User login
A vaginal ring that can be reused for up to 1 year and a progestin-only pill (POP) with a wider window for missed pills are 2 of the novel contraceptive products introduced to the market this year. In addition, an ongoing study of the levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system (IUS) continues to provide evidence on its extended duration of use, now approved through 6 years.
The segesterone acetate (SA) and ethinyl estradiol (EE) vaginal ring (Annovera) is new among contraceptive options. Segesterone acetate is a novel progestin that can be used only via nonoral routes; it binds specifically to progesterone receptors without estrogenic or antiandrogen effects.1 Unlike the etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol ring (NuvaRing; for which generic products became available this past year), which is used for 1 cycle and then thrown away, the SA/EE ring is effective for 13 consecutive cycles. It does not require refrigeration when not in use.2 Because a single ring can be used for 13 cycles, users in locations without laws that mandate a 12-month supply of pills, patches, and rings need less frequent visits to the pharmacy or clinic.
Progestin-only contraceptive pills are an important option for patients who desire hormonal contraception and have contraindications to estrogen, such as migraines with aura, cardiovascular risk factors, and being in the early postpartum period.3 In the United States, current POPs contain norethindrone, which has a 3-hour window for missed pills4; a desogestrel-only pill available outside the United States has a 12-hour window.5 Both are provided as a 28-day pill pack for continuous use, and both result in undesirable bleeding patterns in some users.
The prolonged half-life of drospirenone, another progestin, gives it the potential to increase reliability in the setting of missed or delayed pills and improve bleeding patterns. A new POP contraceptive contains drospirenone (Slynd) and is available in a 28-day pack with a 24-day supply of hormone and a 4-day supply of placebo; it provides a window for missed pill use similar to that for combined hormonal contraception (CHC) as well as a placebo period for a timed withdrawal bleed.6,7
Liletta is a well-known levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS that was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2015. An ongoing clinical trial has been the basis for approval of this IUS for use in increasing durations, from 3 years initially to 4 and then 5 years. The newest data indicate efficacy up to 6 years.8
Continue to: Combined hormonal vaginal system provides a year's contraception with an acceptable safety profile...
Combined hormonal vaginal system provides a year's contraception with an acceptable safety profile
Archer DF, Merkatz RB, Bahamondes L, et al. Efficacy of the 1-year (13-cycle) segesterone acetate and ethinylestradiol contraceptive vaginal system: results of two multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 3 trials. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7:e1054-e1064.
Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
Archer and colleagues reported the results of 2 pivotal multicenter, open-label, phase 3 trials, which included 2,265 users, conducted to evaluate efficacy and return to menses or pregnancy after use of the 1-year (13 cycles) SA/EE contraceptive vaginal system (CVS).
Details of the efficacy study
The study included 1,130 women in a US-only study and 1,135 women in an international study with sites in the United States, Australia, Brazil, Chile, Dominican Republic, Finland, Hungary, and Sweden. Participants used the CVS for 21 days followed by a 7-day use-free interval for up to 13 consecutive cycles; they were instructed not to remove the CVS for more than 2 hours during the 21 days of use.
Primary and secondary efficacy outcomes were calculated using the Pearl Index and an intention-to-treat Kaplan-Meier life table, respectively. At the end of the study, users who desired not to continue hormonal contraception or to become pregnant were followed up for 6 months to evaluate return to menses or pregnancy.
Year-long effectiveness
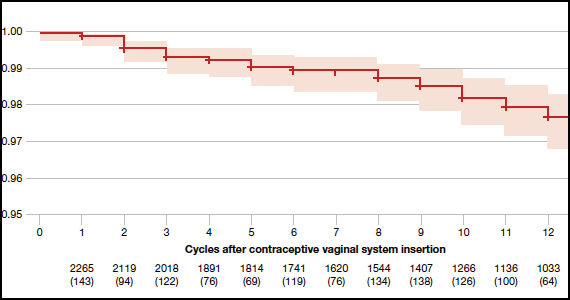
The investigators reported an overall Pearl index of 2.98 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.13-4.06) and a Kaplan-Meier life table cumulative efficacy rate of 97.5% (FIGURE 1), consistent with other recently approved CHC methods. Women from non-European sites, who primarily were US participants, had a Pearl Index of 3.25 (95% CI, 2.35-4.37), and participants from the European sites had a Pearl Index of 0.47 (95% CI, 0.03-2.07). Importantly, CVS removal had a significant impact on efficacy, with a Pearl Index of 5.98 (95% CI, 2.46-9.27) in users reporting CVS removals for longer than 2 hours, suggesting escape ovulation with improper use. The Pearl Index was highest in users aged 18 to 19 years and was not affected by body mass index (BMI), although 91% of users had a BMI of 29.0 kg/m2 or lower.
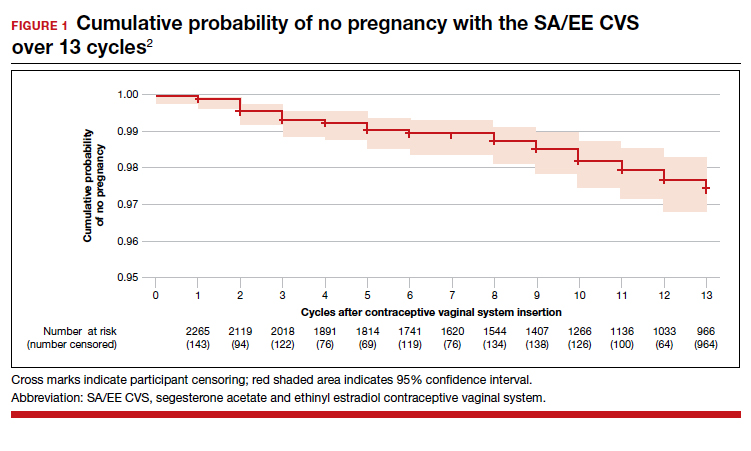
There was no trend for a change in pregnancy risk across 13 cycles, providing evidence of CVS efficacy throughout a full year's use. The follow-up portion of the study included 290 users who were not continuing hormonal contraception at study end; all follow-up participants reported return to menses after method discontinuation.
Clinical safety data
To evaluate safety outcomes from clinical studies on the CVS containing SA/EE, Gemzell-Danielsson and colleagues analyzed 9 studies. Most of the data were derived from 2 phase 3, multicenter trials (as discussed above), with supporting evidence from 7 other studies.
