User login
Mr. B, age 37, presents to a community mental health center for an appointment following a recent emergency department visit. He is diagnosed with schizophrenia, and has been treated for approximately 1 year. Six months ago, Mr. B stopped taking his antipsychotic due to its adverse effects. Despite compliance with another agent, he has become increasingly disorganized and paranoid.
He now believes that his mother, with whom he has lived all his life and who serves as his guardian, is poisoning his food and trying to kill him. She is an employee at a local grocery store, and Mr. B has expressed concern that her coworkers are assisting her in the plot to kill him.
Following a home visit, Mr. B’s case manager indicates that the patient showed them the collection of weapons he is amassing to “defend” himself. This leads to a concern for the safety of the patient, his mother, and others.
Although parricide—killing one’s parent—is a relatively rare event, its sensationalistic nature has long captured the attention of headline writers and the general public. This article discusses the diagnostic and demographic factors that may be seen among individuals who kill their parents, with an emphasis on those who commit matricide (murder of one’s mother) and associated spree killings, where an individual kills multiple people within a single brief but contiguous time period. Understanding these characteristics can help clinicians identify and more safely manage patients who may be at risk of harming their parents in addition to others.
Characteristics of perpetrators of parricide
Worldwide, approximately 2% to 4% of homicides involve parricide, or killing one’s parent.1,2 Most offenders are men in early adulthood, though a proportion are adolescents and some are women.1,3 They are often single, unemployed, and live with the parent prior to the killing.1 Patricide occurs more frequently than matricide.4 In the United States, approximately 150 fathers and 100 mothers are killed by their child each year.5
In a study of all homicides in England and Wales between 1997 and 2014, two-thirds of parricide offenders had previously been diagnosed with a mental disorder.1 One-third were diagnosed with schizophrenia.1 In a Canadian study focusing on 43 adult perpetrators found not criminally responsible,6 most were experiencing psychotic symptoms at the time of parricide; symptoms of a personality disorder were the second-most prevalent symptoms. Similarly, Bourget et al4 studied Canadian coroner records for 64 parents killed by their children. Of the children involved in those parricides, 15% attempted suicide after the killing. Two-thirds of the male offenders evidenced delusional thinking, and/or excessive violence (overkill) was common. Some cases (16%) followed an argument, and some of those perpetrators were intoxicated or psychotic. From our clinical experience, when there are identifiable nonpsychotic triggers, they often can be small things such as an argument over food, smoking, or video games. Often, the perpetrator was financially dependent on their parents and were “trapped in a difficult/hostile/dependence/love relationship” with that parent.6 Adolescent males who kill their parents may not have psychosis7; however, they may be victims of longstanding serious abuse at the hands of their parents. These perpetrators often express relief rather than remorse after committing murder.
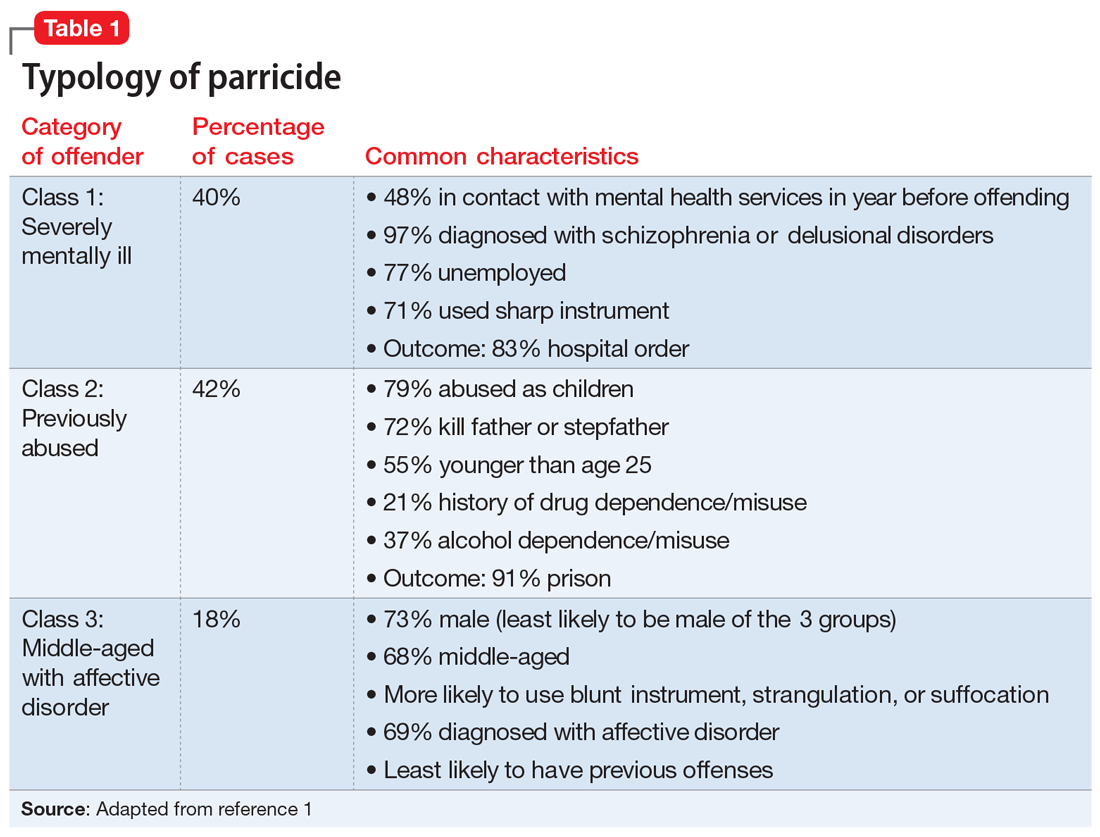
Three categories to classify the perpetrators of parricide have been proposed: severely abused, severely mentally ill, and “dangerously antisocial.”3 While severe mental illness was most common in adult defendants, severe abuse was most common in adolescent offenders. There may be significant commonalities between adolescent and adult perpetrators. A more recent latent class analysis by Bojanic et al1 indicated 3 unique types of parricide offenders (Table 1).
