User login
Excision of abdominal wall endometriosis
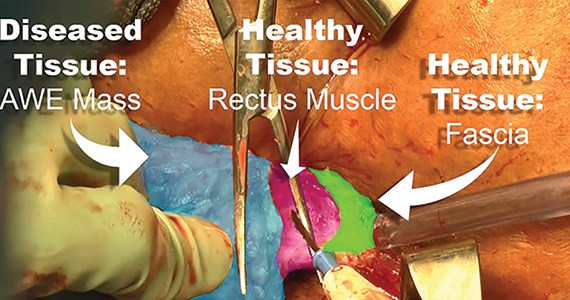
Endometriosis, defined by the ectopic growth of functioning endometrial glands and stroma,1,2 usually affects the peritoneal cavity. However, endometriosis has been identified in the pneumothorax, brain, and within the extraperitoneum, such as the abdominal wall.1-3 Incidence of abdominal wall endometriosis can be up to 12%.3-5 If patients report symptoms, they can include abdominal pain, a palpable mass, pelvic pain consistent with endometriosis, and bleeding from involvement of the overlying skin. Abdominal wall endometriosis can be surgically resected, with complete resolution and a low rate of recurrence.
In the following video, we review the diagnosis of abdominal wall endometriosis, including our imaging of choice, and treatment options. In addition, we illustrate a surgical technique for the excision of abdominal wall endometriosis in a 38-year-old patient with symptomatic disease. We conclude with a review of key surgical steps.
We hope that you find this video useful to your clinical practice.
>> Dr. Arnold P. Advincula, and colleagues

- Burney RO, Giudice LC. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:511-519.
- Ecker AM, Donnellan NM, Shepherd JP, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis: 12 years of experience at a large academic institution. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;211:363.e1-e5.
- Horton JD, Dezee KJ, Ahnfeldt EP, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis: a surgeon’s perspective and review of 445 cases. Am J Surg. 2008;196:207-212.
- Ding Y, Zhu J. A retrospective review of abdominal wall endometriosis in Shanghai, China. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2013;121:41-44.
- Chang Y, Tsai EM, Long CY, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis. J Reproductive Med. 2009;54:155-159.
Endometriosis, defined by the ectopic growth of functioning endometrial glands and stroma,1,2 usually affects the peritoneal cavity. However, endometriosis has been identified in the pneumothorax, brain, and within the extraperitoneum, such as the abdominal wall.1-3 Incidence of abdominal wall endometriosis can be up to 12%.3-5 If patients report symptoms, they can include abdominal pain, a palpable mass, pelvic pain consistent with endometriosis, and bleeding from involvement of the overlying skin. Abdominal wall endometriosis can be surgically resected, with complete resolution and a low rate of recurrence.
In the following video, we review the diagnosis of abdominal wall endometriosis, including our imaging of choice, and treatment options. In addition, we illustrate a surgical technique for the excision of abdominal wall endometriosis in a 38-year-old patient with symptomatic disease. We conclude with a review of key surgical steps.
We hope that you find this video useful to your clinical practice.
>> Dr. Arnold P. Advincula, and colleagues

Endometriosis, defined by the ectopic growth of functioning endometrial glands and stroma,1,2 usually affects the peritoneal cavity. However, endometriosis has been identified in the pneumothorax, brain, and within the extraperitoneum, such as the abdominal wall.1-3 Incidence of abdominal wall endometriosis can be up to 12%.3-5 If patients report symptoms, they can include abdominal pain, a palpable mass, pelvic pain consistent with endometriosis, and bleeding from involvement of the overlying skin. Abdominal wall endometriosis can be surgically resected, with complete resolution and a low rate of recurrence.
In the following video, we review the diagnosis of abdominal wall endometriosis, including our imaging of choice, and treatment options. In addition, we illustrate a surgical technique for the excision of abdominal wall endometriosis in a 38-year-old patient with symptomatic disease. We conclude with a review of key surgical steps.
We hope that you find this video useful to your clinical practice.
>> Dr. Arnold P. Advincula, and colleagues

