User login
Purpura fulminans is a hematologic emergency, with clinical skin necrosis and laboratory testing showing disseminated intravascular coagulation. The thrombotic occlusion usually affects small and medium-sized blood vessels and may involve any organ. Purpura fulminans has been implicated with sepsis, most commonly meningococcal infections; other infections such as Staphylococcus aureus, groups A and B β-hemolytic streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae; and as a sequela to benign childhood infections, such as varicella. Other associations with purpura fulminans include autoimmune disease and heritable or acquired deficiency of anticoagulant proteins, most commonly protein C. We present a rare case of purpura fulminans as the presenting sign of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), an aggressive primary nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma with a high mortality rate and nonspecific skin manifestations in roughly half of all patients involved.
Case Report
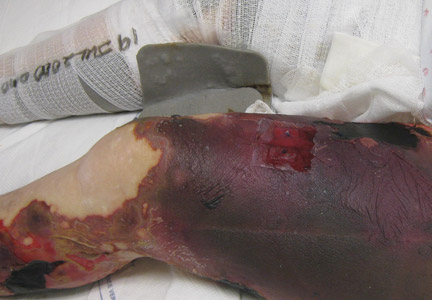
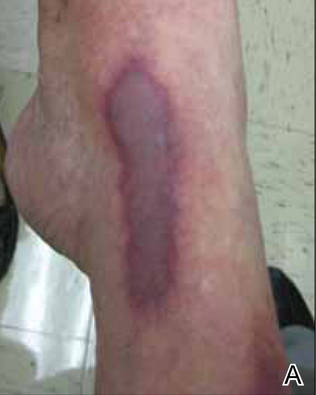
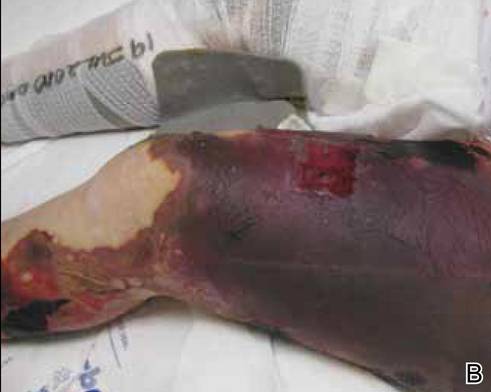
A 56-year-old woman presented with purpuric patches on the left foot (Figure 1A). Seven days after presentation the lesion progressed into ecchymotic geographic plaques and hemorrhagic bullae that spread upward and contralaterally, sparing the digits, trunk, head, neck, and mucous membranes. Ultimately, the involved skin became necrotic and involved 20% of the body surface area (Figure 1B). The lesions were painful with a burning sensation but were not pruritic. The patient also reported intermittent fevers, chills, myalgia, nausea, and shortness of breath. Enlarged lymph nodes were present in the right cervical chain. She denied new medications; stated she had been in good health prior to this episode; and had no history of spontaneous abortion, neurologic symptoms, or other serious illness.
  |
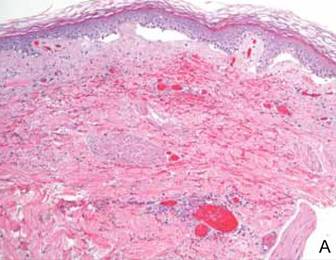
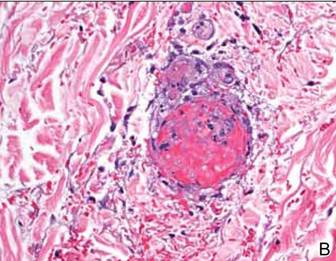
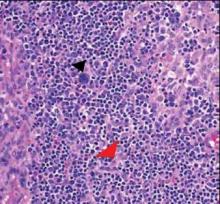
Computed tomography showed prominent diffuse mediastinal, mesenteric, retroperitoneal, and pelvic lymphadenopathy with involvement of the cervical and inguinal areas. Laboratory values showed thrombocytopenia and increased fibrin degradation products. Blood and tissue cultures were negative; the patient also had a negative viral serology, except for Epstein-Barr virus IgG titers (>1:2560). A skin biopsy of the left thigh demonstrated venules and capillaries in the mid and superficial dermis filled with fibrin thrombi without vasculitis (Figure 2). A lymph node biopsy was consistent with a diagnosis of AITL. The lymph node architecture was largely effaced by a polymorphous lymphoid infiltrate that predominantly expanded into paracortical areas and was associated with a prominent arborizing vascular proliferation. The infiltrate was composed of lymphocytes ranging in size from small to medium, with ample cytoplasm, coarsely clumped chromatin, and mildly irregular nuclear membranes. Large atypical lymphocytes with features of immunoblasts were easily identified. An associated inflammatory background composed of eosinophils, plasma cells, and histiocytes was present (Figure 3). The atypical lymphocytes stained positive for CD3and CD10 on immunohistochemistry. Additionally, a subset of large immunoblastlike lymphocytes was positive for Epstein-Barr–encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization.