Continue to: Matricide: A closer look...
Matricide: A closer look
Though multiple studies have found a higher rate of psychosis among perpetrators of matricide, it is important to note that most people with psychotic disorders would never kill their mother. These events, however, tend to grab headlines and may be highly focused upon by the general population. In addition, matricide may be part of a larger crime that draws additional attention. For example, the 1966 University of Texas Bell Tower shooter and the 2012 Sandy Hook Elementary school shooter both killed their mothers before engaging in mass homicide. Often in cases of matricide, a longer-term dysfunctional relationship existed between the mother and the child. The mother is frequently described as controlling and intrusive and the (often adult) child as overly dependent, while the father may be absent or ineffectual. Hostility and mutual dependence are usual hallmarks of these relationships.8
However, in some cases where an individual with a psychotic disorder kills their mother, there may have been a traditional nurturing relationship.8 Alternative motivations unrelated to psychosis must be considered, including crimes motivated by money/inheritance or those perpetrated out of nonpsychotic anger. Green8 described motive categories for matricide that include paranoid and persecutory, altruistic, and other. In the “paranoid and persecutory” group, delusional beliefs about the mother occur; for example, the perpetrator may believe their mother was the devil. Sexual elements are found in some cases.8 Alternatively, the “altruistic” group demonstrated rather selfless reasons for killing, such as altruistic infanticide cases, or killing out of love.9 The altruistic matricide perpetrator may believe their mother is unwell, which may be a delusion or actually true. Finally, the “other” category contains cases related to jealousy, rage, and impulsivity.
In a study of 15 matricidal men in New York conducted by Campion et al,10 individuals seen by forensic psychiatric services for the crime of matricide included those with schizophrenia, substance-induced psychosis, and impulse control disorders. The authors noted there was often “a serious chronic derangement in the relationships of most matricidal men and their mothers.” Psychometric testing in these cases indicated feelings of dependency, weakness, and difficulty accepting an adult role separate from their mother. Some had conceptualized their mothers as a threat to their masculinity, while others had become enraged at their mothers.
Prevention requires addressing underlying issues
As described above, several factors are common among individuals who commit parricide, and these can be used to develop prevention strategies that focus on addressing underlying issues (Table 2). It is important to consider the relationship dynamics between the potential victim and perpetrator, as well as the motive, rather than focusing solely on mental illness or substance misuse.2
Spree killings that start as parricide
Although spree killing is a relatively rare event, a subset of spree killings involve parricide. One infamous recent event occurred in 2012 at Sandy Hook Elementary School, where the gunman killed his mother before going to the school and killing 26 additional people, many of whom were children.11,12 Because such events are rare, and because in these cases there is a high likelihood that the perpetrator is deceased (eg, died by suicide or killed by the police), much remains unknown about specific motivations and causative factors.
Information is often pieced together from postmortem reviews, which can be hampered by hindsight/recall bias and lack of contemporaneous documentation. Even worse, when these events occur, they may lead to a bias that all parricides or mass murders follow the pattern of the most recent case. This can result in overgeneralization of an individual’s history as being actionable risk violence factors for all potential parricide cases both by the public (eg, “My sister’s son has autism, and the Sandy Hook shooter was reported to have autism—should I be worried for my sister?”) and professionals (eg, “Will I be blamed for the next Sandy Hook by not taking more aggressive action even though I am not sure it is clinically warranted?”).
