, could expose a large number of people), and whether there was appropriate documentation of goals of care, health care proxy or referral to social work to discuss advance directives. In addition, we calculated the average length of time between patients’ initial contact with the health care system call center and the return call by the PCP (wait time).Of charts reviewed, the majority (71%) had documentation of appropriate isolation precautions. Although 25% of patients had documentation of a high-risk profession with potential to expose many people, more than half of the patients had no documentation of occupation. Most patients (86%) had no updated documentation regarding goals of care, health care proxy, or advance directives in their urgent care VC visit. The average time between the patient initiating contact with the health care system call center and a return call to the patient from a PCP was 104 minutes (excluding calls received after 3:30
Discussion
This analysis adds to the growing literature on use of VC during the COVID-19 pandemic. Specifically, we describe the population of patients who used VRUCs within a large health care system in a RTVC. This analysis was limited by lack of available testing during the initial phase of the pandemic, which contributed to the lower than expected rates of testing and test positivity in patients managed via VRUCs. In addition, chart review data are limited as the data includes only what was documented during the visit and not the entire discussion during the encounter.
Several important outcomes from this analysis can be applied to interventions in the future, which may have large public health implications: Several hundred patients who reported respiratory symptoms were expeditiously evaluated by a PCP using VC. The average wait time to full clinical assessment was about 1.5 hours. This short duration between contact and evaluation permitted early education about isolation precautions, which may have minimized spread. In addition, this innovation kept patients out of the medical center, eliminating chains of transmission to other vulnerable patients and health care workers.
Our retrospective chart review also revealed that more than half the patients were not queried about their occupation, but of those that were asked, a significant number were in high-risk professions potentially exposing large numbers of people. This would be an important aspect to add to future templated notes to minimize work-related exposures. Also, we identified that few HCPs discussed goals of care with patients. Given the nature of COVID-19 and potential for rapid decompensation especially in vulnerable patients, this also would be important to include in the future.
Conclusions
VC urgent care clinics to address possible COVID-19 symptoms facilitated expeditious PCP assessment while keeping potentially contagious patients outside of high-risk health care environments. Streamlining and optimizing clinical VC assessments will be imperative to future management of COVID-19 and potentially to other future infectious pandemics. This includes development of templated notes incorporating counseling regarding appropriate isolation, questions about high-contact occupations, and goals of care discussions.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Robert F. Walsh, MHA.
1. Bashshur RL, Howell JD, Krupinski EA, Harms KM, Bashshur N, Doarn CR. The empirical foundations of telemedicine interventions in primary care. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(5):342-375. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0045
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using telehealth to expand access to essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Updated June 10, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/telehealth.html
3. Harvey JB, Valenta S, Simpson K, Lyles M, McElligott J. Utilization of outpatient telehealth services in parity and nonparity states 2010-2015. Telemed J E Health. 2019;25(2):132-136. doi:10.1089/tmj.2017.0265
4. Dorsey ER, Topol EJ. State of telehealth. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):154-161. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1601705
5. Rockwell KL, Gilroy AS. Incorporating telemedicine as part of COVID-19 outbreak response systems. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(4):147-148. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2020.42784
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare facility guidance. Updated April 17, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care.html
7. US Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration. Policy changes during COVID-19. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/providers/policy-changes-during-the-covid-19-public-health-emergency
8. Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriation Act of 2020. 134 Stat. 146. Published February 2, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CREC-2021-02-02/html/CREC-2021-02-02-pt1-PgS226.htm
9. US Department of Health and Human Services. Notification of enforcement discretion for telehealth remote communications during the COVID-19 nationwide public health emergency. Updated January 20, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/special-topics/emergency-preparedness/notification-enforcement-discretion-telehealth/index.html
10. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Coverage and payment related to COVID-19 Medicare. 2020. Published March 23, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/03052020-medicare-covid-19-fact-sheet.pdf
11. American Telemedicine Association. ATA commends 2020 Congress for giving HHS authority to waive restrictions on telehealth for Medicare beneficiaries in response to the COVID-19 outbreak [press release]. Published March 5, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.americantelemed.org/press-releases/ata-commends-congress-for-waiving-restrictions-on-telehealth-for-medicare-beneficiaries-in-response-to-the-covid-19-outbreak
12. Hollander JE, Carr BG. Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1679-1681. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2003539
