User login
A new contraceptive method should ideally provide improved access or a higher quality and safety option. Although unintended pregnancy rates in the United States are decreasing, significant disparities across race and socioeconomic status remain,1 and these disparities actually doubled from 1994 to 2011 even though the overall unintended pregnancy rate decreased.1-3 Specifically, people of color, those with lower income, and people with lower education levels had higher rates of unintended pregnancies than did White people with higher education and income, suggesting disparate access to contraception services.1 Thus, as new contraceptive methods are introduced, we must assess if they have the potential to address this disparity as well as continue to provide higher quality and safer options.
In this Update, we critically review the phase 3 data on efficacy and safety for 3 new methods that were introduced to the US market over the past year to evaluate their impact on the current contraceptive landscape.
The first method, newly approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), is a combined oral contraceptive (OC) that contains a novel endogenous estrogen, estetrol, or E4 (Nextstellis). E4 is a natural estrogen produced in the fetal liver that has lower potency and a longer half-life than estradiol. Nextstellis is a monophasic 24/4 OC pill that contains E4 14.2 mg and drospirenone 3 mg in each of the 24 hormone-containing pills. Most combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) in the United States today contain synthetically made ethinyl estradiol (EE) due to its high potency and oral bioavailability. Outside of the reproductive system, EE upregulates the production of hepatic proteins and alters procoagulant and anticoagulant factors, which results in an overall increase in venous thromboembolic (VTE) risk among CHC users.2
After widespread use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) started in the 1960s, data emerged regarding increased VTE risk.3 Subsequent research discovered that the type of estrogen used in CHCs directly correlates with the thrombosis risk due to the hepatic upregulation with both first- and second-pass metabolism. Although this risk was reduced as the EE dose decreased below 50 µg and concurrent VTE risk factors were contraindicated, CHC users still faced a 2-fold increase in VTE risk compared with nonusers.4,5 EE in contraceptive formulations increases VTE risk, likely related to upregulation of procoagulant factors and decreasing anticoagulant proteins.2 By contrast, a phase 2 trial of Nextstellis demonstrated more neutral effects of E4/drospirenone on hemostatic parameters compared with EE/levonorgestrel or EE/drospirenone.6 Furthermore, E4/drospirenone exhibited lower increases in hepatic proteins, such as angiotensinogen, triglycerides, and sex-hormone binding globulin.7 These findings together suggest that this novel CHC pill has a more favorable cardiovascular adverse effect profile compared with currently available CHCs.
The second contraceptive method is a new transdermal patch that contains EE and levonorgestrel (Twirla); this is in contrast to the available EE/norelgestromin contraceptive patch (Xulane). Transdermal contraceptive patches can offer some users easier adherence as compared with a daily OC.8 Until this past year, the only transdermal contraceptive available in the United States was Xulane, which contains a daily dose of EE 35 µg and norelgestromin 150 µg. Norelgestromin is eventually metabolized to levonorgestrel derivatives.9 Twirla is administered in the same manner as Xulane and contains a daily hormone exposure equivalent to a COC containing EE 30 µg and levonorgestrel 120 µg. Similar to EE/norelgestromin, the EE/levonorgestrel patch also is contraindicated in obese patients (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m2) due to decreased efficacy and increased risk for VTE. Additionally, phase 3 data demonstrated decreasing efficacy of Twirla in overweight users (BMI ≥25–30 kg/m2), perhaps further limiting the population that may benefit from this contraceptive method.10 These issues with efficacy and weight likely are related to the fact that levonorgestrel distribution is weight dependent, with evidence of lower plasma levels in obese individuals.11-13
The third new method is a prescription vaginal contraceptive gel with lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate (Phexxi) designed to prevent pregnancy by maintaining an acidic vaginal environment that is inhospitable to sperm. For many decades, vaginal contraceptives, including vaginal spermicidal gels, provided easy access to a nonhormonal and flexible method of moderately effective contraception for many users. Phexxi is a prescription vaginal pH regulator administered as a gel and active for 1 hour after application. All previous vaginal gels sold in the United States are applied similarly, are available over the counter, and include nonoxynol-9, which is a surfactant that damages sperm cell membranes. Recent data from a phase 3 trial demonstrated similar contraceptive effectiveness of Phexxi when compared with available nonoxynol-9 alternatives.14
Continue to: New OC with the novel estrogen E4 demonstrates good safety profile for VTE...
New OC with the novel estrogen E4 demonstrates good safety profile for VTE
Creinin MD, Westhoff CL, Bouchard C, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: North American phase 3 efficacy and safety results. Contraception. 2021;104:222-228.
The COC E4/drospirenone was evaluated in 2 parallel multinational studies. Here, we review the North American data that are more relevant for the US population; the European-Russian data also are published.15
Study examined 1 year’s use of E4/drospirenone
The US–Canadian trial conducted by Creinin and colleagues enrolled 1,864 participants aged 16 to 50 years to evaluate contraceptive efficacy, bleeding patterns, and adverse events with 1-year use (13 cycles) of E4/drospirenone. The primary efficacy group included 1,524 women aged 16 to 35. This study enrolled healthy, heterosexually active participants with a BMI ≤35 kg/m2 and regular menses from 70 sites in the United States and 7 sites in Canada. The dropout rate was 45%, comparable to that in other contraceptive studies. Participants used E4/drospirenone cyclically, taking 1 hormone-containing pill daily for 24 days followed by 4 days of placebo pills.
Contraceptive efficacious, no VTE observed
The researchers reported efficacy as a Pearl Index (PI) of 2.65 pregnancies per 100 woman-years in participants aged 16 to 35 and an overall 13-cycle life-table pregnancy rate of 2.06%. The PI did not differ among nonobese and obese participants in multivariable analysis. Most users experienced scheduled withdrawal bleeding; only 13% to 18% reported absence of scheduled bleeding. Unscheduled bleeding was typically spotting (55.2%), and this decreased with treatment duration from 30% in cycle 1 to 15% to 20% in cycle 5 and on.
Overall, 28.9% of participants reported treatment-related adverse events (AEs), which most commonly were headache (5.0%), metrorrhagia (4.6%), and nausea (3.8%). Investigators reported a minimal change in mean (SD) BMI of 0.4 (1.7) kg/m2 from baseline after 1 year of E4/drospirenone use, and only 0.5% of participants discontinued use due to weight gain. The most common reasons for AE-related treatment discontinuation included metrorrhagia (0.9%), menorrhagia (0.8%), and vaginal hemorrhage (0.5%). Importantly, no cases of VTE occurred in this study of estetrol despite 23% of participants being obese, a known risk factor for VTE.
