User login
Antidepressant Use and Depressive Symptoms in Intensive Care Unit Survivors
As the number of intensive care unit (ICU) survivors has steadily increased over the past few decades, there is growing awareness of the long-term physical, cognitive, and psychological impairments after ICU hospitalization, collectively known as post–intensive care syndrome (PICS).1 Systematic reviews based mostly on research studies suggest that the prevalence of depressive symptoms 2-12 months after ICU discharge is nearly 30%.2-5 Due to the scarcity of established models of care for ICU survivors, there is limited characterization of depressive symptoms and antidepressant regimens in this clinical population. The Critical Care Recovery Center (CCRC) at Eskenazi Hospital is one of the first ICU survivor clinics in the United States and targets a racially diverse, underserved population in the Indianapolis metropolitan area.6 In this study, we examined whether patients had depressive symptoms at their initial CCRC visit, and whether the risk factors for depressive symptoms differed if they were on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit.
METHODS
Referral criteria to the CCRC were 18 years or older, admitted to the Eskenazi ICU, were on mechanical ventilation or delirious for ≥48 hours (major risk factors for the development of PICS), and recommended for follow-up by a critical care physician. The exclusion criterion included was enrollment in hospice or palliative care services. Institutional review board approval was obtained to conduct retrospective analyses of de-identified clinical data. Medical history and medication lists were collected from patients, informal caregivers, and electronic medical records.
Two hundred thirty-three patients were seen in the CCRC from July 2011 to August 2016. Two hundred four patients rated symptoms of depression with either the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9; N = 99) or Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-30; N = 105) at their initial visit to the CCRC prior to receiving any treatment at the CCRC. Twenty-nine patients who did not complete depression questionnaires were excluded from the analyses. Patients with PHQ-9 score ≥10 or GDS score ≥20 were categorized as having moderate to severe depressive symptoms.7,8
Electronic medical records were reviewed to determine whether patients were on an antidepressant at hospital admission, hospital discharge, and the initial CCRC visit prior to any treatment in the CCRC. Patients who were on a tricyclic antidepressant, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (eg, mirtazapine), or norepinephrine and dopaminergic reuptake inhibitor (eg, bupropion) at any dose were designated as being on an antidepressant. Prescribers of antidepressants included primary care providers, clinical providers during their hospital stay, and various outpatient subspecialists other than those in the CCRC.
We then examined whether the risk factors for depressive symptoms differed if patients were on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit. We compared demographic and clinical characteristics between depressed and nondepressed patients not on an antidepressant. We repeated these analyses for those on an antidepressant. Dichotomous outcomes were compared using chi-square testing, and two-way Student t tests for continuous outcomes. Demographic and clinical variables with P < 0.1 were included as covariates in a logistic regression model for depressive symptoms separately for those not an antidepressant and those on an antidepressant. History of depression was not included as a covariate because it is highly collinear with post-ICU depression.
RESULTS
Two hundred four ICU survivors in this study reflected a racially diverse and underserved population (monthly income $745.3 ± $931.5). Although most had respiratory failure and/or delirium during their hospital stay, 94.1% (N = 160) mostly lived independently after discharge. Nearly one-third of patients (N = 69) were on at least 1 antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit. Of these 69 patients, 60.9% (N = 42) had an antidepressant prescription on hospital admission, and 60.9% (N = 42) had an antidepressant prescription on hospital discharge.
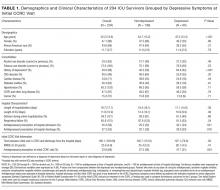
We first compared the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with and without depressive symptoms at their initial CCRC visit. Patients with depressive symptoms were younger, less likely to have cardiac disease, more likely to have a history of depression, more likely to have been prescribed an antidepressant on hospital admission, more likely to be prescribed an antidepressant on hospital discharge, and more likely to be on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit (Table 1).