13. Khairat S, Meng C, Xu Y, Edson B, Gianforcaro R. Interpreting COVID-19 and Virtual Care Trends: Cohort Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020;6(2):e18811. Published 2020 Apr 15. doi:10.2196/18811
14. Ferguson JM, Jacobs J, Yefimova M, Greene L, Heyworth L, Zulman DM. Virtual care expansion in the Veterans Health Administration during the COVID-19 pandemic: clinical services and patient characteristics associated with utilization. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021;28(3):453-462. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocaa284
15. Baum A, Kaboli PJ, Schwartz MD. Reduced in-person and increased telehealth outpatient visits during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(1):129-131. doi:10.7326/M20-3026
16. Spelman JF, Brienza R, Walsh RF, et al. A model for rapid transition to virtual care, VA Connecticut primary care response to COVID-19. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(10):3073-3076. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06041-4
17. Der-Martirosian C, Chu K, Dobalian A. Use of telehealth to improve access to care at the United States Department of Veterans Affairs during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 13]. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2020;1-5. doi:10.1017/dmp.2020.88
Virtual care (VC) has emerged as an effective mode of health care delivery especially in settings where significant barriers to traditional in-person visits exist; a large systematic review supports feasibility of telemedicine in primary care and suggests that telemedicine is at least as effective as traditional care.1 Nevertheless, broad adoption of VC into practice has lagged, impeded by government and private insurance reimbursement requirements as well as the persistent belief that care can best be delivered in person.2-4 Before the COVID-19 pandemic, states that enacted parity legislation that required private insurance companies to provide reimbursement coverage for telehealth services saw a significant increase in the number of outpatient telehealth visits (about ≥ 30% odds compared with nonparity states).3
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, in-person medical appointments were converted to VC visits to reduce increased exposure risks to patients and health care workers.5 Prior government and private sector policies were suspended, and payment restrictions lifted, enabling adoption of VC modalities to rapidly accommodate the emergent need and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations for virtual care.6-11
The CDC guidelines on managing operations during the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need to provide care in the safest way for patients and health care personnel and emphasized the importance of optimizing telehealth services. The federal government facilitated telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic via temporary measures under the COVID-19 public health emergency declaration. This included Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act flexibility to use everyday technology for VC visits, regulatory changes to deliver services to Medicare and Medicaid patients, permission of telehealth services across state lines, and prescribing of controlled substances via telehealth without an in-person medical evaluation.7
In response, health care providers (HCPs) and health care organizations created or expanded on existing telehealth infrastructure, developing virtual urgent care centers and telephone-based programs to evaluate patients remotely via screening questions that triaged them to a correct level of response, with possible subsequent virtual physician evaluation if indicated.12,13
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) also shifted to a VC model in response to COVID-19 guided by a unique perspective from a well-developed prior VC experience.14-16 As a federally funded system, the VHA depends on workload documentation for budgeting. Since 2015, the VHA has provided workload credit and incentivized HCPs (via pay for performance) for the use of VC, including telephone visits, video visits, and secure messaging. These incentives resulted in higher rates of telehealth utilization before the COVID-19 pandemic compared with the private sector (with 4.2% and 0.7% of visits within the VHA being telephone and video visits, respectively, compared with telehealth utilization rates of 1.0% for Medicare recipients and 1.1% in an all-payer database).16
Historically, VHA care has successfully transitioned from in-person care models to exclusively virtual modalities to prevent suspension of medical services during natural disasters. Studies performed during these periods, specifically during the 2017 hurricane season (during which multiple VHA hospitals were closed or had limited in-person service available), supported telehealth as an efficient health care delivery method, and even recommended expanding telehealth services within non-VHA environments to accommodate needs of the general public during crises and postdisaster health care delivery.17
Armed with both a well-established telehealth infrastructure and prior knowledge gained from successful systemwide implementation of virtual care during times of disaster, US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) primary care quickly transitioned to a VC model in response to COVID-19.16 Early in the pandemic, a rapid transition to virtual care (RTVC) model was developed, including implementation of virtual respiratory urgent clinics (VRUCs), defined as virtual respiratory symptom triage clinics, staffed by primary care providers (PCPs) aimed at minimizing patient and health care worker exposure risk.
Methods
VACHS consists of 8 primary care sites, including a major tertiary care center, a smaller medical center with full ambulatory services, and 6 community-based outpatient clinics with only primary care and mental health. There are 80 individual PCPs delivering care to 58,058 veterans. VRUCs were established during the COVID-19 pandemic to cover patients across the entire health care system, using a rotational schedule of VA PCPs.