|
The patient was started on rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone. She received 2 cycles with positive response based on subsequent computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans that showed regression of her disease as well as the lack of formation of new skin lesions. She was transferred to a burn unit where she had continuing treatment and skin grafts. Despite 2 cycles of chemotherapy, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and daily wound care management, the patient died secondary to sepsis 6 months after presentation.
Comment
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma is a primary nodal lymphoma with occasional cutaneous involvement. Cutaneous manifestations occur in roughly half of all patients with AITL1 and have mainly been described as erythematous macules and papules that can resemble a viral exanthem or a drug reaction.2 However, other skin manifestations include urticaria, papulovesicular lesions, nodules, erythroderma,3 and to a lesser degree purpura.4 The lesions have been noted to occur prior to, concurrent with, or anytime during the disease.3,5,6 This aggressive lymphoma has mortality rates ranging from 50% to 72%, and median survival ranges from 11 to 30 months.6
To arrive at the correct diagnosis of AITL, a nodal biopsy with immunochemistry is necessary. Classic findings on histopathology include effacement of normal architecture, marked vascular proliferation, and aggregates of atypical lymphoid cells. CD10 has been shown to be a good objective criterion for the diagnosis of AITL,4 with characteristic tumor cells expressing CD10. Nodal Epstein-Barr virus–positive lymphocytes often are present.2 Other T-cell lymphomas with primarily nodal presentation along with peripheral T-cell lymphoma include peripheral T-cell lymphoma unspecified type and anaplastic large cell lymphoma, according to the World Health Organization classification.7 Anaplastic large cell lymphoma is easily distinguished from AITL based on histopathology, immunostaining, and clinical presentation. Until recently, peripheral T-cell lymphoma unspecified type and reactive lymphoid hyperplasia presented a challenge to differentiate from AITL, especially in the early phases of the disease; however, the introduction of CD10 as a phenotypic marker has been instrumental in distinguishing AITL from other T-cell lymphomas with primary nodal involvement.1,4
The development of purpura fulminans and disseminated intravascular coagulation in a patient with AITL is rare. Although the exact mechanism for the thrombus formation in the skin has not been elucidated, purpura fulminans typically develops secondary to a severe infection. The exact incidence of purpura fulminans in the setting of AITL is unknown, but purpura as a cutaneous eruption has been associated as a clinical finding in AITL.6 Although our case may be a rare presentation of AITL, a prompt and accurate diagnosis can drastically change the prognosis of this aggressive disease.
1. Ferry JA. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 2002;9:273-279.
2. Brown HA, Macon WR, Kurtin PJ, et al. Cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with remarkable heterogeneous Epstein-Barr virus expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:432-438.
3. Bernstein JE, Soltani K, Lorincz AL. Cutaneous manifestations of angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979;1:227-232.
4. Attygalle A, Al-Jehani R, Diss TC, et al. Neoplastic T cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma express CD10. Blood. 2002;99:627-633.
5. Jayaramna AG, Cassarino D, Advani R, et al. Cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: a unique histologic presentation, mimicking an infectious etiology. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33(suppl 2):6-11.
6. Martel P, Laroche L, Courville P, et al. Cutaneous involvement in patients with angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy with dysproteinemia: a clinical, immunohistological, and molecular analysis. Archives of Dermatology. 2000;136:881-886.
7. Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, et al, eds. Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 1st ed. Bethesda, MD: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2001.
