User login
Invasive group A streptococcus (iGAS) infections are rare (4-9 cases/100,000 US population annually) but potentially devastating (approximately 2,300 deaths annually in US), and affect all ages. Cases increase in winter-spring, paralleling the “season” of increased noninvasive GAS, e.g., pharyngitis and scarlet fever. iGAS case rates are lower in children than adults. That said, one well-known pediatric iGAS scenario has been deep cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis during the healing phase of varicella. Other forms of iGAS include bacteremia, pneumonia (particularly when empyema is present), lymphangitis, erysipelas, and toxic shock syndrome. iGAS can occur with/after influenza but has also occurred concurrently with other viral respiratory infections.
Persons with underlying conditions (cancer or immune compromised status; chronic diseases of the heart, kidney or lung; diabetes mellitus) are at higher risk. Other subpopulations at risk for iGAS are illicit drug users, the elderly, homeless persons, nursing home residents, American Indian persons, and Alaska Native persons. Most experts feel that highly toxigenic strains of GAS are responsible for most iGAS. Indeed, most iGAS isolates produce (sometimes hyper-produce) superantigens that cause exaggerated innate immune responses, higher levels of inflammation, and often times tissue destruction, e.g., “flesh eating bacteria.” And who can forget that Jim Henson, creator of the Muppets, died of iGAS?
But why discuss iGAS in 2024? The pattern for iGAS has fluctuated more than usual in the last decade. So much so that the recent upsurge has caught the collective eye of the lay press. So, patients and friends may have questions about why and how iGAS is increasing lately. The bottom line is that no one knows for sure. However, the most recent 2 years of uptick may reflect GAS circulating at relatively high levels even when taking into account that GAS season occurs in winter-spring most years. Yet it seems likely that additional factors may have played a role in the fluctuations noted this past decade, e.g., temporary changes in societal behavior, a new GAS strain with over two dozen mutations, and possibly rapid waning of protection against GAS exotoxins.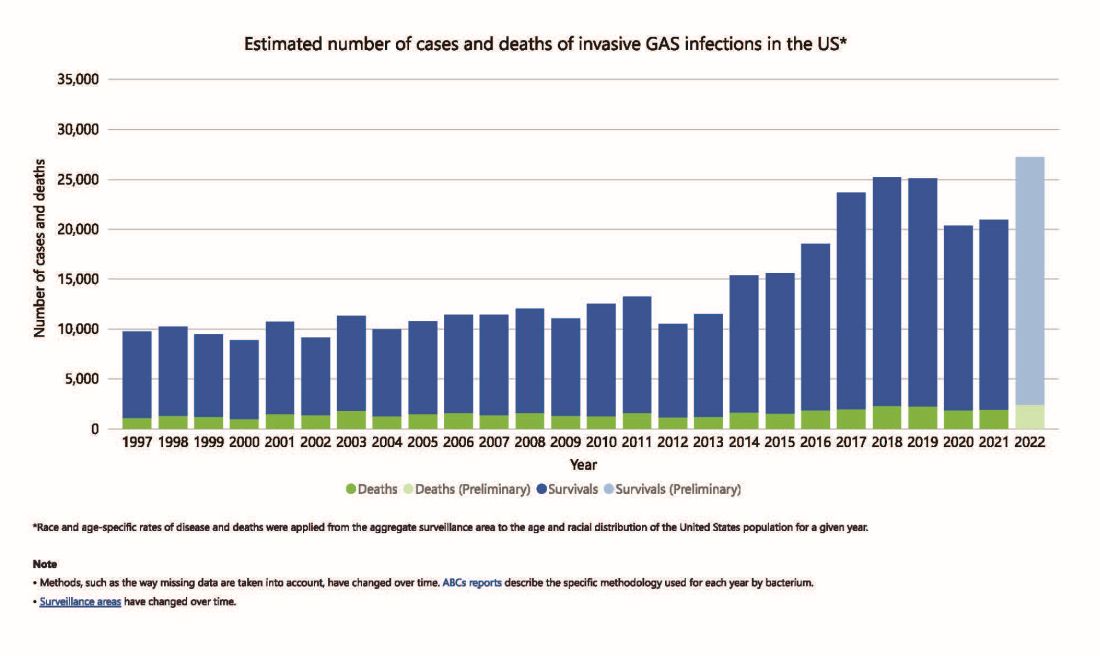
Social Behavior Factor
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic brought extremes of disease and death to the world and dramatic changes in social behavior. A byproduct was dramatic decreases in nearly all infectious diseases, with numerous reports of near absence of many respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses in the 2020-2021 seasons. Interestingly, we did not see a drop in human rhinovirus infections, justifying its nickname as the cockroach of viruses. Reports also emerged about drops in bacterial diseases during 2020-2021 (although not so much for STIs), including noninvasive and invasive GAS disease, and also GAS-associated deaths (lowest since 2016).1 The drop in iGAS during social restrictions makes sense because GAS is spread by direct contact with infected persons or their secretions, and social contact had dramatically decreased particularly in the first 6 months of the pandemic.
