User login
Pacing as a device therapy for heart failure (HF) is headed for what is probably its next big advance.
After decades of biventricular (BiV) pacemaker success in resynchronizing the ventricles and improving clinical outcomes, relatively new conduction-system pacing (CSP) techniques that avoid the pitfalls of right-ventricular (RV) pacing using BiV lead systems have been supplanting traditional cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in selected patients at some major centers. In fact, they are solidly ensconced in a new guideline document addressing indications for CSP and BiV pacing in HF.
But , an alternative when BiV pacing isn’t appropriate or can’t be engaged.
That’s mainly because the limited, mostly observational evidence supporting CSP in the document can’t measure up to the clinical experience and plethora of large, randomized trials behind BiV-CRT.
But that shortfall is headed for change. Several new comparative studies, including a small, randomized trial, have added significantly to evidence suggesting that CSP is at least as effective as traditional CRT for procedural, functional safety, and clinical outcomes.
The new studies “are inherently prone to bias, but their results are really good,” observed Juan C. Diaz, MD. They show improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and symptoms with CSP that are “outstanding compared to what we have been doing for the last 20 years,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Diaz, Clínica Las Vegas, Medellin, Colombia, is an investigator with the observational SYNCHRONY, which is among the new CSP studies formally presented at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society. He is also lead author on its same-day publication in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Dr. Diaz said that CSP, which sustains pacing via the native conduction system, makes more “physiologic sense” than BiV pacing and represents “a step forward” for HF device therapy.
SYNCHRONY compared LBB-area with BiV pacing as the initial strategy for achieving cardiac resynchronization in patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy.
CSP is “a long way” from replacing conventional CRT, he said. But the new studies at the HRS sessions should help extend His-bundle and LBB-area pacing to more patients, he added, given the significant long-term “drawbacks” of BiV pacing. These include inevitable RV pacing, multiple leads, and the risks associated with chronic transvenous leads.
Zachary Goldberger, MD, University of Wisconsin–Madison, went a bit further in support of CSP as invited discussant for the SYNCHRONY presentation.
Given that it improved LVEF, heart failure class, HF hospitalizations (HFH), and mortality in that study and others, Dr. Goldberger said, CSP could potentially “become the dominant mode of resynchronization going forward.”
Other experts at the meeting saw CSP’s potential more as one of several pacing techniques that could be brought to bear for patients with CRT indications.
“Conduction system pacing is going to be a huge complement to biventricular pacing,” to which about 30% of patients have a “less than optimal response,” said Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, chief of clinical electrophysiology, Geisinger Heart Institute, Danville, Pa.
“I don’t think it needs to replace biventricular pacing, because biventricular pacing is a well-established, incredibly powerful therapy,” he told this news organization. But CSP is likely to provide “a good alternative option” in patients with poor responses to BiV-CRT.
It may, however, render some current BiV-pacing alternatives “obsolete,” Dr. Vijayaraman observed. “At our center, at least for the last 5 years, no patient has needed epicardial surgical left ventricular lead placement” because CSP was a better backup option.
Dr. Vijayaraman presented two of the meeting’s CSP vs. BiV pacing comparisons. In one, the 100-patient randomized HOT-CRT trial, contractile function improved significantly on CSP, which could be either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing.
He also presented an observational study of LBB-area pacing at 15 centers in Asia, Europe, and North America and led the authors of its simultaneous publication in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“I think left-bundle conduction system pacing is the future, for sure,” Jagmeet P. Singh, MD, DPhil, told this news organization. Still, it doesn’t always work and when it does, it “doesn’t work equally in all patients,” he said.
“Conduction system pacing certainly makes a lot of sense,” especially in patients with left-bundle-branch block (LBBB), and “maybe not as a primary approach but certainly as a secondary approach,” said Dr. Singh, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who is not a coauthor on any of the three studies.
He acknowledged that CSP may work well as a first-line option in patients with LBBB at some experienced centers. For those without LBBB or who have an intraventricular conduction delay, who represent 45%-50% of current CRT cases, Dr. Singh observed, “there’s still more evidence” that BiV-CRT is a more appropriate initial approach.
Standard CRT may fail, however, even in some patients who otherwise meet guideline-based indications. “We don’t really understand all the mechanisms for nonresponse in conventional biventricular pacing,” observed Niraj Varma, MD, PhD, Cleveland Clinic, also not involved with any of the three studies.
