User login
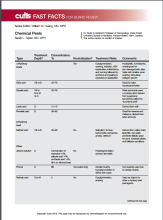
Chemical Peels
After, test your knowledge by answering the 5 practice questions.
Practice Questions
1. Which one of the following peels produces “frosting” after application?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
2. Which one of the following peels is lipophilic?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
3. A Jessner solution peel contains which of the following 4 components?
a. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, ethanol
b. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, methanol
c. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, retinoic acid
d. retinoic acid, resorcinol, phenol, ethanol
e. retinoic acid, resorcinol, glycolic acid, methanol
4. What is the most serious risk associated with phenol peels?
a. cardiac dysrhythmia
b. hearing loss
c. scarring
d. seizure
e. tinnitus
5. Which one of the following peels self-neutralizes?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. lactic acid
d. mandelic acid
e. salicylic acid
The answers appear on the next page.
Practice Question Answers
1. Which one of the following peels produces “frosting” after application?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
2. Which one of the following peels is lipophilic?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
3. A Jessner solution peel contains which of the following 4 components?
a. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, ethanol
b. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, methanol
c. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, retinoic acid
d. retinoic acid, resorcinol, phenol, ethanol
e. retinoic acid, resorcinol, glycolic acid, methanol
4. What is the most serious risk associated with phenol peels?
a. cardiac dysrhythmia
b. hearing loss
c. scarring
d. seizure
e. tinnitus
5. Which one of the following peels self-neutralizes?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. lactic acid
d. mandelic acid
e. salicylic acid
After, test your knowledge by answering the 5 practice questions.
Practice Questions
1. Which one of the following peels produces “frosting” after application?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
2. Which one of the following peels is lipophilic?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
3. A Jessner solution peel contains which of the following 4 components?
a. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, ethanol
b. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, methanol
c. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, retinoic acid
d. retinoic acid, resorcinol, phenol, ethanol
e. retinoic acid, resorcinol, glycolic acid, methanol
4. What is the most serious risk associated with phenol peels?
a. cardiac dysrhythmia
b. hearing loss
c. scarring
d. seizure
e. tinnitus
5. Which one of the following peels self-neutralizes?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. lactic acid
d. mandelic acid
e. salicylic acid
The answers appear on the next page.
Practice Question Answers
1. Which one of the following peels produces “frosting” after application?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
2. Which one of the following peels is lipophilic?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
3. A Jessner solution peel contains which of the following 4 components?
a. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, ethanol
b. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, methanol
c. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, retinoic acid
d. retinoic acid, resorcinol, phenol, ethanol
e. retinoic acid, resorcinol, glycolic acid, methanol
4. What is the most serious risk associated with phenol peels?
a. cardiac dysrhythmia
b. hearing loss
c. scarring
d. seizure
e. tinnitus
5. Which one of the following peels self-neutralizes?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. lactic acid
d. mandelic acid
e. salicylic acid
After, test your knowledge by answering the 5 practice questions.
Practice Questions
1. Which one of the following peels produces “frosting” after application?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
2. Which one of the following peels is lipophilic?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
3. A Jessner solution peel contains which of the following 4 components?
a. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, ethanol
b. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, methanol
c. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, retinoic acid
d. retinoic acid, resorcinol, phenol, ethanol
e. retinoic acid, resorcinol, glycolic acid, methanol
4. What is the most serious risk associated with phenol peels?
a. cardiac dysrhythmia
b. hearing loss
c. scarring
d. seizure
e. tinnitus
5. Which one of the following peels self-neutralizes?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. lactic acid
d. mandelic acid
e. salicylic acid
The answers appear on the next page.
Practice Question Answers
1. Which one of the following peels produces “frosting” after application?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
2. Which one of the following peels is lipophilic?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. mandelic acid
d. salicylic acid
e. trichloroacetic acid
3. A Jessner solution peel contains which of the following 4 components?
a. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, ethanol
b. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, methanol
c. lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, retinoic acid
d. retinoic acid, resorcinol, phenol, ethanol
e. retinoic acid, resorcinol, glycolic acid, methanol
4. What is the most serious risk associated with phenol peels?
a. cardiac dysrhythmia
b. hearing loss
c. scarring
d. seizure
e. tinnitus
5. Which one of the following peels self-neutralizes?
a. citric acid
b. glycolic acid
c. lactic acid
d. mandelic acid
e. salicylic acid
Sunscreen Agents
Neurotoxins
Practice Question Answers: Lasers for Tattoo Removal
1. Which tattoo color is most commonly associated with allergic reactions that are eczematous, lichenoid, or granulomatous?
a. orange
b. purple
c. red
d. white
e. yellow
2. Which of the following lasers is the optimal device to use for tattoo removal?
a. argon laser
b. CO2
c. intense pulsed light
d. pulsed dye laser
e. quality-switched ruby, alexandrite, or Nd:YAG laser
3. Which of the following is the most important treatment end point in tattoo removal?
a. edema
b. erythema
c. immediate darkening
d. immediate whitening
e. pinpoint bleeding
4. Which of the following organisms recently has been implicated in tattoo infections?
a. Mycobacterium chelonae
b. Mycobacterium ulcerans
c. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
d. Staphylococcus aureus
e. Streptococcus pyogenes
5. Darkening of which tattoo color(s) is the most frequently associated and worrisome side effect from a quality-switched laser?
a. light red
b. pink
c. white
d. a and b
e. a, b, and c
1. Which tattoo color is most commonly associated with allergic reactions that are eczematous, lichenoid, or granulomatous?
a. orange
b. purple
c. red
d. white
e. yellow
2. Which of the following lasers is the optimal device to use for tattoo removal?
a. argon laser
b. CO2
c. intense pulsed light
d. pulsed dye laser
e. quality-switched ruby, alexandrite, or Nd:YAG laser
3. Which of the following is the most important treatment end point in tattoo removal?
a. edema
b. erythema
c. immediate darkening
d. immediate whitening
e. pinpoint bleeding
4. Which of the following organisms recently has been implicated in tattoo infections?
a. Mycobacterium chelonae
b. Mycobacterium ulcerans
c. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
d. Staphylococcus aureus
e. Streptococcus pyogenes
5. Darkening of which tattoo color(s) is the most frequently associated and worrisome side effect from a quality-switched laser?
a. light red
b. pink
c. white
d. a and b
e. a, b, and c
1. Which tattoo color is most commonly associated with allergic reactions that are eczematous, lichenoid, or granulomatous?
a. orange
b. purple
c. red
d. white
e. yellow
2. Which of the following lasers is the optimal device to use for tattoo removal?
a. argon laser
b. CO2
c. intense pulsed light
d. pulsed dye laser
e. quality-switched ruby, alexandrite, or Nd:YAG laser
3. Which of the following is the most important treatment end point in tattoo removal?
a. edema
b. erythema
c. immediate darkening
d. immediate whitening
e. pinpoint bleeding
4. Which of the following organisms recently has been implicated in tattoo infections?
a. Mycobacterium chelonae
b. Mycobacterium ulcerans
c. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
d. Staphylococcus aureus
e. Streptococcus pyogenes
5. Darkening of which tattoo color(s) is the most frequently associated and worrisome side effect from a quality-switched laser?
a. light red
b. pink
c. white
d. a and b
e. a, b, and c