However, since 2022 and the return to “normal” social behaviors, both viral diseases (e.g., RSV, influenza, and Norovirus), and some bacterial diseases have rebounded. That said, something else must be contributing, because iGAS rates had increased 4-5 years pre pandemic. In fact, the fluctuating pattern included “normal” annual rates in the early 2000s rising in ~2015 followed by the explainable pandemic drop (by nearly 25%), and not-too-unexpected 2-year postpandemic rise. But interestingly enough, the rebound is higher than might be expected for iGAS and children were overrepresented in first year’s rise (2022 rate for pediatric iGAS was the highest since 1997) while those older than 65 were overrepresented in second year (2023).1
Emergence of M1UK
One potential factor for the prepandemic rise in iGAS infections worldwide is the emergence and worldwide spread of a new GAS emm type variant designated M1UK.2 GAS isolates can be typed into categories designated as emm types based on DNA sequence. There are more than 240 emm types, with 6 being most common — M1, M3, and M28 (each up to 20% of GAS isolates) and M12, M82, and M89 (each up to 10%). M1, M3 and M28 have also been particularly associated with invasive disease. While emm types vary year to year and region by region, the overall emm type distribution among iGAS isolates in the United States had not been unusual since the turn of the century and the US M1 strain was the same as that which had been predominant worldwide (designated M1GLOBAL). This new M1UK sublineage had emerged around 2010 and had been increasing pre pandemic. The M1UK sequence contained a specific set of 27 SNPs (single nucleoside polymorphisms, i.e., single base mutations) and was associated with an uptick in scarlet fever in the United Kingdom starting around 2010. Its prevalence increased up to around 2015 while spreading internationally. It also had enhanced expression of SpeA, a phage-encoded superantigen. Some of the M1UK mutations also appear to alter GAS metabolic processes to allow better survival (better “fitness”) compared with other GAS. So, a more virulent hardier GAS had arisen and seems a reasonable candidate for contributing to the increased iGAS rates.
Waning Antibody to GAS As Potential Factor in Rebound
No consensus exists on correlates of protection from iGAS. However, adults seem to have less noninvasive GAS than children. One potential reason is that frequent GAS re-exposure, regardless of whether disease results, likely boosts anti-GAS antibodies. Pandemic social restrictions temporarily prevented such boosts. In children with developing antibody repertoires, anti-GAS antibodies may have waned below protective levels faster during a year without frequent boosting. Thus, children were iGAS susceptible soon after pandemic restrictions were dropped (2022). Increased iGAS rates in the elderly in 2023 may have occurred because of diminished GAS exposures accelerating immune senescence with anti-GAS antibodies dropping, but less quickly than in children. These speculations are simply hypotheses until future studies can test them.
All that said, how do we use information on increased iGAS in our daily practices? In addition to standard preventive strategies for viral coinfections (e.g., varicella and influenza vaccine), reminding families about rigorous attention to wound care is the one high-risk scenario we have not yet discussed. During 2024, a time of expected increased prevalence of iGAS, early wound care needs to be fastidious. Further, share warning signs with families (e.g., rapidly expanding painful erythema), “streaks” ascending from extremity wounds, fever and a highly painful wound, darkening almost purple color within cellulitis or soft tissue infection, or loss of sensation in the middle of an otherwise painful soft tissue infection. These presentations require immediate medical attention.