Adverse events reported
Among 2,308 CVS users in the phase 3 trials, 87% reported at least 1 adverse effect, with most of mild or moderate severity. These included headache, 26%; nausea, 18%; vaginal discharge, 10%; and metrorrhagia, 7%. Overall, 12% of CVS users discontinued use due to an adverse effect. Two percent of users experienced severe adverse effects, including venous thromboembolism (VTE), allergic reaction, gallbladder disease, and spontaneous abortion.
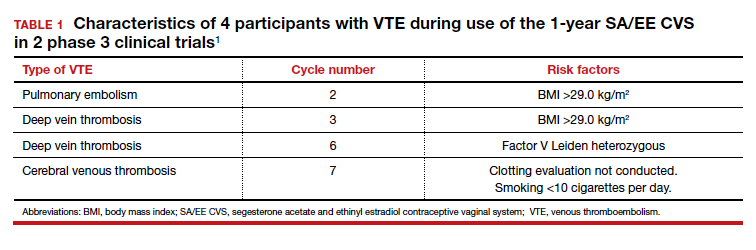
In the US-only phase 3 trial, 2 VTE events occurred in the first 6 months in women with baseline BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2; therefore, enrollment of patients with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 was halted and current users meeting that criteria were discontinued. Notably, no cases of VTE occurred in studies with a segesterone acetate-only CVS; this suggests that risk can be attributed to the estrogen component. Overall, 4 nonfatal VTEs occurred, all among the 1,536 women enrolled in the phase 3 trials (4 of 1,536 [0.3%]); at least 3 of these cases occurred in users with VTE risk factors (TABLE 1). The estimated VTE rate in CVS users with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 is 10.8/10,000 women-years (95% CI, 8.9-13.1).
Complete expulsion of the CVS occurred in 7% of cycles and partial expulsion in 19.5% of cycles; users reported expulsion more frequently in the first cycle, most (about 70%) of which were partial expulsions. Of the laboratory values and vital signs studied, including weight, users had no clinically relevant changes from baseline.
The 13-cycle efficacy and general adverse events rates of the new SA/EE CVS are consistent with those of other CHCs. However, the efficacy and safety findings are not necessarily generalizable to all patients. Because users with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 were excluded following 2 early VTE events in women with a BMI of 29.1 and 30.8 kg/m2 , only 9% of the phase 3 study population had a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 . Clinicians may question whether the 1-year SA/EE CVS is an acceptable method for obese users. We know that EE causes similar changes in hemostatic factors regardless of oral or vaginal route,9 but these studies as well as pharmacokinetic studies typically include relatively few participants. While studies demonstrate that the SA/EE CVS delivers EE 13 µg daily,1 individual hormone absorption can vary. It is possible that the amount of EE in the CVS (17.4 mg) could, in a person predisposed to higher absorption, increase VTE risk. We do not know if this potential or actual risk is different for nonobese and obese users. To be fair, most of the EE-containing combined hormonal contraceptives were approved with study data that did not include obese women; the FDA first discussed the importance of including obese women in contraceptive approval studies in 2007.10 Thus, we do not know if this CVS has a significantly higher VTE risk in obese users than other methods.
All available information is based on cyclic CVS use (28-day cycles with a 7-day use-free interval). No data are available on drug levels, safety, or efficacy over extended periods of continuous use with the same CVS. During counseling, special emphasis should be placed on the increased pregnancy risk for patients who remove the ring for more than 2 hours.
Continue to: New drospirenone pill is an effective POP option...
New drospirenone pill is an effective POP option
Kimble T, Burke AE, Barnhart KT, et al. A 1-year prospective, open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 3 trial of the contraceptive efficacy and safety of the oral progestin-only pill drospirenone 4 mg using a 24/4-day regimen. Contracept X. 2020;2:100020.
Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Multicenter, phase III trials on the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability and safety of a new drospirenone-only pill. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:1549-1557.
In a prospective, single-arm, multicenter phase 3 trial in the United States, Kimble and colleagues evaluated the efficacy and safety of an oral drospirenone POP in a cyclic 24-day hormone/4-day placebo regimen. The trial included 1,006 users. No BMI cutoff was used, and about one-third of study participants were obese (BMI >30.0 kg/m2). Women were instructed to take a missed tablet as soon as remembered if within 24 hours or with the next scheduled dose if more than 24 hours late.
Contraceptive effectiveness
The Pearl Index for nonbreastfeeding users aged 35 years or younger with pregnancies confirmed by a quantitative serum ß-human chorionic gonadotropin test (915 users) was 2.9 (95% CI, 1.5-5.1). Of note, 2 out of 15 on-treatment pregnancies were excluded from this calculation because of protocol site violations, as were 3 pregnancies that were unconfirmed. In the modified full analysis set of 915 users, 36% were obese (BMI≥30 kg/m2), and the Pearl Index was noted to be unaffected by BMI (TABLE 2).

While 61% of women reported adverse effects, more than 95% of these were mild or moderate in intensity, including headache, nausea, dysmenorrhea, metrorrhagia, and breast pain. No VTE occurred. The frequency of hyperkalemia was 0.5%, and there was no evidence of hypotension, which is significant due to the antimineralocorticoid activity of drospirenone. All cases of hyperkalemia were considered mild, and all women were asymptomatic. There were no clinically relevant changes in body weight, gynecologic exam, or other laboratory values.
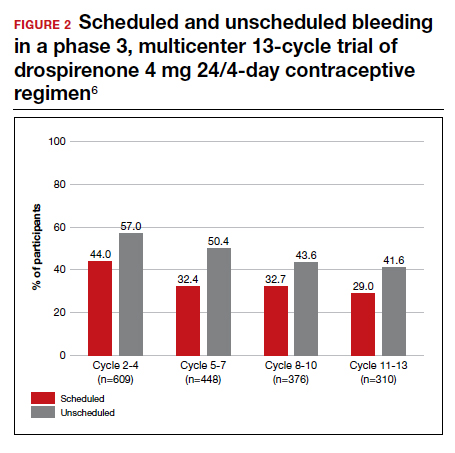
With increased cycles of use, the number of days with bleeding or spotting generally decreased and amenorrhea increased. However, in cycles 11 to 13, 41.6% of users still had unscheduled bleeding (reduced from 57.0% at cycles 2-4), and 29.0% had scheduled bleeding (decreased from 44% at cycles 2-4) (FIGURE 2). With these bleeding patterns, 86.2% of users agreed or strongly agreed that they were satisfied with the product.
