User login
Preparing from the Outside Looking In for Safely Transitioning Pediatric Inpatients to Home
The transition of children from hospital to home introduces a unique set of challenges to patients and families who may not be well-versed in the healthcare system. In addition to juggling the stress and worry of a sick child, which can inhibit the ability to understand complicated discharge instructions prior to leaving the hospital,1 caregivers need to navigate the medical system to ensure continued recovery. The responsibility to fill and administer medications, arrange follow up appointments, and determine when to seek care if the child’s condition changes are burdens we as healthcare providers expect caregivers to manage but may underestimate how frequently they are reliably completed.2-4
In this issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine, the article by Rehm et al.5 adds to the growing body of evidence highlighting challenges that caregivers of children face upon discharge from the hospital. The multicenter, retrospective study of postdischarge encounters for over 12,000 patients discharged from 4 children’s hospitals aimed to evaluate the following: (1) various methods for hospital-initiated postdischarge contact of families, (2) the type and frequency of postdischarge issues, and (3) specific characteristics of pediatric patients most commonly affected by postdischarge issues.
Using standardized questions administered through telephone, text, or e-mail contact, postdischarge issues were identified in 25% of discharges across all hospitals. Notably, there was considerable variation of rates of postdischarge issues among hospitals (from 16% to 62.8%). The hospital with the highest rate of postdischarge issues identified had attending hospitalists calling families after discharge. Thus, postdischarge issues may be most easily identified by providers who are familiar with both the patient and the expected postdischarge care.
Often, postdischarge issues represented events that could be mitigated with intentional planning to better anticipate and address patient and family needs prior to discharge. The vast majority of postdischarge issues identified across all hospitals were related to appointments, accounting for 76.3% of postdischarge issues, which may be attributed to a variety of causes, from inadequate or unclear provider recommendations to difficulty scheduling the appointments. The most common medication postdischarge issue was difficulty filling prescriptions, accounting for 84.8% of the medication issues. “Other” postdischarge issues (12.7%) as reported by caregivers included challenges with understanding discharge instructions and concerns about changes in their child’s clinical status. Forty percent of included patients had a chronic care condition. Older children, patients with more medication classes, shorter length of stay, and neuromuscular chronic care conditions had higher odds of postdischarge issues. Although a high proportion of postdischarge issues suggests a systemic problem addressing the needs of patients and families after hospital discharge, these data likely underestimate the magnitude of the problem; as such, the need for improvement may be higher.
Postdischarge challenges faced by families are not unique to pediatrics. Pediatric and adult medical patients face similar rates of challenges after
Given the prevalence of postdischarge issues after both pediatric and adult hospitalizations, how should hospitalists proceed? Physicians and health systems should explore approaches to better prepare caregivers, perhaps using models akin to the Seamless Transitions and (Re)admissions Network model of enhanced communication, care coordination, and family engagement.10 Pediatric hospitalists can prepare children for discharge long before departure by delivering medications to patients prior to discharge,11,12 providing discharge instructions that are clear and readable,13,14 as well as utilizing admission-discharge teaching nurses,15 inpatient care managers,16,17 and pediatric nurse practitioners18 to aid transition.
While a variety of interventions show promise in securing a successful transition to home from the hospitalist vantage point, a partnership with primary care physicians (PCPs) in our communities is paramount. Though the evidence linking gaps in primary care after discharge and readmission rates remain elusive, effective partnerships with PCPs are important for ensuring discharge plans are carried out, which may ultimately lead to decreased rates of unanticipated adverse outcomes. Several adult studies note that no single intervention is likely to prevent issues after discharge, but interventions should include high-quality communication with and involvement of community partners.9,19,20 In practice, providing a high-quality, reliable handoff can be difficult given competing priorities of busy outpatient clinic schedules and inpatient bed capacity concerns, necessitating efficient discharge practices. Some of these challenges are amenable to quality improvement efforts to improve discharge communication.21 Innovative ideas include collaborating with PCPs earlier in the admission to design the care plan up front, including PCPs in weekly team meetings for patients with chronic care conditions,16,17 and using telehealth to communicate with PCPs.
Ensuring a safe transition to home is our responsibility as hospitalists, but the solutions to doing so reliably require multi-fold interventions that build teams within hospitals, innovative outreach to those patients recently discharged to ensure their well-being and mitigate postdischarge issues and broad community programs—including greater access to primary care—to meet our urgent imperative.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Dr. Auger’s research is funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (1K08HS024735).
1. Solan LG, Beck AF, Brunswick SA, et al. The Family Perspective on Hospital to Home Transitions: A Qualitative Study. Pediatrics. 2015;136(6):e1539-1549. PubMed
2. Misky GJ, Wald HL, Coleman EA. Post-hospitalization transitions: Examining the effects of timing of primary care provider follow-up. J Hosp Med. 2010;5(7):392-397. PubMed
3. Yin HS, Johnson M, Mendelsohn AL, Abrams MA, Sanders LM, Dreyer BP. The health literacy of parents in the United States: a nationally representative study. Pediatrics. 2009;124 Suppl 3:S289-298. PubMed
4. Glick AF, Farkas JS, Nicholson J, et al. Parental Management of Discharge Instructions: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics. 2017. [Epub ahead of print]. PubMed
5. Rehm KP, Brittan MS, Stephens JR, et al. Issues Identified by Post-Discharge Contact after Pediatric Hospitalization: A Multi-site Study (published online ahead of print February 2, 2018) J Hosp Med. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2934
6. Forster AJ, Murff HJ, Peterson JF, Gandhi TK, Bates DW. The incidence and severity of adverse events affecting patients after discharge from the hospital. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(3):161-167. PubMed
7. Hansen LO, Greenwald JL, Budnitz T, et al. Project BOOST: effectiveness of a multihospital effort to reduce rehospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2013;8(8):421-427. PubMed
8. Auerbach AD, Kripalani S, Vasilevskis EE, et al. Preventability and Causes of Readmissions in a National Cohort of General Medicine Patients. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(4):484-493. PubMed
9. Kripalani S, LeFevre F, Phillips CO, Williams MV, Basaviah P, Baker DW. Deficits in communication and information transfer between hospital-based and primary care physicians: implications for patient safety and continuity of care. JAMA. 2007;297(8):831-841. PubMed
10. Auger KA, Simon TD, Cooperberg D, et al. Summary of STARNet: Seamless Transitions and (Re)admissions Network. Pediatrics. 2015;135(1):164-175. PubMed
11. Hatoun J, Bair-Merritt M, Cabral H, Moses J. Increasing Medication Possession at Discharge for Patients With Asthma: The Meds-in-Hand Project. Pediatrics. 2016;137(3):e20150461. PubMed
12. White CM, Statile AM, White DL, et al. Using quality improvement to optimise paediatric discharge efficiency. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(5):428-436. PubMed
13. Unaka N, Statile A, Jerardi K, et al. Improving the Readability of Pediatric Hospital Medicine Discharge Instructions. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(7):551-557. PubMed
14. Wu S, Tyler A, Logsdon T, et al. A Quality Improvement Collaborative to Improve the Discharge Process for Hospitalized Children. Pediatrics. 2016;138(2). PubMed
15. Blankenship JS, Winslow SA. Admission-discharge-teaching nurses: bridging the gap in today’s workforce. J Nurs Adm. 2003;33(1):11-13. PubMed
16. White CM, Thomson JE, Statile AM, et al. Development of a New Care Model for Hospitalized Children With Medical Complexity. Hosp Pediatr. 2017;7(7):410-414. PubMed
17. Statile AM, Schondelmeyer AC, Thomson JE, et al. Improving Discharge Efficiency in Medically Complex Pediatric Patients. Pediatrics. 2016;138(2). PubMed
18. Dunn K, Rogers J. Discharge Facilitation: An Innovative PNP Role. J Pediatr Health Care. 2016;30(5):499-505. PubMed
19. Kripalani S, Jackson AT, Schnipper JL, Coleman EA. Promoting effective transitions of care at hospital discharge: a review of key issues for hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2007;2(5):314-323. PubMed
20. Scott AM, Li J, Oyewole-Eletu S, et al. Understanding Facilitators and Barriers to Care Transitions: Insights from Project ACHIEVE Site Visits. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2017;43(9):433-447. PubMed
21. Shen MW, Hershey D, Bergert L, Mallory L, Fisher ES, Cooperberg D. Pediatric hospitalists collaborate to improve timeliness of discharge communication. Hosp Pediatr. 2013;3(3):258-265. PubMed
The transition of children from hospital to home introduces a unique set of challenges to patients and families who may not be well-versed in the healthcare system. In addition to juggling the stress and worry of a sick child, which can inhibit the ability to understand complicated discharge instructions prior to leaving the hospital,1 caregivers need to navigate the medical system to ensure continued recovery. The responsibility to fill and administer medications, arrange follow up appointments, and determine when to seek care if the child’s condition changes are burdens we as healthcare providers expect caregivers to manage but may underestimate how frequently they are reliably completed.2-4
In this issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine, the article by Rehm et al.5 adds to the growing body of evidence highlighting challenges that caregivers of children face upon discharge from the hospital. The multicenter, retrospective study of postdischarge encounters for over 12,000 patients discharged from 4 children’s hospitals aimed to evaluate the following: (1) various methods for hospital-initiated postdischarge contact of families, (2) the type and frequency of postdischarge issues, and (3) specific characteristics of pediatric patients most commonly affected by postdischarge issues.
Using standardized questions administered through telephone, text, or e-mail contact, postdischarge issues were identified in 25% of discharges across all hospitals. Notably, there was considerable variation of rates of postdischarge issues among hospitals (from 16% to 62.8%). The hospital with the highest rate of postdischarge issues identified had attending hospitalists calling families after discharge. Thus, postdischarge issues may be most easily identified by providers who are familiar with both the patient and the expected postdischarge care.
Often, postdischarge issues represented events that could be mitigated with intentional planning to better anticipate and address patient and family needs prior to discharge. The vast majority of postdischarge issues identified across all hospitals were related to appointments, accounting for 76.3% of postdischarge issues, which may be attributed to a variety of causes, from inadequate or unclear provider recommendations to difficulty scheduling the appointments. The most common medication postdischarge issue was difficulty filling prescriptions, accounting for 84.8% of the medication issues. “Other” postdischarge issues (12.7%) as reported by caregivers included challenges with understanding discharge instructions and concerns about changes in their child’s clinical status. Forty percent of included patients had a chronic care condition. Older children, patients with more medication classes, shorter length of stay, and neuromuscular chronic care conditions had higher odds of postdischarge issues. Although a high proportion of postdischarge issues suggests a systemic problem addressing the needs of patients and families after hospital discharge, these data likely underestimate the magnitude of the problem; as such, the need for improvement may be higher.
