User login
Blisters during pregnancy—just with the second husband
A 33-year-old Hispanic woman who was 5 months pregnant came to the hospital complaining of nausea and vomiting. She had a history of anticardiolipin antibody syndrome, diagnosed originally in 1993 after 2 spontaneous abortions. She had stopped taking warfarin (Coumadin) at the start of her pregnancy, and had been taking heparin for 3 months.
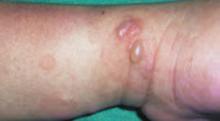
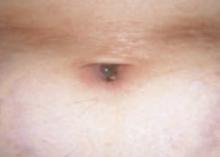
After 4 days of close monitoring, the patient had labor induced for severe life-threatening pre-eclampsia. One day after induction and delivery of a stillborn fetus, she began to develop painful swelling of both hands and feet along with targetoid, urticarial, edematous, deep pink, slightly dusky papules and plaques on her hands, abdomen, lower extremities, and proximal thighs. Some of the edematous sites began to form vesicles and bullae (FIGURE 1 AND 2). When asked about this eruption, the patient mentioned having a similar rash after delivery of one of her children about 10 years before.
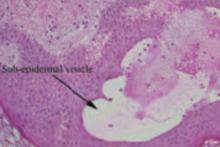
Interestingly, she noted that she only experienced these cutaneous findings during pregnancies with her second husband and not with her first. Biopsies were performed and showed prominent eosinophils in the dermis and a subepidermal vesicle (FIGURE 3).
FIGURE 1
Blisters on the wrist…
FIGURE 2
…and the abdomen
FIGURE 3
Biopsy results
What is your diagnosis?
Diagnosis: Pemphigoid gestationis
The patient had pemphigoid gestationis, also known as herpes gestationis, a rare autoimmune bullous disease of pregnancy and the puerperium.1 Clinically and immunopathologically, pemphigoid gestationis is related to the pemphigoid group of disorders and is not virally mediated.2
In the United States, pemphigoid gestationis has an incidence of 1:10,000 to 1:50,000 pregnancies.3 Clinically, it manifests during the second or third trimester, with a sudden onset of extremely pruritic urticarial papules and plaques usually located around the umbilicus. These lesions often progress to tense vesicles and blisters and spread peripherally to the trunk, often sparing the face, palms, and soles.4 Worsening of the lesions at the time of delivery occurs in 75% of cases, and usually recurs with subsequent pregnancies.5 Occasionally, however, subsequent pregnancies are unaffected, so-called “skip pregnancies.”6 This occurs most often when there has been a change in paternity.7
The exact cause of pemphigoid gestationis is unknown. Investigative efforts lead to the identification of an immunoglobulin G (IgG) autoantibody, which binds to bullous pemphigoid (BP) antigen 2, also called BP180, which is a protein associated with hemidesmosomes of basal keratinocytes.8-10 These hemidesmosomes form the central portion of the dermalepidermal anchoring complex, whose function is to establish a connection between the basal keratinocytes and the upper dermis.11,12 This is critical for maintaining dermal-epidermal adhesion. It is hypothesized that binding of autoantibodies to BP180 initiates an inflammatory reaction, leading to blister formation at the dermal-epidermal junction.13
Pathology and immunology
Histopathologic findings demonstrate subepidermal vesicles, spongiosis, and perivascular lymphocyte, and histiocyte infiltrates with a preponderance of eosinophils.3 The sine qua non of the disease, though, is the demonstration through direct immunofluorescence of complement deposition and IgG in a linear band along the basement membrane.14
There appears to be a genetic predisposition toward the development of pemphigoid gestationis. Associations with human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) DR3 (61%–85%), DR4 (52%), or both (43%–50%) have been reported.3,15,16 Interestingly, 85% of persons with a history of pemphigoid gestationis were found to have anti-HLA antibodies, some of which were directed against paternal HLAs expressed in their placentae.17 These findings raised speculation about a possible immunologic insult against placental antigens during pregnancy. Evidence suggests that circulating autoantibodies in patients with pemphigoid gestationis bind to the dermal-epidermal junction of skin and amnion in which BP180 antigen is also present.18-20
It has been demonstrated that in patients with pemphigoid gestationis the cells of the placenta stroma express abnormal major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules.21,22 This lead to the proposition of 2 possible mechanisms for the initiation of an autoimmune response in pemphigoid gestationis. The first proposes that placental BP180 is presented to the maternal immune system in association with abnormal MHC molecules, which then trigger the production of autoantibodies that cross-react with the skin. Alternatively, the placental stromal cells may evoke an allogeneic reaction against the BP180 antigen presented by paternal MHC molecules of the placental stroma, which then cross-reacts with the skin.23 The latter theory supports the findings in this patient, who developed pemphigoid gestationis during the 2 pregnancies with her second husband and not during the pregnancies with her first husband.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to differentiate the prebullous stage of pemphigoid gestationis from other pregnancy-related dermatoses. These include polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (PEP), pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), erythema multiforme, prurigo annularis, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, and impetigo herpetiformis. Impetigo herpetiformis is not related to bacterial or viral causes, but is rather a manifestation of pustular psoriasis during pregnancy. The target lesions that form in pemphigoid gestationis look just like the target lesions of erythema multiforme.