In some groups, including “patients with larger ventricles,” for example, BiV-CRT doesn’t always narrow the electrocardiographic QRS complex or preexcite delayed left ventricular (LV) activation, hallmarks of successful CRT, he said in an interview.
“I think we need to understand why this occurs in both situations,” but in such cases, CSP alone or as an adjunct to direct LV pacing may be successful. “Sometimes we need both an LV lead and the conduction-system pacing lead.”
Narrower, more efficient use of CSP as a BiV-CRT alternative may also boost its chances for success, Dr. Varma added. “I think we need to refine patient selection.”
HOT-CRT: Randomized CSP vs. BiV pacing trial
Conducted at three centers in a single health system, the His-optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy study (HOT-CRT) randomly assigned 100 patients with primary or secondary CRT indications to either to CSP – by either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing – or to standard BiV-CRT as the first-line resynchronization method.
Treatment crossovers, allowed for either pacing modality in the event of implantation failure, occurred in two patients and nine patients initially assigned to CSP and BiV pacing, respectively (4% vs. 18%), Dr. Vijayaraman reported.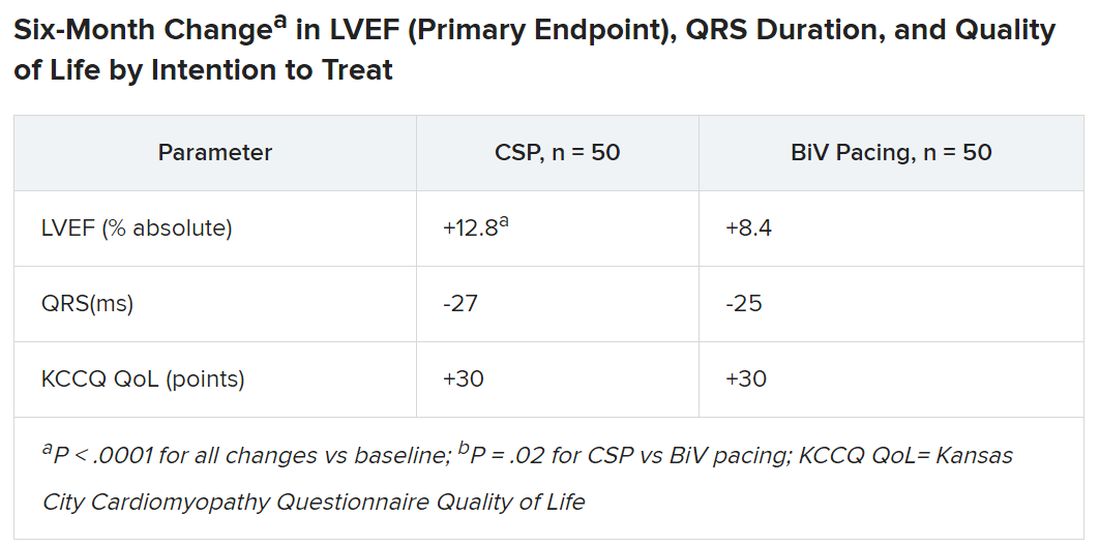
Historically in trials, BiV pacing has elevated LVEF by about 7%, he said. The mean 12-point increase observed with CSP “is huge, in that sense.” HOT-CRT enrolled a predominantly male and White population at centers highly experienced in both CSP and BiV pacing, limiting its broad relevance to practice, as pointed out by both Dr. Vijayaraman and his presentation’s invited discussant, Yong-Mei Cha, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Cha, who is director of cardiac device services at her center, also highlighted the greater rate of crossover from BiV pacing to CSP, 18% vs. 4% in the other direction. “This is a very encouraging result,” because the implant-failure rate for LBB-area pacing may drop once more operators become “familiar and skilled with conduction-system pacing.” Overall, the study supports CSP as “a very good alternative for heart failure patients when BiV pacing fails.”
International comparison of CSP and BiV pacing
In Dr. Vijayaraman’s other study, the observational comparison of LBB-area pacing and BiV-CRT, the CSP technique emerged as a “reasonable alternative to biventricular pacing, not only for improvement in LV function but also to reduce adverse clinical outcomes.”
Indeed, in the international study of 1,778 mostly male patients with primary or secondary CRT indications who received LBB-area or BiV pacing (797 and 981 patients, respectively), those on CSP saw a significant drop in risk for the primary endpoint, death or HFH.
Mean LVEF improved from 27% to 41% in the LBB-area pacing group and 27% to 37% with BiV pacing (P < .001 for both changes) over a follow-up averaging 33 months. The difference in improvement between CSP and BiV pacing was significant at P < .001.