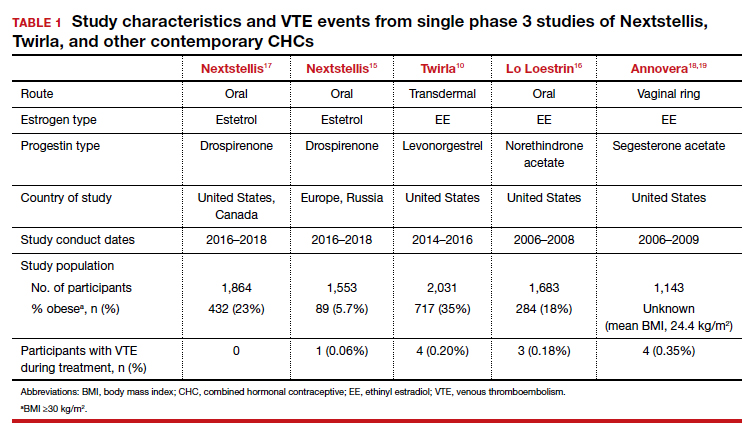
Nextstellis provides safe, effective contraception with a PI comparable to that of other available CHCs as well as a favorable bleeding profile in healthy users who are adherent to treatment. Importantly, contraceptive efficacy was maintained in obese users with a BMI up to 35 kg/m2. In contrast to EE or estradiol, E4 demonstrates a lower impact on the hepatic system, and preliminary findings suggest a lower VTE risk compared with other CHCs on the market. The European phase 3 trial of 1,553 participants also demonstrated a low rate of VTE, with only 1 case diagnosed.15 By contrast, similar phase 3 trials of available CHCs demonstrated more frequent VTE events despite low-dose EE formulations (TABLE 1).10,15-18 In general, most US phase 3 trials have 3 to 4 VTE events in the studied population, and the Nextstellis North American trial, of which 92% of participants were from the United States, had 0. However, confirmation of any potential lower VTE risk requires further analysis from large, population-based postmarketing studies.
Continue to: Efficacy of a new EE/levonorgestrel transdermal patch may be lower in overweight, obese women...
Efficacy of a new EE/levonorgestrel transdermal patch may be lower in overweight, obese women
Nelson AL, Kaunitz AM, Kroll R; SECURE Investigators. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol transdermal delivery system: phase 3 clinical trial results. Contraception. 2021;103:137-143.
To assess the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the transdermal patch Twirla (EE/levonorgestrel) over 1 year of treatment (13 cycles), Nelson and colleagues conducted an open-label, multicenter, US-based phase 3 trial of participants aged 18 years and older with regular cycles. There were no restrictions based on BMI. On average, the study population was overweight, with a mean BMI of 28.3 kg/m2 , and 35% of the population was considered obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2).
Study design
A total of 2,032 participants enrolled in the study, with separate populations defined for specific analysis on safety, contraceptive efficacy, and cycle control. The primary efficacy group included 1,736 participants. Fifty-one percent discontinued the study, most commonly due to “women’s decision” (15%) and lost to follow-up (11%). Users received bleeding diaries and returned periodically throughout the study for evaluation for efficacy, adherence, and adverse events.
Efficacy associated with BMI
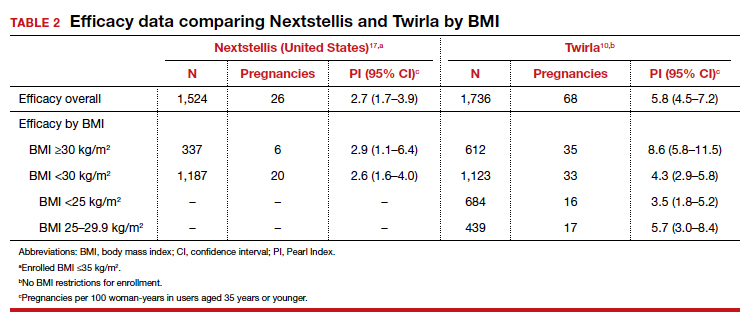
The study results demonstrated an overall PI of 5.8 pregnancies per 100 woman-years for users aged younger than 35. TABLE 2 demonstrates the overall trend of efficacy in relation to BMI.10,15-19 Participants with a higher BMI were found to have a higher PI, revealing lower contraceptive efficacy in more overweight and obese patients. The overall cumulative pregnancy rate over 13 cycles was 5.3%
Participants reported decreasing frequency of bleeding/spotting days over the treatment duration of 13 cycles, from a mean (SD) of 6.2 (4.5) days in cycle 1 to 4.9 (3.5) days in cycle 13. Unscheduled bleeding episodes remained high throughout the study period. Initially, 60% of users reported 1 or more days of unscheduled bleeding in cycle 1, and 42% still reported unscheduled bleeding in cycle 13. In light of this, only 45 participants (2.2%) discontinued the study due to bleeding issues, suggesting perhaps that the bleeding was light. Overall, users experienced acceptable wearability of the patch, and the rate of detachment decreased over the study period from 9.9% in cycle 1 to 2.4% in cycle 13. There were also low rates (0.5%) of moderate to severe irritation. Itching at the adhesion site decreased slightly from 13.1% in cycle 2 to 9.6% in cycle 13.
In general, 27.2% of patch users experienced a study-related AE, most reported as mild to moderate. Nausea (4.1%) and headaches (3.6%) were the most common hormone-related AE. Importantly, 4 obese users experienced 5 VTEs (deep vein thrombosis, n = 2; pulmonary embolism, n = 3) between cycle 5 and 13. Three of these users had additional VTE risk factors, such as air travel and a family history of clots. No users who were of normal weight or overweight experienced VTE.
Available data demonstrate that the EE/norelgestromin patch exposes users to higher serum levels compared with the pill or the ring.20 The higher estrogen exposure with the patch may explain higher estrogen-related adverse effects and may result in increased VTE risk. Initial pharmacokinetic data of the EE/levonorgestrel patch showed lower EE concentrations, similar to marketed COCs and lower than EE/norelgestromin.21 Despite this lower estrogen exposure, the phase 3 trial by Nelson and colleagues did not demonstrate a safer profile with respect to thromboembolic events.
Further, the high PI of 5.8 pregnancies per 100 woman-years calls into question the efficacy of this patch compared with already available CHC options. Indeed, the efficacy appears reasonable in normal-weight individuals, with a PI of 3.5 pregnancies per 100 woman-years; however, this is still higher than its contemporary counterpart, Nextstellis, which has a PI of 2.65 pregnancies per 100 woman-years and included users with a BMI of up to 35 kg/m2 (Table 2). Given the evidence of decreased efficacy, clinicians may consider reserving this option for only normal-weight women who cannot use or prefer not to use another CHC method. Obese individuals (BMI ≥30 kg/m2 ) should not use this patch due to decreased efficacy and increased VTE risk. Lastly, although use in overweight individuals (BMI ≥25 kg/m2) is not absolutely contraindicated, clinicians should counsel the overweight patient on the possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy due to weight, and they may choose to reserve use of this patch in overweight individuals only when no other comparable or more effective method is an option.
Continue to: Novel vaginal pH buffering spermicide is a new Rx-only option...
Novel vaginal pH buffering spermicide is a new Rx-only option
Thomas MA, Chappell BT, Maximos B, et al. A novel vaginal pH regulator: results from the phase 3 AMPOWER contraception clinical trial. Contracept X. 2020;2:100031.
In an open-label phase 3 study, Thomas and colleagues enrolled 1,384 participants aged 18 to 35 with regular cycles at 112 sites in the United States to assess the contraceptive efficacy, safety, and acceptability of Phexxi vaginal gel (lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate) over 7 cycles (6 months). Participants were required to have at least 3 episodes of heterosexual vaginal intercourse per cycle and return throughout the treatment duration for study visits. Fifty-three percent of participants did not complete the study, most frequently due to loss to follow-up (18.1%) and participant withdrawal (12.3%). Most participants were White (69%) and had an average (SD) age of 27.7 (4.5) years.