Patients with depressive symptoms on an antidepressant (n = 65) were younger and more likely to be African American (borderline significance; Supplementary Table 2). Multivariate logistic regression showed that both younger age (OR = 0.92 per year, P = 0.003) and African American race (OR = 4.3, P = 0.024) remained significantly associated with depressive symptoms (Table 2).
DISCUSSION
Our study demonstrated that about one-third of our ICU survivor clinical cohort had untreated or inadequately treated depressive symptoms at their CCRC initial visit. Many patients with depressive symptoms had a history of depression and/or antidepressant prescription on hospital admission. This suggests that pre-ICU depression is a major contributor to post-ICU depression. These findings are consistent with the results of a large retrospective analysis of Danish ICU survivors that found that patients were more likely to have premorbid psychiatric diagnoses, compared with the general population.9 Another ICU survivor research study that excluded patients who were on antidepressants prior to ICU hospitalization found that 49% of these patients were on an antidepressant after their ICU stay.10 Our much lower rate of patients on an antidepressant after their ICU stay may reflect the differences between patient populations, differences in healthcare systems, and differences in clinician prescribing practices.
Younger age was associated with a higher likelihood of depressive symptoms independent of antidepressant status. Findings about the relationship between age and post-ICU depression have varied. The Bringing to Light the Risk Factors and Incidence of Neuropsychological Dysfunction in ICU Survivors group found that older age was associated with more depressive symptoms at 12 months postdischarge.11 On the other hand, a systematic review of post-ICU depression did not find any relationship between age and post-ICU depression.2,3 These differences may be due in part to demographic variations in cohorts.
Our logistic regression models suggest that there may also be different risk factors in patients who had untreated vs inadequately treated depressive symptoms. Patients who were not on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit were more likely to have a lower level of education. This is consistent with the Medical Expenditure Panel Surveys study, which showed that adults with less than a high school education were less likely to receive depression treatment.12 In patients who were on antidepressants at their initial CCRC visit, African Americans were more likely to have depressive symptoms. Possible reasons may include differences in receiving guideline-concordant antidepressant medication treatment, access to mental health subspecialty services, higher prevalence of treatment refractory depression, and differences in responses to antidepressant treatments.13,14
Strengths of our study include detailed characterization for a fairly large ICU survivor clinic population and a racially diverse cohort. To the best of our knowledge, our study is also the first to examine whether there may be different risk factors for depressive symptoms based on antidepressant status. Limitations include the lack of information about nonpharmacologic antidepressant treatment and the inability to assess whether noncompliance, insufficient dose, or insufficient time on antidepressants contributed to inadequate antidepressant treatment. Antidepressants may have also been prescribed for other purposes such as smoking cessation, neuropathic pain, and migraine headaches. However, because 72.4% of patients on antidepressants had a history of depression, it is likely that most of them were on antidepressants to treat depression.
Other limitations include potential biases in our clinical cohort. Over the last 5 years, the CCRC has provided care to more than 200 ICU survivors. With 1100 mechanically ventilated admissions per year, only 1.8% of survivors are seen. The referral criteria for the CCRC is a major source of selection bias, which likely overrepresents PICS. Because patients are seen in the CCRC about 3 months after hospital discharge, there is also informant censoring due to death. Physically sicker survivors in nursing home facilities were less likely to be included. Finally, the small cohort size may have resulted in an underpowered study.
Future studies will need to confirm our findings about the high prevalence of post-ICU depression and different responses to antidepressant medications by certain groups. Pre-ICU depression, lack of antidepressant treatment, and inadequate antidepressant treatment are major causes of post-ICU depression. Currently, the CCRC offers pharmacotherapy, problem-solving therapy, or referral to mental health specialists to treat patients with depressive symptoms. ICU survivor clinics, such as the CCRC, may become important settings that allow for increased access to depression treatment for those at higher risk for post-ICU depression as well as the testing of new antidepressant regimens for those with inadequately treated depression.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Adil Sheikh for assistance with data entry and Cynthia Reynolds for her clinical services. Grant support: The Critical Care Recovery Center (CCRC) is supported by Eskenazi Health Services. SW is supported by NIA 2P30AG010133. SG is supported by NIA 2P30AG010133 and NIA 5R01AG045350. SK is supported by NHBLI 5T32HL091816-07. MB is supported by NIA R01 AG040220-05, AHRQ P30 HS024384-02, CMS 1 L1 CMS331444-02-00 and NIA R01 AG030618-05A1. BK is supported by NIA K23-AG043476 and NHLBI R01HL131730.