In adjusted analysis, the risk for death or HFH was greater for BiV-pacing patients, a difference driven by HFH events.
- Death or HF: hazard ratio, 1.49 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-1.84; P < .001).
- Death: HR, 1.14 (95% CI, 0.88-1.48; P = .313).
- HFH: HR, 1.49 (95% CI, 1.16-1.92; P = .002)
The analysis has all the “inherent biases” of an observational study. The risk for patient-selection bias, however, was somewhat mitigated by consistent practice patterns at participating centers, Dr. Vijayaraman told this news organization.
For example, he said, operators at six of the institutions were most likely to use CSP as the first-line approach, and the same number of centers usually went with BiV pacing.
SYNCHRONY: First-line LBB-area pacing vs. BiV-CRT
Outcomes using the two approaches were similar in the prospective, international, observational study of 371 patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and standard CRT indications. Allocation of 128 patients to LBB-area pacing and 243 to BiV-CRT was based on patient and operator preferences, reported Jorge Romero Jr, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, at the HRS sessions.
Risk for the death-HFH primary endpoint dropped 38% for those initially treated with LBB-area pacing, compared with BiV pacing, primarily because of a lower HFH risk:
- Death or HFH: HR, 0.62 (95% CI, 0.41-0.93; P = .02).
- Death: HR, 0.57 (95% CI, 0.25-1.32; P = .19).
- HFH: HR, 0.61 (95% CI, 0.34-0.93; P = .02)
Patients in the CSP group were also more likely to improve by at least one NYHA (New York Heart Association) class (80.4% vs. 67.9%; P < .001), consistent with their greater absolute change in LVEF (8.0 vs. 3.9 points; P < .01).
The findings “suggest that LBBAP [left-bundle branch area pacing] is an excellent alternative to BiV pacing,” with a comparable safety profile, write Jayanthi N. Koneru, MBBS, and Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD, in an editorial accompanying the published SYNCHRONY report.
“The differences in improvement of LVEF are encouraging for both groups,” but were superior for LBB-area pacing, continue Dr. Koneru and Dr. Ellenbogen, both with Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond. “Whether these results would have regressed to the mean over a longer period of follow-up or diverge further with LBB-area pacing continuing to be superior is unknown.”
Years for an answer?
A large randomized comparison of CSP and BiV-CRT, called Left vs. Left, is currently in early stages, Sana M. Al-Khatib, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said in a media presentation on two of the presented studies. It has a planned enrollment of more than 2,100 patients on optimal meds with an LVEF of 50% or lower and either a QRS duration of at least 130 ms or an anticipated burden of RV pacing exceeding 40%.
The trial, she said, “will take years to give an answer, but it is actually designed to address the question of whether a composite endpoint of time to death or heart failure hospitalization can be improved with conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing.”
Dr. Al-Khatib is a coauthor on the new guideline covering both CSP and BiV-CRT in HF, as are Dr. Cha, Dr. Varma, Dr. Singh, Dr. Vijayaraman, and Dr. Goldberger; Dr. Ellenbogen is one of the reviewers.
Dr. Diaz discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or teaching from Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. Dr. Vijayaraman discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking, teaching, or consulting for Abbott, Medtronic, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific; and receiving research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Varma discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or consulting as an independent contractor for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Impulse Dynamics USA, Cardiologs, Abbott, Pacemate, Implicity, and EP Solutions. Dr. Singh discloses receiving fees for consulting from EBR Systems, Merit Medical Systems, New Century Health, Biotronik, Abbott, Medtronic, MicroPort Scientific, Cardiologs, Sanofi, CVRx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Octagos, Implicity, Orchestra Biomed, Rhythm Management Group, and Biosense Webster; and receiving honoraria or fees for speaking and teaching from Medscape. Dr. Cha had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Romero discloses receiving research grants from Biosense Webster; and speaking or receiving honoraria or fees for consulting, speaking, or teaching, or serving on a board for Sanofi, Boston Scientific, and AtriCure. Dr. Koneru discloses consulting for Medtronic and receiving honoraria from Abbott. Dr. Ellenbogen discloses consulting or lecturing for or receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott. Dr. Goldberger discloses receiving royalty income from and serving as an independent contractor for Elsevier. Dr. Al-Khatib discloses receiving research grants from Medtronic and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pacing as a device therapy for heart failure (HF) is headed for what is probably its next big advance.