Efficacy and AE rates
The investigators reported a cumulative pregnancy rate of 13.7% over 7 cycles (6 months). In this study, 45.2% of women experienced 1 AE, and most were noted to be mild (23.9%) to moderate (18.7%). The most reported AE was vulvovaginal burning (20.0%), followed by vulvovaginal pruritus (11.2%), urinary tract infection (5.7%), and vulvovaginal pain (3.8%). Less than 2% of participants discontinued the study due to an AE. Burning and itching decreased with time and with decreased frequency of use. When used twice per day compared with once per day, burning rates decreased from 4.6% to 2.1%, and itching rates decreased from 1.0% to 0.7%. Serious AEs were uncommon, occurring in 1.3% of users; only 1, cystitis, was noted to be “probably” related to the treatment. ●
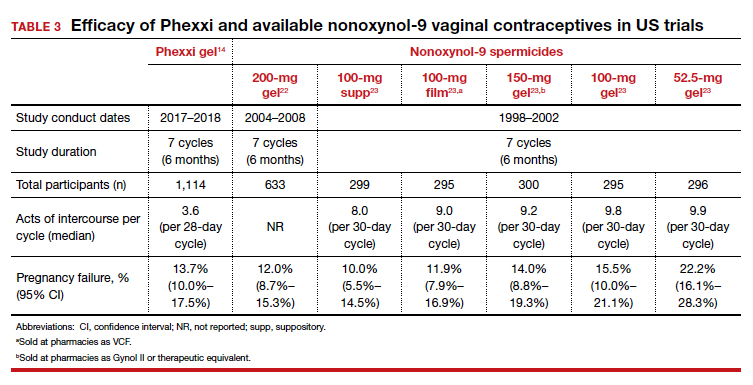
Prior to the approval of Phexxi, all currently available vaginal contraceptive gels in the United States contained nonoxynol-9 as the active ingredient, which is a surfactant that is spermicidal by damaging cell membranes. Although Phexxi provides a novel mechanism of action as a spermicide, the contraceptive efficacy is about the same as available spermicides on the market (see TABLE 3).14,22,23 The FDA calculated a 13-cycle PI to include in the label (27.5 pregnancies per 100 woman-years) based on the results of this study; however, no reliable statistical method exists to calculate a true PI from a 7-cycle study. Thus, we recommend that clinicians counsel patients appropriately based on the 6-month rate noted in the study, and that this rate is similar to that with currently available over-the-counter products. This point is important, as Phexxi is available only by prescription, which may impact patient cost and access.
Equally important is Phexxi’s potential for sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention. In a US-based randomized controlled trial, Phexxi use demonstrated significant risk reduction in gonorrhea and chlamydia infections among participants aged 18 to 45 years.24 That study showed a relative risk reduction of 50% and 78% for chlamydia and gonorrhea, respectively.24 Future research is planned to evaluate this spermicide as a novel STI prevention method. Ultimately, Phexxi may provide an alternative spermicide for users interested in moderately effective contraception and unable to tolerate available nonoxynol-9 formulations. Interested users will have to rely on a prescription, possibly limiting access to this novel spermicide. Further data are required to determine its potential as an STI prevention agent.
- Finer LB, Zolna MR. Declines in unintended pregnancy in the United States, 2008–2011. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:843-852.
- Meade TW. Oral contraceptives, clotting factors, and thrombosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;142(6 pt 2):758-761.
- Royal College of General Practitioners’ Oral Contraception Study. Oral contraceptives, venous thrombosis, and varicose veins. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1978;28:393-399.
- Dinger JC, Heinemann LA, Kühl-Habich D. The safety of a drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive: final results from the European Active Surveillance Study on oral contraceptives based on 142,475 women-years of observation. Contraception. 2007;75:344-354.
- Heinemann LA, Dinger JC. Range of published estimates of venous thromboembolism incidence in young women. Contraception. 2007;75:328-336.
- Douxfils J, Klipping C, Duijkers I, et al. Evaluation of the effect of a new oral contraceptive containing estetrol and drospirenone on hemostasis parameters. Contraception. 2020;102:396-402.
- Klipping C, Duijkers I, Mawet M, et al. Endocrine and metabolic effects of an oral contraceptive containing estetrol and drospirenone. Contraception. 2021;103:213-221.
- Archer DF, Cullins V, Creasy GW, et al. The impact of improved compliance with a weekly contraceptive transdermal system (Ortho Evra) on contraceptive efficacy. Contraception. 2004;69:189-195.
- Stanczyk FZ, Roy S. Metabolism of levonorgestrel, norethindrone, and structurally related contraceptive steroids. Contraception. 1990;42:67-96.
- Nelson AL, Kaunitz AM, Kroll R; SECURE Investigators. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol transdermal delivery system: phase 3 clinical trial results. Contraception. 2021;103:137-143.
- Natavio M, Stanczyk FZ, Molins EAG, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the 1.5 mg levonorgestrel emergency contraceptive in women with normal, obese and extremely obese body mass index. Contraception. 2019;99:306-311.
- Praditpan P, Hamouie A, Basaraba CN, et al. Pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate emergency contraception in women with normal and obese body mass index. Contraception. 2017;95:464-469.
- Westhoff CL, Torgal AH, Mayeda ER, et al. Pharmacokinetics of a combined oral contraceptive in obese and normal-weight women. Contraception. 2010;81:474-480.
- Thomas MA, Chappell BT, Maximos B, et al. A novel vaginal pH regulator: results from the phase 3 AMPOWER contraception clinical trial. Contracept X. 2020;2:100031.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Apter D, Zatik J, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: a clinical study of contraceptive efficacy, bleeding pattern, and safety in Europe and Russia. BJOG. 2021. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16840.
- Archer DF, Nakajima ST, Sawyer AT, et al. Norethindrone acetate 1.0 milligram and ethinyl estradiol 10 micrograms as an ultra low-dose oral contraceptive. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:601-607.
- Creinin MD, Westhoff CL, Bouchard C, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: North American phase 3 efficacy and safety results. Contraception. 2021;104:222-228.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
- Safety and efficacy of a contraceptive vaginal ring delivering Nestorone and ethinyl estradiol. Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT00263341. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show /NCT00263341. Accessed August 23, 2021.
- van den Heuvel MW, van Bragt AJ, Alnabawy AK, et al. Comparison of ethinylestradiol pharmacokinetics in three hormonal contraceptive formulations: the vaginal ring, the transdermal patch and an oral contraceptive. Contraception. 2005;72:168-174.
- Stanczyk FZ, Rubin A, Flood L, et al. Pharmacokinetics, tolerability and cycle control of three transdermal contraceptive delivery systems containing different doses of ethinyl-estradiol and levonorgestrel. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2011;6:231-240.
- Burke AE, Barnhart K, Jensen JT, et al. Contraceptive efficacy, acceptability, and safety of C31G and nonoxynol-9 spermicidal gels: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:1265-1273.
- Raymond EG, Chen PL, Luoto J; Spermicidal Trial Group. Contraceptive effectiveness and safety of five nonoxynol-9 spermicides: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103:430-439.
- Chappell BT, Mena LA, Maximos B, et al. EVO100 prevents chlamydia and gonorrhea in women at high risk of infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;225:162.e1-162.e14.
A new contraceptive method should ideally provide improved access or a higher quality and safety option. Although unintended pregnancy rates in the United States are decreasing, significant disparities across race and socioeconomic status remain,1 and these disparities actually doubled from 1994 to 2011 even though the overall unintended pregnancy rate decreased.1-3 Specifically, people of color, those with lower income, and people with lower education levels had higher rates of unintended pregnancies than did White people with higher education and income, suggesting disparate access to contraception services.1 Thus, as new contraceptive methods are introduced, we must assess if they have the potential to address this disparity as well as continue to provide higher quality and safer options.
In this Update, we critically review the phase 3 data on efficacy and safety for 3 new methods that were introduced to the US market over the past year to evaluate their impact on the current contraceptive landscape.
