User login
Targetable genetic alterations found in 41% of soft tissue sarcomas
, reported Carlo Lucchesi, PhD, of Institut Bergonié in Bordeaux, France, and his associates.
In a cross-sectional study of next-generation sequencing results from 584 patients with soft tissue sarcomas in the American Association for Cancer Research’s GENIE Database, 57% of patients had complex genomics sarcomas (sarcomas with multiple, complex karyotypic abnormalities with no specific pattern), 25% had translocation-related sarcomas (sarcomas with specific reciprocal translocations resulting in oncogenic fusion transcripts), and 18% had simple amplicon sarcomas or sarcomas with inactivating mutations.
A total of 2,697 alterations (1,154 substitutions, 765 gene amplifications, 364 short indels and splicing variants, 346 gene homozygous deletions, and 68 gene rearrangements) were identified in 451 genes. A median of four alterations per case were detected, the researchers wrote in a study published online May 3 in JAMA Oncology.
The researchers identified the 20 genes that were most often altered. The top 5 were TP53, MDM2, CDK4, RB1, and ATRX.
Among these 584 samples, 85% had at least one alteration. The proportions of affected patients in each sarcoma group varied significantly among groups, with the other sarcomas group being the most altered (90.8%) and translocation-related sarcomas being the least mutated (77.8%).
At least one relevant gene alteration that could potentially be used to guide targeted therapy was found in 239 cases (41%) with a statistically significant higher number in other sarcomas (89 cases) and complex genomics sarcomas (131 cases) than in translocation-related sarcomas (19 cases).
This finding of an “unexpectedly high frequency” of clinically relevant genetic alterations supports the premise of the soon-to-be-launched MULTISARC trial, which posits that next-generation sequencing results can be used to guide and improve the treatment outcomes of patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas. For MULTISARC, such patients will be randomized either to an experimental group that will undergo exome and RNA sequencing – and their results will be discussed in a molecular tumor board to tailor the treatment – or to a control group that will not undergo molecular profiling and will receive conventional therapy. The program will include 16 targeted therapies.
The researchers reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lucchesi C et al. JAMA Oncol. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0723.
, reported Carlo Lucchesi, PhD, of Institut Bergonié in Bordeaux, France, and his associates.
In a cross-sectional study of next-generation sequencing results from 584 patients with soft tissue sarcomas in the American Association for Cancer Research’s GENIE Database, 57% of patients had complex genomics sarcomas (sarcomas with multiple, complex karyotypic abnormalities with no specific pattern), 25% had translocation-related sarcomas (sarcomas with specific reciprocal translocations resulting in oncogenic fusion transcripts), and 18% had simple amplicon sarcomas or sarcomas with inactivating mutations.
A total of 2,697 alterations (1,154 substitutions, 765 gene amplifications, 364 short indels and splicing variants, 346 gene homozygous deletions, and 68 gene rearrangements) were identified in 451 genes. A median of four alterations per case were detected, the researchers wrote in a study published online May 3 in JAMA Oncology.
The researchers identified the 20 genes that were most often altered. The top 5 were TP53, MDM2, CDK4, RB1, and ATRX.
Among these 584 samples, 85% had at least one alteration. The proportions of affected patients in each sarcoma group varied significantly among groups, with the other sarcomas group being the most altered (90.8%) and translocation-related sarcomas being the least mutated (77.8%).
At least one relevant gene alteration that could potentially be used to guide targeted therapy was found in 239 cases (41%) with a statistically significant higher number in other sarcomas (89 cases) and complex genomics sarcomas (131 cases) than in translocation-related sarcomas (19 cases).
This finding of an “unexpectedly high frequency” of clinically relevant genetic alterations supports the premise of the soon-to-be-launched MULTISARC trial, which posits that next-generation sequencing results can be used to guide and improve the treatment outcomes of patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas. For MULTISARC, such patients will be randomized either to an experimental group that will undergo exome and RNA sequencing – and their results will be discussed in a molecular tumor board to tailor the treatment – or to a control group that will not undergo molecular profiling and will receive conventional therapy. The program will include 16 targeted therapies.
The researchers reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lucchesi C et al. JAMA Oncol. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0723.
, reported Carlo Lucchesi, PhD, of Institut Bergonié in Bordeaux, France, and his associates.
In a cross-sectional study of next-generation sequencing results from 584 patients with soft tissue sarcomas in the American Association for Cancer Research’s GENIE Database, 57% of patients had complex genomics sarcomas (sarcomas with multiple, complex karyotypic abnormalities with no specific pattern), 25% had translocation-related sarcomas (sarcomas with specific reciprocal translocations resulting in oncogenic fusion transcripts), and 18% had simple amplicon sarcomas or sarcomas with inactivating mutations.
A total of 2,697 alterations (1,154 substitutions, 765 gene amplifications, 364 short indels and splicing variants, 346 gene homozygous deletions, and 68 gene rearrangements) were identified in 451 genes. A median of four alterations per case were detected, the researchers wrote in a study published online May 3 in JAMA Oncology.
The researchers identified the 20 genes that were most often altered. The top 5 were TP53, MDM2, CDK4, RB1, and ATRX.
Among these 584 samples, 85% had at least one alteration. The proportions of affected patients in each sarcoma group varied significantly among groups, with the other sarcomas group being the most altered (90.8%) and translocation-related sarcomas being the least mutated (77.8%).
At least one relevant gene alteration that could potentially be used to guide targeted therapy was found in 239 cases (41%) with a statistically significant higher number in other sarcomas (89 cases) and complex genomics sarcomas (131 cases) than in translocation-related sarcomas (19 cases).
This finding of an “unexpectedly high frequency” of clinically relevant genetic alterations supports the premise of the soon-to-be-launched MULTISARC trial, which posits that next-generation sequencing results can be used to guide and improve the treatment outcomes of patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas. For MULTISARC, such patients will be randomized either to an experimental group that will undergo exome and RNA sequencing – and their results will be discussed in a molecular tumor board to tailor the treatment – or to a control group that will not undergo molecular profiling and will receive conventional therapy. The program will include 16 targeted therapies.
The researchers reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lucchesi C et al. JAMA Oncol. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0723.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Next-generation sequencing results might prove useful for guiding targeted therapy that could improve the treatment outcomes of patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas.
Major finding: At least one targetable genetic alteration was found in 41% of 584 soft tissue sarcomas, and the probability of an alteration was higher in sarcomas with complex genomics than in translocation-related sarcomas.
Study details: A cross-sectional study of next-generation sequencing results from 584 patients with soft tissue sarcomas in the AACR GENIE Database.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
Source: Lucchesi C et al. JAMA Oncol. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0723.
FDA approves test to screen donated blood for Zika virus
The cobas Zika test has been approved for detecting the virus in whole blood, blood components, and donated organs, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced in a press release.