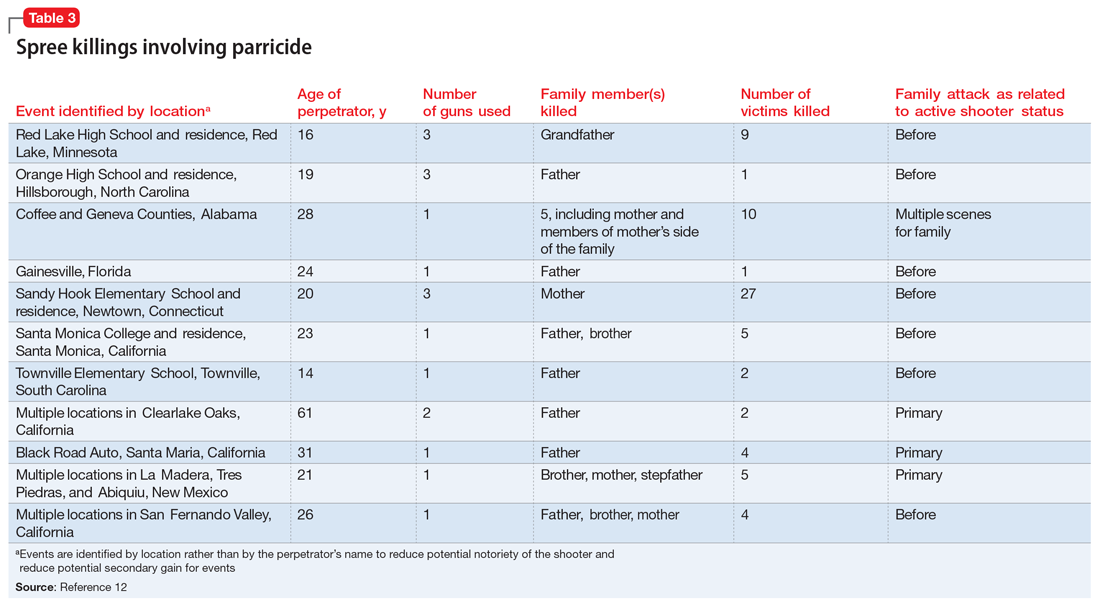
To identify trends for individuals committing parricide who engage in mass murder events (such as spree killing), we reviewed the 2000-2019 FBI active shooter list.12 Of the 333 events identified, 46 could be classified as domestic violence situations (eg, the perpetrator was in a romantic or familial relationship/former relationship and engaged in an active shooting incident involving at least 1 person from that relationship). We classified 11 of those 46 cases as parricide. Ten of those 11 parricides involved a child killing a parent (Table 3), and the other involved a grandchild killing a grandfather who served as their primary caregiver. Of the 11 incidents, mothers were involved (killed or wounded) in 4, and father figures (including the grandfather serving as a father and a stepfather) were killed in 9, with 2 incidents involving both parents. In 4 of the 11 parricides, other family members were killed in addition to the parent (including siblings, grandparents, or extended family). When considering spree shooters who committed parricide, 4 alleged perpetrators died by suicide, 1 was killed at the scene, and the rest were apprehended. The most common active shooting site endangering the public was an educational location (5), followed by commerce locations (4), with 2 involving open spaces. Eight of the 11 parricides occurred before the event was designated as an active shooting. The mean age for a parricide plus spree shooter was 23, once the oldest (age 61) and youngest (age 14) were removed from the calculation. The majority of the cases fell into the age range of 16 to 25 (n = 6), followed by 3 individuals who were age 26 to 31 (n = 3). All suspected individuals were male.
It is difficult to ascertain the existence of prior mental health care because perpetrators’ medical records may be confidential, juvenile court records may be sealed, and there may not even be a trial due to death or suicide (leading to limited forensic psychiatry examination or public testimony). Among those apprehended, many individuals raise some form of mental health defense, but the validity of their diagnosis may be undermined by concerns of possible malingering, especially in cases where the individual did not have a history of psychiatric treatment prior to the event.11 In summary, based on FBI data,12 spree shooters who committed parricide were usually male, in their late adolescence or early 20s, and more frequently targeted father figures. They often committed the parricide first and at a different location from later “active” shootings. Police were usually not aware of the parricide until after the spree is over.
Continue to: Parricide and society...
Parricide and society
For centuries, mothers and fathers have been honored and revered. Therefore, it is not surprising that killing of one’s mother or father attracts a great deal of macabre interest. Examples of parricide are present throughout popular culture, in mythology, comic books, movies, and television. As all psychiatrists know, Oedipus killed his father and married his mother. Other popular culture examples include: Grant Morrison’s Arkham Asylum: A Serious House on Serious Earth, Alfred Hitchcock’s Psycho, Oliver Stone’s Natural Born Killers, Peter Jackson’s Heavenly Creatures, The Affair drama series, and Star Wars: The Force Awakens.13,14
CASE CONTINUED
In Mr. B’s case, it is imperative for the treatment team to inquire about his history of violence, paying particular attention to prior violent acts towards his mother. His clinicians should consider hospitalization with the guardian’s consent if the danger appears imminent, especially considering the presence of weapons at home. They should attempt to stabilize Mr. B on effective, tolerable medications to ameliorate his psychosis, and to refer him for long-term psychotherapy to address difficult dynamic issues in the family relationship and encourage compliance with treatment. These steps may help avert a tragedy.
Bottom Line
Individuals who commit parricide often have a history of psychosis, a mood disorder, childhood abuse, and/or difficult relationship dynamics with the parent they kill. Some go on a spree killing in the community. Through careful consideration of individual risk factors, psychiatrists may help prevent some cases of parent murder by a child and possibly more tragedy in the community.
1. Bojanié L, Flynn S, Gianatsi M, et al. The typology of parricide and the role of mental illness: data-driven approach. Aggress Behav. 2020;46(6):516-522.