The first method, newly approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), is a combined oral contraceptive (OC) that contains a novel endogenous estrogen, estetrol, or E4 (Nextstellis). E4 is a natural estrogen produced in the fetal liver that has lower potency and a longer half-life than estradiol. Nextstellis is a monophasic 24/4 OC pill that contains E4 14.2 mg and drospirenone 3 mg in each of the 24 hormone-containing pills. Most combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) in the United States today contain synthetically made ethinyl estradiol (EE) due to its high potency and oral bioavailability. Outside of the reproductive system, EE upregulates the production of hepatic proteins and alters procoagulant and anticoagulant factors, which results in an overall increase in venous thromboembolic (VTE) risk among CHC users.2
After widespread use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) started in the 1960s, data emerged regarding increased VTE risk.3 Subsequent research discovered that the type of estrogen used in CHCs directly correlates with the thrombosis risk due to the hepatic upregulation with both first- and second-pass metabolism. Although this risk was reduced as the EE dose decreased below 50 µg and concurrent VTE risk factors were contraindicated, CHC users still faced a 2-fold increase in VTE risk compared with nonusers.4,5 EE in contraceptive formulations increases VTE risk, likely related to upregulation of procoagulant factors and decreasing anticoagulant proteins.2 By contrast, a phase 2 trial of Nextstellis demonstrated more neutral effects of E4/drospirenone on hemostatic parameters compared with EE/levonorgestrel or EE/drospirenone.6 Furthermore, E4/drospirenone exhibited lower increases in hepatic proteins, such as angiotensinogen, triglycerides, and sex-hormone binding globulin.7 These findings together suggest that this novel CHC pill has a more favorable cardiovascular adverse effect profile compared with currently available CHCs.
The second contraceptive method is a new transdermal patch that contains EE and levonorgestrel (Twirla); this is in contrast to the available EE/norelgestromin contraceptive patch (Xulane). Transdermal contraceptive patches can offer some users easier adherence as compared with a daily OC.8 Until this past year, the only transdermal contraceptive available in the United States was Xulane, which contains a daily dose of EE 35 µg and norelgestromin 150 µg. Norelgestromin is eventually metabolized to levonorgestrel derivatives.9 Twirla is administered in the same manner as Xulane and contains a daily hormone exposure equivalent to a COC containing EE 30 µg and levonorgestrel 120 µg. Similar to EE/norelgestromin, the EE/levonorgestrel patch also is contraindicated in obese patients (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m2) due to decreased efficacy and increased risk for VTE. Additionally, phase 3 data demonstrated decreasing efficacy of Twirla in overweight users (BMI ≥25–30 kg/m2), perhaps further limiting the population that may benefit from this contraceptive method.10 These issues with efficacy and weight likely are related to the fact that levonorgestrel distribution is weight dependent, with evidence of lower plasma levels in obese individuals.11-13
The third new method is a prescription vaginal contraceptive gel with lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate (Phexxi) designed to prevent pregnancy by maintaining an acidic vaginal environment that is inhospitable to sperm. For many decades, vaginal contraceptives, including vaginal spermicidal gels, provided easy access to a nonhormonal and flexible method of moderately effective contraception for many users. Phexxi is a prescription vaginal pH regulator administered as a gel and active for 1 hour after application. All previous vaginal gels sold in the United States are applied similarly, are available over the counter, and include nonoxynol-9, which is a surfactant that damages sperm cell membranes. Recent data from a phase 3 trial demonstrated similar contraceptive effectiveness of Phexxi when compared with available nonoxynol-9 alternatives.14
Continue to: New OC with the novel estrogen E4 demonstrates good safety profile for VTE...
New OC with the novel estrogen E4 demonstrates good safety profile for VTE
Creinin MD, Westhoff CL, Bouchard C, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: North American phase 3 efficacy and safety results. Contraception. 2021;104:222-228.
The COC E4/drospirenone was evaluated in 2 parallel multinational studies. Here, we review the North American data that are more relevant for the US population; the European-Russian data also are published.15
Study examined 1 year’s use of E4/drospirenone
The US–Canadian trial conducted by Creinin and colleagues enrolled 1,864 participants aged 16 to 50 years to evaluate contraceptive efficacy, bleeding patterns, and adverse events with 1-year use (13 cycles) of E4/drospirenone. The primary efficacy group included 1,524 women aged 16 to 35. This study enrolled healthy, heterosexually active participants with a BMI ≤35 kg/m2 and regular menses from 70 sites in the United States and 7 sites in Canada. The dropout rate was 45%, comparable to that in other contraceptive studies. Participants used E4/drospirenone cyclically, taking 1 hormone-containing pill daily for 24 days followed by 4 days of placebo pills.
Contraceptive efficacious, no VTE observed
The researchers reported efficacy as a Pearl Index (PI) of 2.65 pregnancies per 100 woman-years in participants aged 16 to 35 and an overall 13-cycle life-table pregnancy rate of 2.06%. The PI did not differ among nonobese and obese participants in multivariable analysis. Most users experienced scheduled withdrawal bleeding; only 13% to 18% reported absence of scheduled bleeding. Unscheduled bleeding was typically spotting (55.2%), and this decreased with treatment duration from 30% in cycle 1 to 15% to 20% in cycle 5 and on.
Overall, 28.9% of participants reported treatment-related adverse events (AEs), which most commonly were headache (5.0%), metrorrhagia (4.6%), and nausea (3.8%). Investigators reported a minimal change in mean (SD) BMI of 0.4 (1.7) kg/m2 from baseline after 1 year of E4/drospirenone use, and only 0.5% of participants discontinued use due to weight gain. The most common reasons for AE-related treatment discontinuation included metrorrhagia (0.9%), menorrhagia (0.8%), and vaginal hemorrhage (0.5%). Importantly, no cases of VTE occurred in this study of estetrol despite 23% of participants being obese, a known risk factor for VTE.
Nextstellis provides safe, effective contraception with a PI comparable to that of other available CHCs as well as a favorable bleeding profile in healthy users who are adherent to treatment. Importantly, contraceptive efficacy was maintained in obese users with a BMI up to 35 kg/m2. In contrast to EE or estradiol, E4 demonstrates a lower impact on the hepatic system, and preliminary findings suggest a lower VTE risk compared with other CHCs on the market. The European phase 3 trial of 1,553 participants also demonstrated a low rate of VTE, with only 1 case diagnosed.15 By contrast, similar phase 3 trials of available CHCs demonstrated more frequent VTE events despite low-dose EE formulations (TABLE 1).10,15-18 In general, most US phase 3 trials have 3 to 4 VTE events in the studied population, and the Nextstellis North American trial, of which 92% of participants were from the United States, had 0. However, confirmation of any potential lower VTE risk requires further analysis from large, population-based postmarketing studies.

Continue to: Efficacy of a new EE/levonorgestrel transdermal patch may be lower in overweight, obese women...
Efficacy of a new EE/levonorgestrel transdermal patch may be lower in overweight, obese women
Nelson AL, Kaunitz AM, Kroll R; SECURE Investigators. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol transdermal delivery system: phase 3 clinical trial results. Contraception. 2021;103:137-143.
To assess the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the transdermal patch Twirla (EE/levonorgestrel) over 1 year of treatment (13 cycles), Nelson and colleagues conducted an open-label, multicenter, US-based phase 3 trial of participants aged 18 years and older with regular cycles. There were no restrictions based on BMI. On average, the study population was overweight, with a mean BMI of 28.3 kg/m2 , and 35% of the population was considered obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2).