If such a patient presents, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends admission along with blood and, where possible, wound cultures. If in the context of pneumonia with pleural effusion, culturing pleural fluid is also important. Remember, leading edge cultures are not often positive for GAS, seemingly because GAS exotoxins are found at erythema’s leading edge, not the bacteria. The bacteria are somewhere more central in the inflammatory process. Despite not being prominent among recent iGAS cases, another scenario that could sneak up on you is the infected surgical wound as nascent iGAS.
Finally, remember that nationally increasing numbers of iGAS isolates are resistant to erythromycin and clindamycin, the latter usually recommended to reduce tissue damage in iGAS.3 So, it is important to be aware of susceptibility patterns in your locale and consider an ID consultation. My hope is that you do not see an iGAS case this year, but we all need to remain alert. With a high index of suspicion and rapid diagnosis, you can minimize long-term sequelae and potential fatalities.
While it is too early to tell how the rest of 2024 will turn out, preliminary indications are that GAS is circulating at higher than usual levels (30%-35% GAS positive throat swabs in early April 2024 in Kansas City area) and iGAS rates will likely also be relatively high, particularly if Ontario, Canada, data are any indication.4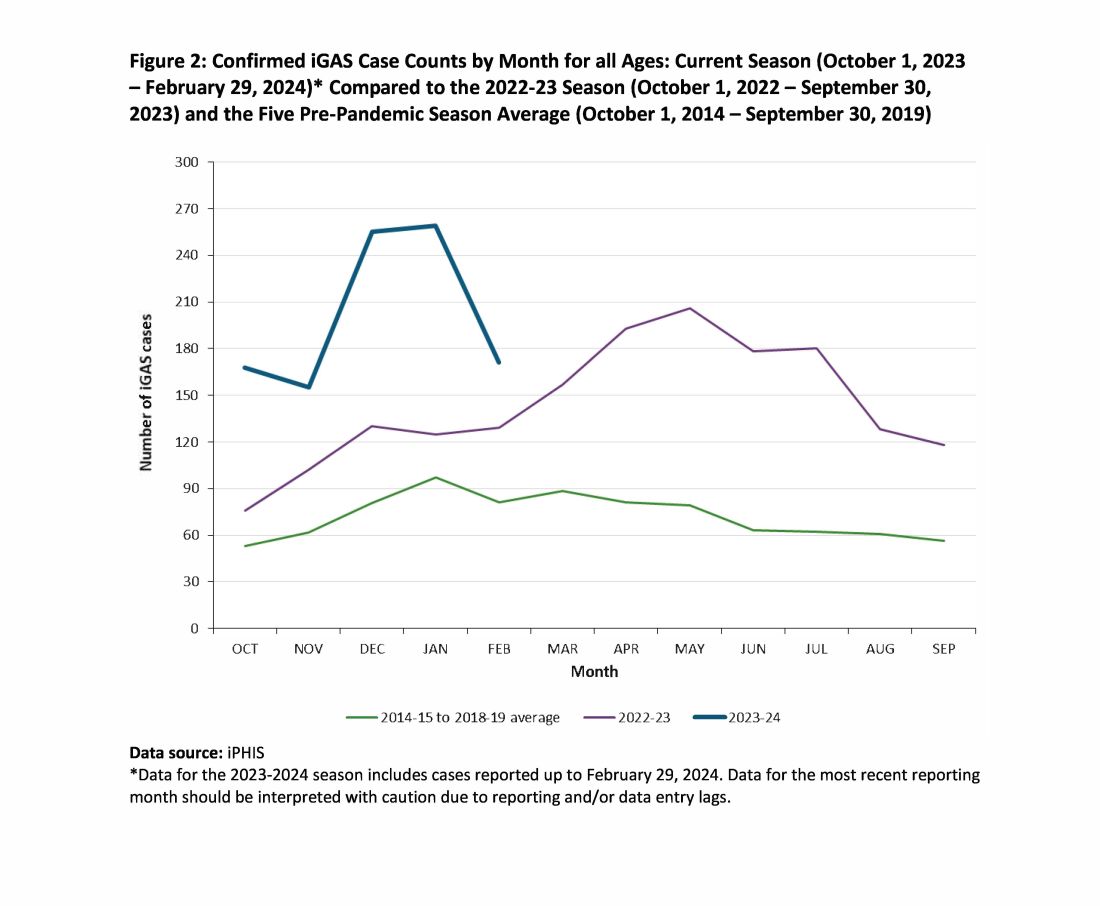
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Current Group A Strep Activity, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. April 2024. CDC webpage on current invasive GAS disease. April 2024.