“Today’s action represents the first approval of a Zika virus detection test for use with screening the nation’s blood supply,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a press release. “Screening blood donations for the Zika virus is critical to preventing infected donations from entering the U.S. blood supply.”
In August 2016, the FDA issued a final guidance document recommending that all individual units of whole blood and blood components be screened with an investigational blood screening test available under an investigational new drug application. Data obtained on the cobas Zika test under its investigational new drug application and from additional studies performed by the manufacturer demonstrated that the cobas Zika test is effective. Testing individual samples from blood donations at five external laboratory sites resulted in a clinical specificity exceeding 99%.
The cobas Zika test is intended for use on the fully automated cobas 6800 and cobas 8800 systems. The cobas Zika test, cobas 6800, and cobas 8800 systems are manufactured by Roche Molecular Systems.
The cobas Zika test has been approved for detecting the virus in whole blood, blood components, and donated organs, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced in a press release.
“Today’s action represents the first approval of a Zika virus detection test for use with screening the nation’s blood supply,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a press release. “Screening blood donations for the Zika virus is critical to preventing infected donations from entering the U.S. blood supply.”
In August 2016, the FDA issued a final guidance document recommending that all individual units of whole blood and blood components be screened with an investigational blood screening test available under an investigational new drug application. Data obtained on the cobas Zika test under its investigational new drug application and from additional studies performed by the manufacturer demonstrated that the cobas Zika test is effective. Testing individual samples from blood donations at five external laboratory sites resulted in a clinical specificity exceeding 99%.
The cobas Zika test is intended for use on the fully automated cobas 6800 and cobas 8800 systems. The cobas Zika test, cobas 6800, and cobas 8800 systems are manufactured by Roche Molecular Systems.
The cobas Zika test has been approved for detecting the virus in whole blood, blood components, and donated organs, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced in a press release.
“Today’s action represents the first approval of a Zika virus detection test for use with screening the nation’s blood supply,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a press release. “Screening blood donations for the Zika virus is critical to preventing infected donations from entering the U.S. blood supply.”
In August 2016, the FDA issued a final guidance document recommending that all individual units of whole blood and blood components be screened with an investigational blood screening test available under an investigational new drug application. Data obtained on the cobas Zika test under its investigational new drug application and from additional studies performed by the manufacturer demonstrated that the cobas Zika test is effective. Testing individual samples from blood donations at five external laboratory sites resulted in a clinical specificity exceeding 99%.
The cobas Zika test is intended for use on the fully automated cobas 6800 and cobas 8800 systems. The cobas Zika test, cobas 6800, and cobas 8800 systems are manufactured by Roche Molecular Systems.
Vemurafenib granted sNDA, priority review for Erdheim-Chester disease
Vemurafenib (Zelboraf) has been granted a supplemental new drug application and priority review by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Erdheim-Chester disease with BRAF V600 mutation, according to a press release issued by Genentech.
The FDA is expected to make a decision on the indication by Dec. 7, 2017. Vemurafenib is approved for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation.
The supportive data for the application came from VE-BASKET, a phase 2, nonrandomized study investigating the use of vemurafenib for people with various BRAF V600 mutation–positive cancers and other diseases. Final results for the 22 people with Erdheim-Chester disease showed a best overall response rate of 54.5% by RECIST v1.1 criteria.
The median duration of response, progression-free survival, and overall survival were not reached at a median follow-up time of 26.6 months. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were new skin cancers, high blood pressure, rash, and joint pain. Initial study results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in August 2015.
Based on available published data, there are fewer than 500 cases of Erdheim-Chester disease in the United States. More than half of affected people have BRAF V600 mutation–positive disease, and there are no approved treatments, according to the release.
Vemurafenib (Zelboraf) has been granted a supplemental new drug application and priority review by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Erdheim-Chester disease with BRAF V600 mutation, according to a press release issued by Genentech.
The FDA is expected to make a decision on the indication by Dec. 7, 2017. Vemurafenib is approved for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation.
The supportive data for the application came from VE-BASKET, a phase 2, nonrandomized study investigating the use of vemurafenib for people with various BRAF V600 mutation–positive cancers and other diseases. Final results for the 22 people with Erdheim-Chester disease showed a best overall response rate of 54.5% by RECIST v1.1 criteria.
The median duration of response, progression-free survival, and overall survival were not reached at a median follow-up time of 26.6 months. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were new skin cancers, high blood pressure, rash, and joint pain. Initial study results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in August 2015.
Based on available published data, there are fewer than 500 cases of Erdheim-Chester disease in the United States. More than half of affected people have BRAF V600 mutation–positive disease, and there are no approved treatments, according to the release.
Vemurafenib (Zelboraf) has been granted a supplemental new drug application and priority review by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Erdheim-Chester disease with BRAF V600 mutation, according to a press release issued by Genentech.
The FDA is expected to make a decision on the indication by Dec. 7, 2017. Vemurafenib is approved for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation.
The supportive data for the application came from VE-BASKET, a phase 2, nonrandomized study investigating the use of vemurafenib for people with various BRAF V600 mutation–positive cancers and other diseases. Final results for the 22 people with Erdheim-Chester disease showed a best overall response rate of 54.5% by RECIST v1.1 criteria.
The median duration of response, progression-free survival, and overall survival were not reached at a median follow-up time of 26.6 months. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events were new skin cancers, high blood pressure, rash, and joint pain. Initial study results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine in August 2015.
Based on available published data, there are fewer than 500 cases of Erdheim-Chester disease in the United States. More than half of affected people have BRAF V600 mutation–positive disease, and there are no approved treatments, according to the release.
Liposomal daunorubicin and cytarabine approved for t-AML, AML-MRC
, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Aug. 3.
Vyxeos is the first FDA-approved treatment specifically for patients with t-AML or AML-MRC, the FDA said in its press release announcing the approval.
“Vyxeos is the first chemotherapy to demonstrate an overall survival advantage over the standard of care in a phase 3 randomized study of older adults with newly-diagnosed therapy-related AML or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes,” Jeffrey E. Lancet, MD, an investigator in the clinical trials of Vyxeos and chair of the department of malignant hematology at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., said in a press release.
Vyxeos was associated with a median overall survival of 9.6 months and a standard combination of cytarabine and daunorubicin (7+3) was associated with a median survival of 5.9 months in a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial of 309 patients aged 60-75 years with newly-diagnosed t-AML or AML-MRC. Data from the study, which is NCT01696084, was the basis for the drug’s approval.
Vyxeos is a fixed-dose combination with each Vyxeos vial containing 44 mg daunorubicin and 100 mg cytarabine encapsulated together in liposomes. As dosing is based on the daunorubicin component, the corresponding cytarabine dose does not need to be calculated. Daunorubicin dosing is calculated on the basis of body surface area (mg/m2).