When there is no blister formation, it is impossible to distinguish pemphigoid gestationis from many of the other cutaneous eruptions of pregnancy. If uncertain, the clinician should perform punch biopsies of the involved skin, with one specimen sent for immunofluoresence studies. The biopsy should not pass directly through a bullae, due to risk of losing the overlying epidermis in the specimen. Do the punch biopsy at the edge of the bulla including some normal skin. Other important laboratory exams to perform would include liver function tests to look for an upward trend associated with intrahepatic cholestasis, and herpes simplex virus antibody testing for the association with erythema multiforme. The cutaneous findings and pertinent tests are listed in the table below in order of increasing potential as a life-threatening dermatosis (TABLE).
TABLE
Differential diagnosis for blisters in pregnancy
| DISEASE | ASSOCIATIONS | DIAGNOSIS | TREATMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymorphous eruption of pregnancy | Nonspecific pruritic eruption of pregnancy | Biopsy to differentiate from prebullous stage of pemphigoid (herpes) gestationis | Mild to mid-potency topical steroids, oral antihistamines |
| Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy | Occur in stretch marks, spare umbilicus; more often in primigravidas | Unless history is very clear, biopsy to differentiate from prebullous stage of pemphigoid gestationis | Emollients, pulse-dye laser during violaceous stage of striae, topical steroids, oral antihistamines |
| Erythema multiforme | Can involve mucous membranes, targetoid lesions, absence of pruritus, centripetal spread, favors palms/soles | Viral, bacterial, or drug-related eruption. Most often with herpes simplex I or II virus. Biopsy to differentiate from pemphigoid gestationis | Acyclovir, valacyclovir if HSV-related, treatment of bacterial infection, or removal of offending drug |
| Pemphigoid gestationis | Blistering, urticarial papules/plaques, pruritus | Biopsy sent for histologic diagnosis and immunofluorescence | Prednisone for short course starting at 1 mg/kg, then tapering over 2–3 months, topical steroids |
| Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | +/- jaundice, otherwise no cutaneous findings other than generalized pruritus, risk of preterm birth | Elevation in liver function tests, cholesterol, triglycerides, dark urine, right upper quadrant pain, nausea, greasy stools | Ursodeoxycholic acid, S-adenosyl-L-methionine |
| Impetigo herpetiformis (pustular psoriasis of pregnancy) | Extremely ill with fever, chills, nausea, vascular instability, pustules rather than vesicles | Biopsy if uncertain, pustules sterile, risk of hypocalcemia, hypoparathyroidism | High dose oral steroids or cyclosporine |
Treatment
Pemphigoid gestationis should resolve spontaneously within 2 to 3 months of delivery. Treatment is aimed at preventing new blisters and relieving pruritus, with topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines in mild cases.2,25 In advanced lesions as seen in this case, 0.3 to 0.5 mg/kg of prednisolone daily is usually sufficient.3,25 Alternative medications include sulfapyridine, dapsone, and cyclosporine, though disease response is variable and their safety is questionable.3
When the skin condition began, the patient was treated with oral antihistamines and topical steroids. On day 2, the diagnosis of pemphigoid gestationis was clear, and she was started on oral prednisone at 60 mg/d, which resulted in rapid symptom improvement in her lesions and swelling. New lesions stopped forming, and systemic steroids were tapered off over the 3 months after delivery. The skin lesions healed and she was given supportive counseling to help her cope with her pregnancy loss.
Conclusion
We have described a rare case of a patient with no cutaneous eruptions during her pregnancies with her first husband, who developed pemphigoid gestationis in 2 pregnancies with her second husband. While it is interesting that our patient also had the anticardiolipin syndrome, most patients do not have both conditions.
Our patient had the classic findings of pemphigoid gestationis with many characteristic lesions (including the umbilicus) making the diagnosis possible before biopsy confirmation. This was fortunate for her because her painful swelling responded quickly to the corticosteroids. When cases are less clinically obvious, biopsy for histopathology and immunofluorescence facilitates differentiation of pemphigoid gestationis from other dermatoses of pregnancy.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard P. Usatine, MD, University of Texas Health Sciences Center at San Antonio, 7703 Floyd Curl Drive, San Antonio, TX 78229-3900. E-mail: usatine@uthscsa.edu
1. Coupe RL. Herpes gestationis. Arch Dermatol 1965;91:633-636.
2. Jenkins RE, Hern S, Black MM. Clinical features and management of 87 patients with pemphigoid gestationis. Clin Exp Dermatol 1999;24:255-259.
3. Al-Fouzan AW, Galadari I, Oumeish I, et al. Herpes gestationis (Pemphigoid gestationis). Clinics Dermatology 2006;24:109-112.