COVID-19 Urgent Clinics Program
Within the first few weeks of the pandemic, VACHS primary care established VRUCS to provide expeditious virtual assessment of respiratory or flu-like symptoms. Using the established telehealth system, the intervention aimed to provide emergent screening, testing, and care to those with potential COVID-19 infections. The model also was designed to minimize exposures to the health care workforce and patients.
Retrospective analysis was performed using information obtained from the electronic health record (EHR) database to describe the characteristics of patients who received care through the VRUCs, such as demographics, era of military service, COVID-19 testing rates and results, as well as subsequent emergency department (ED) visits and hospital admissions. A secondary aim included collection of additional qualitative data via a random sample chart review.
Virtual clinics were established January 22, 2020, and data were analyzed over the next 3 months. Data were retrieved and analyzed from the EHR, and codes were used to categorize the VRUCs.
Results
A total of 445 unique patients used these clinics during this period. Unique patients were defined as individual patients (some may have used a clinic more than once but were counted only once). Of this group, 82% were male, and 48% served in the Gulf War era (1990 to present). A total of 51% of patients received a COVID-19 test (clinics began before wide testing availability), and 10% tested positive. Of all patients using the clinics, approximately 5% were admitted to the hospital, and 18% had at least 1 subsequent ED visit (Table).
A secondary aim included review of a random sample of 99 patient charts to gain additional information regarding whether the patient was given appropriate isolation precautions, was in a high-exposure occupation (eg, could expose a large number of people), and whether there was appropriate documentation of goals of care, health care proxy or referral to social work to discuss advance directives. In addition, we calculated the average length of time between patients’ initial contact with the health care system call center and the return call by the PCP (wait time).Of charts reviewed, the majority (71%) had documentation of appropriate isolation precautions. Although 25% of patients had documentation of a high-risk profession with potential to expose many people, more than half of the patients had no documentation of occupation. Most patients (86%) had no updated documentation regarding goals of care, health care proxy, or advance directives in their urgent care VC visit. The average time between the patient initiating contact with the health care system call center and a return call to the patient from a PCP was 104 minutes (excluding calls received after 3:30
Discussion
This analysis adds to the growing literature on use of VC during the COVID-19 pandemic. Specifically, we describe the population of patients who used VRUCs within a large health care system in a RTVC. This analysis was limited by lack of available testing during the initial phase of the pandemic, which contributed to the lower than expected rates of testing and test positivity in patients managed via VRUCs. In addition, chart review data are limited as the data includes only what was documented during the visit and not the entire discussion during the encounter.
Several important outcomes from this analysis can be applied to interventions in the future, which may have large public health implications: Several hundred patients who reported respiratory symptoms were expeditiously evaluated by a PCP using VC. The average wait time to full clinical assessment was about 1.5 hours. This short duration between contact and evaluation permitted early education about isolation precautions, which may have minimized spread. In addition, this innovation kept patients out of the medical center, eliminating chains of transmission to other vulnerable patients and health care workers.
Our retrospective chart review also revealed that more than half the patients were not queried about their occupation, but of those that were asked, a significant number were in high-risk professions potentially exposing large numbers of people. This would be an important aspect to add to future templated notes to minimize work-related exposures. Also, we identified that few HCPs discussed goals of care with patients. Given the nature of COVID-19 and potential for rapid decompensation especially in vulnerable patients, this also would be important to include in the future.
Conclusions
VC urgent care clinics to address possible COVID-19 symptoms facilitated expeditious PCP assessment while keeping potentially contagious patients outside of high-risk health care environments. Streamlining and optimizing clinical VC assessments will be imperative to future management of COVID-19 and potentially to other future infectious pandemics. This includes development of templated notes incorporating counseling regarding appropriate isolation, questions about high-contact occupations, and goals of care discussions.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Robert F. Walsh, MHA.