Study design
A total of 2,032 participants enrolled in the study, with separate populations defined for specific analysis on safety, contraceptive efficacy, and cycle control. The primary efficacy group included 1,736 participants. Fifty-one percent discontinued the study, most commonly due to “women’s decision” (15%) and lost to follow-up (11%). Users received bleeding diaries and returned periodically throughout the study for evaluation for efficacy, adherence, and adverse events.
Efficacy associated with BMI
The study results demonstrated an overall PI of 5.8 pregnancies per 100 woman-years for users aged younger than 35. TABLE 2 demonstrates the overall trend of efficacy in relation to BMI.10,15-19 Participants with a higher BMI were found to have a higher PI, revealing lower contraceptive efficacy in more overweight and obese patients. The overall cumulative pregnancy rate over 13 cycles was 5.3%

Participants reported decreasing frequency of bleeding/spotting days over the treatment duration of 13 cycles, from a mean (SD) of 6.2 (4.5) days in cycle 1 to 4.9 (3.5) days in cycle 13. Unscheduled bleeding episodes remained high throughout the study period. Initially, 60% of users reported 1 or more days of unscheduled bleeding in cycle 1, and 42% still reported unscheduled bleeding in cycle 13. In light of this, only 45 participants (2.2%) discontinued the study due to bleeding issues, suggesting perhaps that the bleeding was light. Overall, users experienced acceptable wearability of the patch, and the rate of detachment decreased over the study period from 9.9% in cycle 1 to 2.4% in cycle 13. There were also low rates (0.5%) of moderate to severe irritation. Itching at the adhesion site decreased slightly from 13.1% in cycle 2 to 9.6% in cycle 13.
In general, 27.2% of patch users experienced a study-related AE, most reported as mild to moderate. Nausea (4.1%) and headaches (3.6%) were the most common hormone-related AE. Importantly, 4 obese users experienced 5 VTEs (deep vein thrombosis, n = 2; pulmonary embolism, n = 3) between cycle 5 and 13. Three of these users had additional VTE risk factors, such as air travel and a family history of clots. No users who were of normal weight or overweight experienced VTE.
Available data demonstrate that the EE/norelgestromin patch exposes users to higher serum levels compared with the pill or the ring.20 The higher estrogen exposure with the patch may explain higher estrogen-related adverse effects and may result in increased VTE risk. Initial pharmacokinetic data of the EE/levonorgestrel patch showed lower EE concentrations, similar to marketed COCs and lower than EE/norelgestromin.21 Despite this lower estrogen exposure, the phase 3 trial by Nelson and colleagues did not demonstrate a safer profile with respect to thromboembolic events.
Further, the high PI of 5.8 pregnancies per 100 woman-years calls into question the efficacy of this patch compared with already available CHC options. Indeed, the efficacy appears reasonable in normal-weight individuals, with a PI of 3.5 pregnancies per 100 woman-years; however, this is still higher than its contemporary counterpart, Nextstellis, which has a PI of 2.65 pregnancies per 100 woman-years and included users with a BMI of up to 35 kg/m2 (Table 2). Given the evidence of decreased efficacy, clinicians may consider reserving this option for only normal-weight women who cannot use or prefer not to use another CHC method. Obese individuals (BMI ≥30 kg/m2 ) should not use this patch due to decreased efficacy and increased VTE risk. Lastly, although use in overweight individuals (BMI ≥25 kg/m2) is not absolutely contraindicated, clinicians should counsel the overweight patient on the possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy due to weight, and they may choose to reserve use of this patch in overweight individuals only when no other comparable or more effective method is an option.
Continue to: Novel vaginal pH buffering spermicide is a new Rx-only option...
Novel vaginal pH buffering spermicide is a new Rx-only option
Thomas MA, Chappell BT, Maximos B, et al. A novel vaginal pH regulator: results from the phase 3 AMPOWER contraception clinical trial. Contracept X. 2020;2:100031.
In an open-label phase 3 study, Thomas and colleagues enrolled 1,384 participants aged 18 to 35 with regular cycles at 112 sites in the United States to assess the contraceptive efficacy, safety, and acceptability of Phexxi vaginal gel (lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate) over 7 cycles (6 months). Participants were required to have at least 3 episodes of heterosexual vaginal intercourse per cycle and return throughout the treatment duration for study visits. Fifty-three percent of participants did not complete the study, most frequently due to loss to follow-up (18.1%) and participant withdrawal (12.3%). Most participants were White (69%) and had an average (SD) age of 27.7 (4.5) years.
Efficacy and AE rates
The investigators reported a cumulative pregnancy rate of 13.7% over 7 cycles (6 months). In this study, 45.2% of women experienced 1 AE, and most were noted to be mild (23.9%) to moderate (18.7%). The most reported AE was vulvovaginal burning (20.0%), followed by vulvovaginal pruritus (11.2%), urinary tract infection (5.7%), and vulvovaginal pain (3.8%). Less than 2% of participants discontinued the study due to an AE. Burning and itching decreased with time and with decreased frequency of use. When used twice per day compared with once per day, burning rates decreased from 4.6% to 2.1%, and itching rates decreased from 1.0% to 0.7%. Serious AEs were uncommon, occurring in 1.3% of users; only 1, cystitis, was noted to be “probably” related to the treatment. ●
Prior to the approval of Phexxi, all currently available vaginal contraceptive gels in the United States contained nonoxynol-9 as the active ingredient, which is a surfactant that is spermicidal by damaging cell membranes. Although Phexxi provides a novel mechanism of action as a spermicide, the contraceptive efficacy is about the same as available spermicides on the market (see TABLE 3).14,22,23 The FDA calculated a 13-cycle PI to include in the label (27.5 pregnancies per 100 woman-years) based on the results of this study; however, no reliable statistical method exists to calculate a true PI from a 7-cycle study. Thus, we recommend that clinicians counsel patients appropriately based on the 6-month rate noted in the study, and that this rate is similar to that with currently available over-the-counter products. This point is important, as Phexxi is available only by prescription, which may impact patient cost and access.
Equally important is Phexxi’s potential for sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention. In a US-based randomized controlled trial, Phexxi use demonstrated significant risk reduction in gonorrhea and chlamydia infections among participants aged 18 to 45 years.24 That study showed a relative risk reduction of 50% and 78% for chlamydia and gonorrhea, respectively.24 Future research is planned to evaluate this spermicide as a novel STI prevention method. Ultimately, Phexxi may provide an alternative spermicide for users interested in moderately effective contraception and unable to tolerate available nonoxynol-9 formulations. Interested users will have to rely on a prescription, possibly limiting access to this novel spermicide. Further data are required to determine its potential as an STI prevention agent.

A new contraceptive method should ideally provide improved access or a higher quality and safety option. Although unintended pregnancy rates in the United States are decreasing, significant disparities across race and socioeconomic status remain,1 and these disparities actually doubled from 1994 to 2011 even though the overall unintended pregnancy rate decreased.1-3 Specifically, people of color, those with lower income, and people with lower education levels had higher rates of unintended pregnancies than did White people with higher education and income, suggesting disparate access to contraception services.1 Thus, as new contraceptive methods are introduced, we must assess if they have the potential to address this disparity as well as continue to provide higher quality and safer options.
In this Update, we critically review the phase 3 data on efficacy and safety for 3 new methods that were introduced to the US market over the past year to evaluate their impact on the current contraceptive landscape.