4. Shornick JK. Herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1987;17:539-556.
5. Holmes RC, Black MM, Dann J, et al. A comparative study of toxic erythema of pregnancy and herpes gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1982;106:499-510.
6. Cozzani E, Basso M, Parodi A, Rebora A. Pemphigoid gestationis post partum after changing husband. Intn J Dermatol 2005;44:1057-1058.
7. Shornick JK, Black MM. Fetal risks in herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1992;26:63-68.
8. Diaz LA, Ratrie H, III, Saunders WS, et al. Isolation of a human epidermal cDNA corresponding to the 180-kD autoantigen recognized by bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis sera. Immunolocalization of this protein to the hemidesmosome. J Clin Invest 1990;86:1088-1094.
9. Giudice GJ, Emery DJ, Diaz LA. Cloning and primary structural analysis of the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen BP180. J Invest Dermatol 1992;99:243-250.
10. Zillikens D, Giudice GJ. BP180/typeXVIII collagen: its role in acquired and inherited disorders of the dermal-epidermal junction. Arch Dermatol Res 1999;291:187-194.
11. Borradori L, Sonnenberg A. Hemidesmosomes: roles in adhesion, signaling and human diseases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1996;8:647-656.
12. Zillikens D. Acquired skin disease of hemidesmosomes. J Dermatol Sci 1999;20:134-154.
13. Schmidt E, Zillikens D. Autoimmune and inherited subepidermal blistering diseases: advances in the clinic and the laboratory. Adv Dermatol 2000;16:113-157.
14. Shornick JD. Dermatoses of pregnancy. Semin Cutan Med Surg 1998;17:172-181.
15. Holmes RC, Black MM, Jurecka W, et al. Clues to the aetiology and pathogenesis of herpes gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1983;109:131-139.
16. Shornick JK, Stastny P, Gilliam JN. High frequency of histocompatibility antigens DR3 and DR4 in herpes gestationis. J Clin Invest 1981;68:553-555.
17. Shornick JK, Stastny P, Gilliam JN. Paternal histocompatibility (HLA) antigens and maternal anti-HLA antibodies in herpes gestationis. J Invest Dermatol 1983;81:407-409.
18. Ortonne JP, Hsi BL, Verrando P, et al. Herpes gestationis factor reacts with the amniotic epithelial basement membrane. Br J Dermatol 1987;117:147-154.
19. Kelly SE, Bhogal BS, Wojnarowska F, Black MM. Expression of a pemphigoid gestationis-related antigen by human placenta. Br J Dermatol 1988;118:605-611.
20. Fairley JA, Heintz PW, Neuburg M, et al. Expression pattern of the bullous pemphigoid-180 antigen in normal and neoplastic epithelia. Br J Dermatol 1995;133:385-391.
21. Kelly SE, Black MM, Fleming S. Antigen-presenting cells in the skin and placenta in pemphigoid gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1990;122:593-599.
22. Borthwick GM, Holmes RC, Stirrat GM. Abnormal expression of class II MHC antigens in placentae from patients with pemphigoid gestationis. Placenta 1988;9:81-94.
23. Kelly SE, Black MM, Fleming S. Pemphigoid gestationis: a unique mechanism of initiation of an autoimmune response by MHC class II molecules. J Pathol 1989;158:81-82.
24. Borradori L, Saurat JH. Specific dermatoses of pregnancy. Toward a comprehensive view. Arch Dermatol 1994;130:778-780.
25. Shimanovich I, Bröcker EB, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid gestationis: new insights into the pathogenesis lead to novel diagnostic tools. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;109:970-976.
A 33-year-old Hispanic woman who was 5 months pregnant came to the hospital complaining of nausea and vomiting. She had a history of anticardiolipin antibody syndrome, diagnosed originally in 1993 after 2 spontaneous abortions. She had stopped taking warfarin (Coumadin) at the start of her pregnancy, and had been taking heparin for 3 months.
After 4 days of close monitoring, the patient had labor induced for severe life-threatening pre-eclampsia. One day after induction and delivery of a stillborn fetus, she began to develop painful swelling of both hands and feet along with targetoid, urticarial, edematous, deep pink, slightly dusky papules and plaques on her hands, abdomen, lower extremities, and proximal thighs. Some of the edematous sites began to form vesicles and bullae (FIGURE 1 AND 2). When asked about this eruption, the patient mentioned having a similar rash after delivery of one of her children about 10 years before.
Interestingly, she noted that she only experienced these cutaneous findings during pregnancies with her second husband and not with her first. Biopsies were performed and showed prominent eosinophils in the dermis and a subepidermal vesicle (FIGURE 3).
FIGURE 1
Blisters on the wrist…
FIGURE 2
…and the abdomen
FIGURE 3
Biopsy results
What is your diagnosis?