Disclosure
There are no conflicts of interest. None of the above NIH grants supported the CCRC or this work.
1. Needham DM, Davidson J, Cohen H, et al. Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:502-509. PubMed
2. Davydow DS, Gifford JM, Desai SV, Bienvenu OJ, Needham DM. Depression in general intensive care unit survivors: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:796-809. PubMed
3. Rabiee A, Nikayin S, Hashem MD, et al. Depressive symptoms after critical illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(9):1744-1753. PubMed
4. Huang M, Parker AM, Bienvenu OJ, et al. Psychiatric symptoms in acute respiratory distress syndrome survivors: A 1-year national multicenter study. Crit Care Med 2016;44:954-965. PubMed
5. Bienvenu OJ, Colantuoni E, Mendez-Tellez PA, et al. Cooccurrence of and remission from general anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms after acute lung injury: a 2-year longitudinal study. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:642-653. PubMed
6. Khan BA, Lasiter S, Boustani MA. CE: critical care recovery center: an innovative collaborative care model for ICU survivors. Am J Nurs. 2015;115:24-31. PubMed
7. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:606-613. PubMed
8. Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, et al. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. J Psychiatr Res. 1982-1983;17:37-49. PubMed
9. Wuns ch H, Christiansen CF, Johansen MB, et al. Psychiatric diagnoses and psychoactive medication use among nonsurgical critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation. JAMA. 2014;311:1133-1142. PubMed
10. Weinert C, Meller W. Epidemiology of depression and antidepressant therapy after acute respiratory failure. Psychosomatics. 2006;47(5):399-407. PubMed
11. Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, et al. Depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and functional disability in survivors of critical illness in the BRAIN-ICU study: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2:369-379. PubMed
12. Olfson M, Blanco C, Marcus SC. Treatment of adult depression in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1482-1491. PubMed
13. González HM, Vega WA, Williams DR, Tarraf W, West BT, Neighbors HW. Depression care in the United States: too little for too few. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:37-46. PubMed
14. Bailey RK, Patel M, Barker NC, Ali S, Jabeen S. Major depressive disorder in the African American population. J Natl Med Assoc. 2011;103:548-557. PubMed
As the number of intensive care unit (ICU) survivors has steadily increased over the past few decades, there is growing awareness of the long-term physical, cognitive, and psychological impairments after ICU hospitalization, collectively known as post–intensive care syndrome (PICS).1 Systematic reviews based mostly on research studies suggest that the prevalence of depressive symptoms 2-12 months after ICU discharge is nearly 30%.2-5 Due to the scarcity of established models of care for ICU survivors, there is limited characterization of depressive symptoms and antidepressant regimens in this clinical population. The Critical Care Recovery Center (CCRC) at Eskenazi Hospital is one of the first ICU survivor clinics in the United States and targets a racially diverse, underserved population in the Indianapolis metropolitan area.6 In this study, we examined whether patients had depressive symptoms at their initial CCRC visit, and whether the risk factors for depressive symptoms differed if they were on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit.
METHODS
Referral criteria to the CCRC were 18 years or older, admitted to the Eskenazi ICU, were on mechanical ventilation or delirious for ≥48 hours (major risk factors for the development of PICS), and recommended for follow-up by a critical care physician. The exclusion criterion included was enrollment in hospice or palliative care services. Institutional review board approval was obtained to conduct retrospective analyses of de-identified clinical data. Medical history and medication lists were collected from patients, informal caregivers, and electronic medical records.