The first method, newly approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), is a combined oral contraceptive (OC) that contains a novel endogenous estrogen, estetrol, or E4 (Nextstellis). E4 is a natural estrogen produced in the fetal liver that has lower potency and a longer half-life than estradiol. Nextstellis is a monophasic 24/4 OC pill that contains E4 14.2 mg and drospirenone 3 mg in each of the 24 hormone-containing pills. Most combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) in the United States today contain synthetically made ethinyl estradiol (EE) due to its high potency and oral bioavailability. Outside of the reproductive system, EE upregulates the production of hepatic proteins and alters procoagulant and anticoagulant factors, which results in an overall increase in venous thromboembolic (VTE) risk among CHC users.2
After widespread use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) started in the 1960s, data emerged regarding increased VTE risk.3 Subsequent research discovered that the type of estrogen used in CHCs directly correlates with the thrombosis risk due to the hepatic upregulation with both first- and second-pass metabolism. Although this risk was reduced as the EE dose decreased below 50 µg and concurrent VTE risk factors were contraindicated, CHC users still faced a 2-fold increase in VTE risk compared with nonusers.4,5 EE in contraceptive formulations increases VTE risk, likely related to upregulation of procoagulant factors and decreasing anticoagulant proteins.2 By contrast, a phase 2 trial of Nextstellis demonstrated more neutral effects of E4/drospirenone on hemostatic parameters compared with EE/levonorgestrel or EE/drospirenone.6 Furthermore, E4/drospirenone exhibited lower increases in hepatic proteins, such as angiotensinogen, triglycerides, and sex-hormone binding globulin.7 These findings together suggest that this novel CHC pill has a more favorable cardiovascular adverse effect profile compared with currently available CHCs.
The second contraceptive method is a new transdermal patch that contains EE and levonorgestrel (Twirla); this is in contrast to the available EE/norelgestromin contraceptive patch (Xulane). Transdermal contraceptive patches can offer some users easier adherence as compared with a daily OC.8 Until this past year, the only transdermal contraceptive available in the United States was Xulane, which contains a daily dose of EE 35 µg and norelgestromin 150 µg. Norelgestromin is eventually metabolized to levonorgestrel derivatives.9 Twirla is administered in the same manner as Xulane and contains a daily hormone exposure equivalent to a COC containing EE 30 µg and levonorgestrel 120 µg. Similar to EE/norelgestromin, the EE/levonorgestrel patch also is contraindicated in obese patients (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m2) due to decreased efficacy and increased risk for VTE. Additionally, phase 3 data demonstrated decreasing efficacy of Twirla in overweight users (BMI ≥25–30 kg/m2), perhaps further limiting the population that may benefit from this contraceptive method.10 These issues with efficacy and weight likely are related to the fact that levonorgestrel distribution is weight dependent, with evidence of lower plasma levels in obese individuals.11-13
The third new method is a prescription vaginal contraceptive gel with lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate (Phexxi) designed to prevent pregnancy by maintaining an acidic vaginal environment that is inhospitable to sperm. For many decades, vaginal contraceptives, including vaginal spermicidal gels, provided easy access to a nonhormonal and flexible method of moderately effective contraception for many users. Phexxi is a prescription vaginal pH regulator administered as a gel and active for 1 hour after application. All previous vaginal gels sold in the United States are applied similarly, are available over the counter, and include nonoxynol-9, which is a surfactant that damages sperm cell membranes. Recent data from a phase 3 trial demonstrated similar contraceptive effectiveness of Phexxi when compared with available nonoxynol-9 alternatives.14
Continue to: New OC with the novel estrogen E4 demonstrates good safety profile for VTE...
New OC with the novel estrogen E4 demonstrates good safety profile for VTE
Creinin MD, Westhoff CL, Bouchard C, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: North American phase 3 efficacy and safety results. Contraception. 2021;104:222-228.
The COC E4/drospirenone was evaluated in 2 parallel multinational studies. Here, we review the North American data that are more relevant for the US population; the European-Russian data also are published.15
Study examined 1 year’s use of E4/drospirenone
The US–Canadian trial conducted by Creinin and colleagues enrolled 1,864 participants aged 16 to 50 years to evaluate contraceptive efficacy, bleeding patterns, and adverse events with 1-year use (13 cycles) of E4/drospirenone. The primary efficacy group included 1,524 women aged 16 to 35. This study enrolled healthy, heterosexually active participants with a BMI ≤35 kg/m2 and regular menses from 70 sites in the United States and 7 sites in Canada. The dropout rate was 45%, comparable to that in other contraceptive studies. Participants used E4/drospirenone cyclically, taking 1 hormone-containing pill daily for 24 days followed by 4 days of placebo pills.
Contraceptive efficacious, no VTE observed
The researchers reported efficacy as a Pearl Index (PI) of 2.65 pregnancies per 100 woman-years in participants aged 16 to 35 and an overall 13-cycle life-table pregnancy rate of 2.06%. The PI did not differ among nonobese and obese participants in multivariable analysis. Most users experienced scheduled withdrawal bleeding; only 13% to 18% reported absence of scheduled bleeding. Unscheduled bleeding was typically spotting (55.2%), and this decreased with treatment duration from 30% in cycle 1 to 15% to 20% in cycle 5 and on.
Overall, 28.9% of participants reported treatment-related adverse events (AEs), which most commonly were headache (5.0%), metrorrhagia (4.6%), and nausea (3.8%). Investigators reported a minimal change in mean (SD) BMI of 0.4 (1.7) kg/m2 from baseline after 1 year of E4/drospirenone use, and only 0.5% of participants discontinued use due to weight gain. The most common reasons for AE-related treatment discontinuation included metrorrhagia (0.9%), menorrhagia (0.8%), and vaginal hemorrhage (0.5%). Importantly, no cases of VTE occurred in this study of estetrol despite 23% of participants being obese, a known risk factor for VTE.
Nextstellis provides safe, effective contraception with a PI comparable to that of other available CHCs as well as a favorable bleeding profile in healthy users who are adherent to treatment. Importantly, contraceptive efficacy was maintained in obese users with a BMI up to 35 kg/m2. In contrast to EE or estradiol, E4 demonstrates a lower impact on the hepatic system, and preliminary findings suggest a lower VTE risk compared with other CHCs on the market. The European phase 3 trial of 1,553 participants also demonstrated a low rate of VTE, with only 1 case diagnosed.15 By contrast, similar phase 3 trials of available CHCs demonstrated more frequent VTE events despite low-dose EE formulations (TABLE 1).10,15-18 In general, most US phase 3 trials have 3 to 4 VTE events in the studied population, and the Nextstellis North American trial, of which 92% of participants were from the United States, had 0. However, confirmation of any potential lower VTE risk requires further analysis from large, population-based postmarketing studies.

Continue to: Efficacy of a new EE/levonorgestrel transdermal patch may be lower in overweight, obese women...
Efficacy of a new EE/levonorgestrel transdermal patch may be lower in overweight, obese women
Nelson AL, Kaunitz AM, Kroll R; SECURE Investigators. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol transdermal delivery system: phase 3 clinical trial results. Contraception. 2021;103:137-143.
To assess the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the transdermal patch Twirla (EE/levonorgestrel) over 1 year of treatment (13 cycles), Nelson and colleagues conducted an open-label, multicenter, US-based phase 3 trial of participants aged 18 years and older with regular cycles. There were no restrictions based on BMI. On average, the study population was overweight, with a mean BMI of 28.3 kg/m2 , and 35% of the population was considered obese (BMI ≥30 kg/m2).