For the first induction cycle, the recommended Vyxeos dose is daunorubicin 44 mg/m2 (cytarabine 100 mg/m2) infused intravenously over 90 minutes on days 1, 3, and 5. If a second induction cycle is needed, the same dose is administered on days 1 and 3. The recommended dose of Vyxeos for each cycle of consolidation therapy is daunorubicin 29 mg/m2 (cytarabine 65 mg/m2) liposome via intravenous infusion over 90 minutes on days 1 and 3.
Adverse reactions occurring in at least 25% of treated patients in the clinical trial included hemorrhage, febrile neutropenia, rash, edema, nausea, mucositis, diarrhea, constipation, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, abdominal pain, dyspnea, headache, cough, decreased appetite, arrhythmia, pneumonia, bacteremia, chills, sleep disorders, and vomiting.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning not to substitute Vyxeos with other daunorubicin- or cytarabine-containing products. Full prescribing information is available at: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209401s000lbl.pdf
The maker of Vyxeos is Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Aug. 3.
Vyxeos is the first FDA-approved treatment specifically for patients with t-AML or AML-MRC, the FDA said in its press release announcing the approval.
“Vyxeos is the first chemotherapy to demonstrate an overall survival advantage over the standard of care in a phase 3 randomized study of older adults with newly-diagnosed therapy-related AML or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes,” Jeffrey E. Lancet, MD, an investigator in the clinical trials of Vyxeos and chair of the department of malignant hematology at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., said in a press release.
Vyxeos was associated with a median overall survival of 9.6 months and a standard combination of cytarabine and daunorubicin (7+3) was associated with a median survival of 5.9 months in a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial of 309 patients aged 60-75 years with newly-diagnosed t-AML or AML-MRC. Data from the study, which is NCT01696084, was the basis for the drug’s approval.
Vyxeos is a fixed-dose combination with each Vyxeos vial containing 44 mg daunorubicin and 100 mg cytarabine encapsulated together in liposomes. As dosing is based on the daunorubicin component, the corresponding cytarabine dose does not need to be calculated. Daunorubicin dosing is calculated on the basis of body surface area (mg/m2).
For the first induction cycle, the recommended Vyxeos dose is daunorubicin 44 mg/m2 (cytarabine 100 mg/m2) infused intravenously over 90 minutes on days 1, 3, and 5. If a second induction cycle is needed, the same dose is administered on days 1 and 3. The recommended dose of Vyxeos for each cycle of consolidation therapy is daunorubicin 29 mg/m2 (cytarabine 65 mg/m2) liposome via intravenous infusion over 90 minutes on days 1 and 3.
Adverse reactions occurring in at least 25% of treated patients in the clinical trial included hemorrhage, febrile neutropenia, rash, edema, nausea, mucositis, diarrhea, constipation, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, abdominal pain, dyspnea, headache, cough, decreased appetite, arrhythmia, pneumonia, bacteremia, chills, sleep disorders, and vomiting.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning not to substitute Vyxeos with other daunorubicin- or cytarabine-containing products. Full prescribing information is available at: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209401s000lbl.pdf
The maker of Vyxeos is Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
, the Food and Drug Administration announced on Aug. 3.
Vyxeos is the first FDA-approved treatment specifically for patients with t-AML or AML-MRC, the FDA said in its press release announcing the approval.
“Vyxeos is the first chemotherapy to demonstrate an overall survival advantage over the standard of care in a phase 3 randomized study of older adults with newly-diagnosed therapy-related AML or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes,” Jeffrey E. Lancet, MD, an investigator in the clinical trials of Vyxeos and chair of the department of malignant hematology at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., said in a press release.
Vyxeos was associated with a median overall survival of 9.6 months and a standard combination of cytarabine and daunorubicin (7+3) was associated with a median survival of 5.9 months in a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial of 309 patients aged 60-75 years with newly-diagnosed t-AML or AML-MRC. Data from the study, which is NCT01696084, was the basis for the drug’s approval.
Vyxeos is a fixed-dose combination with each Vyxeos vial containing 44 mg daunorubicin and 100 mg cytarabine encapsulated together in liposomes. As dosing is based on the daunorubicin component, the corresponding cytarabine dose does not need to be calculated. Daunorubicin dosing is calculated on the basis of body surface area (mg/m2).
For the first induction cycle, the recommended Vyxeos dose is daunorubicin 44 mg/m2 (cytarabine 100 mg/m2) infused intravenously over 90 minutes on days 1, 3, and 5. If a second induction cycle is needed, the same dose is administered on days 1 and 3. The recommended dose of Vyxeos for each cycle of consolidation therapy is daunorubicin 29 mg/m2 (cytarabine 65 mg/m2) liposome via intravenous infusion over 90 minutes on days 1 and 3.
Adverse reactions occurring in at least 25% of treated patients in the clinical trial included hemorrhage, febrile neutropenia, rash, edema, nausea, mucositis, diarrhea, constipation, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, abdominal pain, dyspnea, headache, cough, decreased appetite, arrhythmia, pneumonia, bacteremia, chills, sleep disorders, and vomiting.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning not to substitute Vyxeos with other daunorubicin- or cytarabine-containing products. Full prescribing information is available at: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209401s000lbl.pdf
The maker of Vyxeos is Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
Ibrutinib becomes first FDA-approved treatment for chronic GVHD
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica) added another notch on its indications belt with its Aug. 2 approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD) after failure of one or more lines of systemic therapy.
The new indication makes ibrutinib the first FDA-approved therapy for the treatment of cGVHD, according to an FDA press release.
Ibrutinib’s other approved indications include chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with 17p deletion, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, marginal zone lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma, according to a press release from the FDA.
The recommended dose of ibrutinib for cGVHD is 420 mg (three 140 mg capsules once daily). Prescribing information is available on the FDA website.
Imbruvica is manufactured by Pharmacyclics.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica) added another notch on its indications belt with its Aug. 2 approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD) after failure of one or more lines of systemic therapy.
The new indication makes ibrutinib the first FDA-approved therapy for the treatment of cGVHD, according to an FDA press release.
Ibrutinib’s other approved indications include chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with 17p deletion, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, marginal zone lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma, according to a press release from the FDA.
The recommended dose of ibrutinib for cGVHD is 420 mg (three 140 mg capsules once daily). Prescribing information is available on the FDA website.
Imbruvica is manufactured by Pharmacyclics.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica) added another notch on its indications belt with its Aug. 2 approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD) after failure of one or more lines of systemic therapy.
The new indication makes ibrutinib the first FDA-approved therapy for the treatment of cGVHD, according to an FDA press release.
Ibrutinib’s other approved indications include chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with 17p deletion, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, marginal zone lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma, according to a press release from the FDA.
The recommended dose of ibrutinib for cGVHD is 420 mg (three 140 mg capsules once daily). Prescribing information is available on the FDA website.
Imbruvica is manufactured by Pharmacyclics.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
Enasidenib gets FDA approval for AML with IDH2 mutations
Enasidenib has been approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and specific mutations in the IDH2 gene, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Aug. 1.