Postdischarge challenges faced by families are not unique to pediatrics. Pediatric and adult medical patients face similar rates of challenges after
Given the prevalence of postdischarge issues after both pediatric and adult hospitalizations, how should hospitalists proceed? Physicians and health systems should explore approaches to better prepare caregivers, perhaps using models akin to the Seamless Transitions and (Re)admissions Network model of enhanced communication, care coordination, and family engagement.10 Pediatric hospitalists can prepare children for discharge long before departure by delivering medications to patients prior to discharge,11,12 providing discharge instructions that are clear and readable,13,14 as well as utilizing admission-discharge teaching nurses,15 inpatient care managers,16,17 and pediatric nurse practitioners18 to aid transition.
While a variety of interventions show promise in securing a successful transition to home from the hospitalist vantage point, a partnership with primary care physicians (PCPs) in our communities is paramount. Though the evidence linking gaps in primary care after discharge and readmission rates remain elusive, effective partnerships with PCPs are important for ensuring discharge plans are carried out, which may ultimately lead to decreased rates of unanticipated adverse outcomes. Several adult studies note that no single intervention is likely to prevent issues after discharge, but interventions should include high-quality communication with and involvement of community partners.9,19,20 In practice, providing a high-quality, reliable handoff can be difficult given competing priorities of busy outpatient clinic schedules and inpatient bed capacity concerns, necessitating efficient discharge practices. Some of these challenges are amenable to quality improvement efforts to improve discharge communication.21 Innovative ideas include collaborating with PCPs earlier in the admission to design the care plan up front, including PCPs in weekly team meetings for patients with chronic care conditions,16,17 and using telehealth to communicate with PCPs.
Ensuring a safe transition to home is our responsibility as hospitalists, but the solutions to doing so reliably require multi-fold interventions that build teams within hospitals, innovative outreach to those patients recently discharged to ensure their well-being and mitigate postdischarge issues and broad community programs—including greater access to primary care—to meet our urgent imperative.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Dr. Auger’s research is funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (1K08HS024735).
The transition of children from hospital to home introduces a unique set of challenges to patients and families who may not be well-versed in the healthcare system. In addition to juggling the stress and worry of a sick child, which can inhibit the ability to understand complicated discharge instructions prior to leaving the hospital,1 caregivers need to navigate the medical system to ensure continued recovery. The responsibility to fill and administer medications, arrange follow up appointments, and determine when to seek care if the child’s condition changes are burdens we as healthcare providers expect caregivers to manage but may underestimate how frequently they are reliably completed.2-4
In this issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine, the article by Rehm et al.5 adds to the growing body of evidence highlighting challenges that caregivers of children face upon discharge from the hospital. The multicenter, retrospective study of postdischarge encounters for over 12,000 patients discharged from 4 children’s hospitals aimed to evaluate the following: (1) various methods for hospital-initiated postdischarge contact of families, (2) the type and frequency of postdischarge issues, and (3) specific characteristics of pediatric patients most commonly affected by postdischarge issues.
Using standardized questions administered through telephone, text, or e-mail contact, postdischarge issues were identified in 25% of discharges across all hospitals. Notably, there was considerable variation of rates of postdischarge issues among hospitals (from 16% to 62.8%). The hospital with the highest rate of postdischarge issues identified had attending hospitalists calling families after discharge. Thus, postdischarge issues may be most easily identified by providers who are familiar with both the patient and the expected postdischarge care.
Often, postdischarge issues represented events that could be mitigated with intentional planning to better anticipate and address patient and family needs prior to discharge. The vast majority of postdischarge issues identified across all hospitals were related to appointments, accounting for 76.3% of postdischarge issues, which may be attributed to a variety of causes, from inadequate or unclear provider recommendations to difficulty scheduling the appointments. The most common medication postdischarge issue was difficulty filling prescriptions, accounting for 84.8% of the medication issues. “Other” postdischarge issues (12.7%) as reported by caregivers included challenges with understanding discharge instructions and concerns about changes in their child’s clinical status. Forty percent of included patients had a chronic care condition. Older children, patients with more medication classes, shorter length of stay, and neuromuscular chronic care conditions had higher odds of postdischarge issues. Although a high proportion of postdischarge issues suggests a systemic problem addressing the needs of patients and families after hospital discharge, these data likely underestimate the magnitude of the problem; as such, the need for improvement may be higher.
Postdischarge challenges faced by families are not unique to pediatrics. Pediatric and adult medical patients face similar rates of challenges after
Given the prevalence of postdischarge issues after both pediatric and adult hospitalizations, how should hospitalists proceed? Physicians and health systems should explore approaches to better prepare caregivers, perhaps using models akin to the Seamless Transitions and (Re)admissions Network model of enhanced communication, care coordination, and family engagement.10 Pediatric hospitalists can prepare children for discharge long before departure by delivering medications to patients prior to discharge,11,12 providing discharge instructions that are clear and readable,13,14 as well as utilizing admission-discharge teaching nurses,15 inpatient care managers,16,17 and pediatric nurse practitioners18 to aid transition.
While a variety of interventions show promise in securing a successful transition to home from the hospitalist vantage point, a partnership with primary care physicians (PCPs) in our communities is paramount. Though the evidence linking gaps in primary care after discharge and readmission rates remain elusive, effective partnerships with PCPs are important for ensuring discharge plans are carried out, which may ultimately lead to decreased rates of unanticipated adverse outcomes. Several adult studies note that no single intervention is likely to prevent issues after discharge, but interventions should include high-quality communication with and involvement of community partners.9,19,20 In practice, providing a high-quality, reliable handoff can be difficult given competing priorities of busy outpatient clinic schedules and inpatient bed capacity concerns, necessitating efficient discharge practices. Some of these challenges are amenable to quality improvement efforts to improve discharge communication.21 Innovative ideas include collaborating with PCPs earlier in the admission to design the care plan up front, including PCPs in weekly team meetings for patients with chronic care conditions,16,17 and using telehealth to communicate with PCPs.
Ensuring a safe transition to home is our responsibility as hospitalists, but the solutions to doing so reliably require multi-fold interventions that build teams within hospitals, innovative outreach to those patients recently discharged to ensure their well-being and mitigate postdischarge issues and broad community programs—including greater access to primary care—to meet our urgent imperative.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Dr. Auger’s research is funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (1K08HS024735).
1. Solan LG, Beck AF, Brunswick SA, et al. The Family Perspective on Hospital to Home Transitions: A Qualitative Study. Pediatrics. 2015;136(6):e1539-1549. PubMed
2. Misky GJ, Wald HL, Coleman EA. Post-hospitalization transitions: Examining the effects of timing of primary care provider follow-up. J Hosp Med. 2010;5(7):392-397. PubMed
3. Yin HS, Johnson M, Mendelsohn AL, Abrams MA, Sanders LM, Dreyer BP. The health literacy of parents in the United States: a nationally representative study. Pediatrics. 2009;124 Suppl 3:S289-298. PubMed
4. Glick AF, Farkas JS, Nicholson J, et al. Parental Management of Discharge Instructions: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics. 2017. [Epub ahead of print]. PubMed
5. Rehm KP, Brittan MS, Stephens JR, et al. Issues Identified by Post-Discharge Contact after Pediatric Hospitalization: A Multi-site Study (published online ahead of print February 2, 2018) J Hosp Med. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2934
6. Forster AJ, Murff HJ, Peterson JF, Gandhi TK, Bates DW. The incidence and severity of adverse events affecting patients after discharge from the hospital. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(3):161-167. PubMed
7. Hansen LO, Greenwald JL, Budnitz T, et al. Project BOOST: effectiveness of a multihospital effort to reduce rehospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2013;8(8):421-427. PubMed
8. Auerbach AD, Kripalani S, Vasilevskis EE, et al. Preventability and Causes of Readmissions in a National Cohort of General Medicine Patients. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(4):484-493. PubMed
9. Kripalani S, LeFevre F, Phillips CO, Williams MV, Basaviah P, Baker DW. Deficits in communication and information transfer between hospital-based and primary care physicians: implications for patient safety and continuity of care. JAMA. 2007;297(8):831-841. PubMed
10. Auger KA, Simon TD, Cooperberg D, et al. Summary of STARNet: Seamless Transitions and (Re)admissions Network. Pediatrics. 2015;135(1):164-175. PubMed
11. Hatoun J, Bair-Merritt M, Cabral H, Moses J. Increasing Medication Possession at Discharge for Patients With Asthma: The Meds-in-Hand Project. Pediatrics. 2016;137(3):e20150461. PubMed
12. White CM, Statile AM, White DL, et al. Using quality improvement to optimise paediatric discharge efficiency. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(5):428-436. PubMed
13. Unaka N, Statile A, Jerardi K, et al. Improving the Readability of Pediatric Hospital Medicine Discharge Instructions. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(7):551-557. PubMed
14. Wu S, Tyler A, Logsdon T, et al. A Quality Improvement Collaborative to Improve the Discharge Process for Hospitalized Children. Pediatrics. 2016;138(2). PubMed
15. Blankenship JS, Winslow SA. Admission-discharge-teaching nurses: bridging the gap in today’s workforce. J Nurs Adm. 2003;33(1):11-13. PubMed
16. White CM, Thomson JE, Statile AM, et al. Development of a New Care Model for Hospitalized Children With Medical Complexity. Hosp Pediatr. 2017;7(7):410-414. PubMed
17. Statile AM, Schondelmeyer AC, Thomson JE, et al. Improving Discharge Efficiency in Medically Complex Pediatric Patients. Pediatrics. 2016;138(2). PubMed
18. Dunn K, Rogers J. Discharge Facilitation: An Innovative PNP Role. J Pediatr Health Care. 2016;30(5):499-505. PubMed
19. Kripalani S, Jackson AT, Schnipper JL, Coleman EA. Promoting effective transitions of care at hospital discharge: a review of key issues for hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2007;2(5):314-323. PubMed
20. Scott AM, Li J, Oyewole-Eletu S, et al. Understanding Facilitators and Barriers to Care Transitions: Insights from Project ACHIEVE Site Visits. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2017;43(9):433-447. PubMed
21. Shen MW, Hershey D, Bergert L, Mallory L, Fisher ES, Cooperberg D. Pediatric hospitalists collaborate to improve timeliness of discharge communication. Hosp Pediatr. 2013;3(3):258-265. PubMed
1. Solan LG, Beck AF, Brunswick SA, et al. The Family Perspective on Hospital to Home Transitions: A Qualitative Study. Pediatrics. 2015;136(6):e1539-1549. PubMed
2. Misky GJ, Wald HL, Coleman EA. Post-hospitalization transitions: Examining the effects of timing of primary care provider follow-up. J Hosp Med. 2010;5(7):392-397. PubMed