Study design
A total of 2,032 participants enrolled in the study, with separate populations defined for specific analysis on safety, contraceptive efficacy, and cycle control. The primary efficacy group included 1,736 participants. Fifty-one percent discontinued the study, most commonly due to “women’s decision” (15%) and lost to follow-up (11%). Users received bleeding diaries and returned periodically throughout the study for evaluation for efficacy, adherence, and adverse events.
Efficacy associated with BMI
The study results demonstrated an overall PI of 5.8 pregnancies per 100 woman-years for users aged younger than 35. TABLE 2 demonstrates the overall trend of efficacy in relation to BMI.10,15-19 Participants with a higher BMI were found to have a higher PI, revealing lower contraceptive efficacy in more overweight and obese patients. The overall cumulative pregnancy rate over 13 cycles was 5.3%

Participants reported decreasing frequency of bleeding/spotting days over the treatment duration of 13 cycles, from a mean (SD) of 6.2 (4.5) days in cycle 1 to 4.9 (3.5) days in cycle 13. Unscheduled bleeding episodes remained high throughout the study period. Initially, 60% of users reported 1 or more days of unscheduled bleeding in cycle 1, and 42% still reported unscheduled bleeding in cycle 13. In light of this, only 45 participants (2.2%) discontinued the study due to bleeding issues, suggesting perhaps that the bleeding was light. Overall, users experienced acceptable wearability of the patch, and the rate of detachment decreased over the study period from 9.9% in cycle 1 to 2.4% in cycle 13. There were also low rates (0.5%) of moderate to severe irritation. Itching at the adhesion site decreased slightly from 13.1% in cycle 2 to 9.6% in cycle 13.
In general, 27.2% of patch users experienced a study-related AE, most reported as mild to moderate. Nausea (4.1%) and headaches (3.6%) were the most common hormone-related AE. Importantly, 4 obese users experienced 5 VTEs (deep vein thrombosis, n = 2; pulmonary embolism, n = 3) between cycle 5 and 13. Three of these users had additional VTE risk factors, such as air travel and a family history of clots. No users who were of normal weight or overweight experienced VTE.
Available data demonstrate that the EE/norelgestromin patch exposes users to higher serum levels compared with the pill or the ring.20 The higher estrogen exposure with the patch may explain higher estrogen-related adverse effects and may result in increased VTE risk. Initial pharmacokinetic data of the EE/levonorgestrel patch showed lower EE concentrations, similar to marketed COCs and lower than EE/norelgestromin.21 Despite this lower estrogen exposure, the phase 3 trial by Nelson and colleagues did not demonstrate a safer profile with respect to thromboembolic events.
Further, the high PI of 5.8 pregnancies per 100 woman-years calls into question the efficacy of this patch compared with already available CHC options. Indeed, the efficacy appears reasonable in normal-weight individuals, with a PI of 3.5 pregnancies per 100 woman-years; however, this is still higher than its contemporary counterpart, Nextstellis, which has a PI of 2.65 pregnancies per 100 woman-years and included users with a BMI of up to 35 kg/m2 (Table 2). Given the evidence of decreased efficacy, clinicians may consider reserving this option for only normal-weight women who cannot use or prefer not to use another CHC method. Obese individuals (BMI ≥30 kg/m2 ) should not use this patch due to decreased efficacy and increased VTE risk. Lastly, although use in overweight individuals (BMI ≥25 kg/m2) is not absolutely contraindicated, clinicians should counsel the overweight patient on the possibility of decreased contraceptive efficacy due to weight, and they may choose to reserve use of this patch in overweight individuals only when no other comparable or more effective method is an option.
Continue to: Novel vaginal pH buffering spermicide is a new Rx-only option...
Novel vaginal pH buffering spermicide is a new Rx-only option
Thomas MA, Chappell BT, Maximos B, et al. A novel vaginal pH regulator: results from the phase 3 AMPOWER contraception clinical trial. Contracept X. 2020;2:100031.
In an open-label phase 3 study, Thomas and colleagues enrolled 1,384 participants aged 18 to 35 with regular cycles at 112 sites in the United States to assess the contraceptive efficacy, safety, and acceptability of Phexxi vaginal gel (lactic acid, citric acid, and potassium bitartrate) over 7 cycles (6 months). Participants were required to have at least 3 episodes of heterosexual vaginal intercourse per cycle and return throughout the treatment duration for study visits. Fifty-three percent of participants did not complete the study, most frequently due to loss to follow-up (18.1%) and participant withdrawal (12.3%). Most participants were White (69%) and had an average (SD) age of 27.7 (4.5) years.
Efficacy and AE rates
The investigators reported a cumulative pregnancy rate of 13.7% over 7 cycles (6 months). In this study, 45.2% of women experienced 1 AE, and most were noted to be mild (23.9%) to moderate (18.7%). The most reported AE was vulvovaginal burning (20.0%), followed by vulvovaginal pruritus (11.2%), urinary tract infection (5.7%), and vulvovaginal pain (3.8%). Less than 2% of participants discontinued the study due to an AE. Burning and itching decreased with time and with decreased frequency of use. When used twice per day compared with once per day, burning rates decreased from 4.6% to 2.1%, and itching rates decreased from 1.0% to 0.7%. Serious AEs were uncommon, occurring in 1.3% of users; only 1, cystitis, was noted to be “probably” related to the treatment. ●
Prior to the approval of Phexxi, all currently available vaginal contraceptive gels in the United States contained nonoxynol-9 as the active ingredient, which is a surfactant that is spermicidal by damaging cell membranes. Although Phexxi provides a novel mechanism of action as a spermicide, the contraceptive efficacy is about the same as available spermicides on the market (see TABLE 3).14,22,23 The FDA calculated a 13-cycle PI to include in the label (27.5 pregnancies per 100 woman-years) based on the results of this study; however, no reliable statistical method exists to calculate a true PI from a 7-cycle study. Thus, we recommend that clinicians counsel patients appropriately based on the 6-month rate noted in the study, and that this rate is similar to that with currently available over-the-counter products. This point is important, as Phexxi is available only by prescription, which may impact patient cost and access.
Equally important is Phexxi’s potential for sexually transmitted infection (STI) prevention. In a US-based randomized controlled trial, Phexxi use demonstrated significant risk reduction in gonorrhea and chlamydia infections among participants aged 18 to 45 years.24 That study showed a relative risk reduction of 50% and 78% for chlamydia and gonorrhea, respectively.24 Future research is planned to evaluate this spermicide as a novel STI prevention method. Ultimately, Phexxi may provide an alternative spermicide for users interested in moderately effective contraception and unable to tolerate available nonoxynol-9 formulations. Interested users will have to rely on a prescription, possibly limiting access to this novel spermicide. Further data are required to determine its potential as an STI prevention agent.

- Finer LB, Zolna MR. Declines in unintended pregnancy in the United States, 2008–2011. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:843-852.
- Meade TW. Oral contraceptives, clotting factors, and thrombosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;142(6 pt 2):758-761.
- Royal College of General Practitioners’ Oral Contraception Study. Oral contraceptives, venous thrombosis, and varicose veins. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1978;28:393-399.
- Dinger JC, Heinemann LA, Kühl-Habich D. The safety of a drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive: final results from the European Active Surveillance Study on oral contraceptives based on 142,475 women-years of observation. Contraception. 2007;75:344-354.
- Heinemann LA, Dinger JC. Range of published estimates of venous thromboembolism incidence in young women. Contraception. 2007;75:328-336.