Diagnosis: Pemphigoid gestationis
The patient had pemphigoid gestationis, also known as herpes gestationis, a rare autoimmune bullous disease of pregnancy and the puerperium.1 Clinically and immunopathologically, pemphigoid gestationis is related to the pemphigoid group of disorders and is not virally mediated.2
In the United States, pemphigoid gestationis has an incidence of 1:10,000 to 1:50,000 pregnancies.3 Clinically, it manifests during the second or third trimester, with a sudden onset of extremely pruritic urticarial papules and plaques usually located around the umbilicus. These lesions often progress to tense vesicles and blisters and spread peripherally to the trunk, often sparing the face, palms, and soles.4 Worsening of the lesions at the time of delivery occurs in 75% of cases, and usually recurs with subsequent pregnancies.5 Occasionally, however, subsequent pregnancies are unaffected, so-called “skip pregnancies.”6 This occurs most often when there has been a change in paternity.7
The exact cause of pemphigoid gestationis is unknown. Investigative efforts lead to the identification of an immunoglobulin G (IgG) autoantibody, which binds to bullous pemphigoid (BP) antigen 2, also called BP180, which is a protein associated with hemidesmosomes of basal keratinocytes.8-10 These hemidesmosomes form the central portion of the dermalepidermal anchoring complex, whose function is to establish a connection between the basal keratinocytes and the upper dermis.11,12 This is critical for maintaining dermal-epidermal adhesion. It is hypothesized that binding of autoantibodies to BP180 initiates an inflammatory reaction, leading to blister formation at the dermal-epidermal junction.13
Pathology and immunology
Histopathologic findings demonstrate subepidermal vesicles, spongiosis, and perivascular lymphocyte, and histiocyte infiltrates with a preponderance of eosinophils.3 The sine qua non of the disease, though, is the demonstration through direct immunofluorescence of complement deposition and IgG in a linear band along the basement membrane.14
There appears to be a genetic predisposition toward the development of pemphigoid gestationis. Associations with human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) DR3 (61%–85%), DR4 (52%), or both (43%–50%) have been reported.3,15,16 Interestingly, 85% of persons with a history of pemphigoid gestationis were found to have anti-HLA antibodies, some of which were directed against paternal HLAs expressed in their placentae.17 These findings raised speculation about a possible immunologic insult against placental antigens during pregnancy. Evidence suggests that circulating autoantibodies in patients with pemphigoid gestationis bind to the dermal-epidermal junction of skin and amnion in which BP180 antigen is also present.18-20
It has been demonstrated that in patients with pemphigoid gestationis the cells of the placenta stroma express abnormal major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules.21,22 This lead to the proposition of 2 possible mechanisms for the initiation of an autoimmune response in pemphigoid gestationis. The first proposes that placental BP180 is presented to the maternal immune system in association with abnormal MHC molecules, which then trigger the production of autoantibodies that cross-react with the skin. Alternatively, the placental stromal cells may evoke an allogeneic reaction against the BP180 antigen presented by paternal MHC molecules of the placental stroma, which then cross-reacts with the skin.23 The latter theory supports the findings in this patient, who developed pemphigoid gestationis during the 2 pregnancies with her second husband and not during the pregnancies with her first husband.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to differentiate the prebullous stage of pemphigoid gestationis from other pregnancy-related dermatoses. These include polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (PEP), pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), erythema multiforme, prurigo annularis, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, and impetigo herpetiformis. Impetigo herpetiformis is not related to bacterial or viral causes, but is rather a manifestation of pustular psoriasis during pregnancy. The target lesions that form in pemphigoid gestationis look just like the target lesions of erythema multiforme.
When there is no blister formation, it is impossible to distinguish pemphigoid gestationis from many of the other cutaneous eruptions of pregnancy. If uncertain, the clinician should perform punch biopsies of the involved skin, with one specimen sent for immunofluoresence studies. The biopsy should not pass directly through a bullae, due to risk of losing the overlying epidermis in the specimen. Do the punch biopsy at the edge of the bulla including some normal skin. Other important laboratory exams to perform would include liver function tests to look for an upward trend associated with intrahepatic cholestasis, and herpes simplex virus antibody testing for the association with erythema multiforme. The cutaneous findings and pertinent tests are listed in the table below in order of increasing potential as a life-threatening dermatosis (TABLE).