After decades of biventricular (BiV) pacemaker success in resynchronizing the ventricles and improving clinical outcomes, relatively new conduction-system pacing (CSP) techniques that avoid the pitfalls of right-ventricular (RV) pacing using BiV lead systems have been supplanting traditional cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in selected patients at some major centers. In fact, they are solidly ensconced in a new guideline document addressing indications for CSP and BiV pacing in HF.
But , an alternative when BiV pacing isn’t appropriate or can’t be engaged.
That’s mainly because the limited, mostly observational evidence supporting CSP in the document can’t measure up to the clinical experience and plethora of large, randomized trials behind BiV-CRT.
But that shortfall is headed for change. Several new comparative studies, including a small, randomized trial, have added significantly to evidence suggesting that CSP is at least as effective as traditional CRT for procedural, functional safety, and clinical outcomes.
The new studies “are inherently prone to bias, but their results are really good,” observed Juan C. Diaz, MD. They show improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and symptoms with CSP that are “outstanding compared to what we have been doing for the last 20 years,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Diaz, Clínica Las Vegas, Medellin, Colombia, is an investigator with the observational SYNCHRONY, which is among the new CSP studies formally presented at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society. He is also lead author on its same-day publication in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Dr. Diaz said that CSP, which sustains pacing via the native conduction system, makes more “physiologic sense” than BiV pacing and represents “a step forward” for HF device therapy.
SYNCHRONY compared LBB-area with BiV pacing as the initial strategy for achieving cardiac resynchronization in patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy.
CSP is “a long way” from replacing conventional CRT, he said. But the new studies at the HRS sessions should help extend His-bundle and LBB-area pacing to more patients, he added, given the significant long-term “drawbacks” of BiV pacing. These include inevitable RV pacing, multiple leads, and the risks associated with chronic transvenous leads.
Zachary Goldberger, MD, University of Wisconsin–Madison, went a bit further in support of CSP as invited discussant for the SYNCHRONY presentation.
Given that it improved LVEF, heart failure class, HF hospitalizations (HFH), and mortality in that study and others, Dr. Goldberger said, CSP could potentially “become the dominant mode of resynchronization going forward.”
Other experts at the meeting saw CSP’s potential more as one of several pacing techniques that could be brought to bear for patients with CRT indications.
“Conduction system pacing is going to be a huge complement to biventricular pacing,” to which about 30% of patients have a “less than optimal response,” said Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, chief of clinical electrophysiology, Geisinger Heart Institute, Danville, Pa.
“I don’t think it needs to replace biventricular pacing, because biventricular pacing is a well-established, incredibly powerful therapy,” he told this news organization. But CSP is likely to provide “a good alternative option” in patients with poor responses to BiV-CRT.
It may, however, render some current BiV-pacing alternatives “obsolete,” Dr. Vijayaraman observed. “At our center, at least for the last 5 years, no patient has needed epicardial surgical left ventricular lead placement” because CSP was a better backup option.
Dr. Vijayaraman presented two of the meeting’s CSP vs. BiV pacing comparisons. In one, the 100-patient randomized HOT-CRT trial, contractile function improved significantly on CSP, which could be either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing.
He also presented an observational study of LBB-area pacing at 15 centers in Asia, Europe, and North America and led the authors of its simultaneous publication in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“I think left-bundle conduction system pacing is the future, for sure,” Jagmeet P. Singh, MD, DPhil, told this news organization. Still, it doesn’t always work and when it does, it “doesn’t work equally in all patients,” he said.
“Conduction system pacing certainly makes a lot of sense,” especially in patients with left-bundle-branch block (LBBB), and “maybe not as a primary approach but certainly as a secondary approach,” said Dr. Singh, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who is not a coauthor on any of the three studies.
He acknowledged that CSP may work well as a first-line option in patients with LBBB at some experienced centers. For those without LBBB or who have an intraventricular conduction delay, who represent 45%-50% of current CRT cases, Dr. Singh observed, “there’s still more evidence” that BiV-CRT is a more appropriate initial approach.
Standard CRT may fail, however, even in some patients who otherwise meet guideline-based indications. “We don’t really understand all the mechanisms for nonresponse in conventional biventricular pacing,” observed Niraj Varma, MD, PhD, Cleveland Clinic, also not involved with any of the three studies.
In some groups, including “patients with larger ventricles,” for example, BiV-CRT doesn’t always narrow the electrocardiographic QRS complex or preexcite delayed left ventricular (LV) activation, hallmarks of successful CRT, he said in an interview.