European multicenter study of drospironene
In a European investigation, Palacios and colleagues pooled and analyzed data from 2 phase 3 multicenter trials to assess the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the same drospirenone-only pill (24 days of drospironene 4 mg and 4 days of placebo) in 1,571 users. No BMI cutoff was used, but overall only 71 participants (4.6%) were obese. One study included desogestrel 0.075 mg (in a regimen of 28 active pills) as a comparator for safety.
The overall Pearl Index for users 35 years or younger (1,251 users) was 1.0 (95% CI, 0.4-2.0). The "method failure Pearl Index" in users 35 years or younger, which included all pregnancies during "perfect medication cycles," was 1.3 (95% CI, 0.5-2.5).
The most common adverse effects were acne (6.6% in study 1 and 4.4% in study 2), headache (4.5% in study 1), and irregular bleeding (4.4% in study 2). No cases of VTE occurred; there was 1 case of asymptomatic hyperkalemia. Additional laboratory values and vital signs showed no significant changes. The trend in bleeding was similar to that in the US studies, but it is interesting to note that there were significantly lower rates of unscheduled bleeding or spotting in drospirenone users than in desogestrel users (67.9% vs 86.5%, respectively; P<.001).
In the US study, the higher Pearl Index compared with that found in the European study (2.9 vs 1.0) likely reflects an increased proportion of study participants with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher, a younger average age of participants, and a historical tendency toward better contraceptive efficacy in European than in US study participants. Kimble and colleagues’ finding of a Pearl Index of 2.9 is similar to that seen with other CHCs and POPs, and the data from the US study are potentially more generalizable.
Among the 2,257 participants in 3 studies, 423 (19%) were obese. No VTE events occurred with drospirenone use, as compared with 4 events in the SA/EE CVS study with 2,308 participants in the phase 3 studies.
Historically, POPs were associated with more days of bleeding than CHCs and require stricter adherence to daily use within a narrow window for missed pills. The new drospirenone-only pill may provide women with more flexibility since it maintains contraceptive efficacy even with 24-hour delayed or missed-pill errors. Although intermenstrual bleeding rates are high, participants still had a very favorable assessment, and the profile may be more tolerable compared with other POPs. Clinicians prescribing this new POP should counsel patients that the cyclic regimen does not always result in regular bleeding patterns.
Continue to: Evidence supports 6 years' use of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS...
Evidence supports 6 years' use of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS
Westhoff CL, Keder LM, Gangestad A, et al. Six-year contraceptive efficacy and continued safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Contraception. 2020;101:159-161.
Two levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS products are on the market, both of which were approved for 5 years of use. The ACCESS IUS study (A Comprehensive Contraceptive Efficacy and Safety Study of an IUS) is an ongoing phase 3 trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS (Liletta) for up to 10 years of use in US women. Westhoff and colleagues presented the data used for this IUS to gain approval for 6 years of use as of October 2019. The report included safety information for all users, with use exceeding 8 years in 122 participants.
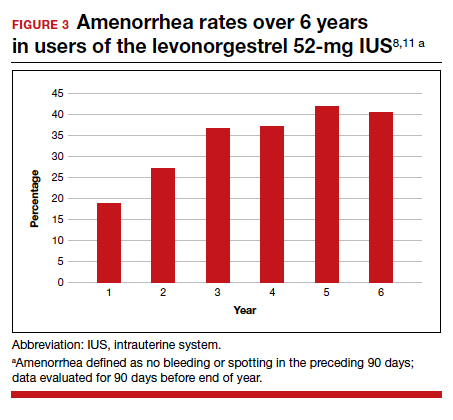
In year 6 of the ongoing trial, there were no on-treatment pregnancies with a 6-year life table pregnancy rate of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.44-1.70). Forty percent of users reported amenorrhea in the 90 days preceding the end of year 6, consistent with prior data after 3 years of use (FIGURE 3). The most common adverse effects over 6 or more years of use were bacterial vulvovaginal infections and urinary tract infections.
Long-term IUS effectiveness
Overall, in users aged 16 to 35 years, 72% discontinued study participation, most frequently due to an adverse event (19.2%) or to seeking pregnancy (15.5%). Through 6 or more years of use, overall discontinuation rates for expulsion (4.0%) and bleeding symptoms (2.3%) were very low, with 2 expulsions occurring in year 6 and only 1 participant discontinuing in year 6 for a bleeding symptom. These findings are consistent with those found at 5 years of IUS use and are representative of continued efficacy as well as overall low frequency of new significant events with extended use.11
Clinicians and patients should be aware of data that support the continued use of levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS products for 6 years, and likely even longer. A low incidence of new significant events and a steady state of amenorrhea are also indications that users who like using a hormonal IUS will likely continue to do so for an extended time, if recommended. This extension, as well as continued study up to 10 years, will allow users who desire reversible long-acting hormonal contraception to have fewer removals and reinsertions; this in turn will decrease the risks and pain associated with IUS insertion and removal as well as health care costs.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
- Archer DF, Merkatz RB, Bahamondes L, et al. Efficacy of the 1-year (13-cycle) segesterone acetate and ethinylestradiol contraceptive vaginal system: results of two multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 3 trials. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7:e1054-e1064.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 206. Use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisiting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- Ortho Micronor [package insert]. Raritan, NJ: Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceutical Inc; 2008.
- Cerazette [package insert]. Oss, Netherlands: Merck Sharp & Dohme Limited; 2019.
- Kimble T, Burke AE, Barnhart KT, et al. A 1-year prospective, open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 3 trial of the contraceptive efficacy and safety of the oral progestin-only pill drospirenone 4 mg using a 24/4-day regimen. Contracept X. 2020;2:100020.
- Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Multicenter, phase III trials on the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability and safety of a new drospirenone-only pill. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:1549-1557.
- Westhoff CL, Keder LM, Gangestad A, et al. Six-year contraceptive efficacy and continued safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Contraception. 2020;101:159-161.
- Sitruk-Ware R, Plu-Bureau G, Menard J, et al. Effects of oral and transvaginal ethinyl estradiol on hemostatic factors and hepatic proteins in a randomized, crossover study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2074-2079.