- Burney RO, Giudice LC. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:511-519.
- Ecker AM, Donnellan NM, Shepherd JP, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis: 12 years of experience at a large academic institution. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;211:363.e1-e5.
- Horton JD, Dezee KJ, Ahnfeldt EP, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis: a surgeon’s perspective and review of 445 cases. Am J Surg. 2008;196:207-212.
- Ding Y, Zhu J. A retrospective review of abdominal wall endometriosis in Shanghai, China. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2013;121:41-44.
- Chang Y, Tsai EM, Long CY, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis. J Reproductive Med. 2009;54:155-159.
- Burney RO, Giudice LC. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012;98:511-519.
- Ecker AM, Donnellan NM, Shepherd JP, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis: 12 years of experience at a large academic institution. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;211:363.e1-e5.
- Horton JD, Dezee KJ, Ahnfeldt EP, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis: a surgeon’s perspective and review of 445 cases. Am J Surg. 2008;196:207-212.
- Ding Y, Zhu J. A retrospective review of abdominal wall endometriosis in Shanghai, China. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2013;121:41-44.
- Chang Y, Tsai EM, Long CY, et al. Abdominal wall endometriosis. J Reproductive Med. 2009;54:155-159.
Minilaparotomy: Minimally invasive approach to abdominal myomectomy
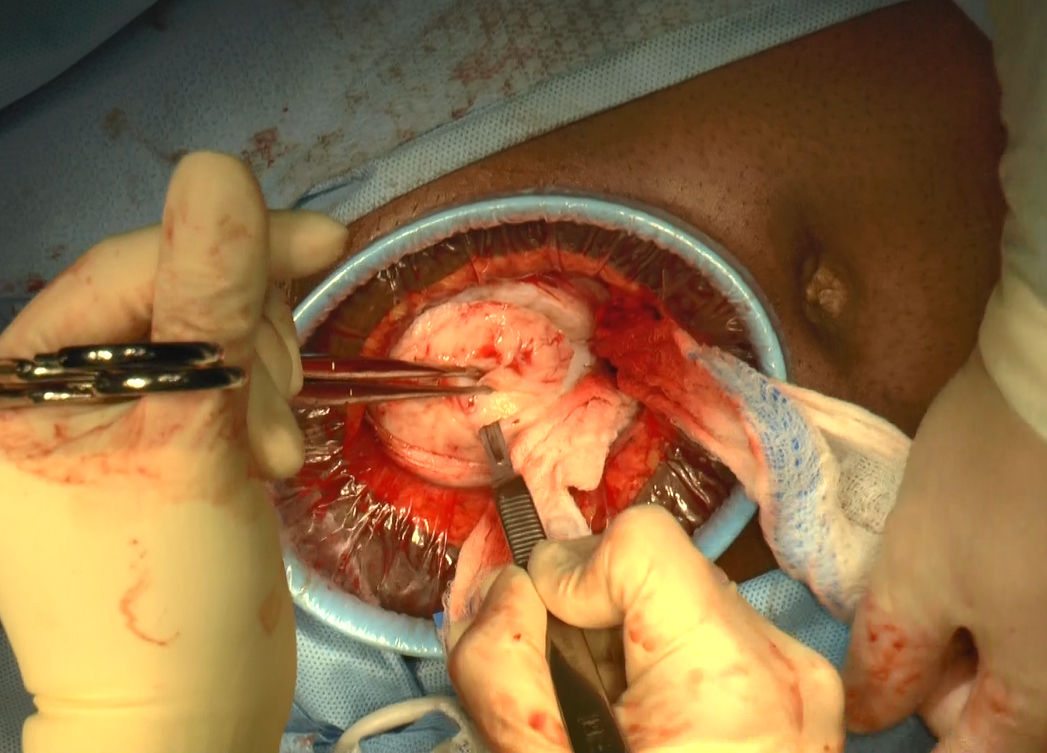
A minilaparotomy is loosely defined as a laparotomy measuring between 4 cm and 6 cm. For the appropriate surgical candidate, a minilaparotomy is a useful alternative to laparotomy or laparoscopy, especially for large pathology.1 Benefits of minilaparotomy include improved pain management and postoperative recovery, as well as improved cosmetic outcome, with comparable blood loss and operative time.2,3