2. Pinals DS. Parricide. In Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2019:113-138.
3. Heide KM. Matricide and stepmatricide victims and offenders: an empirical analysis of US arrest data. Behav Sci Law. 2013;31(2):203-214.
4. Bourget D, Gagné P, Labelle ME. Parricide: a comparative study of matricide versus patricide. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2007;35(3):306-312.
5. Heide KM, Frei A. Matricide: a critique of the literature. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2010;11(1):3-17.
6. Marleau JD, Auclair N, Millaud F. Comparison of factors associated with parricide in adults and adolescents. J Fam Viol. 2006;21:321-325.
7. West SG, Feldsher M. Parricide: characteristics of sons and daughters who kill their parents. Current Psychiatry. 2010;9(11):20-38.
8. Green CM. Matricide by sons. Med Sci Law. 1981;21(3):207-214.
9. Friedman SH. Conclusions. In Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2019:161-164.
10. Campion J, Cravens JM, Rotholc A, et al. A study of 15 matricidal men. Am J Psychiatry. 1985;142(3):312-317.
11. Hall RCW, Friedman SH, Sorrentino R, et al. The myth of school shooters and psychotropic medications. Behav Sci Law. 2019;37(5):540-558.
12. Department of Justice Federal Bureau of Investigation. Active Shooter Incidents: 20-Year Review, 2000-2019. June 1, 2021. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.fbi.gov/file-repository/active-shooter-incidents-20-year-review-2000-2019-060121.pdf/view
13. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Star Wars: The Force Awakens, forensic teaching about matricide. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2017;45(1):128-130.
14. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Deadly and dysfunctional family dynamics: when fiction mirrors fact. In: Packer S, Fredrick DR, eds. Welcome to Arkham Asylum: Essays on Psychiatry and the Gotham City Institution. McFarland; 2019:65-75.
Mr. B, age 37, presents to a community mental health center for an appointment following a recent emergency department visit. He is diagnosed with schizophrenia, and has been treated for approximately 1 year. Six months ago, Mr. B stopped taking his antipsychotic due to its adverse effects. Despite compliance with another agent, he has become increasingly disorganized and paranoid.
He now believes that his mother, with whom he has lived all his life and who serves as his guardian, is poisoning his food and trying to kill him. She is an employee at a local grocery store, and Mr. B has expressed concern that her coworkers are assisting her in the plot to kill him.
Following a home visit, Mr. B’s case manager indicates that the patient showed them the collection of weapons he is amassing to “defend” himself. This leads to a concern for the safety of the patient, his mother, and others.
Although parricide—killing one’s parent—is a relatively rare event, its sensationalistic nature has long captured the attention of headline writers and the general public. This article discusses the diagnostic and demographic factors that may be seen among individuals who kill their parents, with an emphasis on those who commit matricide (murder of one’s mother) and associated spree killings, where an individual kills multiple people within a single brief but contiguous time period. Understanding these characteristics can help clinicians identify and more safely manage patients who may be at risk of harming their parents in addition to others.
Characteristics of perpetrators of parricide
Worldwide, approximately 2% to 4% of homicides involve parricide, or killing one’s parent.1,2 Most offenders are men in early adulthood, though a proportion are adolescents and some are women.1,3 They are often single, unemployed, and live with the parent prior to the killing.1 Patricide occurs more frequently than matricide.4 In the United States, approximately 150 fathers and 100 mothers are killed by their child each year.5
In a study of all homicides in England and Wales between 1997 and 2014, two-thirds of parricide offenders had previously been diagnosed with a mental disorder.1 One-third were diagnosed with schizophrenia.1 In a Canadian study focusing on 43 adult perpetrators found not criminally responsible,6 most were experiencing psychotic symptoms at the time of parricide; symptoms of a personality disorder were the second-most prevalent symptoms. Similarly, Bourget et al4 studied Canadian coroner records for 64 parents killed by their children. Of the children involved in those parricides, 15% attempted suicide after the killing. Two-thirds of the male offenders evidenced delusional thinking, and/or excessive violence (overkill) was common. Some cases (16%) followed an argument, and some of those perpetrators were intoxicated or psychotic. From our clinical experience, when there are identifiable nonpsychotic triggers, they often can be small things such as an argument over food, smoking, or video games. Often, the perpetrator was financially dependent on their parents and were “trapped in a difficult/hostile/dependence/love relationship” with that parent.6 Adolescent males who kill their parents may not have psychosis7; however, they may be victims of longstanding serious abuse at the hands of their parents. These perpetrators often express relief rather than remorse after committing murder.
Three categories to classify the perpetrators of parricide have been proposed: severely abused, severely mentally ill, and “dangerously antisocial.”3 While severe mental illness was most common in adult defendants, severe abuse was most common in adolescent offenders. There may be significant commonalities between adolescent and adult perpetrators. A more recent latent class analysis by Bojanic et al1 indicated 3 unique types of parricide offenders (Table 1).
Continue to: Matricide: A closer look...