The drug is approved for use with a companion diagnostic, the RealTime IDH2 Assay, which is used to detect IDH2 gene mutations. The FDA granted the approval of enasidenib (Idhifa) to the Celgene Corp. and the approval of the companion RealTime IDH2 Assay to Abbott Laboratories. Idhifa had Priority Review and Orphan Drug designations.
In data reported at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association, the overall response rate to enasidenib among 214 patients with IDH2 gene mutations treated at the 100-mg/day dose was 37%. This included 20.1% with a complete remission, 7.9% with complete remission with incomplete recovery of platelets or incomplete hematologic recovery, 3.7% with partial responses, and 5.1% with a morphologic leukemia-free state, according to Eytan M. Stein, MD, an internist and hematologic oncologist at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
According to an FDA press release, 34% of 157 patients who required transfusions of blood or platelets at the start of the study no longer required transfusions after treatment.
For 8%-19% of AML patients, the mutated IDH2 enzyme blocks normal blood cell development and results in an overabundance of immature blood cells, Celgene said in an announcement.
Common side effects of enasidenib, an isocitrate dehydrogenase-2 inhibitor, include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hyperbilirubinemia, and decreased appetite.
Fatal differentiation syndrome can occur and is treated with corticosteroids. The prescribing information for Idhifa includes a boxed warning regarding that risk. Symptoms of differentiation syndrome may include fever, dyspnea, acute respiratory distress, radiographic pulmonary infiltrates, pleural or pericardial effusions, rapid weight gain, peripheral edema, or hepatic, renal or multi-organ dysfunction, according to a press release issued by the FDA.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
Enasidenib has been approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and specific mutations in the IDH2 gene, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Aug. 1.
The drug is approved for use with a companion diagnostic, the RealTime IDH2 Assay, which is used to detect IDH2 gene mutations. The FDA granted the approval of enasidenib (Idhifa) to the Celgene Corp. and the approval of the companion RealTime IDH2 Assay to Abbott Laboratories. Idhifa had Priority Review and Orphan Drug designations.
In data reported at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association, the overall response rate to enasidenib among 214 patients with IDH2 gene mutations treated at the 100-mg/day dose was 37%. This included 20.1% with a complete remission, 7.9% with complete remission with incomplete recovery of platelets or incomplete hematologic recovery, 3.7% with partial responses, and 5.1% with a morphologic leukemia-free state, according to Eytan M. Stein, MD, an internist and hematologic oncologist at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
According to an FDA press release, 34% of 157 patients who required transfusions of blood or platelets at the start of the study no longer required transfusions after treatment.
For 8%-19% of AML patients, the mutated IDH2 enzyme blocks normal blood cell development and results in an overabundance of immature blood cells, Celgene said in an announcement.
Common side effects of enasidenib, an isocitrate dehydrogenase-2 inhibitor, include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hyperbilirubinemia, and decreased appetite.
Fatal differentiation syndrome can occur and is treated with corticosteroids. The prescribing information for Idhifa includes a boxed warning regarding that risk. Symptoms of differentiation syndrome may include fever, dyspnea, acute respiratory distress, radiographic pulmonary infiltrates, pleural or pericardial effusions, rapid weight gain, peripheral edema, or hepatic, renal or multi-organ dysfunction, according to a press release issued by the FDA.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
Enasidenib has been approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and specific mutations in the IDH2 gene, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced on Aug. 1.
The drug is approved for use with a companion diagnostic, the RealTime IDH2 Assay, which is used to detect IDH2 gene mutations. The FDA granted the approval of enasidenib (Idhifa) to the Celgene Corp. and the approval of the companion RealTime IDH2 Assay to Abbott Laboratories. Idhifa had Priority Review and Orphan Drug designations.
In data reported at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association, the overall response rate to enasidenib among 214 patients with IDH2 gene mutations treated at the 100-mg/day dose was 37%. This included 20.1% with a complete remission, 7.9% with complete remission with incomplete recovery of platelets or incomplete hematologic recovery, 3.7% with partial responses, and 5.1% with a morphologic leukemia-free state, according to Eytan M. Stein, MD, an internist and hematologic oncologist at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
According to an FDA press release, 34% of 157 patients who required transfusions of blood or platelets at the start of the study no longer required transfusions after treatment.
For 8%-19% of AML patients, the mutated IDH2 enzyme blocks normal blood cell development and results in an overabundance of immature blood cells, Celgene said in an announcement.
Common side effects of enasidenib, an isocitrate dehydrogenase-2 inhibitor, include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hyperbilirubinemia, and decreased appetite.
Fatal differentiation syndrome can occur and is treated with corticosteroids. The prescribing information for Idhifa includes a boxed warning regarding that risk. Symptoms of differentiation syndrome may include fever, dyspnea, acute respiratory distress, radiographic pulmonary infiltrates, pleural or pericardial effusions, rapid weight gain, peripheral edema, or hepatic, renal or multi-organ dysfunction, according to a press release issued by the FDA.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
Less lenalidomide may be more in frail elderly multiple myeloma patients
In frail elderly patients with multiple myeloma, starting lenalidomide at low doses was associated with fewer adverse events and less treatment discontinuation, and did not compromise overall response rates, in a single-center, retrospective study conducted in Japan.
Although most of the 56 study patients received 5-10 mg/day of lenalidomide, not the recommended 25-mg/day dose, their overall response rate was 73% (complete response in 17% of patients, very good partial response in 19%, and partial response in 37%), Aya Nakaya, MD, PhD, of Kansai Medical University, Hirakata, and colleagues wrote (Acta Haematol. 2017;138:55-60). In addition, 23% of patients had stable disease and 4% had disease progression. Nine patients developed other types of malignancies during treatment with lenalidomide.
Starting patients on a reduced dose and increasing it gradually while monitoring carefully for adverse events meant that patients did not have to stop treatment, the researchers said. Continuous treatment may improve survival, and “treatment with lenalidomide for long periods of time, even in small doses, may yield favorable outcomes.”
The 30 men and 26 women, mean age 76.5 years, were consecutively diagnosed as transplant-ineligible patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma; 34%, 32%, and 34% had stages I-III disease, respectively. The M-protein consisted of IgG in 52% of patients and IgA in 30%, with Bence-Jones protein detected in 14%.
They were treated with lenalidomide plus dexamethasone at a starting dose determined by the treating physician; 73% were treated with lenalidomide as a second-line regimen and 14% as a third-line regimen. During each 28-day treatment cycle, patients received lenalidomide on days 1-21 and dexamethasone (20 or 40 mg) on days 1, 8, 15, and 22.
The most common starting lenalidomide dose was 10 mg/day (45%), followed by 5 mg/day (21%), 15 mg/day (20%), 20 mg/day (4%), and 25 mg/day (10%). The treatment dose used for the longest period was 10 mg/day (46% of patients), followed by 5 mg/day (25%), 15 mg/day (16%), 20 mg/day (4%), and 25 mg/day (9%).