3. Yin HS, Johnson M, Mendelsohn AL, Abrams MA, Sanders LM, Dreyer BP. The health literacy of parents in the United States: a nationally representative study. Pediatrics. 2009;124 Suppl 3:S289-298. PubMed
4. Glick AF, Farkas JS, Nicholson J, et al. Parental Management of Discharge Instructions: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics. 2017. [Epub ahead of print]. PubMed
5. Rehm KP, Brittan MS, Stephens JR, et al. Issues Identified by Post-Discharge Contact after Pediatric Hospitalization: A Multi-site Study (published online ahead of print February 2, 2018) J Hosp Med. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2934
6. Forster AJ, Murff HJ, Peterson JF, Gandhi TK, Bates DW. The incidence and severity of adverse events affecting patients after discharge from the hospital. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(3):161-167. PubMed
7. Hansen LO, Greenwald JL, Budnitz T, et al. Project BOOST: effectiveness of a multihospital effort to reduce rehospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2013;8(8):421-427. PubMed
8. Auerbach AD, Kripalani S, Vasilevskis EE, et al. Preventability and Causes of Readmissions in a National Cohort of General Medicine Patients. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(4):484-493. PubMed
9. Kripalani S, LeFevre F, Phillips CO, Williams MV, Basaviah P, Baker DW. Deficits in communication and information transfer between hospital-based and primary care physicians: implications for patient safety and continuity of care. JAMA. 2007;297(8):831-841. PubMed
10. Auger KA, Simon TD, Cooperberg D, et al. Summary of STARNet: Seamless Transitions and (Re)admissions Network. Pediatrics. 2015;135(1):164-175. PubMed
11. Hatoun J, Bair-Merritt M, Cabral H, Moses J. Increasing Medication Possession at Discharge for Patients With Asthma: The Meds-in-Hand Project. Pediatrics. 2016;137(3):e20150461. PubMed
12. White CM, Statile AM, White DL, et al. Using quality improvement to optimise paediatric discharge efficiency. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(5):428-436. PubMed
13. Unaka N, Statile A, Jerardi K, et al. Improving the Readability of Pediatric Hospital Medicine Discharge Instructions. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(7):551-557. PubMed
14. Wu S, Tyler A, Logsdon T, et al. A Quality Improvement Collaborative to Improve the Discharge Process for Hospitalized Children. Pediatrics. 2016;138(2). PubMed
15. Blankenship JS, Winslow SA. Admission-discharge-teaching nurses: bridging the gap in today’s workforce. J Nurs Adm. 2003;33(1):11-13. PubMed
16. White CM, Thomson JE, Statile AM, et al. Development of a New Care Model for Hospitalized Children With Medical Complexity. Hosp Pediatr. 2017;7(7):410-414. PubMed
17. Statile AM, Schondelmeyer AC, Thomson JE, et al. Improving Discharge Efficiency in Medically Complex Pediatric Patients. Pediatrics. 2016;138(2). PubMed
18. Dunn K, Rogers J. Discharge Facilitation: An Innovative PNP Role. J Pediatr Health Care. 2016;30(5):499-505. PubMed
19. Kripalani S, Jackson AT, Schnipper JL, Coleman EA. Promoting effective transitions of care at hospital discharge: a review of key issues for hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2007;2(5):314-323. PubMed
20. Scott AM, Li J, Oyewole-Eletu S, et al. Understanding Facilitators and Barriers to Care Transitions: Insights from Project ACHIEVE Site Visits. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2017;43(9):433-447. PubMed
21. Shen MW, Hershey D, Bergert L, Mallory L, Fisher ES, Cooperberg D. Pediatric hospitalists collaborate to improve timeliness of discharge communication. Hosp Pediatr. 2013;3(3):258-265. PubMed
© 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine
Radiographs Predict Pneumonia Severity
The 2011 Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America (PIDS/IDSA) guidelines for management of pediatric community‐acquired pneumonia (CAP) recommend that admission chest radiographs be obtained in all children hospitalized with CAP to document the presence and extent of infiltrates and to identify complications.[1] Findings from chest radiographs may also provide clues to etiology and assist with predicting disease outcomes. In adults with CAP, clinical prediction tools use radiographic findings to inform triage decisions, guide management strategies, and predict outcomes.[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] Whether or not radiographic findings could have similar utility among children with CAP is unknown.
Several retrospective studies have examined the ability of chest radiographs to predict pediatric pneumonia disease severity.[8, 9, 10, 11, 12] However, these studies used several different measures of severe pneumonia and/or were limited to young children <5 years of age, leading to inconsistent findings. These studies also rarely considered very severe disease (eg, need for invasive mechanical ventilation) or longitudinal outcome measures such as hospital length of stay. Finally, all of these prior studies were conducted outside of the United States, and most were single‐center investigations, potentially limiting generalizability. We sought to examine associations between admission chest radiographic findings and subsequent hospital care processes and clinical outcomes, including length of stay and resource utilization measures, among children hospitalized with CAP at 4 children's hospitals in the United States.
METHODS
Design and Setting
This study was nested within a multicenter retrospective cohort designed to validate International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD9‐CM) diagnostic codes for pediatric CAP hospitalizations.[13] The Pediatric Health Information System database (Children's Hospital Association, Overland Park, KS) was used to identify children from 4 freestanding pediatric hospitals (Monroe Carell, Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt, Nashville, Tennessee; Children's Mercy Hospitals & Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri; Seattle Children's Hospital, Seattle, Washington; and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, Ohio). The institutional review boards at each participating institution approved the study. The validation study included a 25% random sampling of children 60 days to 18 years of age (n=998) who were hospitalized between January 1, 2010 and December 31, 2010 with at least 1 ICD9‐CM discharge code indicating pneumonia. The diagnosis of CAP was confirmed by medical record review.
Study Population
This study was limited to children from the validation study who met criteria for clinical and radiographic CAP, defined as: (1) abnormal temperature or white blood cell count, (2) signs and symptoms of acute respiratory illness (eg, cough, tachypnea), and (3) chest radiograph indicating pneumonia within 48 hours of admission. Children with atelectasis as the only abnormal radiographic finding and those with complex chronic conditions (eg, cystic fibrosis, malignancy) were excluded using a previously described algorithm.[14]
Outcomes
Several measures of disease severity were assessed. Dichotomous outcomes included supplemental oxygen use, need for intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation. Continuous outcomes included hospital length of stay, and for those requiring supplemental oxygen, duration of oxygen supplementation, measured in hours.
Exposure
To categorize infiltrate patterns and the presence and size of pleural effusions, we reviewed the final report from admission chest radiographs to obtain the final clinical interpretation performed by the attending pediatric radiologist. Infiltrate patterns were classified as single lobar (reference), unilateral multilobar, bilateral multilobar, or interstitial. Children with both lobar and interstitial infiltrates, and those with mention of atelectasis, were classified according to the type of lobar infiltrate. Those with atelectasis only were excluded. Pleural effusions were classified as absent, small, or moderate/large.
Analysis
Descriptive statistics were summarized using frequencies and percentages for categorical variables and median and interquartile range (IQR) values for continuous variables. Our primary exposures were infiltrate pattern and presence and size of pleural effusion on admission chest radiograph. Associations between radiographic findings and disease outcomes were analyzed using logistic and linear regression for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. Continuous outcomes were log‐transformed and normality assumptions verified prior to model development.
Due to the large number of covariates relative to outcome events, we used propensity score methods to adjust for potential confounding. The propensity score estimates the likelihood of a given exposure (ie, infiltrate pattern) conditional on a set of covariates. In this way, the propensity score summarizes potential confounding effects from a large number of covariates into a single variable. Including the propensity score as a covariate in multivariable regression improves model efficiency and helps protect against overfitting.[15] Covariates included in the estimation of the propensity score included age, sex, race/ethnicity, payer, hospital, asthma history, hospital transfer, recent hospitalization (within 30 days), recent emergency department or clinic visit (within 2 weeks), recent antibiotics for acute illness (within 5 days), illness duration prior to admission, tachypnea and/or increased work of breathing (retractions, nasal flaring, or grunting) at presentation, receipt of albuterol and/or corticosteroids during the first 2 calendar days of hospitalization, and concurrent diagnosis of bronchiolitis. All analyses included the estimated propensity score, infiltrate pattern, and pleural effusion (absent, small, or moderate/large).
RESULTS
Study Population
The median age of the 406 children with clinical and radiographic CAP was 3 years (IQR, 16 years) (Table 1). Single lobar infiltrate was the most common radiographic pattern (61%). Children with interstitial infiltrates (10%) were younger than those with lobar infiltrates of any type (median age 1 vs 3 years, P=0.02). A concomitant diagnosis of bronchiolitis was assigned to 34% of children with interstitial infiltrates but only 17% of those with lobar infiltrate patterns (range, 11%20%, P=0.03). Pleural effusion was present in 21% of children and was more common among those with lobar infiltrates, particularly multilobar disease. Only 1 child with interstitial infiltrate had a pleural effusion. Overall, 63% of children required supplemental oxygen, 8% required ICU admission, and 3% required invasive mechanical ventilation. Median length of stay was 51.5 hours (IQR, 3991) and median oxygen duration was 31.5 hours [IQR, 1365]. There were no deaths.
| Characteristic | Infiltrate Patterna | P Valueb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Lobar | Multilobar, Unilateral | Multilobar, Bilateral | Interstitial | ||
| |||||
| No. | 247 (60.8) | 54 (13.3) | 64 (15.8) | 41 (10.1) | |
| Median age, y | 3 [16] | 3 [17] | 3 [15] | 1 [03] | 0.02 |
| Male sex | 124 (50.2) | 32 (59.3) | 41 (64.1) | 30 (73.2) | 0.02 |
| Race | |||||
| Non‐Hispanic white | 133 (53.8) | 36 (66.7) | 37 (57.8) | 17 (41.5) | 0.69 |
| Non‐Hispanic black | 40 (16.2) | 6 (11.1) | 9 (14.1) | 8 (19.5) | |
| Hispanic | 25 (10.1) | 4 (7.4) | 5 (7.8) | 7 (17.1) | |
| Other | 49 (19.9) | 8 (14.8) | 13 (20.4) | 9 (22) | |
| Insurance | |||||
| Public | 130 (52.6) | 26 (48.1) | 33 (51.6) | 25 (61) | 0.90 |
| Private | 116 (47) | 28 (51.9) | 31 (48.4) | 16 (39) | |
| Concurrent diagnosis | |||||
| Asthma | 80 (32.4) | 16 (29.6) | 17 (26.6) | 12 (29.3) | 0.82 |
| Bronchiolitis | 43 (17.4) | 6 (11.1) | 13 (20.3) | 14 (34.1) | 0.03 |
| Effusion | |||||
| None | 201 (81.4) | 31 (57.4) | 48 (75) | 40 (97.6) | <.01 |
| Small | 34 (13.8) | 20 (37) | 11 (17.2) | 0 | |
| Moderate/large | 12 (4.9) | 3 (5.6) | 5 (7.8) | 1 (2.4) | |
Outcomes According to Radiographic Infiltrate Pattern
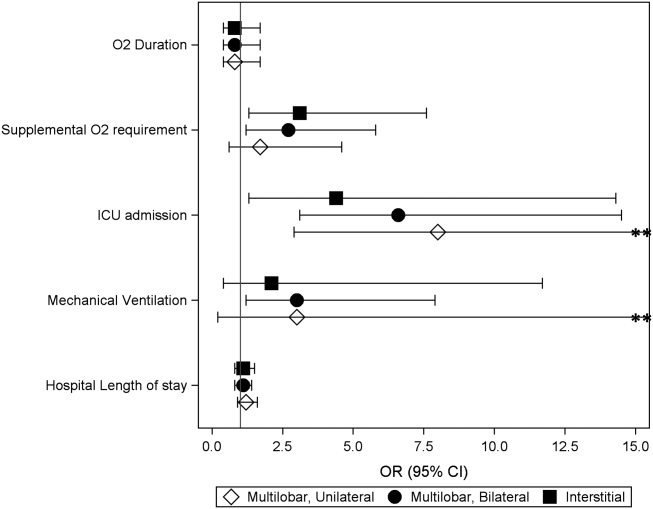
Compared to children with single lobar infiltrates, the odds of ICU admission was significantly increased for those with either unilateral or bilateral multilobar infiltrates (unilateral, adjusted odds ratio [aOR]: 8.0, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.922.2; bilateral, aOR: 6.6, 95% CI: 2.14.5) (Figure 1, Table 2). Patients with bilateral multilobar infiltrates also had higher odds for supplemental oxygen use (aOR: 2.7, 95% CI: 1.25.8) and need for invasive mechanical ventilation (aOR: 3.0, 95% CI: 1.27.9). There were no differences in duration of oxygen supplementation or hospital length of stay for children with single versus multilobar infiltrates.