Two hundred thirty-three patients were seen in the CCRC from July 2011 to August 2016. Two hundred four patients rated symptoms of depression with either the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9; N = 99) or Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-30; N = 105) at their initial visit to the CCRC prior to receiving any treatment at the CCRC. Twenty-nine patients who did not complete depression questionnaires were excluded from the analyses. Patients with PHQ-9 score ≥10 or GDS score ≥20 were categorized as having moderate to severe depressive symptoms.7,8
Electronic medical records were reviewed to determine whether patients were on an antidepressant at hospital admission, hospital discharge, and the initial CCRC visit prior to any treatment in the CCRC. Patients who were on a tricyclic antidepressant, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (eg, mirtazapine), or norepinephrine and dopaminergic reuptake inhibitor (eg, bupropion) at any dose were designated as being on an antidepressant. Prescribers of antidepressants included primary care providers, clinical providers during their hospital stay, and various outpatient subspecialists other than those in the CCRC.
We then examined whether the risk factors for depressive symptoms differed if patients were on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit. We compared demographic and clinical characteristics between depressed and nondepressed patients not on an antidepressant. We repeated these analyses for those on an antidepressant. Dichotomous outcomes were compared using chi-square testing, and two-way Student t tests for continuous outcomes. Demographic and clinical variables with P < 0.1 were included as covariates in a logistic regression model for depressive symptoms separately for those not an antidepressant and those on an antidepressant. History of depression was not included as a covariate because it is highly collinear with post-ICU depression.
RESULTS
Two hundred four ICU survivors in this study reflected a racially diverse and underserved population (monthly income $745.3 ± $931.5). Although most had respiratory failure and/or delirium during their hospital stay, 94.1% (N = 160) mostly lived independently after discharge. Nearly one-third of patients (N = 69) were on at least 1 antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit. Of these 69 patients, 60.9% (N = 42) had an antidepressant prescription on hospital admission, and 60.9% (N = 42) had an antidepressant prescription on hospital discharge.
We first compared the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with and without depressive symptoms at their initial CCRC visit. Patients with depressive symptoms were younger, less likely to have cardiac disease, more likely to have a history of depression, more likely to have been prescribed an antidepressant on hospital admission, more likely to be prescribed an antidepressant on hospital discharge, and more likely to be on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit (Table 1).
Patients with depressive symptoms on an antidepressant (n = 65) were younger and more likely to be African American (borderline significance; Supplementary Table 2). Multivariate logistic regression showed that both younger age (OR = 0.92 per year, P = 0.003) and African American race (OR = 4.3, P = 0.024) remained significantly associated with depressive symptoms (Table 2).
DISCUSSION
Our study demonstrated that about one-third of our ICU survivor clinical cohort had untreated or inadequately treated depressive symptoms at their CCRC initial visit. Many patients with depressive symptoms had a history of depression and/or antidepressant prescription on hospital admission. This suggests that pre-ICU depression is a major contributor to post-ICU depression. These findings are consistent with the results of a large retrospective analysis of Danish ICU survivors that found that patients were more likely to have premorbid psychiatric diagnoses, compared with the general population.9 Another ICU survivor research study that excluded patients who were on antidepressants prior to ICU hospitalization found that 49% of these patients were on an antidepressant after their ICU stay.10 Our much lower rate of patients on an antidepressant after their ICU stay may reflect the differences between patient populations, differences in healthcare systems, and differences in clinician prescribing practices.
Younger age was associated with a higher likelihood of depressive symptoms independent of antidepressant status. Findings about the relationship between age and post-ICU depression have varied. The Bringing to Light the Risk Factors and Incidence of Neuropsychological Dysfunction in ICU Survivors group found that older age was associated with more depressive symptoms at 12 months postdischarge.11 On the other hand, a systematic review of post-ICU depression did not find any relationship between age and post-ICU depression.2,3 These differences may be due in part to demographic variations in cohorts.