Matricide: A closer look
Though multiple studies have found a higher rate of psychosis among perpetrators of matricide, it is important to note that most people with psychotic disorders would never kill their mother. These events, however, tend to grab headlines and may be highly focused upon by the general population. In addition, matricide may be part of a larger crime that draws additional attention. For example, the 1966 University of Texas Bell Tower shooter and the 2012 Sandy Hook Elementary school shooter both killed their mothers before engaging in mass homicide. Often in cases of matricide, a longer-term dysfunctional relationship existed between the mother and the child. The mother is frequently described as controlling and intrusive and the (often adult) child as overly dependent, while the father may be absent or ineffectual. Hostility and mutual dependence are usual hallmarks of these relationships.8
However, in some cases where an individual with a psychotic disorder kills their mother, there may have been a traditional nurturing relationship.8 Alternative motivations unrelated to psychosis must be considered, including crimes motivated by money/inheritance or those perpetrated out of nonpsychotic anger. Green8 described motive categories for matricide that include paranoid and persecutory, altruistic, and other. In the “paranoid and persecutory” group, delusional beliefs about the mother occur; for example, the perpetrator may believe their mother was the devil. Sexual elements are found in some cases.8 Alternatively, the “altruistic” group demonstrated rather selfless reasons for killing, such as altruistic infanticide cases, or killing out of love.9 The altruistic matricide perpetrator may believe their mother is unwell, which may be a delusion or actually true. Finally, the “other” category contains cases related to jealousy, rage, and impulsivity.
In a study of 15 matricidal men in New York conducted by Campion et al,10 individuals seen by forensic psychiatric services for the crime of matricide included those with schizophrenia, substance-induced psychosis, and impulse control disorders. The authors noted there was often “a serious chronic derangement in the relationships of most matricidal men and their mothers.” Psychometric testing in these cases indicated feelings of dependency, weakness, and difficulty accepting an adult role separate from their mother. Some had conceptualized their mothers as a threat to their masculinity, while others had become enraged at their mothers.
Prevention requires addressing underlying issues
As described above, several factors are common among individuals who commit parricide, and these can be used to develop prevention strategies that focus on addressing underlying issues (Table 2). It is important to consider the relationship dynamics between the potential victim and perpetrator, as well as the motive, rather than focusing solely on mental illness or substance misuse.2
Spree killings that start as parricide
Although spree killing is a relatively rare event, a subset of spree killings involve parricide. One infamous recent event occurred in 2012 at Sandy Hook Elementary School, where the gunman killed his mother before going to the school and killing 26 additional people, many of whom were children.11,12 Because such events are rare, and because in these cases there is a high likelihood that the perpetrator is deceased (eg, died by suicide or killed by the police), much remains unknown about specific motivations and causative factors.
Information is often pieced together from postmortem reviews, which can be hampered by hindsight/recall bias and lack of contemporaneous documentation. Even worse, when these events occur, they may lead to a bias that all parricides or mass murders follow the pattern of the most recent case. This can result in overgeneralization of an individual’s history as being actionable risk violence factors for all potential parricide cases both by the public (eg, “My sister’s son has autism, and the Sandy Hook shooter was reported to have autism—should I be worried for my sister?”) and professionals (eg, “Will I be blamed for the next Sandy Hook by not taking more aggressive action even though I am not sure it is clinically warranted?”).
To identify trends for individuals committing parricide who engage in mass murder events (such as spree killing), we reviewed the 2000-2019 FBI active shooter list.12 Of the 333 events identified, 46 could be classified as domestic violence situations (eg, the perpetrator was in a romantic or familial relationship/former relationship and engaged in an active shooting incident involving at least 1 person from that relationship). We classified 11 of those 46 cases as parricide. Ten of those 11 parricides involved a child killing a parent (Table 3), and the other involved a grandchild killing a grandfather who served as their primary caregiver. Of the 11 incidents, mothers were involved (killed or wounded) in 4, and father figures (including the grandfather serving as a father and a stepfather) were killed in 9, with 2 incidents involving both parents. In 4 of the 11 parricides, other family members were killed in addition to the parent (including siblings, grandparents, or extended family). When considering spree shooters who committed parricide, 4 alleged perpetrators died by suicide, 1 was killed at the scene, and the rest were apprehended. The most common active shooting site endangering the public was an educational location (5), followed by commerce locations (4), with 2 involving open spaces. Eight of the 11 parricides occurred before the event was designated as an active shooting. The mean age for a parricide plus spree shooter was 23, once the oldest (age 61) and youngest (age 14) were removed from the calculation. The majority of the cases fell into the age range of 16 to 25 (n = 6), followed by 3 individuals who were age 26 to 31 (n = 3). All suspected individuals were male.
It is difficult to ascertain the existence of prior mental health care because perpetrators’ medical records may be confidential, juvenile court records may be sealed, and there may not even be a trial due to death or suicide (leading to limited forensic psychiatry examination or public testimony). Among those apprehended, many individuals raise some form of mental health defense, but the validity of their diagnosis may be undermined by concerns of possible malingering, especially in cases where the individual did not have a history of psychiatric treatment prior to the event.11 In summary, based on FBI data,12 spree shooters who committed parricide were usually male, in their late adolescence or early 20s, and more frequently targeted father figures. They often committed the parricide first and at a different location from later “active” shootings. Police were usually not aware of the parricide until after the spree is over.
Continue to: Parricide and society...