- Food and Drug Administration Advisory Committee for Reproductive Health Drugs meeting. Final summary minutes, January 23-24, 2007. https://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170404050830/https://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/07/minutes/2007-4274m1.pdf. Accessed July 28, 2020.
- Teal SB, Turok DK, Chen BA, et al. Five-year contraceptive efficacy and safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:63-70.
A vaginal ring that can be reused for up to 1 year and a progestin-only pill (POP) with a wider window for missed pills are 2 of the novel contraceptive products introduced to the market this year. In addition, an ongoing study of the levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system (IUS) continues to provide evidence on its extended duration of use, now approved through 6 years.
The segesterone acetate (SA) and ethinyl estradiol (EE) vaginal ring (Annovera) is new among contraceptive options. Segesterone acetate is a novel progestin that can be used only via nonoral routes; it binds specifically to progesterone receptors without estrogenic or antiandrogen effects.1 Unlike the etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol ring (NuvaRing; for which generic products became available this past year), which is used for 1 cycle and then thrown away, the SA/EE ring is effective for 13 consecutive cycles. It does not require refrigeration when not in use.2 Because a single ring can be used for 13 cycles, users in locations without laws that mandate a 12-month supply of pills, patches, and rings need less frequent visits to the pharmacy or clinic.
Progestin-only contraceptive pills are an important option for patients who desire hormonal contraception and have contraindications to estrogen, such as migraines with aura, cardiovascular risk factors, and being in the early postpartum period.3 In the United States, current POPs contain norethindrone, which has a 3-hour window for missed pills4; a desogestrel-only pill available outside the United States has a 12-hour window.5 Both are provided as a 28-day pill pack for continuous use, and both result in undesirable bleeding patterns in some users.
The prolonged half-life of drospirenone, another progestin, gives it the potential to increase reliability in the setting of missed or delayed pills and improve bleeding patterns. A new POP contraceptive contains drospirenone (Slynd) and is available in a 28-day pack with a 24-day supply of hormone and a 4-day supply of placebo; it provides a window for missed pill use similar to that for combined hormonal contraception (CHC) as well as a placebo period for a timed withdrawal bleed.6,7
Liletta is a well-known levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS that was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2015. An ongoing clinical trial has been the basis for approval of this IUS for use in increasing durations, from 3 years initially to 4 and then 5 years. The newest data indicate efficacy up to 6 years.8
Continue to: Combined hormonal vaginal system provides a year's contraception with an acceptable safety profile...
Combined hormonal vaginal system provides a year's contraception with an acceptable safety profile
Archer DF, Merkatz RB, Bahamondes L, et al. Efficacy of the 1-year (13-cycle) segesterone acetate and ethinylestradiol contraceptive vaginal system: results of two multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 3 trials. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7:e1054-e1064.
Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
Archer and colleagues reported the results of 2 pivotal multicenter, open-label, phase 3 trials, which included 2,265 users, conducted to evaluate efficacy and return to menses or pregnancy after use of the 1-year (13 cycles) SA/EE contraceptive vaginal system (CVS).
Details of the efficacy study
The study included 1,130 women in a US-only study and 1,135 women in an international study with sites in the United States, Australia, Brazil, Chile, Dominican Republic, Finland, Hungary, and Sweden. Participants used the CVS for 21 days followed by a 7-day use-free interval for up to 13 consecutive cycles; they were instructed not to remove the CVS for more than 2 hours during the 21 days of use.
Primary and secondary efficacy outcomes were calculated using the Pearl Index and an intention-to-treat Kaplan-Meier life table, respectively. At the end of the study, users who desired not to continue hormonal contraception or to become pregnant were followed up for 6 months to evaluate return to menses or pregnancy.
Year-long effectiveness
The investigators reported an overall Pearl index of 2.98 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.13-4.06) and a Kaplan-Meier life table cumulative efficacy rate of 97.5% (FIGURE 1), consistent with other recently approved CHC methods. Women from non-European sites, who primarily were US participants, had a Pearl Index of 3.25 (95% CI, 2.35-4.37), and participants from the European sites had a Pearl Index of 0.47 (95% CI, 0.03-2.07). Importantly, CVS removal had a significant impact on efficacy, with a Pearl Index of 5.98 (95% CI, 2.46-9.27) in users reporting CVS removals for longer than 2 hours, suggesting escape ovulation with improper use. The Pearl Index was highest in users aged 18 to 19 years and was not affected by body mass index (BMI), although 91% of users had a BMI of 29.0 kg/m2 or lower.

There was no trend for a change in pregnancy risk across 13 cycles, providing evidence of CVS efficacy throughout a full year's use. The follow-up portion of the study included 290 users who were not continuing hormonal contraception at study end; all follow-up participants reported return to menses after method discontinuation.
Clinical safety data
To evaluate safety outcomes from clinical studies on the CVS containing SA/EE, Gemzell-Danielsson and colleagues analyzed 9 studies. Most of the data were derived from 2 phase 3, multicenter trials (as discussed above), with supporting evidence from 7 other studies.
Adverse events reported
Among 2,308 CVS users in the phase 3 trials, 87% reported at least 1 adverse effect, with most of mild or moderate severity. These included headache, 26%; nausea, 18%; vaginal discharge, 10%; and metrorrhagia, 7%. Overall, 12% of CVS users discontinued use due to an adverse effect. Two percent of users experienced severe adverse effects, including venous thromboembolism (VTE), allergic reaction, gallbladder disease, and spontaneous abortion.
In the US-only phase 3 trial, 2 VTE events occurred in the first 6 months in women with baseline BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2; therefore, enrollment of patients with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 was halted and current users meeting that criteria were discontinued. Notably, no cases of VTE occurred in studies with a segesterone acetate-only CVS; this suggests that risk can be attributed to the estrogen component. Overall, 4 nonfatal VTEs occurred, all among the 1,536 women enrolled in the phase 3 trials (4 of 1,536 [0.3%]); at least 3 of these cases occurred in users with VTE risk factors (TABLE 1). The estimated VTE rate in CVS users with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 is 10.8/10,000 women-years (95% CI, 8.9-13.1).
Complete expulsion of the CVS occurred in 7% of cycles and partial expulsion in 19.5% of cycles; users reported expulsion more frequently in the first cycle, most (about 70%) of which were partial expulsions. Of the laboratory values and vital signs studied, including weight, users had no clinically relevant changes from baseline.