| Outcome | Infiltrate Patterna | P Valueb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Lobar, n=247 | Multilobar, Unilateral, n=54 | Multilobar, Bilateral, n=64 | Interstitial, n=41 | ||
| |||||
| Supplemental O2 requirement | 143 (57.9) | 34 (63) | 46 (71.9) | 31 (75.6) | 0.05 |
| ICU admission | 10 (4) | 9 (16.7) | 9 (14.1) | 4 (9.8) | <0.01 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 5 (2) | 4 (7.4) | 4 (6.3) | 1 (2.4) | 0.13 |
| Hospital length of stay, h | 47 [3779] | 63 [45114] | 56.5 [39.5101] | 62 [3993] | <0.01 |
| O2 duration, h | 27 [1059] | 38 [1777] | 38 [2381] | 34.5 [1765] | 0.18 |
Compared to those with single lobar infiltrates, children with interstitial infiltrates had higher odds of need for supplemental oxygen (aOR: 3.1, 95% CI: 1.37.6) and ICU admission (aOR: 4.4, 95% CI: 1.314.3) but not invasive mechanical ventilation. There were also no differences in duration of oxygen supplementation or hospital length of stay.
Outcomes According to Presence and Size of Pleural Effusion
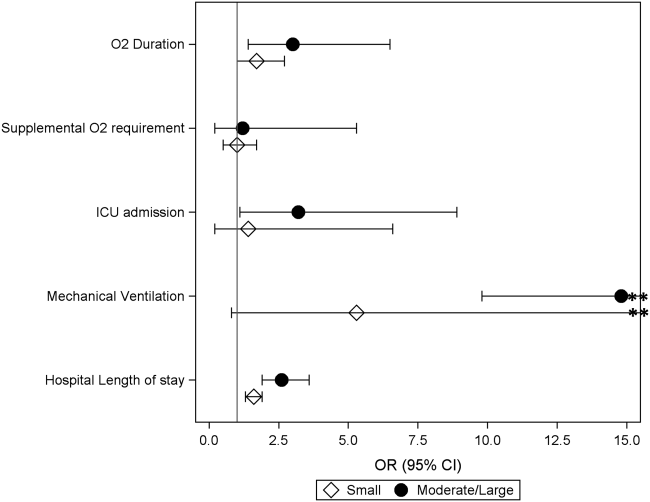
Compared to those without pleural effusion, children with moderate to large effusion had a higher odds of ICU admission (aOR: 3.2, 95% CI: 1.18.9) and invasive mechanical ventilation (aOR: 14.8, 95% CI: 9.822.4), and also had a longer duration of oxygen supplementation (aOR: 3.0, 95% CI: 1.46.5) and hospital length of stay (aOR: 2.6, 95% CI: 1.9‐3.6) (Table 3, Figure 2). The presence of a small pleural effusion was not associated with increased need for supplemental oxygen, ICU admission, or mechanical ventilation compared to those without effusion. However, small effusion was associated with a longer duration of oxygen supplementation (aOR: 1.7, 95% CI: 12.7) and hospital length of stay (aOR: 1.6, 95% CI: 1.3‐1.9).
| Outcome | Pleural Effusion | P Valuea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None, n=320 | Small, n=65 | Moderate/Large, n=21 | ||
| ||||
| Supplemental O2 requirement | 200 (62.5) | 40 (61.5) | 14 (66.7) | 0.91 |
| ICU admission | 22 (6.9) | 6 (9.2) | 4 (19) | 0.12 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 5 (1.6) | 5 (7.7) | 4 (19) | <0.01 |
| Hospital length of stay, h | 48 [37.576] | 72 [45142] | 160 [82191] | <0.01 |
| Oxygen duration, h | 31 [1157] | 38.5 [1887] | 111 [27154] | <0.01 |
DISCUSSION
We evaluated the association between admission chest radiographic findings and subsequent clinical outcomes and hospital care processes for children hospitalized with CAP at 4 children's hospitals in the United States. We conclude that radiographic findings are associated with important inpatient outcomes. Similar to data from adults, findings of moderate to large pleural effusions and bilateral multilobar infiltrates had the strongest associations with severe disease. Such information, in combination with other prognostic factors, may help clinicians identify high‐risk patients and support management decisions, while also helping to inform families about the expected hospital course.
Previous pediatric studies examining the association between radiographic findings and outcomes have produced inconsistent results.[8, 9, 10, 11, 12] All but 1 of these studies documented 1 radiographic characteristics associated with pneumonia disease severity.[11] Further, although most contrasted lobar/alveolar and interstitial infiltrates, only Patria et al. distinguished among lobar infiltrate patterns (eg, single lobar vs multilobar).[12] Similar to our findings, that study demonstrated increased disease severity among children with bilateral multifocal lobar infiltrates. Of the studies that considered the presence of pleural effusion, only 1 demonstrated this finding to be associated with more severe disease.[9] However, none of these prior studies examined size of the pleural effusion.
In our study, the strongest association with severe pneumonia outcomes was among children with moderate to large pleural effusion. Significant pleural effusions are much more commonly due to infection with bacterial pathogens, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pyogenes, and may also indicate infection with more virulent and/or difficult to treat strains.[16, 17, 18, 19] Surgical intervention is also often required. As such, children with significant pleural effusions are often more ill on presentation and may have a prolonged period of recovery.[20, 21, 22]
Similarly, multilobar infiltrates, particularly bilateral, were associated with increased disease severity in terms of need for supplemental oxygen, ICU admission, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation. Although this finding may be expected, it is interesting to note that the duration of supplemental oxygen and hospital length of stay were similar to those with single lobar disease. One potential explanation is that, although children with multilobar disease are more severe at presentation, rates of recovery are similar to those with less extensive radiographic findings, owing to rapidly effective antimicrobials for uncomplicated bacterial pneumonia. This hypothesis also agrees with the 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines, which state that children receiving adequate therapy typically show signs of improvement within 48 to 72 hours regardless of initial severity.[1]
Interstitial infiltrate was also associated with increased severity at presentation but similar length of stay and duration of oxygen requirement compared with single lobar disease. We note that these children were substantially younger than those presenting with any pattern of lobar disease (median age, 1 vs 3 years), were more likely to have a concurrent diagnosis of bronchiolitis (34% vs 17%), and only 1 child with interstitial infiltrates had a documented pleural effusion (vs 23% of children with lobar infiltrates). Primary viral pneumonia is considered more likely to produce interstitial infiltrates on chest radiograph compared to bacterial disease, and although detailed etiologic data are unavailable for this study, our findings above strongly support this assertion.[23, 24]
The 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines recommend admission chest radiographs for all children hospitalized with pneumonia to assess extent of disease and identify complications that may requiring additional evaluation or surgical intervention.[1] Our findings highlight additional potential benefits of admission radiographs in terms of disease prognosis and management decisions. In the initial evaluation of a sick child with pneumonia, clinicians are often presented with a number of potential prognostic factors that may influence disease outcomes. However, it is sometimes difficult for providers to consider all available information and/or the relative importance of a single factor, resulting in inaccurate risk perceptions and management decisions that may contribute to poor outcomes.[25] Similar to adults, the development of clinical prediction rules, which incorporate a variety of important predictors including admission radiographic findings, likely would improve risk assessments and potentially outcomes for children with pneumonia. Such prognostic information is also helpful for clinicians who may use these data to inform and prepare families regarding the expected course of hospitalization.
Our study has several limitations. This study was retrospective and only included a sample of pneumonia hospitalizations during the study period, which may raise confounding concerns and potential for selection bias. However, detailed medical record reviews using standardized case definitions for radiographic CAP were used, and a large sample of children was randomly selected from each institution. In addition, a large number of potential confounders were selected a priori and included in multivariable analyses; propensity score adjustment was used to reduce model complexity and avoid overfitting. Radiographic findings were based on clinical interpretation by pediatric radiologists independent of a study protocol. Prior studies have demonstrated good agreement for identification of alveolar/lobar infiltrates and pleural effusion by trained radiologists, although agreement for interstitial infiltrate is poor.[26, 27] This limitation could result in either over‐ or underestimation of the prevalence of interstitial infiltrates likely resulting in a nondifferential bias toward the null. Microbiologic information, which may inform radiographic findings and disease severity, was also not available. However, because pneumonia etiology is frequently unknown in the clinical setting, our study reflects typical practice. We also did not include children from community or nonteaching hospitals. Thus, although findings may have relevance to community or nonteaching hospitals, our results cannot be generalized.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrates that among children hospitalized with CAP, admission chest radiographic findings are associated with important clinical outcomes and hospital care processes, highlighting additional benefits of the 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines' recommendation for admission chest radiographs for all children hospitalized with pneumonia. These data, in conjunction with other important prognostic information, may help clinicians more rapidly identify children at increased risk for severe illness, and could also offer guidance regarding disease management strategies and facilitate shared decision making with families. Thus, routine admission chest radiography in this population represents a valuable tool that contributes to improved quality of care.
Disclosures
Dr. Williams is supported by funds from the National Institutes of HealthNational Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (K23AI104779). The authors report no conflicts of interest.
- , , , et al. The management of community‐acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53(7):e25–e76.