TABLE
Differential diagnosis for blisters in pregnancy
| DISEASE | ASSOCIATIONS | DIAGNOSIS | TREATMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymorphous eruption of pregnancy | Nonspecific pruritic eruption of pregnancy | Biopsy to differentiate from prebullous stage of pemphigoid (herpes) gestationis | Mild to mid-potency topical steroids, oral antihistamines |
| Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy | Occur in stretch marks, spare umbilicus; more often in primigravidas | Unless history is very clear, biopsy to differentiate from prebullous stage of pemphigoid gestationis | Emollients, pulse-dye laser during violaceous stage of striae, topical steroids, oral antihistamines |
| Erythema multiforme | Can involve mucous membranes, targetoid lesions, absence of pruritus, centripetal spread, favors palms/soles | Viral, bacterial, or drug-related eruption. Most often with herpes simplex I or II virus. Biopsy to differentiate from pemphigoid gestationis | Acyclovir, valacyclovir if HSV-related, treatment of bacterial infection, or removal of offending drug |
| Pemphigoid gestationis | Blistering, urticarial papules/plaques, pruritus | Biopsy sent for histologic diagnosis and immunofluorescence | Prednisone for short course starting at 1 mg/kg, then tapering over 2–3 months, topical steroids |
| Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | +/- jaundice, otherwise no cutaneous findings other than generalized pruritus, risk of preterm birth | Elevation in liver function tests, cholesterol, triglycerides, dark urine, right upper quadrant pain, nausea, greasy stools | Ursodeoxycholic acid, S-adenosyl-L-methionine |
| Impetigo herpetiformis (pustular psoriasis of pregnancy) | Extremely ill with fever, chills, nausea, vascular instability, pustules rather than vesicles | Biopsy if uncertain, pustules sterile, risk of hypocalcemia, hypoparathyroidism | High dose oral steroids or cyclosporine |
Treatment
Pemphigoid gestationis should resolve spontaneously within 2 to 3 months of delivery. Treatment is aimed at preventing new blisters and relieving pruritus, with topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines in mild cases.2,25 In advanced lesions as seen in this case, 0.3 to 0.5 mg/kg of prednisolone daily is usually sufficient.3,25 Alternative medications include sulfapyridine, dapsone, and cyclosporine, though disease response is variable and their safety is questionable.3
When the skin condition began, the patient was treated with oral antihistamines and topical steroids. On day 2, the diagnosis of pemphigoid gestationis was clear, and she was started on oral prednisone at 60 mg/d, which resulted in rapid symptom improvement in her lesions and swelling. New lesions stopped forming, and systemic steroids were tapered off over the 3 months after delivery. The skin lesions healed and she was given supportive counseling to help her cope with her pregnancy loss.
Conclusion
We have described a rare case of a patient with no cutaneous eruptions during her pregnancies with her first husband, who developed pemphigoid gestationis in 2 pregnancies with her second husband. While it is interesting that our patient also had the anticardiolipin syndrome, most patients do not have both conditions.
Our patient had the classic findings of pemphigoid gestationis with many characteristic lesions (including the umbilicus) making the diagnosis possible before biopsy confirmation. This was fortunate for her because her painful swelling responded quickly to the corticosteroids. When cases are less clinically obvious, biopsy for histopathology and immunofluorescence facilitates differentiation of pemphigoid gestationis from other dermatoses of pregnancy.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard P. Usatine, MD, University of Texas Health Sciences Center at San Antonio, 7703 Floyd Curl Drive, San Antonio, TX 78229-3900. E-mail: usatine@uthscsa.edu
A 33-year-old Hispanic woman who was 5 months pregnant came to the hospital complaining of nausea and vomiting. She had a history of anticardiolipin antibody syndrome, diagnosed originally in 1993 after 2 spontaneous abortions. She had stopped taking warfarin (Coumadin) at the start of her pregnancy, and had been taking heparin for 3 months.
After 4 days of close monitoring, the patient had labor induced for severe life-threatening pre-eclampsia. One day after induction and delivery of a stillborn fetus, she began to develop painful swelling of both hands and feet along with targetoid, urticarial, edematous, deep pink, slightly dusky papules and plaques on her hands, abdomen, lower extremities, and proximal thighs. Some of the edematous sites began to form vesicles and bullae (FIGURE 1 AND 2). When asked about this eruption, the patient mentioned having a similar rash after delivery of one of her children about 10 years before.
Interestingly, she noted that she only experienced these cutaneous findings during pregnancies with her second husband and not with her first. Biopsies were performed and showed prominent eosinophils in the dermis and a subepidermal vesicle (FIGURE 3).
FIGURE 1
Blisters on the wrist…
FIGURE 2
…and the abdomen
FIGURE 3
Biopsy results
What is your diagnosis?