Purpura fulminans is a hematologic emergency, with clinical skin necrosis and laboratory testing showing disseminated intravascular coagulation. The thrombotic occlusion usually affects small and medium-sized blood vessels and may involve any organ. Purpura fulminans has been implicated with sepsis, most commonly meningococcal infections; other infections such as Staphylococcus aureus, groups A and B β-hemolytic streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae; and as a sequela to benign childhood infections, such as varicella. Other associations with purpura fulminans include autoimmune disease and heritable or acquired deficiency of anticoagulant proteins, most commonly protein C. We present a rare case of purpura fulminans as the presenting sign of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), an aggressive primary nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma with a high mortality rate and nonspecific skin manifestations in roughly half of all patients involved.
Case Report
A 56-year-old woman presented with purpuric patches on the left foot (Figure 1A). Seven days after presentation the lesion progressed into ecchymotic geographic plaques and hemorrhagic bullae that spread upward and contralaterally, sparing the digits, trunk, head, neck, and mucous membranes. Ultimately, the involved skin became necrotic and involved 20% of the body surface area (Figure 1B). The lesions were painful with a burning sensation but were not pruritic. The patient also reported intermittent fevers, chills, myalgia, nausea, and shortness of breath. Enlarged lymph nodes were present in the right cervical chain. She denied new medications; stated she had been in good health prior to this episode; and had no history of spontaneous abortion, neurologic symptoms, or other serious illness.
  |
Computed tomography showed prominent diffuse mediastinal, mesenteric, retroperitoneal, and pelvic lymphadenopathy with involvement of the cervical and inguinal areas. Laboratory values showed thrombocytopenia and increased fibrin degradation products. Blood and tissue cultures were negative; the patient also had a negative viral serology, except for Epstein-Barr virus IgG titers (>1:2560). A skin biopsy of the left thigh demonstrated venules and capillaries in the mid and superficial dermis filled with fibrin thrombi without vasculitis (Figure 2). A lymph node biopsy was consistent with a diagnosis of AITL. The lymph node architecture was largely effaced by a polymorphous lymphoid infiltrate that predominantly expanded into paracortical areas and was associated with a prominent arborizing vascular proliferation. The infiltrate was composed of lymphocytes ranging in size from small to medium, with ample cytoplasm, coarsely clumped chromatin, and mildly irregular nuclear membranes. Large atypical lymphocytes with features of immunoblasts were easily identified. An associated inflammatory background composed of eosinophils, plasma cells, and histiocytes was present (Figure 3). The atypical lymphocytes stained positive for CD3and CD10 on immunohistochemistry. Additionally, a subset of large immunoblastlike lymphocytes was positive for Epstein-Barr–encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization.
|
The patient was started on rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone. She received 2 cycles with positive response based on subsequent computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans that showed regression of her disease as well as the lack of formation of new skin lesions. She was transferred to a burn unit where she had continuing treatment and skin grafts. Despite 2 cycles of chemotherapy, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and daily wound care management, the patient died secondary to sepsis 6 months after presentation.
Comment
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma is a primary nodal lymphoma with occasional cutaneous involvement. Cutaneous manifestations occur in roughly half of all patients with AITL1 and have mainly been described as erythematous macules and papules that can resemble a viral exanthem or a drug reaction.2 However, other skin manifestations include urticaria, papulovesicular lesions, nodules, erythroderma,3 and to a lesser degree purpura.4 The lesions have been noted to occur prior to, concurrent with, or anytime during the disease.3,5,6 This aggressive lymphoma has mortality rates ranging from 50% to 72%, and median survival ranges from 11 to 30 months.6
To arrive at the correct diagnosis of AITL, a nodal biopsy with immunochemistry is necessary. Classic findings on histopathology include effacement of normal architecture, marked vascular proliferation, and aggregates of atypical lymphoid cells. CD10 has been shown to be a good objective criterion for the diagnosis of AITL,4 with characteristic tumor cells expressing CD10. Nodal Epstein-Barr virus–positive lymphocytes often are present.2 Other T-cell lymphomas with primarily nodal presentation along with peripheral T-cell lymphoma include peripheral T-cell lymphoma unspecified type and anaplastic large cell lymphoma, according to the World Health Organization classification.7 Anaplastic large cell lymphoma is easily distinguished from AITL based on histopathology, immunostaining, and clinical presentation. Until recently, peripheral T-cell lymphoma unspecified type and reactive lymphoid hyperplasia presented a challenge to differentiate from AITL, especially in the early phases of the disease; however, the introduction of CD10 as a phenotypic marker has been instrumental in distinguishing AITL from other T-cell lymphomas with primary nodal involvement.1,4
The development of purpura fulminans and disseminated intravascular coagulation in a patient with AITL is rare. Although the exact mechanism for the thrombus formation in the skin has not been elucidated, purpura fulminans typically develops secondary to a severe infection. The exact incidence of purpura fulminans in the setting of AITL is unknown, but purpura as a cutaneous eruption has been associated as a clinical finding in AITL.6 Although our case may be a rare presentation of AITL, a prompt and accurate diagnosis can drastically change the prognosis of this aggressive disease.