Virtual care (VC) has emerged as an effective mode of health care delivery especially in settings where significant barriers to traditional in-person visits exist; a large systematic review supports feasibility of telemedicine in primary care and suggests that telemedicine is at least as effective as traditional care.1 Nevertheless, broad adoption of VC into practice has lagged, impeded by government and private insurance reimbursement requirements as well as the persistent belief that care can best be delivered in person.2-4 Before the COVID-19 pandemic, states that enacted parity legislation that required private insurance companies to provide reimbursement coverage for telehealth services saw a significant increase in the number of outpatient telehealth visits (about ≥ 30% odds compared with nonparity states).3
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, in-person medical appointments were converted to VC visits to reduce increased exposure risks to patients and health care workers.5 Prior government and private sector policies were suspended, and payment restrictions lifted, enabling adoption of VC modalities to rapidly accommodate the emergent need and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations for virtual care.6-11
The CDC guidelines on managing operations during the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need to provide care in the safest way for patients and health care personnel and emphasized the importance of optimizing telehealth services. The federal government facilitated telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic via temporary measures under the COVID-19 public health emergency declaration. This included Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act flexibility to use everyday technology for VC visits, regulatory changes to deliver services to Medicare and Medicaid patients, permission of telehealth services across state lines, and prescribing of controlled substances via telehealth without an in-person medical evaluation.7
In response, health care providers (HCPs) and health care organizations created or expanded on existing telehealth infrastructure, developing virtual urgent care centers and telephone-based programs to evaluate patients remotely via screening questions that triaged them to a correct level of response, with possible subsequent virtual physician evaluation if indicated.12,13
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) also shifted to a VC model in response to COVID-19 guided by a unique perspective from a well-developed prior VC experience.14-16 As a federally funded system, the VHA depends on workload documentation for budgeting. Since 2015, the VHA has provided workload credit and incentivized HCPs (via pay for performance) for the use of VC, including telephone visits, video visits, and secure messaging. These incentives resulted in higher rates of telehealth utilization before the COVID-19 pandemic compared with the private sector (with 4.2% and 0.7% of visits within the VHA being telephone and video visits, respectively, compared with telehealth utilization rates of 1.0% for Medicare recipients and 1.1% in an all-payer database).16
Historically, VHA care has successfully transitioned from in-person care models to exclusively virtual modalities to prevent suspension of medical services during natural disasters. Studies performed during these periods, specifically during the 2017 hurricane season (during which multiple VHA hospitals were closed or had limited in-person service available), supported telehealth as an efficient health care delivery method, and even recommended expanding telehealth services within non-VHA environments to accommodate needs of the general public during crises and postdisaster health care delivery.17
Armed with both a well-established telehealth infrastructure and prior knowledge gained from successful systemwide implementation of virtual care during times of disaster, US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) primary care quickly transitioned to a VC model in response to COVID-19.16 Early in the pandemic, a rapid transition to virtual care (RTVC) model was developed, including implementation of virtual respiratory urgent clinics (VRUCs), defined as virtual respiratory symptom triage clinics, staffed by primary care providers (PCPs) aimed at minimizing patient and health care worker exposure risk.
Methods
VACHS consists of 8 primary care sites, including a major tertiary care center, a smaller medical center with full ambulatory services, and 6 community-based outpatient clinics with only primary care and mental health. There are 80 individual PCPs delivering care to 58,058 veterans. VRUCs were established during the COVID-19 pandemic to cover patients across the entire health care system, using a rotational schedule of VA PCPs.
COVID-19 Urgent Clinics Program
Within the first few weeks of the pandemic, VACHS primary care established VRUCS to provide expeditious virtual assessment of respiratory or flu-like symptoms. Using the established telehealth system, the intervention aimed to provide emergent screening, testing, and care to those with potential COVID-19 infections. The model also was designed to minimize exposures to the health care workforce and patients.
Retrospective analysis was performed using information obtained from the electronic health record (EHR) database to describe the characteristics of patients who received care through the VRUCs, such as demographics, era of military service, COVID-19 testing rates and results, as well as subsequent emergency department (ED) visits and hospital admissions. A secondary aim included collection of additional qualitative data via a random sample chart review.
Virtual clinics were established January 22, 2020, and data were analyzed over the next 3 months. Data were retrieved and analyzed from the EHR, and codes were used to categorize the VRUCs.
Results
A total of 445 unique patients used these clinics during this period. Unique patients were defined as individual patients (some may have used a clinic more than once but were counted only once). Of this group, 82% were male, and 48% served in the Gulf War era (1990 to present). A total of 51% of patients received a COVID-19 test (clinics began before wide testing availability), and 10% tested positive. Of all patients using the clinics, approximately 5% were admitted to the hospital, and 18% had at least 1 subsequent ED visit (Table).