The most frequent reasons for dose reduction were renal dysfunction (54%), fatigue (20%), hematologic disorder (14%), and rash (9%).
The median treatment period was 9 months (range 1-60 months) and the median follow-up period was 16 months.
The median time to disease progression was 11.8 months (range 8.4-21.9), and the median overall survival was 39.2 months. For those who took 5-10 mg of lenalidomide, the median time to progression was 14.5 months; for those who took lenalidomide at a dose of more than 10 mg, the median time to progression was 8.9 months. The median overall survival of the patients who received a 5- to 10-mg dose of lenalidomide was 38.9 months; the median overall survival of the patients given a dose of more than 10 mg was not available.
The authors declared no competing financial interests in relation to this work.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
In frail elderly patients with multiple myeloma, starting lenalidomide at low doses was associated with fewer adverse events and less treatment discontinuation, and did not compromise overall response rates, in a single-center, retrospective study conducted in Japan.
Although most of the 56 study patients received 5-10 mg/day of lenalidomide, not the recommended 25-mg/day dose, their overall response rate was 73% (complete response in 17% of patients, very good partial response in 19%, and partial response in 37%), Aya Nakaya, MD, PhD, of Kansai Medical University, Hirakata, and colleagues wrote (Acta Haematol. 2017;138:55-60). In addition, 23% of patients had stable disease and 4% had disease progression. Nine patients developed other types of malignancies during treatment with lenalidomide.
Starting patients on a reduced dose and increasing it gradually while monitoring carefully for adverse events meant that patients did not have to stop treatment, the researchers said. Continuous treatment may improve survival, and “treatment with lenalidomide for long periods of time, even in small doses, may yield favorable outcomes.”
The 30 men and 26 women, mean age 76.5 years, were consecutively diagnosed as transplant-ineligible patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma; 34%, 32%, and 34% had stages I-III disease, respectively. The M-protein consisted of IgG in 52% of patients and IgA in 30%, with Bence-Jones protein detected in 14%.
They were treated with lenalidomide plus dexamethasone at a starting dose determined by the treating physician; 73% were treated with lenalidomide as a second-line regimen and 14% as a third-line regimen. During each 28-day treatment cycle, patients received lenalidomide on days 1-21 and dexamethasone (20 or 40 mg) on days 1, 8, 15, and 22.
The most common starting lenalidomide dose was 10 mg/day (45%), followed by 5 mg/day (21%), 15 mg/day (20%), 20 mg/day (4%), and 25 mg/day (10%). The treatment dose used for the longest period was 10 mg/day (46% of patients), followed by 5 mg/day (25%), 15 mg/day (16%), 20 mg/day (4%), and 25 mg/day (9%).
The most frequent reasons for dose reduction were renal dysfunction (54%), fatigue (20%), hematologic disorder (14%), and rash (9%).
The median treatment period was 9 months (range 1-60 months) and the median follow-up period was 16 months.
The median time to disease progression was 11.8 months (range 8.4-21.9), and the median overall survival was 39.2 months. For those who took 5-10 mg of lenalidomide, the median time to progression was 14.5 months; for those who took lenalidomide at a dose of more than 10 mg, the median time to progression was 8.9 months. The median overall survival of the patients who received a 5- to 10-mg dose of lenalidomide was 38.9 months; the median overall survival of the patients given a dose of more than 10 mg was not available.
The authors declared no competing financial interests in relation to this work.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
In frail elderly patients with multiple myeloma, starting lenalidomide at low doses was associated with fewer adverse events and less treatment discontinuation, and did not compromise overall response rates, in a single-center, retrospective study conducted in Japan.
Although most of the 56 study patients received 5-10 mg/day of lenalidomide, not the recommended 25-mg/day dose, their overall response rate was 73% (complete response in 17% of patients, very good partial response in 19%, and partial response in 37%), Aya Nakaya, MD, PhD, of Kansai Medical University, Hirakata, and colleagues wrote (Acta Haematol. 2017;138:55-60). In addition, 23% of patients had stable disease and 4% had disease progression. Nine patients developed other types of malignancies during treatment with lenalidomide.
Starting patients on a reduced dose and increasing it gradually while monitoring carefully for adverse events meant that patients did not have to stop treatment, the researchers said. Continuous treatment may improve survival, and “treatment with lenalidomide for long periods of time, even in small doses, may yield favorable outcomes.”
The 30 men and 26 women, mean age 76.5 years, were consecutively diagnosed as transplant-ineligible patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma; 34%, 32%, and 34% had stages I-III disease, respectively. The M-protein consisted of IgG in 52% of patients and IgA in 30%, with Bence-Jones protein detected in 14%.
They were treated with lenalidomide plus dexamethasone at a starting dose determined by the treating physician; 73% were treated with lenalidomide as a second-line regimen and 14% as a third-line regimen. During each 28-day treatment cycle, patients received lenalidomide on days 1-21 and dexamethasone (20 or 40 mg) on days 1, 8, 15, and 22.
The most common starting lenalidomide dose was 10 mg/day (45%), followed by 5 mg/day (21%), 15 mg/day (20%), 20 mg/day (4%), and 25 mg/day (10%). The treatment dose used for the longest period was 10 mg/day (46% of patients), followed by 5 mg/day (25%), 15 mg/day (16%), 20 mg/day (4%), and 25 mg/day (9%).
The most frequent reasons for dose reduction were renal dysfunction (54%), fatigue (20%), hematologic disorder (14%), and rash (9%).
The median treatment period was 9 months (range 1-60 months) and the median follow-up period was 16 months.
The median time to disease progression was 11.8 months (range 8.4-21.9), and the median overall survival was 39.2 months. For those who took 5-10 mg of lenalidomide, the median time to progression was 14.5 months; for those who took lenalidomide at a dose of more than 10 mg, the median time to progression was 8.9 months. The median overall survival of the patients who received a 5- to 10-mg dose of lenalidomide was 38.9 months; the median overall survival of the patients given a dose of more than 10 mg was not available.
The authors declared no competing financial interests in relation to this work.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
FROM ACTA HAEMATOLOGICA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Although most of the 56 study patients received 5-10 mg/day of lenalidomide, not the recommended 25-mg/day dose, their overall response rate was 73%.
Data source: A single-center, retrospective study of 56 consecutively diagnosed transplant-ineligible patients in Japan.
Disclosures: The authors declared no competing financial interests in relation to this work.
FLT3-L level may point to relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
FLT3-ligand (FLT3-L) levels exceeding 92 pg/mL in bone marrow and 121 pg/mL in peripheral blood are associated with relapsed and refractory disease in patients with multiple myeloma, Normann Steiner, MD, and his colleagues report in a study published in PLoS ONE.