In this video, we illustrate the key surgical steps of a minilaparotomy for the removal of large fibroids. These steps include:
- strategic vertical skin incision
- use of a self-retaining retractor
- infiltrate myometrium with dilute vasopressin
- strategic hysterotomy
- use of tenaculum for upward traction
- 10# blade scalpels for the “lemon wedge” coring technique
- layered closure.
Minilaparotomy myomectomy can be an excellent minimally invasive alternative to a traditional “full laparotomy” for women with large fibroids.
We hope that you find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.
>> Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Laparoscopic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy via minilaparotomy assistance for the massively enlarged adnexal mass
- Pelosi MA 2nd, Pelosi MA 3rd. Pelosi minilaparotomy hysterectomy: a non-endoscopic minimally invasive alternative to laparoscopy and laparotomy. Surg Technol Int. 2004;13:157-167.
- Fanafani F, Fagotti A, Longo R. Minilaparotomy in the management of benign gynecologic disease. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2005;119:232-236.
- Glasser MH. Minilaparotomy: a minimally invasive alternative for major gynecologic abdominal surgery. Perm J. 2005;9:41-45.
A minilaparotomy is loosely defined as a laparotomy measuring between 4 cm and 6 cm. For the appropriate surgical candidate, a minilaparotomy is a useful alternative to laparotomy or laparoscopy, especially for large pathology.1 Benefits of minilaparotomy include improved pain management and postoperative recovery, as well as improved cosmetic outcome, with comparable blood loss and operative time.2,3

In this video, we illustrate the key surgical steps of a minilaparotomy for the removal of large fibroids. These steps include:
- strategic vertical skin incision
- use of a self-retaining retractor
- infiltrate myometrium with dilute vasopressin
- strategic hysterotomy
- use of tenaculum for upward traction
- 10# blade scalpels for the “lemon wedge” coring technique
- layered closure.
Minilaparotomy myomectomy can be an excellent minimally invasive alternative to a traditional “full laparotomy” for women with large fibroids.
We hope that you find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.
>> Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Laparoscopic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy via minilaparotomy assistance for the massively enlarged adnexal mass
A minilaparotomy is loosely defined as a laparotomy measuring between 4 cm and 6 cm. For the appropriate surgical candidate, a minilaparotomy is a useful alternative to laparotomy or laparoscopy, especially for large pathology.1 Benefits of minilaparotomy include improved pain management and postoperative recovery, as well as improved cosmetic outcome, with comparable blood loss and operative time.2,3

In this video, we illustrate the key surgical steps of a minilaparotomy for the removal of large fibroids. These steps include:
- strategic vertical skin incision
- use of a self-retaining retractor
- infiltrate myometrium with dilute vasopressin
- strategic hysterotomy
- use of tenaculum for upward traction
- 10# blade scalpels for the “lemon wedge” coring technique
- layered closure.
Minilaparotomy myomectomy can be an excellent minimally invasive alternative to a traditional “full laparotomy” for women with large fibroids.
We hope that you find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.
>> Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Laparoscopic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy via minilaparotomy assistance for the massively enlarged adnexal mass
- Pelosi MA 2nd, Pelosi MA 3rd. Pelosi minilaparotomy hysterectomy: a non-endoscopic minimally invasive alternative to laparoscopy and laparotomy. Surg Technol Int. 2004;13:157-167.
- Fanafani F, Fagotti A, Longo R. Minilaparotomy in the management of benign gynecologic disease. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2005;119:232-236.
- Glasser MH. Minilaparotomy: a minimally invasive alternative for major gynecologic abdominal surgery. Perm J. 2005;9:41-45.
- Pelosi MA 2nd, Pelosi MA 3rd. Pelosi minilaparotomy hysterectomy: a non-endoscopic minimally invasive alternative to laparoscopy and laparotomy. Surg Technol Int. 2004;13:157-167.
- Fanafani F, Fagotti A, Longo R. Minilaparotomy in the management of benign gynecologic disease. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2005;119:232-236.
- Glasser MH. Minilaparotomy: a minimally invasive alternative for major gynecologic abdominal surgery. Perm J. 2005;9:41-45.
Robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis following sterilization