Parricide and society
For centuries, mothers and fathers have been honored and revered. Therefore, it is not surprising that killing of one’s mother or father attracts a great deal of macabre interest. Examples of parricide are present throughout popular culture, in mythology, comic books, movies, and television. As all psychiatrists know, Oedipus killed his father and married his mother. Other popular culture examples include: Grant Morrison’s Arkham Asylum: A Serious House on Serious Earth, Alfred Hitchcock’s Psycho, Oliver Stone’s Natural Born Killers, Peter Jackson’s Heavenly Creatures, The Affair drama series, and Star Wars: The Force Awakens.13,14
CASE CONTINUED
In Mr. B’s case, it is imperative for the treatment team to inquire about his history of violence, paying particular attention to prior violent acts towards his mother. His clinicians should consider hospitalization with the guardian’s consent if the danger appears imminent, especially considering the presence of weapons at home. They should attempt to stabilize Mr. B on effective, tolerable medications to ameliorate his psychosis, and to refer him for long-term psychotherapy to address difficult dynamic issues in the family relationship and encourage compliance with treatment. These steps may help avert a tragedy.
Bottom Line
Individuals who commit parricide often have a history of psychosis, a mood disorder, childhood abuse, and/or difficult relationship dynamics with the parent they kill. Some go on a spree killing in the community. Through careful consideration of individual risk factors, psychiatrists may help prevent some cases of parent murder by a child and possibly more tragedy in the community.
Mr. B, age 37, presents to a community mental health center for an appointment following a recent emergency department visit. He is diagnosed with schizophrenia, and has been treated for approximately 1 year. Six months ago, Mr. B stopped taking his antipsychotic due to its adverse effects. Despite compliance with another agent, he has become increasingly disorganized and paranoid.
He now believes that his mother, with whom he has lived all his life and who serves as his guardian, is poisoning his food and trying to kill him. She is an employee at a local grocery store, and Mr. B has expressed concern that her coworkers are assisting her in the plot to kill him.
Following a home visit, Mr. B’s case manager indicates that the patient showed them the collection of weapons he is amassing to “defend” himself. This leads to a concern for the safety of the patient, his mother, and others.
Although parricide—killing one’s parent—is a relatively rare event, its sensationalistic nature has long captured the attention of headline writers and the general public. This article discusses the diagnostic and demographic factors that may be seen among individuals who kill their parents, with an emphasis on those who commit matricide (murder of one’s mother) and associated spree killings, where an individual kills multiple people within a single brief but contiguous time period. Understanding these characteristics can help clinicians identify and more safely manage patients who may be at risk of harming their parents in addition to others.
Characteristics of perpetrators of parricide
Worldwide, approximately 2% to 4% of homicides involve parricide, or killing one’s parent.1,2 Most offenders are men in early adulthood, though a proportion are adolescents and some are women.1,3 They are often single, unemployed, and live with the parent prior to the killing.1 Patricide occurs more frequently than matricide.4 In the United States, approximately 150 fathers and 100 mothers are killed by their child each year.5
In a study of all homicides in England and Wales between 1997 and 2014, two-thirds of parricide offenders had previously been diagnosed with a mental disorder.1 One-third were diagnosed with schizophrenia.1 In a Canadian study focusing on 43 adult perpetrators found not criminally responsible,6 most were experiencing psychotic symptoms at the time of parricide; symptoms of a personality disorder were the second-most prevalent symptoms. Similarly, Bourget et al4 studied Canadian coroner records for 64 parents killed by their children. Of the children involved in those parricides, 15% attempted suicide after the killing. Two-thirds of the male offenders evidenced delusional thinking, and/or excessive violence (overkill) was common. Some cases (16%) followed an argument, and some of those perpetrators were intoxicated or psychotic. From our clinical experience, when there are identifiable nonpsychotic triggers, they often can be small things such as an argument over food, smoking, or video games. Often, the perpetrator was financially dependent on their parents and were “trapped in a difficult/hostile/dependence/love relationship” with that parent.6 Adolescent males who kill their parents may not have psychosis7; however, they may be victims of longstanding serious abuse at the hands of their parents. These perpetrators often express relief rather than remorse after committing murder.
Three categories to classify the perpetrators of parricide have been proposed: severely abused, severely mentally ill, and “dangerously antisocial.”3 While severe mental illness was most common in adult defendants, severe abuse was most common in adolescent offenders. There may be significant commonalities between adolescent and adult perpetrators. A more recent latent class analysis by Bojanic et al1 indicated 3 unique types of parricide offenders (Table 1).
Continue to: Matricide: A closer look...