In the study of 14 patients with monoclonal gamm opathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), 42 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, and 27 patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma, there was a 61% probability that patients with FLT3-L levels above 92 pg/mL in bone marrow had relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and a 79% probability that those with FLT3-L levels of 92 pg/mL or less had not relapsed and were not refractory. Based on FLT3-L levels in peripheral blood, values of 121 pg/mL or more were associated with a 71% probability of relapsed or refractory disease. The likelihood of not having relapses or refractory disease was 87% for patients with values less than 121 pg/mL.
“FLT3-L could be useful as a marker to identify (relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma) patients and should be evaluated as a potential target for future therapy strategies,” Dr. Steiner of Innsbruck (Austria) Medical University, and his fellow researchers wrote in PLoS ONE.
The researchers obtained bone marrow aspirates from all patients. Peripheral blood was examined from 4 MGUS patients, 31 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, and 16 patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma. Peripheral blood was also obtained from 16 control subjects.
The levels of four potential risk factors were measured – soluble TIE2, FLT3-L, endostatin, and osteoactivin. The most significant association with risk was seen with FLT3-L levels.
Expression of soluble TIE2 in bone marrow differed significantly among the three patient cohorts and may be driven by the same factors that influence FLT3-L levels. However, soluble TIE2 levels were not as effective at differentiating patients at risk for disease progression, the researchers wrote.
Soluble TIE2 expression in bone marrow was highest in MGUS patients (median 4003.97 pg/mL) in comparison to relapsed or refractory disease (median 2223.26 pg/mL; P = .03) and to newly diagnosed patients with myeloma (median 861.98 pg/mL; P less than .001). A statistically significant difference among bone marrow levels of soluble TIE2 was observed for newly diagnosed patients and those with relapsed or refractory disease (P = .03).
However, soluble TIE2 in peripheral blood plasma did not differ significantly in the three cohorts nor did it differ between patients and controls.
In contrast to TIE2 and FLT3-L, levels of endostatin were lowest (median 146.50 ng/mL) in bone marrow plasma samples of patients with relapsed or refractory disease. Levels were higher in MGUS patients (median 190.37 mg/dL) than in newly diagnosed myeloma patients (median 170.15 mg/mL; P = .5).
Similar to soluble TIE2, plasma levels of endostatin in peripheral blood did not differ significantly in the three patient cohorts. Measurements of endostatin in bone marrow and peripheral blood correlated significantly (P less than .001), and peripheral blood levels differed significantly (P less than .001) for patients and control persons.
Osteoactivin expression was highest in the MGUS cohort, with median bone marrow plasma levels of 36 ng/mL as compared with median levels of 24.92 ng/mL in newly diagnosed myeloma patients and 22.30 ng/mL in patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma. Osteoactivin levels in peripheral blood did not differ significantly in the three cohorts, but differed between patients and control subjects. Osteoactivin measures in bone marrow and peripheral blood correlated significantly.
Citation: Steiner N, et al. High levels of FLT3-ligand in bone marrow and peripheral blood of patients with advanced multiple myeloma. PLoS ONE 2017 Jul 20;12:e0181487. doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181487.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
FLT3-ligand (FLT3-L) levels exceeding 92 pg/mL in bone marrow and 121 pg/mL in peripheral blood are associated with relapsed and refractory disease in patients with multiple myeloma, Normann Steiner, MD, and his colleagues report in a study published in PLoS ONE.
In the study of 14 patients with monoclonal gamm opathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), 42 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, and 27 patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma, there was a 61% probability that patients with FLT3-L levels above 92 pg/mL in bone marrow had relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and a 79% probability that those with FLT3-L levels of 92 pg/mL or less had not relapsed and were not refractory. Based on FLT3-L levels in peripheral blood, values of 121 pg/mL or more were associated with a 71% probability of relapsed or refractory disease. The likelihood of not having relapses or refractory disease was 87% for patients with values less than 121 pg/mL.
“FLT3-L could be useful as a marker to identify (relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma) patients and should be evaluated as a potential target for future therapy strategies,” Dr. Steiner of Innsbruck (Austria) Medical University, and his fellow researchers wrote in PLoS ONE.
The researchers obtained bone marrow aspirates from all patients. Peripheral blood was examined from 4 MGUS patients, 31 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, and 16 patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma. Peripheral blood was also obtained from 16 control subjects.
The levels of four potential risk factors were measured – soluble TIE2, FLT3-L, endostatin, and osteoactivin. The most significant association with risk was seen with FLT3-L levels.
Expression of soluble TIE2 in bone marrow differed significantly among the three patient cohorts and may be driven by the same factors that influence FLT3-L levels. However, soluble TIE2 levels were not as effective at differentiating patients at risk for disease progression, the researchers wrote.
Soluble TIE2 expression in bone marrow was highest in MGUS patients (median 4003.97 pg/mL) in comparison to relapsed or refractory disease (median 2223.26 pg/mL; P = .03) and to newly diagnosed patients with myeloma (median 861.98 pg/mL; P less than .001). A statistically significant difference among bone marrow levels of soluble TIE2 was observed for newly diagnosed patients and those with relapsed or refractory disease (P = .03).
However, soluble TIE2 in peripheral blood plasma did not differ significantly in the three cohorts nor did it differ between patients and controls.
In contrast to TIE2 and FLT3-L, levels of endostatin were lowest (median 146.50 ng/mL) in bone marrow plasma samples of patients with relapsed or refractory disease. Levels were higher in MGUS patients (median 190.37 mg/dL) than in newly diagnosed myeloma patients (median 170.15 mg/mL; P = .5).
Similar to soluble TIE2, plasma levels of endostatin in peripheral blood did not differ significantly in the three patient cohorts. Measurements of endostatin in bone marrow and peripheral blood correlated significantly (P less than .001), and peripheral blood levels differed significantly (P less than .001) for patients and control persons.
Osteoactivin expression was highest in the MGUS cohort, with median bone marrow plasma levels of 36 ng/mL as compared with median levels of 24.92 ng/mL in newly diagnosed myeloma patients and 22.30 ng/mL in patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma. Osteoactivin levels in peripheral blood did not differ significantly in the three cohorts, but differed between patients and control subjects. Osteoactivin measures in bone marrow and peripheral blood correlated significantly.
Citation: Steiner N, et al. High levels of FLT3-ligand in bone marrow and peripheral blood of patients with advanced multiple myeloma. PLoS ONE 2017 Jul 20;12:e0181487. doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181487.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
FLT3-ligand (FLT3-L) levels exceeding 92 pg/mL in bone marrow and 121 pg/mL in peripheral blood are associated with relapsed and refractory disease in patients with multiple myeloma, Normann Steiner, MD, and his colleagues report in a study published in PLoS ONE.