Our logistic regression models suggest that there may also be different risk factors in patients who had untreated vs inadequately treated depressive symptoms. Patients who were not on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit were more likely to have a lower level of education. This is consistent with the Medical Expenditure Panel Surveys study, which showed that adults with less than a high school education were less likely to receive depression treatment.12 In patients who were on antidepressants at their initial CCRC visit, African Americans were more likely to have depressive symptoms. Possible reasons may include differences in receiving guideline-concordant antidepressant medication treatment, access to mental health subspecialty services, higher prevalence of treatment refractory depression, and differences in responses to antidepressant treatments.13,14
Strengths of our study include detailed characterization for a fairly large ICU survivor clinic population and a racially diverse cohort. To the best of our knowledge, our study is also the first to examine whether there may be different risk factors for depressive symptoms based on antidepressant status. Limitations include the lack of information about nonpharmacologic antidepressant treatment and the inability to assess whether noncompliance, insufficient dose, or insufficient time on antidepressants contributed to inadequate antidepressant treatment. Antidepressants may have also been prescribed for other purposes such as smoking cessation, neuropathic pain, and migraine headaches. However, because 72.4% of patients on antidepressants had a history of depression, it is likely that most of them were on antidepressants to treat depression.
Other limitations include potential biases in our clinical cohort. Over the last 5 years, the CCRC has provided care to more than 200 ICU survivors. With 1100 mechanically ventilated admissions per year, only 1.8% of survivors are seen. The referral criteria for the CCRC is a major source of selection bias, which likely overrepresents PICS. Because patients are seen in the CCRC about 3 months after hospital discharge, there is also informant censoring due to death. Physically sicker survivors in nursing home facilities were less likely to be included. Finally, the small cohort size may have resulted in an underpowered study.
Future studies will need to confirm our findings about the high prevalence of post-ICU depression and different responses to antidepressant medications by certain groups. Pre-ICU depression, lack of antidepressant treatment, and inadequate antidepressant treatment are major causes of post-ICU depression. Currently, the CCRC offers pharmacotherapy, problem-solving therapy, or referral to mental health specialists to treat patients with depressive symptoms. ICU survivor clinics, such as the CCRC, may become important settings that allow for increased access to depression treatment for those at higher risk for post-ICU depression as well as the testing of new antidepressant regimens for those with inadequately treated depression.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Adil Sheikh for assistance with data entry and Cynthia Reynolds for her clinical services. Grant support: The Critical Care Recovery Center (CCRC) is supported by Eskenazi Health Services. SW is supported by NIA 2P30AG010133. SG is supported by NIA 2P30AG010133 and NIA 5R01AG045350. SK is supported by NHBLI 5T32HL091816-07. MB is supported by NIA R01 AG040220-05, AHRQ P30 HS024384-02, CMS 1 L1 CMS331444-02-00 and NIA R01 AG030618-05A1. BK is supported by NIA K23-AG043476 and NHLBI R01HL131730.
Disclosure
There are no conflicts of interest. None of the above NIH grants supported the CCRC or this work.
As the number of intensive care unit (ICU) survivors has steadily increased over the past few decades, there is growing awareness of the long-term physical, cognitive, and psychological impairments after ICU hospitalization, collectively known as post–intensive care syndrome (PICS).1 Systematic reviews based mostly on research studies suggest that the prevalence of depressive symptoms 2-12 months after ICU discharge is nearly 30%.2-5 Due to the scarcity of established models of care for ICU survivors, there is limited characterization of depressive symptoms and antidepressant regimens in this clinical population. The Critical Care Recovery Center (CCRC) at Eskenazi Hospital is one of the first ICU survivor clinics in the United States and targets a racially diverse, underserved population in the Indianapolis metropolitan area.6 In this study, we examined whether patients had depressive symptoms at their initial CCRC visit, and whether the risk factors for depressive symptoms differed if they were on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit.