“I think we need to understand why this occurs in both situations,” but in such cases, CSP alone or as an adjunct to direct LV pacing may be successful. “Sometimes we need both an LV lead and the conduction-system pacing lead.”
Narrower, more efficient use of CSP as a BiV-CRT alternative may also boost its chances for success, Dr. Varma added. “I think we need to refine patient selection.”
HOT-CRT: Randomized CSP vs. BiV pacing trial
Conducted at three centers in a single health system, the His-optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy study (HOT-CRT) randomly assigned 100 patients with primary or secondary CRT indications to either to CSP – by either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing – or to standard BiV-CRT as the first-line resynchronization method.
Treatment crossovers, allowed for either pacing modality in the event of implantation failure, occurred in two patients and nine patients initially assigned to CSP and BiV pacing, respectively (4% vs. 18%), Dr. Vijayaraman reported.
Historically in trials, BiV pacing has elevated LVEF by about 7%, he said. The mean 12-point increase observed with CSP “is huge, in that sense.” HOT-CRT enrolled a predominantly male and White population at centers highly experienced in both CSP and BiV pacing, limiting its broad relevance to practice, as pointed out by both Dr. Vijayaraman and his presentation’s invited discussant, Yong-Mei Cha, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Cha, who is director of cardiac device services at her center, also highlighted the greater rate of crossover from BiV pacing to CSP, 18% vs. 4% in the other direction. “This is a very encouraging result,” because the implant-failure rate for LBB-area pacing may drop once more operators become “familiar and skilled with conduction-system pacing.” Overall, the study supports CSP as “a very good alternative for heart failure patients when BiV pacing fails.”
International comparison of CSP and BiV pacing
In Dr. Vijayaraman’s other study, the observational comparison of LBB-area pacing and BiV-CRT, the CSP technique emerged as a “reasonable alternative to biventricular pacing, not only for improvement in LV function but also to reduce adverse clinical outcomes.”
Indeed, in the international study of 1,778 mostly male patients with primary or secondary CRT indications who received LBB-area or BiV pacing (797 and 981 patients, respectively), those on CSP saw a significant drop in risk for the primary endpoint, death or HFH.
Mean LVEF improved from 27% to 41% in the LBB-area pacing group and 27% to 37% with BiV pacing (P < .001 for both changes) over a follow-up averaging 33 months. The difference in improvement between CSP and BiV pacing was significant at P < .001.
In adjusted analysis, the risk for death or HFH was greater for BiV-pacing patients, a difference driven by HFH events.
- Death or HF: hazard ratio, 1.49 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-1.84; P < .001).
- Death: HR, 1.14 (95% CI, 0.88-1.48; P = .313).
- HFH: HR, 1.49 (95% CI, 1.16-1.92; P = .002)
The analysis has all the “inherent biases” of an observational study. The risk for patient-selection bias, however, was somewhat mitigated by consistent practice patterns at participating centers, Dr. Vijayaraman told this news organization.
For example, he said, operators at six of the institutions were most likely to use CSP as the first-line approach, and the same number of centers usually went with BiV pacing.
SYNCHRONY: First-line LBB-area pacing vs. BiV-CRT
Outcomes using the two approaches were similar in the prospective, international, observational study of 371 patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and standard CRT indications. Allocation of 128 patients to LBB-area pacing and 243 to BiV-CRT was based on patient and operator preferences, reported Jorge Romero Jr, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, at the HRS sessions.
Risk for the death-HFH primary endpoint dropped 38% for those initially treated with LBB-area pacing, compared with BiV pacing, primarily because of a lower HFH risk:
- Death or HFH: HR, 0.62 (95% CI, 0.41-0.93; P = .02).
- Death: HR, 0.57 (95% CI, 0.25-1.32; P = .19).
- HFH: HR, 0.61 (95% CI, 0.34-0.93; P = .02)
Patients in the CSP group were also more likely to improve by at least one NYHA (New York Heart Association) class (80.4% vs. 67.9%; P < .001), consistent with their greater absolute change in LVEF (8.0 vs. 3.9 points; P < .01).
The findings “suggest that LBBAP [left-bundle branch area pacing] is an excellent alternative to BiV pacing,” with a comparable safety profile, write Jayanthi N. Koneru, MBBS, and Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD, in an editorial accompanying the published SYNCHRONY report.
“The differences in improvement of LVEF are encouraging for both groups,” but were superior for LBB-area pacing, continue Dr. Koneru and Dr. Ellenbogen, both with Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond. “Whether these results would have regressed to the mean over a longer period of follow-up or diverge further with LBB-area pacing continuing to be superior is unknown.”