- Douxfils J, Klipping C, Duijkers I, et al. Evaluation of the effect of a new oral contraceptive containing estetrol and drospirenone on hemostasis parameters. Contraception. 2020;102:396-402.
- Klipping C, Duijkers I, Mawet M, et al. Endocrine and metabolic effects of an oral contraceptive containing estetrol and drospirenone. Contraception. 2021;103:213-221.
- Archer DF, Cullins V, Creasy GW, et al. The impact of improved compliance with a weekly contraceptive transdermal system (Ortho Evra) on contraceptive efficacy. Contraception. 2004;69:189-195.
- Stanczyk FZ, Roy S. Metabolism of levonorgestrel, norethindrone, and structurally related contraceptive steroids. Contraception. 1990;42:67-96.
- Nelson AL, Kaunitz AM, Kroll R; SECURE Investigators. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol transdermal delivery system: phase 3 clinical trial results. Contraception. 2021;103:137-143.
- Natavio M, Stanczyk FZ, Molins EAG, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the 1.5 mg levonorgestrel emergency contraceptive in women with normal, obese and extremely obese body mass index. Contraception. 2019;99:306-311.
- Praditpan P, Hamouie A, Basaraba CN, et al. Pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate emergency contraception in women with normal and obese body mass index. Contraception. 2017;95:464-469.
- Westhoff CL, Torgal AH, Mayeda ER, et al. Pharmacokinetics of a combined oral contraceptive in obese and normal-weight women. Contraception. 2010;81:474-480.
- Thomas MA, Chappell BT, Maximos B, et al. A novel vaginal pH regulator: results from the phase 3 AMPOWER contraception clinical trial. Contracept X. 2020;2:100031.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Apter D, Zatik J, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: a clinical study of contraceptive efficacy, bleeding pattern, and safety in Europe and Russia. BJOG. 2021. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16840.
- Archer DF, Nakajima ST, Sawyer AT, et al. Norethindrone acetate 1.0 milligram and ethinyl estradiol 10 micrograms as an ultra low-dose oral contraceptive. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:601-607.
- Creinin MD, Westhoff CL, Bouchard C, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: North American phase 3 efficacy and safety results. Contraception. 2021;104:222-228.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
- Safety and efficacy of a contraceptive vaginal ring delivering Nestorone and ethinyl estradiol. Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT00263341. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show /NCT00263341. Accessed August 23, 2021.
- van den Heuvel MW, van Bragt AJ, Alnabawy AK, et al. Comparison of ethinylestradiol pharmacokinetics in three hormonal contraceptive formulations: the vaginal ring, the transdermal patch and an oral contraceptive. Contraception. 2005;72:168-174.
- Stanczyk FZ, Rubin A, Flood L, et al. Pharmacokinetics, tolerability and cycle control of three transdermal contraceptive delivery systems containing different doses of ethinyl-estradiol and levonorgestrel. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2011;6:231-240.
- Burke AE, Barnhart K, Jensen JT, et al. Contraceptive efficacy, acceptability, and safety of C31G and nonoxynol-9 spermicidal gels: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:1265-1273.
- Raymond EG, Chen PL, Luoto J; Spermicidal Trial Group. Contraceptive effectiveness and safety of five nonoxynol-9 spermicides: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103:430-439.
- Chappell BT, Mena LA, Maximos B, et al. EVO100 prevents chlamydia and gonorrhea in women at high risk of infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;225:162.e1-162.e14.
- Finer LB, Zolna MR. Declines in unintended pregnancy in the United States, 2008–2011. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:843-852.
- Meade TW. Oral contraceptives, clotting factors, and thrombosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;142(6 pt 2):758-761.
- Royal College of General Practitioners’ Oral Contraception Study. Oral contraceptives, venous thrombosis, and varicose veins. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1978;28:393-399.
- Dinger JC, Heinemann LA, Kühl-Habich D. The safety of a drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive: final results from the European Active Surveillance Study on oral contraceptives based on 142,475 women-years of observation. Contraception. 2007;75:344-354.
- Heinemann LA, Dinger JC. Range of published estimates of venous thromboembolism incidence in young women. Contraception. 2007;75:328-336.
- Douxfils J, Klipping C, Duijkers I, et al. Evaluation of the effect of a new oral contraceptive containing estetrol and drospirenone on hemostasis parameters. Contraception. 2020;102:396-402.
- Klipping C, Duijkers I, Mawet M, et al. Endocrine and metabolic effects of an oral contraceptive containing estetrol and drospirenone. Contraception. 2021;103:213-221.
- Archer DF, Cullins V, Creasy GW, et al. The impact of improved compliance with a weekly contraceptive transdermal system (Ortho Evra) on contraceptive efficacy. Contraception. 2004;69:189-195.
- Stanczyk FZ, Roy S. Metabolism of levonorgestrel, norethindrone, and structurally related contraceptive steroids. Contraception. 1990;42:67-96.
- Nelson AL, Kaunitz AM, Kroll R; SECURE Investigators. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol transdermal delivery system: phase 3 clinical trial results. Contraception. 2021;103:137-143.
- Natavio M, Stanczyk FZ, Molins EAG, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the 1.5 mg levonorgestrel emergency contraceptive in women with normal, obese and extremely obese body mass index. Contraception. 2019;99:306-311.
- Praditpan P, Hamouie A, Basaraba CN, et al. Pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate emergency contraception in women with normal and obese body mass index. Contraception. 2017;95:464-469.
- Westhoff CL, Torgal AH, Mayeda ER, et al. Pharmacokinetics of a combined oral contraceptive in obese and normal-weight women. Contraception. 2010;81:474-480.
- Thomas MA, Chappell BT, Maximos B, et al. A novel vaginal pH regulator: results from the phase 3 AMPOWER contraception clinical trial. Contracept X. 2020;2:100031.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Apter D, Zatik J, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: a clinical study of contraceptive efficacy, bleeding pattern, and safety in Europe and Russia. BJOG. 2021. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16840.
- Archer DF, Nakajima ST, Sawyer AT, et al. Norethindrone acetate 1.0 milligram and ethinyl estradiol 10 micrograms as an ultra low-dose oral contraceptive. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:601-607.
- Creinin MD, Westhoff CL, Bouchard C, et al. Estetrol-drospirenone combination oral contraceptive: North American phase 3 efficacy and safety results. Contraception. 2021;104:222-228.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
- Safety and efficacy of a contraceptive vaginal ring delivering Nestorone and ethinyl estradiol. Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT00263341. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show /NCT00263341. Accessed August 23, 2021.
- van den Heuvel MW, van Bragt AJ, Alnabawy AK, et al. Comparison of ethinylestradiol pharmacokinetics in three hormonal contraceptive formulations: the vaginal ring, the transdermal patch and an oral contraceptive. Contraception. 2005;72:168-174.
- Stanczyk FZ, Rubin A, Flood L, et al. Pharmacokinetics, tolerability and cycle control of three transdermal contraceptive delivery systems containing different doses of ethinyl-estradiol and levonorgestrel. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2011;6:231-240.
- Burke AE, Barnhart K, Jensen JT, et al. Contraceptive efficacy, acceptability, and safety of C31G and nonoxynol-9 spermicidal gels: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:1265-1273.
- Raymond EG, Chen PL, Luoto J; Spermicidal Trial Group. Contraceptive effectiveness and safety of five nonoxynol-9 spermicides: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103:430-439.
- Chappell BT, Mena LA, Maximos B, et al. EVO100 prevents chlamydia and gonorrhea in women at high risk of infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;225:162.e1-162.e14.