2. Li Y et al. Expansion of Invasive Group A Streptococcus M1UK Lineage in Active Bacterial Core Surveillance, United States, 2019-2021 Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29(10):2116-2120. doi: 10.3201/eid2910.230675.
3. Andreoni F et al. Clindamycin Affects Group A Streptococcus Virulence Factors and Improves Clinical Outcome. J Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 15;215(2):269-277. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw229.
4. Group A Streptococcal Disease, Invasive (iGAS), Public Health Ontario.
Invasive group A streptococcus (iGAS) infections are rare (4-9 cases/100,000 US population annually) but potentially devastating (approximately 2,300 deaths annually in US), and affect all ages. Cases increase in winter-spring, paralleling the “season” of increased noninvasive GAS, e.g., pharyngitis and scarlet fever. iGAS case rates are lower in children than adults. That said, one well-known pediatric iGAS scenario has been deep cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis during the healing phase of varicella. Other forms of iGAS include bacteremia, pneumonia (particularly when empyema is present), lymphangitis, erysipelas, and toxic shock syndrome. iGAS can occur with/after influenza but has also occurred concurrently with other viral respiratory infections.
Persons with underlying conditions (cancer or immune compromised status; chronic diseases of the heart, kidney or lung; diabetes mellitus) are at higher risk. Other subpopulations at risk for iGAS are illicit drug users, the elderly, homeless persons, nursing home residents, American Indian persons, and Alaska Native persons. Most experts feel that highly toxigenic strains of GAS are responsible for most iGAS. Indeed, most iGAS isolates produce (sometimes hyper-produce) superantigens that cause exaggerated innate immune responses, higher levels of inflammation, and often times tissue destruction, e.g., “flesh eating bacteria.” And who can forget that Jim Henson, creator of the Muppets, died of iGAS?
But why discuss iGAS in 2024? The pattern for iGAS has fluctuated more than usual in the last decade. So much so that the recent upsurge has caught the collective eye of the lay press. So, patients and friends may have questions about why and how iGAS is increasing lately. The bottom line is that no one knows for sure. However, the most recent 2 years of uptick may reflect GAS circulating at relatively high levels even when taking into account that GAS season occurs in winter-spring most years. Yet it seems likely that additional factors may have played a role in the fluctuations noted this past decade, e.g., temporary changes in societal behavior, a new GAS strain with over two dozen mutations, and possibly rapid waning of protection against GAS exotoxins.
Social Behavior Factor
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic brought extremes of disease and death to the world and dramatic changes in social behavior. A byproduct was dramatic decreases in nearly all infectious diseases, with numerous reports of near absence of many respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses in the 2020-2021 seasons. Interestingly, we did not see a drop in human rhinovirus infections, justifying its nickname as the cockroach of viruses. Reports also emerged about drops in bacterial diseases during 2020-2021 (although not so much for STIs), including noninvasive and invasive GAS disease, and also GAS-associated deaths (lowest since 2016).1 The drop in iGAS during social restrictions makes sense because GAS is spread by direct contact with infected persons or their secretions, and social contact had dramatically decreased particularly in the first 6 months of the pandemic.