Matricide: A closer look
Though multiple studies have found a higher rate of psychosis among perpetrators of matricide, it is important to note that most people with psychotic disorders would never kill their mother. These events, however, tend to grab headlines and may be highly focused upon by the general population. In addition, matricide may be part of a larger crime that draws additional attention. For example, the 1966 University of Texas Bell Tower shooter and the 2012 Sandy Hook Elementary school shooter both killed their mothers before engaging in mass homicide. Often in cases of matricide, a longer-term dysfunctional relationship existed between the mother and the child. The mother is frequently described as controlling and intrusive and the (often adult) child as overly dependent, while the father may be absent or ineffectual. Hostility and mutual dependence are usual hallmarks of these relationships.8
However, in some cases where an individual with a psychotic disorder kills their mother, there may have been a traditional nurturing relationship.8 Alternative motivations unrelated to psychosis must be considered, including crimes motivated by money/inheritance or those perpetrated out of nonpsychotic anger. Green8 described motive categories for matricide that include paranoid and persecutory, altruistic, and other. In the “paranoid and persecutory” group, delusional beliefs about the mother occur; for example, the perpetrator may believe their mother was the devil. Sexual elements are found in some cases.8 Alternatively, the “altruistic” group demonstrated rather selfless reasons for killing, such as altruistic infanticide cases, or killing out of love.9 The altruistic matricide perpetrator may believe their mother is unwell, which may be a delusion or actually true. Finally, the “other” category contains cases related to jealousy, rage, and impulsivity.
In a study of 15 matricidal men in New York conducted by Campion et al,10 individuals seen by forensic psychiatric services for the crime of matricide included those with schizophrenia, substance-induced psychosis, and impulse control disorders. The authors noted there was often “a serious chronic derangement in the relationships of most matricidal men and their mothers.” Psychometric testing in these cases indicated feelings of dependency, weakness, and difficulty accepting an adult role separate from their mother. Some had conceptualized their mothers as a threat to their masculinity, while others had become enraged at their mothers.
Prevention requires addressing underlying issues
As described above, several factors are common among individuals who commit parricide, and these can be used to develop prevention strategies that focus on addressing underlying issues (Table 2). It is important to consider the relationship dynamics between the potential victim and perpetrator, as well as the motive, rather than focusing solely on mental illness or substance misuse.2
Spree killings that start as parricide
Although spree killing is a relatively rare event, a subset of spree killings involve parricide. One infamous recent event occurred in 2012 at Sandy Hook Elementary School, where the gunman killed his mother before going to the school and killing 26 additional people, many of whom were children.11,12 Because such events are rare, and because in these cases there is a high likelihood that the perpetrator is deceased (eg, died by suicide or killed by the police), much remains unknown about specific motivations and causative factors.
Information is often pieced together from postmortem reviews, which can be hampered by hindsight/recall bias and lack of contemporaneous documentation. Even worse, when these events occur, they may lead to a bias that all parricides or mass murders follow the pattern of the most recent case. This can result in overgeneralization of an individual’s history as being actionable risk violence factors for all potential parricide cases both by the public (eg, “My sister’s son has autism, and the Sandy Hook shooter was reported to have autism—should I be worried for my sister?”) and professionals (eg, “Will I be blamed for the next Sandy Hook by not taking more aggressive action even though I am not sure it is clinically warranted?”).
To identify trends for individuals committing parricide who engage in mass murder events (such as spree killing), we reviewed the 2000-2019 FBI active shooter list.12 Of the 333 events identified, 46 could be classified as domestic violence situations (eg, the perpetrator was in a romantic or familial relationship/former relationship and engaged in an active shooting incident involving at least 1 person from that relationship). We classified 11 of those 46 cases as parricide. Ten of those 11 parricides involved a child killing a parent (Table 3), and the other involved a grandchild killing a grandfather who served as their primary caregiver. Of the 11 incidents, mothers were involved (killed or wounded) in 4, and father figures (including the grandfather serving as a father and a stepfather) were killed in 9, with 2 incidents involving both parents. In 4 of the 11 parricides, other family members were killed in addition to the parent (including siblings, grandparents, or extended family). When considering spree shooters who committed parricide, 4 alleged perpetrators died by suicide, 1 was killed at the scene, and the rest were apprehended. The most common active shooting site endangering the public was an educational location (5), followed by commerce locations (4), with 2 involving open spaces. Eight of the 11 parricides occurred before the event was designated as an active shooting. The mean age for a parricide plus spree shooter was 23, once the oldest (age 61) and youngest (age 14) were removed from the calculation. The majority of the cases fell into the age range of 16 to 25 (n = 6), followed by 3 individuals who were age 26 to 31 (n = 3). All suspected individuals were male.
It is difficult to ascertain the existence of prior mental health care because perpetrators’ medical records may be confidential, juvenile court records may be sealed, and there may not even be a trial due to death or suicide (leading to limited forensic psychiatry examination or public testimony). Among those apprehended, many individuals raise some form of mental health defense, but the validity of their diagnosis may be undermined by concerns of possible malingering, especially in cases where the individual did not have a history of psychiatric treatment prior to the event.11 In summary, based on FBI data,12 spree shooters who committed parricide were usually male, in their late adolescence or early 20s, and more frequently targeted father figures. They often committed the parricide first and at a different location from later “active” shootings. Police were usually not aware of the parricide until after the spree is over.
Continue to: Parricide and society...