In the study of 14 patients with monoclonal gamm opathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), 42 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, and 27 patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma, there was a 61% probability that patients with FLT3-L levels above 92 pg/mL in bone marrow had relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and a 79% probability that those with FLT3-L levels of 92 pg/mL or less had not relapsed and were not refractory. Based on FLT3-L levels in peripheral blood, values of 121 pg/mL or more were associated with a 71% probability of relapsed or refractory disease. The likelihood of not having relapses or refractory disease was 87% for patients with values less than 121 pg/mL.
“FLT3-L could be useful as a marker to identify (relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma) patients and should be evaluated as a potential target for future therapy strategies,” Dr. Steiner of Innsbruck (Austria) Medical University, and his fellow researchers wrote in PLoS ONE.
The researchers obtained bone marrow aspirates from all patients. Peripheral blood was examined from 4 MGUS patients, 31 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, and 16 patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma. Peripheral blood was also obtained from 16 control subjects.
The levels of four potential risk factors were measured – soluble TIE2, FLT3-L, endostatin, and osteoactivin. The most significant association with risk was seen with FLT3-L levels.
Expression of soluble TIE2 in bone marrow differed significantly among the three patient cohorts and may be driven by the same factors that influence FLT3-L levels. However, soluble TIE2 levels were not as effective at differentiating patients at risk for disease progression, the researchers wrote.
Soluble TIE2 expression in bone marrow was highest in MGUS patients (median 4003.97 pg/mL) in comparison to relapsed or refractory disease (median 2223.26 pg/mL; P = .03) and to newly diagnosed patients with myeloma (median 861.98 pg/mL; P less than .001). A statistically significant difference among bone marrow levels of soluble TIE2 was observed for newly diagnosed patients and those with relapsed or refractory disease (P = .03).
However, soluble TIE2 in peripheral blood plasma did not differ significantly in the three cohorts nor did it differ between patients and controls.
In contrast to TIE2 and FLT3-L, levels of endostatin were lowest (median 146.50 ng/mL) in bone marrow plasma samples of patients with relapsed or refractory disease. Levels were higher in MGUS patients (median 190.37 mg/dL) than in newly diagnosed myeloma patients (median 170.15 mg/mL; P = .5).
Similar to soluble TIE2, plasma levels of endostatin in peripheral blood did not differ significantly in the three patient cohorts. Measurements of endostatin in bone marrow and peripheral blood correlated significantly (P less than .001), and peripheral blood levels differed significantly (P less than .001) for patients and control persons.
Osteoactivin expression was highest in the MGUS cohort, with median bone marrow plasma levels of 36 ng/mL as compared with median levels of 24.92 ng/mL in newly diagnosed myeloma patients and 22.30 ng/mL in patients with relapsed or refractory myeloma. Osteoactivin levels in peripheral blood did not differ significantly in the three cohorts, but differed between patients and control subjects. Osteoactivin measures in bone marrow and peripheral blood correlated significantly.
Citation: Steiner N, et al. High levels of FLT3-ligand in bone marrow and peripheral blood of patients with advanced multiple myeloma. PLoS ONE 2017 Jul 20;12:e0181487. doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181487.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
FROM PLOS ONE
Key clinical point: .
Major finding: There was a 61% probability that patients with FLT3-L levels above 92 pg/mL in bone marrow had relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and a 79% probability that those with FLT3-L levels of 92 pg/mL or less had not relapsed and were not refractory.
Data source: A study of 14 patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, 42 patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, and 27 patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma, plus 16 control subjects.
Disclosures: The study was not sponsored, and the authors had no relevant disclosures.
Citation: Steiner N, et al. High levels of FLT3-ligand in bone marrow and peripheral blood of patients with advanced multiple myeloma. PLoS ONE 2017 Jul 20;12:e0181487. doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181487
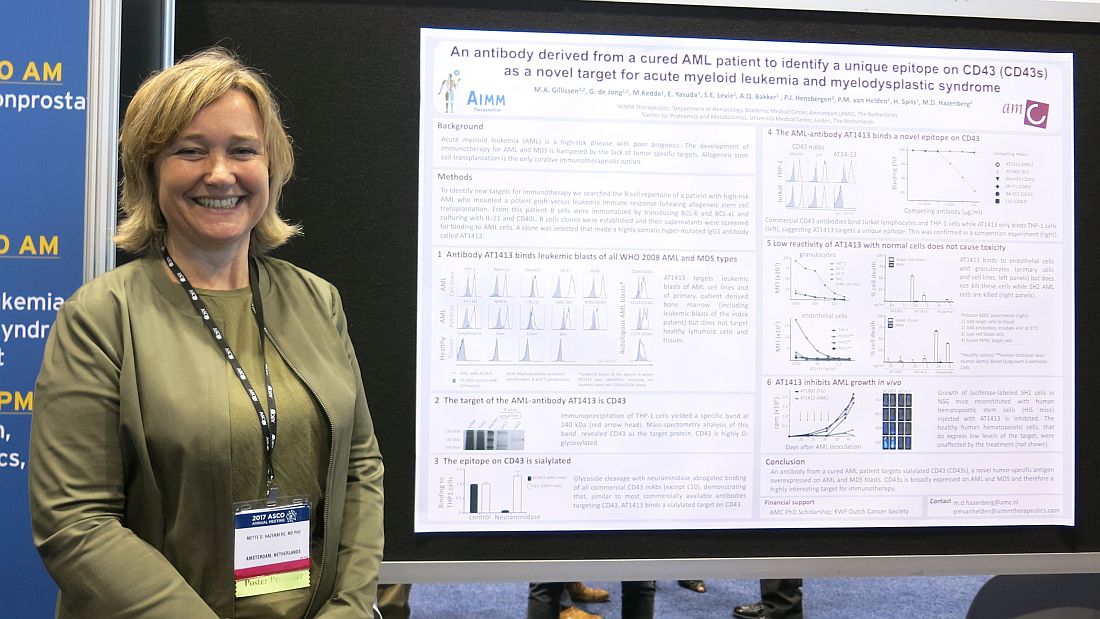
Antibody from AML survivor may prove therapeutic
CHICAGO – A therapeutic target and possibly a treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome may lie in the immortalized B cells of a patient whose acute myeloid leukemia was cured after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
A B cell clone isolated from this patient makes a hypermutated immunoglobulin G1 antibody that binds leukemic blasts of all World Health Organization 2008 AML and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) types, based on cells obtained from 60 AML or MDS patients, but does not target healthy cells and lymphoid tissue, Mette D. Hazenberg, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“CD43 is broadly expressed on AML and MDS and, therefore, is a highly interesting target for immunotherapy,” said Dr. Hazenberg of AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam.
The growth of luciferase-labeled AML cells expressing CD43s was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NOD scid-gamma mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413. Healthy human hematopoietic cells, which express low levels of the target, were not affected by the treatment.
Next steps include further in vivo preclinical studies, according to Dr. Hazenberg.
AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – A therapeutic target and possibly a treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome may lie in the immortalized B cells of a patient whose acute myeloid leukemia was cured after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
A B cell clone isolated from this patient makes a hypermutated immunoglobulin G1 antibody that binds leukemic blasts of all World Health Organization 2008 AML and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) types, based on cells obtained from 60 AML or MDS patients, but does not target healthy cells and lymphoid tissue, Mette D. Hazenberg, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“CD43 is broadly expressed on AML and MDS and, therefore, is a highly interesting target for immunotherapy,” said Dr. Hazenberg of AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam.
The growth of luciferase-labeled AML cells expressing CD43s was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NOD scid-gamma mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413. Healthy human hematopoietic cells, which express low levels of the target, were not affected by the treatment.
Next steps include further in vivo preclinical studies, according to Dr. Hazenberg.
AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – A therapeutic target and possibly a treatment for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome may lie in the immortalized B cells of a patient whose acute myeloid leukemia was cured after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
A B cell clone isolated from this patient makes a hypermutated immunoglobulin G1 antibody that binds leukemic blasts of all World Health Organization 2008 AML and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) types, based on cells obtained from 60 AML or MDS patients, but does not target healthy cells and lymphoid tissue, Mette D. Hazenberg, MD, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
“CD43 is broadly expressed on AML and MDS and, therefore, is a highly interesting target for immunotherapy,” said Dr. Hazenberg of AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam.
The growth of luciferase-labeled AML cells expressing CD43s was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NOD scid-gamma mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413. Healthy human hematopoietic cells, which express low levels of the target, were not affected by the treatment.
Next steps include further in vivo preclinical studies, according to Dr. Hazenberg.
AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
AT ASCO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The growth of luciferase-labeled SH2 cells was inhibited in highly immunodeficient NSG (NOD scid-gamma) mice that were reconstituted with human hematopoietic stem cells injected with AT1413.
Data source: Cellular studies and studies in severely immunodeficient mice.
Disclosures: Dr. Hazenberg is with AIMM Therapeutics and Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam. AIMM Therapeutics is a biotech company comprising a joint venture between Immpact and the Academic Medical Center (AMC) at the University of Amsterdam. The study was supported by an AMC PhD scholarship and the KWF Dutch Cancer Society.
Lenalidomide consolidation linked to extended overall survival in non-del(11q) CLL
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide consolidation therapy was associated with an extended survival plateau for patients with non-del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), based on results from the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
This unique survival plateau indicates future studies should continue to examine the role of lenalidomide, compared with fludarabine plus rituximab therapy, as well as the incorporation of lenalidomide into other novel treatment regimens, Amy Ruppert, MAS, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
All patients received 6 months of FR or FCR therapy, then patients underwent full staging. At 10 months, patients who had been randomized to the FR + lenalidomide group received lenalidomide 5 mg on days 1-21 of the first 28 day cycle and lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1-21 of the subsequent 5 cycles. At 18 months, patients in the FR+L group underwent full staging, and all patients underwent full staging at 24 months.
Based on pretreatment central interphase cytogenetic screening, patients who had del(11q22.3) in at least 20% of their cells were excluded from the primary analysis of 2-year progression-free survival.
Median progression-free survival was significantly shorter with FR, compared with FR+L (P = .03) and FCR (P less than .01), at 43 months (95% CI, 33-50), 66 months (95% CI, 45-not reached), and 78 months (95% CI, 58-not reached), respectively.
Median overall survival has not been reached for any arm of the study. While overall survival was similar across all arms at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up, there was a plateau in overall survival with no events seen beyond 41 months in the FR+L arm. Events continued to occur in the FR and FCR arms, reported Ms. Ruppert of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Ohio State University, Columbus. At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide consolidation therapy was associated with an extended survival plateau for patients with non-del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), based on results from the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
This unique survival plateau indicates future studies should continue to examine the role of lenalidomide, compared with fludarabine plus rituximab therapy, as well as the incorporation of lenalidomide into other novel treatment regimens, Amy Ruppert, MAS, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
All patients received 6 months of FR or FCR therapy, then patients underwent full staging. At 10 months, patients who had been randomized to the FR + lenalidomide group received lenalidomide 5 mg on days 1-21 of the first 28 day cycle and lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1-21 of the subsequent 5 cycles. At 18 months, patients in the FR+L group underwent full staging, and all patients underwent full staging at 24 months.
Based on pretreatment central interphase cytogenetic screening, patients who had del(11q22.3) in at least 20% of their cells were excluded from the primary analysis of 2-year progression-free survival.
Median progression-free survival was significantly shorter with FR, compared with FR+L (P = .03) and FCR (P less than .01), at 43 months (95% CI, 33-50), 66 months (95% CI, 45-not reached), and 78 months (95% CI, 58-not reached), respectively.
Median overall survival has not been reached for any arm of the study. While overall survival was similar across all arms at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up, there was a plateau in overall survival with no events seen beyond 41 months in the FR+L arm. Events continued to occur in the FR and FCR arms, reported Ms. Ruppert of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Ohio State University, Columbus. At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide consolidation therapy was associated with an extended survival plateau for patients with non-del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), based on results from the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
This unique survival plateau indicates future studies should continue to examine the role of lenalidomide, compared with fludarabine plus rituximab therapy, as well as the incorporation of lenalidomide into other novel treatment regimens, Amy Ruppert, MAS, said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
All patients received 6 months of FR or FCR therapy, then patients underwent full staging. At 10 months, patients who had been randomized to the FR + lenalidomide group received lenalidomide 5 mg on days 1-21 of the first 28 day cycle and lenalidomide 10 mg on days 1-21 of the subsequent 5 cycles. At 18 months, patients in the FR+L group underwent full staging, and all patients underwent full staging at 24 months.
Based on pretreatment central interphase cytogenetic screening, patients who had del(11q22.3) in at least 20% of their cells were excluded from the primary analysis of 2-year progression-free survival.
Median progression-free survival was significantly shorter with FR, compared with FR+L (P = .03) and FCR (P less than .01), at 43 months (95% CI, 33-50), 66 months (95% CI, 45-not reached), and 78 months (95% CI, 58-not reached), respectively.
Median overall survival has not been reached for any arm of the study. While overall survival was similar across all arms at 1, 2, and 3 years of follow-up, there was a plateau in overall survival with no events seen beyond 41 months in the FR+L arm. Events continued to occur in the FR and FCR arms, reported Ms. Ruppert of the Comprehensive Cancer Center at Ohio State University, Columbus. At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.
mdales@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @maryjodales
AT ASCO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: At 48 months, the hazard ratio for overall survival in FR+L vs. FR was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.10-0.70; P = .01).
Data source: Results from 342 patients in the phase 2 CALGB 10404 trial.
Disclosures: Ms. Ruppert had no financial disclosures. The study is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and Celgene.