However, since 2022 and the return to “normal” social behaviors, both viral diseases (e.g., RSV, influenza, and Norovirus), and some bacterial diseases have rebounded. That said, something else must be contributing, because iGAS rates had increased 4-5 years pre pandemic. In fact, the fluctuating pattern included “normal” annual rates in the early 2000s rising in ~2015 followed by the explainable pandemic drop (by nearly 25%), and not-too-unexpected 2-year postpandemic rise. But interestingly enough, the rebound is higher than might be expected for iGAS and children were overrepresented in first year’s rise (2022 rate for pediatric iGAS was the highest since 1997) while those older than 65 were overrepresented in second year (2023).1
Emergence of M1UK
One potential factor for the prepandemic rise in iGAS infections worldwide is the emergence and worldwide spread of a new GAS emm type variant designated M1UK.2 GAS isolates can be typed into categories designated as emm types based on DNA sequence. There are more than 240 emm types, with 6 being most common — M1, M3, and M28 (each up to 20% of GAS isolates) and M12, M82, and M89 (each up to 10%). M1, M3 and M28 have also been particularly associated with invasive disease. While emm types vary year to year and region by region, the overall emm type distribution among iGAS isolates in the United States had not been unusual since the turn of the century and the US M1 strain was the same as that which had been predominant worldwide (designated M1GLOBAL). This new M1UK sublineage had emerged around 2010 and had been increasing pre pandemic. The M1UK sequence contained a specific set of 27 SNPs (single nucleoside polymorphisms, i.e., single base mutations) and was associated with an uptick in scarlet fever in the United Kingdom starting around 2010. Its prevalence increased up to around 2015 while spreading internationally. It also had enhanced expression of SpeA, a phage-encoded superantigen. Some of the M1UK mutations also appear to alter GAS metabolic processes to allow better survival (better “fitness”) compared with other GAS. So, a more virulent hardier GAS had arisen and seems a reasonable candidate for contributing to the increased iGAS rates.
Waning Antibody to GAS As Potential Factor in Rebound
No consensus exists on correlates of protection from iGAS. However, adults seem to have less noninvasive GAS than children. One potential reason is that frequent GAS re-exposure, regardless of whether disease results, likely boosts anti-GAS antibodies. Pandemic social restrictions temporarily prevented such boosts. In children with developing antibody repertoires, anti-GAS antibodies may have waned below protective levels faster during a year without frequent boosting. Thus, children were iGAS susceptible soon after pandemic restrictions were dropped (2022). Increased iGAS rates in the elderly in 2023 may have occurred because of diminished GAS exposures accelerating immune senescence with anti-GAS antibodies dropping, but less quickly than in children. These speculations are simply hypotheses until future studies can test them.
All that said, how do we use information on increased iGAS in our daily practices? In addition to standard preventive strategies for viral coinfections (e.g., varicella and influenza vaccine), reminding families about rigorous attention to wound care is the one high-risk scenario we have not yet discussed. During 2024, a time of expected increased prevalence of iGAS, early wound care needs to be fastidious. Further, share warning signs with families (e.g., rapidly expanding painful erythema), “streaks” ascending from extremity wounds, fever and a highly painful wound, darkening almost purple color within cellulitis or soft tissue infection, or loss of sensation in the middle of an otherwise painful soft tissue infection. These presentations require immediate medical attention.
If such a patient presents, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends admission along with blood and, where possible, wound cultures. If in the context of pneumonia with pleural effusion, culturing pleural fluid is also important. Remember, leading edge cultures are not often positive for GAS, seemingly because GAS exotoxins are found at erythema’s leading edge, not the bacteria. The bacteria are somewhere more central in the inflammatory process. Despite not being prominent among recent iGAS cases, another scenario that could sneak up on you is the infected surgical wound as nascent iGAS.
Finally, remember that nationally increasing numbers of iGAS isolates are resistant to erythromycin and clindamycin, the latter usually recommended to reduce tissue damage in iGAS.3 So, it is important to be aware of susceptibility patterns in your locale and consider an ID consultation. My hope is that you do not see an iGAS case this year, but we all need to remain alert. With a high index of suspicion and rapid diagnosis, you can minimize long-term sequelae and potential fatalities.
While it is too early to tell how the rest of 2024 will turn out, preliminary indications are that GAS is circulating at higher than usual levels (30%-35% GAS positive throat swabs in early April 2024 in Kansas City area) and iGAS rates will likely also be relatively high, particularly if Ontario, Canada, data are any indication.4
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Current Group A Strep Activity, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. April 2024. CDC webpage on current invasive GAS disease. April 2024.