The 13-cycle efficacy and general adverse events rates of the new SA/EE CVS are consistent with those of other CHCs. However, the efficacy and safety findings are not necessarily generalizable to all patients. Because users with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 were excluded following 2 early VTE events in women with a BMI of 29.1 and 30.8 kg/m2 , only 9% of the phase 3 study population had a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 . Clinicians may question whether the 1-year SA/EE CVS is an acceptable method for obese users. We know that EE causes similar changes in hemostatic factors regardless of oral or vaginal route,9 but these studies as well as pharmacokinetic studies typically include relatively few participants. While studies demonstrate that the SA/EE CVS delivers EE 13 µg daily,1 individual hormone absorption can vary. It is possible that the amount of EE in the CVS (17.4 mg) could, in a person predisposed to higher absorption, increase VTE risk. We do not know if this potential or actual risk is different for nonobese and obese users. To be fair, most of the EE-containing combined hormonal contraceptives were approved with study data that did not include obese women; the FDA first discussed the importance of including obese women in contraceptive approval studies in 2007.10 Thus, we do not know if this CVS has a significantly higher VTE risk in obese users than other methods.
All available information is based on cyclic CVS use (28-day cycles with a 7-day use-free interval). No data are available on drug levels, safety, or efficacy over extended periods of continuous use with the same CVS. During counseling, special emphasis should be placed on the increased pregnancy risk for patients who remove the ring for more than 2 hours.
Continue to: New drospirenone pill is an effective POP option...
New drospirenone pill is an effective POP option
Kimble T, Burke AE, Barnhart KT, et al. A 1-year prospective, open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 3 trial of the contraceptive efficacy and safety of the oral progestin-only pill drospirenone 4 mg using a 24/4-day regimen. Contracept X. 2020;2:100020.
Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Multicenter, phase III trials on the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability and safety of a new drospirenone-only pill. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:1549-1557.
In a prospective, single-arm, multicenter phase 3 trial in the United States, Kimble and colleagues evaluated the efficacy and safety of an oral drospirenone POP in a cyclic 24-day hormone/4-day placebo regimen. The trial included 1,006 users. No BMI cutoff was used, and about one-third of study participants were obese (BMI >30.0 kg/m2). Women were instructed to take a missed tablet as soon as remembered if within 24 hours or with the next scheduled dose if more than 24 hours late.
Contraceptive effectiveness
The Pearl Index for nonbreastfeeding users aged 35 years or younger with pregnancies confirmed by a quantitative serum ß-human chorionic gonadotropin test (915 users) was 2.9 (95% CI, 1.5-5.1). Of note, 2 out of 15 on-treatment pregnancies were excluded from this calculation because of protocol site violations, as were 3 pregnancies that were unconfirmed. In the modified full analysis set of 915 users, 36% were obese (BMI≥30 kg/m2), and the Pearl Index was noted to be unaffected by BMI (TABLE 2).

While 61% of women reported adverse effects, more than 95% of these were mild or moderate in intensity, including headache, nausea, dysmenorrhea, metrorrhagia, and breast pain. No VTE occurred. The frequency of hyperkalemia was 0.5%, and there was no evidence of hypotension, which is significant due to the antimineralocorticoid activity of drospirenone. All cases of hyperkalemia were considered mild, and all women were asymptomatic. There were no clinically relevant changes in body weight, gynecologic exam, or other laboratory values.
With increased cycles of use, the number of days with bleeding or spotting generally decreased and amenorrhea increased. However, in cycles 11 to 13, 41.6% of users still had unscheduled bleeding (reduced from 57.0% at cycles 2-4), and 29.0% had scheduled bleeding (decreased from 44% at cycles 2-4) (FIGURE 2). With these bleeding patterns, 86.2% of users agreed or strongly agreed that they were satisfied with the product.

European multicenter study of drospironene
In a European investigation, Palacios and colleagues pooled and analyzed data from 2 phase 3 multicenter trials to assess the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the same drospirenone-only pill (24 days of drospironene 4 mg and 4 days of placebo) in 1,571 users. No BMI cutoff was used, but overall only 71 participants (4.6%) were obese. One study included desogestrel 0.075 mg (in a regimen of 28 active pills) as a comparator for safety.
The overall Pearl Index for users 35 years or younger (1,251 users) was 1.0 (95% CI, 0.4-2.0). The "method failure Pearl Index" in users 35 years or younger, which included all pregnancies during "perfect medication cycles," was 1.3 (95% CI, 0.5-2.5).
The most common adverse effects were acne (6.6% in study 1 and 4.4% in study 2), headache (4.5% in study 1), and irregular bleeding (4.4% in study 2). No cases of VTE occurred; there was 1 case of asymptomatic hyperkalemia. Additional laboratory values and vital signs showed no significant changes. The trend in bleeding was similar to that in the US studies, but it is interesting to note that there were significantly lower rates of unscheduled bleeding or spotting in drospirenone users than in desogestrel users (67.9% vs 86.5%, respectively; P<.001).
In the US study, the higher Pearl Index compared with that found in the European study (2.9 vs 1.0) likely reflects an increased proportion of study participants with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher, a younger average age of participants, and a historical tendency toward better contraceptive efficacy in European than in US study participants. Kimble and colleagues’ finding of a Pearl Index of 2.9 is similar to that seen with other CHCs and POPs, and the data from the US study are potentially more generalizable.
Among the 2,257 participants in 3 studies, 423 (19%) were obese. No VTE events occurred with drospirenone use, as compared with 4 events in the SA/EE CVS study with 2,308 participants in the phase 3 studies.
Historically, POPs were associated with more days of bleeding than CHCs and require stricter adherence to daily use within a narrow window for missed pills. The new drospirenone-only pill may provide women with more flexibility since it maintains contraceptive efficacy even with 24-hour delayed or missed-pill errors. Although intermenstrual bleeding rates are high, participants still had a very favorable assessment, and the profile may be more tolerable compared with other POPs. Clinicians prescribing this new POP should counsel patients that the cyclic regimen does not always result in regular bleeding patterns.
Continue to: Evidence supports 6 years' use of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS...
Evidence supports 6 years' use of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS
Westhoff CL, Keder LM, Gangestad A, et al. Six-year contraceptive efficacy and continued safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Contraception. 2020;101:159-161.