Diagnosis: Pemphigoid gestationis
The patient had pemphigoid gestationis, also known as herpes gestationis, a rare autoimmune bullous disease of pregnancy and the puerperium.1 Clinically and immunopathologically, pemphigoid gestationis is related to the pemphigoid group of disorders and is not virally mediated.2
In the United States, pemphigoid gestationis has an incidence of 1:10,000 to 1:50,000 pregnancies.3 Clinically, it manifests during the second or third trimester, with a sudden onset of extremely pruritic urticarial papules and plaques usually located around the umbilicus. These lesions often progress to tense vesicles and blisters and spread peripherally to the trunk, often sparing the face, palms, and soles.4 Worsening of the lesions at the time of delivery occurs in 75% of cases, and usually recurs with subsequent pregnancies.5 Occasionally, however, subsequent pregnancies are unaffected, so-called “skip pregnancies.”6 This occurs most often when there has been a change in paternity.7
The exact cause of pemphigoid gestationis is unknown. Investigative efforts lead to the identification of an immunoglobulin G (IgG) autoantibody, which binds to bullous pemphigoid (BP) antigen 2, also called BP180, which is a protein associated with hemidesmosomes of basal keratinocytes.8-10 These hemidesmosomes form the central portion of the dermalepidermal anchoring complex, whose function is to establish a connection between the basal keratinocytes and the upper dermis.11,12 This is critical for maintaining dermal-epidermal adhesion. It is hypothesized that binding of autoantibodies to BP180 initiates an inflammatory reaction, leading to blister formation at the dermal-epidermal junction.13
Pathology and immunology
Histopathologic findings demonstrate subepidermal vesicles, spongiosis, and perivascular lymphocyte, and histiocyte infiltrates with a preponderance of eosinophils.3 The sine qua non of the disease, though, is the demonstration through direct immunofluorescence of complement deposition and IgG in a linear band along the basement membrane.14
There appears to be a genetic predisposition toward the development of pemphigoid gestationis. Associations with human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) DR3 (61%–85%), DR4 (52%), or both (43%–50%) have been reported.3,15,16 Interestingly, 85% of persons with a history of pemphigoid gestationis were found to have anti-HLA antibodies, some of which were directed against paternal HLAs expressed in their placentae.17 These findings raised speculation about a possible immunologic insult against placental antigens during pregnancy. Evidence suggests that circulating autoantibodies in patients with pemphigoid gestationis bind to the dermal-epidermal junction of skin and amnion in which BP180 antigen is also present.18-20
It has been demonstrated that in patients with pemphigoid gestationis the cells of the placenta stroma express abnormal major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules.21,22 This lead to the proposition of 2 possible mechanisms for the initiation of an autoimmune response in pemphigoid gestationis. The first proposes that placental BP180 is presented to the maternal immune system in association with abnormal MHC molecules, which then trigger the production of autoantibodies that cross-react with the skin. Alternatively, the placental stromal cells may evoke an allogeneic reaction against the BP180 antigen presented by paternal MHC molecules of the placental stroma, which then cross-reacts with the skin.23 The latter theory supports the findings in this patient, who developed pemphigoid gestationis during the 2 pregnancies with her second husband and not during the pregnancies with her first husband.
Differential diagnosis
It is important to differentiate the prebullous stage of pemphigoid gestationis from other pregnancy-related dermatoses. These include polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (PEP), pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), erythema multiforme, prurigo annularis, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, and impetigo herpetiformis. Impetigo herpetiformis is not related to bacterial or viral causes, but is rather a manifestation of pustular psoriasis during pregnancy. The target lesions that form in pemphigoid gestationis look just like the target lesions of erythema multiforme.
When there is no blister formation, it is impossible to distinguish pemphigoid gestationis from many of the other cutaneous eruptions of pregnancy. If uncertain, the clinician should perform punch biopsies of the involved skin, with one specimen sent for immunofluoresence studies. The biopsy should not pass directly through a bullae, due to risk of losing the overlying epidermis in the specimen. Do the punch biopsy at the edge of the bulla including some normal skin. Other important laboratory exams to perform would include liver function tests to look for an upward trend associated with intrahepatic cholestasis, and herpes simplex virus antibody testing for the association with erythema multiforme. The cutaneous findings and pertinent tests are listed in the table below in order of increasing potential as a life-threatening dermatosis (TABLE).
TABLE
Differential diagnosis for blisters in pregnancy
| DISEASE | ASSOCIATIONS | DIAGNOSIS | TREATMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymorphous eruption of pregnancy | Nonspecific pruritic eruption of pregnancy | Biopsy to differentiate from prebullous stage of pemphigoid (herpes) gestationis | Mild to mid-potency topical steroids, oral antihistamines |
| Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy | Occur in stretch marks, spare umbilicus; more often in primigravidas | Unless history is very clear, biopsy to differentiate from prebullous stage of pemphigoid gestationis | Emollients, pulse-dye laser during violaceous stage of striae, topical steroids, oral antihistamines |
| Erythema multiforme | Can involve mucous membranes, targetoid lesions, absence of pruritus, centripetal spread, favors palms/soles | Viral, bacterial, or drug-related eruption. Most often with herpes simplex I or II virus. Biopsy to differentiate from pemphigoid gestationis | Acyclovir, valacyclovir if HSV-related, treatment of bacterial infection, or removal of offending drug |
| Pemphigoid gestationis | Blistering, urticarial papules/plaques, pruritus | Biopsy sent for histologic diagnosis and immunofluorescence | Prednisone for short course starting at 1 mg/kg, then tapering over 2–3 months, topical steroids |
| Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy | +/- jaundice, otherwise no cutaneous findings other than generalized pruritus, risk of preterm birth | Elevation in liver function tests, cholesterol, triglycerides, dark urine, right upper quadrant pain, nausea, greasy stools | Ursodeoxycholic acid, S-adenosyl-L-methionine |
| Impetigo herpetiformis (pustular psoriasis of pregnancy) | Extremely ill with fever, chills, nausea, vascular instability, pustules rather than vesicles | Biopsy if uncertain, pustules sterile, risk of hypocalcemia, hypoparathyroidism | High dose oral steroids or cyclosporine |
Treatment
Pemphigoid gestationis should resolve spontaneously within 2 to 3 months of delivery. Treatment is aimed at preventing new blisters and relieving pruritus, with topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines in mild cases.2,25 In advanced lesions as seen in this case, 0.3 to 0.5 mg/kg of prednisolone daily is usually sufficient.3,25 Alternative medications include sulfapyridine, dapsone, and cyclosporine, though disease response is variable and their safety is questionable.3
When the skin condition began, the patient was treated with oral antihistamines and topical steroids. On day 2, the diagnosis of pemphigoid gestationis was clear, and she was started on oral prednisone at 60 mg/d, which resulted in rapid symptom improvement in her lesions and swelling. New lesions stopped forming, and systemic steroids were tapered off over the 3 months after delivery. The skin lesions healed and she was given supportive counseling to help her cope with her pregnancy loss.