2. Li Y et al. Expansion of Invasive Group A Streptococcus M1UK Lineage in Active Bacterial Core Surveillance, United States, 2019-2021 Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29(10):2116-2120. doi: 10.3201/eid2910.230675.
3. Andreoni F et al. Clindamycin Affects Group A Streptococcus Virulence Factors and Improves Clinical Outcome. J Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 15;215(2):269-277. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw229.
4. Group A Streptococcal Disease, Invasive (iGAS), Public Health Ontario.
Invasive group A streptococcus (iGAS) infections are rare (4-9 cases/100,000 US population annually) but potentially devastating (approximately 2,300 deaths annually in US), and affect all ages. Cases increase in winter-spring, paralleling the “season” of increased noninvasive GAS, e.g., pharyngitis and scarlet fever. iGAS case rates are lower in children than adults. That said, one well-known pediatric iGAS scenario has been deep cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis during the healing phase of varicella. Other forms of iGAS include bacteremia, pneumonia (particularly when empyema is present), lymphangitis, erysipelas, and toxic shock syndrome. iGAS can occur with/after influenza but has also occurred concurrently with other viral respiratory infections.
Persons with underlying conditions (cancer or immune compromised status; chronic diseases of the heart, kidney or lung; diabetes mellitus) are at higher risk. Other subpopulations at risk for iGAS are illicit drug users, the elderly, homeless persons, nursing home residents, American Indian persons, and Alaska Native persons. Most experts feel that highly toxigenic strains of GAS are responsible for most iGAS. Indeed, most iGAS isolates produce (sometimes hyper-produce) superantigens that cause exaggerated innate immune responses, higher levels of inflammation, and often times tissue destruction, e.g., “flesh eating bacteria.” And who can forget that Jim Henson, creator of the Muppets, died of iGAS?
But why discuss iGAS in 2024? The pattern for iGAS has fluctuated more than usual in the last decade. So much so that the recent upsurge has caught the collective eye of the lay press. So, patients and friends may have questions about why and how iGAS is increasing lately. The bottom line is that no one knows for sure. However, the most recent 2 years of uptick may reflect GAS circulating at relatively high levels even when taking into account that GAS season occurs in winter-spring most years. Yet it seems likely that additional factors may have played a role in the fluctuations noted this past decade, e.g., temporary changes in societal behavior, a new GAS strain with over two dozen mutations, and possibly rapid waning of protection against GAS exotoxins.
Social Behavior Factor
The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic brought extremes of disease and death to the world and dramatic changes in social behavior. A byproduct was dramatic decreases in nearly all infectious diseases, with numerous reports of near absence of many respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses in the 2020-2021 seasons. Interestingly, we did not see a drop in human rhinovirus infections, justifying its nickname as the cockroach of viruses. Reports also emerged about drops in bacterial diseases during 2020-2021 (although not so much for STIs), including noninvasive and invasive GAS disease, and also GAS-associated deaths (lowest since 2016).1 The drop in iGAS during social restrictions makes sense because GAS is spread by direct contact with infected persons or their secretions, and social contact had dramatically decreased particularly in the first 6 months of the pandemic.