- , , , et al. A prediction rule to identify low‐risk patients with community‐acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(4):243–250.
- , , , et al. SMART‐COP: a tool for predicting the need for intensive respiratory or vasopressor support in community‐acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(3):375–384.
- , , , et al. Development and validation of a clinical prediction rule for severe community‐acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;174(11):1249–1256.
- , , , et al. Risk stratification of early admission to the intensive care unit of patients with no major criteria of severe community‐acquired pneumonia: development of an international prediction rule. Crit Care. 2009;13(2):R54.
- , , , et al. Do pulmonary radiographic findings at presentation predict mortality in patients with community‐acquired pneumonia? Arch Intern Med. 1996;156(19):2206–2212.
- , , , , , . Safety and efficacy of CURB65‐guided antibiotic therapy in community‐acquired pneumonia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(2):416–423.
- , , . Severity of childhood community‐acquired pneumonia and chest radiographic findings. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2009;44(3):249–252.
- , , , et al. Can chest x‐ray predict pneumonia severity? Pediatr Pulmonol. 2004;38(6):465–469.
- , , , . Children with pneumonia: how do they present and how are they managed? Arch Dis Child. 2007;92(5):394–398.
- , , . Role of chest X‐ray in predicting outcome of acute severe pneumonia. Indian Pediatr. 2008;45(11):893–898.
- , , , , , . Association between radiological findings and severity of community‐acquired pneumonia in children. Ital J Pediatr. 2013;39:56.
- , , , et al. Identifying pediatric community‐acquired pneumonia hospitalizations: accuracy of administrative billing codes. JAMA Pediatrics. 2013;167(9):851–858.
- , , , , , . Deaths attributed to pediatric complex chronic conditions: national trends and implications for supportive care services. Pediatrics. 2001;107(6):E99.
- , . Invited commentary: propensity scores. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;150(4):327–333.
- , , , . Increasing incidence of empyema complicating childhood community‐acquired pneumonia in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(6):805–813.
- , , , et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of community‐acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. Pediatrics. 2004;113(4):701–707.
- , , , et al. Molecular analysis improves pathogen identification and epidemiologic study of pediatric parapneumonic empyema. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30(4):289–294.
- , . Parapneumonic pleural effusion and empyema in children. Review of a 19‐year experience, 1962–1980. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1983;22(6):414–419.
- , , , et al. Risk factors of progressive community‐acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children: a prospective study [published online ahead of print August 28, 2013]. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2013.06.009.
- , , , , . Community‐acquired lobar pneumonia in children in the era of universal 7‐valent pneumococcal vaccination: a review of clinical presentations and antimicrobial treatment from a Canadian pediatric hospital. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:133.
- , , , et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of complicated pneumococcal pneumonia in a pediatric population. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006;41(8):726–734.
- , , , , , . Differentiation of bacterial and viral pneumonia in children. Thorax. 2002;57(5):438–441.
- , , , et al. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in children: update 2011. Thorax. 2011;66(suppl 2):ii1–ii23.
- , , , et al. Community acquired pneumonia: aetiology and usefulness of severity criteria on admission. Thorax. 1996;51(10):1010–1016.
- , , , et al. Variability in the interpretation of chest radiographs for the diagnosis of pneumonia in children. J Hosp Med. 2012;7(4):294–298.
- , , , et al. Interobserver reliability of the chest radiograph in community‐acquired pneumonia. PORT Investigators. Chest. 1996;110(2):343–350.
The 2011 Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America (PIDS/IDSA) guidelines for management of pediatric community‐acquired pneumonia (CAP) recommend that admission chest radiographs be obtained in all children hospitalized with CAP to document the presence and extent of infiltrates and to identify complications.[1] Findings from chest radiographs may also provide clues to etiology and assist with predicting disease outcomes. In adults with CAP, clinical prediction tools use radiographic findings to inform triage decisions, guide management strategies, and predict outcomes.[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] Whether or not radiographic findings could have similar utility among children with CAP is unknown.
Several retrospective studies have examined the ability of chest radiographs to predict pediatric pneumonia disease severity.[8, 9, 10, 11, 12] However, these studies used several different measures of severe pneumonia and/or were limited to young children <5 years of age, leading to inconsistent findings. These studies also rarely considered very severe disease (eg, need for invasive mechanical ventilation) or longitudinal outcome measures such as hospital length of stay. Finally, all of these prior studies were conducted outside of the United States, and most were single‐center investigations, potentially limiting generalizability. We sought to examine associations between admission chest radiographic findings and subsequent hospital care processes and clinical outcomes, including length of stay and resource utilization measures, among children hospitalized with CAP at 4 children's hospitals in the United States.
METHODS
Design and Setting
This study was nested within a multicenter retrospective cohort designed to validate International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD9‐CM) diagnostic codes for pediatric CAP hospitalizations.[13] The Pediatric Health Information System database (Children's Hospital Association, Overland Park, KS) was used to identify children from 4 freestanding pediatric hospitals (Monroe Carell, Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt, Nashville, Tennessee; Children's Mercy Hospitals & Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri; Seattle Children's Hospital, Seattle, Washington; and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, Ohio). The institutional review boards at each participating institution approved the study. The validation study included a 25% random sampling of children 60 days to 18 years of age (n=998) who were hospitalized between January 1, 2010 and December 31, 2010 with at least 1 ICD9‐CM discharge code indicating pneumonia. The diagnosis of CAP was confirmed by medical record review.
Study Population
This study was limited to children from the validation study who met criteria for clinical and radiographic CAP, defined as: (1) abnormal temperature or white blood cell count, (2) signs and symptoms of acute respiratory illness (eg, cough, tachypnea), and (3) chest radiograph indicating pneumonia within 48 hours of admission. Children with atelectasis as the only abnormal radiographic finding and those with complex chronic conditions (eg, cystic fibrosis, malignancy) were excluded using a previously described algorithm.[14]
Outcomes
Several measures of disease severity were assessed. Dichotomous outcomes included supplemental oxygen use, need for intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation. Continuous outcomes included hospital length of stay, and for those requiring supplemental oxygen, duration of oxygen supplementation, measured in hours.
Exposure
To categorize infiltrate patterns and the presence and size of pleural effusions, we reviewed the final report from admission chest radiographs to obtain the final clinical interpretation performed by the attending pediatric radiologist. Infiltrate patterns were classified as single lobar (reference), unilateral multilobar, bilateral multilobar, or interstitial. Children with both lobar and interstitial infiltrates, and those with mention of atelectasis, were classified according to the type of lobar infiltrate. Those with atelectasis only were excluded. Pleural effusions were classified as absent, small, or moderate/large.
Analysis
Descriptive statistics were summarized using frequencies and percentages for categorical variables and median and interquartile range (IQR) values for continuous variables. Our primary exposures were infiltrate pattern and presence and size of pleural effusion on admission chest radiograph. Associations between radiographic findings and disease outcomes were analyzed using logistic and linear regression for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. Continuous outcomes were log‐transformed and normality assumptions verified prior to model development.
Due to the large number of covariates relative to outcome events, we used propensity score methods to adjust for potential confounding. The propensity score estimates the likelihood of a given exposure (ie, infiltrate pattern) conditional on a set of covariates. In this way, the propensity score summarizes potential confounding effects from a large number of covariates into a single variable. Including the propensity score as a covariate in multivariable regression improves model efficiency and helps protect against overfitting.[15] Covariates included in the estimation of the propensity score included age, sex, race/ethnicity, payer, hospital, asthma history, hospital transfer, recent hospitalization (within 30 days), recent emergency department or clinic visit (within 2 weeks), recent antibiotics for acute illness (within 5 days), illness duration prior to admission, tachypnea and/or increased work of breathing (retractions, nasal flaring, or grunting) at presentation, receipt of albuterol and/or corticosteroids during the first 2 calendar days of hospitalization, and concurrent diagnosis of bronchiolitis. All analyses included the estimated propensity score, infiltrate pattern, and pleural effusion (absent, small, or moderate/large).
RESULTS
Study Population
The median age of the 406 children with clinical and radiographic CAP was 3 years (IQR, 16 years) (Table 1). Single lobar infiltrate was the most common radiographic pattern (61%). Children with interstitial infiltrates (10%) were younger than those with lobar infiltrates of any type (median age 1 vs 3 years, P=0.02). A concomitant diagnosis of bronchiolitis was assigned to 34% of children with interstitial infiltrates but only 17% of those with lobar infiltrate patterns (range, 11%20%, P=0.03). Pleural effusion was present in 21% of children and was more common among those with lobar infiltrates, particularly multilobar disease. Only 1 child with interstitial infiltrate had a pleural effusion. Overall, 63% of children required supplemental oxygen, 8% required ICU admission, and 3% required invasive mechanical ventilation. Median length of stay was 51.5 hours (IQR, 3991) and median oxygen duration was 31.5 hours [IQR, 1365]. There were no deaths.
| Characteristic | Infiltrate Patterna | P Valueb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Lobar | Multilobar, Unilateral | Multilobar, Bilateral | Interstitial | ||
| |||||
| No. | 247 (60.8) | 54 (13.3) | 64 (15.8) | 41 (10.1) | |
| Median age, y | 3 [16] | 3 [17] | 3 [15] | 1 [03] | 0.02 |
| Male sex | 124 (50.2) | 32 (59.3) | 41 (64.1) | 30 (73.2) | 0.02 |
| Race | |||||
| Non‐Hispanic white | 133 (53.8) | 36 (66.7) | 37 (57.8) | 17 (41.5) | 0.69 |
| Non‐Hispanic black | 40 (16.2) | 6 (11.1) | 9 (14.1) | 8 (19.5) | |
| Hispanic | 25 (10.1) | 4 (7.4) | 5 (7.8) | 7 (17.1) | |
| Other | 49 (19.9) | 8 (14.8) | 13 (20.4) | 9 (22) | |
| Insurance | |||||
| Public | 130 (52.6) | 26 (48.1) | 33 (51.6) | 25 (61) | 0.90 |
| Private | 116 (47) | 28 (51.9) | 31 (48.4) | 16 (39) | |
| Concurrent diagnosis | |||||
| Asthma | 80 (32.4) | 16 (29.6) | 17 (26.6) | 12 (29.3) | 0.82 |
| Bronchiolitis | 43 (17.4) | 6 (11.1) | 13 (20.3) | 14 (34.1) | 0.03 |
| Effusion | |||||
| None | 201 (81.4) | 31 (57.4) | 48 (75) | 40 (97.6) | <.01 |
| Small | 34 (13.8) | 20 (37) | 11 (17.2) | 0 | |
| Moderate/large | 12 (4.9) | 3 (5.6) | 5 (7.8) | 1 (2.4) | |
Outcomes According to Radiographic Infiltrate Pattern
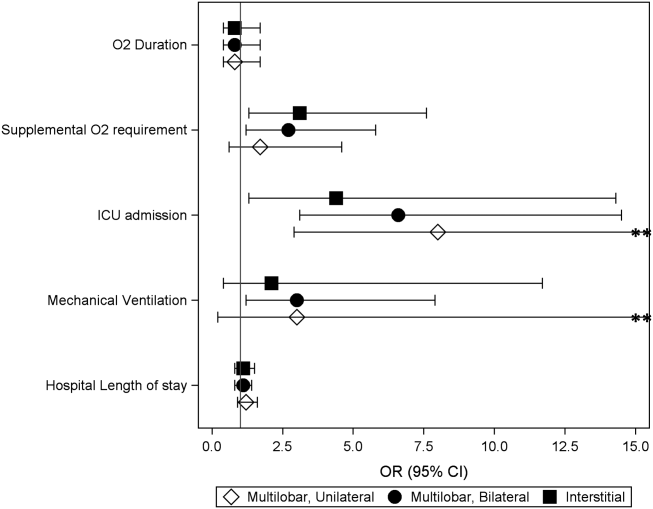
Compared to children with single lobar infiltrates, the odds of ICU admission was significantly increased for those with either unilateral or bilateral multilobar infiltrates (unilateral, adjusted odds ratio [aOR]: 8.0, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.922.2; bilateral, aOR: 6.6, 95% CI: 2.14.5) (Figure 1, Table 2). Patients with bilateral multilobar infiltrates also had higher odds for supplemental oxygen use (aOR: 2.7, 95% CI: 1.25.8) and need for invasive mechanical ventilation (aOR: 3.0, 95% CI: 1.27.9). There were no differences in duration of oxygen supplementation or hospital length of stay for children with single versus multilobar infiltrates.