METHODS
Referral criteria to the CCRC were 18 years or older, admitted to the Eskenazi ICU, were on mechanical ventilation or delirious for ≥48 hours (major risk factors for the development of PICS), and recommended for follow-up by a critical care physician. The exclusion criterion included was enrollment in hospice or palliative care services. Institutional review board approval was obtained to conduct retrospective analyses of de-identified clinical data. Medical history and medication lists were collected from patients, informal caregivers, and electronic medical records.
Two hundred thirty-three patients were seen in the CCRC from July 2011 to August 2016. Two hundred four patients rated symptoms of depression with either the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9; N = 99) or Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-30; N = 105) at their initial visit to the CCRC prior to receiving any treatment at the CCRC. Twenty-nine patients who did not complete depression questionnaires were excluded from the analyses. Patients with PHQ-9 score ≥10 or GDS score ≥20 were categorized as having moderate to severe depressive symptoms.7,8
Electronic medical records were reviewed to determine whether patients were on an antidepressant at hospital admission, hospital discharge, and the initial CCRC visit prior to any treatment in the CCRC. Patients who were on a tricyclic antidepressant, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (eg, mirtazapine), or norepinephrine and dopaminergic reuptake inhibitor (eg, bupropion) at any dose were designated as being on an antidepressant. Prescribers of antidepressants included primary care providers, clinical providers during their hospital stay, and various outpatient subspecialists other than those in the CCRC.
We then examined whether the risk factors for depressive symptoms differed if patients were on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit. We compared demographic and clinical characteristics between depressed and nondepressed patients not on an antidepressant. We repeated these analyses for those on an antidepressant. Dichotomous outcomes were compared using chi-square testing, and two-way Student t tests for continuous outcomes. Demographic and clinical variables with P < 0.1 were included as covariates in a logistic regression model for depressive symptoms separately for those not an antidepressant and those on an antidepressant. History of depression was not included as a covariate because it is highly collinear with post-ICU depression.
RESULTS
Two hundred four ICU survivors in this study reflected a racially diverse and underserved population (monthly income $745.3 ± $931.5). Although most had respiratory failure and/or delirium during their hospital stay, 94.1% (N = 160) mostly lived independently after discharge. Nearly one-third of patients (N = 69) were on at least 1 antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit. Of these 69 patients, 60.9% (N = 42) had an antidepressant prescription on hospital admission, and 60.9% (N = 42) had an antidepressant prescription on hospital discharge.
We first compared the demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with and without depressive symptoms at their initial CCRC visit. Patients with depressive symptoms were younger, less likely to have cardiac disease, more likely to have a history of depression, more likely to have been prescribed an antidepressant on hospital admission, more likely to be prescribed an antidepressant on hospital discharge, and more likely to be on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit (Table 1).
Patients with depressive symptoms on an antidepressant (n = 65) were younger and more likely to be African American (borderline significance; Supplementary Table 2). Multivariate logistic regression showed that both younger age (OR = 0.92 per year, P = 0.003) and African American race (OR = 4.3, P = 0.024) remained significantly associated with depressive symptoms (Table 2).
DISCUSSION
Our study demonstrated that about one-third of our ICU survivor clinical cohort had untreated or inadequately treated depressive symptoms at their CCRC initial visit. Many patients with depressive symptoms had a history of depression and/or antidepressant prescription on hospital admission. This suggests that pre-ICU depression is a major contributor to post-ICU depression. These findings are consistent with the results of a large retrospective analysis of Danish ICU survivors that found that patients were more likely to have premorbid psychiatric diagnoses, compared with the general population.9 Another ICU survivor research study that excluded patients who were on antidepressants prior to ICU hospitalization found that 49% of these patients were on an antidepressant after their ICU stay.10 Our much lower rate of patients on an antidepressant after their ICU stay may reflect the differences between patient populations, differences in healthcare systems, and differences in clinician prescribing practices.