Conclusion
We have described a rare case of a patient with no cutaneous eruptions during her pregnancies with her first husband, who developed pemphigoid gestationis in 2 pregnancies with her second husband. While it is interesting that our patient also had the anticardiolipin syndrome, most patients do not have both conditions.
Our patient had the classic findings of pemphigoid gestationis with many characteristic lesions (including the umbilicus) making the diagnosis possible before biopsy confirmation. This was fortunate for her because her painful swelling responded quickly to the corticosteroids. When cases are less clinically obvious, biopsy for histopathology and immunofluorescence facilitates differentiation of pemphigoid gestationis from other dermatoses of pregnancy.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard P. Usatine, MD, University of Texas Health Sciences Center at San Antonio, 7703 Floyd Curl Drive, San Antonio, TX 78229-3900. E-mail: usatine@uthscsa.edu
1. Coupe RL. Herpes gestationis. Arch Dermatol 1965;91:633-636.
2. Jenkins RE, Hern S, Black MM. Clinical features and management of 87 patients with pemphigoid gestationis. Clin Exp Dermatol 1999;24:255-259.
3. Al-Fouzan AW, Galadari I, Oumeish I, et al. Herpes gestationis (Pemphigoid gestationis). Clinics Dermatology 2006;24:109-112.
4. Shornick JK. Herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1987;17:539-556.
5. Holmes RC, Black MM, Dann J, et al. A comparative study of toxic erythema of pregnancy and herpes gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1982;106:499-510.
6. Cozzani E, Basso M, Parodi A, Rebora A. Pemphigoid gestationis post partum after changing husband. Intn J Dermatol 2005;44:1057-1058.
7. Shornick JK, Black MM. Fetal risks in herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1992;26:63-68.
8. Diaz LA, Ratrie H, III, Saunders WS, et al. Isolation of a human epidermal cDNA corresponding to the 180-kD autoantigen recognized by bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis sera. Immunolocalization of this protein to the hemidesmosome. J Clin Invest 1990;86:1088-1094.
9. Giudice GJ, Emery DJ, Diaz LA. Cloning and primary structural analysis of the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen BP180. J Invest Dermatol 1992;99:243-250.
10. Zillikens D, Giudice GJ. BP180/typeXVIII collagen: its role in acquired and inherited disorders of the dermal-epidermal junction. Arch Dermatol Res 1999;291:187-194.
11. Borradori L, Sonnenberg A. Hemidesmosomes: roles in adhesion, signaling and human diseases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1996;8:647-656.
12. Zillikens D. Acquired skin disease of hemidesmosomes. J Dermatol Sci 1999;20:134-154.
13. Schmidt E, Zillikens D. Autoimmune and inherited subepidermal blistering diseases: advances in the clinic and the laboratory. Adv Dermatol 2000;16:113-157.
14. Shornick JD. Dermatoses of pregnancy. Semin Cutan Med Surg 1998;17:172-181.
15. Holmes RC, Black MM, Jurecka W, et al. Clues to the aetiology and pathogenesis of herpes gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1983;109:131-139.
16. Shornick JK, Stastny P, Gilliam JN. High frequency of histocompatibility antigens DR3 and DR4 in herpes gestationis. J Clin Invest 1981;68:553-555.
17. Shornick JK, Stastny P, Gilliam JN. Paternal histocompatibility (HLA) antigens and maternal anti-HLA antibodies in herpes gestationis. J Invest Dermatol 1983;81:407-409.
18. Ortonne JP, Hsi BL, Verrando P, et al. Herpes gestationis factor reacts with the amniotic epithelial basement membrane. Br J Dermatol 1987;117:147-154.
19. Kelly SE, Bhogal BS, Wojnarowska F, Black MM. Expression of a pemphigoid gestationis-related antigen by human placenta. Br J Dermatol 1988;118:605-611.
20. Fairley JA, Heintz PW, Neuburg M, et al. Expression pattern of the bullous pemphigoid-180 antigen in normal and neoplastic epithelia. Br J Dermatol 1995;133:385-391.