A secondary aim included review of a random sample of 99 patient charts to gain additional information regarding whether the patient was given appropriate isolation precautions, was in a high-exposure occupation (eg, could expose a large number of people), and whether there was appropriate documentation of goals of care, health care proxy or referral to social work to discuss advance directives. In addition, we calculated the average length of time between patients’ initial contact with the health care system call center and the return call by the PCP (wait time).Of charts reviewed, the majority (71%) had documentation of appropriate isolation precautions. Although 25% of patients had documentation of a high-risk profession with potential to expose many people, more than half of the patients had no documentation of occupation. Most patients (86%) had no updated documentation regarding goals of care, health care proxy, or advance directives in their urgent care VC visit. The average time between the patient initiating contact with the health care system call center and a return call to the patient from a PCP was 104 minutes (excluding calls received after 3:30
Discussion
This analysis adds to the growing literature on use of VC during the COVID-19 pandemic. Specifically, we describe the population of patients who used VRUCs within a large health care system in a RTVC. This analysis was limited by lack of available testing during the initial phase of the pandemic, which contributed to the lower than expected rates of testing and test positivity in patients managed via VRUCs. In addition, chart review data are limited as the data includes only what was documented during the visit and not the entire discussion during the encounter.
Several important outcomes from this analysis can be applied to interventions in the future, which may have large public health implications: Several hundred patients who reported respiratory symptoms were expeditiously evaluated by a PCP using VC. The average wait time to full clinical assessment was about 1.5 hours. This short duration between contact and evaluation permitted early education about isolation precautions, which may have minimized spread. In addition, this innovation kept patients out of the medical center, eliminating chains of transmission to other vulnerable patients and health care workers.
Our retrospective chart review also revealed that more than half the patients were not queried about their occupation, but of those that were asked, a significant number were in high-risk professions potentially exposing large numbers of people. This would be an important aspect to add to future templated notes to minimize work-related exposures. Also, we identified that few HCPs discussed goals of care with patients. Given the nature of COVID-19 and potential for rapid decompensation especially in vulnerable patients, this also would be important to include in the future.
Conclusions
VC urgent care clinics to address possible COVID-19 symptoms facilitated expeditious PCP assessment while keeping potentially contagious patients outside of high-risk health care environments. Streamlining and optimizing clinical VC assessments will be imperative to future management of COVID-19 and potentially to other future infectious pandemics. This includes development of templated notes incorporating counseling regarding appropriate isolation, questions about high-contact occupations, and goals of care discussions.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Robert F. Walsh, MHA.
1. Bashshur RL, Howell JD, Krupinski EA, Harms KM, Bashshur N, Doarn CR. The empirical foundations of telemedicine interventions in primary care. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(5):342-375. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0045
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using telehealth to expand access to essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Updated June 10, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/telehealth.html
3. Harvey JB, Valenta S, Simpson K, Lyles M, McElligott J. Utilization of outpatient telehealth services in parity and nonparity states 2010-2015. Telemed J E Health. 2019;25(2):132-136. doi:10.1089/tmj.2017.0265
4. Dorsey ER, Topol EJ. State of telehealth. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):154-161. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1601705
5. Rockwell KL, Gilroy AS. Incorporating telemedicine as part of COVID-19 outbreak response systems. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(4):147-148. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2020.42784
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare facility guidance. Updated April 17, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care.html
7. US Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration. Policy changes during COVID-19. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/providers/policy-changes-during-the-covid-19-public-health-emergency
8. Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriation Act of 2020. 134 Stat. 146. Published February 2, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CREC-2021-02-02/html/CREC-2021-02-02-pt1-PgS226.htm
9. US Department of Health and Human Services. Notification of enforcement discretion for telehealth remote communications during the COVID-19 nationwide public health emergency. Updated January 20, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/special-topics/emergency-preparedness/notification-enforcement-discretion-telehealth/index.html
10. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Coverage and payment related to COVID-19 Medicare. 2020. Published March 23, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/03052020-medicare-covid-19-fact-sheet.pdf