Years for an answer?
A large randomized comparison of CSP and BiV-CRT, called Left vs. Left, is currently in early stages, Sana M. Al-Khatib, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said in a media presentation on two of the presented studies. It has a planned enrollment of more than 2,100 patients on optimal meds with an LVEF of 50% or lower and either a QRS duration of at least 130 ms or an anticipated burden of RV pacing exceeding 40%.
The trial, she said, “will take years to give an answer, but it is actually designed to address the question of whether a composite endpoint of time to death or heart failure hospitalization can be improved with conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing.”
Dr. Al-Khatib is a coauthor on the new guideline covering both CSP and BiV-CRT in HF, as are Dr. Cha, Dr. Varma, Dr. Singh, Dr. Vijayaraman, and Dr. Goldberger; Dr. Ellenbogen is one of the reviewers.
Dr. Diaz discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or teaching from Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. Dr. Vijayaraman discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking, teaching, or consulting for Abbott, Medtronic, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific; and receiving research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Varma discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or consulting as an independent contractor for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Impulse Dynamics USA, Cardiologs, Abbott, Pacemate, Implicity, and EP Solutions. Dr. Singh discloses receiving fees for consulting from EBR Systems, Merit Medical Systems, New Century Health, Biotronik, Abbott, Medtronic, MicroPort Scientific, Cardiologs, Sanofi, CVRx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Octagos, Implicity, Orchestra Biomed, Rhythm Management Group, and Biosense Webster; and receiving honoraria or fees for speaking and teaching from Medscape. Dr. Cha had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Romero discloses receiving research grants from Biosense Webster; and speaking or receiving honoraria or fees for consulting, speaking, or teaching, or serving on a board for Sanofi, Boston Scientific, and AtriCure. Dr. Koneru discloses consulting for Medtronic and receiving honoraria from Abbott. Dr. Ellenbogen discloses consulting or lecturing for or receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott. Dr. Goldberger discloses receiving royalty income from and serving as an independent contractor for Elsevier. Dr. Al-Khatib discloses receiving research grants from Medtronic and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pacing as a device therapy for heart failure (HF) is headed for what is probably its next big advance.
After decades of biventricular (BiV) pacemaker success in resynchronizing the ventricles and improving clinical outcomes, relatively new conduction-system pacing (CSP) techniques that avoid the pitfalls of right-ventricular (RV) pacing using BiV lead systems have been supplanting traditional cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in selected patients at some major centers. In fact, they are solidly ensconced in a new guideline document addressing indications for CSP and BiV pacing in HF.
But , an alternative when BiV pacing isn’t appropriate or can’t be engaged.
That’s mainly because the limited, mostly observational evidence supporting CSP in the document can’t measure up to the clinical experience and plethora of large, randomized trials behind BiV-CRT.
But that shortfall is headed for change. Several new comparative studies, including a small, randomized trial, have added significantly to evidence suggesting that CSP is at least as effective as traditional CRT for procedural, functional safety, and clinical outcomes.
The new studies “are inherently prone to bias, but their results are really good,” observed Juan C. Diaz, MD. They show improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and symptoms with CSP that are “outstanding compared to what we have been doing for the last 20 years,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Diaz, Clínica Las Vegas, Medellin, Colombia, is an investigator with the observational SYNCHRONY, which is among the new CSP studies formally presented at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society. He is also lead author on its same-day publication in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Dr. Diaz said that CSP, which sustains pacing via the native conduction system, makes more “physiologic sense” than BiV pacing and represents “a step forward” for HF device therapy.
SYNCHRONY compared LBB-area with BiV pacing as the initial strategy for achieving cardiac resynchronization in patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy.
CSP is “a long way” from replacing conventional CRT, he said. But the new studies at the HRS sessions should help extend His-bundle and LBB-area pacing to more patients, he added, given the significant long-term “drawbacks” of BiV pacing. These include inevitable RV pacing, multiple leads, and the risks associated with chronic transvenous leads.
Zachary Goldberger, MD, University of Wisconsin–Madison, went a bit further in support of CSP as invited discussant for the SYNCHRONY presentation.
Given that it improved LVEF, heart failure class, HF hospitalizations (HFH), and mortality in that study and others, Dr. Goldberger said, CSP could potentially “become the dominant mode of resynchronization going forward.”
Other experts at the meeting saw CSP’s potential more as one of several pacing techniques that could be brought to bear for patients with CRT indications.