However, since 2022 and the return to “normal” social behaviors, both viral diseases (e.g., RSV, influenza, and Norovirus), and some bacterial diseases have rebounded. That said, something else must be contributing, because iGAS rates had increased 4-5 years pre pandemic. In fact, the fluctuating pattern included “normal” annual rates in the early 2000s rising in ~2015 followed by the explainable pandemic drop (by nearly 25%), and not-too-unexpected 2-year postpandemic rise. But interestingly enough, the rebound is higher than might be expected for iGAS and children were overrepresented in first year’s rise (2022 rate for pediatric iGAS was the highest since 1997) while those older than 65 were overrepresented in second year (2023).1
Emergence of M1UK
One potential factor for the prepandemic rise in iGAS infections worldwide is the emergence and worldwide spread of a new GAS emm type variant designated M1UK.2 GAS isolates can be typed into categories designated as emm types based on DNA sequence. There are more than 240 emm types, with 6 being most common — M1, M3, and M28 (each up to 20% of GAS isolates) and M12, M82, and M89 (each up to 10%). M1, M3 and M28 have also been particularly associated with invasive disease. While emm types vary year to year and region by region, the overall emm type distribution among iGAS isolates in the United States had not been unusual since the turn of the century and the US M1 strain was the same as that which had been predominant worldwide (designated M1GLOBAL). This new M1UK sublineage had emerged around 2010 and had been increasing pre pandemic. The M1UK sequence contained a specific set of 27 SNPs (single nucleoside polymorphisms, i.e., single base mutations) and was associated with an uptick in scarlet fever in the United Kingdom starting around 2010. Its prevalence increased up to around 2015 while spreading internationally. It also had enhanced expression of SpeA, a phage-encoded superantigen. Some of the M1UK mutations also appear to alter GAS metabolic processes to allow better survival (better “fitness”) compared with other GAS. So, a more virulent hardier GAS had arisen and seems a reasonable candidate for contributing to the increased iGAS rates.
Waning Antibody to GAS As Potential Factor in Rebound
No consensus exists on correlates of protection from iGAS. However, adults seem to have less noninvasive GAS than children. One potential reason is that frequent GAS re-exposure, regardless of whether disease results, likely boosts anti-GAS antibodies. Pandemic social restrictions temporarily prevented such boosts. In children with developing antibody repertoires, anti-GAS antibodies may have waned below protective levels faster during a year without frequent boosting. Thus, children were iGAS susceptible soon after pandemic restrictions were dropped (2022). Increased iGAS rates in the elderly in 2023 may have occurred because of diminished GAS exposures accelerating immune senescence with anti-GAS antibodies dropping, but less quickly than in children. These speculations are simply hypotheses until future studies can test them.
All that said, how do we use information on increased iGAS in our daily practices? In addition to standard preventive strategies for viral coinfections (e.g., varicella and influenza vaccine), reminding families about rigorous attention to wound care is the one high-risk scenario we have not yet discussed. During 2024, a time of expected increased prevalence of iGAS, early wound care needs to be fastidious. Further, share warning signs with families (e.g., rapidly expanding painful erythema), “streaks” ascending from extremity wounds, fever and a highly painful wound, darkening almost purple color within cellulitis or soft tissue infection, or loss of sensation in the middle of an otherwise painful soft tissue infection. These presentations require immediate medical attention.
If such a patient presents, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends admission along with blood and, where possible, wound cultures. If in the context of pneumonia with pleural effusion, culturing pleural fluid is also important. Remember, leading edge cultures are not often positive for GAS, seemingly because GAS exotoxins are found at erythema’s leading edge, not the bacteria. The bacteria are somewhere more central in the inflammatory process. Despite not being prominent among recent iGAS cases, another scenario that could sneak up on you is the infected surgical wound as nascent iGAS.
Finally, remember that nationally increasing numbers of iGAS isolates are resistant to erythromycin and clindamycin, the latter usually recommended to reduce tissue damage in iGAS.3 So, it is important to be aware of susceptibility patterns in your locale and consider an ID consultation. My hope is that you do not see an iGAS case this year, but we all need to remain alert. With a high index of suspicion and rapid diagnosis, you can minimize long-term sequelae and potential fatalities.
While it is too early to tell how the rest of 2024 will turn out, preliminary indications are that GAS is circulating at higher than usual levels (30%-35% GAS positive throat swabs in early April 2024 in Kansas City area) and iGAS rates will likely also be relatively high, particularly if Ontario, Canada, data are any indication.4
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Mo. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Current Group A Strep Activity, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. April 2024. CDC webpage on current invasive GAS disease. April 2024.
2. Li Y et al. Expansion of Invasive Group A Streptococcus M1UK Lineage in Active Bacterial Core Surveillance, United States, 2019-2021 Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29(10):2116-2120. doi: 10.3201/eid2910.230675.
3. Andreoni F et al. Clindamycin Affects Group A Streptococcus Virulence Factors and Improves Clinical Outcome. J Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 15;215(2):269-277. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw229.
4. Group A Streptococcal Disease, Invasive (iGAS), Public Health Ontario.