Younger age was associated with a higher likelihood of depressive symptoms independent of antidepressant status. Findings about the relationship between age and post-ICU depression have varied. The Bringing to Light the Risk Factors and Incidence of Neuropsychological Dysfunction in ICU Survivors group found that older age was associated with more depressive symptoms at 12 months postdischarge.11 On the other hand, a systematic review of post-ICU depression did not find any relationship between age and post-ICU depression.2,3 These differences may be due in part to demographic variations in cohorts.
Our logistic regression models suggest that there may also be different risk factors in patients who had untreated vs inadequately treated depressive symptoms. Patients who were not on an antidepressant at their initial CCRC visit were more likely to have a lower level of education. This is consistent with the Medical Expenditure Panel Surveys study, which showed that adults with less than a high school education were less likely to receive depression treatment.12 In patients who were on antidepressants at their initial CCRC visit, African Americans were more likely to have depressive symptoms. Possible reasons may include differences in receiving guideline-concordant antidepressant medication treatment, access to mental health subspecialty services, higher prevalence of treatment refractory depression, and differences in responses to antidepressant treatments.13,14
Strengths of our study include detailed characterization for a fairly large ICU survivor clinic population and a racially diverse cohort. To the best of our knowledge, our study is also the first to examine whether there may be different risk factors for depressive symptoms based on antidepressant status. Limitations include the lack of information about nonpharmacologic antidepressant treatment and the inability to assess whether noncompliance, insufficient dose, or insufficient time on antidepressants contributed to inadequate antidepressant treatment. Antidepressants may have also been prescribed for other purposes such as smoking cessation, neuropathic pain, and migraine headaches. However, because 72.4% of patients on antidepressants had a history of depression, it is likely that most of them were on antidepressants to treat depression.
Other limitations include potential biases in our clinical cohort. Over the last 5 years, the CCRC has provided care to more than 200 ICU survivors. With 1100 mechanically ventilated admissions per year, only 1.8% of survivors are seen. The referral criteria for the CCRC is a major source of selection bias, which likely overrepresents PICS. Because patients are seen in the CCRC about 3 months after hospital discharge, there is also informant censoring due to death. Physically sicker survivors in nursing home facilities were less likely to be included. Finally, the small cohort size may have resulted in an underpowered study.
Future studies will need to confirm our findings about the high prevalence of post-ICU depression and different responses to antidepressant medications by certain groups. Pre-ICU depression, lack of antidepressant treatment, and inadequate antidepressant treatment are major causes of post-ICU depression. Currently, the CCRC offers pharmacotherapy, problem-solving therapy, or referral to mental health specialists to treat patients with depressive symptoms. ICU survivor clinics, such as the CCRC, may become important settings that allow for increased access to depression treatment for those at higher risk for post-ICU depression as well as the testing of new antidepressant regimens for those with inadequately treated depression.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Adil Sheikh for assistance with data entry and Cynthia Reynolds for her clinical services. Grant support: The Critical Care Recovery Center (CCRC) is supported by Eskenazi Health Services. SW is supported by NIA 2P30AG010133. SG is supported by NIA 2P30AG010133 and NIA 5R01AG045350. SK is supported by NHBLI 5T32HL091816-07. MB is supported by NIA R01 AG040220-05, AHRQ P30 HS024384-02, CMS 1 L1 CMS331444-02-00 and NIA R01 AG030618-05A1. BK is supported by NIA K23-AG043476 and NHLBI R01HL131730.
Disclosure
There are no conflicts of interest. None of the above NIH grants supported the CCRC or this work.