“Conduction system pacing is going to be a huge complement to biventricular pacing,” to which about 30% of patients have a “less than optimal response,” said Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, chief of clinical electrophysiology, Geisinger Heart Institute, Danville, Pa.
“I don’t think it needs to replace biventricular pacing, because biventricular pacing is a well-established, incredibly powerful therapy,” he told this news organization. But CSP is likely to provide “a good alternative option” in patients with poor responses to BiV-CRT.
It may, however, render some current BiV-pacing alternatives “obsolete,” Dr. Vijayaraman observed. “At our center, at least for the last 5 years, no patient has needed epicardial surgical left ventricular lead placement” because CSP was a better backup option.
Dr. Vijayaraman presented two of the meeting’s CSP vs. BiV pacing comparisons. In one, the 100-patient randomized HOT-CRT trial, contractile function improved significantly on CSP, which could be either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing.
He also presented an observational study of LBB-area pacing at 15 centers in Asia, Europe, and North America and led the authors of its simultaneous publication in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“I think left-bundle conduction system pacing is the future, for sure,” Jagmeet P. Singh, MD, DPhil, told this news organization. Still, it doesn’t always work and when it does, it “doesn’t work equally in all patients,” he said.
“Conduction system pacing certainly makes a lot of sense,” especially in patients with left-bundle-branch block (LBBB), and “maybe not as a primary approach but certainly as a secondary approach,” said Dr. Singh, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who is not a coauthor on any of the three studies.
He acknowledged that CSP may work well as a first-line option in patients with LBBB at some experienced centers. For those without LBBB or who have an intraventricular conduction delay, who represent 45%-50% of current CRT cases, Dr. Singh observed, “there’s still more evidence” that BiV-CRT is a more appropriate initial approach.
Standard CRT may fail, however, even in some patients who otherwise meet guideline-based indications. “We don’t really understand all the mechanisms for nonresponse in conventional biventricular pacing,” observed Niraj Varma, MD, PhD, Cleveland Clinic, also not involved with any of the three studies.
In some groups, including “patients with larger ventricles,” for example, BiV-CRT doesn’t always narrow the electrocardiographic QRS complex or preexcite delayed left ventricular (LV) activation, hallmarks of successful CRT, he said in an interview.
“I think we need to understand why this occurs in both situations,” but in such cases, CSP alone or as an adjunct to direct LV pacing may be successful. “Sometimes we need both an LV lead and the conduction-system pacing lead.”
Narrower, more efficient use of CSP as a BiV-CRT alternative may also boost its chances for success, Dr. Varma added. “I think we need to refine patient selection.”
HOT-CRT: Randomized CSP vs. BiV pacing trial
Conducted at three centers in a single health system, the His-optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy study (HOT-CRT) randomly assigned 100 patients with primary or secondary CRT indications to either to CSP – by either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing – or to standard BiV-CRT as the first-line resynchronization method.
Treatment crossovers, allowed for either pacing modality in the event of implantation failure, occurred in two patients and nine patients initially assigned to CSP and BiV pacing, respectively (4% vs. 18%), Dr. Vijayaraman reported.
Historically in trials, BiV pacing has elevated LVEF by about 7%, he said. The mean 12-point increase observed with CSP “is huge, in that sense.” HOT-CRT enrolled a predominantly male and White population at centers highly experienced in both CSP and BiV pacing, limiting its broad relevance to practice, as pointed out by both Dr. Vijayaraman and his presentation’s invited discussant, Yong-Mei Cha, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Cha, who is director of cardiac device services at her center, also highlighted the greater rate of crossover from BiV pacing to CSP, 18% vs. 4% in the other direction. “This is a very encouraging result,” because the implant-failure rate for LBB-area pacing may drop once more operators become “familiar and skilled with conduction-system pacing.” Overall, the study supports CSP as “a very good alternative for heart failure patients when BiV pacing fails.”
International comparison of CSP and BiV pacing
In Dr. Vijayaraman’s other study, the observational comparison of LBB-area pacing and BiV-CRT, the CSP technique emerged as a “reasonable alternative to biventricular pacing, not only for improvement in LV function but also to reduce adverse clinical outcomes.”
Indeed, in the international study of 1,778 mostly male patients with primary or secondary CRT indications who received LBB-area or BiV pacing (797 and 981 patients, respectively), those on CSP saw a significant drop in risk for the primary endpoint, death or HFH.