Two levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS products are on the market, both of which were approved for 5 years of use. The ACCESS IUS study (A Comprehensive Contraceptive Efficacy and Safety Study of an IUS) is an ongoing phase 3 trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS (Liletta) for up to 10 years of use in US women. Westhoff and colleagues presented the data used for this IUS to gain approval for 6 years of use as of October 2019. The report included safety information for all users, with use exceeding 8 years in 122 participants.
In year 6 of the ongoing trial, there were no on-treatment pregnancies with a 6-year life table pregnancy rate of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.44-1.70). Forty percent of users reported amenorrhea in the 90 days preceding the end of year 6, consistent with prior data after 3 years of use (FIGURE 3). The most common adverse effects over 6 or more years of use were bacterial vulvovaginal infections and urinary tract infections.

Long-term IUS effectiveness
Overall, in users aged 16 to 35 years, 72% discontinued study participation, most frequently due to an adverse event (19.2%) or to seeking pregnancy (15.5%). Through 6 or more years of use, overall discontinuation rates for expulsion (4.0%) and bleeding symptoms (2.3%) were very low, with 2 expulsions occurring in year 6 and only 1 participant discontinuing in year 6 for a bleeding symptom. These findings are consistent with those found at 5 years of IUS use and are representative of continued efficacy as well as overall low frequency of new significant events with extended use.11
Clinicians and patients should be aware of data that support the continued use of levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS products for 6 years, and likely even longer. A low incidence of new significant events and a steady state of amenorrhea are also indications that users who like using a hormonal IUS will likely continue to do so for an extended time, if recommended. This extension, as well as continued study up to 10 years, will allow users who desire reversible long-acting hormonal contraception to have fewer removals and reinsertions; this in turn will decrease the risks and pain associated with IUS insertion and removal as well as health care costs.
A vaginal ring that can be reused for up to 1 year and a progestin-only pill (POP) with a wider window for missed pills are 2 of the novel contraceptive products introduced to the market this year. In addition, an ongoing study of the levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system (IUS) continues to provide evidence on its extended duration of use, now approved through 6 years.
The segesterone acetate (SA) and ethinyl estradiol (EE) vaginal ring (Annovera) is new among contraceptive options. Segesterone acetate is a novel progestin that can be used only via nonoral routes; it binds specifically to progesterone receptors without estrogenic or antiandrogen effects.1 Unlike the etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol ring (NuvaRing; for which generic products became available this past year), which is used for 1 cycle and then thrown away, the SA/EE ring is effective for 13 consecutive cycles. It does not require refrigeration when not in use.2 Because a single ring can be used for 13 cycles, users in locations without laws that mandate a 12-month supply of pills, patches, and rings need less frequent visits to the pharmacy or clinic.
Progestin-only contraceptive pills are an important option for patients who desire hormonal contraception and have contraindications to estrogen, such as migraines with aura, cardiovascular risk factors, and being in the early postpartum period.3 In the United States, current POPs contain norethindrone, which has a 3-hour window for missed pills4; a desogestrel-only pill available outside the United States has a 12-hour window.5 Both are provided as a 28-day pill pack for continuous use, and both result in undesirable bleeding patterns in some users.
The prolonged half-life of drospirenone, another progestin, gives it the potential to increase reliability in the setting of missed or delayed pills and improve bleeding patterns. A new POP contraceptive contains drospirenone (Slynd) and is available in a 28-day pack with a 24-day supply of hormone and a 4-day supply of placebo; it provides a window for missed pill use similar to that for combined hormonal contraception (CHC) as well as a placebo period for a timed withdrawal bleed.6,7
Liletta is a well-known levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS that was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2015. An ongoing clinical trial has been the basis for approval of this IUS for use in increasing durations, from 3 years initially to 4 and then 5 years. The newest data indicate efficacy up to 6 years.8
Continue to: Combined hormonal vaginal system provides a year's contraception with an acceptable safety profile...
Combined hormonal vaginal system provides a year's contraception with an acceptable safety profile
Archer DF, Merkatz RB, Bahamondes L, et al. Efficacy of the 1-year (13-cycle) segesterone acetate and ethinylestradiol contraceptive vaginal system: results of two multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 3 trials. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7:e1054-e1064.
Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
Archer and colleagues reported the results of 2 pivotal multicenter, open-label, phase 3 trials, which included 2,265 users, conducted to evaluate efficacy and return to menses or pregnancy after use of the 1-year (13 cycles) SA/EE contraceptive vaginal system (CVS).
Details of the efficacy study
The study included 1,130 women in a US-only study and 1,135 women in an international study with sites in the United States, Australia, Brazil, Chile, Dominican Republic, Finland, Hungary, and Sweden. Participants used the CVS for 21 days followed by a 7-day use-free interval for up to 13 consecutive cycles; they were instructed not to remove the CVS for more than 2 hours during the 21 days of use.
Primary and secondary efficacy outcomes were calculated using the Pearl Index and an intention-to-treat Kaplan-Meier life table, respectively. At the end of the study, users who desired not to continue hormonal contraception or to become pregnant were followed up for 6 months to evaluate return to menses or pregnancy.
Year-long effectiveness
The investigators reported an overall Pearl index of 2.98 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.13-4.06) and a Kaplan-Meier life table cumulative efficacy rate of 97.5% (FIGURE 1), consistent with other recently approved CHC methods. Women from non-European sites, who primarily were US participants, had a Pearl Index of 3.25 (95% CI, 2.35-4.37), and participants from the European sites had a Pearl Index of 0.47 (95% CI, 0.03-2.07). Importantly, CVS removal had a significant impact on efficacy, with a Pearl Index of 5.98 (95% CI, 2.46-9.27) in users reporting CVS removals for longer than 2 hours, suggesting escape ovulation with improper use. The Pearl Index was highest in users aged 18 to 19 years and was not affected by body mass index (BMI), although 91% of users had a BMI of 29.0 kg/m2 or lower.

There was no trend for a change in pregnancy risk across 13 cycles, providing evidence of CVS efficacy throughout a full year's use. The follow-up portion of the study included 290 users who were not continuing hormonal contraception at study end; all follow-up participants reported return to menses after method discontinuation.
Clinical safety data
To evaluate safety outcomes from clinical studies on the CVS containing SA/EE, Gemzell-Danielsson and colleagues analyzed 9 studies. Most of the data were derived from 2 phase 3, multicenter trials (as discussed above), with supporting evidence from 7 other studies.