Purpura fulminans is a hematologic emergency, with clinical skin necrosis and laboratory testing showing disseminated intravascular coagulation. The thrombotic occlusion usually affects small and medium-sized blood vessels and may involve any organ. Purpura fulminans has been implicated with sepsis, most commonly meningococcal infections; other infections such as Staphylococcus aureus, groups A and B β-hemolytic streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae; and as a sequela to benign childhood infections, such as varicella. Other associations with purpura fulminans include autoimmune disease and heritable or acquired deficiency of anticoagulant proteins, most commonly protein C. We present a rare case of purpura fulminans as the presenting sign of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), an aggressive primary nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma with a high mortality rate and nonspecific skin manifestations in roughly half of all patients involved.
Case Report
A 56-year-old woman presented with purpuric patches on the left foot (Figure 1A). Seven days after presentation the lesion progressed into ecchymotic geographic plaques and hemorrhagic bullae that spread upward and contralaterally, sparing the digits, trunk, head, neck, and mucous membranes. Ultimately, the involved skin became necrotic and involved 20% of the body surface area (Figure 1B). The lesions were painful with a burning sensation but were not pruritic. The patient also reported intermittent fevers, chills, myalgia, nausea, and shortness of breath. Enlarged lymph nodes were present in the right cervical chain. She denied new medications; stated she had been in good health prior to this episode; and had no history of spontaneous abortion, neurologic symptoms, or other serious illness.
  |
Computed tomography showed prominent diffuse mediastinal, mesenteric, retroperitoneal, and pelvic lymphadenopathy with involvement of the cervical and inguinal areas. Laboratory values showed thrombocytopenia and increased fibrin degradation products. Blood and tissue cultures were negative; the patient also had a negative viral serology, except for Epstein-Barr virus IgG titers (>1:2560). A skin biopsy of the left thigh demonstrated venules and capillaries in the mid and superficial dermis filled with fibrin thrombi without vasculitis (Figure 2). A lymph node biopsy was consistent with a diagnosis of AITL. The lymph node architecture was largely effaced by a polymorphous lymphoid infiltrate that predominantly expanded into paracortical areas and was associated with a prominent arborizing vascular proliferation. The infiltrate was composed of lymphocytes ranging in size from small to medium, with ample cytoplasm, coarsely clumped chromatin, and mildly irregular nuclear membranes. Large atypical lymphocytes with features of immunoblasts were easily identified. An associated inflammatory background composed of eosinophils, plasma cells, and histiocytes was present (Figure 3). The atypical lymphocytes stained positive for CD3and CD10 on immunohistochemistry. Additionally, a subset of large immunoblastlike lymphocytes was positive for Epstein-Barr–encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization.
|
The patient was started on rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone. She received 2 cycles with positive response based on subsequent computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans that showed regression of her disease as well as the lack of formation of new skin lesions. She was transferred to a burn unit where she had continuing treatment and skin grafts. Despite 2 cycles of chemotherapy, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and daily wound care management, the patient died secondary to sepsis 6 months after presentation.