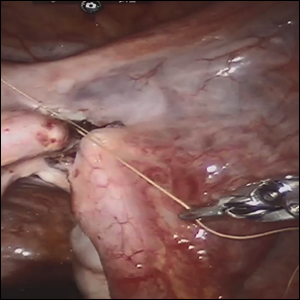
Female sterilization is the most common method of contraception worldwide, and the second most common contraceptive method used in the United States. Approximately 643,000 sterilization procedures are performed annually.1 Approximately 1% to 3% of women who undergo sterilization will subsequently undergo a sterilization reversal.2 Although multiple variables have been identified, change in marital status is the most commonly cited reason for desiring a tubal reversal.3,4 Tubal anastomosis can be a technically challenging surgical procedure when done by laparoscopy, especially given the microsurgical elements that are required. Several modifications, including limiting the number of sutures, have evolved as a result of its tedious nature.5 By leveraging 3D magnification, articulating instruments, and tremor filtration, it is only natural that robotic surgery has been applied to tubal anastomosis.
In this video, we review some background information surrounding a tubal reversal, followed by demonstration of a robotic interpretation of a 2-stitch anastomosis technique in a patient who successfully conceived and delivered.6 Overall robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis is a feasible and safe option for women who desire reversal of surgical sterilization, with pregnancy and live-birth rates comparable to those observed when an open technique is utilized.7 I hope that you will find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.
- Chan LM, Westhoff CL. Tubal sterilization trends in the United States. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1-6.
- Moss CC. Sterilization: a review and update. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2015-12-01;42:713-724.
- Gordts S, Campo R, Puttemans P, Gordts S. Clinical factors determining pregnancy outcome after microsurgical tubal anastomosis. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1198-1202.
- Chi I-C, Jones DB. Incidence, risk factors, and prevention of poststerilization regret in women. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1994;49:722-732.
- Dubuisson JB, Swolin K. Laparoscopic tubal anastomosis (the one stitch technique): preliminary results. Human Reprod. 1995;10:2044-2046.
- Bissonnette FCA, Lapensee L, Bouzayen R. Outpatient laparoscopic tubal anastomosis and subsequent fertility. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:549-552.
- Caillet M, Vandromme J, Rozenberg S, Paesmans M, Germay O, Degueldre M. Robotically assisted laparoscopic microsurgical tubal anastomosis: a retrospective study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1844-1847.

Female sterilization is the most common method of contraception worldwide, and the second most common contraceptive method used in the United States. Approximately 643,000 sterilization procedures are performed annually.1 Approximately 1% to 3% of women who undergo sterilization will subsequently undergo a sterilization reversal.2 Although multiple variables have been identified, change in marital status is the most commonly cited reason for desiring a tubal reversal.3,4 Tubal anastomosis can be a technically challenging surgical procedure when done by laparoscopy, especially given the microsurgical elements that are required. Several modifications, including limiting the number of sutures, have evolved as a result of its tedious nature.5 By leveraging 3D magnification, articulating instruments, and tremor filtration, it is only natural that robotic surgery has been applied to tubal anastomosis.
In this video, we review some background information surrounding a tubal reversal, followed by demonstration of a robotic interpretation of a 2-stitch anastomosis technique in a patient who successfully conceived and delivered.6 Overall robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis is a feasible and safe option for women who desire reversal of surgical sterilization, with pregnancy and live-birth rates comparable to those observed when an open technique is utilized.7 I hope that you will find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.