Mean LVEF improved from 27% to 41% in the LBB-area pacing group and 27% to 37% with BiV pacing (P < .001 for both changes) over a follow-up averaging 33 months. The difference in improvement between CSP and BiV pacing was significant at P < .001.
In adjusted analysis, the risk for death or HFH was greater for BiV-pacing patients, a difference driven by HFH events.
- Death or HF: hazard ratio, 1.49 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-1.84; P < .001).
- Death: HR, 1.14 (95% CI, 0.88-1.48; P = .313).
- HFH: HR, 1.49 (95% CI, 1.16-1.92; P = .002)
The analysis has all the “inherent biases” of an observational study. The risk for patient-selection bias, however, was somewhat mitigated by consistent practice patterns at participating centers, Dr. Vijayaraman told this news organization.
For example, he said, operators at six of the institutions were most likely to use CSP as the first-line approach, and the same number of centers usually went with BiV pacing.
SYNCHRONY: First-line LBB-area pacing vs. BiV-CRT
Outcomes using the two approaches were similar in the prospective, international, observational study of 371 patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and standard CRT indications. Allocation of 128 patients to LBB-area pacing and 243 to BiV-CRT was based on patient and operator preferences, reported Jorge Romero Jr, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, at the HRS sessions.
Risk for the death-HFH primary endpoint dropped 38% for those initially treated with LBB-area pacing, compared with BiV pacing, primarily because of a lower HFH risk:
- Death or HFH: HR, 0.62 (95% CI, 0.41-0.93; P = .02).
- Death: HR, 0.57 (95% CI, 0.25-1.32; P = .19).
- HFH: HR, 0.61 (95% CI, 0.34-0.93; P = .02)
Patients in the CSP group were also more likely to improve by at least one NYHA (New York Heart Association) class (80.4% vs. 67.9%; P < .001), consistent with their greater absolute change in LVEF (8.0 vs. 3.9 points; P < .01).
The findings “suggest that LBBAP [left-bundle branch area pacing] is an excellent alternative to BiV pacing,” with a comparable safety profile, write Jayanthi N. Koneru, MBBS, and Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD, in an editorial accompanying the published SYNCHRONY report.
“The differences in improvement of LVEF are encouraging for both groups,” but were superior for LBB-area pacing, continue Dr. Koneru and Dr. Ellenbogen, both with Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond. “Whether these results would have regressed to the mean over a longer period of follow-up or diverge further with LBB-area pacing continuing to be superior is unknown.”
Years for an answer?
A large randomized comparison of CSP and BiV-CRT, called Left vs. Left, is currently in early stages, Sana M. Al-Khatib, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said in a media presentation on two of the presented studies. It has a planned enrollment of more than 2,100 patients on optimal meds with an LVEF of 50% or lower and either a QRS duration of at least 130 ms or an anticipated burden of RV pacing exceeding 40%.
The trial, she said, “will take years to give an answer, but it is actually designed to address the question of whether a composite endpoint of time to death or heart failure hospitalization can be improved with conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing.”
Dr. Al-Khatib is a coauthor on the new guideline covering both CSP and BiV-CRT in HF, as are Dr. Cha, Dr. Varma, Dr. Singh, Dr. Vijayaraman, and Dr. Goldberger; Dr. Ellenbogen is one of the reviewers.
Dr. Diaz discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or teaching from Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. Dr. Vijayaraman discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking, teaching, or consulting for Abbott, Medtronic, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific; and receiving research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Varma discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or consulting as an independent contractor for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Impulse Dynamics USA, Cardiologs, Abbott, Pacemate, Implicity, and EP Solutions. Dr. Singh discloses receiving fees for consulting from EBR Systems, Merit Medical Systems, New Century Health, Biotronik, Abbott, Medtronic, MicroPort Scientific, Cardiologs, Sanofi, CVRx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Octagos, Implicity, Orchestra Biomed, Rhythm Management Group, and Biosense Webster; and receiving honoraria or fees for speaking and teaching from Medscape. Dr. Cha had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Romero discloses receiving research grants from Biosense Webster; and speaking or receiving honoraria or fees for consulting, speaking, or teaching, or serving on a board for Sanofi, Boston Scientific, and AtriCure. Dr. Koneru discloses consulting for Medtronic and receiving honoraria from Abbott. Dr. Ellenbogen discloses consulting or lecturing for or receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott. Dr. Goldberger discloses receiving royalty income from and serving as an independent contractor for Elsevier. Dr. Al-Khatib discloses receiving research grants from Medtronic and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HEART RHYTHM 2023