11. American Telemedicine Association. ATA commends 2020 Congress for giving HHS authority to waive restrictions on telehealth for Medicare beneficiaries in response to the COVID-19 outbreak [press release]. Published March 5, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.americantelemed.org/press-releases/ata-commends-congress-for-waiving-restrictions-on-telehealth-for-medicare-beneficiaries-in-response-to-the-covid-19-outbreak
12. Hollander JE, Carr BG. Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1679-1681. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2003539
13. Khairat S, Meng C, Xu Y, Edson B, Gianforcaro R. Interpreting COVID-19 and Virtual Care Trends: Cohort Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020;6(2):e18811. Published 2020 Apr 15. doi:10.2196/18811
14. Ferguson JM, Jacobs J, Yefimova M, Greene L, Heyworth L, Zulman DM. Virtual care expansion in the Veterans Health Administration during the COVID-19 pandemic: clinical services and patient characteristics associated with utilization. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021;28(3):453-462. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocaa284
15. Baum A, Kaboli PJ, Schwartz MD. Reduced in-person and increased telehealth outpatient visits during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(1):129-131. doi:10.7326/M20-3026
16. Spelman JF, Brienza R, Walsh RF, et al. A model for rapid transition to virtual care, VA Connecticut primary care response to COVID-19. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(10):3073-3076. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06041-4
17. Der-Martirosian C, Chu K, Dobalian A. Use of telehealth to improve access to care at the United States Department of Veterans Affairs during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 13]. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2020;1-5. doi:10.1017/dmp.2020.88
1. Bashshur RL, Howell JD, Krupinski EA, Harms KM, Bashshur N, Doarn CR. The empirical foundations of telemedicine interventions in primary care. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(5):342-375. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0045
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using telehealth to expand access to essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Updated June 10, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/telehealth.html
3. Harvey JB, Valenta S, Simpson K, Lyles M, McElligott J. Utilization of outpatient telehealth services in parity and nonparity states 2010-2015. Telemed J E Health. 2019;25(2):132-136. doi:10.1089/tmj.2017.0265
4. Dorsey ER, Topol EJ. State of telehealth. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):154-161. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1601705
5. Rockwell KL, Gilroy AS. Incorporating telemedicine as part of COVID-19 outbreak response systems. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(4):147-148. doi:10.37765/ajmc.2020.42784
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Healthcare facility guidance. Updated April 17, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care.html
7. US Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration. Policy changes during COVID-19. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://telehealth.hhs.gov/providers/policy-changes-during-the-covid-19-public-health-emergency
8. Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriation Act of 2020. 134 Stat. 146. Published February 2, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/CREC-2021-02-02/html/CREC-2021-02-02-pt1-PgS226.htm
9. US Department of Health and Human Services. Notification of enforcement discretion for telehealth remote communications during the COVID-19 nationwide public health emergency. Updated January 20, 2021. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/special-topics/emergency-preparedness/notification-enforcement-discretion-telehealth/index.html
10. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Coverage and payment related to COVID-19 Medicare. 2020. Published March 23, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/03052020-medicare-covid-19-fact-sheet.pdf
11. American Telemedicine Association. ATA commends 2020 Congress for giving HHS authority to waive restrictions on telehealth for Medicare beneficiaries in response to the COVID-19 outbreak [press release]. Published March 5, 2020. Accessed August 20, 2021. https://www.americantelemed.org/press-releases/ata-commends-congress-for-waiving-restrictions-on-telehealth-for-medicare-beneficiaries-in-response-to-the-covid-19-outbreak
12. Hollander JE, Carr BG. Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1679-1681. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2003539
13. Khairat S, Meng C, Xu Y, Edson B, Gianforcaro R. Interpreting COVID-19 and Virtual Care Trends: Cohort Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020;6(2):e18811. Published 2020 Apr 15. doi:10.2196/18811
14. Ferguson JM, Jacobs J, Yefimova M, Greene L, Heyworth L, Zulman DM. Virtual care expansion in the Veterans Health Administration during the COVID-19 pandemic: clinical services and patient characteristics associated with utilization. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021;28(3):453-462. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocaa284
15. Baum A, Kaboli PJ, Schwartz MD. Reduced in-person and increased telehealth outpatient visits during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ann Intern Med. 2021;174(1):129-131. doi:10.7326/M20-3026
16. Spelman JF, Brienza R, Walsh RF, et al. A model for rapid transition to virtual care, VA Connecticut primary care response to COVID-19. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(10):3073-3076. doi:10.1007/s11606-020-06041-4
17. Der-Martirosian C, Chu K, Dobalian A. Use of telehealth to improve access to care at the United States Department of Veterans Affairs during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 13]. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2020;1-5. doi:10.1017/dmp.2020.88