Parricide and society
For centuries, mothers and fathers have been honored and revered. Therefore, it is not surprising that killing of one’s mother or father attracts a great deal of macabre interest. Examples of parricide are present throughout popular culture, in mythology, comic books, movies, and television. As all psychiatrists know, Oedipus killed his father and married his mother. Other popular culture examples include: Grant Morrison’s Arkham Asylum: A Serious House on Serious Earth, Alfred Hitchcock’s Psycho, Oliver Stone’s Natural Born Killers, Peter Jackson’s Heavenly Creatures, The Affair drama series, and Star Wars: The Force Awakens.13,14
CASE CONTINUED
In Mr. B’s case, it is imperative for the treatment team to inquire about his history of violence, paying particular attention to prior violent acts towards his mother. His clinicians should consider hospitalization with the guardian’s consent if the danger appears imminent, especially considering the presence of weapons at home. They should attempt to stabilize Mr. B on effective, tolerable medications to ameliorate his psychosis, and to refer him for long-term psychotherapy to address difficult dynamic issues in the family relationship and encourage compliance with treatment. These steps may help avert a tragedy.
Bottom Line
Individuals who commit parricide often have a history of psychosis, a mood disorder, childhood abuse, and/or difficult relationship dynamics with the parent they kill. Some go on a spree killing in the community. Through careful consideration of individual risk factors, psychiatrists may help prevent some cases of parent murder by a child and possibly more tragedy in the community.
1. Bojanié L, Flynn S, Gianatsi M, et al. The typology of parricide and the role of mental illness: data-driven approach. Aggress Behav. 2020;46(6):516-522.
2. Pinals DS. Parricide. In Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2019:113-138.
3. Heide KM. Matricide and stepmatricide victims and offenders: an empirical analysis of US arrest data. Behav Sci Law. 2013;31(2):203-214.
4. Bourget D, Gagné P, Labelle ME. Parricide: a comparative study of matricide versus patricide. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2007;35(3):306-312.
5. Heide KM, Frei A. Matricide: a critique of the literature. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2010;11(1):3-17.
6. Marleau JD, Auclair N, Millaud F. Comparison of factors associated with parricide in adults and adolescents. J Fam Viol. 2006;21:321-325.
7. West SG, Feldsher M. Parricide: characteristics of sons and daughters who kill their parents. Current Psychiatry. 2010;9(11):20-38.
8. Green CM. Matricide by sons. Med Sci Law. 1981;21(3):207-214.
9. Friedman SH. Conclusions. In Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2019:161-164.
10. Campion J, Cravens JM, Rotholc A, et al. A study of 15 matricidal men. Am J Psychiatry. 1985;142(3):312-317.
11. Hall RCW, Friedman SH, Sorrentino R, et al. The myth of school shooters and psychotropic medications. Behav Sci Law. 2019;37(5):540-558.
12. Department of Justice Federal Bureau of Investigation. Active Shooter Incidents: 20-Year Review, 2000-2019. June 1, 2021. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.fbi.gov/file-repository/active-shooter-incidents-20-year-review-2000-2019-060121.pdf/view
13. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Star Wars: The Force Awakens, forensic teaching about matricide. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2017;45(1):128-130.
14. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Deadly and dysfunctional family dynamics: when fiction mirrors fact. In: Packer S, Fredrick DR, eds. Welcome to Arkham Asylum: Essays on Psychiatry and the Gotham City Institution. McFarland; 2019:65-75.
1. Bojanié L, Flynn S, Gianatsi M, et al. The typology of parricide and the role of mental illness: data-driven approach. Aggress Behav. 2020;46(6):516-522.
2. Pinals DS. Parricide. In Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2019:113-138.
3. Heide KM. Matricide and stepmatricide victims and offenders: an empirical analysis of US arrest data. Behav Sci Law. 2013;31(2):203-214.
4. Bourget D, Gagné P, Labelle ME. Parricide: a comparative study of matricide versus patricide. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2007;35(3):306-312.
5. Heide KM, Frei A. Matricide: a critique of the literature. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2010;11(1):3-17.
6. Marleau JD, Auclair N, Millaud F. Comparison of factors associated with parricide in adults and adolescents. J Fam Viol. 2006;21:321-325.
7. West SG, Feldsher M. Parricide: characteristics of sons and daughters who kill their parents. Current Psychiatry. 2010;9(11):20-38.
8. Green CM. Matricide by sons. Med Sci Law. 1981;21(3):207-214.
9. Friedman SH. Conclusions. In Friedman SH, ed. Family Murder: Pathologies of Love and Hate. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2019:161-164.
10. Campion J, Cravens JM, Rotholc A, et al. A study of 15 matricidal men. Am J Psychiatry. 1985;142(3):312-317.
11. Hall RCW, Friedman SH, Sorrentino R, et al. The myth of school shooters and psychotropic medications. Behav Sci Law. 2019;37(5):540-558.
12. Department of Justice Federal Bureau of Investigation. Active Shooter Incidents: 20-Year Review, 2000-2019. June 1, 2021. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.fbi.gov/file-repository/active-shooter-incidents-20-year-review-2000-2019-060121.pdf/view
13. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Star Wars: The Force Awakens, forensic teaching about matricide. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2017;45(1):128-130.
14. Friedman SH, Hall RCW. Deadly and dysfunctional family dynamics: when fiction mirrors fact. In: Packer S, Fredrick DR, eds. Welcome to Arkham Asylum: Essays on Psychiatry and the Gotham City Institution. McFarland; 2019:65-75.