1. Needham DM, Davidson J, Cohen H, et al. Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:502-509. PubMed
2. Davydow DS, Gifford JM, Desai SV, Bienvenu OJ, Needham DM. Depression in general intensive care unit survivors: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:796-809. PubMed
3. Rabiee A, Nikayin S, Hashem MD, et al. Depressive symptoms after critical illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(9):1744-1753. PubMed
4. Huang M, Parker AM, Bienvenu OJ, et al. Psychiatric symptoms in acute respiratory distress syndrome survivors: A 1-year national multicenter study. Crit Care Med 2016;44:954-965. PubMed
5. Bienvenu OJ, Colantuoni E, Mendez-Tellez PA, et al. Cooccurrence of and remission from general anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms after acute lung injury: a 2-year longitudinal study. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:642-653. PubMed
6. Khan BA, Lasiter S, Boustani MA. CE: critical care recovery center: an innovative collaborative care model for ICU survivors. Am J Nurs. 2015;115:24-31. PubMed
7. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:606-613. PubMed
8. Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, et al. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. J Psychiatr Res. 1982-1983;17:37-49. PubMed
9. Wuns ch H, Christiansen CF, Johansen MB, et al. Psychiatric diagnoses and psychoactive medication use among nonsurgical critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation. JAMA. 2014;311:1133-1142. PubMed
10. Weinert C, Meller W. Epidemiology of depression and antidepressant therapy after acute respiratory failure. Psychosomatics. 2006;47(5):399-407. PubMed
11. Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, et al. Depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and functional disability in survivors of critical illness in the BRAIN-ICU study: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2:369-379. PubMed
12. Olfson M, Blanco C, Marcus SC. Treatment of adult depression in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1482-1491. PubMed
13. González HM, Vega WA, Williams DR, Tarraf W, West BT, Neighbors HW. Depression care in the United States: too little for too few. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:37-46. PubMed
14. Bailey RK, Patel M, Barker NC, Ali S, Jabeen S. Major depressive disorder in the African American population. J Natl Med Assoc. 2011;103:548-557. PubMed
1. Needham DM, Davidson J, Cohen H, et al. Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:502-509. PubMed
2. Davydow DS, Gifford JM, Desai SV, Bienvenu OJ, Needham DM. Depression in general intensive care unit survivors: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:796-809. PubMed
3. Rabiee A, Nikayin S, Hashem MD, et al. Depressive symptoms after critical illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(9):1744-1753. PubMed
4. Huang M, Parker AM, Bienvenu OJ, et al. Psychiatric symptoms in acute respiratory distress syndrome survivors: A 1-year national multicenter study. Crit Care Med 2016;44:954-965. PubMed
5. Bienvenu OJ, Colantuoni E, Mendez-Tellez PA, et al. Cooccurrence of and remission from general anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms after acute lung injury: a 2-year longitudinal study. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:642-653. PubMed
6. Khan BA, Lasiter S, Boustani MA. CE: critical care recovery center: an innovative collaborative care model for ICU survivors. Am J Nurs. 2015;115:24-31. PubMed
7. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:606-613. PubMed
8. Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, et al. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. J Psychiatr Res. 1982-1983;17:37-49. PubMed
9. Wuns ch H, Christiansen CF, Johansen MB, et al. Psychiatric diagnoses and psychoactive medication use among nonsurgical critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation. JAMA. 2014;311:1133-1142. PubMed
10. Weinert C, Meller W. Epidemiology of depression and antidepressant therapy after acute respiratory failure. Psychosomatics. 2006;47(5):399-407. PubMed
11. Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, et al. Depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and functional disability in survivors of critical illness in the BRAIN-ICU study: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2:369-379. PubMed
12. Olfson M, Blanco C, Marcus SC. Treatment of adult depression in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1482-1491. PubMed
13. González HM, Vega WA, Williams DR, Tarraf W, West BT, Neighbors HW. Depression care in the United States: too little for too few. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:37-46. PubMed
14. Bailey RK, Patel M, Barker NC, Ali S, Jabeen S. Major depressive disorder in the African American population. J Natl Med Assoc. 2011;103:548-557. PubMed
© 2017 Society of Hospital Medicine