| Outcome | Infiltrate Patterna | P Valueb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Lobar, n=247 | Multilobar, Unilateral, n=54 | Multilobar, Bilateral, n=64 | Interstitial, n=41 | ||
| |||||
| Supplemental O2 requirement | 143 (57.9) | 34 (63) | 46 (71.9) | 31 (75.6) | 0.05 |
| ICU admission | 10 (4) | 9 (16.7) | 9 (14.1) | 4 (9.8) | <0.01 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 5 (2) | 4 (7.4) | 4 (6.3) | 1 (2.4) | 0.13 |
| Hospital length of stay, h | 47 [3779] | 63 [45114] | 56.5 [39.5101] | 62 [3993] | <0.01 |
| O2 duration, h | 27 [1059] | 38 [1777] | 38 [2381] | 34.5 [1765] | 0.18 |
Compared to those with single lobar infiltrates, children with interstitial infiltrates had higher odds of need for supplemental oxygen (aOR: 3.1, 95% CI: 1.37.6) and ICU admission (aOR: 4.4, 95% CI: 1.314.3) but not invasive mechanical ventilation. There were also no differences in duration of oxygen supplementation or hospital length of stay.
Outcomes According to Presence and Size of Pleural Effusion
Compared to those without pleural effusion, children with moderate to large effusion had a higher odds of ICU admission (aOR: 3.2, 95% CI: 1.18.9) and invasive mechanical ventilation (aOR: 14.8, 95% CI: 9.822.4), and also had a longer duration of oxygen supplementation (aOR: 3.0, 95% CI: 1.46.5) and hospital length of stay (aOR: 2.6, 95% CI: 1.9‐3.6) (Table 3, Figure 2). The presence of a small pleural effusion was not associated with increased need for supplemental oxygen, ICU admission, or mechanical ventilation compared to those without effusion. However, small effusion was associated with a longer duration of oxygen supplementation (aOR: 1.7, 95% CI: 12.7) and hospital length of stay (aOR: 1.6, 95% CI: 1.3‐1.9).
| Outcome | Pleural Effusion | P Valuea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None, n=320 | Small, n=65 | Moderate/Large, n=21 | ||
| ||||
| Supplemental O2 requirement | 200 (62.5) | 40 (61.5) | 14 (66.7) | 0.91 |
| ICU admission | 22 (6.9) | 6 (9.2) | 4 (19) | 0.12 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 5 (1.6) | 5 (7.7) | 4 (19) | <0.01 |
| Hospital length of stay, h | 48 [37.576] | 72 [45142] | 160 [82191] | <0.01 |
| Oxygen duration, h | 31 [1157] | 38.5 [1887] | 111 [27154] | <0.01 |

DISCUSSION
We evaluated the association between admission chest radiographic findings and subsequent clinical outcomes and hospital care processes for children hospitalized with CAP at 4 children's hospitals in the United States. We conclude that radiographic findings are associated with important inpatient outcomes. Similar to data from adults, findings of moderate to large pleural effusions and bilateral multilobar infiltrates had the strongest associations with severe disease. Such information, in combination with other prognostic factors, may help clinicians identify high‐risk patients and support management decisions, while also helping to inform families about the expected hospital course.
Previous pediatric studies examining the association between radiographic findings and outcomes have produced inconsistent results.[8, 9, 10, 11, 12] All but 1 of these studies documented 1 radiographic characteristics associated with pneumonia disease severity.[11] Further, although most contrasted lobar/alveolar and interstitial infiltrates, only Patria et al. distinguished among lobar infiltrate patterns (eg, single lobar vs multilobar).[12] Similar to our findings, that study demonstrated increased disease severity among children with bilateral multifocal lobar infiltrates. Of the studies that considered the presence of pleural effusion, only 1 demonstrated this finding to be associated with more severe disease.[9] However, none of these prior studies examined size of the pleural effusion.
In our study, the strongest association with severe pneumonia outcomes was among children with moderate to large pleural effusion. Significant pleural effusions are much more commonly due to infection with bacterial pathogens, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pyogenes, and may also indicate infection with more virulent and/or difficult to treat strains.[16, 17, 18, 19] Surgical intervention is also often required. As such, children with significant pleural effusions are often more ill on presentation and may have a prolonged period of recovery.[20, 21, 22]
Similarly, multilobar infiltrates, particularly bilateral, were associated with increased disease severity in terms of need for supplemental oxygen, ICU admission, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation. Although this finding may be expected, it is interesting to note that the duration of supplemental oxygen and hospital length of stay were similar to those with single lobar disease. One potential explanation is that, although children with multilobar disease are more severe at presentation, rates of recovery are similar to those with less extensive radiographic findings, owing to rapidly effective antimicrobials for uncomplicated bacterial pneumonia. This hypothesis also agrees with the 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines, which state that children receiving adequate therapy typically show signs of improvement within 48 to 72 hours regardless of initial severity.[1]
Interstitial infiltrate was also associated with increased severity at presentation but similar length of stay and duration of oxygen requirement compared with single lobar disease. We note that these children were substantially younger than those presenting with any pattern of lobar disease (median age, 1 vs 3 years), were more likely to have a concurrent diagnosis of bronchiolitis (34% vs 17%), and only 1 child with interstitial infiltrates had a documented pleural effusion (vs 23% of children with lobar infiltrates). Primary viral pneumonia is considered more likely to produce interstitial infiltrates on chest radiograph compared to bacterial disease, and although detailed etiologic data are unavailable for this study, our findings above strongly support this assertion.[23, 24]
The 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines recommend admission chest radiographs for all children hospitalized with pneumonia to assess extent of disease and identify complications that may requiring additional evaluation or surgical intervention.[1] Our findings highlight additional potential benefits of admission radiographs in terms of disease prognosis and management decisions. In the initial evaluation of a sick child with pneumonia, clinicians are often presented with a number of potential prognostic factors that may influence disease outcomes. However, it is sometimes difficult for providers to consider all available information and/or the relative importance of a single factor, resulting in inaccurate risk perceptions and management decisions that may contribute to poor outcomes.[25] Similar to adults, the development of clinical prediction rules, which incorporate a variety of important predictors including admission radiographic findings, likely would improve risk assessments and potentially outcomes for children with pneumonia. Such prognostic information is also helpful for clinicians who may use these data to inform and prepare families regarding the expected course of hospitalization.
Our study has several limitations. This study was retrospective and only included a sample of pneumonia hospitalizations during the study period, which may raise confounding concerns and potential for selection bias. However, detailed medical record reviews using standardized case definitions for radiographic CAP were used, and a large sample of children was randomly selected from each institution. In addition, a large number of potential confounders were selected a priori and included in multivariable analyses; propensity score adjustment was used to reduce model complexity and avoid overfitting. Radiographic findings were based on clinical interpretation by pediatric radiologists independent of a study protocol. Prior studies have demonstrated good agreement for identification of alveolar/lobar infiltrates and pleural effusion by trained radiologists, although agreement for interstitial infiltrate is poor.[26, 27] This limitation could result in either over‐ or underestimation of the prevalence of interstitial infiltrates likely resulting in a nondifferential bias toward the null. Microbiologic information, which may inform radiographic findings and disease severity, was also not available. However, because pneumonia etiology is frequently unknown in the clinical setting, our study reflects typical practice. We also did not include children from community or nonteaching hospitals. Thus, although findings may have relevance to community or nonteaching hospitals, our results cannot be generalized.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrates that among children hospitalized with CAP, admission chest radiographic findings are associated with important clinical outcomes and hospital care processes, highlighting additional benefits of the 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines' recommendation for admission chest radiographs for all children hospitalized with pneumonia. These data, in conjunction with other important prognostic information, may help clinicians more rapidly identify children at increased risk for severe illness, and could also offer guidance regarding disease management strategies and facilitate shared decision making with families. Thus, routine admission chest radiography in this population represents a valuable tool that contributes to improved quality of care.
Disclosures
Dr. Williams is supported by funds from the National Institutes of HealthNational Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (K23AI104779). The authors report no conflicts of interest.
The 2011 Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America (PIDS/IDSA) guidelines for management of pediatric community‐acquired pneumonia (CAP) recommend that admission chest radiographs be obtained in all children hospitalized with CAP to document the presence and extent of infiltrates and to identify complications.[1] Findings from chest radiographs may also provide clues to etiology and assist with predicting disease outcomes. In adults with CAP, clinical prediction tools use radiographic findings to inform triage decisions, guide management strategies, and predict outcomes.[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] Whether or not radiographic findings could have similar utility among children with CAP is unknown.
Several retrospective studies have examined the ability of chest radiographs to predict pediatric pneumonia disease severity.[8, 9, 10, 11, 12] However, these studies used several different measures of severe pneumonia and/or were limited to young children <5 years of age, leading to inconsistent findings. These studies also rarely considered very severe disease (eg, need for invasive mechanical ventilation) or longitudinal outcome measures such as hospital length of stay. Finally, all of these prior studies were conducted outside of the United States, and most were single‐center investigations, potentially limiting generalizability. We sought to examine associations between admission chest radiographic findings and subsequent hospital care processes and clinical outcomes, including length of stay and resource utilization measures, among children hospitalized with CAP at 4 children's hospitals in the United States.