Adverse events reported
Among 2,308 CVS users in the phase 3 trials, 87% reported at least 1 adverse effect, with most of mild or moderate severity. These included headache, 26%; nausea, 18%; vaginal discharge, 10%; and metrorrhagia, 7%. Overall, 12% of CVS users discontinued use due to an adverse effect. Two percent of users experienced severe adverse effects, including venous thromboembolism (VTE), allergic reaction, gallbladder disease, and spontaneous abortion.
In the US-only phase 3 trial, 2 VTE events occurred in the first 6 months in women with baseline BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2; therefore, enrollment of patients with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 was halted and current users meeting that criteria were discontinued. Notably, no cases of VTE occurred in studies with a segesterone acetate-only CVS; this suggests that risk can be attributed to the estrogen component. Overall, 4 nonfatal VTEs occurred, all among the 1,536 women enrolled in the phase 3 trials (4 of 1,536 [0.3%]); at least 3 of these cases occurred in users with VTE risk factors (TABLE 1). The estimated VTE rate in CVS users with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 is 10.8/10,000 women-years (95% CI, 8.9-13.1).
Complete expulsion of the CVS occurred in 7% of cycles and partial expulsion in 19.5% of cycles; users reported expulsion more frequently in the first cycle, most (about 70%) of which were partial expulsions. Of the laboratory values and vital signs studied, including weight, users had no clinically relevant changes from baseline.

The 13-cycle efficacy and general adverse events rates of the new SA/EE CVS are consistent with those of other CHCs. However, the efficacy and safety findings are not necessarily generalizable to all patients. Because users with a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 were excluded following 2 early VTE events in women with a BMI of 29.1 and 30.8 kg/m2 , only 9% of the phase 3 study population had a BMI greater than 29.0 kg/m2 . Clinicians may question whether the 1-year SA/EE CVS is an acceptable method for obese users. We know that EE causes similar changes in hemostatic factors regardless of oral or vaginal route,9 but these studies as well as pharmacokinetic studies typically include relatively few participants. While studies demonstrate that the SA/EE CVS delivers EE 13 µg daily,1 individual hormone absorption can vary. It is possible that the amount of EE in the CVS (17.4 mg) could, in a person predisposed to higher absorption, increase VTE risk. We do not know if this potential or actual risk is different for nonobese and obese users. To be fair, most of the EE-containing combined hormonal contraceptives were approved with study data that did not include obese women; the FDA first discussed the importance of including obese women in contraceptive approval studies in 2007.10 Thus, we do not know if this CVS has a significantly higher VTE risk in obese users than other methods.
All available information is based on cyclic CVS use (28-day cycles with a 7-day use-free interval). No data are available on drug levels, safety, or efficacy over extended periods of continuous use with the same CVS. During counseling, special emphasis should be placed on the increased pregnancy risk for patients who remove the ring for more than 2 hours.
Continue to: New drospirenone pill is an effective POP option...
New drospirenone pill is an effective POP option
Kimble T, Burke AE, Barnhart KT, et al. A 1-year prospective, open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 3 trial of the contraceptive efficacy and safety of the oral progestin-only pill drospirenone 4 mg using a 24/4-day regimen. Contracept X. 2020;2:100020.
Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Multicenter, phase III trials on the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability and safety of a new drospirenone-only pill. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:1549-1557.
In a prospective, single-arm, multicenter phase 3 trial in the United States, Kimble and colleagues evaluated the efficacy and safety of an oral drospirenone POP in a cyclic 24-day hormone/4-day placebo regimen. The trial included 1,006 users. No BMI cutoff was used, and about one-third of study participants were obese (BMI >30.0 kg/m2). Women were instructed to take a missed tablet as soon as remembered if within 24 hours or with the next scheduled dose if more than 24 hours late.
Contraceptive effectiveness
The Pearl Index for nonbreastfeeding users aged 35 years or younger with pregnancies confirmed by a quantitative serum ß-human chorionic gonadotropin test (915 users) was 2.9 (95% CI, 1.5-5.1). Of note, 2 out of 15 on-treatment pregnancies were excluded from this calculation because of protocol site violations, as were 3 pregnancies that were unconfirmed. In the modified full analysis set of 915 users, 36% were obese (BMI≥30 kg/m2), and the Pearl Index was noted to be unaffected by BMI (TABLE 2).

While 61% of women reported adverse effects, more than 95% of these were mild or moderate in intensity, including headache, nausea, dysmenorrhea, metrorrhagia, and breast pain. No VTE occurred. The frequency of hyperkalemia was 0.5%, and there was no evidence of hypotension, which is significant due to the antimineralocorticoid activity of drospirenone. All cases of hyperkalemia were considered mild, and all women were asymptomatic. There were no clinically relevant changes in body weight, gynecologic exam, or other laboratory values.
With increased cycles of use, the number of days with bleeding or spotting generally decreased and amenorrhea increased. However, in cycles 11 to 13, 41.6% of users still had unscheduled bleeding (reduced from 57.0% at cycles 2-4), and 29.0% had scheduled bleeding (decreased from 44% at cycles 2-4) (FIGURE 2). With these bleeding patterns, 86.2% of users agreed or strongly agreed that they were satisfied with the product.

European multicenter study of drospironene
In a European investigation, Palacios and colleagues pooled and analyzed data from 2 phase 3 multicenter trials to assess the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of the same drospirenone-only pill (24 days of drospironene 4 mg and 4 days of placebo) in 1,571 users. No BMI cutoff was used, but overall only 71 participants (4.6%) were obese. One study included desogestrel 0.075 mg (in a regimen of 28 active pills) as a comparator for safety.
The overall Pearl Index for users 35 years or younger (1,251 users) was 1.0 (95% CI, 0.4-2.0). The "method failure Pearl Index" in users 35 years or younger, which included all pregnancies during "perfect medication cycles," was 1.3 (95% CI, 0.5-2.5).
The most common adverse effects were acne (6.6% in study 1 and 4.4% in study 2), headache (4.5% in study 1), and irregular bleeding (4.4% in study 2). No cases of VTE occurred; there was 1 case of asymptomatic hyperkalemia. Additional laboratory values and vital signs showed no significant changes. The trend in bleeding was similar to that in the US studies, but it is interesting to note that there were significantly lower rates of unscheduled bleeding or spotting in drospirenone users than in desogestrel users (67.9% vs 86.5%, respectively; P<.001).