Comment
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma is a primary nodal lymphoma with occasional cutaneous involvement. Cutaneous manifestations occur in roughly half of all patients with AITL1 and have mainly been described as erythematous macules and papules that can resemble a viral exanthem or a drug reaction.2 However, other skin manifestations include urticaria, papulovesicular lesions, nodules, erythroderma,3 and to a lesser degree purpura.4 The lesions have been noted to occur prior to, concurrent with, or anytime during the disease.3,5,6 This aggressive lymphoma has mortality rates ranging from 50% to 72%, and median survival ranges from 11 to 30 months.6
To arrive at the correct diagnosis of AITL, a nodal biopsy with immunochemistry is necessary. Classic findings on histopathology include effacement of normal architecture, marked vascular proliferation, and aggregates of atypical lymphoid cells. CD10 has been shown to be a good objective criterion for the diagnosis of AITL,4 with characteristic tumor cells expressing CD10. Nodal Epstein-Barr virus–positive lymphocytes often are present.2 Other T-cell lymphomas with primarily nodal presentation along with peripheral T-cell lymphoma include peripheral T-cell lymphoma unspecified type and anaplastic large cell lymphoma, according to the World Health Organization classification.7 Anaplastic large cell lymphoma is easily distinguished from AITL based on histopathology, immunostaining, and clinical presentation. Until recently, peripheral T-cell lymphoma unspecified type and reactive lymphoid hyperplasia presented a challenge to differentiate from AITL, especially in the early phases of the disease; however, the introduction of CD10 as a phenotypic marker has been instrumental in distinguishing AITL from other T-cell lymphomas with primary nodal involvement.1,4
The development of purpura fulminans and disseminated intravascular coagulation in a patient with AITL is rare. Although the exact mechanism for the thrombus formation in the skin has not been elucidated, purpura fulminans typically develops secondary to a severe infection. The exact incidence of purpura fulminans in the setting of AITL is unknown, but purpura as a cutaneous eruption has been associated as a clinical finding in AITL.6 Although our case may be a rare presentation of AITL, a prompt and accurate diagnosis can drastically change the prognosis of this aggressive disease.
1. Ferry JA. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 2002;9:273-279.
2. Brown HA, Macon WR, Kurtin PJ, et al. Cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with remarkable heterogeneous Epstein-Barr virus expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:432-438.
3. Bernstein JE, Soltani K, Lorincz AL. Cutaneous manifestations of angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979;1:227-232.
4. Attygalle A, Al-Jehani R, Diss TC, et al. Neoplastic T cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma express CD10. Blood. 2002;99:627-633.
5. Jayaramna AG, Cassarino D, Advani R, et al. Cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: a unique histologic presentation, mimicking an infectious etiology. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33(suppl 2):6-11.
6. Martel P, Laroche L, Courville P, et al. Cutaneous involvement in patients with angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy with dysproteinemia: a clinical, immunohistological, and molecular analysis. Archives of Dermatology. 2000;136:881-886.
7. Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, et al, eds. Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 1st ed. Bethesda, MD: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2001.
1. Ferry JA. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 2002;9:273-279.
2. Brown HA, Macon WR, Kurtin PJ, et al. Cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with remarkable heterogeneous Epstein-Barr virus expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28:432-438.
3. Bernstein JE, Soltani K, Lorincz AL. Cutaneous manifestations of angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979;1:227-232.
4. Attygalle A, Al-Jehani R, Diss TC, et al. Neoplastic T cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma express CD10. Blood. 2002;99:627-633.
5. Jayaramna AG, Cassarino D, Advani R, et al. Cutaneous involvement by angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: a unique histologic presentation, mimicking an infectious etiology. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33(suppl 2):6-11.
6. Martel P, Laroche L, Courville P, et al. Cutaneous involvement in patients with angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy with dysproteinemia: a clinical, immunohistological, and molecular analysis. Archives of Dermatology. 2000;136:881-886.
7. Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, et al, eds. Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 1st ed. Bethesda, MD: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2001.
Practice Points
- Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) is a primary nodal lymphoma with occasional nonspecific cutaneous involvement that may be morbilliform, maculopapular, erythrodermic, or rarely purpuric.
- To arrive at the correct diagnosis of AITL, a nodal biopsy with immunochemistry is necessary.
- CD10 positivity is a good objective criterion for the diagnosis of AITL, and Epstein-Barr virus–positive lymphocytes are nearly always present.