METHODS
Design and Setting
This study was nested within a multicenter retrospective cohort designed to validate International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD9‐CM) diagnostic codes for pediatric CAP hospitalizations.[13] The Pediatric Health Information System database (Children's Hospital Association, Overland Park, KS) was used to identify children from 4 freestanding pediatric hospitals (Monroe Carell, Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt, Nashville, Tennessee; Children's Mercy Hospitals & Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri; Seattle Children's Hospital, Seattle, Washington; and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, Ohio). The institutional review boards at each participating institution approved the study. The validation study included a 25% random sampling of children 60 days to 18 years of age (n=998) who were hospitalized between January 1, 2010 and December 31, 2010 with at least 1 ICD9‐CM discharge code indicating pneumonia. The diagnosis of CAP was confirmed by medical record review.
Study Population
This study was limited to children from the validation study who met criteria for clinical and radiographic CAP, defined as: (1) abnormal temperature or white blood cell count, (2) signs and symptoms of acute respiratory illness (eg, cough, tachypnea), and (3) chest radiograph indicating pneumonia within 48 hours of admission. Children with atelectasis as the only abnormal radiographic finding and those with complex chronic conditions (eg, cystic fibrosis, malignancy) were excluded using a previously described algorithm.[14]
Outcomes
Several measures of disease severity were assessed. Dichotomous outcomes included supplemental oxygen use, need for intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation. Continuous outcomes included hospital length of stay, and for those requiring supplemental oxygen, duration of oxygen supplementation, measured in hours.
Exposure
To categorize infiltrate patterns and the presence and size of pleural effusions, we reviewed the final report from admission chest radiographs to obtain the final clinical interpretation performed by the attending pediatric radiologist. Infiltrate patterns were classified as single lobar (reference), unilateral multilobar, bilateral multilobar, or interstitial. Children with both lobar and interstitial infiltrates, and those with mention of atelectasis, were classified according to the type of lobar infiltrate. Those with atelectasis only were excluded. Pleural effusions were classified as absent, small, or moderate/large.
Analysis
Descriptive statistics were summarized using frequencies and percentages for categorical variables and median and interquartile range (IQR) values for continuous variables. Our primary exposures were infiltrate pattern and presence and size of pleural effusion on admission chest radiograph. Associations between radiographic findings and disease outcomes were analyzed using logistic and linear regression for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. Continuous outcomes were log‐transformed and normality assumptions verified prior to model development.
Due to the large number of covariates relative to outcome events, we used propensity score methods to adjust for potential confounding. The propensity score estimates the likelihood of a given exposure (ie, infiltrate pattern) conditional on a set of covariates. In this way, the propensity score summarizes potential confounding effects from a large number of covariates into a single variable. Including the propensity score as a covariate in multivariable regression improves model efficiency and helps protect against overfitting.[15] Covariates included in the estimation of the propensity score included age, sex, race/ethnicity, payer, hospital, asthma history, hospital transfer, recent hospitalization (within 30 days), recent emergency department or clinic visit (within 2 weeks), recent antibiotics for acute illness (within 5 days), illness duration prior to admission, tachypnea and/or increased work of breathing (retractions, nasal flaring, or grunting) at presentation, receipt of albuterol and/or corticosteroids during the first 2 calendar days of hospitalization, and concurrent diagnosis of bronchiolitis. All analyses included the estimated propensity score, infiltrate pattern, and pleural effusion (absent, small, or moderate/large).
RESULTS
Study Population
The median age of the 406 children with clinical and radiographic CAP was 3 years (IQR, 16 years) (Table 1). Single lobar infiltrate was the most common radiographic pattern (61%). Children with interstitial infiltrates (10%) were younger than those with lobar infiltrates of any type (median age 1 vs 3 years, P=0.02). A concomitant diagnosis of bronchiolitis was assigned to 34% of children with interstitial infiltrates but only 17% of those with lobar infiltrate patterns (range, 11%20%, P=0.03). Pleural effusion was present in 21% of children and was more common among those with lobar infiltrates, particularly multilobar disease. Only 1 child with interstitial infiltrate had a pleural effusion. Overall, 63% of children required supplemental oxygen, 8% required ICU admission, and 3% required invasive mechanical ventilation. Median length of stay was 51.5 hours (IQR, 3991) and median oxygen duration was 31.5 hours [IQR, 1365]. There were no deaths.
| Characteristic | Infiltrate Patterna | P Valueb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Lobar | Multilobar, Unilateral | Multilobar, Bilateral | Interstitial | ||
| |||||
| No. | 247 (60.8) | 54 (13.3) | 64 (15.8) | 41 (10.1) | |
| Median age, y | 3 [16] | 3 [17] | 3 [15] | 1 [03] | 0.02 |
| Male sex | 124 (50.2) | 32 (59.3) | 41 (64.1) | 30 (73.2) | 0.02 |
| Race | |||||
| Non‐Hispanic white | 133 (53.8) | 36 (66.7) | 37 (57.8) | 17 (41.5) | 0.69 |
| Non‐Hispanic black | 40 (16.2) | 6 (11.1) | 9 (14.1) | 8 (19.5) | |
| Hispanic | 25 (10.1) | 4 (7.4) | 5 (7.8) | 7 (17.1) | |
| Other | 49 (19.9) | 8 (14.8) | 13 (20.4) | 9 (22) | |
| Insurance | |||||
| Public | 130 (52.6) | 26 (48.1) | 33 (51.6) | 25 (61) | 0.90 |
| Private | 116 (47) | 28 (51.9) | 31 (48.4) | 16 (39) | |
| Concurrent diagnosis | |||||
| Asthma | 80 (32.4) | 16 (29.6) | 17 (26.6) | 12 (29.3) | 0.82 |
| Bronchiolitis | 43 (17.4) | 6 (11.1) | 13 (20.3) | 14 (34.1) | 0.03 |
| Effusion | |||||
| None | 201 (81.4) | 31 (57.4) | 48 (75) | 40 (97.6) | <.01 |
| Small | 34 (13.8) | 20 (37) | 11 (17.2) | 0 | |
| Moderate/large | 12 (4.9) | 3 (5.6) | 5 (7.8) | 1 (2.4) | |
Outcomes According to Radiographic Infiltrate Pattern
Compared to children with single lobar infiltrates, the odds of ICU admission was significantly increased for those with either unilateral or bilateral multilobar infiltrates (unilateral, adjusted odds ratio [aOR]: 8.0, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.922.2; bilateral, aOR: 6.6, 95% CI: 2.14.5) (Figure 1, Table 2). Patients with bilateral multilobar infiltrates also had higher odds for supplemental oxygen use (aOR: 2.7, 95% CI: 1.25.8) and need for invasive mechanical ventilation (aOR: 3.0, 95% CI: 1.27.9). There were no differences in duration of oxygen supplementation or hospital length of stay for children with single versus multilobar infiltrates.

| Outcome | Infiltrate Patterna | P Valueb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Lobar, n=247 | Multilobar, Unilateral, n=54 | Multilobar, Bilateral, n=64 | Interstitial, n=41 | ||
| |||||
| Supplemental O2 requirement | 143 (57.9) | 34 (63) | 46 (71.9) | 31 (75.6) | 0.05 |
| ICU admission | 10 (4) | 9 (16.7) | 9 (14.1) | 4 (9.8) | <0.01 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 5 (2) | 4 (7.4) | 4 (6.3) | 1 (2.4) | 0.13 |
| Hospital length of stay, h | 47 [3779] | 63 [45114] | 56.5 [39.5101] | 62 [3993] | <0.01 |
| O2 duration, h | 27 [1059] | 38 [1777] | 38 [2381] | 34.5 [1765] | 0.18 |
Compared to those with single lobar infiltrates, children with interstitial infiltrates had higher odds of need for supplemental oxygen (aOR: 3.1, 95% CI: 1.37.6) and ICU admission (aOR: 4.4, 95% CI: 1.314.3) but not invasive mechanical ventilation. There were also no differences in duration of oxygen supplementation or hospital length of stay.
Outcomes According to Presence and Size of Pleural Effusion
Compared to those without pleural effusion, children with moderate to large effusion had a higher odds of ICU admission (aOR: 3.2, 95% CI: 1.18.9) and invasive mechanical ventilation (aOR: 14.8, 95% CI: 9.822.4), and also had a longer duration of oxygen supplementation (aOR: 3.0, 95% CI: 1.46.5) and hospital length of stay (aOR: 2.6, 95% CI: 1.9‐3.6) (Table 3, Figure 2). The presence of a small pleural effusion was not associated with increased need for supplemental oxygen, ICU admission, or mechanical ventilation compared to those without effusion. However, small effusion was associated with a longer duration of oxygen supplementation (aOR: 1.7, 95% CI: 12.7) and hospital length of stay (aOR: 1.6, 95% CI: 1.3‐1.9).
| Outcome | Pleural Effusion | P Valuea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None, n=320 | Small, n=65 | Moderate/Large, n=21 | ||
| ||||
| Supplemental O2 requirement | 200 (62.5) | 40 (61.5) | 14 (66.7) | 0.91 |
| ICU admission | 22 (6.9) | 6 (9.2) | 4 (19) | 0.12 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 5 (1.6) | 5 (7.7) | 4 (19) | <0.01 |
| Hospital length of stay, h | 48 [37.576] | 72 [45142] | 160 [82191] | <0.01 |
| Oxygen duration, h | 31 [1157] | 38.5 [1887] | 111 [27154] | <0.01 |

DISCUSSION
We evaluated the association between admission chest radiographic findings and subsequent clinical outcomes and hospital care processes for children hospitalized with CAP at 4 children's hospitals in the United States. We conclude that radiographic findings are associated with important inpatient outcomes. Similar to data from adults, findings of moderate to large pleural effusions and bilateral multilobar infiltrates had the strongest associations with severe disease. Such information, in combination with other prognostic factors, may help clinicians identify high‐risk patients and support management decisions, while also helping to inform families about the expected hospital course.
Previous pediatric studies examining the association between radiographic findings and outcomes have produced inconsistent results.[8, 9, 10, 11, 12] All but 1 of these studies documented 1 radiographic characteristics associated with pneumonia disease severity.[11] Further, although most contrasted lobar/alveolar and interstitial infiltrates, only Patria et al. distinguished among lobar infiltrate patterns (eg, single lobar vs multilobar).[12] Similar to our findings, that study demonstrated increased disease severity among children with bilateral multifocal lobar infiltrates. Of the studies that considered the presence of pleural effusion, only 1 demonstrated this finding to be associated with more severe disease.[9] However, none of these prior studies examined size of the pleural effusion.