In the US study, the higher Pearl Index compared with that found in the European study (2.9 vs 1.0) likely reflects an increased proportion of study participants with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher, a younger average age of participants, and a historical tendency toward better contraceptive efficacy in European than in US study participants. Kimble and colleagues’ finding of a Pearl Index of 2.9 is similar to that seen with other CHCs and POPs, and the data from the US study are potentially more generalizable.
Among the 2,257 participants in 3 studies, 423 (19%) were obese. No VTE events occurred with drospirenone use, as compared with 4 events in the SA/EE CVS study with 2,308 participants in the phase 3 studies.
Historically, POPs were associated with more days of bleeding than CHCs and require stricter adherence to daily use within a narrow window for missed pills. The new drospirenone-only pill may provide women with more flexibility since it maintains contraceptive efficacy even with 24-hour delayed or missed-pill errors. Although intermenstrual bleeding rates are high, participants still had a very favorable assessment, and the profile may be more tolerable compared with other POPs. Clinicians prescribing this new POP should counsel patients that the cyclic regimen does not always result in regular bleeding patterns.
Continue to: Evidence supports 6 years' use of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS...
Evidence supports 6 years' use of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS
Westhoff CL, Keder LM, Gangestad A, et al. Six-year contraceptive efficacy and continued safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Contraception. 2020;101:159-161.
Two levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS products are on the market, both of which were approved for 5 years of use. The ACCESS IUS study (A Comprehensive Contraceptive Efficacy and Safety Study of an IUS) is an ongoing phase 3 trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS (Liletta) for up to 10 years of use in US women. Westhoff and colleagues presented the data used for this IUS to gain approval for 6 years of use as of October 2019. The report included safety information for all users, with use exceeding 8 years in 122 participants.
In year 6 of the ongoing trial, there were no on-treatment pregnancies with a 6-year life table pregnancy rate of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.44-1.70). Forty percent of users reported amenorrhea in the 90 days preceding the end of year 6, consistent with prior data after 3 years of use (FIGURE 3). The most common adverse effects over 6 or more years of use were bacterial vulvovaginal infections and urinary tract infections.

Long-term IUS effectiveness
Overall, in users aged 16 to 35 years, 72% discontinued study participation, most frequently due to an adverse event (19.2%) or to seeking pregnancy (15.5%). Through 6 or more years of use, overall discontinuation rates for expulsion (4.0%) and bleeding symptoms (2.3%) were very low, with 2 expulsions occurring in year 6 and only 1 participant discontinuing in year 6 for a bleeding symptom. These findings are consistent with those found at 5 years of IUS use and are representative of continued efficacy as well as overall low frequency of new significant events with extended use.11
Clinicians and patients should be aware of data that support the continued use of levonorgestrel 52-mg IUS products for 6 years, and likely even longer. A low incidence of new significant events and a steady state of amenorrhea are also indications that users who like using a hormonal IUS will likely continue to do so for an extended time, if recommended. This extension, as well as continued study up to 10 years, will allow users who desire reversible long-acting hormonal contraception to have fewer removals and reinsertions; this in turn will decrease the risks and pain associated with IUS insertion and removal as well as health care costs.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
- Archer DF, Merkatz RB, Bahamondes L, et al. Efficacy of the 1-year (13-cycle) segesterone acetate and ethinylestradiol contraceptive vaginal system: results of two multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 3 trials. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7:e1054-e1064.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 206. Use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisiting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- Ortho Micronor [package insert]. Raritan, NJ: Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceutical Inc; 2008.
- Cerazette [package insert]. Oss, Netherlands: Merck Sharp & Dohme Limited; 2019.
- Kimble T, Burke AE, Barnhart KT, et al. A 1-year prospective, open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 3 trial of the contraceptive efficacy and safety of the oral progestin-only pill drospirenone 4 mg using a 24/4-day regimen. Contracept X. 2020;2:100020.
- Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Multicenter, phase III trials on the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability and safety of a new drospirenone-only pill. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:1549-1557.
- Westhoff CL, Keder LM, Gangestad A, et al. Six-year contraceptive efficacy and continued safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Contraception. 2020;101:159-161.
- Sitruk-Ware R, Plu-Bureau G, Menard J, et al. Effects of oral and transvaginal ethinyl estradiol on hemostatic factors and hepatic proteins in a randomized, crossover study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2074-2079.
- Food and Drug Administration Advisory Committee for Reproductive Health Drugs meeting. Final summary minutes, January 23-24, 2007. https://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170404050830/https://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/07/minutes/2007-4274m1.pdf. Accessed July 28, 2020.
- Teal SB, Turok DK, Chen BA, et al. Five-year contraceptive efficacy and safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:63-70.
- Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sitruk-Ware R, Creinin MD, et al. Segesterone acetate/ethinyl estradiol 12-month contraceptive vaginal system safety evaluation. Contraception. 2019;99:323-328.
- Archer DF, Merkatz RB, Bahamondes L, et al. Efficacy of the 1-year (13-cycle) segesterone acetate and ethinylestradiol contraceptive vaginal system: results of two multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 3 trials. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7:e1054-e1064.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG practice bulletin No. 206. Use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisiting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- Ortho Micronor [package insert]. Raritan, NJ: Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceutical Inc; 2008.
- Cerazette [package insert]. Oss, Netherlands: Merck Sharp & Dohme Limited; 2019.
- Kimble T, Burke AE, Barnhart KT, et al. A 1-year prospective, open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 3 trial of the contraceptive efficacy and safety of the oral progestin-only pill drospirenone 4 mg using a 24/4-day regimen. Contracept X. 2020;2:100020.
- Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Multicenter, phase III trials on the contraceptive efficacy, tolerability and safety of a new drospirenone-only pill. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2019;98:1549-1557.
- Westhoff CL, Keder LM, Gangestad A, et al. Six-year contraceptive efficacy and continued safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Contraception. 2020;101:159-161.
- Sitruk-Ware R, Plu-Bureau G, Menard J, et al. Effects of oral and transvaginal ethinyl estradiol on hemostatic factors and hepatic proteins in a randomized, crossover study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2074-2079.
- Food and Drug Administration Advisory Committee for Reproductive Health Drugs meeting. Final summary minutes, January 23-24, 2007. https://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170404050830/https://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/07/minutes/2007-4274m1.pdf. Accessed July 28, 2020.
- Teal SB, Turok DK, Chen BA, et al. Five-year contraceptive efficacy and safety of a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine system. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:63-70.