Female sterilization is the most common method of contraception worldwide, and the second most common contraceptive method used in the United States. Approximately 643,000 sterilization procedures are performed annually.1 Approximately 1% to 3% of women who undergo sterilization will subsequently undergo a sterilization reversal.2 Although multiple variables have been identified, change in marital status is the most commonly cited reason for desiring a tubal reversal.3,4 Tubal anastomosis can be a technically challenging surgical procedure when done by laparoscopy, especially given the microsurgical elements that are required. Several modifications, including limiting the number of sutures, have evolved as a result of its tedious nature.5 By leveraging 3D magnification, articulating instruments, and tremor filtration, it is only natural that robotic surgery has been applied to tubal anastomosis.
In this video, we review some background information surrounding a tubal reversal, followed by demonstration of a robotic interpretation of a 2-stitch anastomosis technique in a patient who successfully conceived and delivered.6 Overall robot-assisted laparoscopic tubal anastomosis is a feasible and safe option for women who desire reversal of surgical sterilization, with pregnancy and live-birth rates comparable to those observed when an open technique is utilized.7 I hope that you will find this video beneficial to your clinical practice.
- Chan LM, Westhoff CL. Tubal sterilization trends in the United States. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1-6.
- Moss CC. Sterilization: a review and update. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2015-12-01;42:713-724.
- Gordts S, Campo R, Puttemans P, Gordts S. Clinical factors determining pregnancy outcome after microsurgical tubal anastomosis. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1198-1202.
- Chi I-C, Jones DB. Incidence, risk factors, and prevention of poststerilization regret in women. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1994;49:722-732.
- Dubuisson JB, Swolin K. Laparoscopic tubal anastomosis (the one stitch technique): preliminary results. Human Reprod. 1995;10:2044-2046.
- Bissonnette FCA, Lapensee L, Bouzayen R. Outpatient laparoscopic tubal anastomosis and subsequent fertility. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:549-552.
- Caillet M, Vandromme J, Rozenberg S, Paesmans M, Germay O, Degueldre M. Robotically assisted laparoscopic microsurgical tubal anastomosis: a retrospective study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1844-1847.
- Chan LM, Westhoff CL. Tubal sterilization trends in the United States. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1-6.
- Moss CC. Sterilization: a review and update. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2015-12-01;42:713-724.
- Gordts S, Campo R, Puttemans P, Gordts S. Clinical factors determining pregnancy outcome after microsurgical tubal anastomosis. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:1198-1202.
- Chi I-C, Jones DB. Incidence, risk factors, and prevention of poststerilization regret in women. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1994;49:722-732.
- Dubuisson JB, Swolin K. Laparoscopic tubal anastomosis (the one stitch technique): preliminary results. Human Reprod. 1995;10:2044-2046.
- Bissonnette FCA, Lapensee L, Bouzayen R. Outpatient laparoscopic tubal anastomosis and subsequent fertility. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:549-552.
- Caillet M, Vandromme J, Rozenberg S, Paesmans M, Germay O, Degueldre M. Robotically assisted laparoscopic microsurgical tubal anastomosis: a retrospective study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1844-1847.
Excision of a Bartholin gland cyst
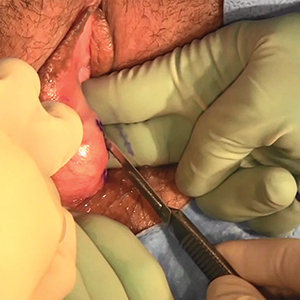
Bartholin gland cysts comprise up to 2% of all outpatient gynecology visits each year1 and are a common consult for trainees in obstetrics and gynecology. Although excision of a Bartholin gland cyst is a procedure performed infrequently, knowledge of its anatomy and physiology is important for ObGyn trainees and practicing gynecologists, especially when attempts at conservative management have been exhausted.
Before proceeding with surgical excision, it is important to understand the basics of Bartholin gland anatomy, pathologies, and treatment options. This video demonstrates the excisional technique for a 46-year-old woman with a recurrent, symptomatic Bartholin gland cyst who failed prior conservative management. I hope that you will find this video from my colleagues beneficial to your clinical practice.

- Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004;8(3):195–204.
Bartholin gland cysts comprise up to 2% of all outpatient gynecology visits each year1 and are a common consult for trainees in obstetrics and gynecology. Although excision of a Bartholin gland cyst is a procedure performed infrequently, knowledge of its anatomy and physiology is important for ObGyn trainees and practicing gynecologists, especially when attempts at conservative management have been exhausted.
Before proceeding with surgical excision, it is important to understand the basics of Bartholin gland anatomy, pathologies, and treatment options. This video demonstrates the excisional technique for a 46-year-old woman with a recurrent, symptomatic Bartholin gland cyst who failed prior conservative management. I hope that you will find this video from my colleagues beneficial to your clinical practice.

Bartholin gland cysts comprise up to 2% of all outpatient gynecology visits each year1 and are a common consult for trainees in obstetrics and gynecology. Although excision of a Bartholin gland cyst is a procedure performed infrequently, knowledge of its anatomy and physiology is important for ObGyn trainees and practicing gynecologists, especially when attempts at conservative management have been exhausted.
Before proceeding with surgical excision, it is important to understand the basics of Bartholin gland anatomy, pathologies, and treatment options. This video demonstrates the excisional technique for a 46-year-old woman with a recurrent, symptomatic Bartholin gland cyst who failed prior conservative management. I hope that you will find this video from my colleagues beneficial to your clinical practice.

- Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004;8(3):195–204.
- Marzano DA, Haefner HK. The bartholin gland cyst: past, present, and future. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2004;8(3):195–204.