In our study, the strongest association with severe pneumonia outcomes was among children with moderate to large pleural effusion. Significant pleural effusions are much more commonly due to infection with bacterial pathogens, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pyogenes, and may also indicate infection with more virulent and/or difficult to treat strains.[16, 17, 18, 19] Surgical intervention is also often required. As such, children with significant pleural effusions are often more ill on presentation and may have a prolonged period of recovery.[20, 21, 22]
Similarly, multilobar infiltrates, particularly bilateral, were associated with increased disease severity in terms of need for supplemental oxygen, ICU admission, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation. Although this finding may be expected, it is interesting to note that the duration of supplemental oxygen and hospital length of stay were similar to those with single lobar disease. One potential explanation is that, although children with multilobar disease are more severe at presentation, rates of recovery are similar to those with less extensive radiographic findings, owing to rapidly effective antimicrobials for uncomplicated bacterial pneumonia. This hypothesis also agrees with the 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines, which state that children receiving adequate therapy typically show signs of improvement within 48 to 72 hours regardless of initial severity.[1]
Interstitial infiltrate was also associated with increased severity at presentation but similar length of stay and duration of oxygen requirement compared with single lobar disease. We note that these children were substantially younger than those presenting with any pattern of lobar disease (median age, 1 vs 3 years), were more likely to have a concurrent diagnosis of bronchiolitis (34% vs 17%), and only 1 child with interstitial infiltrates had a documented pleural effusion (vs 23% of children with lobar infiltrates). Primary viral pneumonia is considered more likely to produce interstitial infiltrates on chest radiograph compared to bacterial disease, and although detailed etiologic data are unavailable for this study, our findings above strongly support this assertion.[23, 24]
The 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines recommend admission chest radiographs for all children hospitalized with pneumonia to assess extent of disease and identify complications that may requiring additional evaluation or surgical intervention.[1] Our findings highlight additional potential benefits of admission radiographs in terms of disease prognosis and management decisions. In the initial evaluation of a sick child with pneumonia, clinicians are often presented with a number of potential prognostic factors that may influence disease outcomes. However, it is sometimes difficult for providers to consider all available information and/or the relative importance of a single factor, resulting in inaccurate risk perceptions and management decisions that may contribute to poor outcomes.[25] Similar to adults, the development of clinical prediction rules, which incorporate a variety of important predictors including admission radiographic findings, likely would improve risk assessments and potentially outcomes for children with pneumonia. Such prognostic information is also helpful for clinicians who may use these data to inform and prepare families regarding the expected course of hospitalization.
Our study has several limitations. This study was retrospective and only included a sample of pneumonia hospitalizations during the study period, which may raise confounding concerns and potential for selection bias. However, detailed medical record reviews using standardized case definitions for radiographic CAP were used, and a large sample of children was randomly selected from each institution. In addition, a large number of potential confounders were selected a priori and included in multivariable analyses; propensity score adjustment was used to reduce model complexity and avoid overfitting. Radiographic findings were based on clinical interpretation by pediatric radiologists independent of a study protocol. Prior studies have demonstrated good agreement for identification of alveolar/lobar infiltrates and pleural effusion by trained radiologists, although agreement for interstitial infiltrate is poor.[26, 27] This limitation could result in either over‐ or underestimation of the prevalence of interstitial infiltrates likely resulting in a nondifferential bias toward the null. Microbiologic information, which may inform radiographic findings and disease severity, was also not available. However, because pneumonia etiology is frequently unknown in the clinical setting, our study reflects typical practice. We also did not include children from community or nonteaching hospitals. Thus, although findings may have relevance to community or nonteaching hospitals, our results cannot be generalized.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrates that among children hospitalized with CAP, admission chest radiographic findings are associated with important clinical outcomes and hospital care processes, highlighting additional benefits of the 2011 PIDS/IDSA guidelines' recommendation for admission chest radiographs for all children hospitalized with pneumonia. These data, in conjunction with other important prognostic information, may help clinicians more rapidly identify children at increased risk for severe illness, and could also offer guidance regarding disease management strategies and facilitate shared decision making with families. Thus, routine admission chest radiography in this population represents a valuable tool that contributes to improved quality of care.
Disclosures
Dr. Williams is supported by funds from the National Institutes of HealthNational Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (K23AI104779). The authors report no conflicts of interest.
- , , , et al. The management of community‐acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53(7):e25–e76.
- , , , et al. A prediction rule to identify low‐risk patients with community‐acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(4):243–250.
- , , , et al. SMART‐COP: a tool for predicting the need for intensive respiratory or vasopressor support in community‐acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(3):375–384.
- , , , et al. Development and validation of a clinical prediction rule for severe community‐acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;174(11):1249–1256.
- , , , et al. Risk stratification of early admission to the intensive care unit of patients with no major criteria of severe community‐acquired pneumonia: development of an international prediction rule. Crit Care. 2009;13(2):R54.
- , , , et al. Do pulmonary radiographic findings at presentation predict mortality in patients with community‐acquired pneumonia? Arch Intern Med. 1996;156(19):2206–2212.
- , , , , , . Safety and efficacy of CURB65‐guided antibiotic therapy in community‐acquired pneumonia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(2):416–423.
- , , . Severity of childhood community‐acquired pneumonia and chest radiographic findings. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2009;44(3):249–252.
- , , , et al. Can chest x‐ray predict pneumonia severity? Pediatr Pulmonol. 2004;38(6):465–469.
- , , , . Children with pneumonia: how do they present and how are they managed? Arch Dis Child. 2007;92(5):394–398.
- , , . Role of chest X‐ray in predicting outcome of acute severe pneumonia. Indian Pediatr. 2008;45(11):893–898.
- , , , , , . Association between radiological findings and severity of community‐acquired pneumonia in children. Ital J Pediatr. 2013;39:56.
- , , , et al. Identifying pediatric community‐acquired pneumonia hospitalizations: accuracy of administrative billing codes. JAMA Pediatrics. 2013;167(9):851–858.
- , , , , , . Deaths attributed to pediatric complex chronic conditions: national trends and implications for supportive care services. Pediatrics. 2001;107(6):E99.
- , . Invited commentary: propensity scores. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;150(4):327–333.
- , , , . Increasing incidence of empyema complicating childhood community‐acquired pneumonia in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(6):805–813.
- , , , et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of community‐acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. Pediatrics. 2004;113(4):701–707.
- , , , et al. Molecular analysis improves pathogen identification and epidemiologic study of pediatric parapneumonic empyema. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30(4):289–294.
- , . Parapneumonic pleural effusion and empyema in children. Review of a 19‐year experience, 1962–1980. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1983;22(6):414–419.
- , , , et al. Risk factors of progressive community‐acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children: a prospective study [published online ahead of print August 28, 2013]. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2013.06.009.
- , , , , . Community‐acquired lobar pneumonia in children in the era of universal 7‐valent pneumococcal vaccination: a review of clinical presentations and antimicrobial treatment from a Canadian pediatric hospital. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:133.
- , , , et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of complicated pneumococcal pneumonia in a pediatric population. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006;41(8):726–734.
- , , , , , . Differentiation of bacterial and viral pneumonia in children. Thorax. 2002;57(5):438–441.
- , , , et al. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in children: update 2011. Thorax. 2011;66(suppl 2):ii1–ii23.
- , , , et al. Community acquired pneumonia: aetiology and usefulness of severity criteria on admission. Thorax. 1996;51(10):1010–1016.
- , , , et al. Variability in the interpretation of chest radiographs for the diagnosis of pneumonia in children. J Hosp Med. 2012;7(4):294–298.
- , , , et al. Interobserver reliability of the chest radiograph in community‐acquired pneumonia. PORT Investigators. Chest. 1996;110(2):343–350.
- , , , et al. The management of community‐acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53(7):e25–e76.
- , , , et al. A prediction rule to identify low‐risk patients with community‐acquired pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(4):243–250.
- , , , et al. SMART‐COP: a tool for predicting the need for intensive respiratory or vasopressor support in community‐acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(3):375–384.
- , , , et al. Development and validation of a clinical prediction rule for severe community‐acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;174(11):1249–1256.
- , , , et al. Risk stratification of early admission to the intensive care unit of patients with no major criteria of severe community‐acquired pneumonia: development of an international prediction rule. Crit Care. 2009;13(2):R54.
- , , , et al. Do pulmonary radiographic findings at presentation predict mortality in patients with community‐acquired pneumonia? Arch Intern Med. 1996;156(19):2206–2212.
- , , , , , . Safety and efficacy of CURB65‐guided antibiotic therapy in community‐acquired pneumonia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(2):416–423.
- , , . Severity of childhood community‐acquired pneumonia and chest radiographic findings. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2009;44(3):249–252.
- , , , et al. Can chest x‐ray predict pneumonia severity? Pediatr Pulmonol. 2004;38(6):465–469.
- , , , . Children with pneumonia: how do they present and how are they managed? Arch Dis Child. 2007;92(5):394–398.
- , , . Role of chest X‐ray in predicting outcome of acute severe pneumonia. Indian Pediatr. 2008;45(11):893–898.
- , , , , , . Association between radiological findings and severity of community‐acquired pneumonia in children. Ital J Pediatr. 2013;39:56.
- , , , et al. Identifying pediatric community‐acquired pneumonia hospitalizations: accuracy of administrative billing codes. JAMA Pediatrics. 2013;167(9):851–858.
- , , , , , . Deaths attributed to pediatric complex chronic conditions: national trends and implications for supportive care services. Pediatrics. 2001;107(6):E99.
- , . Invited commentary: propensity scores. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;150(4):327–333.
- , , , . Increasing incidence of empyema complicating childhood community‐acquired pneumonia in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(6):805–813.
- , , , et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of community‐acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. Pediatrics. 2004;113(4):701–707.
- , , , et al. Molecular analysis improves pathogen identification and epidemiologic study of pediatric parapneumonic empyema. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30(4):289–294.
- , . Parapneumonic pleural effusion and empyema in children. Review of a 19‐year experience, 1962–1980. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1983;22(6):414–419.
- , , , et al. Risk factors of progressive community‐acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children: a prospective study [published online ahead of print August 28, 2013]. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2013.06.009.
- , , , , . Community‐acquired lobar pneumonia in children in the era of universal 7‐valent pneumococcal vaccination: a review of clinical presentations and antimicrobial treatment from a Canadian pediatric hospital. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:133.
- , , , et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of complicated pneumococcal pneumonia in a pediatric population. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006;41(8):726–734.
- , , , , , . Differentiation of bacterial and viral pneumonia in children. Thorax. 2002;57(5):438–441.
- , , , et al. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in children: update 2011. Thorax. 2011;66(suppl 2):ii1–ii23.
- , , , et al. Community acquired pneumonia: aetiology and usefulness of severity criteria on admission. Thorax. 1996;51(10):1010–1016.
- , , , et al. Variability in the interpretation of chest radiographs for the diagnosis of pneumonia in children. J Hosp Med. 2012;7(4):294–298.
- , , , et al. Interobserver reliability of the chest radiograph in community‐acquired pneumonia. PORT Investigators. Chest. 1996;110(2):343–350.
© 2014 Society of Hospital Medicine