21. Kelly SE, Black MM, Fleming S. Antigen-presenting cells in the skin and placenta in pemphigoid gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1990;122:593-599.
22. Borthwick GM, Holmes RC, Stirrat GM. Abnormal expression of class II MHC antigens in placentae from patients with pemphigoid gestationis. Placenta 1988;9:81-94.
23. Kelly SE, Black MM, Fleming S. Pemphigoid gestationis: a unique mechanism of initiation of an autoimmune response by MHC class II molecules. J Pathol 1989;158:81-82.
24. Borradori L, Saurat JH. Specific dermatoses of pregnancy. Toward a comprehensive view. Arch Dermatol 1994;130:778-780.
25. Shimanovich I, Bröcker EB, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid gestationis: new insights into the pathogenesis lead to novel diagnostic tools. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;109:970-976.
1. Coupe RL. Herpes gestationis. Arch Dermatol 1965;91:633-636.
2. Jenkins RE, Hern S, Black MM. Clinical features and management of 87 patients with pemphigoid gestationis. Clin Exp Dermatol 1999;24:255-259.
3. Al-Fouzan AW, Galadari I, Oumeish I, et al. Herpes gestationis (Pemphigoid gestationis). Clinics Dermatology 2006;24:109-112.
4. Shornick JK. Herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1987;17:539-556.
5. Holmes RC, Black MM, Dann J, et al. A comparative study of toxic erythema of pregnancy and herpes gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1982;106:499-510.
6. Cozzani E, Basso M, Parodi A, Rebora A. Pemphigoid gestationis post partum after changing husband. Intn J Dermatol 2005;44:1057-1058.
7. Shornick JK, Black MM. Fetal risks in herpes gestationis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1992;26:63-68.
8. Diaz LA, Ratrie H, III, Saunders WS, et al. Isolation of a human epidermal cDNA corresponding to the 180-kD autoantigen recognized by bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis sera. Immunolocalization of this protein to the hemidesmosome. J Clin Invest 1990;86:1088-1094.
9. Giudice GJ, Emery DJ, Diaz LA. Cloning and primary structural analysis of the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen BP180. J Invest Dermatol 1992;99:243-250.
10. Zillikens D, Giudice GJ. BP180/typeXVIII collagen: its role in acquired and inherited disorders of the dermal-epidermal junction. Arch Dermatol Res 1999;291:187-194.
11. Borradori L, Sonnenberg A. Hemidesmosomes: roles in adhesion, signaling and human diseases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1996;8:647-656.
12. Zillikens D. Acquired skin disease of hemidesmosomes. J Dermatol Sci 1999;20:134-154.
13. Schmidt E, Zillikens D. Autoimmune and inherited subepidermal blistering diseases: advances in the clinic and the laboratory. Adv Dermatol 2000;16:113-157.
14. Shornick JD. Dermatoses of pregnancy. Semin Cutan Med Surg 1998;17:172-181.
15. Holmes RC, Black MM, Jurecka W, et al. Clues to the aetiology and pathogenesis of herpes gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1983;109:131-139.
16. Shornick JK, Stastny P, Gilliam JN. High frequency of histocompatibility antigens DR3 and DR4 in herpes gestationis. J Clin Invest 1981;68:553-555.
17. Shornick JK, Stastny P, Gilliam JN. Paternal histocompatibility (HLA) antigens and maternal anti-HLA antibodies in herpes gestationis. J Invest Dermatol 1983;81:407-409.
18. Ortonne JP, Hsi BL, Verrando P, et al. Herpes gestationis factor reacts with the amniotic epithelial basement membrane. Br J Dermatol 1987;117:147-154.
19. Kelly SE, Bhogal BS, Wojnarowska F, Black MM. Expression of a pemphigoid gestationis-related antigen by human placenta. Br J Dermatol 1988;118:605-611.
20. Fairley JA, Heintz PW, Neuburg M, et al. Expression pattern of the bullous pemphigoid-180 antigen in normal and neoplastic epithelia. Br J Dermatol 1995;133:385-391.
21. Kelly SE, Black MM, Fleming S. Antigen-presenting cells in the skin and placenta in pemphigoid gestationis. Br J Dermatol 1990;122:593-599.
22. Borthwick GM, Holmes RC, Stirrat GM. Abnormal expression of class II MHC antigens in placentae from patients with pemphigoid gestationis. Placenta 1988;9:81-94.
23. Kelly SE, Black MM, Fleming S. Pemphigoid gestationis: a unique mechanism of initiation of an autoimmune response by MHC class II molecules. J Pathol 1989;158:81-82.
24. Borradori L, Saurat JH. Specific dermatoses of pregnancy. Toward a comprehensive view. Arch Dermatol 1994;130:778-780.
25. Shimanovich I, Bröcker EB, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid gestationis: new insights into the pathogenesis lead to novel diagnostic tools. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 2002;109:970-976.